Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure and Data Collection
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Discrete Variables of the Lower-Extremity Joints during Walking
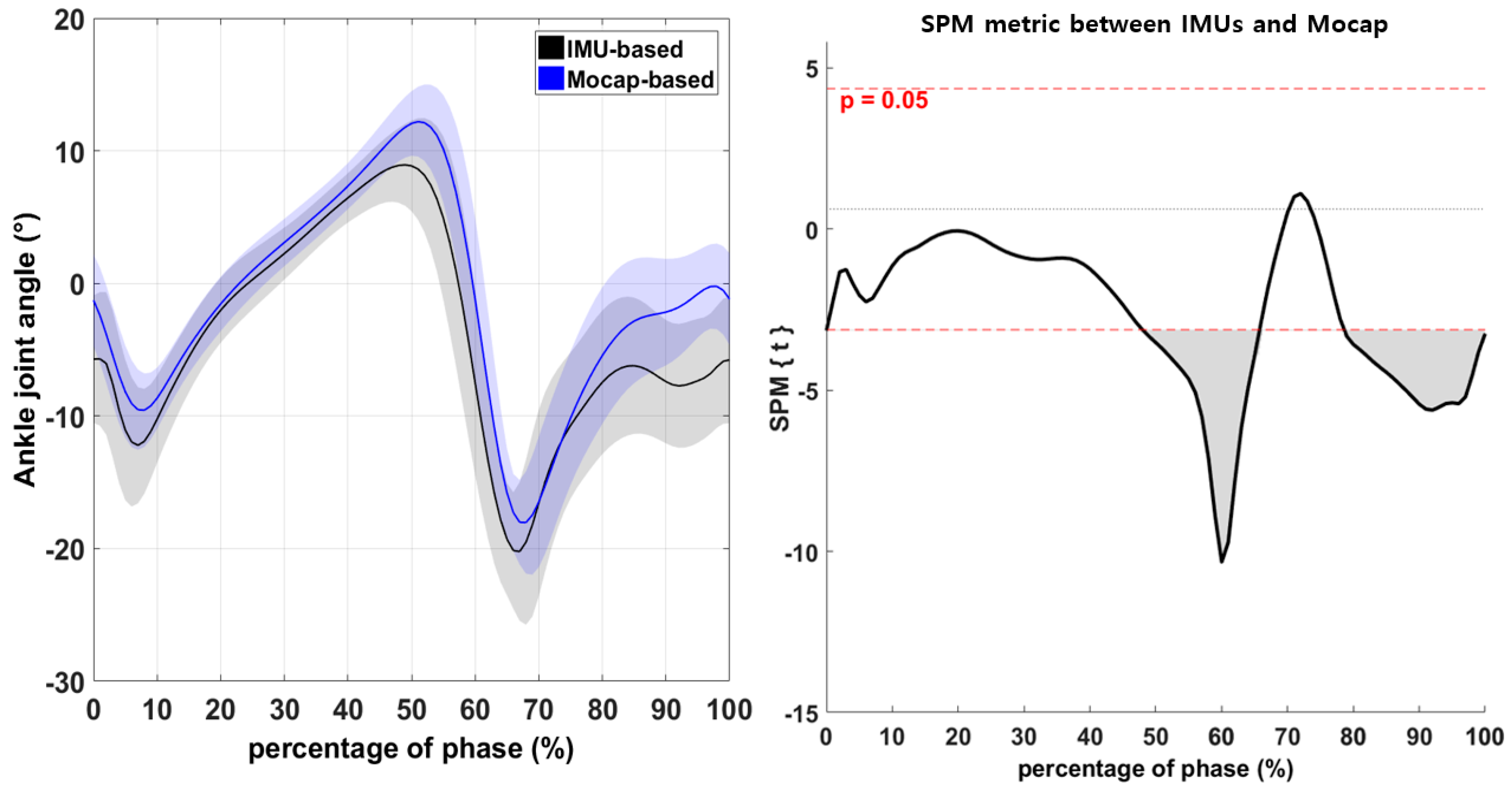
3.2. Continuous Variables of the Lower-Extremity Joints during Walking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Lach, J.; Lo, B.; Yang, G.Z. Toward Pervasive Gait Analysis With Wearable Sensors: A Systematic Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R. Gait analysis methods in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2006, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ancillao, A. Analysis and measurement of human motion: Modern protocols and clinical considerations. J. Rob. Mech. Eng. Res. 2016, 1, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Lo, K.H. Clinical applications of sensors for human posture and movement analysis: A review. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2007, 31, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, K.; Boissy, P.; Hamel, M.; Duval, C. Inertial measures of motion for clinical biomechanics: Comparative assessment of accuracy under controlled conditions—Effect of velocity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, C.; Salvia, P.; Lubansu, A.; Feipel, V.; Aminian, K. A wearable inertial system to assess the cervical spine mobility: Comparison with an optoelectronic-based motion capture evaluation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Noort, J.C.; Ferrari, A.; Cutti, A.G.; Becher, J.G.; Harlaar, J. Gait analysis in children with cerebral palsy via inertial and magnetic sensors. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2013, 51, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayagoitia, R.E.; Nene, A.V.; Veltink, P.H. Accelerometer and rate gyroscope measurement of kinematics: An inexpensive alternative to optical motion analysis systems. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amri, M.; Nicholas, K.; Button, K.; Sparkes, V.; Sheeran, L.; Davies, J.L. Inertial measurement units for clinical movement analysis: Reliability and concurrent validity. Sensors 2018, 18, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berner, K.; Cockcroft, J.; Morris, L.D.; Louw, Q. Concurrent validity and within-session reliability of gait kinematics measured using an inertial motion capture system with repeated calibration. J. Bodyw. Mov. Therapies 2020, 24, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picerno, P. 25 years of lower limb joint kinematics by using inertial and magnetic sensors: A review of methodological approaches. Gait Posture 2017, 51, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusca, M.; Negrini, F.; Perego, P.; Magoni, L.; Molteni, F.; Andreoni, G. Validation of a wearable IMU system for gait analysis: Protocol and application to a new system. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iosa, M.; Picerno, P.; Paolucci, S.; Morone, G. Wearable inertial sensors for human movement analysis. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2016, 13, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Chiari, L.; Holmstrom, L.; Salarian, A.; Horak, F.B. Validity and reliability of an IMU-based method to detect APAs prior to gait initiation. Gait Posture 2016, 43, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abyarjoo, F.; Barreto, A.; Cofino, J.; Ortega, F.R. Implementing a sensor fusion algorithm for 3D orientation detection with inertial/magnetic sensors. In Innovations and Advances in Computing, Informatics, Systems Sciences, Networking and Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, M.; Schön, T.B. Magnetometer calibration using inertial sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5679–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabatini, A.M. Kalman-filter-based orientation determination using inertial/magnetic sensors: Observability analysis and performance