Online Multiple Athlete Tracking with Pose-Based Long-Term Temporal Dependencies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a Pose-based Triple Stream Networks (PTSN) based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, capable of modeling long-term temporal pose dynamics of athletes and generating robust association affinities.
- We design a multi-state online matching algorithm based on multiple detection states and reliable transitions with the association affinities, improves the robustness to noisy detections and occlusion.
- We evaluate our method by comparing it with recently proposed advanced multi-object trackers on the APIDIS, NCAA Basketball and VolleyTrack databases, and the experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
2. Related Works
2.1. Athlete Tracking
2.2. Multi-Object Tracking
2.3. Human Pose Estimation
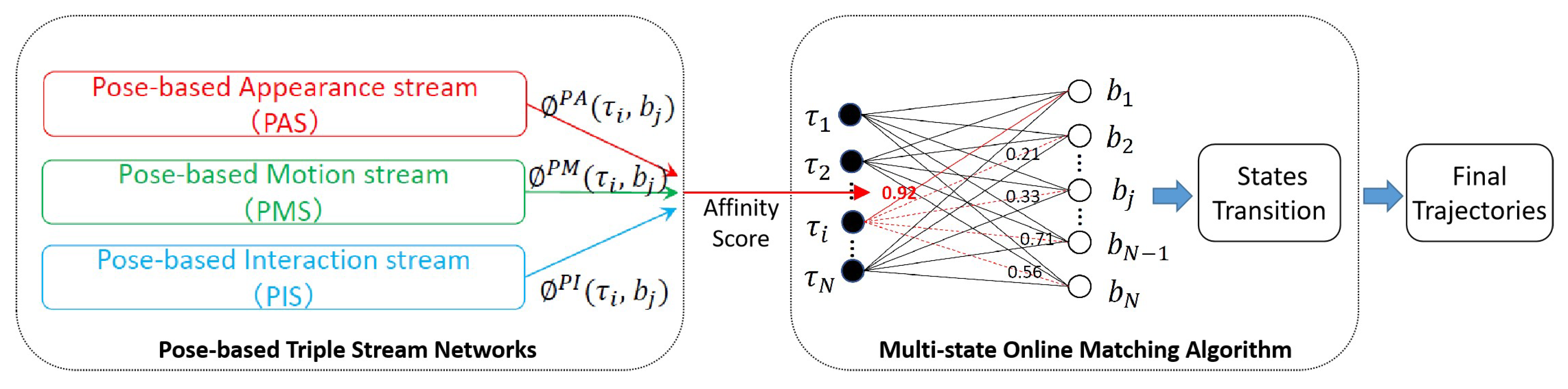
3. Multi-Athlete Tracking Approach
3.1. Overall Architecture of PTSN
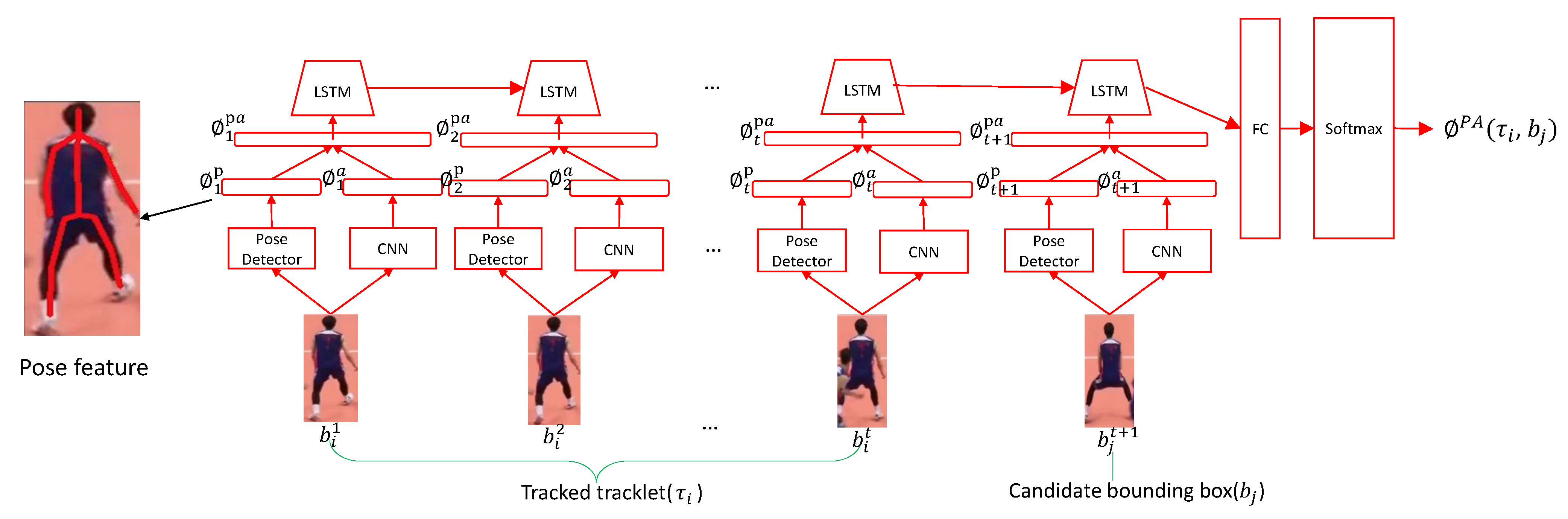
3.2. Pose-Based Appearance Stream(PAS)
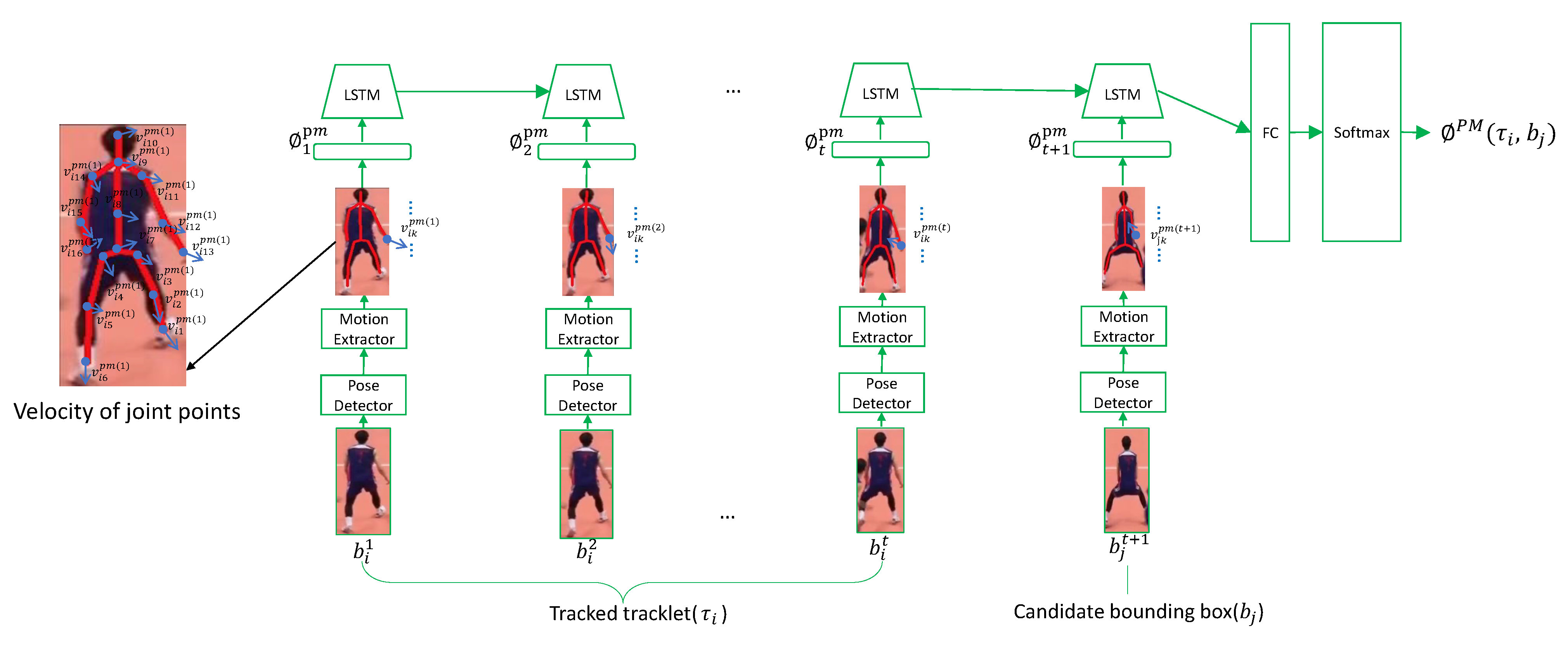
3.3. Pose-Based Motion Stream (PMS)
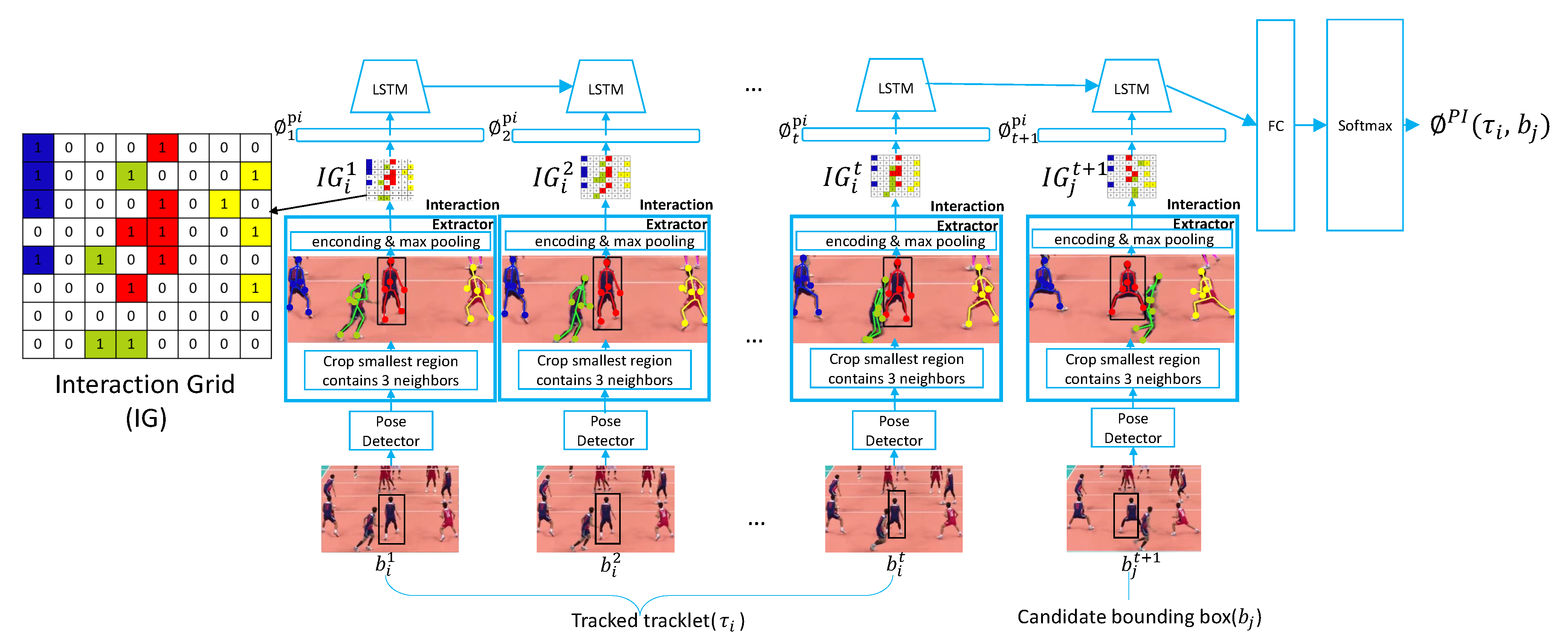
3.4. Pose-Based Interaction Stream (PIS)
3.5. Multi-State Online Matching Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Multi-State Online Matching Algorithm. |
| Inputs: |
| Outputs: |
| 1: Initial: , , , |
| 2: for to do |
| 3: = NMS() |
| 4: for do |
| 5: , where max(PTSN()), |
| 6: if PTSN(, ) then |
| 7: add to and remove from |
| 8: predict from and add to |
| 9: else |
| 10: move to |
| 11: end if |
| 12: end for |
| 13: for do |
| 14: = where max(PTSN()), |
| 15: if PTSN() then |
| 16: add to ; remove from and move to |
| 17: predict from and add to |
| 18: else |
| 19: if then |
| 20: move to |
| 21: end if |
| 22: end if |
| 23: for do |
| 24: start a new tracklet with and insert it into |
| 25: end for |
| 26: end for |
| 27: end for |
| 28: for do |
| 29: if then |
| 30: add to |
| 31: end if |
| 32: end for |
4. Experiment
4.1. Databases
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Indexes
