Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
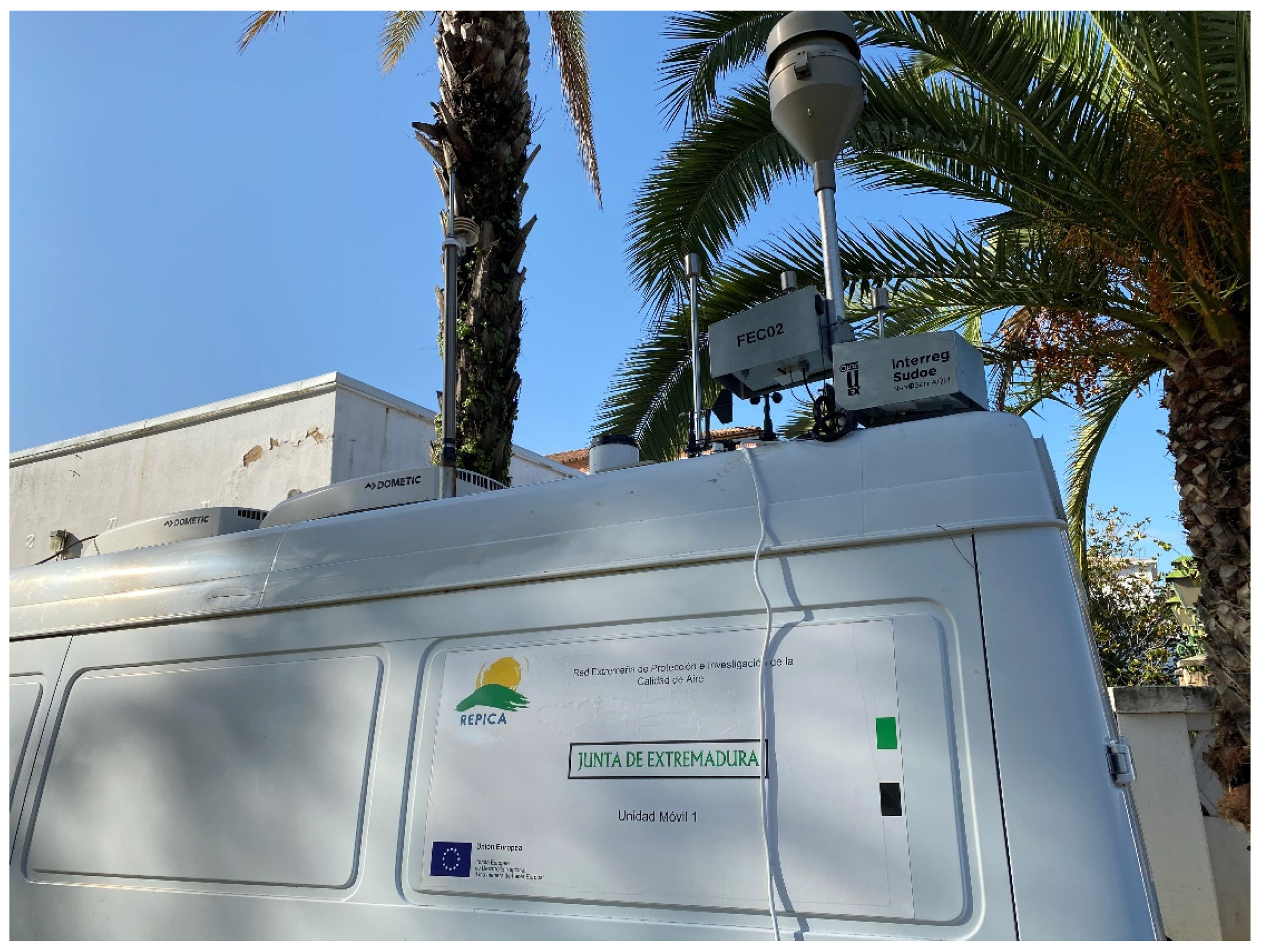
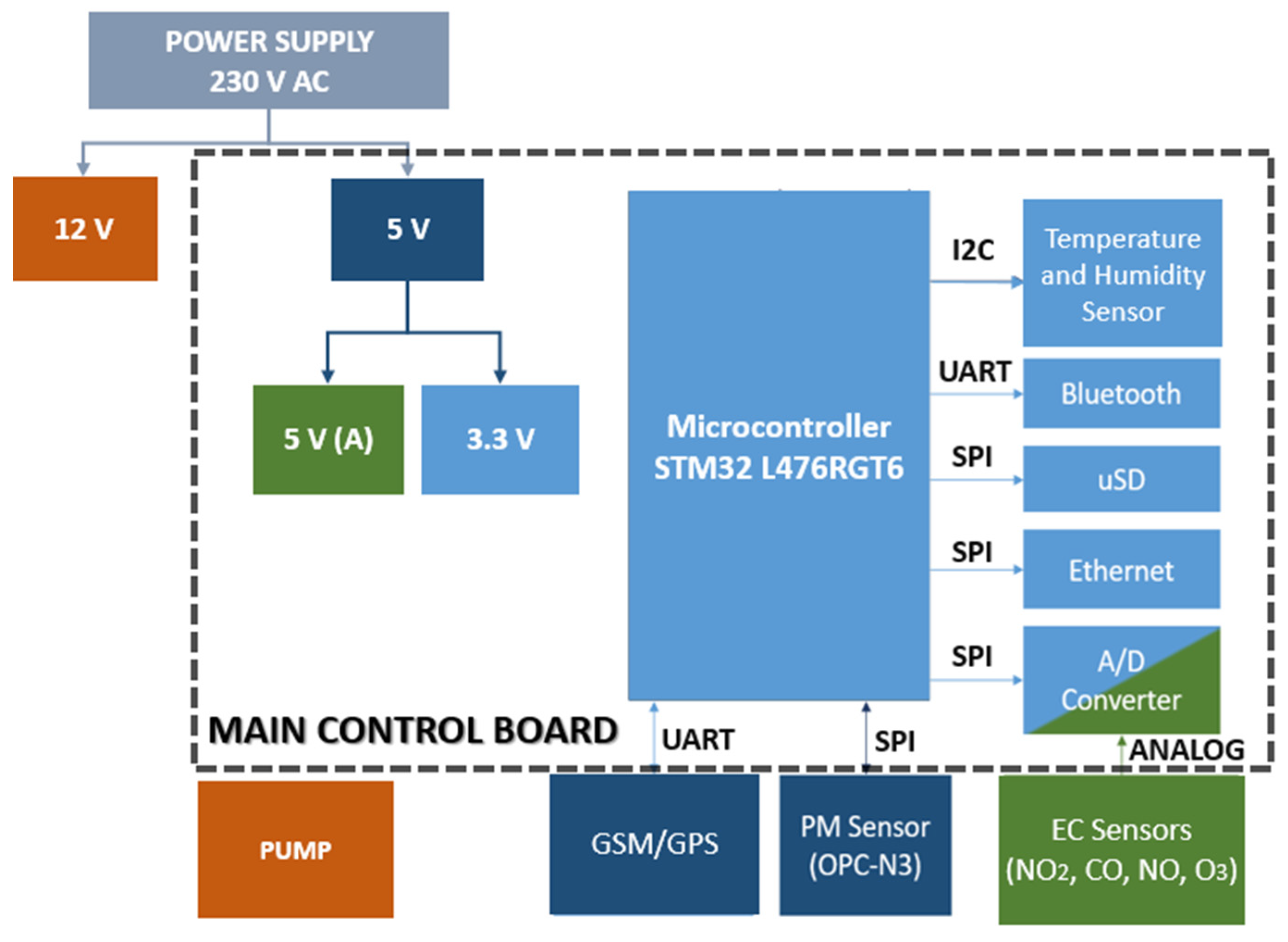
2.1. Sensor Device
2.2. Gas Sensors
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Reference Methods
- −
- O3: THERMO 49i-B3ZAA (UV absorption);
- −
- NOx: THERMO 42i-BZMTPAA (chemiluminiscence);
- −
- PM: DIGITEL DHA-80 (high volume sampler + gravimetric analysis). GRIMM 180 (optical laser light aerosol spectrometers) nonofficial data.
