Smart Textiles for Improved Quality of Life and Cognitive Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment
1.2. Personalized Textiles for Quality of Life
1.3. Gamification of Cognitive Tests in Textiles
2. Background Study
2.1. Assistive Technology
2.2. Wearable Technology
2.3. Smart Textiles
2.3.1. Sensors and Electronics Integrated into the Textile—“Sensorized Garments”
2.3.2. Plugging Components into a Conductive Grid—The “Wearable Motherboard”
2.4. Smart Textiles for Quality of Life
2.5. Smart Textiles for Cognitive Assessment
Gamification of Cognitive Tests
2.6. Desirable Properties and Performance Requirements
3. Design and Methodology
3.1. Design Considerations
3.2. Knowledge Elicitation
3.3. Design
3.4. Digital Inputs (Switches)
3.5. Data Logging and Communication
- (a)
- From the MP3 player—data collected are (i) timestamp, (ii) track name, (iii) track length, and (iv) play time.
- (b)
- (c)
- Cat and the tree—data collected are timestamp corresponding to the detection on the capacitive sliding sensors (items 1 and 2 in Figure 3b), including frequency.
3.6. Energy Consumption
- LEDs, 20 × 20 mA = 0.4 A
- Neo-pixels RGB, 10 × 60 mA = 0.6 A
- Raspberry Pi 4, 3 A
- LEDs, 20 × 5 mA = 0.1 A
- Neo-pixels RGB, 10 × 60 mA = 0.6 A
- Arduino Nano 33 IoT board, 0.2 A
- Scenario 1—The prototype is used for gaming with LEDs illuminated, stroking the cat, and playing the MP3 player through the Bluetooth speaker. The current consumed would be 300 mA maximum. This would give an estimated operational battery life of 14 h.
- Scenario 2—Just playing the MP3 player through the Bluetooth speaker. The current consumed would be 200 mA. This would give an estimated operational battery life of 22 h.
- Scenario 3—The system is in standby mode. The current consumed would be 10 mA. This would give an estimated operational battery life of 440 h.
3.7. Laundering in Care Home Setting
4. Results and Discussion
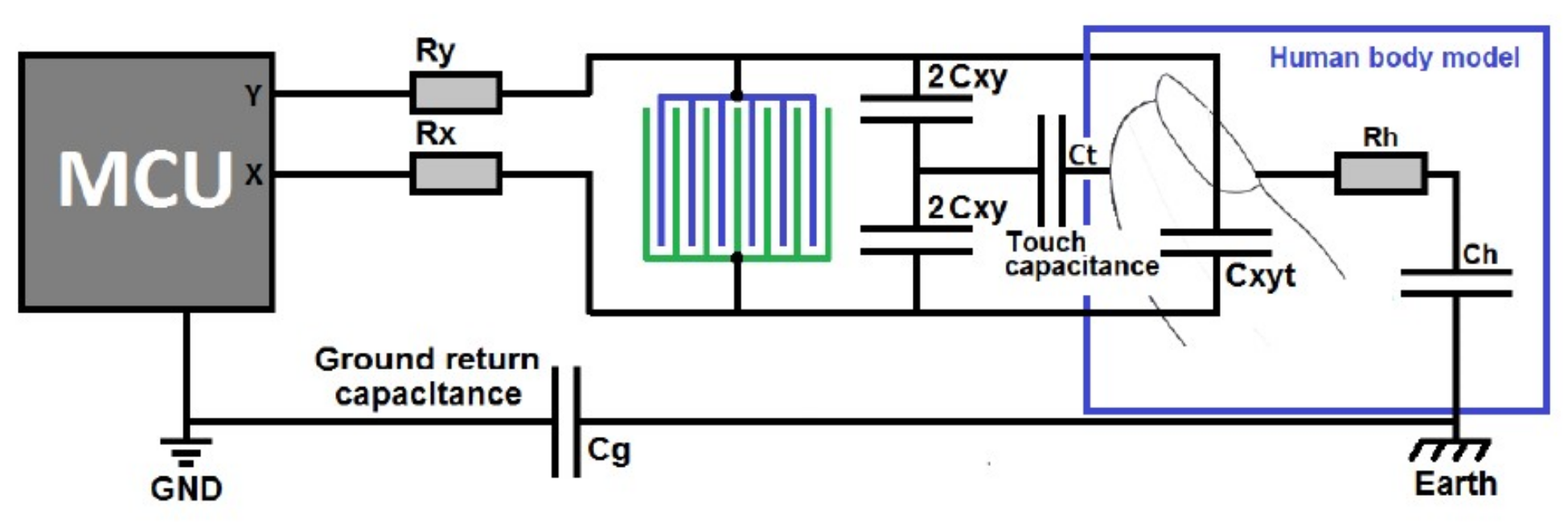
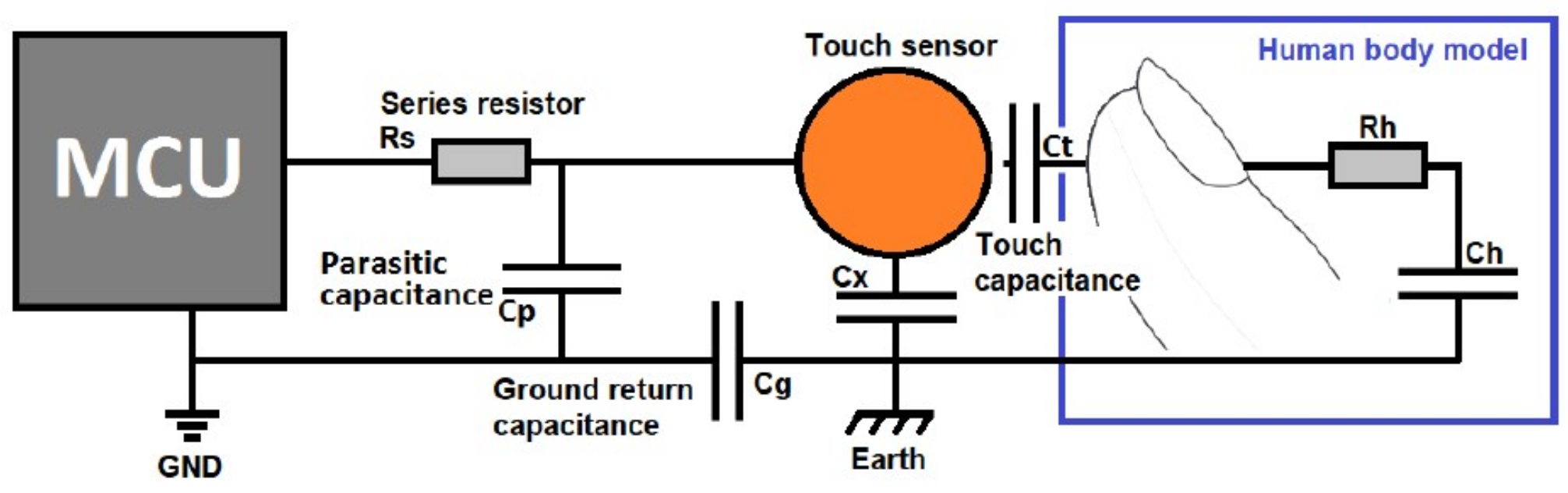
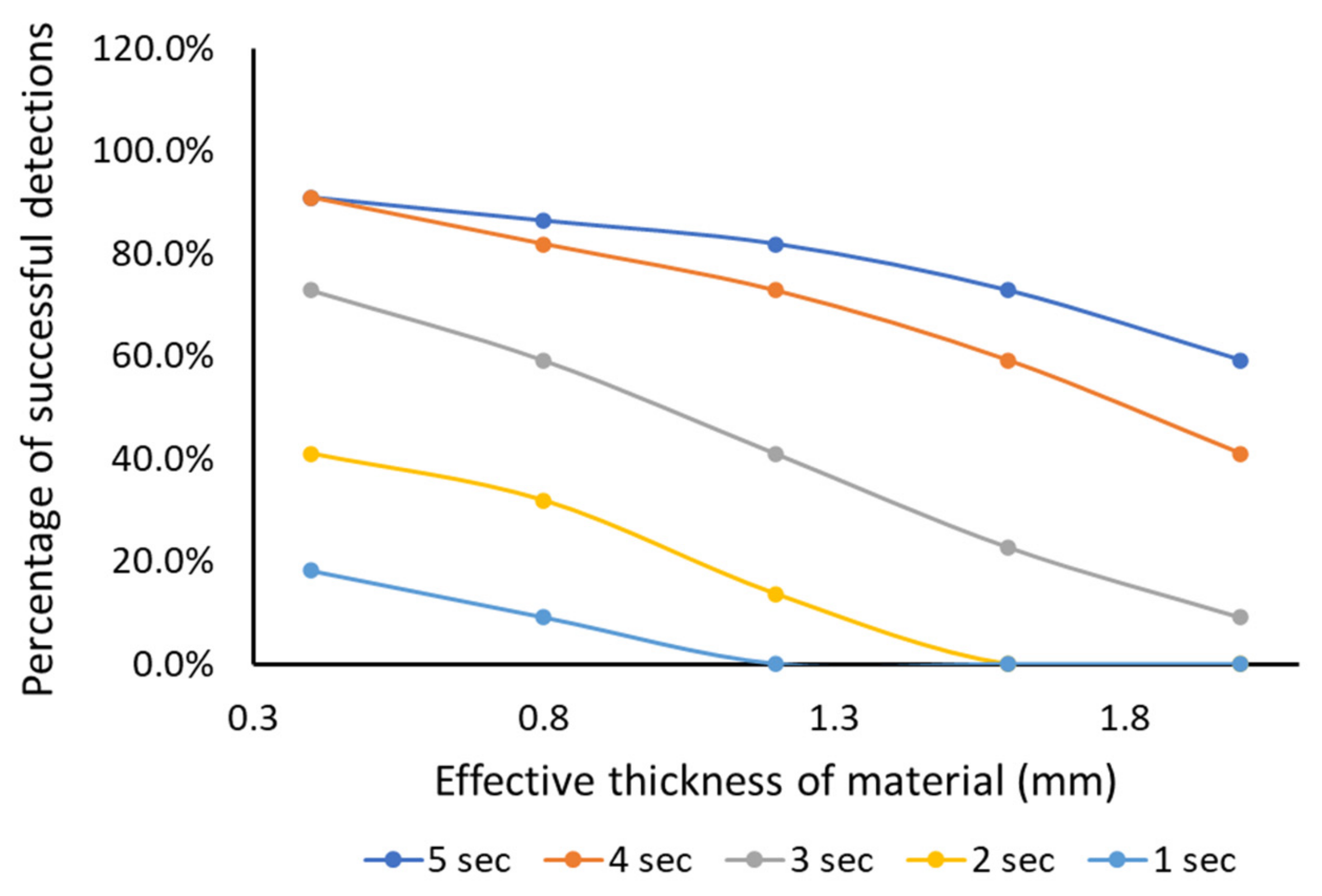
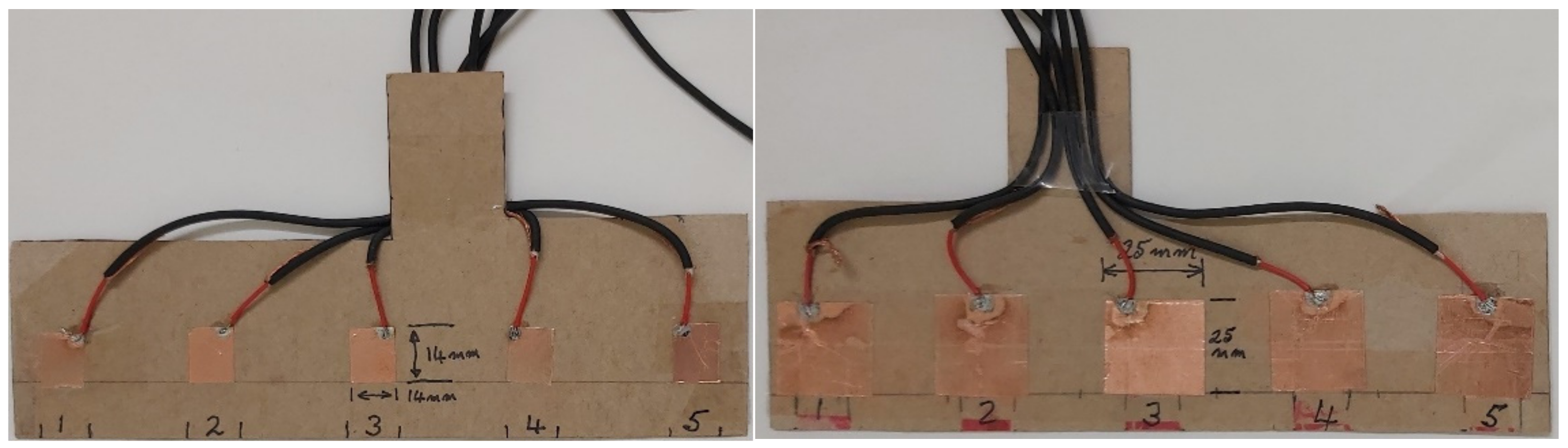
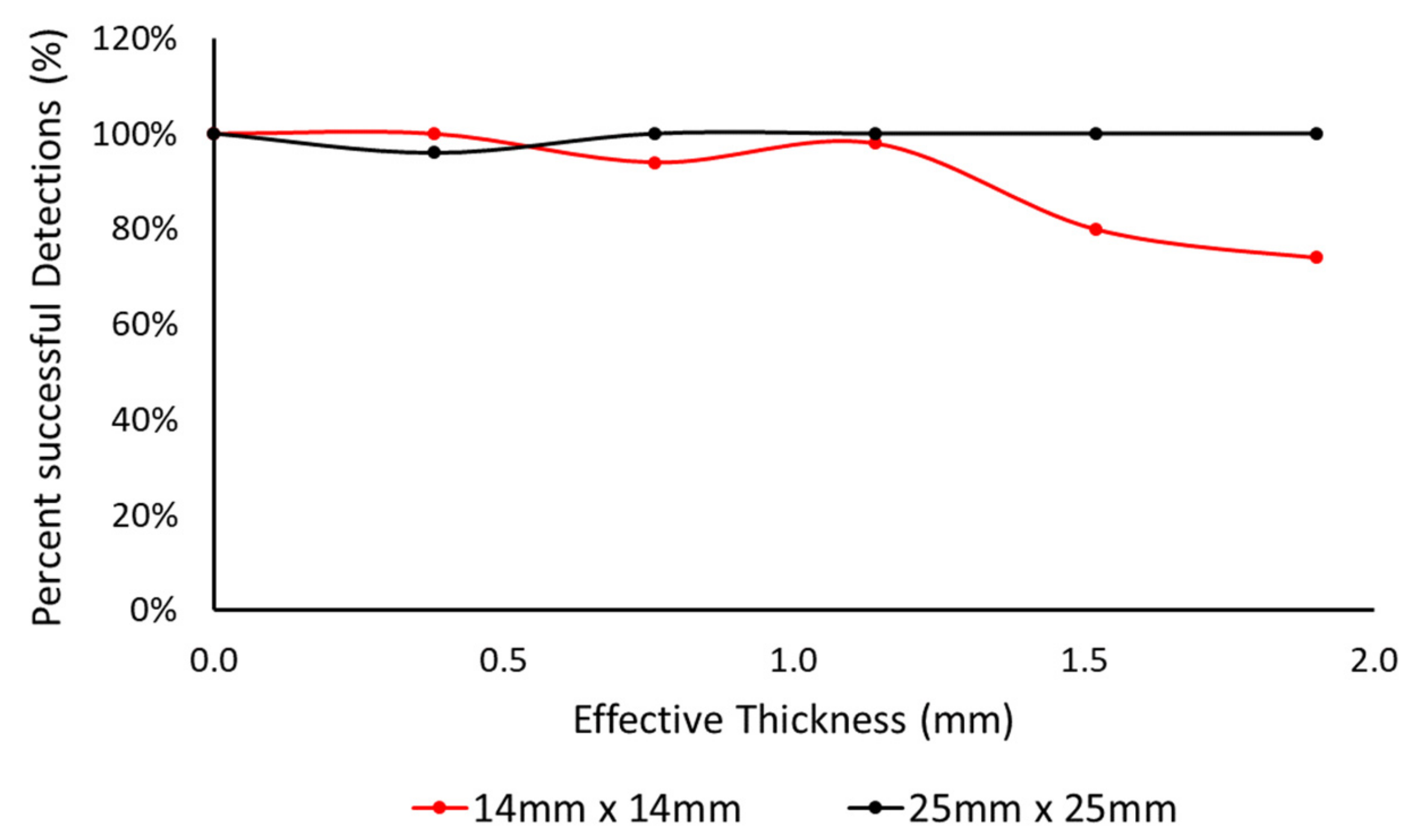
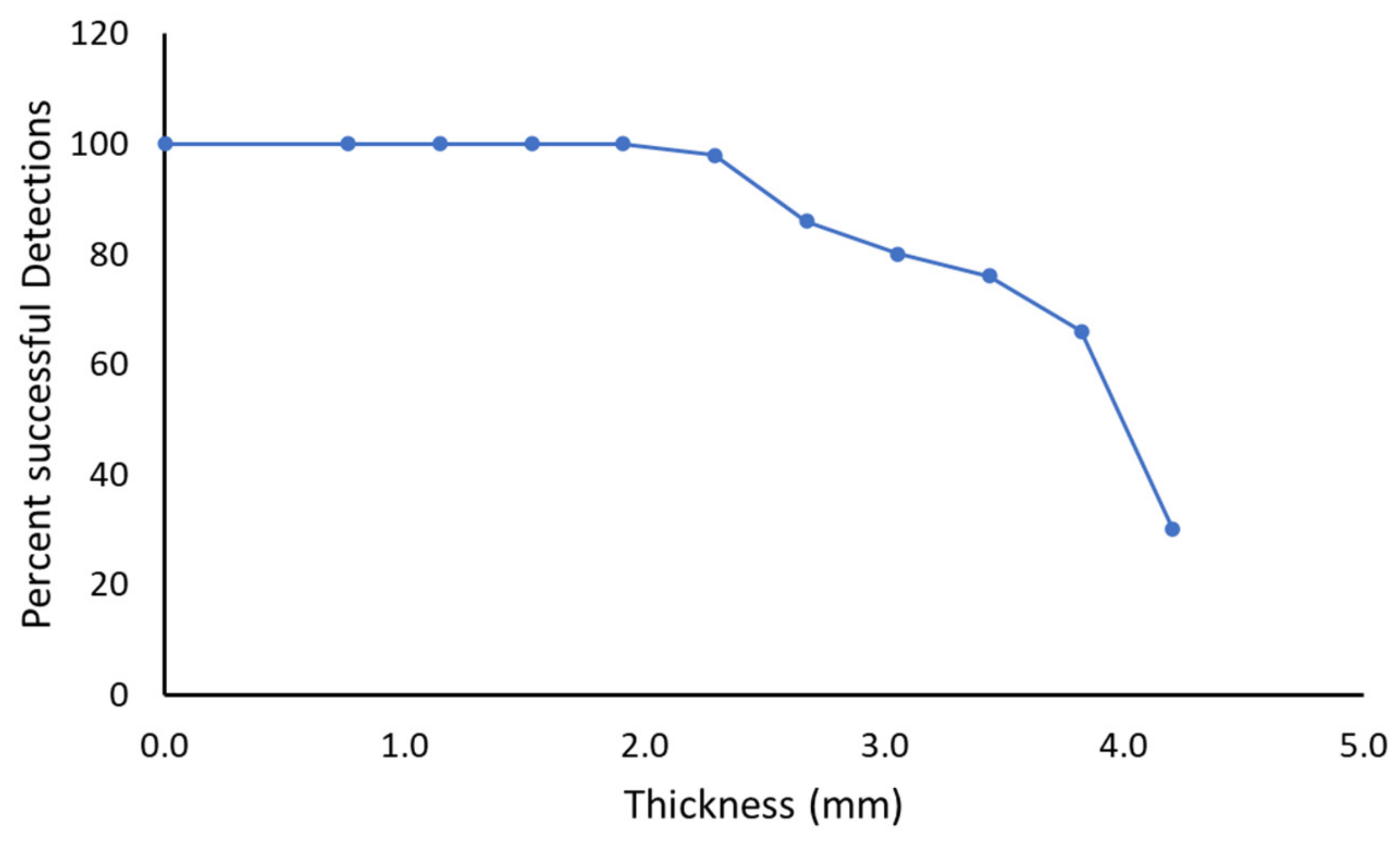
4.1. Capacitive Slider Switch Sensor Performance
4.2. Detection Performance of Capacitive Touch Sensors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Chertkow, H.; Massoud, F.; Nasreddine, Z.; Belleville, S.; Joanette, Y.; Bocti, C.; Drolet, V.; Kirk, J.; Freedman, M.; Bergman, H. Diagnosis and treatment of dementia: 3. Mild cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment without dementia. CMAJ 2008, 178, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nasreddine, Z.; Phillips, N.; BÃodirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Dementia: A Public Health Priority. World Health Organ. 