Microwave Specular Measurements and Ocean Surface Wave Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
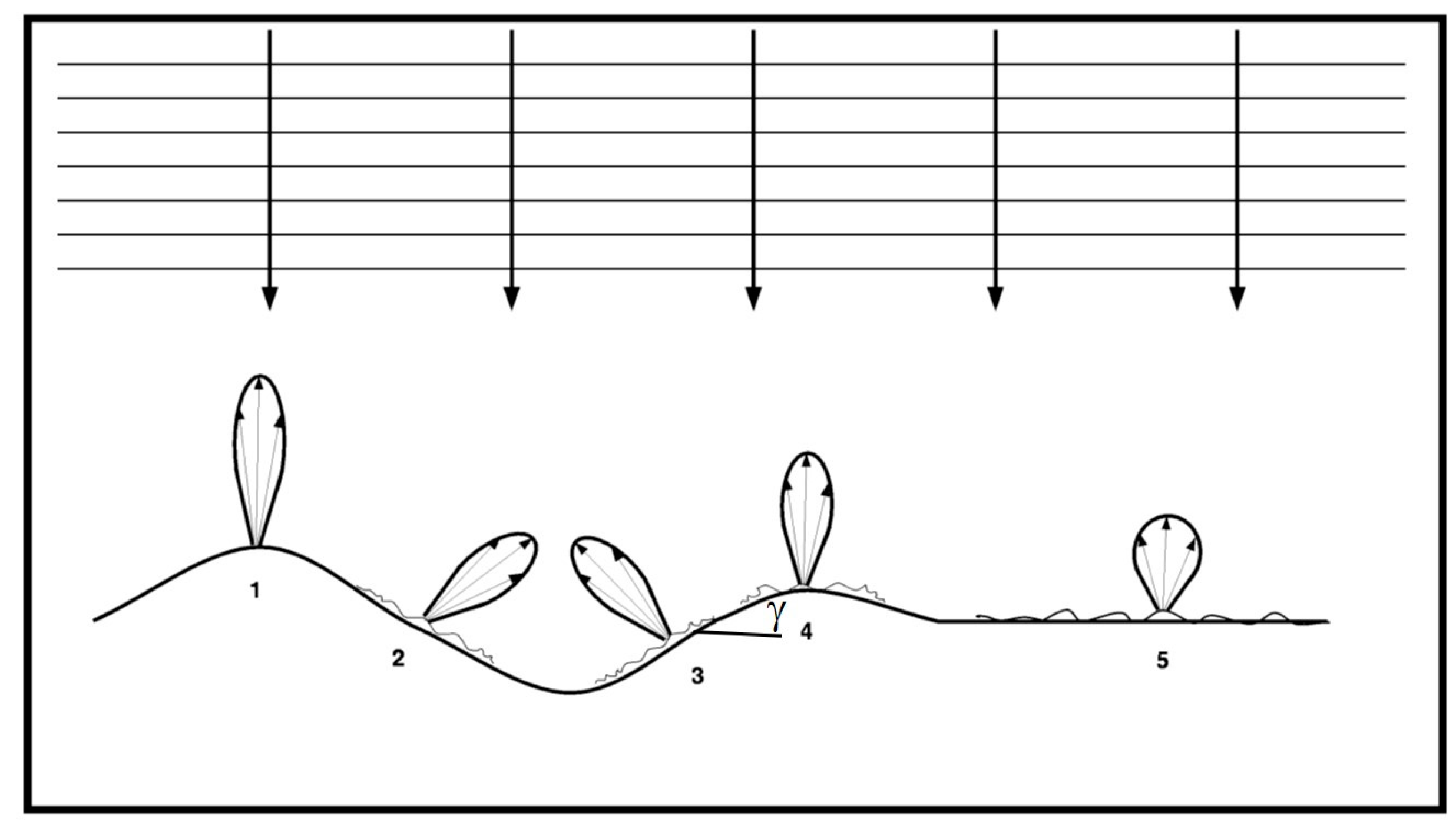
2. Review of Specular Point Theory
3. Application
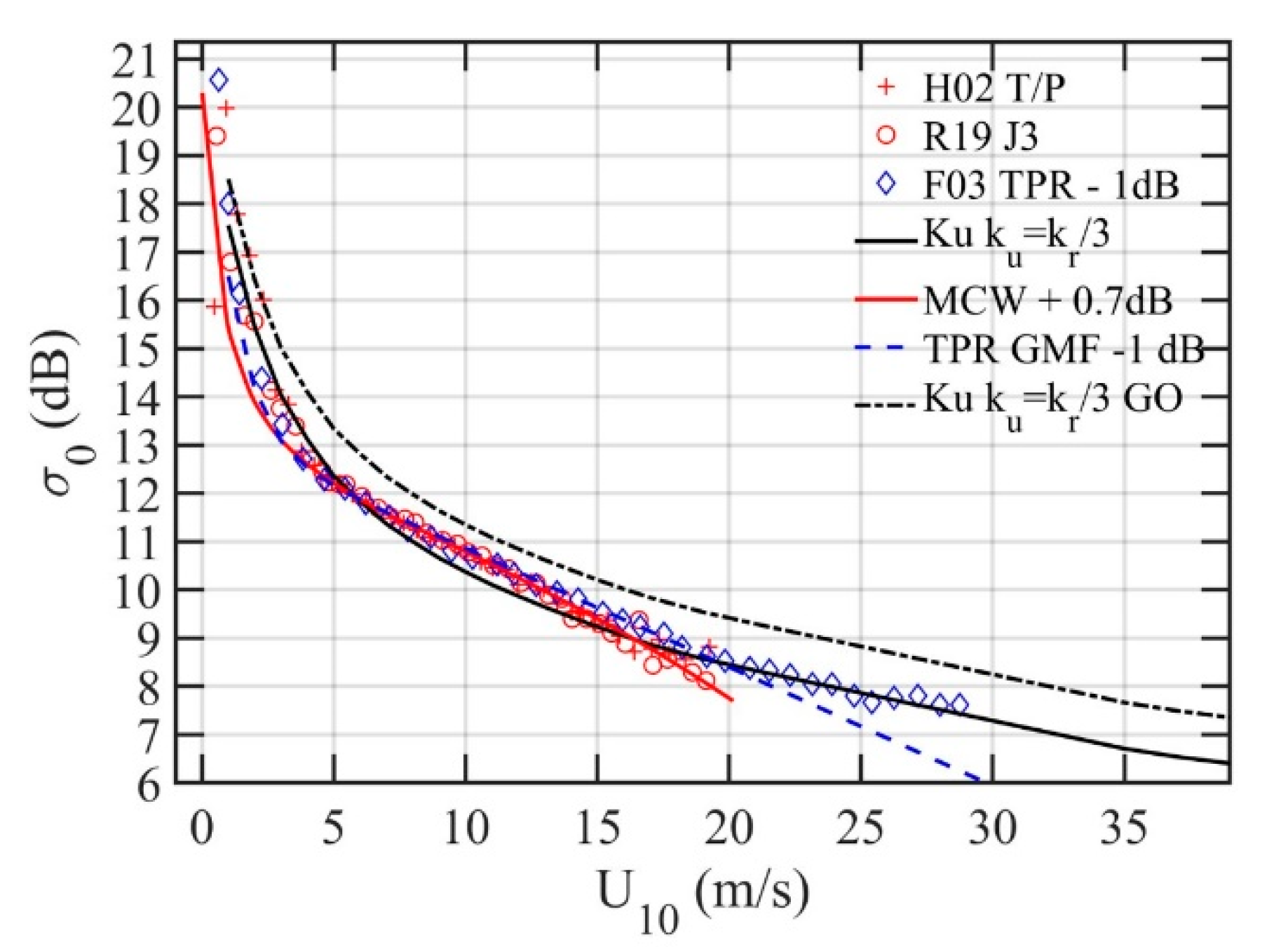
3.1. Ku Band Altimeter Analysis
3.2. L Band CYGNSS Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. LPMSS, Wind Speed, and Wave Development Stage
4.2. Surface Reflectivity Considering Wave Breaking
4.3. Frequency Dependence and Verification
- TOPEX/POSEIDON (T/P) altimeter NRCS (13.575 GHz) and collocated National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Data Buoy Center (NDBC) buoy datasets in three geographic regions (Gulf of Alaska and Bering Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Hawaii islands) have been reported in [13,14] with up to seven years of simultaneous measurements and a total of 2174 (U10, σ0) pairs. The maximum wind speed in the datasets is about 20 m/s. The maximum temporal and spatial differences between buoy and altimeter data are 0.5 h and 100 km, respectively. These data are referred to as H02 from here on.
