Low-Cost and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor with Mold-Printed Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Polydimethylsiloxane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polymer Composite
2.2. Sensor Principle
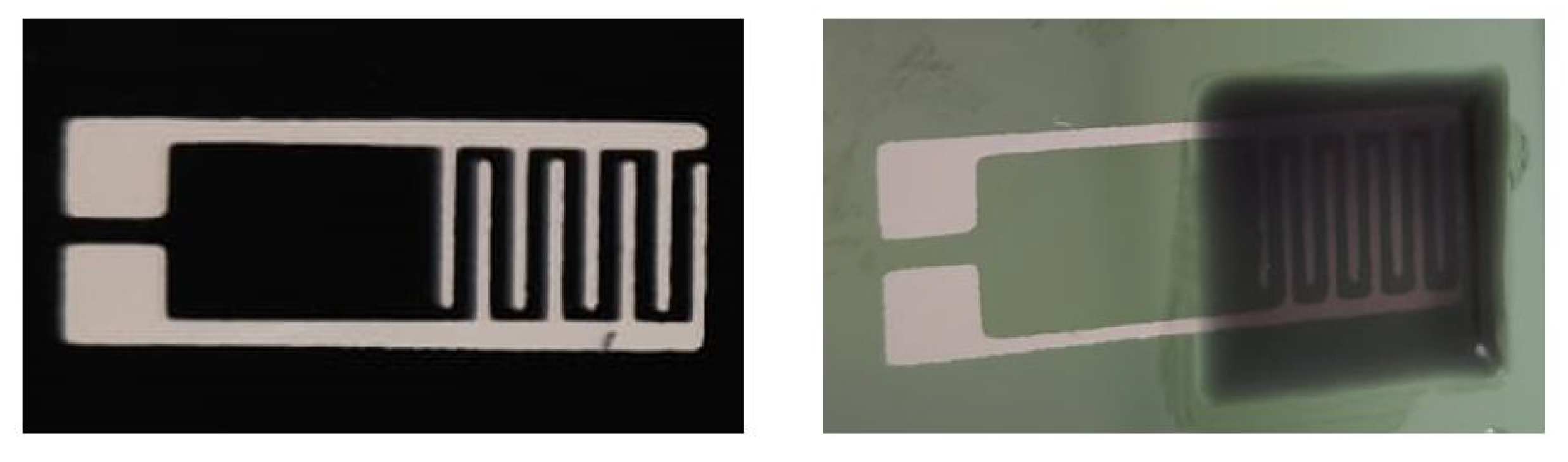
2.3. Sensor Dimensions
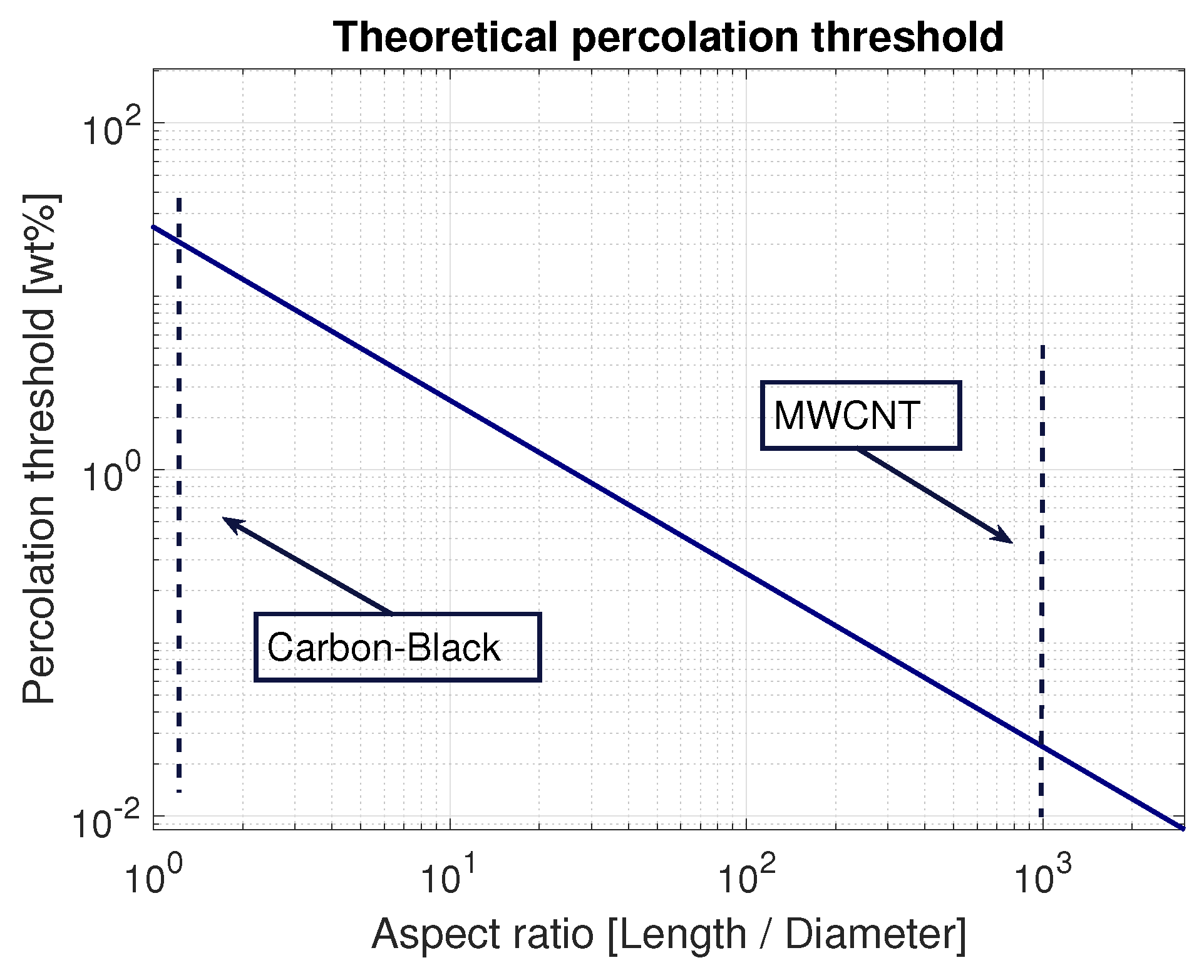
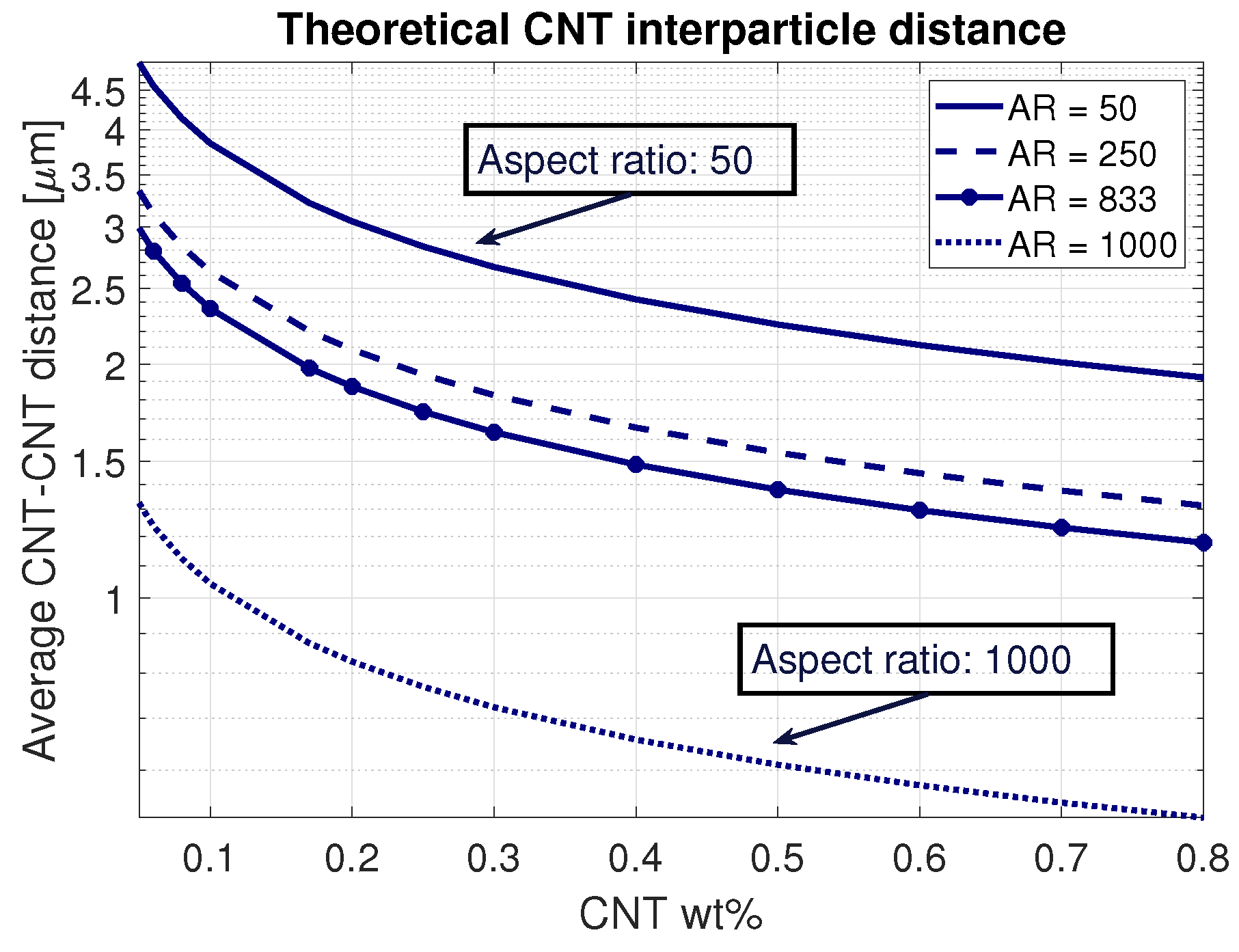
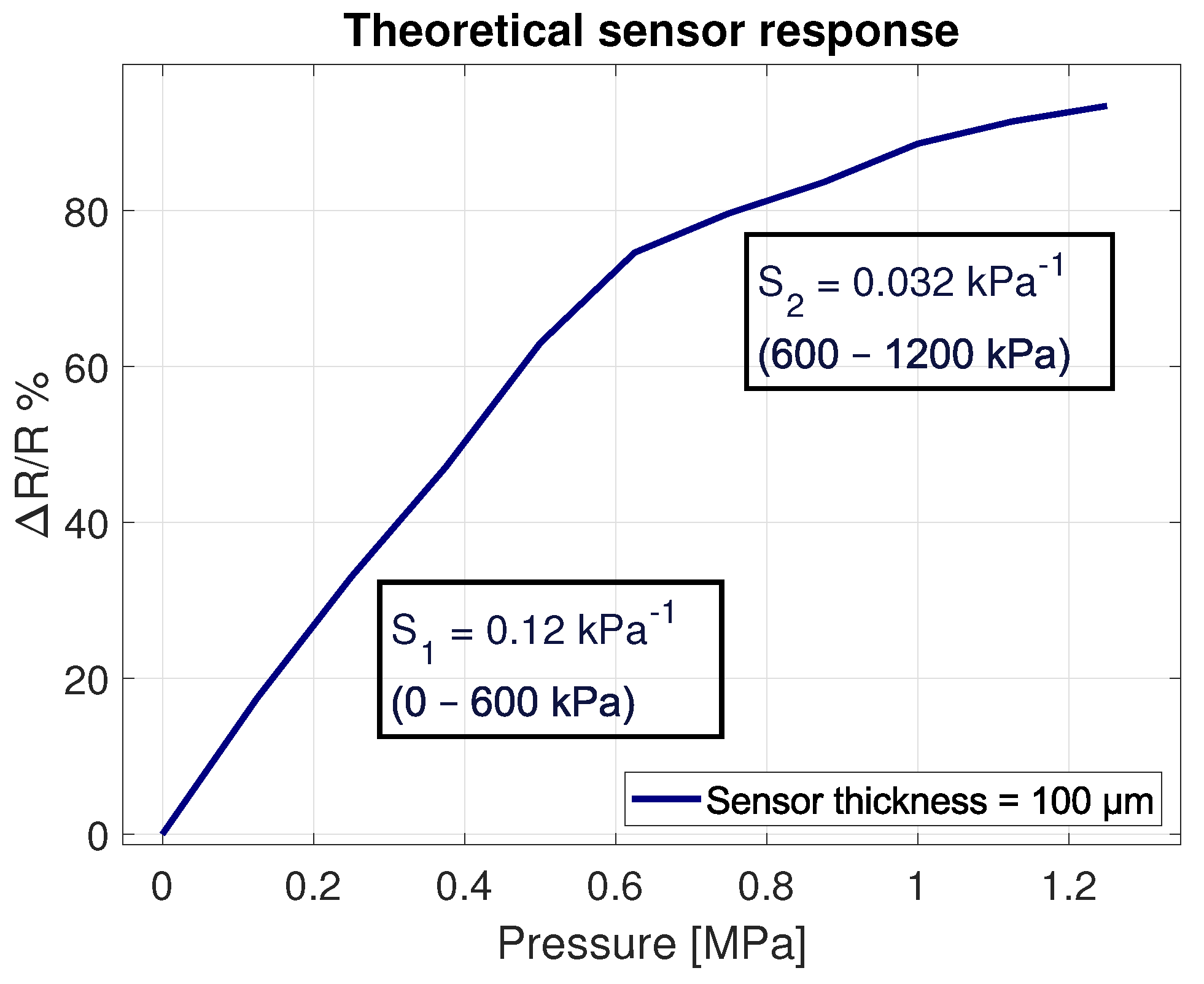
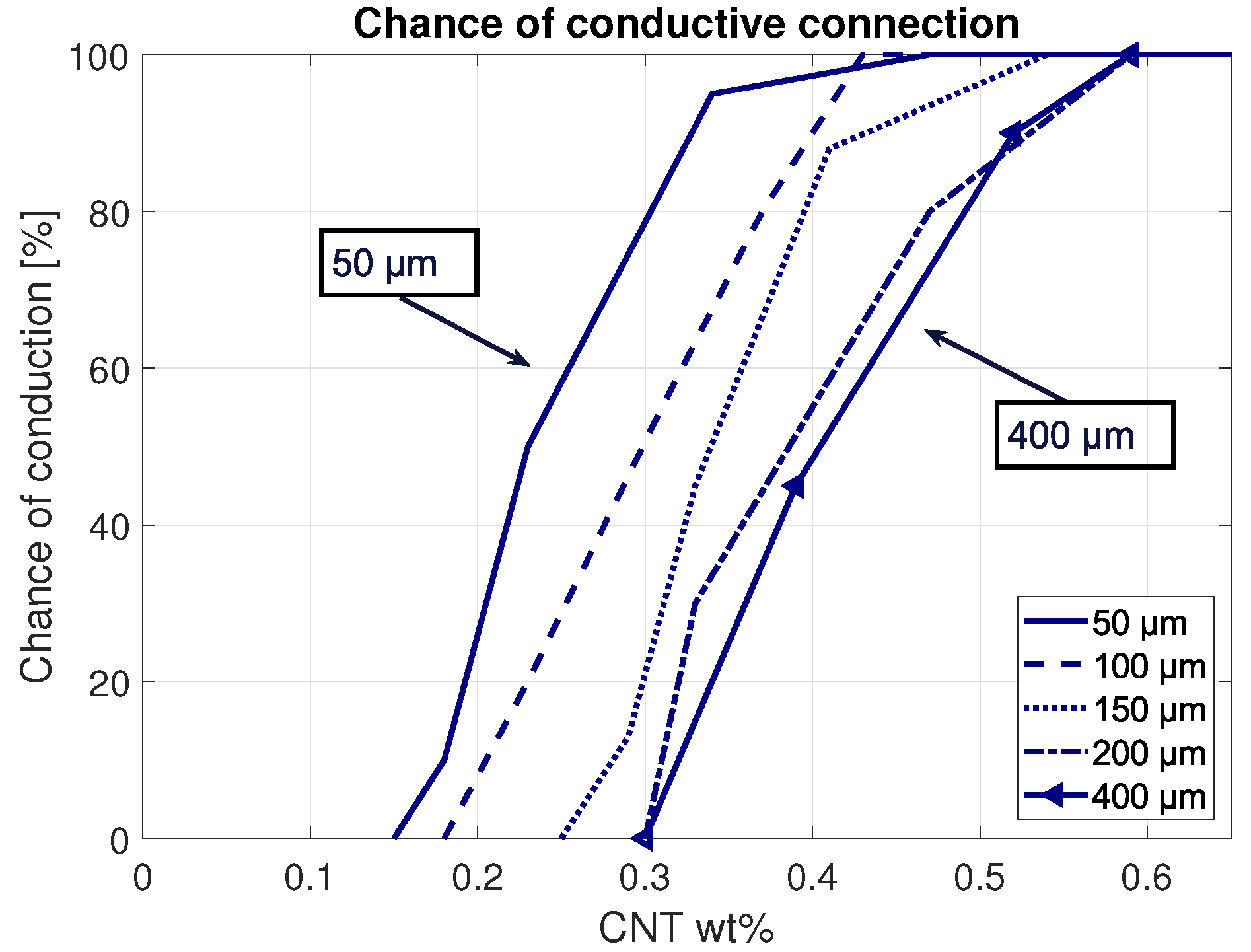
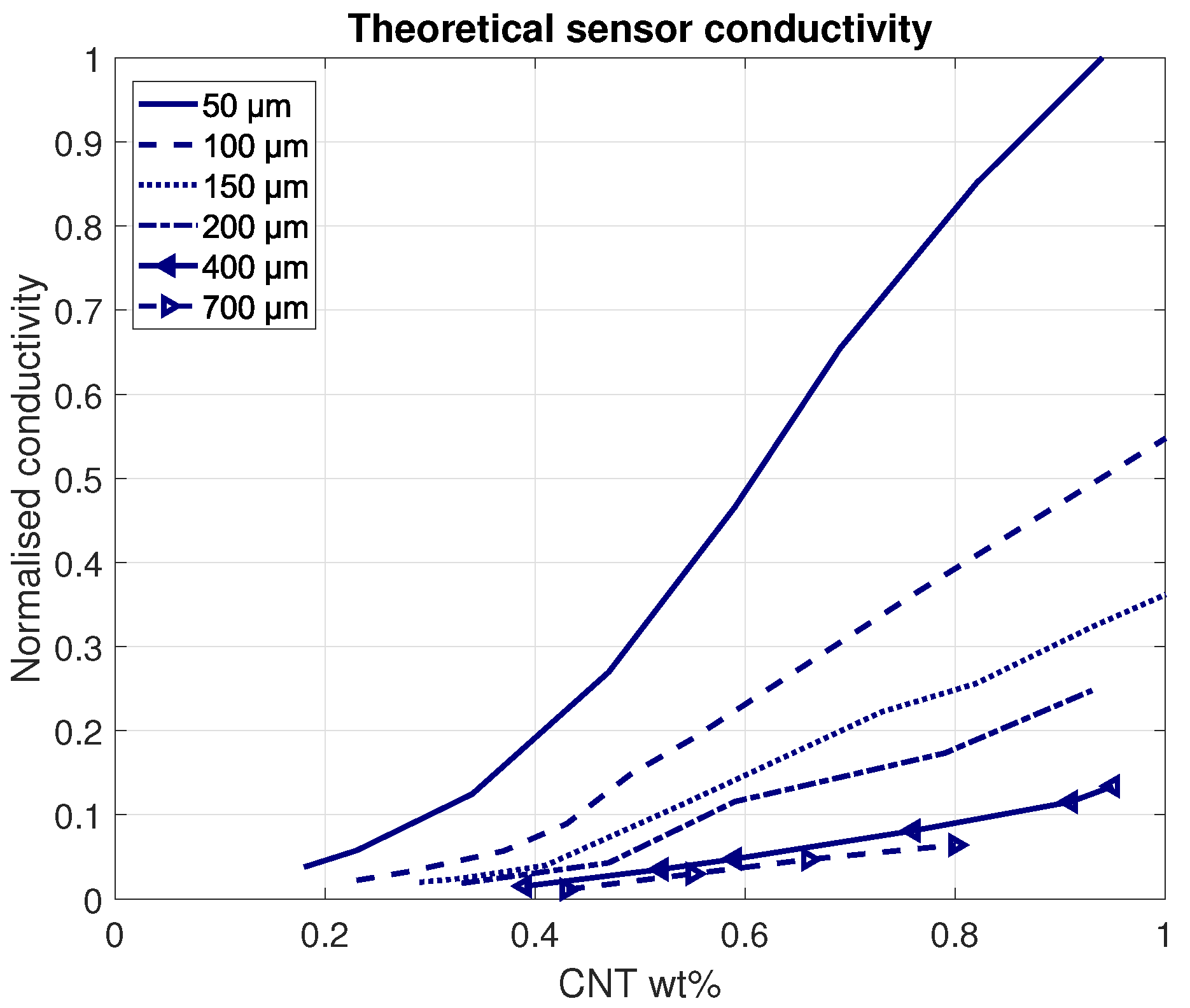
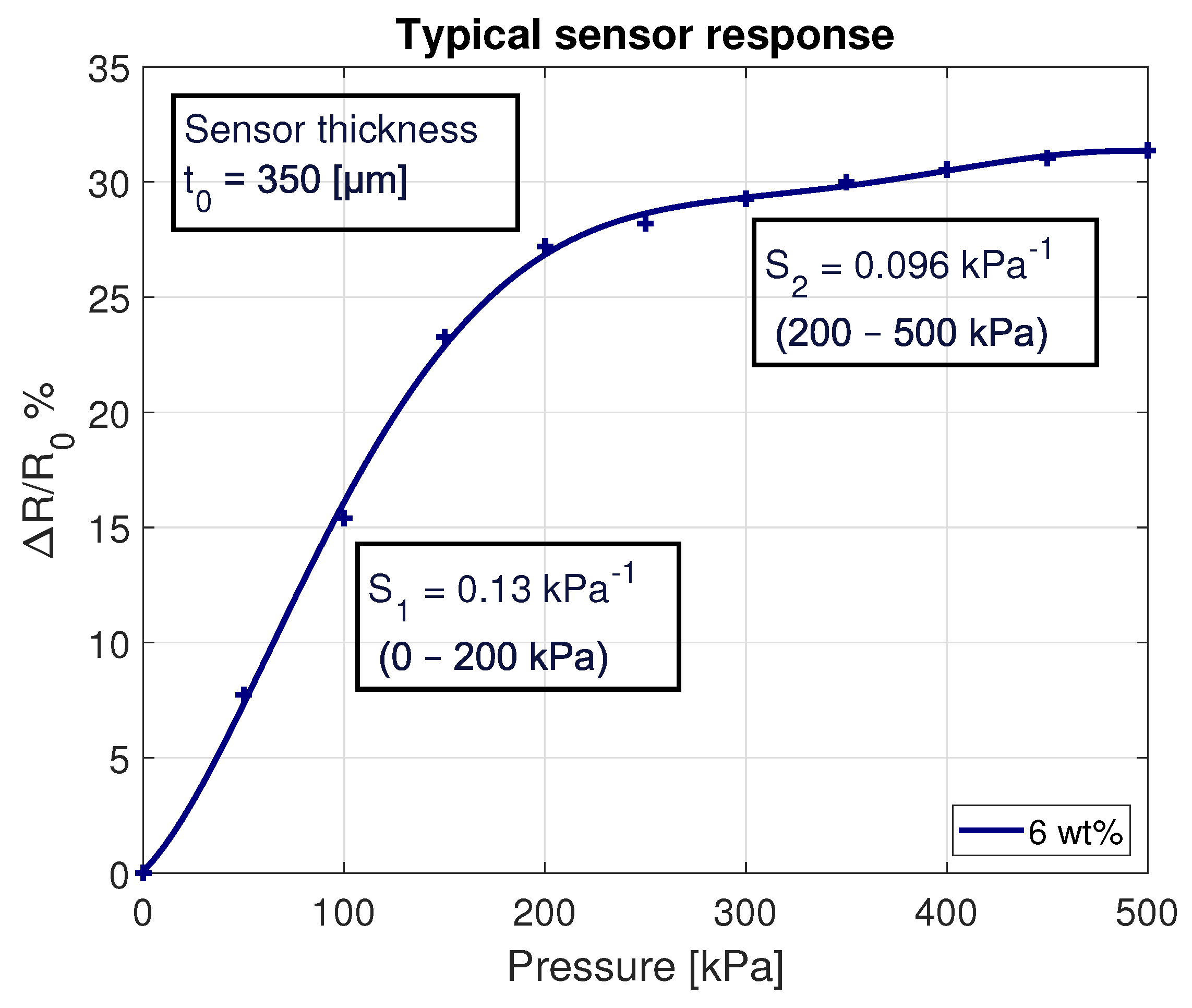
3. Numerical Results
4. Experimental Results
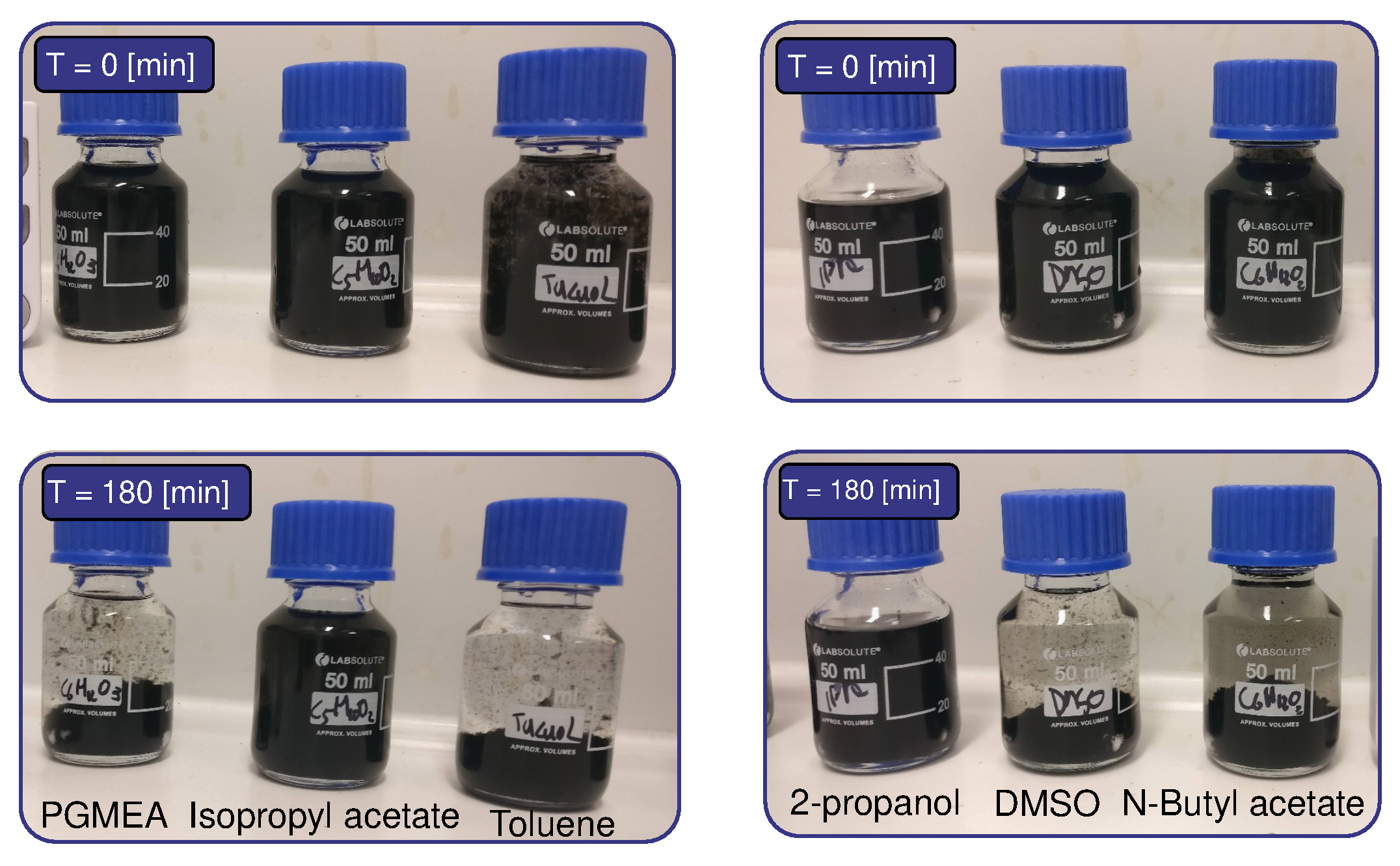
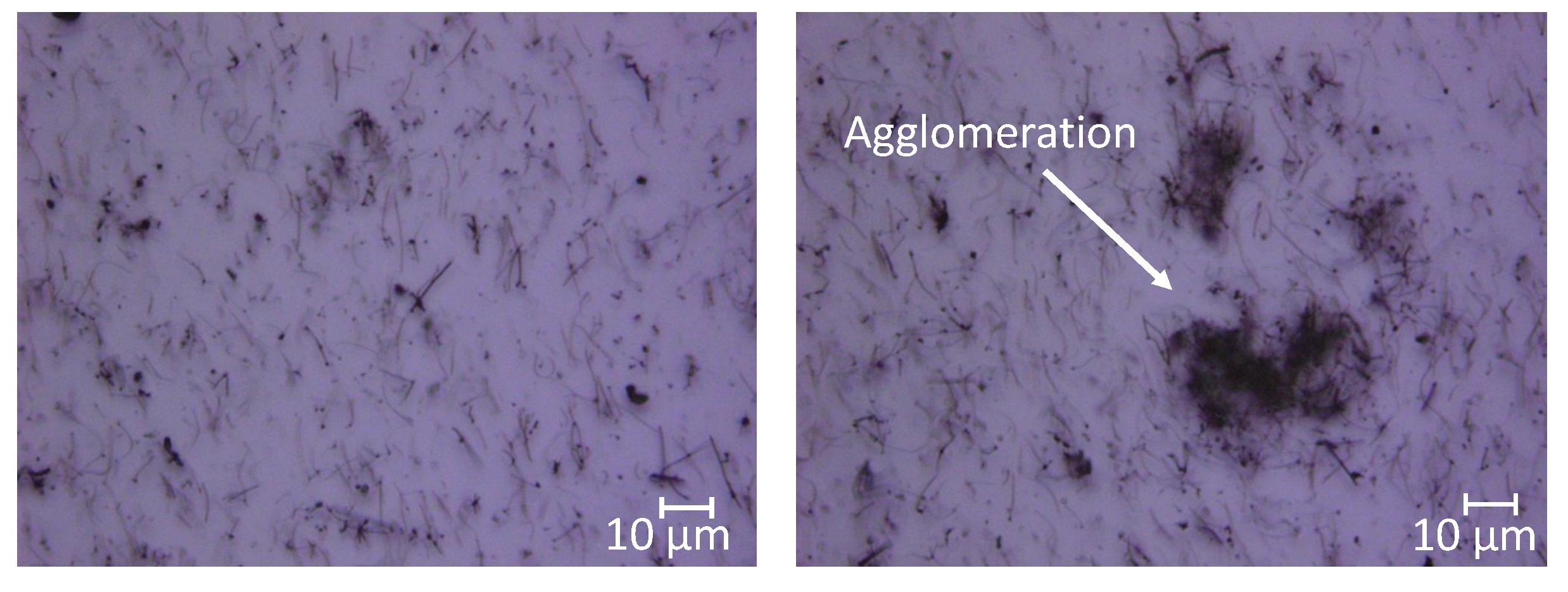
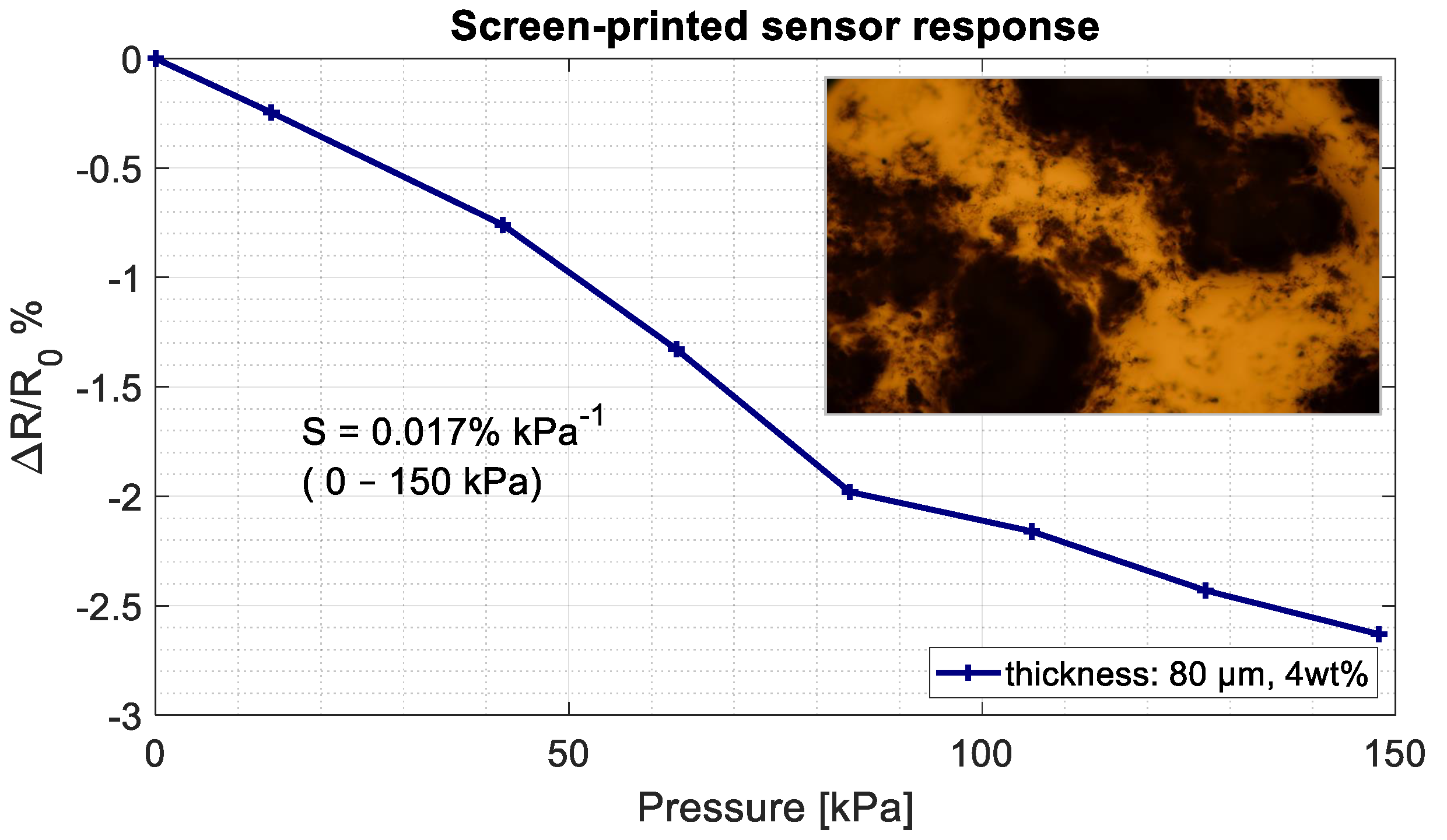
4.1. Screen-Printed Sensitive Layer
4.2. 3D Mold-Printed Sensitive Layer
5. Discussion of Different Sensor Fabrication Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Ma, P.C.; Chow, W.S.; To, C.K.; Tang, B.Z.; Kim, J.K. Correlations