Model Evaluation of the Influence of the Plunger Stroke on Functional Parameters of the Low-Pressure Pulse Gas Solenoid Injector
Abstract
:1. Introduction
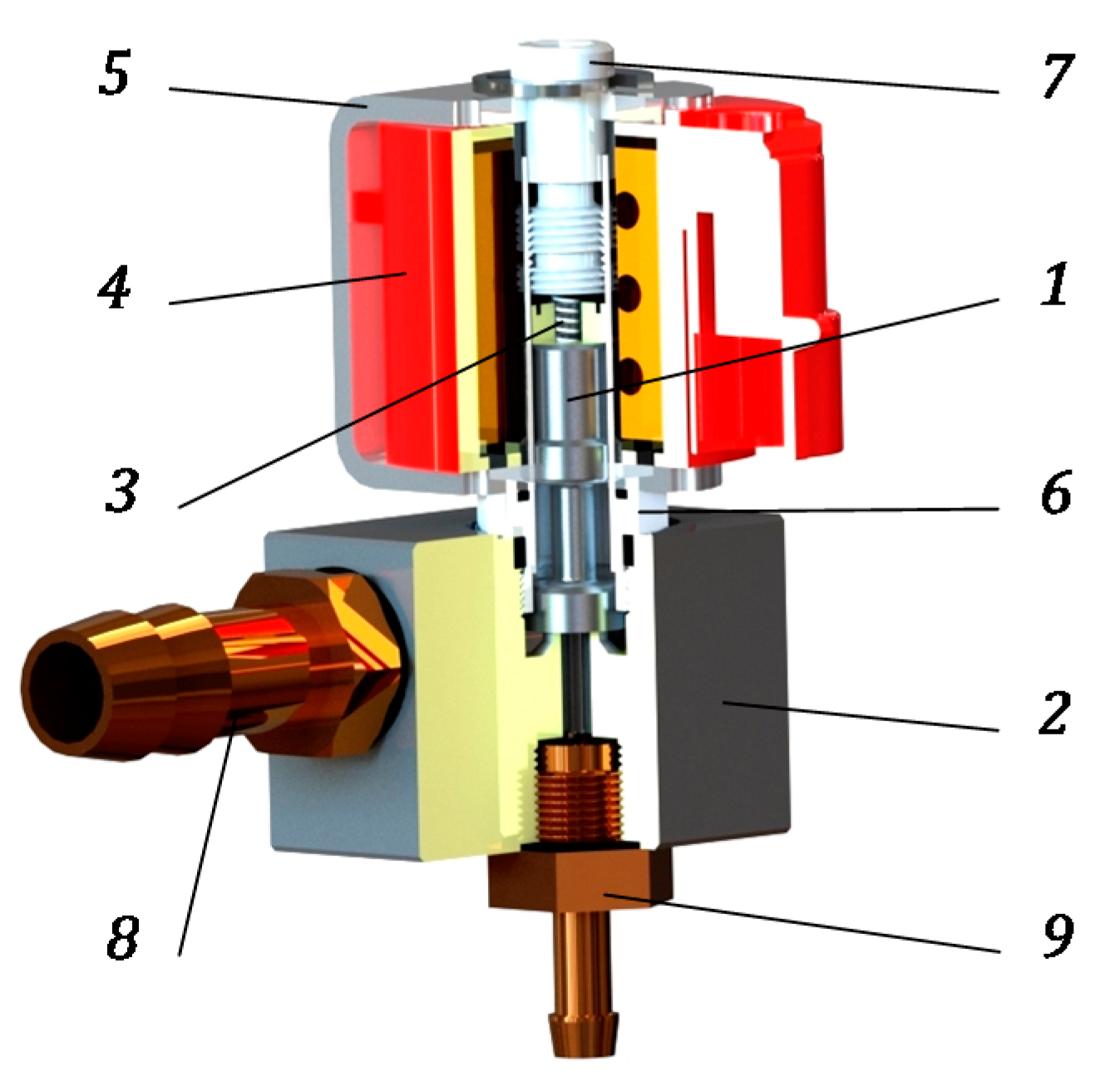
2. The Subject of the Modeling
3. Mathematical Modeling
- the plunger position depends on the resultant forces acting in the system, the effect of reflection from elements susceptible in the return positions is omitted;
- the electromagnetic force results from the operation of the coil without interference;
- the force generated by the pressure spring is due to its stiffness and pretension, the vibrations are omitted;
- the force from the pressure is distributed evenly and depends on the characteristic area and plunger position;
- the friction force responsible for damping takes into consideration different components depending on the position and movement of the plunger;
- the drag force due to its low impact on plunger movement was omitted.
