Distinguishing Drones from Birds in a UAV Searching Laser Scanner Based on Echo Depolarization Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
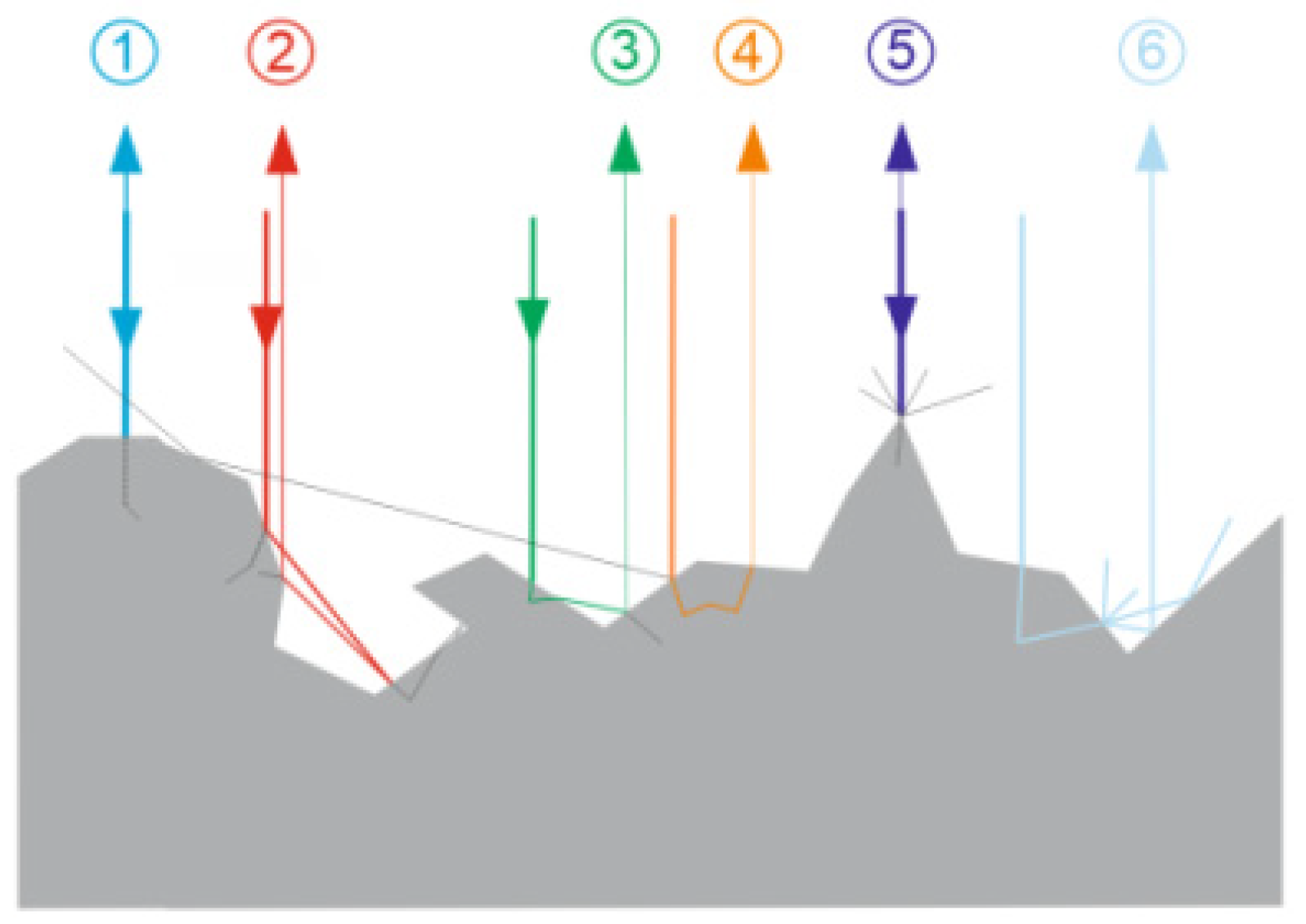
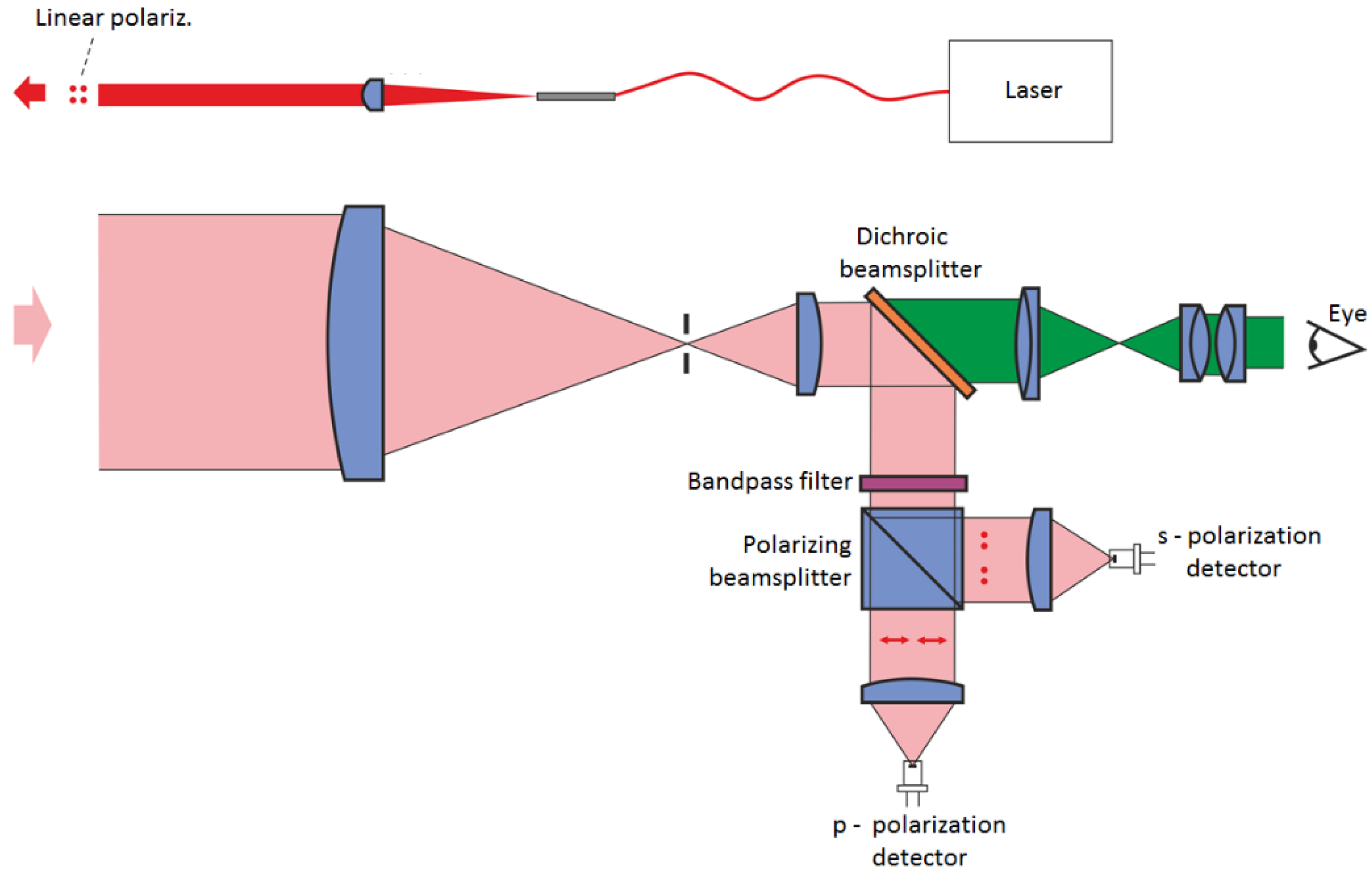
2. Materials and Methods
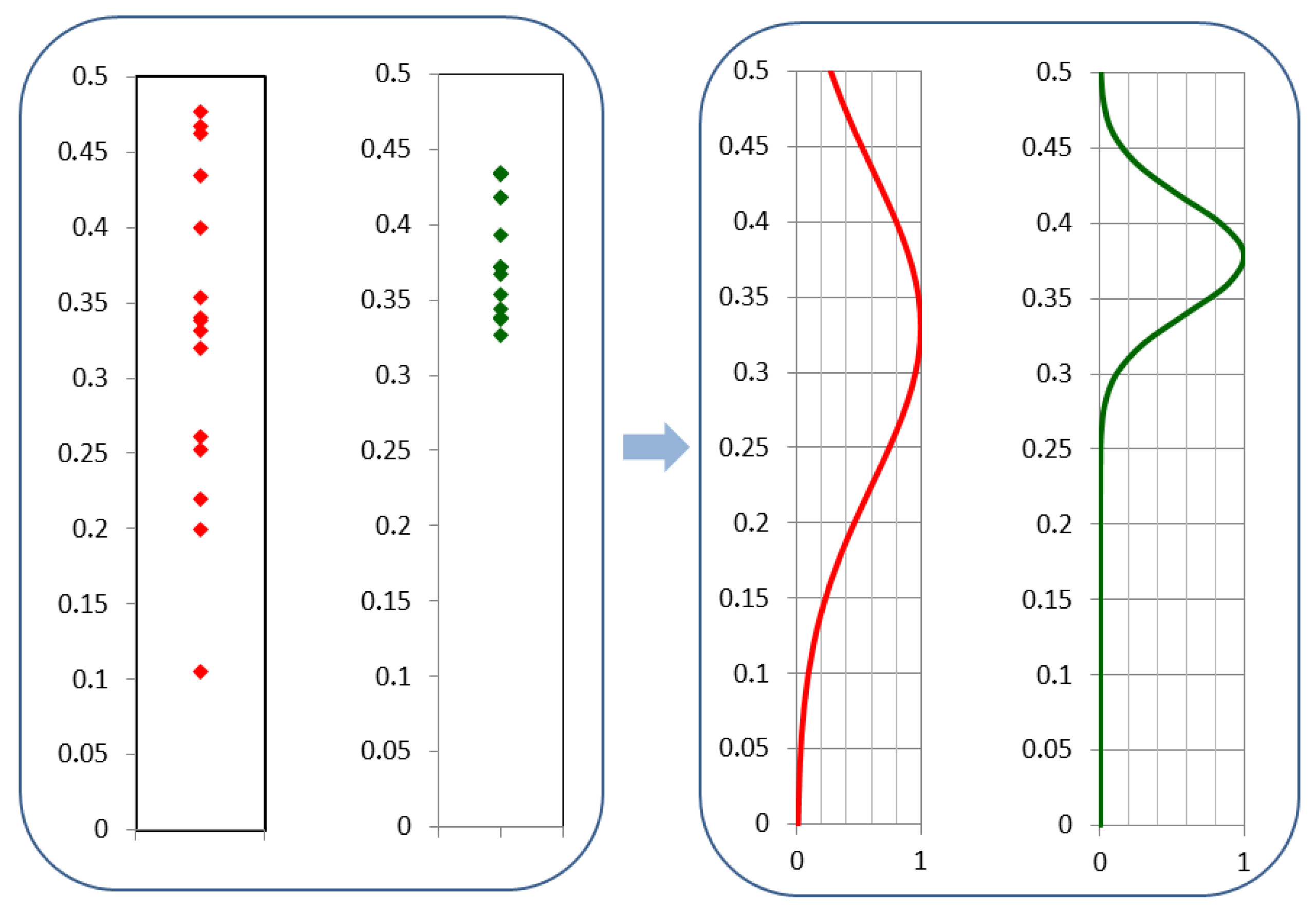
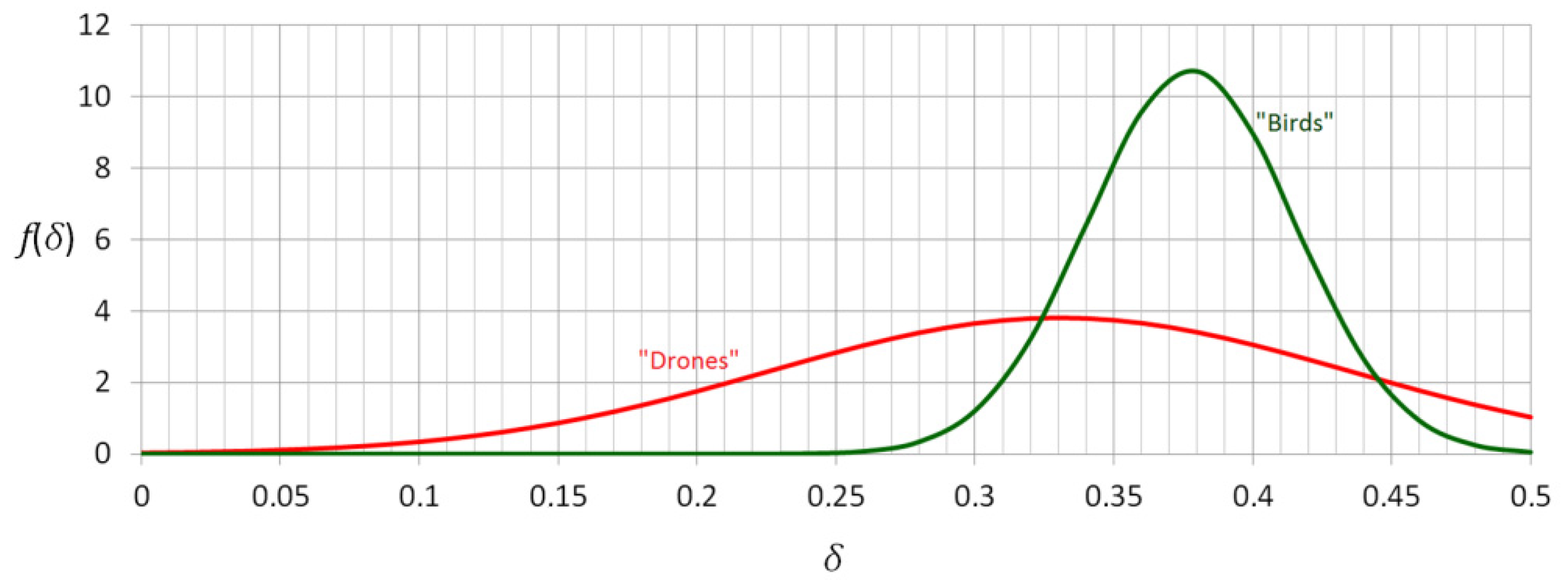
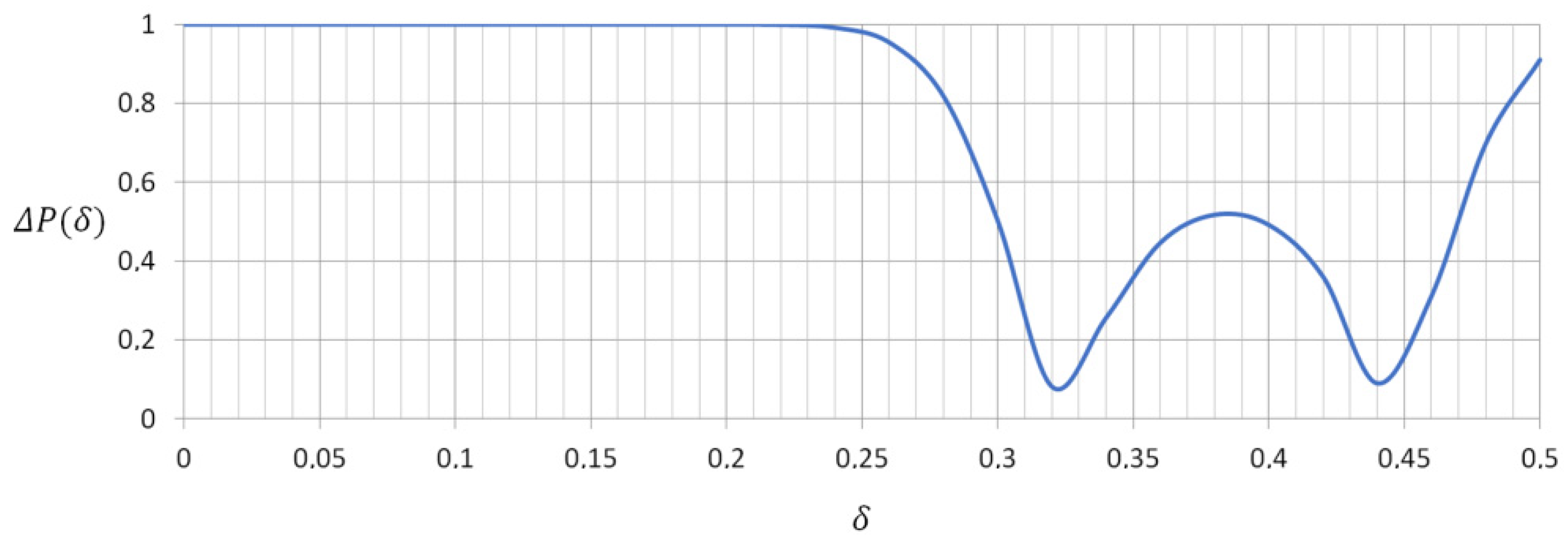
3. Results
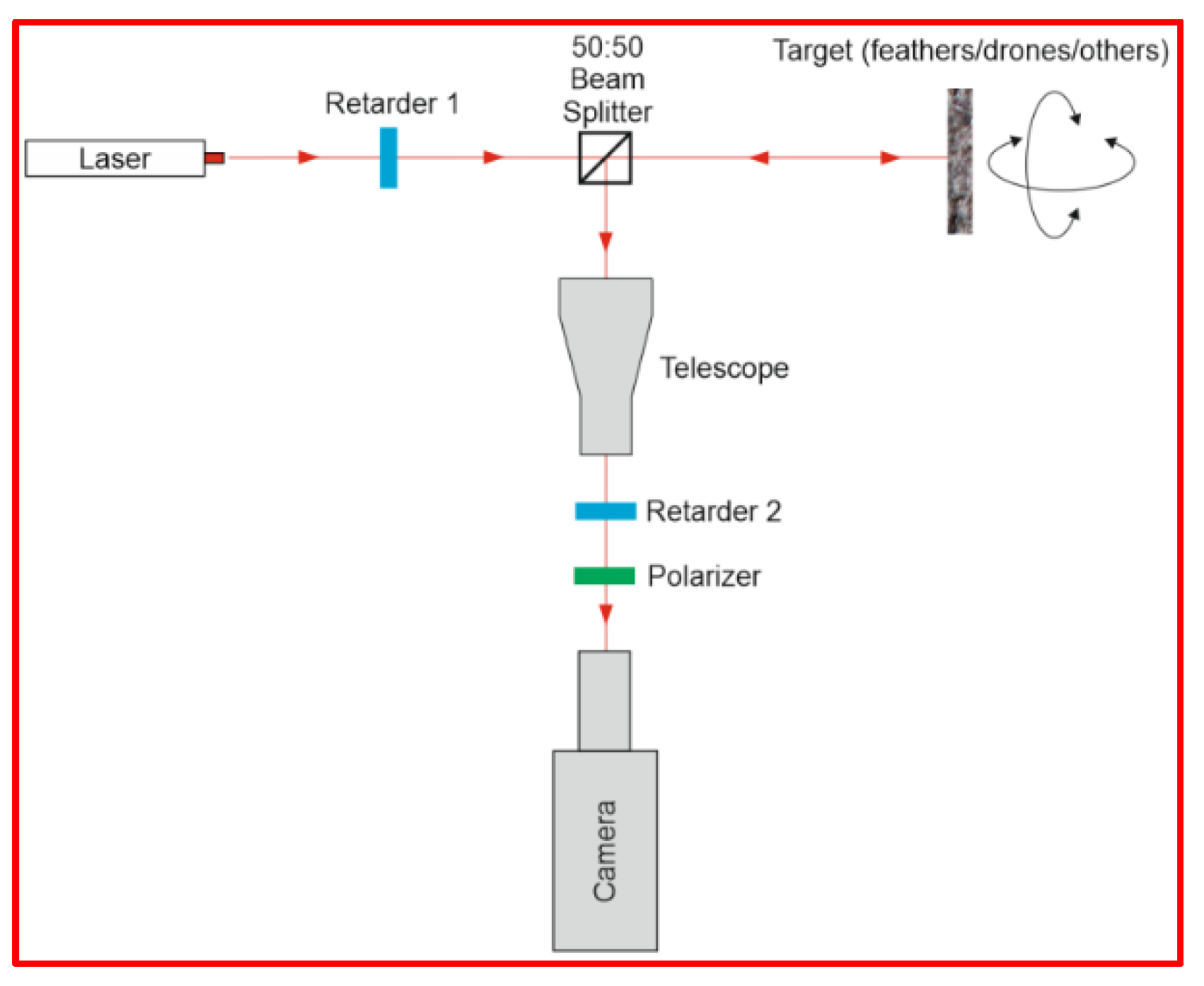
3.1. Scanner Prototype Development
3.2. Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhi, Y.; Fu, Z.; Sun, X.; Yu, J. Security and Privacy Issues of UAV: A Survey. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 25, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Brohi, S.N.; Jhanjhi, N. UAV’s Applications, Architecture, Security Issues and Attack Scenarios: A Survey. In Intelligent Computing and Innovation on Data Science; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Peng, S.L., Son, L., Suseendran, G., Balaganesh, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhaqm, A.; Ikuesan, R.A.; Kebande, V.R.; Razak, S.; Ghabban, F.M. Research Challenges and Opportunities in Drone Forensics Models. Electronics 2021, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statement on the Security Threat Posed by Unmanned Aerial Systems and Possible Countermeasures. 2015. Available online: https://radionavlab.ae.utexas.edu/images/stories/files/papers/statement-humphreys-20150318.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- The Guardian. Gatwick Drone Disruption Cost Airport Just £1.4m. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2019/jun/18/gatwick-drone-disruption-cost-airport-just-14m (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Shi, X.; Yang, C.; Xie, W.; Liang, C.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J. Anti-Drone System with Multiple Surveillance Technologies: Architecture, Implementation, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, P. World Civil Unmanned Aerial Systems Market Profile and Forecast 2017. Available online: http://tealgroup.com/images/TGCTOC/WCUAS2017TOC_EO.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Liu, H.; Fan, K.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, N. Real-Time Small Drones Detection Based on Pruned YOLOv4. Sensors 2021, 21, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluccia, A.; Fascista, A.; Schumann, A.; Sommer, L.; Dimou, A.; Zarpalas, D.; Méndez, M.; Iglesia, D.; González, I.; Mercier, J.P.; et al. Drone vs. Bird Detection: Deep Learning Algorithms and Results from a Grand Challenge. Sensors 2021, 21, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Gao, C.; Qi, F.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L. Small UAV Detection in Videos from a Single Moving Camera. In Proceedings of the CCF Chinese Conference on Computer Vision, Tianjin, China, 11–14 October 2017; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Naus, K.; Maksimiuk, D. A method of fast and simultaneous calibration of many mobile FMCW radars operating in a network anti-drone system. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Oh, B.S.; Sun, L.; Toh, K.A.; Lin, Z. EMD-Based Entropy Features for micro-Doppler Mini-UAV Classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.S.; Guo, X.; Wan, F.; Toh, K.A.; Lin, Z. Micro-Doppler mini-UAV classification using empirical-mode decomposition features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, P.; Harmanny, R.I.; de Wit, J.J.; Egiazarian, K.; Astola, J. Classification of small UAVs and birds by micro-Doppler signatures. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2014, 6, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmann, L.; Biallawons, O.; Klare, J.; Panhuber, R.; Klenke, R.; Ender, J. Micro-Doppler analysis and classification of UAVs at Ka band. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 28–30 June 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Pinelli, G. Classification of Drones with a Surveillance Radar Signal. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems (ICVS), Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–25 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvik, B.; Olsen, K.E.; Griffiths, H. Classification of birds and UAVs based on radar polarimetry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioranelli, F.; Ritchie, M.; Griffiths, H.; Borrion, H. Classification of loaded/unloaded micro-drones using multistatic radar. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 1813–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Jiang, X. Regularized 2D complex-log spectral analysis and subspace reliability analysis of micro-Doppler signature for UAV detection. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 69, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, G.J.; Randeny, T.; Wei, J.; Madanayake, A. Deep learning based doppler radar for micro UAS detection and classification. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2016—2016 IEEE Military Communications Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–3 November 2016; pp. 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabianca, P.; Zhang, Y. Acoustic-Based UAV Detection Using Late Fusion of Deep Neural Networks. Drones 2021, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.Z.; Kaleem, Z.; Jamalipour, A. Machine Learning Inspired Sound-Based Amateur Drone Detection for Public Safety Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, M.M.; Sallouha, H.; Chiumento, A.; Rajendran, S.; Vinogradov, E.; Pollin, S. Key Technologies and System Trade-offs for Detection and Localization of Amateur Drones. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ANTIDRONE. Anti-Drone System Overview and Technology Comparison. Available online: https://antidrone.eu/blog/anti-drone-publications/anti-drone-system-overview-and-technology-comparison.html (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Samaras, S.; Diamantidou, E.; Ataloglou, D.; Sakellariou, N.; Vafeiadis, A.; Magoulianitis, V.; Lalas, A.; Dimou, A.; Zarpalas, D.; Votis, K.; et al. Deep Learning on Multi Sensor Data for Counter UAV Applications-A Systematic Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taha, B.; Shoufan, A. Machine Learning-Based Drone Detection and Classification: State-of-the-Art in Research. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 138669–138682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Rajendran, S.; Pollin, S.; Scheers, B. Combined RF-based drone detection and classification. TechRxiv. Preprint. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, A.; Parisi, G.; Fascista, A. Detection and Classification of Multirotor Drones in Radar Sensor Networks: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emadi, S.; Al-Ali, A.; Al-Ali, A. Audio-Based Drone Detection and Identification Using Deep Learning Techniques with Dataset Enhancement through Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBoo, B.J.; Sasian, J.M.; Chipman, R.A. Depolarization of diffusely reflecting man-made objects. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 5434–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, R. Cloude, Depolarization synthesis: Understanding the optics of Mueller matrix depolarization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2013, 30, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.W.; Chipman, R.A.; Kupinski, M.K. Effects of surface roughness and albedo on depolarization in Mueller matrices. In Proceedings of the Defense + Commercial Sensing 2020—Digitial Forum, 27 April—8 May 2020; Online; p. 11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, G.A.; Ernst, J.D. High-sensitivity analysis of polarization by surface reflection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2018, 29, 1171–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuchin, V.V. Polarized light interaction with tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 071114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallberg, T.; Eriksson, J.; Björkert, S.; Kariis, H. Optical polarization and the dependence of angle of incidence for different surfaces: Comparison between different wavelengths from UV to IR. In Proceedings of the Security + Defence 2018, Berlin, Germany, 10–13 September 2018; p. 10794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmit, G.J.; Rouse, J.W.; Blanchard, A.J. Depolarization of light back scattered from rough dielectrics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1975, 65, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, P.T.; Boerner, W.M. Depolarization of specular scatter as an aid to discriminating between a rough dielectric surface and an "identical" rough metallic surface. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1979, 69, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nee, S.M.F. Polarization of specular reflection and near-specular scattering by a rough surface. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 3570–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.; Nonaka, K. Light depolarization in off-specular reflection on submicro rough metal surfaces with imperfectly random roughness. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 023107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Ochoa, L.F.; Lacoste, D.; Lenke, R.; Schurtenberger, P.; Scheffold, F. Depolarization of backscattered linearly polarized light. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2004, 21, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pöller, F.; Bloise, F.S.; Jakobi, M.; Wang, S.; Dong, J.; Koch, A.W. Non-Contact Roughness Measurement in Sub-Micron Range by Considering Depolarization Effects. Sensors 2019, 19, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Hao, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q. Depolarization of laser beam propagating through atmosphere based on multiple Rayleigh scattering model. In Proceedings of the SPIE/COS Photonics Asia, Beijing, China, 10–12 October 2016; p. 10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtanowski, J.; Zygmunt, M.; Drozd, T.; Jakubaszek, M.; Życzkowski, M.; Muzal, M. Distinguishing Drones from Birds in a UAV Searching Laser Scanner Based on Echo Depolarization Measurement. Sensors 2021, 21, 5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165597
Wojtanowski J, Zygmunt M, Drozd T, Jakubaszek M, Życzkowski M, Muzal M. Distinguishing Drones from Birds in a UAV Searching Laser Scanner Based on Echo Depolarization Measurement. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165597
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtanowski, Jacek, Marek Zygmunt, Tadeusz Drozd, Marcin Jakubaszek, Marek Życzkowski, and Michał Muzal. 2021. "Distinguishing Drones from Birds in a UAV Searching Laser Scanner Based on Echo Depolarization Measurement" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165597
APA StyleWojtanowski, J., Zygmunt, M., Drozd, T., Jakubaszek, M., Życzkowski, M., & Muzal, M. (2021). Distinguishing Drones from Birds in a UAV Searching Laser Scanner Based on Echo Depolarization Measurement. Sensors, 21(16), 5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165597