between percolation threshold, dispersion state, and aspect ratio of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, T.; Wang, P. Thin flexible pressure sensor array based on carbon black/silicone rubber nanocomposite. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräbner, D.; Tintelott, M.; Schön, K.; Lang, W. Screen-Printed Resistive Pressure Sensors: Influence of Electrode Geometry on the Performance and on Cross-Sensitivity to Strain and Temperature. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1837, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.S.; Goldberg, D.; Large, E.; Kim, I. Highly Sensitive Flexible/Stretchable Smart Insole Pressure Sensor with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Polydimethylsiloxane Double-Layer Composites. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE SENSORS, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A review and analysis of electrical percolation in carbon nanotube polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, C.; Kanoun, O. Printable, Piezoresistive Carbon Nanotube-Elastomer Composite for Pressure Sensors. TM-Tech. Mess. 2013, 80, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Spencer, J.L.; Kaiser, A.B.; Arnold, W.M. Electric-field oriented carbon nanotubes in different dielectric solvents. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2004, 4, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Pothnis, J.R.; Kim, J.K. Effects of carbon nanotube alignment on electrical and mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Part A 2013, 49, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Choi, J.W. Improved dispersion of carbon nanotubes in polymers at high concentrations. Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Bower, C.; Zhou, O. Alignment of carbon nanotubes in a polymer matrix by mechanical