4.4. Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomez, G.; López, P.H.; Link, D.; Eskofier, B. Tracking of ball and players in beach volleyball videos. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauthner, T.; Koch, C.; Tilp, M.; Bischof, H. Visual tracking of athletes in beach volleyball using a single camera. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Sport 2007, 6, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Ai, H.; Liu, L.; Lao, S. Multiple Player Tracking in Sports Video: A Dual-Mode Two-Way Bayesian Inference Approach With Progressive Observation Modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1652–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Carr, P.; Collins, R.T.; Liu, Y. Tracking sports players with context-conditioned motion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 1830–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Shitrit, H.B.; Berclaz, J.; Fleuret, F.; Fua, P. Multi-Commodity Network Flow for Tracking Multiple People. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghian, A.; Alahi, A.; Savarese, S. Tracking the Untrackable: Learning to Track Multiple Cues with Long-Term Dependencies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, R.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Cremers, D.; Rosenhahn, B. Improvements to Frank-Wolfe optimization for multi-detector multi-object tracking. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.01909. [Google Scholar]
- Dicle, C.; Camps, O.I.; Sznaier, M. The way they move: Tracking multiple targets with similar appearance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2304–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Li, F.; Ciptadi, A.; Rehg, J.M. Multiple Hypothesis Tracking Revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 4696–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, N.; Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. A Robust Multi-Athlete Tracking Algorithm by Exploiting Discriminant Features and Long-Term Dependencies. In International Conference on MultiMedia Modeling; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11295, pp. 