Beat-to-Beat Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Signal Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
2.3. Deep Learning
2.3.1. LSTM Network
2.3.2. Proposed Model Architecture
3. Results
3.1. Feature Analysis
3.2. General Model Analysis
3.3. Reproducibility Analysis
3.4. Evaluation Using International Standard
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogedegbe, G.; Pickering, T. Principles and techniques of blood pressure measurement. Cardiol. Clin. 2010, 28, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Baek, H.; Doh, K.; Jeong, J.; Ahn, S.; Oh, I.Y.; Kim, K. Validation of the mobile wireless digital automatic blood pressure monitor using the cuff pressure oscillometric method, for clinical use and self-management, according to international protocols. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2018, 8, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.T. Pulse transit time technique for cuffless unobtrusive blood pressure measurement: From theory to algorithm. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.Y.; Poon, C.C.; Zhang, Y.T. An evaluation of the cuffless blood pressure estimation based on pulse transit time technique: A half year study on normotensive subjects. Cardiovasc. Eng. 2009, 9, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kobayashi, T.; Ichikawa, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Togawa, T. Continuous estimation of systolic blood pressure using the pulse arrival time and intermittent calibration. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, C.; Zhang, Y. Cuff-less and noninvasive measurements of arterial blood pressure by pulse transit time. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 17–18 January 2006; pp. 5877–5880. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.R.; Zhang, Y.T.; Liu, J.; Dai, W.X.; Tsang, H.K. Continuous Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Using Pulse Transit Time and Photoplethysmogram Intensity Ratio. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, R.A.; Symeonides, C.N.; Webb, D.J.; Maxwell, S.R. Pulse transit time measured from the ECG: An unreliable marker of beat-to-beat blood pressure. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Lee, K.M.; Park, K.S. Non-constrained monitoring of systolic blood pressure on a weighing scale. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Roh, J.; Cho, D.; Hyeong, J.; Kim, S. A Chair-Based Unconstrained/Nonintrusive Cuffless Blood Pressure Monitoring System Using a Two-Channel Ballistocardiogram. Sensors 2019, 19, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, O.; Plawiak, P.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Arrhythmia detection using deep convolutional neural network with long duration ECG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 102, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Chaudhuri, S.; Munshi, S. Obstructive sleep apnoea detection using convolutional neural network based deep learning framework. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2018, 8, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundo, F.; Conoci, S.; Ortis, A.; Battiato, S. An Advanced Bio-Inspired PhotoPlethysmoGraphy (PPG) and ECG Pattern Recognition System for Medical Assessment. Sensors 2018, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.-T. Continuous cuff-less blood pressure estimation based on combined information using deep learning approach. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2018, 8, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Harfiya, L.N.; Purwandari, K.; Lin, Y.D. Real-Time Cuffless Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Deep Learning Model. Sensors 2020, 20, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.; Lee, D.; Han, S.; Hariyani, Y.S.; Lim, Y.; Sohn, I.; Park, K.; Park, C. End-to-End Deep Learning Architecture for Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Attention Mechanism. Sensors 2020, 20, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, E.; Petrie, J.; Littler, W.; de Swiet, M.; Padfield, P.L.; O’Malley, K.; Jamieson, M.; Altman, D.; Bland, M.; Atkins, N. The British Hypertension Society protocol for the evaluation of automated and semi-automated blood pressure measuring devices with special reference to ambulatory systems. J. Hypertens 1990, 8, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachuee, M.; Kiani, M.M.; Mohammadzade, H.; Shabany, M. Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Algorithms for Continuous Health-Care Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slapničar, G.; Mlakar, N.; Lustrek, M. Blood Pressure Estimation from Photoplethysmogram Using a Spectro-Temporal Deep Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Li, Y.H.; Chang, C.C.; Harfiya, L.N. Generalized Deep Neural Network Model for Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation with Photoplethysmogram Signal Only. Sensors 2020, 20, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.-W.H.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Anthony Celi, L.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, A freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Ding, X.-R.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Liu, J.; Miao, F.; Zhao, N. Long-term blood pressure prediction with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical & Health Informatics (BHI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 March 2018; pp. 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M. The 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Clinical Practice Guideline for High Blood Pressure in Adults. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

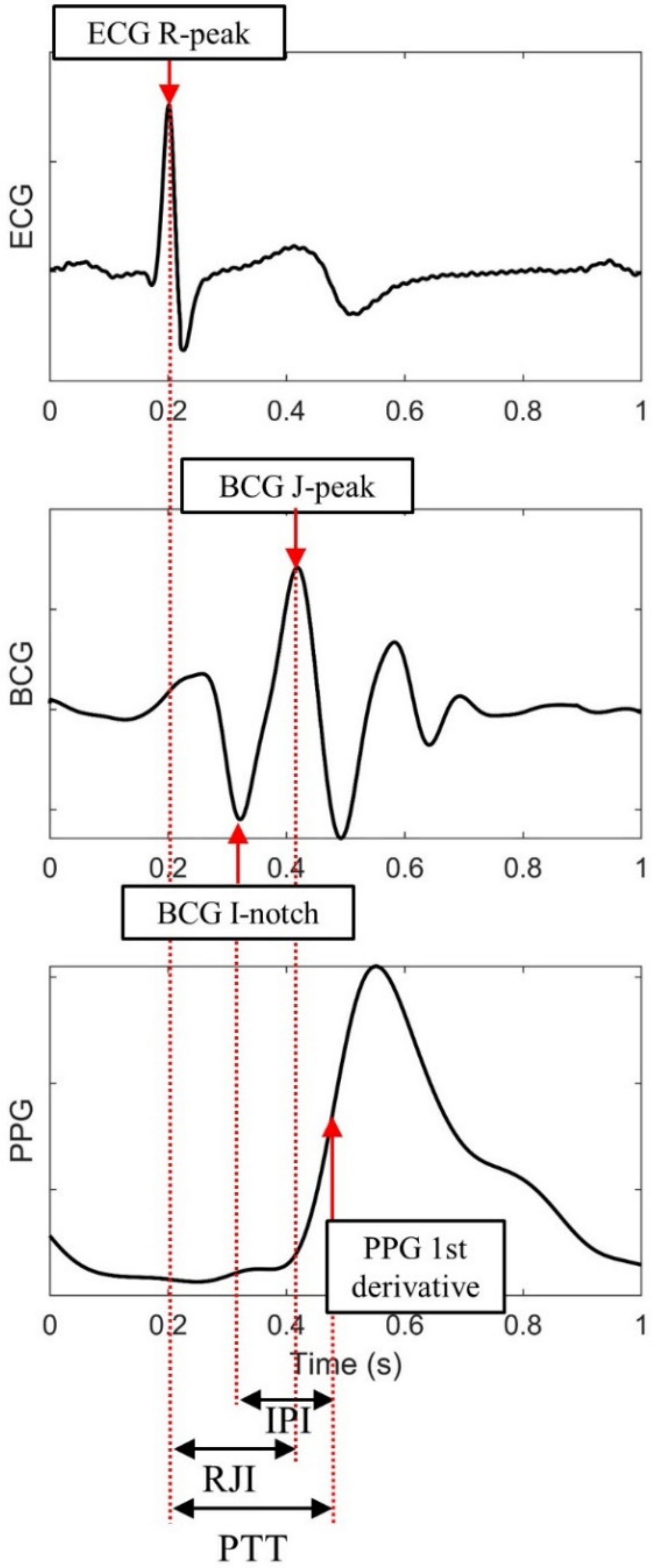






| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| R-R Interval (RRI) | ECG R-peak to R-peak interval |
| Pulse Transit Time (PTT) | ECG R-peak to dPPG peak interval |
| R-J Interval (RJI) | ECG R-peak to BCG J-peak interval |
| I-P Interval (IPI) | BCG I notch to dPPG peak interval |
| ECGamp | Amplitude of ECG R-peak |
| BCGamp | Amplitude of BCG J-peak |
| PPGamp | Amplitude of dPPG peak |
| Inputs | Features |
|---|---|
| ECG | RRI, ECGamp |
| ECG, BCG | RRI, RJI, ECGamp, BCGamp |
| ECG, PPG | RRI, PTT, ECGamp, PPGamp |
| ECG, PPG, BCG | RRI, PTT, RJI, IPI, ECGamp, BCGamp, PPGamp |
| Inputs | SBP | DBP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | CC | MAE | RMSE | CC | |
| ECG | 3.81 | 4.75 | 0.50 | 2.70 | 3.40 | 0.51 |
| ECG, BCG | 3.50 | 4.42 | 0.59 | 2.51 | 3.15 | 0.62 |
| ECG, PPG | 2.84 | 3.57 | 0.74 | 2.29 | 2.88 | 0.70 |
| ECG, PPG, BCG | 2.62 | 3.36 | 0.77 | 2.03 | 2.57 | 0.76 |
| Model | Systolic Blood Pressure(SBP) | Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | CC | MAE | RMSE | CC | |
| Personal | 2.62 | 3.36 | 0.77 | 2.03 | 2.57 | 0.76 |
| LOSO | 10.01 | 11.26 | 0.40 | 5.64 | 6.52 | 0.40 |
| Tuned LOSO | 2.56 | 3.25 | 0.80 | 2.05 | 2.61 | 0.76 |
| Train | Test | Model | SBP | DBP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | CC | MAE | RMSE | CC | |||
| Visit #1 | Visit #2 | Personal | 7.12 | 8.99 | 0.41 | 6.22 | 7.61 | 0.38 |
| LOSO | 10.23 | 11.49 | 0.41 | 5.94 | 6.81 | 0.41 | ||
| Tuned LOSO | 5.81 | 6.78 | 0.53 | 5.34 | 6.14 | 0.51 | ||
| Visit #2 | Visit #1 | Personal | 6.23 | 7.60 | 0.45 | 5.20 | 6.27 | 0.41 |
| LOSO | 10.82 | 11.97 | 0.45 | 6.17 | 7.06 | 0.41 | ||
| Tuned LOSO | 5.84 | 6.85 | 0.52 | 5.14 | 5.97 | 0.49 | ||
| Total | Personal | 6.67 | 8.29 | 0.43 | 5.71 | 6.94 | 0.40 | |