4. Impact of Plunger Stroke on Functional Parameters of the Injector
5. Summary and Conclusions
- The presented new mathematical model was successfully validated. The simulated opening and closing times differed respectively, by 0.4% and 2.8% from the declaration in the injector technical documentation.
- The proposed mathematical description of the reluctance of the coil and its inductance are the basis of the modular model architecture. Further modifications can be introduced to this submodel, for improved simulation accuracy, by accounting for the reluctance of the electromagnetic circuit components and their location.
- The plunger forces’ analysis showed the dominant role of electromagnetic coil force, pressure, and the spring force. On the other hand, the forces responsible for frictional damping are of an order of magnitude lower.
- As the plunger stroke increases, the asymmetry of the opening time/closing time direct influence is noticeable, which may affect the amount of fuel dosing.
- A comparison of the results with the calculations of other authors has shown compatibility. The proposed model is more responsive to the variability of forces and movement conditions.
- The innovative concept of coil inductance modeling, incorporating the core dynamics, proposed in this paper is correct, was found to be valid within the constraints of the adopted literature reference data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Acronyms
| EFA | Example of First Abbreviation |
| AMFA | Alternative Motor Fuels Act |
| CAFÉ | Corporate Average Fuel Economy |
| CAI | Controlled Auto-Ignition |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| CNG | Compressed Natural Gas |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| ECU | Electronic Control Unit |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| HCCI | Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition |
| HPDI | High Pressure Direct Injection |
| LPG | Liquefied Petroleum Gas |
| PWM | Pulse-Width Modulation signal |
| RCCI | Reactivity Controlled Compression Ignition |
| RDE | Real Driving Emissions test |
| WLTC | Worldwide harmonized Light vehicles Test Cycle |
| A1 | cross area over the plunger, m2 |
| A2 | cross area under the plunger, m2 |
| ac | distance of the plunger center of mass from the edge of the coil, m |
| dc | internal diameter of the coil, m |
| Dc | outer diameter of the coil, m |
| Fe | electromagnetic force, N |
| Ff | friction force, N |
| Ffk | kinetic friction force, N |
| Ffs | static friction force, N |
| Ffv | viscous friction force, N |
| Fm | resistance force of mass inertial, N |
| FN | normal force, N |
| Fp | pressure force, N |
| Fs | spring force, N |
| g | gravitational acceleration, m⋅s−2 |
| ga | air gap between the plunger and the inner edge of the coil, m |
| Hc | coil length, m |
| hc | length of plunger outside the valve cabinet, m |
| I | current, A |
| k | spring stiffness, N⋅m−1 |
| L | inductance, H |
| m | plunger mass, kg |
| Nc | number of turns of coil, - |
| p1 | gas pressure, Pa |
| p2 | inlet manifold pressure, Pa |
| R | resistance, Ω |
| RM | magnetic reluctance, H−1 |
| tc | closing time, s |
| tinj | injection time, s |
| to | opening time, s |
| U | voltage, V |
| x | plunger displacement, m |
| x0 | initial tension the spring, m |
| Δto | opening time difference, % |
| Δtc | closing time difference, % |
| μ0 | permeability of vacuum, H⋅m−1 |
| μk | coefficient of coefficient of kinetic friction, - |
| μs | coefficient of static friction, - |
| μv | coefficient of coefficient of viscous friction, N⋅s⋅m−1 |
References
- Streimikiene, D.; Baležentis, T.; Baležentiene, L. Comparative assessment of road transport technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 20, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslavičius, L.; Keršys, A.; Mockus, S.; Keršiene, N.; Starevičius, M. Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as a medium-term option in the transition to sustainable fuels and transport. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, T.; Kypreos, S.; Turton, H.; Barreto, L. An energy-economic scenario analysis of alternative fuels for personal transport using the Global Multi-regional MARKAL model (GMM). Energy 2009, 34, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Helfand, G.E. The Alternative Motor Fuels Act, alternative-fuel vehicles, and greenhouse gas emissions. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2009, 43, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Union. Council Directive 2014/94/EU of 22 October 2014 on the Deployment of Alternative Fuels Infrastructure. Official Journal of the European Union, 28 October 2014; L 307/1. [Google Scholar]