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L. Scaling and occlusion robust athlete tracking in sports videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 1526–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, S.; Ess, A.; Schindler, K.; Gool, L.V. You’ll never walk alone: Modeling social behavior for multi-target tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Breitenstein, M.D.; Reichlin, F.; Leibe, B.; Koller-Meier, E.; Gool, L.J.V. Online Multiperson Tracking-by-Detection from a Single, Uncalibrated Camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1820–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; Dehghan, A.; Oreifej, O.; Hand, E.; Shah, M. Part-based multiple-person tracking with partial occlusion handling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kieritz, H.; Becker, S.; Hübner, W.; Arens, M. Online multi-person tracking using Integral Channel Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 23–26 August 2016; pp. 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Nevatia, R. How does person identity recognition help multi-person tracking? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1217–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Berg, A.C.; Ortiz, L.E.; Berg, T.L. Who are you with and where are you going? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1345–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsiavash, H.; Ramanan, D.; Fowlkes, C.C. Globally-optimal greedy algorithms for tracking a variable number of objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milan, A.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. Continuous Energy Minimization for Multitarget Tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, N.; del Rincón, J.M.; Miller, P.C. Enhancing Linear Programming with Motion Modeling for Multi-target Tracking. In Proceedings of the Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 6–9 January 2015; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milan, A.; Schindler, K.; Roth, S. Multi-Target Tracking by Discrete-Continuous Energy Minimization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 2054–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagot-Bouquet, L.; Audigier, R.; Dhome, Y.; Lerasle, F. Improving Multi-frame Data Association with Sparse Representations for Robust Near-online Multi-object Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 774–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Yan, J. Poi: Multiple object tracking with high performance detection and appearance feature. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Leal-Taixé, L.; Milan, A.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. Motchallenge 2015: Towards a benchmark for multi-target tracking. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.01942. [Google Scholar]