evaluation. Sensors 2011, 11, 9182–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Abbas, J. Comparison of Angle Measurements between Vicon and MyoMotion Systems; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Hou, B.; Lin, Z.; Guo, M. Modeling and Compensation of Random Drift of MEMS Gyroscopes Based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine Optimized by Chaotic Particle Swarm Optimization. Sensors 2017, 17, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teufl, W.; Miezal, M.; Taetz, B.; Fröhlich, M.; Bleser, G. Validity, test-retest reliability and long-term stability of magnetometer free inertial sensor based 3D joint kinematics. Sensors 2018, 18, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolink, S.; Naisas, H.; Senden, R.; Essers, H.; Heyligers, I.; Meijer, K.; Grimm, B. Validity of an inertial measurement unit to assess pelvic orientation angles during gait, sit–stand transfers and step-up transfers: Comparison with an optoelectronic motion capture system. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.; Dawes, H.; Collett, J.; Howells, K. IMU: Inertial sensing of vertical CoM movement. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafer, J.F.; Provenzano, S.G.; Kern, K.L.; Agresta, C.E.; Grant, J.A.; Zernicke, R.F. Measuring markers of aging and knee osteoarthritis gait using inertial measurement units. J. Biomech. 2020, 99, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice, S.M.; Phillips, E.J.; Millett, E.L.; Hunter, A.; Philippa, B. Comparing inertial measurement units and marker-based biomechanical models during dynamic rotation of the torso. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 20, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beange, K.H.; Chan, A.D.; Beaudette, S.M.; Graham, R.B. Concurrent validity of a wearable IMU for objective assessments of functional movement quality and control of the lumbar spine. J. Biomech. 2019, 97, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitras, I.; Dupuis, F.; Bielmann, M.; Campeau-Lecours, A.; Mercier, C.; Bouyer, L.J.; Roy, J.-S. Validity and reliability of wearable sensors for joint angle estimation: A systematic review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sole, G.; Pataky, T.; Tengman, E.; Hager, C. Analysis of three-dimensional knee kinematics during stair descent two decades post-ACL rupture—Data revisited using statistical parametric mapping. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2017, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataky, T.C.; Robinson, M.A.; Vanrenterghem, J. Vector field statistical analysis of kinematic and force trajectories. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friston, K.J.; Holmes, A.P.; Poline, J.B.; Grasby, P.J.; Williams, S.C.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Turner, R. Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited. Neuroimage 1995, 2, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Santago, A.C., II; Vidt, M.E.; Saul, K.R. Analysis of effects of loading and postural demands on upper limb reaching in older adults using statistical parametric mapping. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2806–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pataky, T.C. One-dimensional statistical parametric mapping in Python. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 15, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.A.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Pataky, T.C. Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) for alpha-based statistical analyses of multi-muscle EMG time-series. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrien, B.; Goossens, M.; Baeyens, J.-P. Statistical parametric mapping of biomechanical one-dimensional data with Bayesian inference. Int. Biomech. 2019, 6, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, C.; Killeen, T.; Easthope, C.S.; Curt, A.; Bolliger, M.; Linnebank, M.; Zörner, B.; Filli, L. Familiarization with treadmill walking: How much is enough? Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tylkowski, C.M.; Simon, S.R.; Mansour, J.M. The Frank Stinchfield Award Paper. Internal rotation gait in spastic cerebral palsy. Hip 1982, 89–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Siegler, S.; Allard, P.; Kirtley, C.; Leardini, A.; Rosenbaum, D.; Whittle, M.; D’Lima, D.D.; Cristofolini, L.; Witte, H.; et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate system of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion—Part I: Ankle, hip, and spine. International Society of Biomechanics. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORAXON. Available online: https://www.noraxon.com/noraxon-download/imu-technology-overview/ (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Eerdekens, M.; Peerlinck, K.; Staes, F.; Hermans, C.; Lobet, S.; Deschamps, K. The biomechanical behaviour of ankle and foot joints during walking with shoes in patients with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.; Burnfield, J.M. Gait analysis: Normal and pathological function. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1993, 35, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Vargas, A.I.; Galán-Mercant, A.; Williams, J.M. The use of inertial sensors system for human motion analysis. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2010, 15, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G.; Sheret, I.; McMillan, L.; Siliverdis, K.; Sha, N.; Hodgins, D.; Kenney, L.; Howard, D. Inertial sensor-based knee flexion/extension angle estimation. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebel, K.; Boissy, P.; Nguyen, H.; Duval, C. Inertial measurement systems for segments and joints kinematics assessment: Towards an understanding of the variations in sensors accuracy. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramia, C.; Torricelli, D.; Schmid, M.; Munoz-Gonzalez, A.; Gonzalez-Vargas, J.; Grandas, F.; Pons, J.L. IMU-based classification of Parkinson’s disease from gait: A sensitivity analysis on sensor location and feature selection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, M.; Beato, M.; McErlain-Naylor, S.A. Inter-unit reliability of IMU Step metrics using IMeasureU Blue Trident inertial measurement units for running-based team sport tasks. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| (Unit: deg) | Variable | System | Mean ± SD | t (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip-joint angle (+ flexion / − extension) | Max | IMU | 27.18 ± 4.66 | 1.88 (0.09) |
| Mocap | 25.70 ± 3.85 | |||
| Min | IMU | −12.97 ± 3.83 | 1.83 (0.10) | |
| Mocap | −14.41 ± 2.23 | |||
| ROM | IMU | 39.89 ± 3.81 | 0.01 (1.00) | |
| Mocap | 39.88 ± 3.22 | |||
| Knee-joint angle (+ flexion /− extension) | Max | IMU | 67.66 ± 5.79 | 3.29 (0.01) * |
| Mocap | 64.58 ± 5.21 | |||
| Min | IMU | −5.66 ± 5.79 | −1.84 (0.10) | |
| Mocap | −3.18 ± 3.11 | |||
| ROM | IMU | 72.67 ± 5.34 | 7.07 (0.01) * | |
| Mocap | 67.20 ± 4.66 | |||
| Ankle-joint angle (+ dorsi flexion /− plantar flexion) | Max | IMU | 9.63 ± 2.90 | −5.33 (0.01) * |
| Mocap | 12.66 ± 2.71 | |||
| Min | IMU | −23.16 ± 5.09 | −5.20 (0.01) * | |
| Mocap | −19.44 ± 3.79 | |||
| ROM | IMU | 31.84 ± 5.75 | 0.15 (0.89) | |
| Mocap | 31.71 ± 4.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Yoon, S. Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM). Sensors 2021, 21, 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667
Park S, Yoon S. Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM). Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sangheon, and Sukhoon Yoon. 2021. "Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM)" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667
APA StylePark, S., & Yoon, S. (2021). Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM). Sensors, 21(11), 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667