2.5. Field Measurement Campaign
2.6. Calibration Procedure
2.6.1. Manufacturer Algorithm
2.6.2. Single Linear Regression
2.6.3. Multilinear Regression
2.6.4. Multilayer Perceptron Regressor
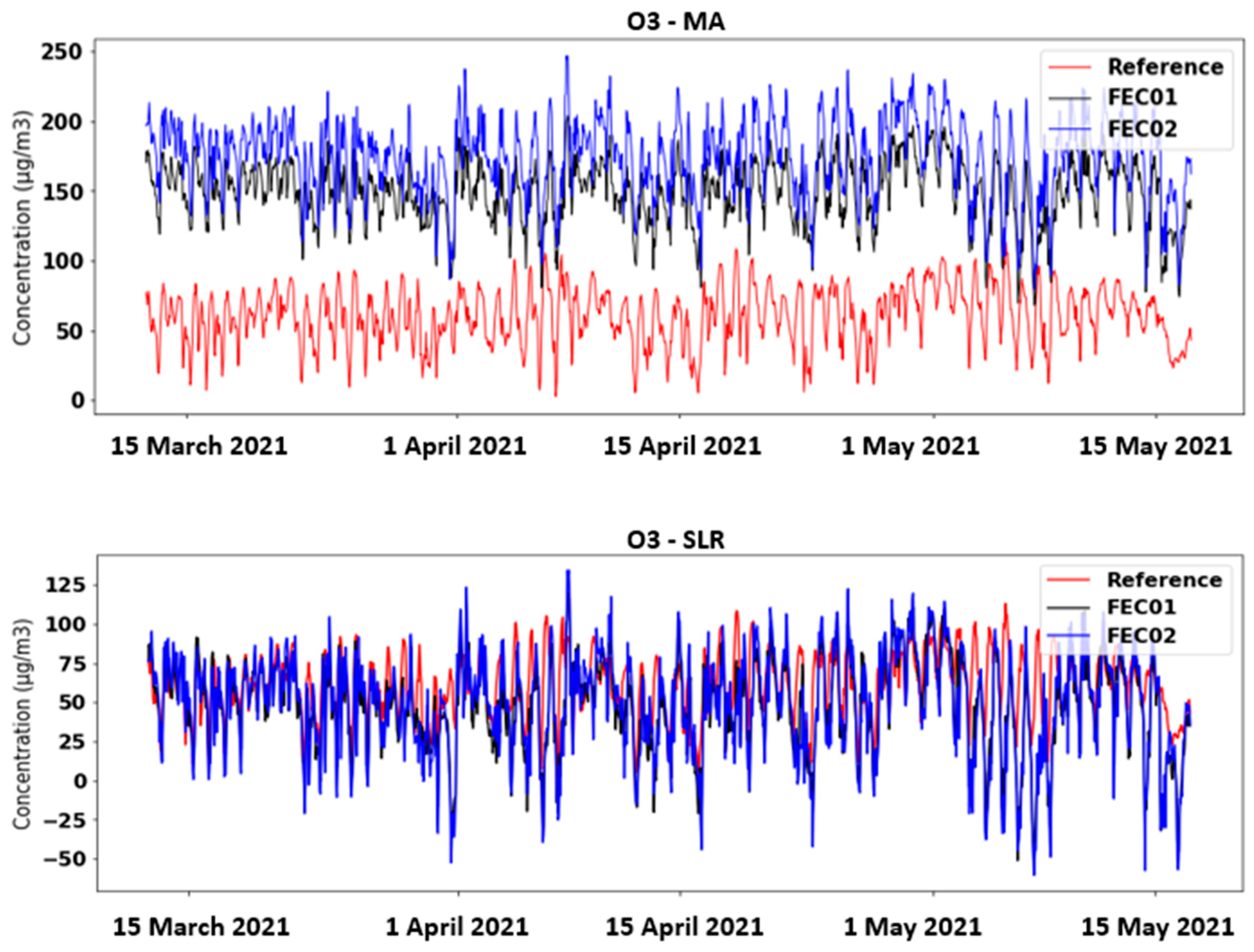
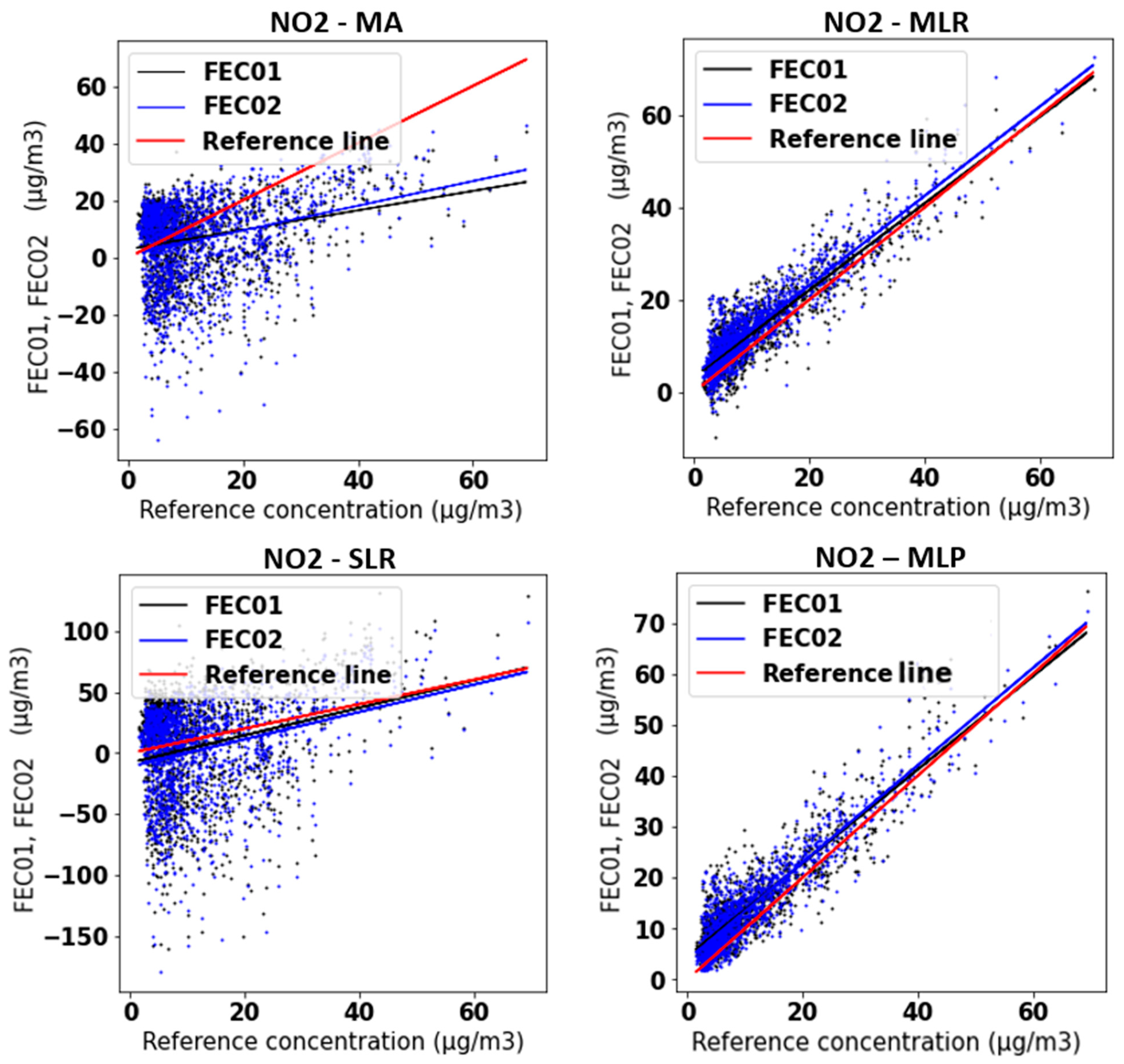
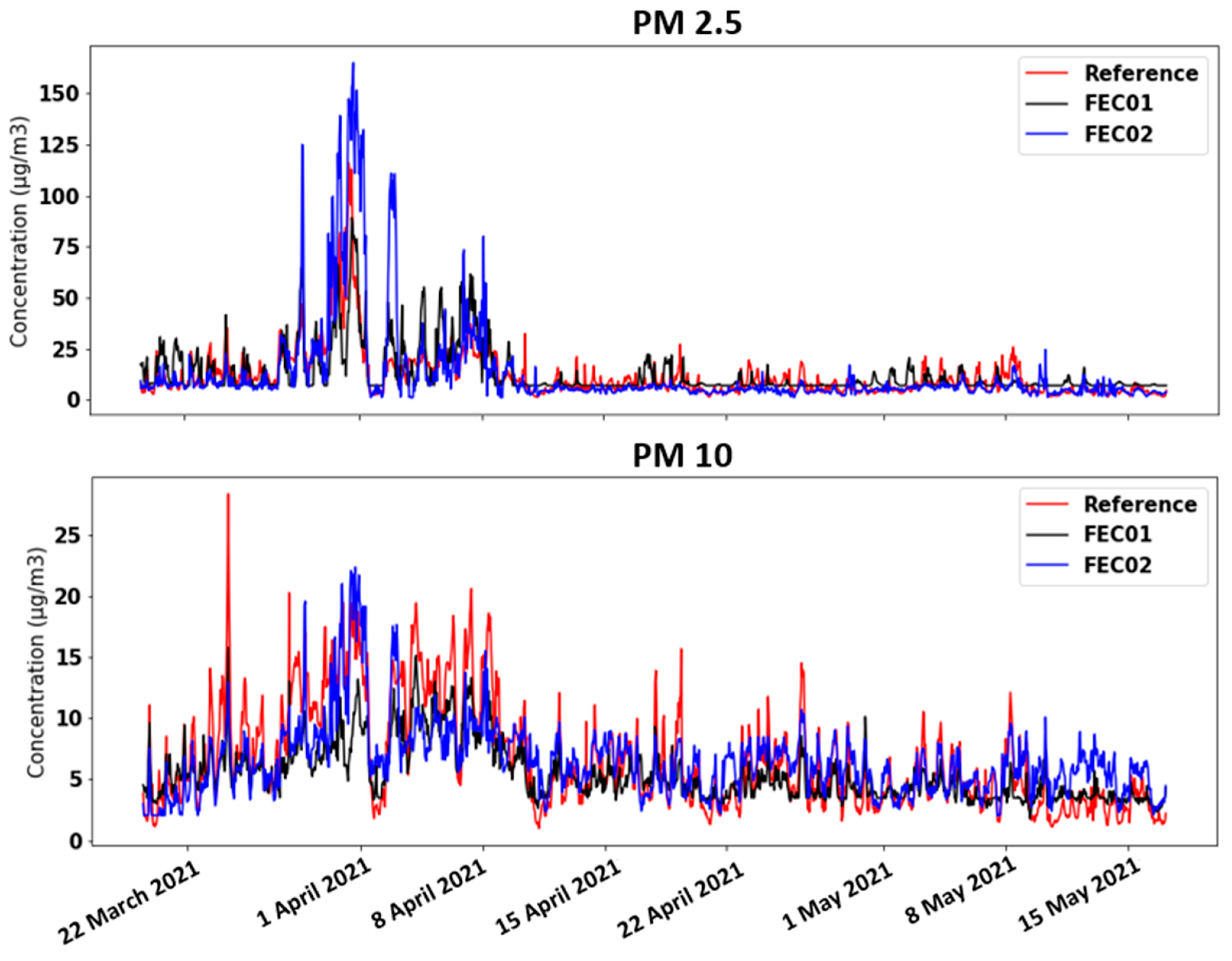
3. Results and Discussion
Model Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, L.G.; Cole, T.B.; Dao, K.; Chang, Y.C.; Coburn, J.; Garrick, J.M. Effects of air pollution on the nervous system and its possible role in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 210, 107523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.; Skrzypek, M.; Kowalski, M.; Cyrys, J. Effect of NOx and NO2 concentration increase in ambient air to daily bronchitis and asthma exacerbation, Silesian Voivodeship in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardini, F.; Attademo, L.; Trezzi, R.; Gobbicchi, C.; Balducci, P.M.; Del Bello, V.; Menculini, G.; Pauselli, L.; Piselli, M.; Sciarma, T.; et al. Air pollutants and daily number of admissions to psychiatric emergency services: Evidence for detrimental mental health effects of ozone. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 29, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, M.C.; Andersen, Z.J.; Baccarelli, A.; Diver, W.R.; Gapstur, S.M.; Pope, C.A.; Prada, D.; Samet, J.; Thurston, G.; Cohen, A. Outdoor air pollution and cancer: An overview of the current evidence and public health recommendations. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 460–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, J.D.; Ebisu, K. Changes in U.S. air pollution during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; van der A, R.J.; Eskes, H.J.; Mijling, B.; Stavrakou, T.; van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Veefkind, J.P. NOx Emissions Reduction and Rebound in China Due to the COVID-19 Crisis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, J.L.; Samsun, R.C.; Peters, R.; Stolten, D. The impact of diesel vehicles on NOx and PM10 emissions from road transport in urban morphological zones: A case study in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürçam, S.; Konuralp, E.; Ekici, S. Determining the effect of air transportation on air pollution in the most polluted city in Turkey. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2021, 93, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsback, K.R.; Kerry, D.; Croft, B.; Ford, B.; Jathar, S.H.; Carter, E.; Martin, R.V.; Pierce, J.R. Beyond SOxreductions from shipping: Assessing the impact of NOx and carbonaceous-particle controls on human health and climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Vu, T.; Kotthaus, S.; Harrison, R.M.; Grimmond, S.; Yue, S.; Zhu, T.; Lee, J.; Han, Y.; Demuzere, M.; et al. Introduction to the special issue ‘In-depth study of air pollution sources and processes within Beijing and its surrounding region (APHH-Beijing)’. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7519–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolluru, S.S.R.; Patra, A.K.; Nazneen; Shiva Nagendra, S.M. Association of air pollution and meteorological variables with COVID-19 incidence: Evidence from five megacities in India. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Tao, Y.; Kwan, M.-P.; Chai, Y. Assessing Mobility-Based Real-Time Air Pollution Exposure in Space and Time Using Smart Sensors and GPS Trajectories in Beijing. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2020, 110, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- nanosenaqm.eu|Desarrollo y Validación en Campo de un Sistema de Nanosensores de bajo Consumo y Bajo Coste Para la Monitorización en Tiempo Real de la Calidad del Aire Ambiente. Available online: https://www.nanosenaqm.eu/ (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Karagulian, F.; Barbiere, M.; Kotsev, A.; Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Lagler, F.; Redon, N.; Crunaire, S.; Borowiak, A. Review of the Performance of Low-Cost Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Dahiya, M.; Kumar, R.; Nanda, C. Sensors and systems for air quality assessment monitoring and management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleixandre, M.; Gerboles, M. Review of small commercial sensors for indicative monitoring of ambient gas. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2012, 30, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; Jiang, Q.; De Jonge, D.; Bocconi, S. Field calibration of electrochemical NO2 sensors in a citizen science context. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1297–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Zoest, V.; Osei, F.B.; Stein, A.; Hoek, G. Calibration of low-cost NO2 sensors in an urban air quality network. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, C.; Costa, A.M.; Ginja, J.; Amorim, M.; Coutinho, M.; Karatzas, K.; Sioumis, T.; Katsifarakis, N.; Konstantinidis, K.; De Vito, S.; et al. Assessment of air quality microsensors versus reference methods: The EuNetAir joint exercise. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vito, S.; Esposito, E.; Salvato, M.; Popoola, O.; Formisano, F.; Jones, R.; Di Francia, G. Calibrating chemical multisensory devices for real world applications: An in-depth comparison of quantitative machine learning approaches. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1191–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrego, C.; Ginja, J.; Coutinho, M.; Ribeiro, C.; Karatzas, K.; Sioumis, T.; Katsifarakis, N.; Konstantinidis, K.; De Vito, S.; Esposito, E.; et al. Assessment of air quality microsensors versus reference methods: The EuNetAir Joint Exercise–Part II. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 193, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malings, C.; Tanzer, R.; Hauryliuk, A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Zimmerman, N.; Kara, L.B.; Presto, A.A.; Subramanian, R. Development of a general calibration model and long-term performance evaluation of low-cost sensors for air pollutant gas monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dachyar, M.; Zagloel, T.Y.M.; Saragih, L.R. Knowledge growth and development: Internet of things (IoT) research, 2006–2018. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, J.; Jo, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Han, W. Development of an IoT-Based indoor air quality monitoring platform. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 8749764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, I.R.; Wang, D.C.; Tsai, J.J.P.; Al-Hamadi, H. Trust-Based IoT Cloud Participatory Sensing of Air Quality. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 105, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrani, H.; Lounas, R.; Bennai, M.T.; Salhi, D.E.; Djerbi, R. Air quality monitoring using IoT: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Internet of Things (SmartIoT), Tianjin, China, 9–11 August 2019; pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, P.; Herrero, J.; Suárez, J.; Lozano, J.; Arroyo, P.; Herrero, J.L.