Wavelet Analysis of Overnight Airflow to Detect Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Database
3. Methods
3.1. Feature Extraction
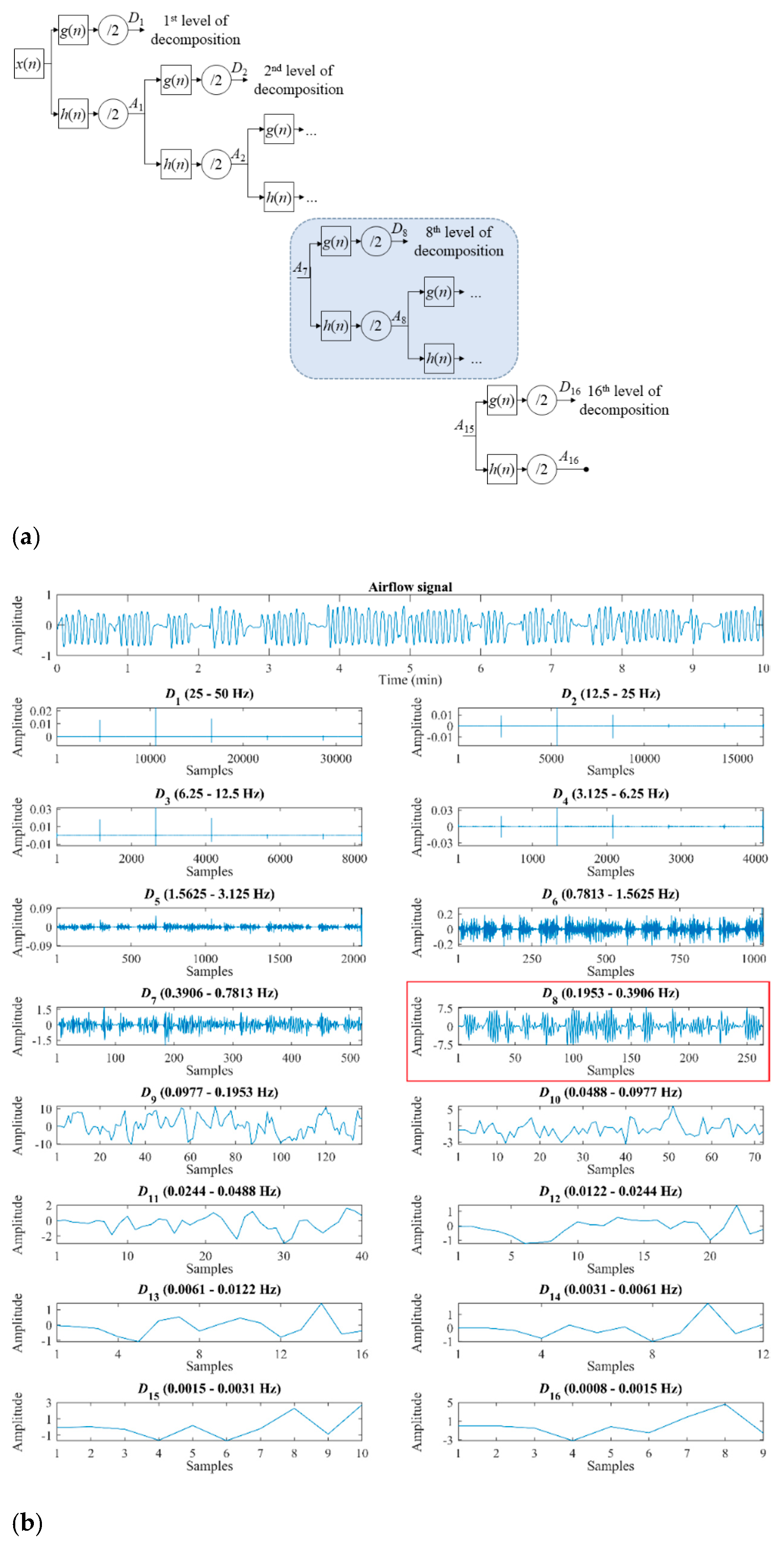
3.1.1. Wavelet Features
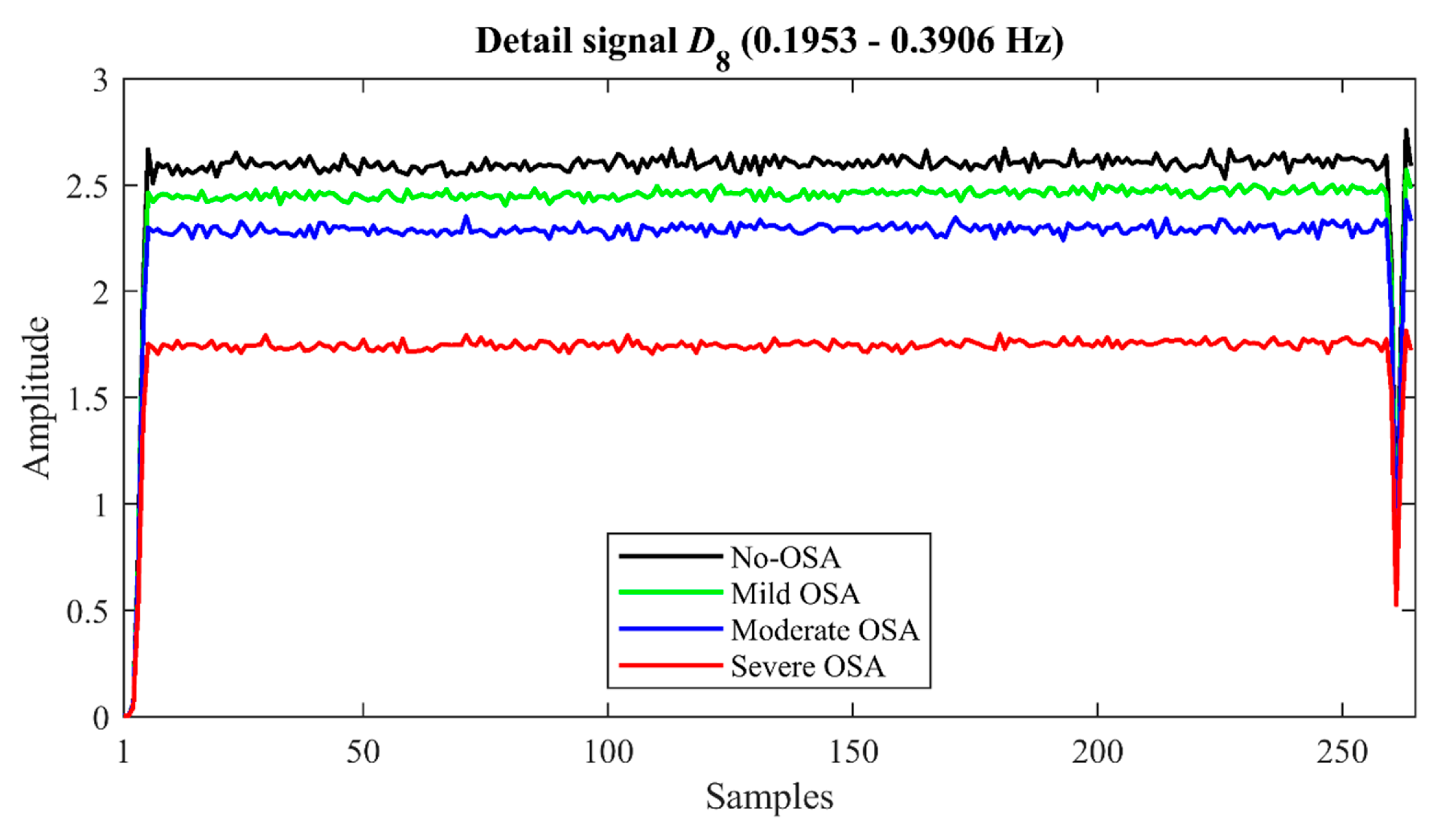
- Four statistical moments (M1D8–M4D8). Mean (M1D8), standard deviation (M2D8), skewness (M3D8), and kurtosis (M4D8) are computed to measure central tendency, dispersion, asymmetry, and peakedness of the distribution of the coefficients of D8 [25].
- Maximum and minimum (MaxD8 and MinD8). They are the highest (MaxD8) and the lowest (MinD8) value of the coefficients of the detail signal D8. These features allow to quantify the maximum and minimum amplitude reached in this decomposition level [25].
