Trends and Challenges of Wearable Multimodal Technologies for Stroke Risk Prediction
Abstract
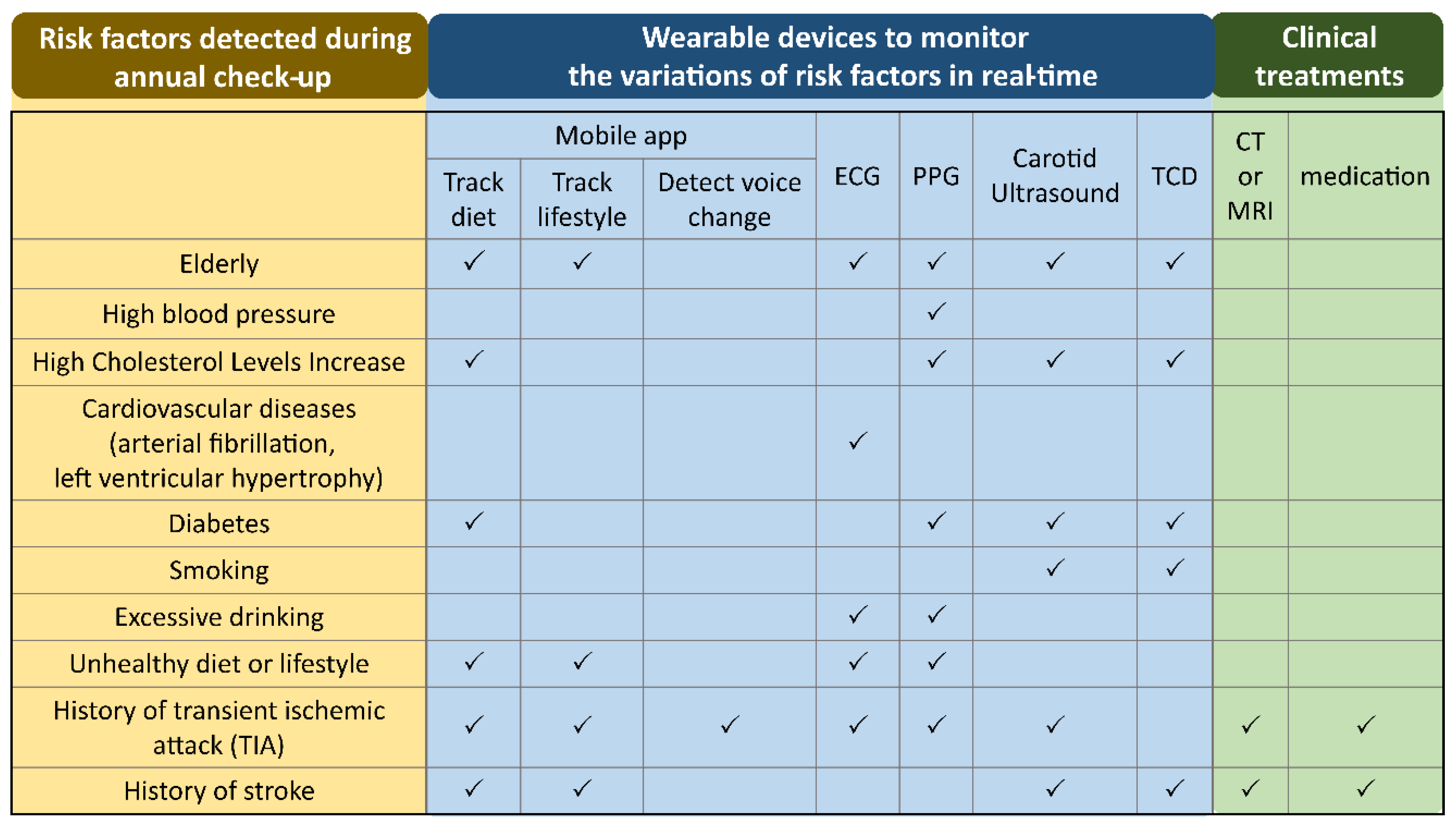
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Wearable Devices for Stroke Risk Prediction
3.1. Questionnaires and Scoring Systems via Mobile Applications
3.2. Sensor for Air Pollution Embedded in Smart Phone
3.3. Devices for ECG Monitoring
3.4. Devices for Vascular Related Risk Factors Monitoring
3.4.1. Blood Pressure Monitoring
3.4.2. Blood Flow Dynamics Monitored by Doppler Ultrasonographic System
3.5. Devices for Carotid Plaque Characterization and Cerebral Microembolization Monitoring
3.5.1. Carotid Ultrasound for Carotid Plaques Characterization
3.5.2. TCD for Cerebral Microembolization Monitoring
3.6. Gait and Motion Monitoring
3.7. Devices for EEG Monitoring
3.8. fNIRS Devices for Hemodynamic Signals Monitoring
4. Comparison and Combination of Various Techniques
5. Perspectives of Stroke Prediction
5.1. Strategies of Using Wearable Technologies for Stroke Risk Prediction
5.2. EEG-fNIRS Multimodal Recording for Stroke Risk Prediction
5.3. Challenges and Limitations of EEG-fNIRS Multimodal Recording and Possible Solutions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.O.; Nguyen, M.; Roth, G.A.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Abate, D.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.E.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Wu, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Anderson, C.S.; Sandercock, P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; et al. Stroke in China: Advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.; Callaway, C.; Carson, A.; Chamberlain, A.; Chang, A.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, E56–E528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Kinni, H.; Lewandowski, C.; Nowak, R.; Levy, P. Management of Hypertension in Stroke. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2014, 64, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Norrving, B.; George, M.G.; Foltz, J.L.; Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A. Prevention of stroke: A strategic global imperative. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrving, B.; Barrick, J.; Davalos, A.; Dichgans, M.; Cordonnier, C.; Guekht, A.; Kutluk, K.; Mikulik, R.; Wardlaw, J.; Richard, E.; et al. Action Plan for Stroke in Europe 2018–2030. Eur. Stroke J. 2018, 3, 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brainin, M.; Feigin, V.; Bath, P.M.; Collantes, E.; Martins, S.; Pandian, J.; Sacco, R.; Teuschl, Y. Multi-level community interventions for primary stroke prevention: A conceptual approach by the World Stroke Organization. Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, D.M.; Brown, R.D., Jr. The Challenges of Stroke Prediction Scores. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Gorelick, P.B.; Dichgans, M.; Wang, W.; Pandian, J.D.; Martins, S.C.O.; Owolabi, M.O.; Wood, D.A.; et al. What Is the Best Mix of Population-Wide and High-Risk Targeted Strategies of Primary Stroke and Cardiovascular Disease Prevention? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.D. Uses of ultrasound in stroke prevention. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirsat, M.S.; Fermé, E.; Câmara, J. Machine Learning for Brain Stroke: A Review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinelli, L.A. Detecting At-Risk Alcohol Drinking Behavior: Integrating Individual Cardiovascular Signs and Symptom Appraisal. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raheja, H.; Namana, V.; Chopra, K.; Sinha, A.; Gupta, S.; Kamholz, S.; Moskovits, N.; Shani, J.; Hollander, G. Electrocardiogram Changes with Acute Alcohol Intoxication: A Systematic Review. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2018, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, B.; Cong, Y. The Probability of Ischaemic Stroke Prediction with a Multi-Neural-Network Model. Sensors 2020, 20, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, C.; Zhao, R.; Sun, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Gao, D. Privacy-preserving technology to help millions of people: Federated prediction model for stroke prevention. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10517. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Pan, X.-F.; Yu, C.; Lv, J.