Metal-Oxide Based Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications in Electrical and Electrochemical Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Conductometric Type Sensors: Building Basics and Sensing Mechanisms
3. An Overview on MOX Nanomaterials Used for Gas Sensing
4. Electrochemical Sensor: Building Basics and Sensing Mechanisms
5. An Overview on MOX Nanomaterials Used for Biosensing Detection
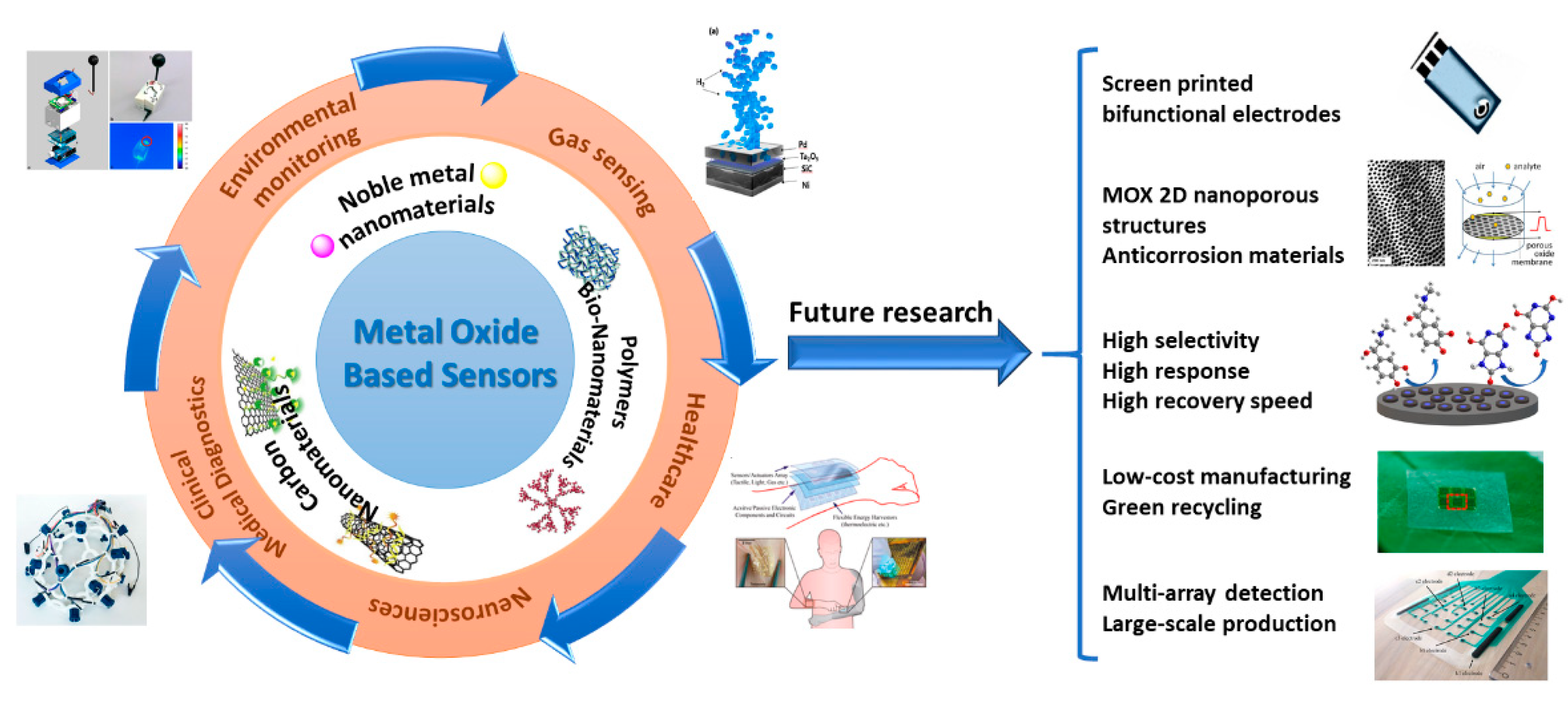
6. MOX-Based Sensors Drawbacks and Future Perspectives and Challenges
- (i)
- Low selectivity and low response/recovery speed for a long time and after repeated bending/recovering, without degradation of the sensor components. In this respect, one should take advantage of the light illumination of conductometric sensors to improve their sensing response at room-temperature operation.