- Energy (ED8). This feature measures the quadratic amplitude of the detail signal D8, providing information about the activity produced in the resolution level associated to the representative frequency band of the normal breathing [25,41]. It is computed as the sum of the modulus of the detail coefficients squared [22,23]:
- Wavelet entropy (WE). It is an extension of the well-known Shannon’s entropy. Therefore, this feature allows quantifying the energy distribution changes generated in the decomposition process, offering information about the underlying dynamical behavior and the irregularity of the signal [22,25,41]:where pj is the normalized energy distribution at the decomposition level j:
3.1.2. Oximetry Index
3.2. Feature Selection
3.3. Machine-Learning Approaches
3.3.1. Multiclass Classification
3.3.2. Regression
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Training Group
4.1.1. Extracted Features
4.1.2. Feature Selection
4.1.3. Optimization of Adaboost.M2 and BY-MLP
4.2. Test Group
5. Discussion
5.1. Training Group
5.2. Feature Selection and Diagnostic Performance
5.3. Comparison with Other Studies
5.4. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statement
References
- Kaditis, A.G.; Alvarez, M.L.A.; Boudewyns, A.; Alexopoulos, E.I.; Ersu, R.; Joosten, K.; Larramona, H.; Miano, S.; Narang, I.; Trang, H.; et al. Obstructive sleep disordered breathing in 2- to 18-year-old children: Diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Ward, S.D.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Lehmann, C.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e714–e755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, S.J.; Gozal, D.; Smith, D.L.; Philby, M.F.; Kaylegian, J.; Gozal, K.L. Effect of sleep-disordered breathing severity on cognitive performance measures in a large community cohort of young school-aged children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blechner, M.; Williamson, A.A. Consequences of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2016, 46, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.L.M.; Canet, T.; Alarco, C.M.; Estivill, E.; Julián, F.E.; Gozal, D.; Luque, J.M.J.; Roselló, L.M.A.; Pérez, M.F.; Andreu, M.M.; et al. Consensus document on sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome in children. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2011, 47, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Gozal, D.; Ramirez, H.M.; Bandla, H.P.R.; Gozal, K.L. Overnight Polysomnography versus Respiratory Polygraphy in the Diagnosis of Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep 2014, 37, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Álvarez, A.M.L.; Santos, T.J.; Carbajo, O.E.; Guevara, C.J.A.; Egüia, N.A.I.; Gozal, K.L.; Gozal, D. Reliability of home respiratory polygraphy for the diagnosis of sleep apnea in children. Chest 2015, 147, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil, E.; Bailon, R.; Vergara, J.M.; Laguna, P. PTT Variability for Discrimination of Sleep Apnea Related Decreases in the Amplitude Fluctuations of PPG Signal in Children. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, P.; Garde, A.; Karlen, W.; Petersen, C.L.; Wensley, D.; Dumont, G.A.; Mark Ansermino, J. Evaluation of cardiac modulation in children in response to apnea/hypopnea using the Phone OximeterTM. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouldice, R.B.; Brien, O.L.M.; Brien, O.C.; De Chazal, P.; Gozal, D.; Heneghan, C. Detection of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Pediatric Subjects using Surface Lead Electrocardiogram Features. Sleep 2004, 27, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, B.V.; Tobal, G.G.; Gozal, K.L.; Álvarez, D.; Villar, V.F.; Crespo, A.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Irregularity and Variability Analysis of Airflow Recordings to Facilitate the Diagnosis of Paediatric Sleep Apnoea-Hypopnoea Syndrome. Entropy 2017, 19, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, J.J.; Tobal, G.G.C.; García, M.; Gozal, K.L.; Montero, M.A.; Álvarez, D.