- A one-year Tropical Rainfall Mapping Mission (TRMM) Precipitation Radar (TPR, 13.8 GHz) dataset [10] with more than 1.13 × 107 (U10, σ0) pairs. The TPR dataset is quite unusual because the wind sensor and altimeter are on the same satellite. The nadir footprint of the TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) wind sensor is collocated with the footprint of the TPR, and there is no need for temporal interpolation. The spatial resolution of TPR altimeter is about 4.3 km and that of the TMI is about 25 km, so the spatial separation between TPR, NRCS, and TMI wind speed data is no more than ± 12.5 km. The maximum wind speed in the dataset as presented in their Figure 4 is about 29 m/s. These data are referred to as F03 from here on.
- An extensive collection of 33 years wind speed, wave height, and altimeter NRCS from 13 satellite missions ranging from Geosat to Sentinel-3A and Jason-3 [64]. The altimeter NRCS is merged with European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model wind speed in 1° × 1° grids; their Figure 3 shows an example of the Jason-3 (J3) NRCS dependence on wind speed. The maximum wind speed is about 20 m/s. These data are referred to as R19 from here on.
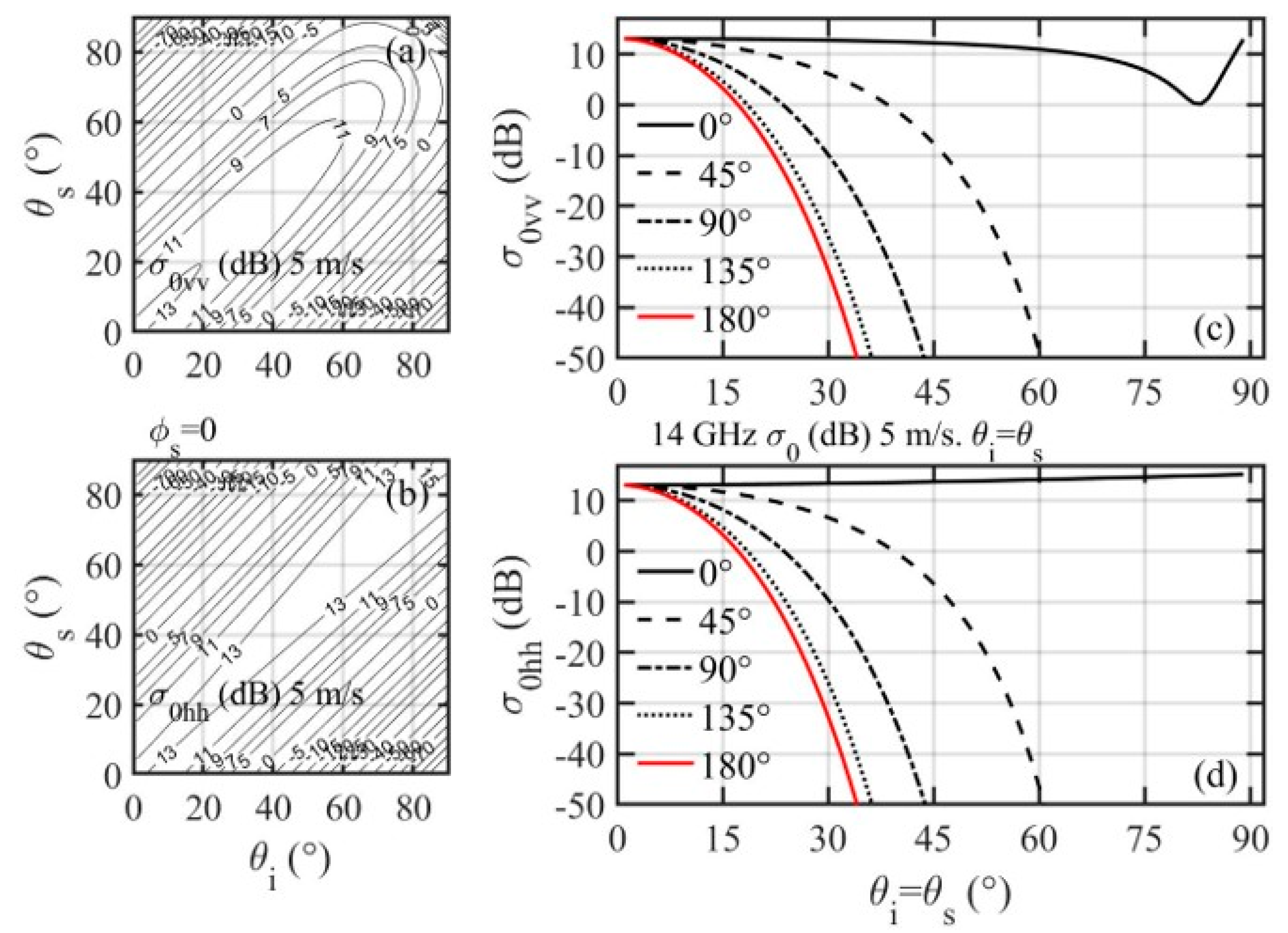
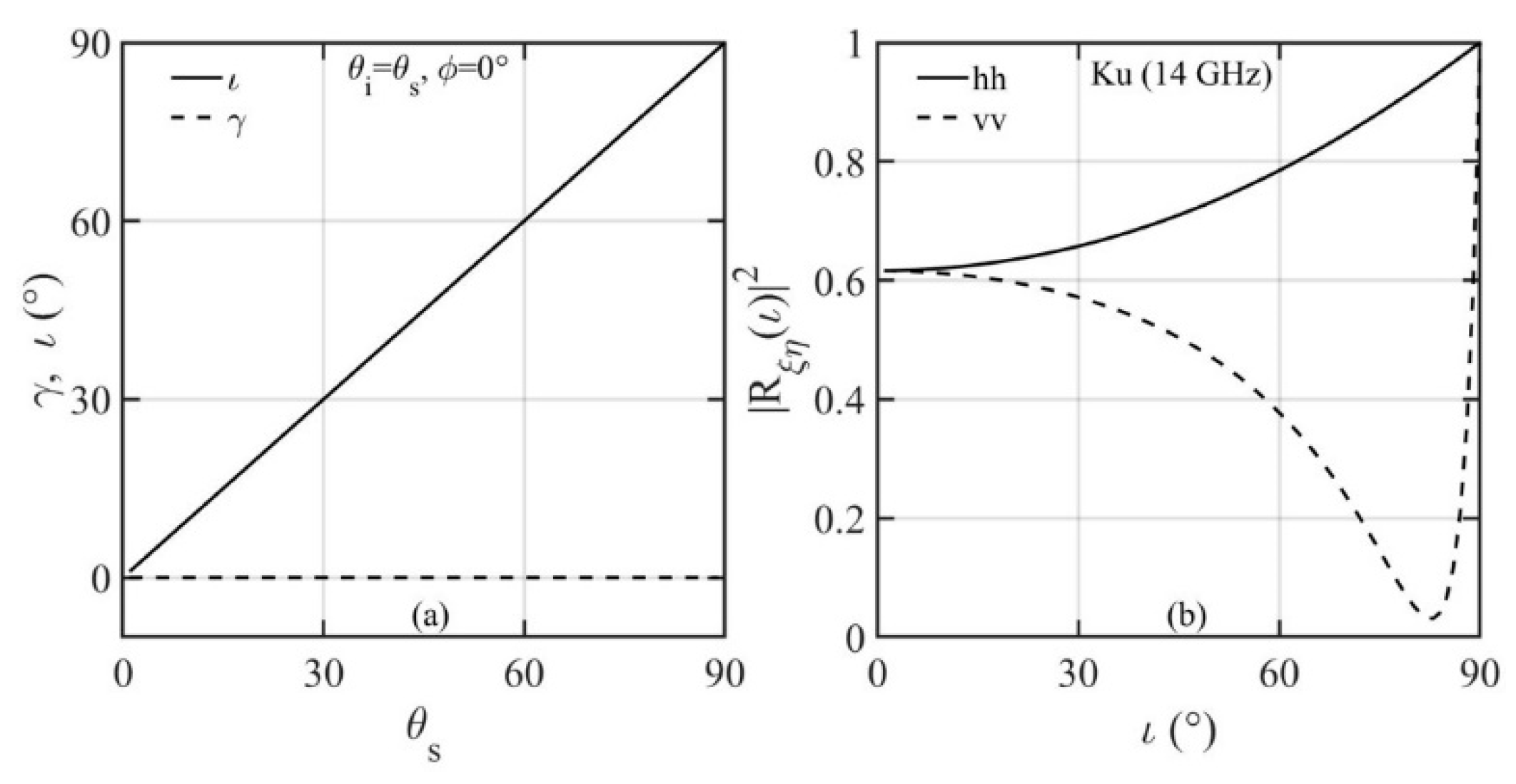
4.4. Incidence and Scattering Angle Dependence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crombie, D.D. Doppler Spectrum of Sea Echo at 13.56 Mc./s. Nature 1955, 175, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W. Backscattering from Capillary Waves with Application to Sea Clutter. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1966, 14, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W. A New Model for Sea Clutter. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1968, 16, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodis, R. A Note on the Theory of Scattering from an Irregular Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1966, 14, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, D.E. Rough Surface Scattering Based on the Specular Point Theory. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1968, 16, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, D.E. Radar Clutter in an Air Defense System-I: Clutter Physics; TR DAAH01-67-C-1921; Battelle Memorial Institute: Columbus, OH, USA, 1968; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. The Statistical Analysis of a Random Moving Surface. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1957, A249, 321–387. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela, G.P. Theories for the Interaction of Electromagnetic and Oceanic Waves—A Review. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1978, 13, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, F.C.; Walton, W.T.; Hines, D.E.; Walter, B.A.; Peng, C.Y. Sea Surface Mean Square Slope from Ku-band Backscatter Data. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 11411–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, M.; Vanhoff, B. The Relationship between Winds, Surface Roughness, and Radar Backscatter at Low Incidence Angles from TRMM Precipitation Radar Measurements. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.S.; Munk, W. Statistics of the Sea Surface Derived from Sun Glitter. J. Mar. Res. 1954, 13, 198–227. [Google Scholar]