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Wireless Sensor Network Combined with Cloud Computing for Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatzidiakou, L.; Krause, A.; Popoola, O.; Di Antonio, A.; Kellaway, M.; Han, Y.; Squires, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Characterising low-cost sensors in highly portable platforms to quantify personal exposure in diverse environments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4643–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Alvia, L.; Palermo, E.; Del Prete, Z. Validation and application of a novel solution for environmental monitoring: A three months study at “Minerva Medica” archaeological site in Rome. Measurement 2018, 129, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerrett, M.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Popoola, O.; Jones, R.; Cohen, R.C.; Almanza, E.; de Nazelle, A.; Mead, I.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Cole-Hunter, T.; et al. Validating novel air pollution sensors to improve exposure estimates for epidemiological analyses and citizen science. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD). Field Evaluation AlphaSense OPC-N3 Sensor; SCAQMD: Diamond Bar, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marinov, M.; Topalov, I.P.; Hinov, N.L.; Hensel, S. Mobile platform for particulate matter monitoring. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Creative Business for Smart and Sustainable Growth, CreBUS 2019, Sandanski, Bulgaria, 18–21 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stetter, J.R.; Li, J. Amperometric gas sensors—A review. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Mead, M.I.; Jones, R.L. Development of a baseline-temperature correction methodology for electrochemical sensors and its implications for long-term stability. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alphasense Ltd. Alphasense Application Note-AAN 803-05; Alphasense Ltd.: Great Notley, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, P.; Silva, J.; Araujo, F.; Silva, C.; Gil, P.; Arrais, J.P.; Coutinho, D.; Salgueiro, P.; Rato, L.; Saias, J.; et al. NanoSen-AQM: From sensors to users. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2020, 16, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.; Lucas, P.; Araujo, F.; Silva, C.; Gil, P.; Cardoso, A.; Arrais, J.; Ribeiro, B.; Coutinho, D.; Salgueiro, P.; et al. An online platform for real-time air quality monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th Experiment International Conference (Exp.at’19), Funchal, Portugal, 12–14 June 2019; Volume 0569, pp. 