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Assessment of Airflow and Oximetry Signals to Detect Pediatric Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome Using AdaBoost. Entropy 2020, 22, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornero, R.; Gozal, K.L.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Philby, M.F.; Álvarez, A.M.L.; Álvarez, D.; Dayyat, E.A.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.S.; Tamae Kakazu, M.; et al. Nocturnal Oximetry-based Evaluation of Habitually Snoring Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, A.; Hoppenbrouwer, X.; Dehkordi, P.; Zhou, G.; Rollinson, A.U.; Wensley, D.; Dumont, G.A.; Ansermino, J.M. Pediatric pulse oximetry-based OSA screening at different thresholds of the apnea-hypopnea index with an expression of uncertainty for inconclusive classifications. Sleep Med. 2019, 60, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for Scoring Respiratory Events in Sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobal, G.G.C.; Álvarez, A.M.L.; Álvarez, D.; Del Campo, F.; Santos, T.J.; Hornero, R. Diagnosis of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea: Preliminary findings using automatic analysis of airflow and oximetry recordings obtained at patients’ home. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 18, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, B.V.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Gozal, K.L.; Álvarez, D.; Villar, V.F.; Núñez, P.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Usefulness of recurrence plots from airflow recordings to aid in paediatric sleep apnoea diagnosis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 183, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaditis, A.; Gozal, K.L.; Gozal, D. Pediatric OSAS: Oximetry can provide answers when polysomnography is not available. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 27, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eyck, A.; Verhulst, S.L. Improving the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in children with nocturnal oximetry-based evaluations. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, V.G.; Bohn, S.G.; Flemons, W.W.; Remmers, J.E. Comparison of Home Oximetry Monitoring with Laboratory Polysomnography in Children. CHEST J. 2003, 124, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oeverland, B.; Skatvedt, O.; Kvarner, K.J.; Akre, H. Pulseoximetry: Sufficient to diagnose severe sleep apnea. Sleep Med. 2002, 3, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figliola, A.; Serrano, E. Analysis of physiological time series using wavelet transforms. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1997, 16, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Martin, M.T.; Figliola, A.; Keller, K.; Plastino, A. EEG analysis using wavelet-based information tools. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 153, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioul, O.; Vetterli, M. Wavelets and Signal Processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1991, 8, 14–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villar, V.F.; Álvarez, D.; Gozal, K.L.; Tobal, G.G.C.; García, B.V.; Crespo, A.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Wavelet analysis of oximetry recordings to assist in the automated detection of moderate-to-severe pediatric sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; Lee, R.G.; Tseng, C.L.; Zhou, H.K.; Chao, C.F.; Jiang, J.A. A new approach for identifying sleep apnea syndrome using wavelet transform and neural networks. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2006, 18, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khandoker, A.; Palaniswami, M.; Karmakar, C. Support Vector Machines for Automated Recognition of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome from Electrocardiogram Recordings. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, F.O.; Berdiñas, G.B.; Betanzos, A.A.; Bonillo, M.V. A new method for sleep apnea classification using wavelets and feedforward neural networks. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 34, pp. 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tagluk, E.M.; Akin, M.; Sezgin, N. Classification of sleep apnea by using wavelet transform and artificial neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Hernández, C.A.; Crespo, A.