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, T.; Chen, Z.; et al. Self-Rated Health Status and Risk of Incident Stroke in 0.5 Million Chinese Adults: The China Kadoorie Biobank Study. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharma, K.K.; Parellangi. Use of mobile-stroke risk scale and lifestyle guidance promote healthy lifestyles and decrease stroke risk factors. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2020, 7, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, R.; Hale, L.; Barker-Collo, S.; Theadom, A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; George, A.; Arroll, B.; Ranta, A.; Waters, D.; Wilson, D.; et al. Mobile Technology for Primary Stroke Prevention. Stroke 2019, 50, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Shen, C.; Yu, L.; Lu, F.; et al. Predicting 10-Year and Lifetime Stroke Risk in Chinese Population. Stroke 2019, 50, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Kannel, W.B. Probability of stroke: A risk profile from the Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyman, D.A.; Siebert, V.; Jia, X.; Alam, M.; Levine, G.N.; Virani, S.S.; Birnbaum, Y. Risk Assessment of Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Current Shortcomings and Future Directions. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2019, 33, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.G.; Pearce, L.A.; Halperin, J.L.; Hylek, E.M.; Albers, G.W.; Anderson, D.C.; Connolly, S.J.; Friday, G.H.; Gage, B.F.; Go, A.S.; et al. Comparison of 12 risk stratification schemes to predict stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Stroke 2008, 39, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muse, E.D.; Wineinger, N.E.; Spencer, E.G.; Peters, M.; Henderson, R.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Barrett, P.M.; Rivera, S.P.; Wohlgemuth, J.G.; Devlin, J.J.; et al. Validation of a genetic risk score for atrial fibrillation: A prospective multicenter cohort study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pokorney, S.D.; Gersh, B.J.; Ahmad, A.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Blank, M.; Coylewright, M.; DiBattiste, P.; Healey, J.S.; Hedrich, O.; Hylek, E.M. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: Closing the gap. Am. Heart J. 2019, 210, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estol, C.J. Is breathing our polluted air a risk factor for stroke? Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Miller, M.R.; Shah, A.S.V. Air Pollution and Stroke. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.L.; Xiang, X.; Li, M.; Juan, J.; Song, J.; Cao, Y.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, L.B.; et al. Association between ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for ischemic stroke: A nationwide time-series analysis. PLoS Med. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maag, B.; Zhou, Z.; Thiele, L. W-Air: Enabling Personal Air Pollution Monitoring on Wearables. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2018, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, D.; Mahdavipour, O.; Sabino, J.; White, R.M.; Paprotny, I. Vertically-stacked MEMS PM2.5 sensor for wearable applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 299, 111569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhnini, N.; Yu, J.E.; Jones, R.M.; Chattopadhyay, D. Personal Air Pollution Monitoring Technologies: User Practices and Preferences. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, A.J.; Corbucci, G.; Padeletti, L. Usefulness of Continuous Electrocardiographic Monitoring for Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noseworthy Peter, A.; Kaufman Elizabeth, S.; Chen Lin, Y.; Chung Mina, K.; Elkind Mitchell, S.V.; Joglar José, A.; Leal Miguel, A.; McCabe Pamela, J.; Pokorney Sean, D.; Yao, X.; et al. Subclinical and Device-Detected Atrial Fibrillation: Pondering the Knowledge Gap: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e944–e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel Boulos, M.N.; Haywood, G. Opportunistic atrial fibrillation screening and detection in “self-service health check-up stations”: A brief overview of current technology potential and possibilities. mHealth 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Perera, T.; Elliott, A.D.; Twomey, D.J.; Kumar, S.; Munwar, D.A.; Khokhar, K.B.; Thiyagarajah, A.