- Leduc, P.; Dubar, B.; Ranini, A.; Monnier, G. Downsizing of gasoline engine: An efficient way to reduce CO2 emissions. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 58, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeuland, N.; Montagne, X.; Duret, P. New HCCI/CAI combustion process development: Methodology for determination of relevant fuel parameters. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 59, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldsson, G. Closed-Loop Combustion Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine Using Variable Compression Ratio and Fast Thermal Management; Division of Combustion Engines, Lund Institute of Technology: Lund, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mikulski, M.; Balakrishnan, P.R.; Doosje, E.; Bekdemir, C. Variable Valve Actuation Strategies for Better Efficiency Load Range and Thermal Management in an RCCI Engine. SAE Tech. Pap. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitukiewicz, G.; Dychto, R.; Leyko, J. Relationship between LPG fuel and gasoline injection duration for gasoline direct injection engines. Fuel 2015, 153, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, K.F.; Gitano-Briggs, H.W. Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as an alternative fuel in spark ignition engine: Performance and emission characteristics. In Proceedings of the ICEE 2009—Proceeding 2009 3rd International Conference on Energy and Environment: Advancement Towards Global Sustainability, Malacca, Malaysia, 7–8 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ristovski, Z.D.; Jayaratne, E.R.; Morawska, L.; Ayoko, G.A.; Lim, M. Particle and carbon dioxide emissions from passenger vehicles operating on unleaded petrol and LPG fuel. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 345, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Woodburn, J. Trends in Automotive Emission Legislation: Impact on LD Engine Development, Fuels, Lubricants and Test Methods: A Global View, with a Focus on WLTP and RDE Regulations. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2019, 5, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waluś, K.J.; Warguła, Ł.; Krawiec, P.; Adamiec, J.M. Legal regulations of restrictions of air pollution made by non-road mobile machinery—The case study for Europe: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3243–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warguła, Ł.; Krawiec, P.; Waluś, K.J.; Kukla, M. Fuel Consumption Test Results for a Self-Adaptive, Maintenance-Free Wood Chipper Drive Control System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalligeros, S.; Zannikos, F.; Stournas, S.; Lois, E.; Anastopoulos, G.; Karonis, D. Impact of gasoline quality on engine performance and emissions. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Lemnos Island, Greece, 8–10 September 2003; pp. 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Anandarajah, G.; McDowall, W.; Ekins, P. Decarbonising road transport with hydrogen and electricity: Long term global technology learning scenarios. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3419–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigor’ev, M.A.; Naumovich, N.I.; Belousov, E.V. A traction electric drive for electric cars. Russ. Electr. Eng. 2015, 86, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marčič, S.; Marčič, M.; Praunseis, Z. Mathematical model for the injector of a common rail fuel-injection system. Engineering 2015, 7, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raslavičius, L.; Azzopardi, B.; Keršys, A.; Starevičius, M.; Bazaras, Ž.; Makaras, R. Electric vehicles challenges and opportunities: Lithuanian review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslavičius, L.; Keršys, A.; Makaras, R. Management of hybrid powertrain dynamics and energy consumption for 2WD, 4WD, and HMMWV vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, Z.; Maréchal, F. Gasoline hybrid pneumatic engine for efficient vehicle powertrain hybridization. Appl. Energy 2015, 151, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AC STAG 500 DIS. Available online: https://www.ac.com.pl (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Borawski, A. Modification of a fourth generation LPG installation improving the power supply to a spark ignition engine. Eksploat. I Niezawodn. 2015, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendeker, M.; Jakliński, P.; Czarnigowski, J.; Boulet, P.; Breaban, F. Operational Parameters of Lpg Fueled Si Engine—Comparison of Simultaneous and Sequential Port Injection; Technical Report; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, January 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnigowski, J. Teoretyczno-Empiryczne Studium Modelowania Impulsowego Wtryskiwacza Gazu; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Lubelskiej: Lublin, Poland, 2012; ISBN PL 978-83-63569-09-9. [Google Scholar]
