Enhancing SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Two-Step Task-Related Component Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Algorithms
2.1. Benchmark SSVEP EEG Dataset and Preprocessing
2.2. Conventional SSVEP Frequency Recognition Methods
2.2.1. Standard Canonical Correlation Analysis
2.2.2. Extended Canonical Correlation Analysis
2.2.3. Standard Task-Related Component Analysis
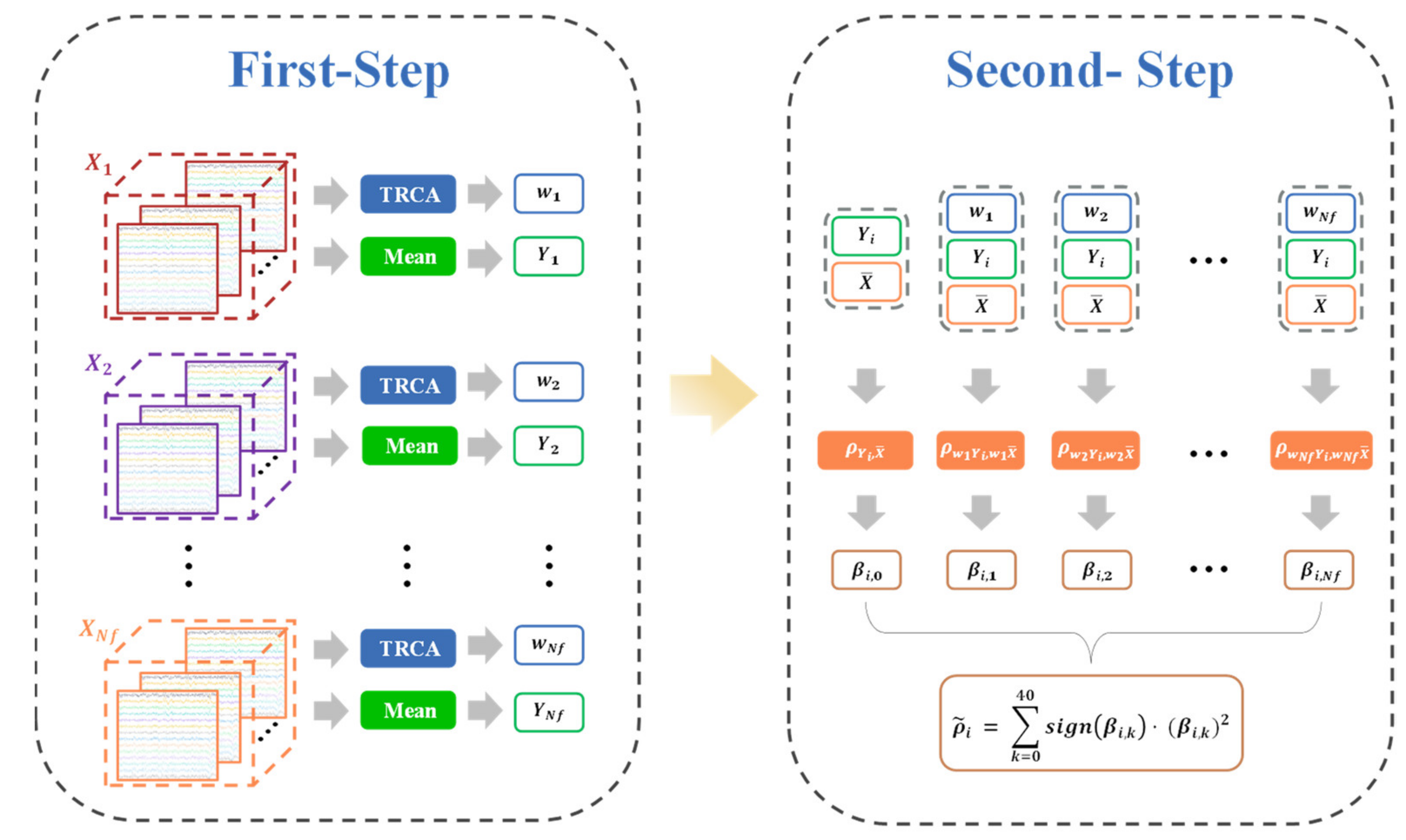
2.3. The Proposed Two-Step TRCA
2.4. Frequency Recognition Based on Filter Bank Approach
3. Results
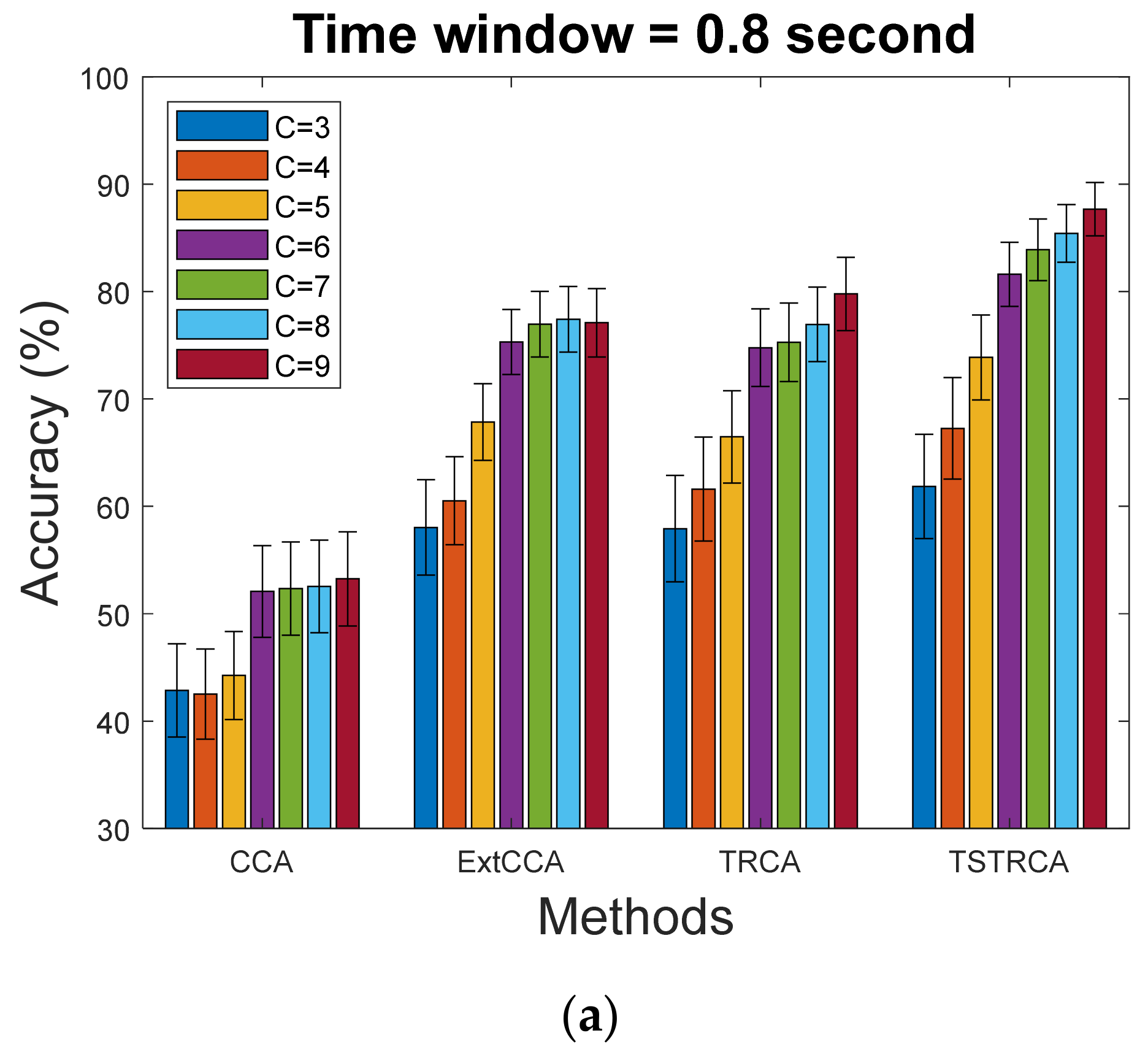
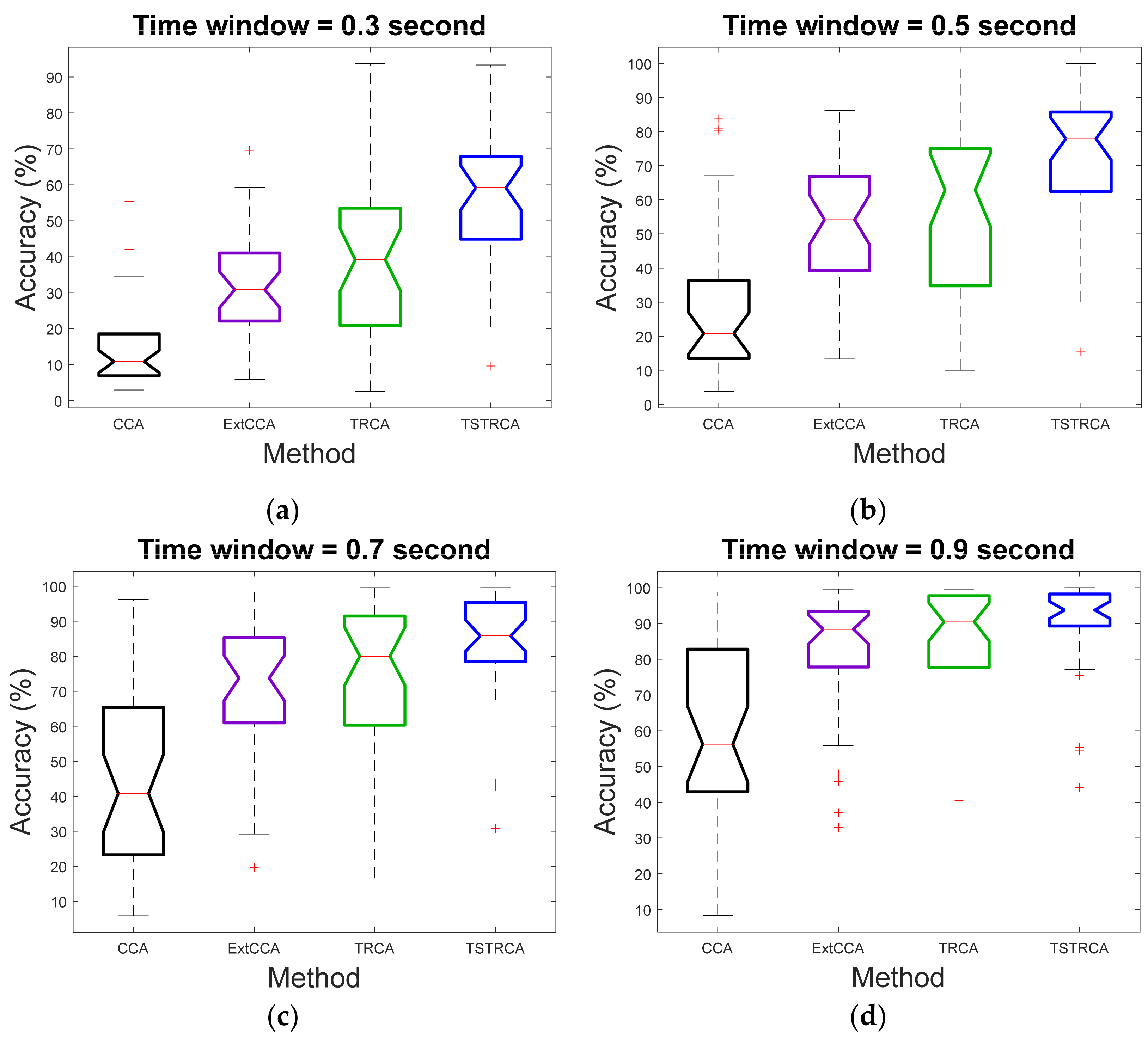
3.1. Performance Evaluation
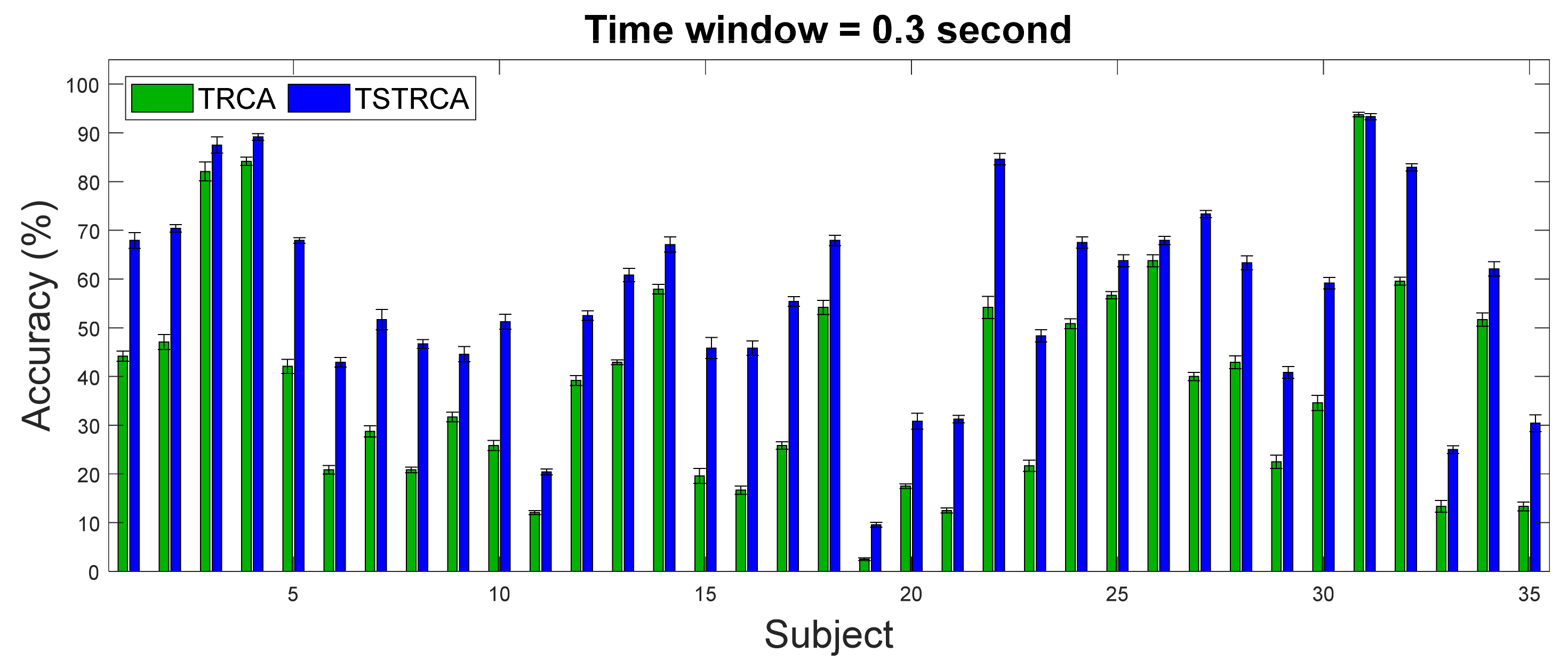
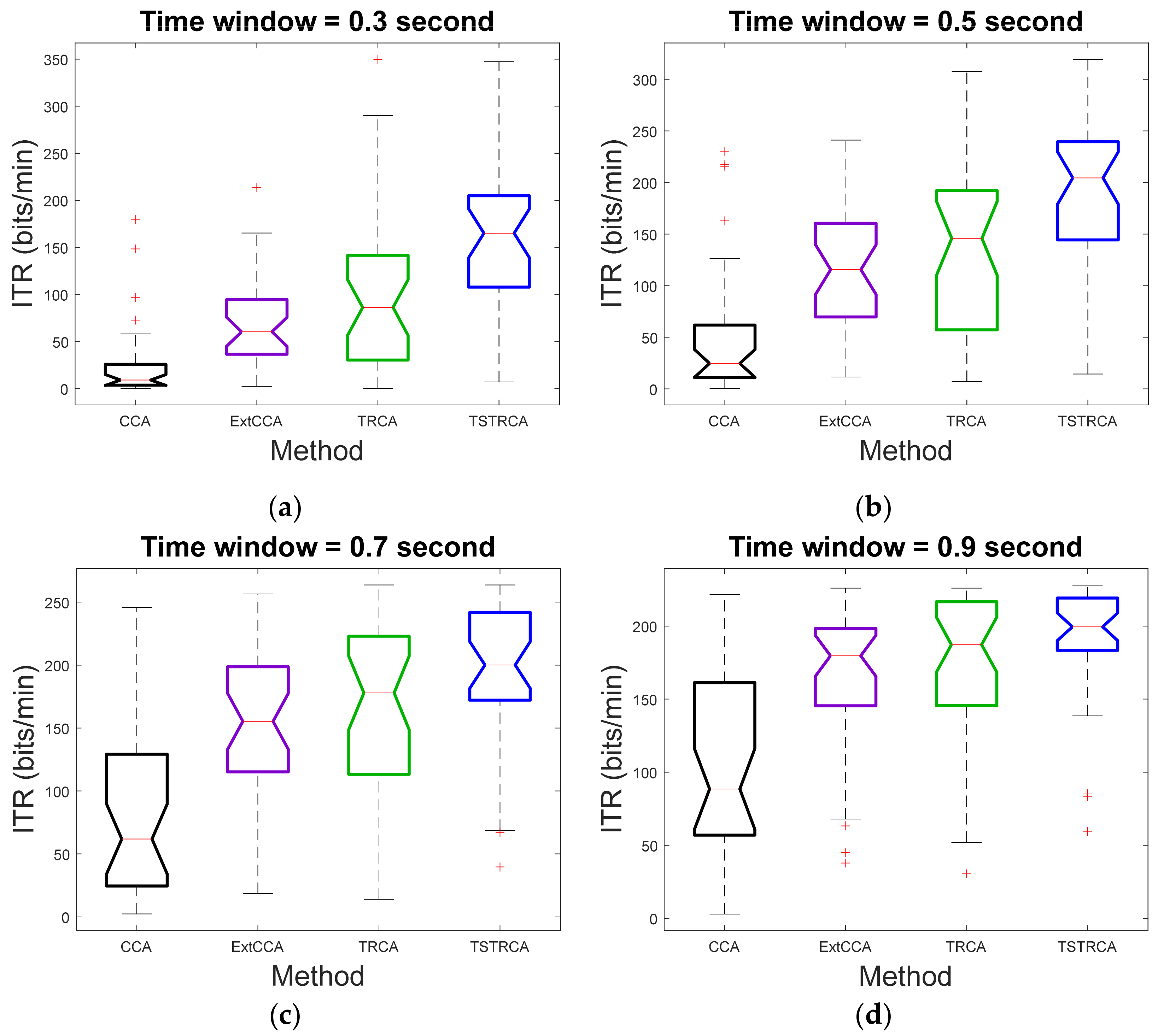
3.2. Target Identification Performance
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain Computer Interfaces, a Review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, J.N.; Wolpaw, J.R. Clinical Applications of Brain-Computer Interfaces: Current State and Future Prospects. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, R.; Maitra, T.; Hafizul Islam, S.; Hassan, M.M.; Alamri, A.; Fortino, G. A novel machine learning based feature selection for motor imagery EEG signal classification in Internet of medical things environment. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 98, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Bi, L. EEG Signals-Based Longitudinal Control System for a Brain-Controlled Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, S. Indoor Simulated Training Environment for Brain-Controlled Wheelchair Based on Steady-State Visual Evoked Potentials. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Gao, X. A high-ITR SSVEP-based BCI speller. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2014, 1, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İşcan, Z.; Nikulin, V.V. Steady state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) based brain-computer interface (BCI) performance under different perturbations. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martišius, I.; Damaševičius, R. A Prototype SSVEP Based Real Time BCI Gaming System. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 3861425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, L.; Belkacem, A.N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Liu, H. EEG-Controlled Wall-Crawling Cleaning Robot Using SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6968713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Gao, X. Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, G.; Gao, X.; Yan, Z.; Hong, B.; Gao, S. An online multi-channel SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a canonical correlation analysis method. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Mitsukura, Y.; Jung, T.-P. A high-speed brain speller using steady-state visual evoked potentials. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2014, 24, 1450019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Jin, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Cichocki, A. L1-Regularized Multiway Canonical Correlation Analysis for SSVEP-Based BCI. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 21, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Cichocki, A. Frequency recognition in ssvep-based bci using multiset canonical correlation analysis. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2013, 24, 1450013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.R.K.; Reddy, M.R. Latent common source extraction via a generalized canonical correlation framework for frequency recognition in SSVEP based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 046004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Jung, T.-P. A Comparison Study of Canonical Correlation Analysis Based Methods for Detecting Steady-State Visual Evoked Potentials. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, H.; Katura, T.; Sato, H. Task-related component analysis for functional neuroimaging and application to near-infrared spectroscopy data. NeuroImage 2013, 64, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Jung, T. Enhancing Detection of SSVEPs for a High-Speed Brain Speller Using Task-Related Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Xu, P.; Yao, D. Fusing Canonical Coefficients for Frequency Recognition in SSVEP-Based BCI. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 52467–52472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Gao, S. A Benchmark Dataset for SSVEP-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Weifeng, L.; Liu, W.; Tao, D. A Survey on Canonical Correlation Analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Jung, T.-P. Enhancing detection of steady-state visual evoked potentials using individual training data. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 3037–3040. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, K.K.; Chin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, C. Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern (FBCSP). In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Hong Kong, China, 1–8 June 2008; pp. 2390–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Jung, T.-P.; Gao, X. Filter bank canonical correlation analysis for implementing a high-speed SSVEP-based brain–computer interface. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Li, F.; Yin, E.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, Q.; Tanaka, T.; Yao, D.; Xu, P. Correlated Component Analysis for Enhancing the Performance of SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, D.J.; Sarnacki, W.A.; Wolpaw, J.R. Brain–computer interface (BCI) operation: Optimizing information transfer rates. Biol. Psychol. 2003, 63, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary Judith, A.; Baghavathi Priya, S. Multiset Task Related Component Analysis (M-TRCA) for SSVEP Frequency Recognition in BCI. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Deng, X.; Wang, G. Spatial Fusion of Maximum Signal Fraction Analysis for Frequency Recognition in SSVEP-Based BCI. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 61, 102042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, D.; Holland, G.; Cosic, I. The Relationship between EEG, PPG and Oxymetric Signal Responses During the OSAH Events: A Pilot Sleep Study. In Proceedings of the 5th World Sleep Congress of the WFSRSMS (WorldSleep07), Cairns, QLD, Australia, 2–6 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baldoumas, G.; Peschos, D.; Tatsis, G.; Chronopoulos, S.K.; Christofilakis, V.; Kostarakis, P.; Varotsos, P.; Sarlis, N.V.; Skordas, E.S.; Bechlioulis, A.; et al. A Prototype Photoplethysmography Electronic Device that Distinguishes Congestive Heart Failure from Healthy Individuals by Applying Natural Time Analysis. Electronics 2019, 8, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldoumas, G.; Peschos, D.; Tatsis, G.; Christofilakis, V.; Chronopoulos, S.K.; Kostarakis, P.; Varotsos, P.A.; Sarlis, N.V.; Skordas, E.S.; Bechlioulis, A.; et al. Remote Sensing Natural Time Analysis of Heartbeat Data by Means of a Portable Photoplethysmography Device. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA | ExtCCA | TRCA | TSTRCA | ||
| Accuracy | F(6, 204) | 1.39 | 5.59 | 4.22 | 7.43 |
| p | 0.22 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| ITR | F(6, 204) | 1.29 | 5.57 | 4.1 | 7.74 |