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Nalliah, C.J.; et al. Subclinical device-detected atrial fibrillation and stroke risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyaswamy, T.; Balasubramanian, M. Ambulatory cardiac bio-signals: From mirage to clinical reality through a decade of progress. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakadze, N.; Martin, S.S. How useful is the smartwatch ECG? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alusi, M.A.; Ding, E.; McManus, D.D.; Lubitz, S.A. Wearing Your Heart on Your Sleeve: The Future of Cardiac Rhythm Monitoring. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Tran, N.; Gadhoumi, K.; Pelter, M.M.; Do, D.H.; Lee, R.J.; Colorado, R.; Meisel, K.; Hu, X. Photoplethysmography based atrial fibrillation detection: A review. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamel, H.; O’Neal, W.T.; Okin, P.M.; Loehr, L.R.; Alonso, A.; Soliman, E.Z. Electrocardiographic left atrial abnormality and stroke subtype in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, H.; Healey, J. Cardioembolic Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.K.; Soliman, E.Z. ECG abnormalities and stroke incidence. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 11, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Tse, G.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Letsas, K.P.; Ali-Hasan-Al-Saegh, S.; Kamel, H.; Li, G.P.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Liu, T. P-Wave Indices and Risk of Ischemic Stroke A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2017, 48, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lees, T.; Shad-Kaneez, F.; Simpson, A.M.; Nassif, N.T.; Lin, Y.; Lal, S. Heart Rate Variability as a Biomarker for Predicting Stroke, Post-stroke Complications and Functionality. Biomark. Insights 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraco, G.; Iadecola, C. Hypertension: A harbinger of stroke and dementia. Hypertension 2013, 62, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorelick, P.B.; Qureshi, S.; Farooq, M.U. Management of blood pressure in stroke. Int. J. Cardiol. Hypertens. 2019, 3, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, S.; GholamHosseini, H.; Lowe, A. Non-invasive continuous blood pressure monitoring systems: Current and proposed technology issues and challenges. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T. Recent Research and Developing Trends of Wearable Sensors for Detecting Blood Pressure. Sensors 2018, 18, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Hajj, C.; Kyriacou, P.A. A review of machine learning techniques in photoplethysmography for the non-invasive cuff-less measurement of blood pressure. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 58, 101870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosanee, M.; Chan, G.; Welykholowa, K.; Cooper, R.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Zheng, D.; Allen, J.; Abbott, D.; Menon, C.; Lovell, N.H.; et al. Cuffless Single-Site Photoplethysmography for Blood Pressure Monitoring. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Huang, B.; Gong, H.; et al. Monitoring of the central blood pressure waveform via a conformal ultrasonic device. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Sinha, A.D.; Agarwal, R. Home blood pressure monitoring: How good a predictor of long-term risk? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2011, 13, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermida, R.C.; Ayala, D.E.; Smolensky, M.H.; Fernández, J.R.; Mojón, A.; Portaluppi, F. Sleep-time blood pressure: Unique sensitive prognostic marker of vascular risk and therapeutic target for prevention. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 33, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Saito, I.; Kushiro, T.; Teramukai, S.; Tomono, Y.; Okuda, Y.; Shimada, K. Morning Home Blood Pressure Is a Strong Predictor of Coronary Artery Disease: The HONEST Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.-H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.-T. Investigation on Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Using Physiological Parameters. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 272691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asayama, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Kikuya, M.; Obara, T.; Metoki, H.; Inoue, R.; Hara, A.; Hirose, T.; Hoshi, H.; Hashimoto, J.; et al. Prediction of Stroke by Home “Morning” Versus “Evening” Blood Pressure Values. Hypertension 2006, 48, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.