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NanoSen-AQM Platform. Available online: https://nanosenaqm.dei.uc.pt/ (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Silva, J.; Lucas, P.; Araujo, F.; Silva, C.; Gil, P.; Cardoso, A.; Arrais, J.; Ribeiro, B.; Coutinho, D.; Salgueiro, P.; et al. A hybrid application for real-time air quality monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th Experiment International Conference (exp.at’19), Funchal, Portugal, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.S.; Williams, L.R.; Lewis, D.K.; Magoon, G.R.; Onasch, T.B.; Kaminsky, M.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jayne, J.T. Use of electrochemical sensors for measurement of air pollution: Correcting interference response and validating measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Technique | Inputs | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer Algorithm (laboratory calibration) (MA) | NO2_WE (mV), NO2_AE (mV), T (°C) | NO2 (µg/m3) |
| NO_WE (mV), NO_AE (mV), T (°C) | NO (µg/m3) | |
| CO_WE (mV), CO_AE (mV), T (°C) | CO (µg/m3) | |
| O3_WE (mV), O3_AE (mV), T (°C) | O3 (µg/m3) | |
| - | PM10 (µg/m3), PM2.5 (µg/m3) | |
| Simple Linear Regression (SLR) | NO2 (µg/m3) | NO2 (µg/m3) |
| NO (µg/m3) | NO (µg/m3) | |
| CO (µg/m3) | CO (µg/m3) | |
| O3 (µg/m3) | O3 (µg/m3) | |
| PM10 (µg/m3) | PM10 (µg/m3) | |
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | PM2.5 (µg/m3) | |
| Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) | NO2_WE (mV), NO2_AE (mV), NO_WE (mV), NO_AE (mV), CO_WE (mV), CO_AE (mV), O3_WE (mV), O3_AE (mV), T (°C), RH (%) | NO2 (µg/m3) |
| NO (µg/m3) | ||
| CO (µg/m3) | ||
| O3 (µg/m3) | ||
| PM1 (µg/m3), PM2.5 (µg/m3), PM10 (µg/m3), T (°C), RH (%), SFR | PM10 (µg/m3) | |
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | ||
| Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) | NO2_WE (mV), NO2_AE (mV), NO_WE (mV), NO_AE (mV), CO_WE (mV), CO_AE (mV), O3_WE (mV), O3_AE (mV), T (°C), RH (%) | NO2 (µg/m3) |
| NO (µg/m3) | ||
| CO (µg/m3) | ||
| O3 (µg/m3) | ||
| PM1 (µg/m3), PM2.5 (µg/m3), PM10 (µg/m3), T (°C), RH (%), SFR | PM10 (µg/m3) | |
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) |
| Pollutants | R2 | MAE | MSE | R2 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA | SLR | MLR | MLP | MA | SLR | MLR | MLP | MA | SLR | MLR | MLP | MA | SLR | MLR | MLP | ||
| FEC01 | NO2 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 11.89 | 35.59 | 0.94 | 3.65 | 230.13 | 1784.15 | 26.34 | 23.80 | −1.24 | −16.40 | 0.73 | 0.75 |
| NO | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 28.41 | 10.17 | 2.06 | 1.25 | 869.89 | 149.22 | 7.52 | 3.60 | −15.79 | −1.88 | 0.84 | 0.92 | |