- Milan, A.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. MOT16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.00831. [Google Scholar]
- Leal-Taixe, L.; Canton-Ferrer, C.; Schindler, K. Learning by Tracking: Siamese CNN for Robust Target Association. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Iqbal, U.; Insafutdinov, E.; Pishchulin, L.; Milan, A.; Gall, J.; Schiele, B. PoseTrack: A Benchmark for Human Pose Estimation and Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5167–5176. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Long-Term Action Dependence-Based Hierarchical Deep Association for Multi-Athlete Tracking in Sports Videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7957–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Andriluka, M.; Andres, B.; Schiele, B. Multiple People Tracking by Lifted Multicut and Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3701–3710. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ding, H.; Shahroudy, A.; Duan, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G.; Kot, A.C. Feature Boosting Network For 3D Pose Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Adaptive Computationally Efficient Network for Monocular 3D Hand Pose Estimation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2020—16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Part IV; Volume 12349, pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2016—14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. Part VIII. Volume 9912, pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime Multi-person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1302–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Huang, Z.; Deng, J. Associative Embedding: End-to-End Learning for Joint Detection and Grouping. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 2277–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, A.; Rivlin, E.; Shimshoni, I. Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 1, pp. 798–805. [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer, K.W.; Chawla, N.V.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. CoRR 2011. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/1106.1813 (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Chawla, N.V. Data Mining for Imbalanced Datasets: An Overview. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook, 2nd ed.; Maimon, O., Rokach, L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardin, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Evaluating multiple object tracking performance: The CLEAR MOT metrics. J. Image Video Process. 2008, 246309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Nevatia, R. Learning to associate: Hybridboosted multi-target tracker for crowded scene. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Perazzi, F.; Pont-Tuset, J.; McWilliams, B.; Van Gool, L.; Gross, M.; Sorkine-Hornung, A. A benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology for video object segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 724–732. [Google Scholar]



| Components | MOTA↑ | MOTP↑ | MT↑ | ML↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | IDS↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | 71.3 | 62.5 | 41.67 | 49.12 | 954 | 2191 | 578 |
| PAS | 79.5 | 68.2 | 43.77 | 40.11 | 502 | 1488 | 394 |
| PMS | 80.5 | 70.1 | 45.40 | 41.30 | 450 | 1100 | 278 |
| PIS | 77.3 | 69.1 | 43.00 | 45.70 | 498 | 1510 | 147 |
| PAS + PMS | 80.9 | 71.0 | 50.34 | 35.09 | 438 | 1086 | 153 |
| PAS + PMS + PIS | 84.7 | 76.4 | 56.60 | 33.30 | 296 | 792 | 54 |
| Methods | Mode | IDF1↑ | MOTA↑ | MOTP↑ | MT↑ | ML↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | IDS↓ | FPS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDPNN16 [6] | Online | 53.6 | 74.1 | 80.1 | 55.6 | 21.5 | 768 | 2812 | 192 | 1.2 |
| CEM [19] | Offline | 47.0 | 64.2 | 77.1 | 45.6 | 22.8 | 1506 | 3037 | 185 | 1.1 |
| MHT_DAM [9] | Offline | 49.3 | 73.5 | 79.1 | 50.7 | 23.2 | 863 | 2785 | 231 | 0.8 |
| ELP [20] | Offline | 57.0 | 76.0 | 80.8 | 56.6 | 21.0 | 794 | 2559 | 197 | 3.7 |
| Siamese CNN [26] | Offline | 54.4 | 75.6 | 80.7 | 56.3 | 22.2 | 716 | 2664 | 213 | 6.2 |
| Ours | Online | 58.0 | 75.2 | 80.5 | 52.6 | 21.0 | 748 | 2967 | 237 | 30 |