-D.; Shen, X.-L.; Zhao, R.; Tao, X.-X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.-J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.-T.; Yao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Pulse pressure as an independent predictor of stroke: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2016, 105, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecobici, M.; Stoicescu, C. Arterial Stiffness and Hypertension—Which Comes First? Maedica (Buchar) 2017, 12, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda, D.; Esparza, A.; Ghamari, M.; Soltanpur, C.; Nazeran, H. A review on wearable photoplethysmography sensors and their potential future applications in health care. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 4, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Wu, T.T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Meng, P.; Ji, N.; Sun, Y.; et al. The role of carotid stenosis ultrasound scale in the prediction of ischemic stroke. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamthikar, A.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, N.N.; Araki, T.; Saba, L.; Nicolaides, A.; Sharma, A.; Omerzu, T.; Suri, H.S.; Gupta, A.; et al. Chapter 15—A special report on changing trends in preventive stroke/cardiovascular risk assessment via B-mode ultrasonography. In Cognitive Informatics, Computer Modelling, and Cognitive Science; Sinha, G.R., Suri, J.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Yoon, J.; Kang, J.; Kim, M.; Jang, W.S.; Shin, N.Y.; Yoo, Y. Design and Implementation of a New Wireless Carotid Neckband Doppler System with Wearable Ultrasound Sensors: Preliminary Results. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Cheng, H.M.; Bai, C.H.; Yeh, W.T.; Chen, J.R.; Pan, W.H. Blood Pressure, Carotid Flow Pulsatility, and the Risk of Stroke: A Community-Based Study. Stroke 2016, 47, 2262–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ooi, Y.C.; Gonzalez, N.R. Management of extracranial carotid artery disease. Cardiol. Clin. 2015, 33, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Friera, L.; Ibanez, B.; Fuster, V. Imaging subclinical atherosclerosis: Is it ready for prime time? A review. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2014, 7, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.W.; Markus, H.S.; Bots, M.L.; Rosvall, M.; Sitzer, M. Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 2007, 115, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shomaji, S.; Dehghanzadeh, P.; Roman, A.; Forte, D.; Bhunia, S.; Mandal, S. Early Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases Using Wearable Ultrasound Device. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2019, 8, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skagen, K.; Skjelland, M.; Zamani, M.; Russell, D. Unstable carotid artery plaque: New insights and controversies in diagnostics and treatment. Croat. Med. J. 2016, 57, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, L.; Yuan, C.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Balu, N.; Qiao, Y.; DeMarco, J.K.; Saam, T.; Moody, A.R.; Li, D.; Matouk, C.C.; et al. Carotid Artery Wall Imaging: Perspective and Guidelines from the ASNR Vessel Wall Imaging Study Group and Expert Consensus Recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.M.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, P.K.; Rajan, J.; Saba, L.; Nobutaka, I.; Laird, J.R.; Nicolades, A.; Suri, J.S. A Review on Carotid Ultrasound Atherosclerotic Tissue Characterization and Stroke Risk Stratification in Machine Learning Framework. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2015, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, L.; Saam, T.; Jäger, H.R.; Yuan, C.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Saloner, D.; Wasserman, B.A.; Bonati, L.H.; Wintermark, M. Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, A.M.; Nambi, V.; Naqvi, T.Z.; Feinstein, S.B.; Kim, E.S.H.; Park, M.M.; Becher, H.; Sillesen, H. Recommendations for the Assessment of Carotid Arterial Plaque by Ultrasound for the Characterization of Atherosclerosis and Evaluation of Cardiovascular Risk: From the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2020, 33, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cires-Drouet, R.S.; Mozafarian, M.; Ali, A.; Sikdar, S.; Lal, B.K. Imaging of high-risk carotid plaques: Ultrasound. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 30, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, S.; Sorond, F. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound: Technique and application. Semin. Neurol. 2012, 32, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markus, H.S.; King, A.; Shipley, M.; Topakian, R.; Cullinane, M.; Reihill, S.; Bornstein, N.M.; Schaafsma, A. Asymptomatic embolisation for prediction of stroke in the Asymptomatic Carotid Emboli Study (ACES): A prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, A.; Markus, H.S. Doppler Embolic Signals in Cerebrovascular Disease and Prediction of Stroke Risk. Stroke 2009, 40, 3711–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, A.; Shipley, M.; Markus, H. Optimizing Protocols for Risk Prediction in Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis Using Embolic Signal Detection. Stroke 2011, 42, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, M.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.; Breteler, M. Transcranial Doppler hemodynamic parameters and risk of stroke: The Rotterdam study. Stroke 2007, 38, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upadhyay, S.P.; Mallick, P.N.; Elmatite, W. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) Ultrasonography and its Clinical Application-A Review and Update. Dev. Anaesth. Pain Manag. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, J.; Yap, K.H.; Ahmad, G.; Ghosh, J. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound: A review of the physical principles and major applications in critical care. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2013, 2013, 629378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrangelo, S.J. A Wearable Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Phased Array System. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mackinnon Andrew, D.; Aaslid, R.; Markus Hugh, S. Long-Term Ambulatory Monitoring for Cerebral Emboli Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound. Stroke 2004, 35, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.J.; Hussain, I.; Hong, S.; Kim, D.; Park, H.; Benjamin, H.C.M. Real-time Gait Monitoring System for Consumer Stroke Prediction Service. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–6 January 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Hong, S.; Hussain, I.; Kim, D.; Seo, Y.; Park, S.J. Gait Monitoring System for Stroke Prediction of Aging Adults. In Proceedings of the AHFE 2019 International Conference on Human Factors and Wearable Technologies, Washington, DC, USA, 24–28 July 2019; pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Plettemeier, D.; Bärhold, M.; Bauer, T.; et al. Towards Wearable-Inertial-Sensor-Based Gait Posture Evaluation for Subjects with Unbalanced Gaits. Sensors 2020, 20, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahmiri, S. Gait Nonlinear Patterns Related to Parkinson’s Disease and Age. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceira-Elvira, P.; Popa, T.; Schmid, A.-C.; Hummel, F.C. Wearable technology in stroke rehabilitation: Towards improved diagnosis and treatment of upper-limb motor impairment. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, M.; Holstein, F.; Schlosser, R.; Schiller, J. Next Generation Cooperative Wearables: Generalized Activity Assessment Computed Fully Distributed Within a Wireless Body Area Network. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16793–16807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurobit. Available online: https://www.neurobittech.com/product.html (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Subramaniyam, M.; Lee, K.-S.; Park, S.J.; Min, S. Development of Mobile Application Program for Stroke Prediction Using Machine Learning with Voice Onset Time Data. In HCI International 2020—Posters; Stephanidis, C., Antona, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, A.; Memon, Z.A.; Ullah, S.; Hussain, I. Cyber Physical System for Stroke Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 37444–37453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyam, M.; Singh, D.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, D.J.; Im, J.N.; Lee, K.S.; Min, S.N. IoT based wake-up stroke prediction—Recent trends and directions. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering (ICAME), SRM Inst Sci & Technol, Kattankulathur, India, 22–24 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnigan, S.; Wong, A.; Read, S. Defining abnormal slow EEG activity in acute ischaemic stroke: Delta/alpha ratio as an optimal QEEG index. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almajidy, R.K.; Mankodiya, K.; Abtahi, M.; Hofmann, U.G. A Newcomer’s Guide to Functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy Experiments. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quaresima, V.; Ferrari, M. A Mini-Review on Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS): Where Do We Stand, and Where Should We Go? Photonics 2019, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayatilleka, I.; Halgamuge, M.N. Chapter 1—Internet of Things in healthcare: Smart devices, sensors, and systems related to diseases and health conditions. In Real-Time Data Analytics for Large Scale Sensor Data; Das, H., Dey, N., Emilia Balas, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 6, pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, R.; Krishna, S.; Anju, N.; Aslam, M.S.; Deepa, O.S. Iot based patient monitoring and diagnostic prediction tool using ensemble classifier. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Udupi, India, 13–16 September 2017; pp. 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcheick, H.; Nasser, H.; Dbouk, M.; Nasser, A. Stroke Prediction Context-Aware Health Care System. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE First International Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), Washington, DC, USA, 27–29 June 2016; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, B.A.; Navar, A.M.; Pencina, M.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Opportunities and challenges in developing risk prediction models with electronic health records data: A systematic review. J. Am. Med Inform. Assoc. Jamia 2017, 24, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashistha, R.; Yadav, D.; Chhabra, D.; Shukla, P. Chapter 5—Artificial Intelligence Integration for Neurodegenerative Disorders. In Leveraging Biomedical and Healthcare Data; Kobeissy, F., Alawieh, A., Zaraket, F.A., Wang, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, G.; Song, Y.; Im, H.; Park, J. Clinical Implication of Machine Learning in Predicting the Occurrence of Cardiovascular Disease Using Big Data (Nationwide Cohort Data in Korea). IEEE Access 2020, 8, 157643–157653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Lan, T.H.; Peng, G.S.; Lee, C.C. Development of an intelligent decision support system for ischemic stroke risk assessment in a population-based electronic health record database. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Dudley, J.T. Deep learning for healthcare: Review, opportunities and challenges. Brief Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Ye, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, B. Chronic Diseases and Health Monitoring Big Data: A Survey. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 11, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, G.; Blumen, H.M.; Devanne, H.; Pirondini, E.; Delval, A.; Van De Ville, D. Brain imaging of locomotion in neurological conditions. Neurophysiol. Clin. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 48, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraf, S.; Sun, J. Advances in Functional Brain Imaging: A Comprehensive Survey for Engineers and Physical Scientists. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 640–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassab, A.; Le Lan, J.; Tremblay, J.; Vannasing, P.; Dehbozorgi, M.; Pouliot, P.; Gallagher, A.; Lesage, F.; Sawan, M.; Nguyen, D.K. Multichannel wearable fNIRS-EEG system for long-term clinical monitoring. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Assessment of mental stress effects on prefrontal cortical activities using canonical correlation analysis: An fNIRS-EEG study. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, L.; El-Merhi, A.; Liljencrantz, J.; Naredi, S.; Staron, M.; Odenstedt Hergès, H. Cerebral ischemia detection using artificial intelligence (CIDAI)—A study protocol. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2020, 64, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-T. Multimodal neurocritical monitoring. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, G.; Zanoletti, M.; Re, R.; Germinario, B.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Roveri, L. Time-domain near-infrared spectroscopy in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Bai, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Sui, H. Quantitative electroencephalograph in acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Hametner, C.; Stanarcevic, P.; Stampfl, S.; Rohde, S.; Veltkamp, R.; Bösel, J. Noninvasive Cerebral Oximetry during Endovascular Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Observational Study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burghaus, L.; Hilker, R.; Dohmen, C.; Bosche, B.; Winhuisen, L.; Galldiks, N.; Szelies, B.; Heiss, W.-D. Early electroencephalography in acute ischemic stroke: Prediction of a malignant course? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2007, 109, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigo, F.; Schneider, M.; Wagenpfeil, G.; Unger, M.M.; Holzhoffer, C.; Walter, S.; Faßbender, K.; Lochner, P. Early poststroke seizures following thrombolysis and/or thrombectomy for acute stroke: Clinical and stroke characteristics. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 104, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.; Horst, F.; Müller, S.; Steinberg, F.; Doppelmayr, M. Current State and Future Prospects of EEG and fNIRS in Robot-Assisted Gait Rehabilitation: A Brief Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaciong, Z.; Siński, M.; Lewandowski, J. Blood pressure control and primary prevention of stroke: Summary of the recent clinical trial data and meta-analyses. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-H.; Ovbiagele, B.; Hong, K.-S.; Kwon, S.U. Association of Systolic Blood Pressure with Progression of Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.-J.; Wong, K.-S.; Chen, X.-Y. Intracranial Atherosclerosis: From Microscopy to High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinti, P.; Tachtsidis, I.; Hamilton, A.; Hirsch, J.; Aichelburg, C.; Gilbert, S.; Burgess, P.W. The present and future use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) for cognitive neuroscience. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1464, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, F.; Tachtsidis, I. Clinical Brain Monitoring with Time Domain NIRS: A Review and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, T.; Nambu, I.; Takeda, K.; Aihara, T.; Yamashita, O.; Isogaya, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Otaka, Y.; Wada, Y.; Kawato, M.; et al. Reduction of global interference of scalp-hemodynamics in functional near-infrared spectroscopy using short distance probes. NeuroImage 2016, 141, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Feng, W.; Wang, P. A Systemic Review of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Stroke: Current Application and Future Directions. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durduran, T.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse correlation spectroscopy for non-invasive, micro-vascular cerebral blood flow measurement. NeuroImage 2014, 85, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- fNIRS EEG Package. Available online: https://www.artinis.com/nirs-eeg-package (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Kassab, A.; Sawan, M. The NIRS Cap: Key Part of Emerging Wearable Brain-Device Interfaces, Developments in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. In Developments in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy; Kyprianidis, K.G., Skvaril, J., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau-Zhu, A.; Lau, M.P.H.; McLoughlin, G. Mobile EEG in research on neurodevelopmental disorders: Opportunities and challenges. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 36, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torun, S.; Özdemir, G. Very Early Morning Increase in Onset of Ischemic Stroke. Ann. Saudi Med. 1994, 14, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Risk Factors |
|---|
| Sex |
| Age |
| Geographic region (northern/southern China, divided by the Yangtze River) |
| Waist circumference |
| Total cholesterol |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| Blood pressure |
| Antihypertensive medications within the past two weeks |
| Diabetes Mellitus |
| Current smoker |