- Bréon, F.M.; Henriot, N. Spaceborne Observations of Ocean Glint Reflectance and Modeling of Wave Slope Distributions. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C06005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Teague, W.J.; Jacobs, G.A.; Wang, D.W. A Statistical Comparison of Wind Speed, Wave Height and Wave Period Derived from Satellite Altimeters and Ocean Buoys in the Gulf of Mexico Region. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 10451–10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Wang, D.W.; Teague, W.J.; Jacobs, G.A.; Wesson, J.; Burrage, D.; Miller, J. Anatomy of the Ocean Surface Roughness; NRL/FR/7330-02-10036; Naval Research Laboratory, Formal Rep: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, P.A.; Burrage, D.; Wang, D.W.; Wesson, J. Ocean Surface Roughness Spectrum in High Wind Condition for Microwave Backscatter and Emission Computations. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2168–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Fois, F. Surface Roughness and Breaking Wave Properties Retrieved from Polarimetric Microwave Radar Backscattering. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 3640–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Fan, Y. Low-Frequency Mean Square Slopes and Dominant Wave Spectral Properties: Toward Tropical Cyclone Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7359–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzberg, S.J.; Dunion, J.P. Comparison of Reflected GPS Wind Speed Retrievals with Dropsondes in Tropical Cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzberg, S.J.; Dunion, J.P.; Ganoe, G.G. Comparison of Reflected GPS Wind Speed Retrievals with Dropsondes in Tropical Cyclones. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S. Space Based GNSS Scatterometry: Ocean Wind Sensing Using Empirically Calibrated Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4853–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S.; Zavorotny, V.; Akos, D.; Hrbek, S.; PopStefanija, I.; Walsh, E.J.; Masters, D.; Grant, M. Study of Surface Wind and Mean Square Slope Correlation in Hurricane Ike with Multiple Sensors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.S. Wind Speed Retrieval Algorithm for the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) Mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 54, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Balasubramaniam, R. Development of the CYGNSS Geophysical Model Function for Wind Speed. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, R.; Ruf, C. Azimuthal Dependence of GNSS-R Scattering Cross-Section in Hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillibridge, J.; Scharroo, S.; Abdalla, S.; Vandemark, D. One- and Two-Dimensional Wind Speed Models for Ka-Band Altimetry. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, C.