Current Trends and Challenges in Pediatric Access to Sensorless and Sensor-Based Upper Limb Exoskeletons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Upper Limb Biomechanics and Diagnoses in Pediatrics
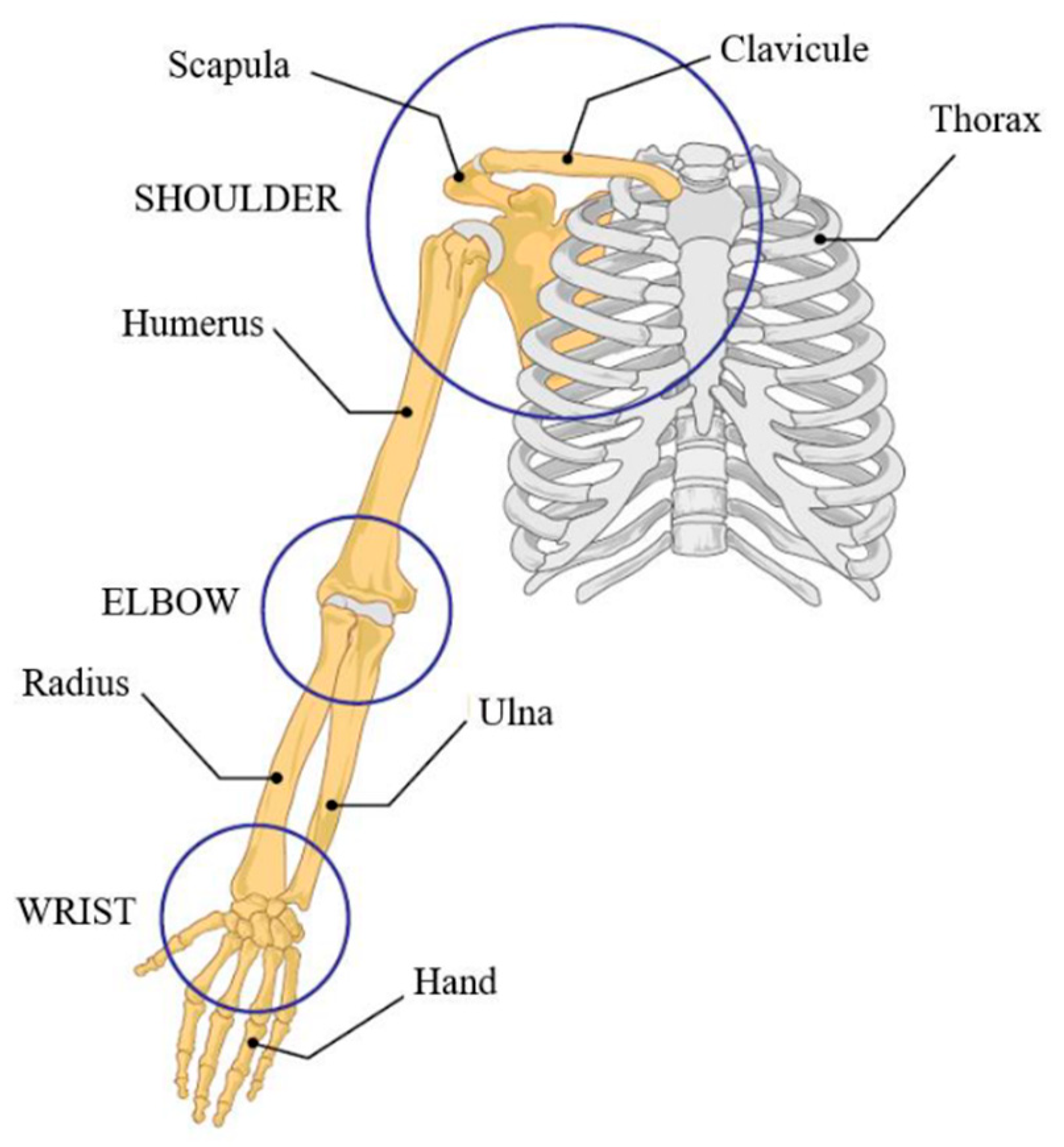
2.1. Upper Limb Biomechanics
2.2. Diagnoses in Pediatrics
2.2.1. Cerebral Palsy
2.2.2. Muscular Dystrophy
2.2.3. Spinal Muscular Atrophy
2.2.4. Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
2.2.5. Brachial Plexus Palsy
2.2.6. Transitioning to Adulthood
3. Classification of Sensorless and Sensor-Based Upper Limb Exoskeletons
4. Upper Limb Exoskeleton in Pediatrics
4.1. Sensorless Exoskeletons
4.1.1. Dynamic Orthosis
4.1.2. Elbow Flexion Assist Orthosis
4.1.3. Playskin Lift
4.1.4. Playskin Air
4.1.5. Wilmington Robotic EXoskeleton (WREX) and P-WREX+
4.2. Sensor-Based Exoskeletons
4.2.1. Armeo Spring
4.2.2. ChARMin
4.2.3. CT-DEA-Based Exoskeleton
4.2.4. Hand Exoskeleton
4.2.5. IOTA
4.2.6. MyoPal
4.2.7. PEXO
4.2.8. Soft Exoskeleton
4.3. Current Trends
5. Discussion
5.1. Rehabilitation Exoskeletons
5.2. Assistance Exoskeletons
5.3. Challenges for Pediatric Access
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emery, A. The Muscular Dystrophies. Lancet 2002, 359, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, M.R.; Wang, C.H. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Lancet 2008, 371, 2120–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odding, E.; Roebroeck, M.E.; Stam, H.J. The Epidemiology of Cerebral Palsy: Incidence, Impairments and Risk Factors. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamshad, M.; Van Heest, A.E.; Pleasure, D. Arthrogryposis: A Review and Update. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Looven, R.; Le Roy, L.; Tanghe, E.; Samijn, B.; Roets, E.; Pauwels, N.; Deschepper, E.; De Muynck, M.; Vingerhoets, G.; Van den Broeck, C. Risk Factors for Neonatal Brachial Plexus Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, M.A.; Harbourne, R.T.; Dusing, S.C.; McCoy, S.W. Grounding Early Intervention: Physical Therapy Cannot Just Be about Motor Skills Anymore. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magermans, D.J.; Chadwick, E.K.J.; Veeger, H.E.J.; van der Helm, F.C.T. Requirements for Upper Extremity Motions during Activities of Daily Living. Clin. Biomech. Bristol Avon 2005, 20, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, M.N.; Kurillo, G.; Chan, V.; Han, J.J. Motion Sensor-Acquired Reachable Workspace Correlates with Patient-Reported Upper Extremity Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Function in Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-A.; Lee, J.-A.; Hwang, P.-W.; Lee, M.-J.; Kim, H.-K.; Park, J.-J.; You, J.H.; Lee, D.-R.; Lee, N.-G. The Effect of Comprehensive Hand Repetitive Intensive Strength Training (CHRIST) Using Motion Analysis in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, M.; Frey, J.; Shohan, M.J.; Malek, S.; Mousa, S.A. Current and Emerging Therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 220, 107719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-J.; Liu, W.-Y.; Yang, T.-F.; Chen, C.-L.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chan, R.-C. Pediatric Aquatic Therapy on Motor Function and Enjoyment in Children Diagnosed with Cerebral Palsy of Various Motor Severities. J. Child Neurol. 2015, 30, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.A.; Durham, S.; Ewins, D.J.; Swain, I.D. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Review. Arch. Dis. Child. 2012, 97, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U.; Riener, R. Design of the Pediatric Arm Rehabilitation Robot ChARMin. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–15 August 2014; pp. 530–535. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N.; Aisen, M.L.; Volpe, B.T. Robot-Aided Neurorehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. Publ. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 1998, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nef, T.; Guidali, M.; Riener, R. ARMin III – Arm Therapy Exoskeleton with an Ergonomic Shoulder Actuation. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2009, 6, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, J.C.; Rosen, J.; Burns, S. Upper-Limb Powered Exoskeleton Design. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Agrawal, S.K. Design of a Cable-Driven Arm Exoskeleton (CAREX) for Neural Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Rahman, M.J.; Cristobal, O.L.; Saad, M.; Kenné, J.P.; Archambault, P.S. Development of a Whole Arm Wearable Robotic Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation and to Assist Upper Limb Movements. Robotica 2015, 33, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.-Q. IntelliArm: An Exoskeleton for Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Neurological Impairments. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE RAS EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 19–22 October 2008; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Wei, R.; Perez, M.; Shepard, B.; Koeneman, E.; Koeneman, J.; He, J. RUPERT: An Exoskeleton Robot for Assisting Rehabilitation of Arm Functions. In Proceedings of the Virtual Rehabilitation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25–27 August 2008; pp. 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Kiguchi, K.; Li, Y. SUEFUL-7: A 7DOF Upper-Limb Exoskeleton Robot with Muscle-Model-Oriented EMG-Based Control. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1126–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, U.; Klamroth, V.; van Hedel, H.J.A.; Riener, R. ChARMin: A Robot for Pediatric Arm Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 3908–3913. [Google Scholar]
- Falzarano, V.; Marini, F.; Morasso, P.; Zenzeri, J. Devices and Protocols for Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation of Children with Neuromotor Disorders. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berdina, O.N.; Bairova, T.A.; Rychkova, L.V.; Sheptunov, S.A. The Pediatric Robotic-Assisted Rehabilitation Complex for Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: Background and Product Design. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Quality Management, Transport and Information Security, Information Technologies” (IT QM IS), St. Petersburg, Russia, 24–30 September 2017; pp. 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Gull, M.A.; Bai, S.; Bak, T. A Review on Design of Upper Limb Exoskeletons. Robotics 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Bandara, D.S.V.; Kiguchi, K.; Mann, G.K.I. Developments in Hardware Systems of Active Upper-Limb Exoskeleton Robots: A Review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Pretty, C.G.; Adams, M.; Chen, X. Review of Upper Limb Hybrid Exoskeletons. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 15169–15178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmat, N.; Zuo, J.; Meng, W.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S.Q.; Liang, H. Upper Limb Rehabilitation Using Robotic Exoskeleton Systems: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2018, 2, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demofonti, A.; Carpino, G.; Zollo, L.; Johnson, M.J. Affordable Robotics for Upper Limb Stroke Rehabilitation in Developing Countries: A Systematic Review. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2021, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Brahmi, B.; Ahmed, T.; Assad-Uz-Zaman, M.; Rahman, M.H. Chapter 9—Exoskeletons in upper limb rehabilitation: A review to find key challenges to improve functionality. In Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering; Boubaker, O., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 235–265. ISBN 978-0-12-821350-6. [Google Scholar]
- Qassim, H.M.; Wan Hasan, W.Z. A Review on Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robots. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosch-Villaronga, E.; Čartolovni, A.; Pierce, R.L. Promoting Inclusiveness in Exoskeleton Robotics: Addressing Challenges for Pediatric Access. Paladyn J. Behav. Robot. 2020, 11, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, H. Development, Dynamic Modeling, and Multi-Modal Control of a Therapeutic Exoskeleton for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Training. Sensors 2018, 18, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarrasse, N.; Morel, G. Connecting a Human Limb to an Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, P.; Alekhya, S.; Majidirad, A.; Hakansson, N.A.; Desai, J.; Yihun, Y. Shoulder Kinematics Assessment towards Exoskeleton Development. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinold, J.A.; Masjedi, M.; Johnson, G.R.; Bull, A.M. Musculoskeletal Shoulder Models: A Technical Review and Proposals for Research Foci. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2013, 227, 1041–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitenberger, M.; Raison, M.; Périé, D.; Begon, M. Refinement of the Upper Limb Joint Kinematics and Dynamics Using a Subject-Specific Closed-Loop Forearm Model. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2015, 33, 413–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, N.; Lenzi, T.; Roccella, S.; De Rossi, S.M.M.; Cattin, E.; Giovacchini, F.; Vecchi, F.; Carrozza, M.C. NEUROExos: A Powered Elbow Exoskeleton for Physical Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, S.; Morgan, C.; Walker, K.; Novak, I. Cerebral Palsy-Don’t Delay. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2011, 17, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Boyd, R.; Ziviani, J.; Chatfield, M.D.; Ware, R.S.; Sakzewski, L. Stability of the Manual Ability Classification System in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U.; van Hedel, H.J.A.; Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Riener, R. ChARMin: The First Actuated Exoskeleton Robot for Pediatric Arm Rehabilitation. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Lloyd-Puryear, M. Report of MDA Muscle Disease Symposium on Newborn Screening for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Issues & Opinions: Newborn Screening for DMD. Muscle Nerve 2013, 48, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lally, C.; Jones, C.; Farwell, W.; Reyna, S.P.; Cook, S.F.; Flanders, W.D. Indirect Estimation of the Prevalence of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type I, II, and III in the United States. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Berry, P.; Brown, M.; Phillips, L.; Evans, S.H. Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2017, 47, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.L. The Transition to Adulthood for Children With Cerebral Palsy: What Do We Know About Their Health Care Needs? J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2007, 27, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viner, R. Transition from Paediatric to Adult Care. Bridging the Gaps or Passing the Buck? Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 81, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapp, C.E.; Torres, M.M. The Adult With Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Fam. Med. 2000, 9, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, Y.; Mistry, B.; Gibson, B.E. Transitioning to Adulthood with a Progressive Condition: Best Practice Assumptions and Individual Experiences of Young Men with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oskoui, M.; Levy, G.; Garland, C.J.; Gray, J.M.; O’Hagen, J.; De Vivo, D.C.; Kaufmann, P. The Changing Natural History of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1. Neurology 2007, 69, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, M.A.; Park, S.B.; Vucic, S.; Carey, K.A.; Turner, B.J.; Gillingwater, T.H.; Swoboda, K.J.; Kiernan, M.C. Emerging Therapies and Challenges in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, R.; Dahan-Oliel, N. Arthrogryposis. In Pediatric Lower Limb Deformities: Principles and Techniques of Management; Sabharwal, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2016; pp. 297–311. ISBN 978-3-319-17097-8. [Google Scholar]
- van der Holst, M. Neonatal Brachial Plexus Palsy: Impact throughout the Lifespan. Ph.D. Thesis, Leiden University, EZ Leiden, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki, G.S.; Beck, O.N.; Kang, I.; Young, A.J. The Exoskeleton Expansion: Improving Walking and Running Economy. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garavaglia, L.; Pagliano, E.; Arnoldi, M.T.; LoMauro, A.; Zanin, R.; Baranello, G.; Aliverti, A.; Pittaccio, S. Two Single Cases Treated by a New Pseudoelastic Upper-Limb Orthosis for Secondary Dystonia of the Young. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 1260–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, J.; Shank, T.M.; Castro, M.N.; Ryan, L.E.; Costa, J.; Rahman, T. Elbow Flexion Assist Orthosis for Arthrogryposis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 494–498. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.L.; Lobo, M.A. Design and Development of the First Exoskeletal Garment to Enhance Arm Mobility for Children with Movement Impairments. Assist. Technol. 2018, 30, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Greenspan, B.; Mascitelli, T.; Raccuglia, M.; Denner, K.; Duda, R.; Lobo, M.A. Design of the Playskin AirTM: A User-Controlled, Soft Pneumatic Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2019 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 15–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, T.; Galloway, C.; Kokkoni, E.; Lobo, M. Development and Testing of a Modular Upper Extremity Exoskeleton for Infants. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Angers, France, 3–6 March 2014; SCITEPRESS—Science and Technology Publications, Lda: Setubal, Portugal, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 316–319. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, M.; Shank, T.M.; Eppes, M.; Hossain, J.; Rahman, T. User Evaluation of a Dynamic Arm Orthosis for People With Neuromuscular Disorders. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, T.M.; Wee, J.; Ty, J.; Rahman, T. Quantitative Measures with WREX Usage. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 1375–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Hocoma Armeo Spring: Supporting the Recovery of Arm and Hand Function. Available online: https://www.hocoma.com/solutions/armeo-spring/ (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Cimolin, V.; Germiniasi, C.; Galli, M.; Condoluci, C.; Beretta, E.; Piccinini, L. Robot-Assisted Upper Limb Training for Hemiplegic Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Dev. Phys. Disabil. 