A General Solution to Determine Strain Profile in the Core of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors under Any Arbitrary Strain Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Modeling of the Strain Transfer
2.1. Governing Equation
2.2. Discussion on the Governing Equation on the Strain-Lag Parameter
3. Generalized Solution for Determining the Strain Profile in an Optical Fiber under Any Arbitrary Strain Distribution
3.1. Presentation of the Generalized Solution
- ✧
- Case:
- ✧
- Case:
- ✧
- Case:
3.2. Applications
3.2.1. Uniform Strain Field
3.2.2. Non-Uniform Strain Field
4. Experimentation and Results
4.1. Uniform Strain Field
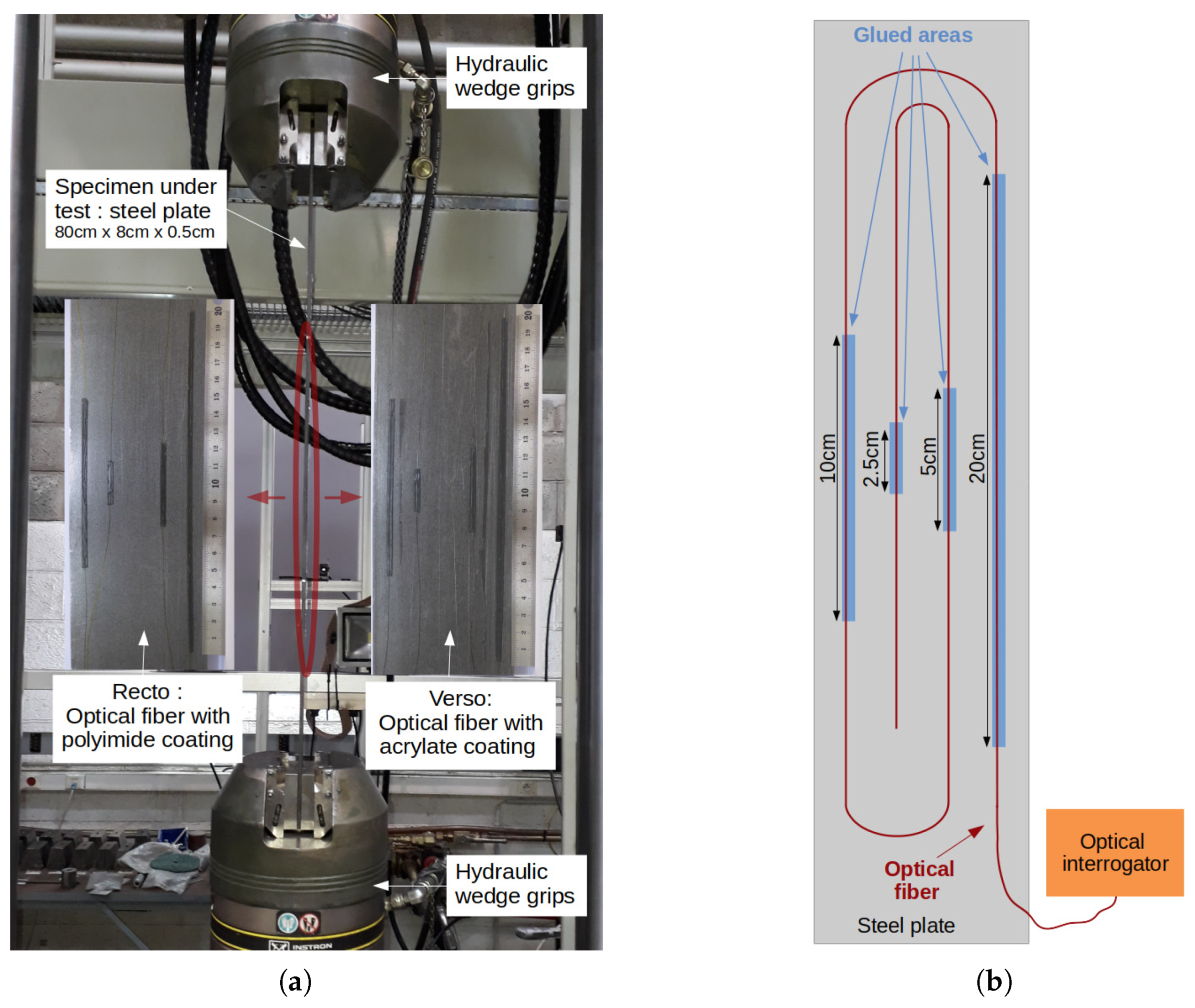
4.1.1. Description of the Experiment
4.1.2. Results and Discussions
4.2. Non-Uniform Strain Field
4.2.1. Description of the Experiment
4.2.2. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Strain-Lag Parameter for a Three-Layers and Four-Layers System
Appendix B. Particular Solution of Equation (12)
Appendix C. Derivation of the Parameters A1, B1, A2, B2, A3 and B3
- ✧
- Case:
- ✧
- Case:
- ✧
- Case:
References
- Bado, M.; Casas, J. A review of recent distributed optical fiber sensors applications for civil engineering structural health monitoring. J. Sens. 2021, 21, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrias, A.; Casas, J.; Villalba, S. A Review of distributed optical fiber sensors for civil engineering applications. J. Sens. 2016, 16, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferdinand, P. The evolution of optical fiber sensors technologies during the 35 last years and their Applications in structure health monitoring. In Proceedings of the EWSHM-7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, Nantes, France, 8–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Glisic, B. Distributed fiber optic sensing technologies and applications—An overview. ACI Spec. Publ. 2013, 292, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Monsberger, C.M.; Lienhart, W.; Hayden, M. Distributed fiber optic sensing along driven ductile piles: Design, sensor installation and monitoring benefits. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 10, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, W. Optical fiber methods in nondestructive evaluation. In Handbook of Advanced Nondestructive Evaluation; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 595–642. [Google Scholar]
- Tur, M. Dynamic and distributed fiber-optic sensing has come of age. In Proceedings of the Keynote Presentation at IWSHM, Stanford, CA, USA, 11 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Davidi, R.; Ben-Simon, U.; Shoham, S.; Kressel, I.; Gorbatov, N.; Tur, M. The importance of fiber coating and bonding process in accurate high spatial resolution strain measurements. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–28 September 2018; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, F.; Libo, Y. Mechanics of Bond and Interface Shear Transfer in Optical Fiber Sensors. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkersen, O. Die Nietkraft Verteilung in Zugbeanspruchten mit Konstanten Laschenquerschritten. Luftahrt Forschungen 1938, 15, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, H.L. The elasticity and strength of paper and other fibrous materials. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1952, 3, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, H.; Ren, L.; Song, G. Strain transferring analysis of fiber Bragg grating sensors. Opt. Eng. 2006, 45, 024402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Ansari, F. Theoretical and experimental investigations into crack detection with BOTDR-distributed fiber optic sensors. J. Eng. Mech. 2013, 139, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, G.; Ansari, F.; Liu, Q. Elasto-Plastic Bonding of Embedded Optical Fiber Sensors in Concrete. J. Eng. Mech. 2002, 128, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiang, P. Strain transfer analysis of optical fiber based sensors embedded in an asphalt pavement structure. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 075106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henault, J.-M. Approche Méthodologique pour l’Evaluation des Performances et de Ladurabilité des Systèmes de Mesure Répartie de Déformation: Application à un Câble à Fibre Optique Noyé dans le Béton. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Est, Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bassil, A.; Chapeleau, X.; Leduc, D.; Abraham, O. Concrete crack monitoring using a novel strain transfer model for fiber optics sensors: An imperfect bonding theory. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassil, A. Distributed Fiber Optics Sensing for Crack Monitoring of Concrete Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Nantes & Ifsttar, Bouguenais, France, 26 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Nassif, H.; Chen, G. Strain transfer effect in distributed fiber optic sensors under an arbitrary field. Automat. Constr. 2021, 124, 103597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcetelli, F.; Rossi, L.; Di Sante, R.; Bolognini, G. Strain Transfer in Surface-Bonded Optical Fiber Sensors. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisbrich, M.; Holschemacher, K. Comparison between different fiber coatings and adhesives on steel surfaces for distributed optical strain measurements based on Rayleigh backscattering. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2018, 7, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alj, I.; Quiertant, M.; Khadour, A.; Grando, Q.; Terrade, B.; Renaud, J.-C.; Benzarti, K. Experimental and numerical investigation on the strain response of distributed optical fiber sensors bonded to concrete: Influence of the adhesive stiffness on crack monitoring performance. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrias, A.; Casas, J.R.; Villalba, S. Distributed optical fibre sensors in concrete structures: Performance of bonding adhesives and influence of spatial resolution. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, S.C.; Huang, C.Y. Effect of coating on the strain transfer of optical fiber sensors. J. Sens. 2011, 11, 6926–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.W.; Jeong, M.S.; Lee, I.; Kim, E.H.; Kwon, I.B.; Hwang, T.K. Determination of the maximum strains experienced by composite structures using metal coated optical fiber sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 78, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreger, S.; Gifford, D.; Froggatt, M.; Soller, B.; Wolfe, M.; Mark, E.; Brian, J.; Matthew, S. High Resolution Distributed Strain or Temperature Measurements in Single-and Multi-mode Fiber Using Swept-Wavelength Interferometry. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Sensors, Cancun, Mexico, 23–27 October 2006; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Güemes, A.; Fernández-López, A.; Soller, B. Optical Fiber Distributed Sensing—Physical Principles and Applications. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 9, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Optical Fibers Components | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber’s Core | Optical Cladding | Coating | ||
| Material | Silica | Silica | Acrylate | Polyimide |
| Diameter [m] | 9 | 125 | 250 | 160 |
| Young’s modulus [GPa] | 72 | 72 | 2.10 | 3 |
| Shear modulus [GPa] | 30 | 30 | 8.10 | 1.43 |
| OF with Polyimide Coating | a (m) | b (m) | (m/m) | (m) | (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 20 cm | 0.0885 ± | 0.2884 ± | 908 ± 2 | 1774 ± 200 | 1112 ± 54 |
| = 10 cm | 0.1410 ± | 0.2405 ± | 911 ± 2 | 1259 ± 84 | 1061 ± 57 |
| = 5 cm | 0.1653 ± | 0.2127 ± | 6 | 1074 ± 152 | 1058 ± 148 |
| = 2.5 cm | 0.1587 ± | 0.1844 ± | 935 ± 15 | 837 ± 160 | 1047 ± 303 |
| OF with Acrylate Coating | a (m) | b (m) | (m/m) | (m) | (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 20 cm | 0.1012 ± | 0.2962 ± | 905 ± 4 | 183 ± 8 | 32 ± 1 |
| = 10 cm | 0.1488 ± | 0.2512 ± | fixed to 900 | 163 ± 9 | 30 ± 1 |
| = 5 cm | 0.1739 ± | 0.2241 ± | fixed to 900 | 206 ± 27 | 30 ± 1 |
| = 2.5 cm | fixed to 0.1875 | fixed to 0.2125 | fixed to 900 | 194 ± 22 | 33 ± 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chapeleau, X.; Bassil, A. A General Solution to Determine Strain Profile in the Core of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors under Any Arbitrary Strain Fields. Sensors 2021, 21, 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165423
Chapeleau X, Bassil A. A General Solution to Determine Strain Profile in the Core of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors under Any Arbitrary Strain Fields. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165423
Chicago/Turabian StyleChapeleau, Xavier, and Antoine Bassil. 2021. "A General Solution to Determine Strain Profile in the Core of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors under Any Arbitrary Strain Fields" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165423
APA StyleChapeleau, X., & Bassil, A. (2021). A General Solution to Determine Strain Profile in the Core of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors under Any Arbitrary Strain Fields. Sensors, 21(16), 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165423