2020. Available online: https//www.who.int/mental_health/publications/dementia_report_2012/en/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Jiancaro, T. Exploring Technology, Design and Dementia: Design Approaches, Considerations and Implications for an Emerging Field; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mancioppi, G.; Fiorini, L.; Sportiello, M.T.; Cavallo, F. Novel Technological Solutions for Assessment, Treatment, and Assistance in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Neuroinform. 2019, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prince, M.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.; Wu, Y.; Prina, M. World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. Alzheimer’s Dis. Int. London Alzheimer’s Dis. Int. 2015. Available online: https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/world-alzheimer-report-2015--the-global-impact-of-dementia(ae525fda-1938-4892-8daa-a2222a672254).html (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Bharucha, A.J.; Anand, V.; Forlizzi, J.; Dew, M.A.; Reynolds, C.F.; Stevens, S.; Wactlar, H. Intelligent assistive technology applications to dementia care: Current capabilities, limitations, and future challenges. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2009, 17, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, M.E. Intelligent technology for an aging population: The use of AI to assist elders with cognitive impairment. AI Mag. 2005, 26, 9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Isaia, B.; Brown, L.J.E.; Beeby, S. E-textiles for healthy ageing. Sensors 2019, 19, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posch, I.; Stark, L.; Fitzpatrick, G. Etextiles: Reviewing a practice through its tool/kits. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Wearable Computers, London, UK, 9–13 September 2019; pp. 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treadaway, C.; Kenning, G. Sensor e-Textiles: Person centred co-design for people with late stage dementia. Work. Older People 2016, 20, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, A.; Van Langenhove, L.; Guermonprez, P.; Deguillemont, D. A roadmap on smart textiles. Text. Prog. 2010, 42, 99–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, A.; Cavicchioli, M.; Strati, S.; Aliverti, A.; Cintorrino, I.A.; Lauricella, G.; Rossi, C. Smart Textiles and Sensorized Garments for Physiological Monitoring: A Review of Available Solutions and Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K. Smart textiles: Transforming the practice of medicalisation and health care. Sociol. Health Illn. 2019, 41, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, A.; Collier, L. Sensory Design for Dementia Care—The Benefits of Textiles. J. Text. Des. Res. Pract. 