| Methods | Mode | IDF1↑ | MOTA↑ | MOTP↑ | MT↑ | ML↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | IDS↓ | FPS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDPNN16 [6] | Online | 42.2 | 73.2 | 74.9 | 45.0 | 5.0 | 174 | 1133 | 85 | 1.7 |
| CEM [19] | Offline | 36.1 | 50.8 | 52.1 | 25.0 | 15.0 | 831 | 1698 | 70 | 1.5 |
| MHT_DAM [9] | Offline | 44.5 | 69.2 | 68.6 | 35.0 | 10.0 | 153 | 1140 | 84 | 1.1 |
| ELP [20] | Offline | 44.8 | 75.8 | 77.4 | 45.0 | 5.0 | 167 | 1008 | 86 | 4.3 |
| Siamese CNN [26] | Offline | 44.4 | 75.2 | 76.9 | 45.0 | 0 | 164 | 1033 | 91 | 7.6 |
| Ours | Online | 48.5 | 72.2 | 73.6 | 35.0 | 5.0 | 133 | 1240 | 74 | 34 |
| Methods | Mode | IDF1↑ | MOTA↑ | MOTP↑ | MT↑ | ML↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | IDS↓ | FPS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDPNN16 [6] | Online | 78.3 | 72.7 | 64.0 | 45.5 | 18.3 | 560 | 882 | 85 | 1.1 |
| CEM [19] | Offline | 82.8 | 80.1 | 76.2 | 57.1 | 11.4 | 378 | 726 | 68 | 1.1 |
| MHT_DAM [9] | Offline | 80.9 | 84.9 | 76.3 | 55.3 | 35.1 | 314 | 818 | 94 | 0.7 |
| ELP [20] | Offline | 84.4 | 83.3 | 75.1 | 54.3 | 28.2 | 325 | 748 | 63 | 2.6 |
| Siamese CNN [26] | Offline | 81.4 | 83.3 | 75.2 | 55.7 | 18.2 | 375 | 768 | 93 | 6.0 |
| Ours | Online | 85.0 | 84.7 | 76.4 | 56.6 | 33.3 | 296 | 792 | 54 | 28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, L.; Zhu, M.; Ran, N.; Liu, Q.; He, R. Online Multiple Athlete Tracking with Pose-Based Long-Term Temporal Dependencies. Sensors 2021, 21, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010197
Kong L, Zhu M, Ran N, Liu Q, He R. Online Multiple Athlete Tracking with Pose-Based Long-Term Temporal Dependencies. Sensors. 2021; 21(1):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010197
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Longteng, Mengxiao Zhu, Nan Ran, Qingjie Liu, and Rui He. 2021. "Online Multiple Athlete Tracking with Pose-Based Long-Term Temporal Dependencies" Sensors 21, no. 1: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010197
APA StyleKong, L., Zhu, M., Ran, N., Liu, Q., & He, R. (2021). Online Multiple Athlete Tracking with Pose-Based Long-Term Temporal Dependencies. Sensors, 21(1), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010197