2019, 31, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, E.; Iammarrone, F.S.; Pedrocchi, A.; Biffi, E.; Gagliardi, C.; Turconi, A.C.; Maghini, C.; Germiniasi, C.; Reni, G. A New Quantitative Performance Parameter for Monitoring Robotics Rehabilitation Treatment. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, Oldenburg, Germany, 20–23 May 2014; ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering): Brussels, Belgium, 2014; pp. 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Behboodi, A.; DeSantis, C.; Lubsen, J.; Lee, S.C.K. A Mechanized Pediatric Elbow Joint Powered by a De-Based Artificial Skeletal Muscle. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 4930–4935. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, M.; Secciani, N.; Ridolfi, A.; Vannetti, F.; Pasquini, G. Kinematics-Based Strategy for the Design of a Pediatric Hand Exoskeleton Prototype. In Advances in Italian Mechanism Science; Carbone, G., Gasparetto, A., Eds.; Mechanisms and Machine Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2019; Volume 68, pp. 501–508. ISBN 978-3-030-03319-4. [Google Scholar]
- Aubin, P.; Petersen, K.; Sallum, H.; Walsh, C.; Correia, A.; Stirling, L. A Pediatric Robotic Thumb Exoskeleton for At-Home Rehabilitation: The Isolated Orthosis for Thumb Actuation (IOTA). Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 2014, 7, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myomo MyoPal: Increased Function for Children with a Paralyzed or Weakened Arm. Available online: https://myomo.com/myopal/ (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Bützer, T.; Dittli, J.; Lieber, J.; van Hedel, H.J.A.; Meyer-Heim, A.; Lambercy, O.; Gassert, R. PEXO—A Pediatric Whole Hand Exoskeleton for Grasping Assistance in Task-Oriented Training. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkoni, E.; Liu, Z.; Karydis, K. Development of a Soft Robotic Wearable Device to Assist Infant Reaching. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, E.; Cesareo, A.; Biffi, E.; Schafer, C.; Galbiati, S.; Strazzer, S. Rehabilitation of Upper Limb in Children with Acquired Brain Injury: A Preliminary Comparative Study. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, e4208492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marini, F.; Hughes, C.M.L.; Squeri, V.; Doglio, L.; Moretti, P.; Morasso, P.; Masia, L. Robotic Wrist Training after Stroke: Adaptive Modulation of Assistance in Pediatric Rehabilitation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 91, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliaux, M.; Renders, A.; Dispa, D.; Holvoet, D.; Sapin, J.; Dehez, B.; Detrembleur, C.; Lejeune, T.M.; Stoquart, G. Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Therapy in Cerebral Palsy: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesareo, A.; Beretta, E.; Biffi, E.; Strazzer, S.; Reni, G. A Comparative Study Among Constraint, Robot-Aided and Standard Therapies in Upper Limb Rehabilitation of Children with Acquired Brain Injury. In Proceedings of the XIV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2016, Paphos, Cyprus, 31 March–2 April 2016; Kyriacou, E., Christofides, S., Pattichis, C.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.Z.; Ong, H.T.; Tan, J.X.; Lin, J.; Burdet, E.; Ge, S.S.; Teo, C.L. Pediatric Rehabilitation with the ReachMAN’s Modular Handle. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milano, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3933–3936. [Google Scholar]