2017, 5, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Hoey, J.; Nugent, C.D.; Cook, D.J.; Yu, Z.; Member, S. Sensor-Based Activity Recognition. IEEE Trans. Syst. MAN Cybern. C Appl. Rev. 2012, 42, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Shu, L.; Yang, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Smart Textile-Integrated Microelectronic Systems for Wearable Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, A.; Atalay, O.; Husain, M.D.; Fernando, A.; Potluri, P. Piezofilm yarn sensor-integrated knitted fabric for healthcare applications. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 47, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stavropoulos, T.G.; Meditskos, G.; Kompatsiaris, I. DemaWare2: Integrating sensors, multimedia and semantic analysis for the ambient care of dementia. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2017, 34, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekel, K.; Damian, M.; Wattmo, C.; Hausner, L.; Bullock, R.; Connelly, P.J.; Dubois, B.; Eriksdotter, M.; Ewers, M.; Graessel, E.; et al. Mild cognitive impairment and deficits in instrumental activities of daily living: A systematic review. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mileski, M.; Topinka, J.B.; Brooks, M.; Lonidier, C.; Linker, K.; Veen, K. Vander Sensory and memory stimulation as a means to care for individuals with dementia in long-term care facilities. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein-Levitas, N. Dance/Movement Therapy and Sensory Stimulation: A Holistic Approach to Dementia Care. Am. J. Danc. Ther. 2016, 38, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusar-poli, L.; Bieleninik, Ł.; Brondino, N.; Chen, X.; Gold, C.; Bieleninik, Ł.; Brondino, N.; Chen, X.; Fusar-poli, L. The effect of music therapy on cognitive functions in patients with dementia: A systematic review and systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Ment. Health 2018, 22, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcdermott, O.; Orrell, M.; Mette, H. The importance of music for people with dementia: The perspectives of people with dementia, family carers, staff and music therapists. Aging Ment. Health 2014, 18, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnakers, C.; Magee, W.L.; Harris, B. Sensory stimulation and music therapy programs for treating disorders of consciousness. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mann, G.; Oatley, G. Positive Design of Smart Interactive Fabric Artifacts for People with Dementia. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 5th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Perth, WA, Australia, 2–4 April 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, C.B.; Borson, S.; Boustani, M.; Chodosh, J.; Reuben, D.; Verghese, J.; Thies, W.; Fried, L.B. Alzheimer’s Association recommendations for operationalizing the detection of cognitive impairment during the Medicare Annual Wellness Visit in a primary care setting. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Poon, C.C.Y.; Bonato, P.; Member, S. Wearable Medical Systems for p-Health. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 1, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axisa, F.; Schmitt, P.M.; Gehin, C.; Delhomme, G.; McAdams, E.; Dittmar, A. Flexible technologies and smart clothing for citizen medicine, home healthcare, and disease prevention. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, F.; De Paolis, L.T. A Comprehensive Review of Serious Games in Health Professions. Int. J. Comput. Games Technol. 2014, 2014, 787968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelardeux, C.; Alvarez, J.; Montaut, T.; Galaup, M.; Lagarrigue, P. Healthcare Games and the Metaphoric Approach. In Serious Games for Healthcare: Applications and Implications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 24–49. [Google Scholar]
- Briceño, E.M.; Mehdipanah, R.; Gonzales, X.F.; Langa, K.M.; Levine, D.A.; Garcia, N.M.; Longoria, R.; Giordani, B.J.; Heeringa, S.G.; Morgenstern, L.B. Neuropsychological assessment of mild cognitive impairment in Latinx adults: A scoping review. Neuropsychology 2020, 34, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teubner-Rhodes, S.; Vaden, K.I.; Dubno, J.R.; Eckert, M.A. Cognitive persistence: Development and validation of a novel measure from the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Neuropsychologia 2017, 102, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastermind (Board Game). Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mastermind_(board_game) (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Caprani, N.; Greaney, J.; Porter, N. A Review of Memory Aid Devices for an Ageing Population. PsychNology J. 2006, 4, 205–243. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.D. Gamification and the Psychology of Game Design in Transforming Mental Health Care. J. Am. Psychiatr. Nurses Assoc. 