| Parental history of stroke |
| Risk Factors | Percentage of Stroke-Related Risk Factor | Detection/Characterization Method |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle behaviors (combining many factors) | 75% | Questionnaires |
| Hypertension | 50% | Wearables to measure vascular related parameters |
| Air pollution | 30% | APP on smart phone |
| Atrial fibrillation and abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) | 20% | Wearables to measure ECG |
| Carotid plaque | 15% | Carotid ultrasound |
| Intracranial Atherosclerosis | 10% | Transcranial Doppler (TCD) |
| Question-Naires via Mobile APP | Mobile Phone, Air Pollution Sensor | ECG | PPG | Carotid Ultra-Sound Neckband | TCD Headband | Accelerometer + Pressure Sensors | Goggle | EMG | EEG | fNIRS | CT | MRI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compact, light weighted | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Low-cost of the equipment/per test | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Accessibility | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Self-service (No assistant needed) | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++ | + | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Frequency of test (++++: anytime, +: only when needed) | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | + | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | + | + |
| Short preparation and response time | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | + | + |
| Data continuity | + | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | + | + |
| High time resolution | NA | ++++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | + | + |
| High spatial resolution | NA | NA | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ |
| Broad field of view | NA | NA | ++ | + | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| Often used in which stage of stroke course | Prediction | Prediction | Predic-tion | Predic-tion | Prediction | Prediction | Prediction, rehabilitation | Detec-tion | Detec-tion, rehabili-tation | Rehabilitation | Rehabilitation | Detec-tion | Detec-tion |
| Limitations of EEG, fNIRS or a Multimodal EEG-fNIRS System for Stroke Risk Prediction | Possible Solutions to Overcome the Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
| EEG | Spatial resolution of 5–9 cm [120] | fNIRS with spatial resolution of 2–3 cm can be combined with EEG to increase the spatial resolution [120]. |
| fNIRS | Poor sensitivity to the deep brain cortex, where 20% of stroke, named lacunar stroke, occurs [111] | Introduce high-density diffuse optical tomo/topography (DOT) [121] |
| Signals are affected by the scalp-related hemoglobin oscillation or contamination from extra-cerebral layers |
| |
| ||
| Absolute values of [HbOxy], [HBDeoxy], [HbT = HbOxy + HbDeoxy] (∝ cerebral blood volume), StO2 (hemoglobin oxygen saturation) are not available, only the variation is available, so the threshold values for stroke onsets cannot be determined | Use TD-NIRS and FD-NIRS to characterize the absolute values of hemoglobin species [111,121]. | |
| CBF cannot be perfectly measured | Diffuse correlation spectroscopy (DCS) can continuously monitor CBF index [124]. | |
| EEG-fNIRS |
| Sophisticated hardware developments and integration of fNIRS optodes and EEG electrodes are needed [125]. |
| ||
| The cap/headset may cause discomfort for long-term use | A wireless EEG-fNIRS system and a proper design, even customization, of the fixation devices are needed [126,127]. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-H.; Sawan, M. Trends and Challenges of Wearable Multimodal Technologies for Stroke Risk Prediction. Sensors 2021, 21, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020460
Chen Y-H, Sawan M. Trends and Challenges of Wearable Multimodal Technologies for Stroke Risk Prediction. Sensors. 2021; 21(2):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020460
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yun-Hsuan, and Mohamad Sawan. 2021. "Trends and Challenges of Wearable Multimodal Technologies for Stroke Risk Prediction" Sensors 21, no. 2: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020460
APA StyleChen, Y.-H., & Sawan, M. (2021). Trends and Challenges of Wearable Multimodal Technologies for Stroke Risk Prediction. Sensors, 21(2), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020460