- Holley, D.; Theriault, A.; Kamara, S.; Anewenter, V.; Hughes, D.; Johnson, M.J. Restoring ADL Function after Wrist Surgery in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Novel Bilateral Robot System Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Latt, W.T.; Luu, T.P.; Kuah, C.; Tech, A.W. Towards an Upper-Limb Exoskeleton System for Assistance in Activities of Daily Living (ADLs). In Proceedings of the International Convention on Rehabilitation Engineering & Assistive Technology, Singapore, 20 August 2014; Singapore Therapeutic, Assistive & Rehabilitative Technologies (START) Centre: Midview City, Singapore, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, U.; Rauter, G.; Riener, R. Assist-as-Needed Path Control for the PASCAL Rehabilitation Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, B.; Usselman, C.; Dotan, R.; Brunton, L.; Klentrou, P.; Shaw, J.; Gabriel, D. Child-Adult Differences in Muscle Strength and Activation Pattern during Isometric Elbow Flexion and Extension. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owings, C.L.; Chaffin, D.B.; Snyder, R.G.; Norcutt, R.H. Strength Characteristics of U.S. Children for Product Safety Design. Final Report; The Consumer Product Safety Commission: Bethesda, MD, USA; The University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Eek, M.N.; Kroksmark, A.-K.; Beckung, E. Isometric Muscle Torque in Children 5 to 15 Years of Age: Normative Data. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnemer, A.; Shevell, M.; Law, M.; Poulin, C.; Rosenbaum, P. Level of Motivation in Mastering Challenging Tasks in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, L.; Achiche, S.; Docquier, Q.; Fisette, P.; Raison, M. A Procedure to Optimize the Geometric and Dynamic Designs of Assistive Upper Limb Exoskeletons. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2021, 51, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.G.; Reid, C.R.; Rempel, D.D.; Treaster, D. Introduction to the Human Factors Special Issue on User-Centered Design for Exoskeleton. Hum. Factors 2020, 62, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ármannsdóttir, A.L.; Beckerle, P.; Moreno, J.C.; van Asseldonk, E.H.F.; Manrique-Sancho, M.-T.; del-Ama, A.J.; Veneman, J.F.; Briem, K. Assessing the Involvement of Users During Development of Lower Limb Wearable Robotic Exoskeletons: A Survey Study. Hum. Factors 2020, 62, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borgers, N.; de Leeuw, E.; Hox, J. Children as Respondents in Survey Research: Cognitive Development and Response Quality 1. Bull. Sociol. Methodol. Méthodologie Sociol. 2000, 66, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Raison, M.; Torres, A.; Gaudet, G.; Achiche, S. From On-Body Sensors to in-Body Data for Health Monitoring and Medical Robotics: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2014 Global Information Infrastructure and Networking Symposium (GIIS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–19 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Duivenvoorden, M.; Lee, K.; Raison, M.M.; Achiche, M.S. Sensor Fusion in Upper Limb Area Networks: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2017 Global Information Infrastructure and Networking Symposium (GIIS), Saint Pierre, France, 25–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan, M.C.; Foulds, R.A. Evaluation of Admittance Control as an Alternative to Passive Arm Supports to Increase Upper Extremity Function for Individuals with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizoua, C.; Raison, M.; Boukhenous, S.; Attari, M.; Achiche, S. Development of a Bracelet with Strain-Gauge Matrix for Movement Intention Identification in Traumatic Amputees. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, H.; Kong, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, P. A Novel Fatigue Detection Method for Rehabilitation Training of Upper Limb Exoskeleton Robot Using Multi-Information Fusion. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420974295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisian, S.V.; Ishmael, M.K.; Lenzi, T. Self-Aligning Mechanism Improves Comfort and Performance with a Powered Knee Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Device Name | Application Domain | Motorization Solution | Targeted Population(s) | Degrees of Freedom | Supported Movement(s) | Company/Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Orthosis | Assistance | Passive–SMA | Other | 3 | Elbow–FE Wrist–FE Thumb and Digits–FE | Garavaglia et al. [54] |
| Elbow Flexion Assist Orthosis | Assistance | Passive–Springs | AMC | 1 | Elbow–FE | Wee et al. [55] |
| Playskin Lift | Assistance | Passive–Wire | AMC, BPP, Other | 1 | Shoulder–FE | Hall et Lobo [56] |
| Playskin Air | Assistance | Active–Soft | AMC, BPP, Other | 1 | Shoulder–AA | Li et al. [57] |
| P-WREX+ | Assistance | Passive–Springs | AMC, BPP, Other | 4 | Shoulder–FE, AA Elbow–FE | Rahman et al. [58] |
| WREX | Assistance | Passive–Springs | DMD, AMC, CP, SMA | 4 | Shoulder–FE, AA Elbow–FE | Gunn et al. [59], Shank et al. [60] |
| Device Name | Application Domain | Motorization Solution | Type of Sensor(s) | Targeted Population(s) | Degrees of Freedom | Supported Movement(s) | Company/Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armeo Spring | Rehabilitation | Passive–Springs | Position, Pressure | CP, Other | 6 | Shoulder–FE, AA, IE Elbow–FE Forearm–PS Wrist–FE | Hocoma [61], Cimolin et al. [62], Peri et al. [63] |
| ChARMin | Rehabilitation | Active–Electric | Position | CP, Other | 6 | Shoulder–FE, AA, IE Elbow–FE Forearm–PS Wrist–FE | Keller et al. [13,22,41] |
| CT-DEA-Based Exoskeleton | Assistance | Active–Soft | Position, Force | N/A | 1 | Elbow–FE | Behboodi et al. [64] |
| Hand Exoskeleton | Assistance | Active–Electric | Position | CP | 2 | Digits–FE | Bianchi et al. [65] |
| Isolated Orthosis for Thumb Actuation | Rehabilitation | Active–Electric | Position, Bend | CP, Other | 2 | Thumb–FE, AA | Aubin et al. [66] |
| MyoPal | Assistance | Active–Electric | EMG, Position | BPP, CP, Other | 2 | Elbow–FE Thumb and Digits–FE | Myomo [67] |
| PEXO | Assistance | Active–Electric | EMG, Position | CP, Other | 3 | Thumb and Digits–FE | Bützer et al. [68] |
| Soft Exoskeleton | Assistance | Active–Soft | EMG | CP, Other | 4 | Shoulder–AA Elbow–FE | Kokkoni et al. [69] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaudet, G.; Raison, M.; Achiche, S. Current Trends and Challenges in Pediatric Access to Sensorless and Sensor-Based Upper Limb Exoskeletons. Sensors 2021, 21, 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103561
Gaudet G, Raison M, Achiche S. Current Trends and Challenges in Pediatric Access to Sensorless and Sensor-Based Upper Limb Exoskeletons. Sensors. 2021; 21(10):3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103561
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaudet, Guillaume, Maxime Raison, and Sofiane Achiche. 2021. "Current Trends and Challenges in Pediatric Access to Sensorless and Sensor-Based Upper Limb Exoskeletons" Sensors 21, no. 10: 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103561