| LOSO | 10.52 | 11.73 | 0.43 | 6.06 | 6.94 | 0.41 | ||
| Tuned LOSO | 5.82 | 6.82 | 0.53 | 5.24 | 6.06 | 0.50 | ||
| Cumulative Absolute Error Percentage | Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤5 mmHg | ≤10 mmHg | ≤15 mmHg | |||
| BHS standard | 60% | 85% | 95% | A | |
| 50% | 75% | 90% | B | ||
| 40% | 65% | 85% | C | ||
| Worse than C | D | ||||
| Proposed model (one-day test) | SBP | 89.3% | 99.4% | 100.0% | A |
| DBP | 94.7% | 99.8% | 100.0% | A | |
| Proposed model (multi-day test) | SBP | 51.6% | 81.4% | 96.3% | B |
| DBP | 56.1% | 87.9% | 98.3% | B | |
| ME (mmHg) | STD (mmHg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AAMI Standard | 5 | 8 | |
| Proposed model (one-day test) | SBP | −0.09 | 3.15 |
| DBP | −0.07 | 2.52 | |
| Proposed model (multi-day test) | SBP | −0.07 | 7.30 |
| DBP | −0.17 | 6.4 |
| Model | Equation | MAE (mmHg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | DBP | ||
| Chen et al. [5] | 4.32 | - | |
| Poon et al. [6] | 4.70 | 3.28 | |
| Ding et al. [7] | 4.47 | 3.15 | |
| MLR model (w/o BCG features) | 4.25 | 3.16 | |
| MLR model (with BCG features) | 4.17 | 3.12 | |
| MLR model (with previous features) | ) | 3.71 | 2.65 |
| Proposed model | Long short-term memory (LSTM) | 2.62 | 2.03 |
| Author | Dataset | Model | Input | Validation Method | SBP Error (mmHg) | DBP Error (mmHg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | |||||
| Kachuee et al. [19] | N = 1000 10 min (MIMIC III) | AdaBoost | ECG, PPG features | Personal | 8.21 | 4.31 | ||
| 10-fold cross validation | 11.17 | 5.35 | ||||||
| Slapničar et al. [20] | 510 subjects 700 h (MIMIC III) | ResNet | Raw PPG | LOSO | 15.41 | 12.38 | ||
| Tuned LOSO | 9.43 | 6.88 | ||||||
| Hsu et al. [21] | N = 9000 (MIMIC II) | DNN | PPG features | 10-fold cross-validation | 3.21 | 4.63 | 2.23 | 3.21 |
| Wu et al. [14] | N = 85 | DNN | ECG, PPG features | 10-fold cross-validation | 3.31 | 4.60 | 2.22 | 3.15 |
| Su et al. [23] | N = 84 10 min | Bi-LSTM | ECG, PPG features | Personal (one-day) | 3.73 | 2.43 | ||
| Personal (multi-day) | 5.81 | 5.21 | ||||||
| Previous work [16] | N = 15 30 min | CNN, Bi-GRU, attention | Raw ECG, PPG, BCG | Personal | 4.06 | 5.42 | 3.33 | 4.30 |
| Proposed work | N = 18 30 min | Bi-LSTM | ECG, PPG, BCG features | Tuned LOSO (one-day) | 2.56 | 3.25 | 2.05 | 2.61 |
| Tuned LOSO (multi-day) | 5.82 | 6.82 | 5.24 | 6.06 | ||||
| LOSO | 10.01 | 11.26 | 5.60 | 6.52 | ||||
| BP Class | SBP | DBP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (mmHg) | Accuracy | Range (mmHg) | Accuracy | |
| Normal | BP < 120 | 84% | BP < 80 | 90% |
| Prehypertension | BP < 130 | 82% | ||
| Stage 1 Hypertension | BP < 140 | 97% | BP < 90 | 89% |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | 140 | 98% | 0 | 100% |
| Total | 81% | 89% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Kwon, H.; Son, D.; Eom, H.; Park, C.; Lim, Y.; Seo, C.; Park, K. Beat-to-Beat Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010096
Lee D, Kwon H, Son D, Eom H, Park C, Lim Y, Seo C, Park K. Beat-to-Beat Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network. Sensors. 2021; 21(1):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010096
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dongseok, Hyunbin Kwon, Dongyeon Son, Heesang Eom, Cheolsoo Park, Yonggyu Lim, Chulhun Seo, and Kwangsuk Park. 2021. "Beat-to-Beat Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network" Sensors 21, no. 1: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010096
APA StyleLee, D., Kwon, H., Son, D., Eom, H., Park, C., Lim, Y., Seo, C., & Park, K. (2021). Beat-to-Beat Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network. Sensors, 21(1), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010096