2016, 22, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.; Wagner, S.R.; Pedersen, C.F.; Aysha Beevi, F.H.; Hansen, F.O. Ambient Assisted Living healthcare frameworks, platforms, standards, and quality attributes. Sensors 2014, 14, 4312–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Brief History of Wearable Computing. Available online: https://www.media.mit.edu/wearables/lizzy/timeline.html#1994c (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Mullen, T.R.; Kothe, C.A.E.; Chi, Y.M.; Ojeda, A.; Kerth, T.; Makeig, S.; Jung, T.; Cauwenberghs, G. Real-Time Neuroimaging and Cognitive Monitoring Using Wearable Dry EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Chan, C. A ZigBee-Based Location-Aware Fall Detection System for Improving Elderly Telecare. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4233–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Wearable and Implantable Wireless Sensor Network Solutions for Healthcare Monitoring. Sensors 2011, 11, 5561–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setz, C.; Arnrich, B.; Schumm, J.; Marca, R.L.; Troster, G.; Ehlert, U. Using a Wearable EDA Device. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, T.M.; Holmes, N.; Meyer, S.; Boto, E.; Roberts, G.; Litvak, V.; Bestmann, S.; Leggett, J.; Buck, S.; Duque-mu, L.; et al. NeuroImage Cognitive neuroscience using wearable magnetometer arrays: Non-invasive assessment of language function. Neuroimage 2018, 181, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, C.S.; Wah, T.Y.; Shuja, J.; Daghighi, B. Mining personal data using smartphones and wearable devices: A survey. Sensors 2015, 15, 4430–4469. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, K.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Richter, W.; Pillai, P.; Satyanarayanan, M. Towards Wearable Cognitive Assistance. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Bretton Woods, NH, USA; 2014; pp. 68–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Kwak, D.; Ha, J.; Kim, J. Dual-memory neural networks for modeling cognitive activities of humans via wearable sensors. Neural Netw. 2017, 92, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Hu, W.; Ha, K.; Amos, B.; Pillai, P.; Hauptmann, A.; Satyanarayanan, M. Early Implementation Experience with Wearable Cognitive Assistance Applications. In Proceedings of the MobiSys’15: The 13th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Florence, Italy, 18 May 2015; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguin Muñoz, M.; Klatzky, R.; Wang, J.; Pillai, P.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Gross, J. Impact of delayed response on wearable cognitive assistance. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jayaraman, S. Smart Textiles: Wearable Electronic Systems. MRS Bull. 2003, 28, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipton, R.B.; Katz, M.J.; Kuslansky, G.; Sliwinski, M.J.; Stewart, W.F.; Verghese, J.; Crystal, H.A.; Buschke, H. Screening for dementia by telephone using the memory impairment screen. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevay, S.; Lim, C.S.; Gowans, G. Textile Connections E-textiles to enhance connectedness for older adults experiencing loneliness. Des. J. 2017, 20, S4065–S4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, H.A.; Van Kampen, S.; Takwoingi, Y.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Pearson, M.; Hyde, C.J. The comparative diagnostic accuracy of the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) and the General Practitioner assessment of Cognition (GPCOG) for identifying dementia in primary care: A systematic review protocol. Diagn. Progn. Res. 2017, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.Y.; Ellis, K.A.; Harrington, K.; Ames, D.; Ralph, N.; Masters, C.L.; Rowe, C.; Savage, G.; Darby, D.; Maruff, P.; et al. Use of the CogState Brief Battery in the assessment of Alzheimer ’ s disease related cognitive impairment in the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) study. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2012, 34, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jayaraman, S. Smart textile-based wearable biomedical systems: A transition plan for research to reality. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 14, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S. A Note on Smart Textiles. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2014, 13, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Marculescu, D.; Marculescu, R.; Zamora, N.H.; Stanley-marbell, P.; Khosla, P.K.; Park, S.; Jayaraman, S.; Jung, S.; Lauterbach, C.; Weber, W.; et al. Electronic Textiles: A Platform for Pervasive Computing. Proc. IEEE 2003, 91, 1995–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Jayaraman, S. Enhancing the Quality of Life through Wearable Technology. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalsamy, C.; Park, S.; Rajamanickam, R.; Jayaraman, S. The Wearable Motherboard: The First Generation Responsive Textile Structures Medical Applications. Virtual Real. 1999, 4, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirály, E.; Szabó, Á.; Szita, B.; Kovács, V.; Fodor, Z.; Marosi, C.; Salacz, P.; Hidasi, Z.; Maros, V.; Hanák, P. Monitoring the early signs of cognitive decline in elderly by computer games: An MRI study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lectum®—The World’s First Flexible, Glass-Free EPDs. Available online: https://www.plasticlogic.com/displays/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Lumsden, J.; Edwards, E.A.; Lawrence, N.S.; Coyle, D.; Munafò, M.R. Gamification of Cognitive Assessment and Cognitive Training: A Systematic Review of Applications and Efficacy. JMIR Serious Games 2016, 4, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Lukowicz, P.; Henze, N.; Schmidt, A.; Amft, O.; Salvatore, G.A.; Tröster, G. Smart textiles: From niche to mainstream. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2013, 12, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, B.; Connor, M.O.; Shaw, J.; Breen, L. A Narrative Review of Dignity Therapy Research. Aust. Psychol. 2017, 52, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, S. Gamification: Making work fun, or making fun of work? Bus. Inf. Rev. 2014, 31, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beber, B.C.; Kochhann, R.; Matias, B.; Chaves, M.L.F. The Clock Drawing Test: Performance differences between the free-drawn and incomplete-copy versions in patients with MCI and dementia. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2016, 10, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhus, E.; Barceló, F. Brain and Cognition the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test and the cognitive assessment of prefrontal executive functions: A critical update. Brain Cogn. 2009, 71, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winderickx, J.; Bellier, P.; Duflot, P.; Mentens, N. Communication and Security Trade-Offs for Battery-Powered Devices: A Case Study on Wearable Medical Sensor Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 67466–67476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savulich, G.; Piercy, T.; Fox, C.; Rowe, J.B.; Brien, J.T.O.; Barbara, J. Cognitive Training Using a Novel Memory Game on an iPad in Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (aMCI). J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LilyPad MP3 (Sparkfun). Available online: https://www.sparkfun.com/products/11013 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Johnston, B.; Lawton, S.; Mccaw, C.; Murray, J.; Pringle, J.; Munro, G.; Rodriguez, C. Living well with dementia: Enhancing dignity and quality of life, using a novel intervention, Dignity Therapy. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2016, 11, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuksanovic, D.; Green, H.J.; Dyck, M.; Morrissey, S.A. Dignity Therapy and Life Review for Palliative Care Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2017, 53, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentley, B.; Connor, M.O.; Williams, A.; Breen, L.J. Dignity therapy online: Piloting an online psychosocial intervention for people with terminal illness. Digit. Health 2020, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chochinov, H.M.; Hack, T.; Hassard, T.; Kristjanson, L.J.; Mcclement, S. Dignity Therapy: A Novel Psychotherapeutic Intervention for Patients Near the End of Life. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, J.-W.; Park, S.-J. Serious Game of Increase Cognitive Function for Elderly Using Arduino. J. Korean Inst. Inf. Technol. 2015, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, F.; Microchip Technology Inc. Capacitive Touch Sensor Design Guide. Microchip AN2934. 2020, pp. 1–39. Available online: http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/AN2934-Capacitive-Touch-Sensor-Design-Guide-00002934A.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Ge, C.; Yin, C.; Liu, Z.; Fang, L.; Zhu, J.; Ling, H. A privacy preserve big data analysis system for wearable wireless sensor network. Comput. Secur. 2020, 96, 101887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatley, G.C. Themes in data mining, big data, and crime analytics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2021, e1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





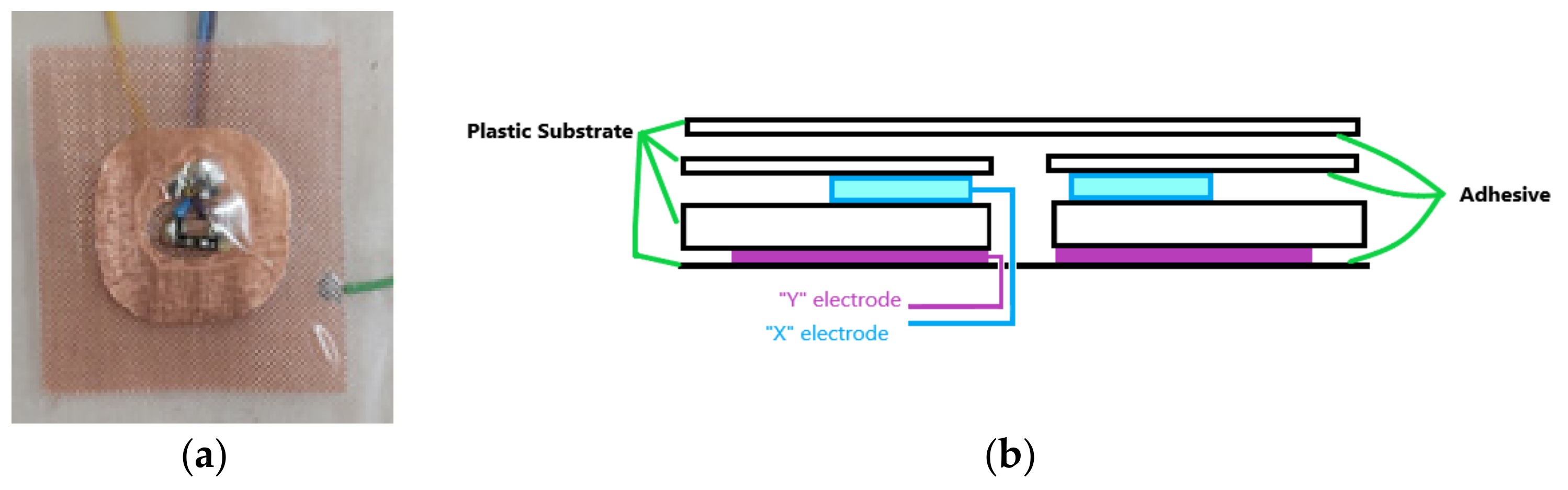
| Location Number in Figure 3b | Description | Location Number in Figure 3b | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 2 | Capacitive sliding sensors | 11 | Arduino Nano 33 IoT |
| 3 | Dual detector for the capacitive sliding sensors | 12 | SD card for primary data logging |
| 4 | Capacitive touch sensors for switching the MP3 player | 13 | MP3 player |
| 5 | Detector for the capacitive touch sensors for switching the MP3 player | 14 | 3.5 mm stereo jack for headphones |
| 6 | 8-channel multiplexer | 15 | Battery pack |
| 7, 8, 9, 10 | LED array with capacitive touch sensors for switching the gaming. It also includes the detectors for the sensors |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oatley, G.; Choudhury, T.; Buckman, P. Smart Textiles for Improved Quality of Life and Cognitive Assessment. Sensors 2021, 21, 8008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238008
Oatley G, Choudhury T, Buckman P. Smart Textiles for Improved Quality of Life and Cognitive Assessment. Sensors. 2021; 21(23):8008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238008
Chicago/Turabian StyleOatley, Giles, Tanveer Choudhury, and Paul Buckman. 2021. "Smart Textiles for Improved Quality of Life and Cognitive Assessment" Sensors 21, no. 23: 8008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238008
APA StyleOatley, G., Choudhury, T., & Buckman, P. (2021). Smart Textiles for Improved Quality of Life and Cognitive Assessment. Sensors, 21(23), 8008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238008