| CO | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.38 | - | 60.79 | 0.06 | 45.36 | - | 5125.31 | 0.01 | 3211.12 | - | −0.21 | −0.51 | 0.17 | - | |
| O3 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 87.11 | 17.30 | 10.86 | 9.22 | 7981.32 | 724.46 | 145.11 | 106.02 | −18.24 | −0.75 | 0.66 | 0.75 | |
| PM10 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 18.16 | 3.14 | 2.38 | 1.72 | 443.78 | 22.73 | 9.92 | 5.36 | −24.66 | −0.31 | 0.47 | 0.61 | |
| PM2.5 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 9.50 | 111.40 | 8.10 | 5.93 | 147.95 | 23.3 × 103 | 117.56 | 85.19 | −0.06 | −166.01 | 0.20 | 0.42 | |
| FEC02 | NO2 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 12.34 | 27.94 | 4.11 | 3.81 | 266.46 | 1423.04 | 27.21 | 24.09 | −1.60 | −12.88 | 0.72 | 0.75 |
| NO | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 6.91 | 9.14 | 2.09 | 1.76 | 76.90 | 117.12 | 7.59 | 6.40 | −0.48 | −1.25 | 0.84 | 0.86 | |
| CO | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.38 | - | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.05 | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | - | −0.67 | −0.89 | 0.16 | - | |
| O3 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 113.27 | 21.08 | 9.69 | 8.85 | 13.4 × 103 | 987.01 | 123.47 | 104.44 | −31.52 | −1.38 | 0.71 | 0.76 | |
| PM10 | 0.58 | 0.48 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 11.28 | 4.27 | 2.12 | 1.99 | 299.25 | 59.96 | 7.27 | 7.37 | −16.30 | −2.46 | 0.61 | 0.60 | |
| PM2.5 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 6.27 | 4 × 103 | 6.75 | 6.15 | 139.13 | 4.48 × 107 | 115.44 | 211.02 | 0.00 | −3.2 × 105 | 0.22 | 0.43 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arroyo, P.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection. Sensors 2021, 21, 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186228
Arroyo P, Gómez-Suárez J, Suárez JI, Lozano J. Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection. Sensors. 2021; 21(18):6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186228
Chicago/Turabian StyleArroyo, Patricia, Jaime Gómez-Suárez, José Ignacio Suárez, and Jesús Lozano. 2021. "Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection" Sensors 21, no. 18: 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186228
APA StyleArroyo, P., Gómez-Suárez, J., Suárez, J. I., & Lozano, J. (2021). Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection. Sensors, 21(18), 6228. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186228