- Szpica, D.; Czaban, J. Operational assessment of selected gasoline and LPG vapour injector dosage regularity. Mechanika 2014, 20, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szpica, D. Investigating fuel dosage non-repeatability of low-pressure gas-phase injectors. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2018, 59, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieczkowski, G. Static electromechanical characteristics of piezoelectric converters with various thickness and length of piezoelectric layers. Acta Mech. Autom. 2019, 13, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mieczkowski, G.; Borawski, A.; Szpica, D. Static electromechanical characteristic of a three-layer circular piezoelectric transducer. Sensors 2020, 20, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.H.; Jiang, F. Simulation research on fuel injection system of 16v265H diesel engine introduced from U.S. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on E-Product E-Service and E-Entertainment, Henan, China, 7–9 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Qian, X. RETRACTED ARTICLE: The calculation of main parameters of the gasoline engine fuel injection system. In Proceedings of the ICCASM 2010–2010 International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling, Taiyuan, China, 22–24 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mieczkowski, G.; Molski, K.; Seweryn, A. Finite-element modeling of stresses and displacements near the tips of pointed inclusions. Mater. Sci. 2007, 43, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczuk, A.; Caban, J.; Aleshkin, A.V.; Savinykh, P.A.; Isupov, A.Y.; Ivanov, I.I. Modeling and simulation of particle motion in the operation area of a centrifugal rotary chopper machine. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brumercik, F.; Lukac, M.; Caban, J.; Krzysiak, Z.; Glowacz, A. Comparison of selected parameters of a planetary gearbox with involute and convex-concave teeth flank profiles. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehlfeldt, D.; Weckenmann, H.; Stöhr, G. Modeling of piezoelectrically actuated fuel injectors. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-J.; Fu, Q.-F.; Qu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Du, M.-L.; Xu, B.-R. Spray characteristics of gelled propellants in swirl injectors. Fuel 2012, 97, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawski, A. Simulation studies of LPG injector used in 4th generation installations. Combust. Engines 2015, 160, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bensetti, M.; Le Bihan, Y.; Marchand, C. Development of an hybrid 3D FEM for the modeling of micro-coil sensors and actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 129, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Z.D.; Guo, H.; Xie, N.L. Simulation and analysis on electro-magneticthermal coupling of solenoid GDI injector. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacurar, C.; Topa, V.; Munteanu, C.; Racasan, A.; Hebedean, C.; Oglejan, R.; Vlad, G. Solenoid Actuator Parametric Analysis and Numerical Modeling. Acta Electroteh. 2015, 56, 246–251. [Google Scholar]
- Bali, E.; Erzan Topcu, E. Design on-off type solenoid valve for electropneumatic brake system and investigation of its static characteristics. Int. J. Adv. Automot. Technol. 2018, 2, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendeker, M.; Jakliński, P.; Grabowski, Ł.; Pietrykowski, K.; Czarnigowski, J.; Hunicz, J. Model of CNG flap valve injector for internal combustion engines. Combust. Engines 2007, 131, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnigowski, J.; Jakliński, P.; Wendeker, M.; Pietrykowski, K.; Grabowski, Ł. The analyses of the phenomena inside a CNG flap-valve injector during gas flow. Combust. Engines 2009, 136, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Szpica, D. Simplified numerical simulation as the base for throttle flow characteristics designation. Mechanika 2015, 21, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, N.B.; Lim, O. Improvement of Electromagnetic Force and Dynamic Response of a Solenoid Injector Based on the Effects of Key Parameters. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Ghaffari, A.; Najafi, F. Modeling and identification of a solenoid valve for PWM control applications. Comptes Rendus Mec. 2009, 337, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpica, D. Modeling of current limitation through the PWM signal in LPG injectors. In Proceedings of the Transport Means—Proceedings of the International Conference, Juodkrante, Lithuania, 5–7 October 2016; pp. 536–539. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Liu, H.; Tao, G.L.; Man, J.; Zhong, W. Development of an ε-type actuator for enhancing high-speed electro-pneumatic ejector valve performance. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.K.; Jensen, D.S. Potential viability of a fast-acting micro-solenoid valve for pulsed detonation fuel injection. In Proceedings of the 41st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, Nevada, 6–9 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dongiovanni, C.; Dongiovanni, C.; Coppo, M. Accurate Modelling of an Injector for Common Rail Systems. In Fuel Injection; Siano, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2010; pp. 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Z.D.; Guo, H.; Xie, N.L. Electro-magnetic-thermal coupling of GDI injector. Jilin Daxue Xuebao J. Jilin Univ. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavec, E.; Ladisic, I.; Vidovic, M. The impact of coil winding angle on the force of DC solenoid electromagnetic actuator. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 17, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Dai, Z.K.; Xu, X.I.; Tian, L. Multi-domain modeling and simulation of proportional solenoid valve. J. Cent. South. Univ. Technol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhao, Y. Coil inductance model based solenoid on/off valve spool displacement sensing via laser calibration. Sensors 2018, 18, 4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.X.; Su, M.; Zhang, D.B. Response characteristic of high-speed on/off valve with double voltage driving circuit. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 220, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cvetkovic, D.; Cosic, I.; Subic, A. Improved performance of the electromagnetic fuel injector solenoid actuator using a modelling approach. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2008, 27, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunge, S.P.; Kurode, S.; Chhibber, B. Proportional actuator from on off solenoid valve using sliding modes. In Proceedings of the 1st International and 16th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms, Uttarakhand, India, 18–20 December 2013; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Morselli, R.; Corti, E.; Rizzoni, G. Energy based model of a common rail injector. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Control Applications, Glasgow, UK, 18–20 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Borawski, A. Common methods in analysing the tribological properties of brake pads and discs-A review. Acta Mech. Autom. 2019, 13, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.E.; Sun, X.Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.G. Parameter analysis of aerodynamic drag force in stratospheric airship. Gongcheng Lixue Eng. Mech. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, N.N.; Palii, A.V.; Saenko, A.V.; Maevskii, A.M. A Method of Body Shape Optimization for Decreasing the Aerodynamic Drag Force in Gas Flow. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnigowski, J.; Wendeker, M.; Jakliński, P.; Rola, M.; Grabowski, Ł.; Pietrykowski, K. CFD Model of Fuel Rail for LPG Systems; Technical Report; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, January 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Hou, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Ehsani, M. Study on the dynamic characteristics of pneumatic ABS solenoid valve for commercial vehicle. In Proceedings of the VPPC 2007—Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Arlington, TX, USA, 9–12 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Szpica, D.; Kusznier, M. Modelling of the low pressure gas injector operation. Acta Mech. Autom. 