| p | 0.26 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Channels | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Accuracy | F(3, 102) | 3.26 | 5.73 | 10.6 | 13.63 | 15.07 | 17.2 | 18.6 |
| p | 0.002 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| ITR | F(3, 102) | 3.66 | 6.21 | 10.55 | 12.8 | 14.53 | 16.83 | 18.68 |
| p | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Method (Average ± std. dev. in %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA | ExtCCA | TRCA | TSTRCA | |
| Precision | 22.19 ± 21.63 | 42.73 ± 19.86 | 48.57 ± 25.62 | 64.33 ± 22.81 |
| Recall | 28.94 ± 23.24 | 52.43 ± 19.84 | 56.32 ± 24.89 | 71.92 ± 20.59 |
| F1-score | 25.14 ± 22.45 | 46.94 ± 20.02 | 52 ± 25.46 | 67.78 ± 21.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.K.; Choi, Y.-S. Enhancing SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Two-Step Task-Related Component Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041315
Lee HK, Choi Y-S. Enhancing SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Two-Step Task-Related Component Analysis. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyeon Kyu, and Young-Seok Choi. 2021. "Enhancing SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Two-Step Task-Related Component Analysis" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041315
APA StyleLee, H. K., & Choi, Y.-S. (2021). Enhancing SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Two-Step Task-Related Component Analysis. Sensors, 21(4), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041315