stretching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubramaniam, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, H. Homogeneous carbon nanotube/polymer composites for electrical applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2928–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Dahiya, R.; Tinku, S.; Lorenzelli, L. Conformable tactile sensing using screen printed P (VDF-TrFE) and MWCNT-PDMS composites. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE SENSORS, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 862–865. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Lee, J.; Hong, C.K.; Shim, S.E. Effect of dispersion state of carbon nanotube on the thermal conductivity of poly (dimethyl siloxane) composites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczak, D.; Słoma, M.; Wróblewski, G.; Młożniak, A.; Jakubowska, M. Screen-printed resistive pressure sensors containing graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 17304–17312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyo, S.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, M.O.; Chung, T.; Oh, Y.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, J. Development of a flexible three-axis tactile sensor based on screen-printed carbon nanotube-polymer composite. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 075012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Rajput, M.; Singla, N.; Kumar, V.; Lahiri, D. Electric field and current assisted alignment of CNT inside polymer matrix and its effects on electrical and mechanical properties. Polymer 2016, 89, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J. Theoretical estimation on the percolation threshold for polymer matrix composites with hybrid fillers. Compos. Struct. 2015, 124, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Marom, G.; Kim, J.K. Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumstorff, G.; Paul, S.; Lang, W. Integration without disruption: The basic challenge of sensor integration. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 14, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.Y.; Hwang, H.R.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, J.W.; Lee, S.H. Simple and cost-effective method of highly conductive and elastic carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane composite for wearable electronics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Zhi, C. Polymer Nanocomposites; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, W. Identifying and Reducing visual Clutter for Process Graph Layouts. Master’s Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tiller, W.; Hanson, E.G. Offsets of two-dimensional profiles. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1984, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.D.; McCluskey, D.K.; Tan, C.K.L.; Tracey, M.C. Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, U.; Krause, B.; Steinbach, C.; Pötschke, P.; Voit, B. Dispersability of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in polycarbonate-chloroform solutions. Polymer 2014, 55, 6335–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräbner, D.; Tintelott, M.; Dumstorff, G.; Lang, W. Low-cost thin and flexible screen-printed pressure sensor. In Proceedings of the Eurosensors 2017, Paris, France, 3–6 September 2017; p. 616. [Google Scholar]
- Tintelott, M.; Dumstorff, G.; Lucklum, F.; Gräbner, D. Flexible printed pressure sensor integrated into inner wall of a 3D tube using additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE SENSORS, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Rijk, T.M.; Lang, W. Low-Cost and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor with Mold-Printed Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Polydimethylsiloxane. Sensors 2021, 21, 5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155069
de Rijk TM, Lang W. Low-Cost and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor with Mold-Printed Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Polydimethylsiloxane. Sensors. 2021; 21(15):5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155069
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Rijk, Tim Mike, and Walter Lang. 2021. "Low-Cost and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor with Mold-Printed Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Polydimethylsiloxane" Sensors 21, no. 15: 5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155069
APA Stylede Rijk, T. M., & Lang, W. (2021). Low-Cost and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor with Mold-Printed Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Polydimethylsiloxane. Sensors, 21(15), 5069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155069