2020, 14, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnigowski, J.; Jakliński, P.; Zyska, T.; Duk, M. Model empiryczny prądu w obwodzie impulsowego wtryskiwacza gazu. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpica, D. Validation of indirect methods used in the operational assessment of LPG vapor phase pulse injectors. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2018, 118, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtek Type 30—Technical Data. Available online: https://www.valtek.it (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Passarini, L.C.; Pinotti, M. A new model for fast-acting electromagnetic fuel injector analysis and design. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2003, 25, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarini, L.C.; Nakajima, P.R. Development of a high-speed solenoid valve: An investigation of the importance of the armature mass on the dynamic response. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2003, 25, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawski, A. Analiza Procesu Zasilania Silników Spalinowych o Zapłonie Iskrowym Alternatywnym Układem LPG IV Generacji; Bialystok University of Technology: Bialystok, Porland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Szpica, D. Comparative analysis of the characteristics of a low-pressure gas-phase injector. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2017, 58, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| nozzle size | 4 × 10−3 m |
| piston stroke | 0.4 × 10−3 m |
| coil resistance | 3 Ω |
| opening time | 3.4 × 10−3 s |
| closing time | 2.2 × 10−3 s |
| maximum working pressure | 4.5 × 103 Pa |
| operating temperature | (−20… + 120) + 273.15 K |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| injection time | tinj = 5 × 10−3 s |
| mass of the piston and needle | m = 5 × 10−3 kg |
| resistance/impedance | R = 3 Ω |
| initial tension the spring | x0 = 0.75 × 10−3 m |
| coefficient of static friction | μs = 0.61 |
| coefficient of kinematic friction | μk = 0.47 |
| coefficient of viscous friction | μv = 0.009 N⋅s⋅m−1 |
| normal force | FN = m g |
| cross area over the valve | A1 = 32.56 × 10−6 m2 |
| cross area under the valve | A2 = 12.56 × 10−6 m2 |
| gas pressure | p1 = 1 × 105 Pa + p2 |
| inlet manifold pressure | p2 = 1 × 105 Pa |
| Boundary Conditions | |
| at t = 0 | U = 12 V; x = 0 m |
| after the time t = tinj, | U = 0 V |
| xmax, × 10−3 m | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| to, × 10−3 s | 2.82 | 3.05 | 3.23 | 3.39 | 3.52 | 3.64 | 3.76 | 3.87 | 3.97 | 4.07 |
| tc, × 10−3 s | 1.22 | 1.65 | 1.93 | 2.14 | 2.30 | 2.43 | 2.55 | 2.64 | 2.72 | 2.79 |
| Source | Method | to, × 10−3 s | tc, × 10−3 s | Δto, % | Δtc, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [68] | manufacturer | 3.40 | 2.20 | − | − |
| this paper | modeling | 3.386 | 2.138 | −0.41 | −2.82 |
| Ref. [65] | modeling | 3.47 | 2.15 | 2.05 | −2.27 |
| Ref. [71] | modeling | 3.50 | 2.50 | −2.94 | 13.64 |
| Ref. [26] | experiment (current line) | 3.30 | − | −2.94 | − |
| Ref. [71] | experiment (high speed camera) | 3.50 | 2.50 | 2.94 | 13.64 |
| Ref. [72] | experiment (1 pressure sensor) | 3.10 | 2.54 | −8.82 | 15.45 |
| Ref. [26] | experiment (2 pressure sensor) | − | 1 | − | −54.55 |
| Ref. [72] | experiment (vibration sensor) | 2.70 | 2.45 | −20.59 | 11.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szpica, D.; Kusznier, M. Model Evaluation of the Influence of the Plunger Stroke on Functional Parameters of the Low-Pressure Pulse Gas Solenoid Injector. Sensors 2021, 21, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010234
Szpica D, Kusznier M. Model Evaluation of the Influence of the Plunger Stroke on Functional Parameters of the Low-Pressure Pulse Gas Solenoid Injector. Sensors. 2021; 21(1):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010234
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzpica, Dariusz, and Michał Kusznier. 2021. "Model Evaluation of the Influence of the Plunger Stroke on Functional Parameters of the Low-Pressure Pulse Gas Solenoid Injector" Sensors 21, no. 1: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010234
APA StyleSzpica, D., & Kusznier, M. (2021). Model Evaluation of the Influence of the Plunger Stroke on Functional Parameters of the Low-Pressure Pulse Gas Solenoid Injector. Sensors, 21(1), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010234