-A.; Poisson, J.-C.; Piras, F.; Amarouche, L.; Lalaurie, J.C. Ku-/Ka-Band Extrapolation of the Altimeter Cross Section and Assessment with Jason2/AltiKa Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5679–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Ainsworth, T.L. L-Band Ocean Surface Roughness. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3988–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Fan, Y.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J.; García-Nava, H. Ocean Surface Wave Spectra inside Tropical Cyclones. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 2393–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A. Deriving L-Band Tilting Ocean Surface Roughness from Measurements by Operational Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfouhaily, T.; Chapron, B.; Katsaro, K.; Vandemark, D. A Unified Directional Spectrum for Long and Short Wind-Driven Waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 15781–15796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Chang, P.S.; Clarizia, M.P.; Gleason, S.; Jelenak, Z.; Majumdar, S.J.; Morris, M.; Murray, J.; Musko, S.; Posselt, D.J.; et al. CYGNSS Handbook; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Gleason, S.; Cardellach, E.; Camps, A. Tutorial on Remote Sensing Using GNSS Bistatic Radar of Opportunity. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2014, 2, 8–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, W.J.; Moskowitz, L. A Proposed Spectral Form for Fully Developed Wind Seas Based on the Similarity Theory of S. A. Kitaigorodskii. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 5181–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Bouws, E.; Carlson, H.; Cartwright, D.E.; Enke, K.; Ewing, J.A.; Gienapp, H.; Hasselmann, D.E.; Kruseman, P.; et al. Measurements of Wind-Wave Growth and Swell Decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z. 1973, A8, 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselmann, K.; Ross, D.B.; Müller, P.; Sell, W. A Parametric Wave Prediction Mode. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1976, 6, 200–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelan, M.A.; Hamilton, J.; Hui, W.H. Directional Spectra of Wind-Generated Waves. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1985, A315, 509–562. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, L.A.; Swift, C.T. An Improved Model for the Dielectric Constant of Sea Water at Microwave Frequencies. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1977, 25, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. Wind-Vector Retrievals under Rain with Passive Satellite Microwave Radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3065–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, S.H.; Dinardo, S.J.; Fore, A.G.; Li, F.K. Passive and Active L-Band Microwave Observations and Modeling of Ocean Surface Winds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3087–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, S.H.; Tang, W.; Fore, A.G.; Neumann, G.; Hayashi, A.K.; Freedman, J.C.; Lagerloef, G.S.E. L-Band Passive and Active Microwave Geophysical Model Functions of Ocean Surface Winds and Applications to Aquarius Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4619–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, B.W.; Uhlhorn, E.W. Improved Stepped Frequency Microwave Radiometer Tropical Cyclone Surface Winds in Heavy Precipitation. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 2392–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Ricciardulli, L. The Emission and Scattering of L-Band Microwave Radiation from Rough Ocean Surfaces and Wind Speed Measurements from the Aquarius Sensor. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 6499–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Chapron, B.; Zabolotskikh, E.; Donlon, C.; Quilfen, Y.; Guimbard, S.; Piolle, J.F. A Revised L-Band Radio-Brightness Sensitivity to Extreme Winds under Tropical Cyclones: The Five Year SMOS-Storm Database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, S.H.; Fore, A.G.; Tang, W.; Hayashi, A.K.; Stiles, B.W.; Reul, N.; Weng, Y.; Zhang, F. SMAP L-Band Passive Microwave Observations of Ocean Surface Wind during Severe Storms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 7339–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Ricciardulli, L.; Wentz, F.J. Capability of the SMAP Mission to Measure Ocean Surface Winds in Storms. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1660–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapp, J.W.; Alsweiss, S.O.; Jelenak, Z.; Chang, P.S.; Carswell, J. Stepped Frequency Microwave Radiometer Wind-Speed Retrieval Improvements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Reul, N.; Meissner, T.; Yueh, S.H. Whitecap and Wind Stress Observations by Microwave Radiometers: Global Coverage and Extreme Conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2019, 49, 2291–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Reul, N.; Meissner, T.; Yueh, S.H. Ocean Surface Foam and Microwave Emission: Dependence on Frequency and Incidence Angle. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8223–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchak, J.R.; Gardner, L.G.; Hipp, J.W.; Victor, J.M. High Dielectric Constant Microwave Probes for Sensing Soil Moisture. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvola, A.H. Mixing Rules with Complex Dielectric Coefficients. Subsurf. Sens. Technol. Appl. 2000, 1, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvola, A.H.; Kong, J.A. Effective Permittivity of Dielectric Mixtures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Near-Nadir Microwave Specular Returns from the Sea Surface—Altimeter Algorithms for Wind and Wind Stress. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, J. An Improved Model of the Ocean Surface Wave Vector Spectrum and Its Effects on Radar Backscatter. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 16269–16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, P.S.; Morris, C.S.; Hsiao, S.V. Comparison of TOPEX/POSEIDON Sigma0 and Significant Wave Height Distributions to Geosat. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 24369–24381. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.S. Quasi-specular scattering from the air-sea interface. In Surface Waves and Fluxes; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 2, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.S.; Stanley, H.R.; Roy, N.A. The Wind Speed Measurement Capability of Spaceborne Radar Altimeters. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1981, 6, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; McCabe, P.J. A Review of Satellite Altimeter Measurement of Sea Surface Wind Speed; with a Proposed New Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 4707–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Wentz, F.J. Further Development of an Improved Altimeter Wind Speed Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 14250–14260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, D.L.; Chelton, D.B. A Geosat Altimeter Wind Speed Algorithm and a Method for Altimeter Wind Speed Algorithm Development. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 8853–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebuchi, N.; Kawamura, H. Validation of Wind Speeds and Significant Wave Heights Observed by the TOPEX Altimeter around Japan. J. Oceanogr. 1994, 50, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, M.H.; Challenor, P.G. A New Approach for Determining Fully Empirical Altimeter Wind Speed Model Functions. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 25051–25062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.F.R. Intercomparison of Wave and Wind Data from TOPEX/POSEIDON. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 3817–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, S. Ku-Band Radar Altimeter Surface Wind Speed Algorithm; TR 524, European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2007; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Ribal, A.; Young, I.R. 33 Years of Globally Calibrated Wave Height and Wind Speed Data Based on Altimeter Observations. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, N.J. Bistatic Radar; SciTech Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2005; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, N.J.; Griffiths, H.D. Advances in Bistatic Radar; SciTech Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2007; p. 493. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ashwal, W.A.M. Measurement and Modelling of Bistatic Sea Clutter. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2011; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Kabakchiev, K.H. Maritime Forward Scatter Radar: Data Collection and Clutter Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2014; p. 240. [Google Scholar]