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Villar, V.F.; García, B.V.; Moreno, F.; Arroyo, C.A.; Ruiz, T.; Hornero, R.; et al. A machine learning-based test for adult sleep apnoea screening at home using oximetry and airflow. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Várady, P.; Micsik, T.; Benedek, S.; Benyó, Z. A novel method for the detection of apnea and hypopnea events in respiration signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, S.G. A Theory for Multiresolution Signal Decomposition: The Wavelet Representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Steele, C.M.; Chau, T. Classification of healthy and abnormal swallows based on accelerometry and nasal airflow signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermit, M.; Eide, Å.J.; Lindblad, T.; Waldemark, K. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome by monitoring patients airflow signals. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2000, 21, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyduch, H.M. Nonlinear Alleviation of Edge Effects in the Context of Minimizing Prediction Errors. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gogolewski, D. Influence of the edge effect on the wavelet analysis process. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2020, 152, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Daubechies, I. The Wavelet Transform, Time-Frequency Localization and Signal Analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1990, 36, 961–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, B.V.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Gozal, K.L.; Alvarez, D.; Villar, V.F.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Usefulness of Spectral Analysis of Respiratory Rate Variability to Help in Pediatric Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 4580–4583. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, S.; Thompson, M.; Stevens, R.; Heneghan, C.; Plüddemann, A.; MacOnochie, I.; Tarassenko, L.; Mant, D. Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: A systematic review of observational studies. Lancet 2011, 377, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosso, O.A.; Blanco, S.; Yordanova, J.; Kolev, V.; Figliola, A.; Schürmann, M.; Bașar, E. Wavelet entropy: A new tool for analysis of short duration brain electrical signals. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 105, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkonen, J.T. Discrete Wavelet Transforms-Theory and Applications; InTech: Melbourne, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- García, B.V.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Gozal, K.L.; Álvarez, D.; Villar, V.F.; Crespo, A.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Análisis espectral de la señal de flujo aéreo como ayuda al diagnóstico del síndrome de apnea-hipopnea del sueño en niños. In Proceedings of the XXXIV Congreso Anual de la Sociedad Española de Ingeniería Biomédica, Valencia, Spain, 23–25 November 2016; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, B.H.; Dempsey, J.A.; Weber, S.M.; Badr, M.S.; Skatrud, J.B.; Young, T.B.; Jacques, A.J.; Seow, K.C. Automated detection and classification of sleep-disordered breathing from conventional polysomnography data. Sleep 1997, 20, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, H. Feature Selection for High-Dimensional Data: A Fast Correlation-Based Filter Solution. In Proceedings of the Twentieth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03), Washington, DC, USA, 21–24 August 2003; pp. 856–863. [Google Scholar]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A. An Introduction to Variable and Feature Selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 1157–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Wu, Y.; Gozal, K.L.; Ni, X.; Hornero, R.; Gozal, D. Cloud Algorithm-Driven Oximetry-Based Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Symptomatic Habitually-Snoring Children. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobal, G.G.C.; Member, S.; Alvarez, D.; Del Campo, F.; Hornero, R.; Member, S. Utility of AdaBoost to Detect Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome from Single-Channel Airflow. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 3rd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann/Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-12-374856-0. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A Decision-Theoretic Generalization of On-Line Learning and an Application to Boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobal, G.G.C.; Alvarez, D.; Crespo, A.; Del Campo, F.; Hornero, R. Evaluation of Machine-Learning Approaches to Estimate Sleep Apnea Severity from at-Home Oximetry Recordings. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal Inform. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, J.V.; Hornero, R.; Lvarez, D.; Nabney, I.T.; Del Campo, F.; Zamarrón, C. The classification of oximetry signals using Bayesian neural networks to assist in the detection of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.M. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Diagnostic tests 4: Likelihood ratios. BMJ 2004, 329, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, B.V.; Tobal, G.G.C.; Gozal, K.L.; Villar, V.F.; Álvarez, D.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Bispectral analysis of overnight airflow to improve the pediatric sleep apnea diagnosis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 129, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coifman, R.R.; Meyer, Y.; Quake, S.; Wickerhauser, M.V. Signal processing and compression with wavelet packets. In Wavelets and their Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, M.; García, R.; Dias, M. A Systematic Review of Detecting Sleep Apnea Using Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Characteristic | All | Training Group | Test Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| #Subjects | 946 | 570 (60%) | 376 (40%) |
| Age (years) | 6 [6] | 6 [5] | 6 [6] |
| #Males | 584 (61.7%) | 339 (59.5%) | 245 (65.2%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 17.9 [6.2] | 17.7 [6.7] | 18.1 [6.0] |
| AHI (e/h) | 3.8 [7.8] | 4.2 [8.3] | 3.3 [6.4] |
| #No-OSA | 163 (17.2%) | 91 (16.0%) | 72 (19.1%) |
| #Mild OSA | 386 (40.8%) | 223 (39.1%) | 163 (43.4%) |
| #Moderate OSA | 172 (18.2%) | 111 (19.5%) | 61 (16.2%) |
| #Severe OSA | 225 (23.8%) | 145 (25.4%) | 80 (21.3%) |
| Feature | No-OSA | Mild OSA | Moderate OSA | Severe OSA | RHO | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | |||
| M1D8 | 2.62 | 0.97 | 2.46 | 0.86 | 2.29 | 1.03 | 1.67 | 1.08 | −0.4024 | <<0.01 |
| M2D8 | 2.64 | 1.27 | 2.34 | 1.20 | 2.27 | 1.34 | 1.61 | 1.28 | −0.3058 | <0.01 |
| M3D8 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.4413 | <<0.01 |
| M4D8 | 2.87 | 2.76 | 2.98 | 1.96 | 3.58 | 2.92 | 5.32 | 4.34 | 0.3666 | <0.01 |
| MaxD8 | 6.67 | 1.09 | 6.61 | 0.99 | 6.59 | 1.36 | 6.21 | 1.44 | −0.1662 | <0.01 |
| MinD8 (10−3) | 2.87 | 0.84 | 2.60 | 0.93 | 2.52 | 1.14 | 1.86 | 1.06 | −0.4154 | <<0.01 |
| ED8 (103) | 2.68 | 1.56 | 2.36 | 1.41 | 2.19 | 1.67 | 1.33 | 1.44 | −0.3809 | <0.01 |
| WE | 0.26 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.2793 | <0.01 |
| ODI3 | 1.16 | 2.02 | 2.21 | 3.24 | 4.36 | 5.98 | 14.28 | 18.68 | 0.6979 | <<0.01 |
| AHI cut-off = 1 e/h | ||||||||
| Model | Se (%) [95%CI] | Sp (%) [95%CI] | Acc (%) [95%CI] | PPV (%) [95%CI] | NPV (%) [95%CI] | LR+ [95%CI] | LR- [95%CI] | kappa2 |
| ABAF | 79.89 a,b,c,d [77.10,82.46] | 47.24 a,b,c,d [39.35,54.83] | 73.61 a,b,c,d [70.86,76.27] | 86.43 a,b,c,d [83.88,88.85] | 35.62 a,b,c,d [29.29,41.47] | 1.52 a,b,c,d [1.36,1.88] | 0.43 a,b,c,d [0.36,0.57] | 0.2395 a,b,c,d [0.1692,0.3059] |
| ABAF,ODI3 | 80.26 a,e,f,g [77.63,83.05] | 68.07 a,e,f,g [61.85,74.49] | 77.97 a,e,f,g [75.54,80.51] | 91.45 a,e,f,g [89.31,93.30] | 44.94 a,e,f,g [38.97,51.32] | 2.56 a,e,f,g [2.20,3.47] | 0.29 a,e,f,g [0.25,0.35] | 0.4040 a,e,f,g [0.3406,0.4677] |
| BY-MLPAF | 100.00 b,e,h,i [100.00, 100.00] | 0.00 b,e,h,i [0.00, 0.00] | 80.85 b,e,h,i [78.47,83.18] | 80.85 b,e,h,i [78.47,83.18] | ND b,e,h,i | 1.00 b,e,h,i [1.00, 1.00] | ND b,e,h,i | 0.00 b,e,h,i [0.00, 0,00] |