- Gashinova, M.; Kabakchiev, K.; Daniel, L.; Hoare, E.; Sizov, V.; Cherniakov, M. Measured Forward-Scatter Sea Clutter at near-Zero Grazing Angle: Analysis of Spectral and Statistical Properties. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2014, 8, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, A.; Ayari, Y.; Khenchaf, A.; Coatanhay, A. Bistatic Scattering from an Anisotropic Sea Surface: Numerical Comparison between the First-Order SSA and the TSM Models. Waves Random Complex Media 2006, 16, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, D.E.; Peake, W.H. Scattering from Surfaces with Different Roughness Scales: Analysis and Interpretation; TR BAT-197A-10-3; Battelle Memorial Institute: Columbus, OH, USA, 1967; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Voronovich, A.G. Small-Slope Approximation for Electromagnetic Wave Scattering at the Rough Interface of Two Dielectric Half-Spaces. Waves Random Media 1994, 4, 337–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, M.Y.; Khenchaf, A.; Coatanhay, A. Simulations of the Bistatic Scattering Using Two-Scale Model and the Unified Sea Spectrum. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 013532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronovich, A.G. A Two-Scale Model from the Point of View of the Smallslope Approximation. Waves Random Media 1996, 6, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Stoffelen, A.; de Haan, S. An Improved C-Band Scatterometer Ocean Geophysical Model Function: CMOD5. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, C03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Stoffelen, A.; van Zadelhoff, G.-J.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Shen, H. Cross Polarization Geophysical Model Function for C-Band Radar Backscattering from the Ocean Surface and Wind Speed Retrieval. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Adriaan, J.; Verspeek, V.; Vogelzang, J.; Verhoef, A. The CMOD7 Geophysical Model Function for ASCAT and ERS Wind Retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2023–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, T.V.; Khenchaf, A.; Comblet, F.; Nahum, C. Assessment of Wind Speed Estimation from C-Band Sentinel-1 Images Using Empirical and Electromagnetic Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4075–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, T.V.; Messager, C.; Honnorat, M.; Sahl, R.; Khenchaf, A. Use of Sentinel-1 C-Band SAR Images for Convective System Surface Wind Pattern Detection. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, P.A.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Ouellette, J.D. Microwave Specular Measurements and Ocean Surface Wave Properties. Sensors 2021, 21, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041486
Hwang PA, Ainsworth TL, Ouellette JD. Microwave Specular Measurements and Ocean Surface Wave Properties. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041486
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Paul A., Thomas L. Ainsworth, and Jeffrey D. Ouellette. 2021. "Microwave Specular Measurements and Ocean Surface Wave Properties" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041486
APA StyleHwang, P. A., Ainsworth, T. L., & Ouellette, J. D. (2021). Microwave Specular Measurements and Ocean Surface Wave Properties. Sensors, 21(4), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041486