| BY-MLPAF,ODI3 | 91.16 c,f,h,j [89.14,93.02] | 43.28 c,f,h,j [36.45,50.59] | 81.96 c,f,h,j [79.46,84.25] | 87.18 c,f,h,j [84.93,89.18] | 53.55 c,f,h,j [45.68,61.85] | 1.62 c,f,h,j [1.46,1.92] | 0.21 c,f,h,j [0.16,0.29] | 0.3696 c,f,h,j [0.2944,0.4413] |
| ODI3 | 59.78 d,g,i,j [56.66,63.32] | 86.06 d,g,i,j [80.83,90.79] | 64.81 d,g,i,j [61.89,67.97] | 94.79 d,g,i,j [92.83,96.64] | 33.68 d,g,i,j [29.46,38.12] | 4.59 d,g,i,j [3.52,10.83] | 0.47 d,g,i,j [0.42,0.52] | 0.2875 d,g,i,j [0.2424,0.3422] |
| AHI cut-off = 5 e/h | ||||||||
| Model | Se (%) [95%CI] | Sp (%) [95%CI] | Acc (%) [95%CI] | PPV (%) [95%CI] | NPV (%) [95%CI] | LR+ [95%CI] | LR- [95%CI] | kappa2 |
| ABAF | 74.43 a,b,c,d [70.10,79.12] | 47.18 a,b,c,d [43.31,51.21] | 57.46 a,c,d [54.40,60.51] | 45.81 a,c,d [42.12,49.93] | 75.57 a,b,c,d [71.57,79.90] | 1.42 a,c,d [1.30,1.58] | 0.54 a,b,c,d [0.44,0.65] | 0.1928 a,c,d [0.1408,0.2467] |
| ABAF,ODI3 | 68.03 a,e,f,g [63.10,72.79] | 90.28 a,e,f,g [87.94,92.45] | 81.91 a,e,f [79.50,84.36] | 80.78 a,e,f,g [76.22,85.18] | 82.49 a,e,f,g [79.67,85.32] | 7.18 a,e,f,g [5.91,11.14] | 0.35 a,e,f,g [0.30,0.41] | 0.6009 a,e,f [0.5497,0.6540] |
| BY-MLPAF | 77.25 b,e,h,i [73.13,81.50] | 45.05 b,e,h,i [41.40,49,13] | 57.14 e,h,i [54.20,60.27] | 45.82 e,h,i [42.03,49.81] | 76.89 b,e,h,i [72.83,81.24] | 1.41 e,h,i [1.30,1.57] | 0.50 b,e,h,i [0.41,0.62] | 0.1967 e,h,i [0.1475,0.2481] |
| BY-MLPAF,ODI3 | 79.32 c,f,h,j [74.90,83.50] | 83.83 c,f,h,j [80.92,86.61] | 82.14 c,f,h,j [79.84,84.40] | 74.57 c,f,h,j [70.37,79.04] | 87.17 c,f,h,j [84.52,89.91] | 4.97 c,f,h,j [4.28,6.52] | 0.25 c,f,h,j [0.20,0.30] | 0.6221 c,f,h,j [0.5754,0.6696] |
| ODI3 | 69.45 d,g,i,j [64.63,74.16] | 89.38 d,g,i,j [86.91,91.68] | 81.88 d,i,j [79.54,84.25] | 79.79 d,g,i,j [75.04,83.97] | 83.01 d,g,i,j [80.30,85.84] | 6.68 d,g,i,j [5.60,10.17] | 0.34 d,g,i,j [0.29,0.40] | 0.6024 d,i,j [0.5509,0.6553] |
| AHI cut-off = 10 e/h | ||||||||
| Model | Se (%) [95%CI] | Sp (%) [95%CI] | Acc (%) [95%CI] | PPV (%) [95%CI] | NPV (%) [95%CI] | LR+ [95%CI] | LR- [95%CI] | kappa2 |
| ABAF | 41.06 a,b,c,d [34.66,47.67] | 85.52 a,b,c,d [83.13,87.83] | 76.07 a,b,c,d [73.51,78.39] | 43.30 a,b,c,d [36.89,50.53] | 84.28 a,b,c,d [81.92,86.60] | 2.86 a,b,c,d [2.36,3.80] | 0.69 a,b,c,d [0.61,0.77] | 0.2697 a,b,c,d [0.2040,0.3363] |
| ABAF,ODI3 | 72.37 a,e,f,g [66.59,77.90] | 95.99 a,e,f,g [94.60,97.31] | 90.99 a,e,f,g [89.29,92.61] | 83.01 a,e,f,g [77.43,88.45] | 92.76 a,e,f,g [91.03,94.44] | 18.99 a,e,f,g [14.60,51.76] | 0.29 a,e,f,g [0.23,0.35] | 0.7159 a,e,g [0.6605,0.7677] |
| BY-MLPAF | 50.00 b,e,h,i [42.96,56.68] | 75.96 b,e,h,i [73.18,78.80] | 70.47 b,e,h,i [67.77,73.07] | 35.97 b,e,h,i [30.57,41.70] | 84.86 b,e,h,i [82.28,87.30] | 2.10 b,e,h,i [1.77,2.55] | 0.66 b,e,h,i [0.57,0.76] | 0.2271 b,e,h,i [0.1623,0.2886] |
| BY-MLPAF,ODI3 | 74.85 c,f,h,j [68.75,80.51] | 95.00 c,f,h,j [93.42,96.46] | 90.69 c,f,h,j [88.87,92.47] | 80.04 c,f,h,j [74.53,85.78] | 93.32 c,f,h,j [91.66,94.91] | 15.60 c,f,h,j [12.23,30.31] | 0.26 c,f,h,j [0.21,0.33] | 0.7141 c,h,j [0.6570,0.7660] |
| ODI3 | 81.05 d,g,i,j [75.71,86.12] | 88.58 d,g,i,j [86.34,90.76] | 87.00 d,g,i,j [84.93,89.06] | 65.84 d,g,i,j [60.31,71.74] | 94.55 d,g,i,j [93.01,96.10] | 7.23 d,g,i,j [6.10,9.98] | 0.21 d,g,i,j [0.16,0.27] | 0.6422 d,g,i,j [0.5894,0.6956] |
| kappa4 [95%CI] | Acc4 (%) [95%CI] | |
|---|---|---|
| ABAF | 0.1126 [0.0796,0.1466] a,b,c,d | 30.52 [27.90,33.37] a,b,c,d |
| ABAF,ODI3 | 0.4021 [0.3605,0.4463] a,e,f,g | 57.46 [54.47,60.60] a,e,f |
| BY-MLPAF | 0.0664 [0.0342,0.1004] b,e,h,i | 32.53 [29.87,35.20] b,e,h,i |
| BY-MLPAF,ODI3 | 0.4088 [0.3637,0.4493] c,f,h,j | 58.57 [55.36,61.47] c,f,h,j |
| ODI3 | 0.3826 [0.3362,0.4258] d,g,i,j | 57.23 [53.95,60.22] d,i,j |
| Study | Nº Subjects (Total Dataset/Test Set) | Signal | Methods (Analysis/Selection/Classification) | AHI cut-off (e/h) | Se (%) | Sp (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | LR+ | LR- | Acc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shouldice et al. (2004) [10] | 50/25 | ECG | Temporal and spectral analysis/–/ QDA | 1 | 85.70 | 81.80 | 85.70 | 81.80 | 4.71 | 0.18 | 84.00 |
| Gil et al. (2010) [8] | 21/21 | PPG | Analysis of HRV, PTTV, and DAP events/Wrap method/LDA | 5 | 75.00 | 85.70 | - | - | 5.24 * | 0.29 * | 80.00 |
| Dehkordi et al. (2016) [9] | 146/146 | PPG | Temporal, spectral, and detrended fluctuation analysis/LASSO/LASSO | 5 | 76.00 | 68.00 | - | - | 2.38 * | 0.35 * | 71.00 |
| Hornero et al. (2017) [13] | 4,191/3,602 | SpO2 | Statistical, spectral, non-linear analysis, and ODI3/FCBF/ MLP | 1 | 84.02 | 53.19 | 81.64 | 57.34 | 1.79 | 0.30 | 75.15 |
| 5 | 68.16 | 87.19 | 68.62 | 86.95 | 5.32 | 0.37 | 81.65 | ||||
| 10 | 68.66 | 94.07 | 67.68 | 94.31 | 11.58 | 0.33 | 90.17 | ||||
| Vaquerizo-Villar et al. (2018) [25] | 981/392 | SpO2 | Statistical, spectral, wavelet analysis, and ODI3/FCBF/SVM | 5 | 71.90 | 91.10 | 83.80 | 84.50 | 14.60 | 0.31 | 84.00 |
| Xu et al. (2019) [47] | 432/432 | SpO2 | ODI3 and 3rd statistical moment of the spectral band of interest/FCBF/MLP | 1 | 95.34 | 19.10 | 81.96 * | 51.52 * | 1.18 | 0.25 | 79.63 |
| 5 | 77.78 | 80.46 | 72.28 * | 84.68 * | 3.99 | 0.27 | 79.40 | ||||
| 10 | 73.53 | 92.73 | 75.76 * | 91.89 * | 10.07 | 0.29 | 88.19 | ||||
| Garde et al. (2019) [14] | 207/207 | SpO2 PRV | Temporal and spectral analysis/Stepwise-selection/LR | 1 | 80.00 | 65.00 | - | - | 2.29 * | 0.31 * | 75.00 |
| 5 | 85.00 | 79.00 | - | - | 4.05 * | 0.19 * | 82.00 | ||||
| 10 | 82.00 | 91.00 | - | - | 9.11 * | 0.20 * | 89.00 | ||||
| Barroso-García et al. (2020) [17] | 946/376 | AF ODI3 | Recurrence quantification analysis and ODI3/FCBF/BY-MLP | 1 | 97.70 | 22.22 | 84.14 | 69.57 | 1.26 | 0.10 | 83.24 |
| 5 | 78.72 | 78.30 | 68.52 | 85.98 | 3.63 | 0.27 | 78.46 | ||||
| 10 | 78.75 | 94.26 | 78.75 | 94.26 | 13.71 | 0.23 | 90.96 | ||||
| Jiménez- García et al. (2020) [12] | 974/390 | AF SpO2 | Statistical, non-linear, spectral analysis, and ODI3/FCBF / Multiclass AdaBoost.M2 with LDA | 1 | 92.06 | 36.00 | 85.80 | 51.92 | 1.44 | 0.22 | 81.28 |
| 5 | 76.03 | 85.66 | 76.03 | 85.66 | 5.30 | 0.28 | 82.05 | ||||
| 10 | 62.65 | 97.72 | 88.14 | 90.63 | 27.48 | 0.38 | 90.26 | ||||
| Barroso-García et al. (2021) [56] | 946/376 | AF ODI3 | Bispectral analysis and ODI3/FCBF/MLP | 1 | 98.03 | 15.27 | 83.01 | 65.01 | 1.16 | 0.14 | 82.16 |
| 5 | 81.56 | 83.00 | 74.17 | 88.25 | 4.85 | 0.22 | 82.49 | ||||
| 10 | 72.29 | 94.98 | 79.58 | 92.69 | 15.01 | 0.29 | 90.15 | ||||
| This study | 946/376 | AF ODI3 | Wavelet analysis and ODI3/FCBF/Multiclass AdaBoost.M2 with decision trees | 1 | 80.26 | 68.07 | 91.45 | 44.94 | 2.56 | 0.29 | 77.97 |
| 5 | 68.03 | 90.28 | 80.78 | 82.49 | 7.18 | 0.35 | 81.91 | ||||
| 10 | 72.37 | 95.99 | 83.01 | 92.76 | 18.99 | 0.29 | 90.99 | ||||
| Wavelet analysis and ODI3/FCBF/BY-MLP | 1 | 91.16 | 43.28 | 87.18 | 53.55 | 1.62 | 0.21 | 81.96 | |||
| 5 | 79.32 | 83.83 | 74.57 | 87.17 | 4.97 | 0.25 | 82.14 | ||||
| 10 | 74.85 | 95.00 | 80.04 | 93.32 | 15.60 | 0.26 | 90.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barroso-García, V.; Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Gozal, D.; Vaquerizo-Villar, F.; Álvarez, D.; del Campo, F.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Hornero, R. Wavelet Analysis of Overnight Airflow to Detect Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. Sensors 2021, 21, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041491
Barroso-García V, Gutiérrez-Tobal GC, Gozal D, Vaquerizo-Villar F, Álvarez D, del Campo F, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Hornero R. Wavelet Analysis of Overnight Airflow to Detect Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041491
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarroso-García, Verónica, Gonzalo C. Gutiérrez-Tobal, David Gozal, Fernando Vaquerizo-Villar, Daniel Álvarez, Félix del Campo, Leila Kheirandish-Gozal, and Roberto Hornero. 2021. "Wavelet Analysis of Overnight Airflow to Detect Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041491
APA StyleBarroso-García, V., Gutiérrez-Tobal, G. C., Gozal, D., Vaquerizo-Villar, F., Álvarez, D., del Campo, F., Kheirandish-Gozal, L., & Hornero, R. (2021). Wavelet Analysis of Overnight Airflow to Detect Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children. Sensors, 21(4), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041491