- (ii)
- Restricted sensing performance at room temperature, also due to the influence of humidity level. Thus, NRT gas sensors with a rapid response should be still engineered to meet the need for timely triggering of the alarm.
- (iii)
- High degree of responsivity and selectivity for multiple-agent sensors should be still reached.
- (iv)
- The interaction between the target molecules and chemisorbed oxygen species (such as O2− and O− ions) is almost known, a clear understanding of the interaction mechanisms of some groups bearing oxygen atoms (such as OH−) with the target molecules is missing. This investigation could be the starting point to develop surface modification procedures useful to minimize OH− effects. As regarding biosensors, the peculiar chemical-physical properties that metal oxide nanohybrids on appropriately modified electrodes offer (with respect to other materials conventionally used to fabricate these biosensors) have been described in this review in view of specific sensing applications.
- (v)
- A limited production of flexible and wearable sensor arrays for electroactive biomolecules detection; this is due to the relatively low mechanical robustness (mainly on flexible substrates) currently obtained. Therefore, this is still the major challenge to be addressed in gas sensors manufacture.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hulanicki, A.; Glab, S.; Ingman, F. Chemical sensors: Definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electrochemical Sensor Market-Growth, Trends, Covid-19 Impact, and Forecasts (2021–2026). Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/global-electrochemical-sensors-market-industry (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Wong, M.S. Nanostructured Supported Metal Oxides. In Metal Oxides: Chemistry and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.L. Metal Oxides. Metals 2020, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Mezzasalma, A.M.; Mondio, G.; Serafino, T.; Barreca, F.; Caridi, F. Optical and structural properties of pulsed laser ablation deposited ZnO thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silipigni, L.; Barreca, F.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Spanò, T.; Piazza, S.; Sunseri, C.; Inguanta, R. Template Electrochemical Growth and Properties of Mo Oxide Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 22299–22308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Mao, Q.; Hou, D.; Yang, J. A review of recent applications of porous metals and metal oxide in energy storage, sensing and catalysis. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 949–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Arbiol, J.; Cirera, A.; Cornet, A.; Morante, J.R. Surface activation by Pt-nanoclusters on titania for gas sensing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 19, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Choi, S.-W.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, C.; Kim, S.S. Synthesis and Gas Sensing Properties of TiO2–ZnO Core-Shell Nanofibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2551–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, R.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, K.; Han, E. Approaches to Enhancing Gas Sensing Properties: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şerban, I.; Enesca, A. Metal Oxides-Based Semiconductors for Biosensors Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enesca, A.; Andronic, L.; Duta, A. Optimization of Opto-Electrical and Photocatalytic Properties of SnO2 Thin Films Using Zn2+ and W6+ Dopant Ions. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaly, M.; Lacatusu, I.; Enesca, I.A.; Meghea, A. Hybride Nanomaterials Based on Silica Coated C60 Clusters Obtained by Microemulsion Technique. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 483, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visa, M.; Andronic, L.; Enesca, A. Behavior of the new composites obtained from fly ash and titanium dioxide in removing of the pollutants from wastewater. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 388, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduraiveeran, G. Bionanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensing platforms for biomedical applications. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, Y.S. Review of metal oxide semiconductors-based thin-film transistors for point-of-care sensor applications. J. Inf. Disp. 2020, 21, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Brinzari, V.; Cho, B.K. Conductometric gas sensors based on metal oxides modified with gold nanoparticles: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1033–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, G. First Fifty Years of Chemoresistive Gas Sensors. Chemosensors 2015, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, W. Surface engineering of one-dimensional tin oxide nanostructures for chemical sensors. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Cho, B.K. Engineering approaches for the improvement of conductometric gas sensor parameters: Part 1. Improvement of sensor sensitivity and selectivity (short survey). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 709–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.G.; Jung, Y.; Han, S.D.; Shim, Y.-S.; Shin, B.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Jun, S.C.; Park, H.-H.; et al. Chemiresistive Electronic Nose toward Detection of Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20969–20976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-based gas sensors for detection of benzene, toluene and xylene (BTX) gases: A review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4342–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Resistance-based H2S gas sensors using metal oxide nanostructures: A review of recent advances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetchakun, K.; Samerjai, T.; Tamaekong, N.; Liewhiran, C.; Siriwong, C.; Kruefu, V.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Tuantranont, A.; Phanichphant, S. Semiconducting metal oxides as sensors for environmentally hazardous gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Chen, C.; Meng, L.; Lin, Y.S. Self-Assembled Monolayer of Metal Oxide Nanosheet and Structure and Gas-Sensing Property Relationship. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, W.-T.; Jang, J.-S.; Kim, I.-D. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Chemiresistive Sensors. Chem 2019, 5, 1938–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Vomiero, A.; Sberveglieri, G. Quasi-one dimensional metal oxide semiconductors: Preparation, characterization and application as chemical sensors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackin, C.; Schroeder, V.; Zurutuza, A.; Su, C.; Kong, J.; Swager, T.M.; Palacios, T. Chemiresistive Graphene Sensors for Ammonia Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16169–16176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, S.G. Two-Dimensional Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Gas Sensor Applications. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. How shell thickness can affect the gas sensing properties of nanostructured materials: Survey of literature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 270–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Tang, T.; Zhou, C. Tuning electronic properties of In2O3 nanowires by doping control. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariammal, R.N.; Ramachandran, K. Increasing the reactive sites of ZnO nanoparticles by Li doping for ethanol sensing. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 015024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varpula, A.; Novikov, S.; Haarahiltunen, A.; Kuivalainen, P. Transient characterization techniques for resistive metal-oxide gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 159, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govardhan, K.; Grace, A.N. Metal/Metal Oxide Doped Semiconductor Based Metal Oxide Gas Sensors—A Review. Sens. Lett. 2016, 14, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Leonardi, S.G.; Santoro, M.; Donato, N.; Neri, G.; Neri, F. Synthesis, characterization and hydrogen sensing properties of nanosized colloidal rhodium oxides prepared by Pulsed Laser Ablation in water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.G.; Chang, P.; Fan, Z. Quasi-one-dimensional metal oxide materials—Synthesis, properties and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2006, 52, 49–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.W.; Dai, Z.R.; Wang, Z.L. Nanobelts of Semiconducting Oxides. Science 2001, 291, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Han, S.; Tang, T.; Han, J.; Zhou, C. In2O3 nanowires as chemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E. Metal oxide nano-crystals for gas sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G. Nanostructures and Nanomaterials; Imperial College Press: London, UK. Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/p305 (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Nunes, D.; Pimentel, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Pereira, S.; Branquinho, R.; Barquinha, P.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Metal oxide nanostructures for sensor applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoa, N.D.; Duy, N.V.; El-Safty, S.A.; Hieu, N.V. Meso-/Nanoporous Semiconducting Metal Oxides for Gas Sensor Applications. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 972025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Gas sensing mechanism of metal oxides: The role of ambient atmosphere, type of semiconductor and gases—A review. Sci. Lett. J. 2014, 4, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Conduction Model of Metal Oxide Gas Sensors. J. Electroceramics 2001, 7, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Egashira, M. Basic Aspects and Challenges of Semiconductor Gas Sensors. MRS Bull. 2013, 24, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H. Gas sensors using hierarchical and hollow oxide nanostructures: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postica, V.; Gröttrup, J.; Adelung, R.; Lupan, O.; Mishra, A.K.; de Leeuw, N.H.; Ababii, N.; Carreira, J.F.C.; Rodrigues, J.; Sedrine, N.B.; et al. Multifunctional Materials: A Case Study of the Effects of Metal Doping on ZnO Tetrapods with Bismuth and Tin Oxides. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulowicz, I.; Hrkac, V.; Kaps, S.; Cretu, V.; Lupan, O.; Braniste, T.; Duppel, V.; Tiginyanu, I.; Kienle, L.; Adelung, R.; et al. Three-Dimensional SnO2 Nanowire Networks for Multifunctional Applications: From High-Temperature Stretchable Ceramics to Ultraresponsive Sensors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Luo, J.; Torun, H.; Hu, P.; Yang, C.; Grundmann, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Advances in designs and mechanisms of semiconducting metal oxide nanostructures for high-precision gas sensors operated at room temperature. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 470–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.; Lv, X.; Hu, Z.; Xu, A.; Feng, C. Semiconductor Metal Oxides as Chemoresistive Sensors for Detecting Volatile Organic Compounds. Sensors 2019, 19, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Suematsu, K.; Watanabe, K.; Nishibori, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Shimanoe, K. Determination of Effective Oxygen Adsorption Species for CO Sensing Based on Electric Properties of Indium Oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B275–B280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choopun, S.; Hongsith, N.; Wongrat, E. Metal-Oxide Nanowires for Gas Sensor. In Nanowires—Recent Advances; Peng, X., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasiri, N.; Clarke, C. Nanostructured Chemiresistive Gas Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Agrawal, A.V.; Moradi, M.; Yousefi, R. Chapter 6—Nanosensors for gas sensing applications. In Nanomaterials for Air Remediation; Abdeltif, A., Assadi, A.A., Nguyen-Tri, P., Nguyen, T.A., Rtimi, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Han, S.H.; Cho, B.K. Material Design for Metal Oxide Chemiresistive Gas Sensors. J. Sens. Sci. Technol. 2013, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhowmick, T.; Ambardekar, V.; Ghosh, A.; Dewan, M.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P.; Nag, S.; Basu Majumder, S. Multilayered and Chemiresistive Thin and Thick Film Gas Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. In Multilayer Thin Films—Versatile Applications for Materials Engineering; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulzolf, S.C.; LeGore, L.J.; Lad, R.J. Heteroepitaxial growth of tungsten oxide films on sapphire for chemical gas sensors. Thin Solid Film 2001, 400, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.A.; Gul, M.; Abbas, M.; Amin, M. Synthesis of Metal Oxide Semiconductor Nanostructures for Gas Sensors. In Gas Sensors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Detection of hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by metal oxide nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15119–15141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Janghorban, K.; Hashemi, B.; Neri, G. Metal-core@metal oxide-shell nanomaterials for gas-sensing applications: A review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Tang, N.; He, K.; Hu, X.; Li, M.; Li, K. Gas-Sensing Performances of Metal Oxide Nanostructures for Detecting Dissolved Gases: A Mini Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Lee, J.-H.; Majhi, S.M.; Weber, M.; Bechelany, M.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive gas sensors based on metal-oxide nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 241102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Leonardi, S.G.; Pistone, A.; Mavilia, L.; Neri, G. Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Hjiri, M.; Dhahri, R.; El Mir, L.; Sabatino, G.; Barreca, F.; Neri, F.; Leonardi, S.G.; Pistone, A.; Neri, G. Ammonia sensing properties of V-doped ZnO:Ca nanopowders prepared by sol–gel synthesis. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 226, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.D.; Van Quy, N.; Cho, Y.; Kim, D. An ammonia gas sensor based on non-catalytically synthesized carbon nanotubes on an anodic aluminum oxide template. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Core Writing Team. Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L., Eds.; Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/SYR_AR5_FINAL_full.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Kannan, P.K.; Saraswathi, R.; Rayappan, J.B.B. CO2 gas sensing properties of DC reactive magnetron sputtered ZnO thin film. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 13115–13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Leonardi, S.G.; Donato, N.; Neri, G. CO and NO2 Selective Monitoring by ZnO-Based Sensors. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neri, G. Metal Oxide Nanostructures for Solid State Gas Sensors: A Recent Patent Survey. Recent Pat. Mater. Sci. 2011, 4, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, R.; Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Barreca, F.; Donato, N.; Bonavita, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. ZnO:Ca nanopowders with enhanced CO2 sensing properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 255503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.G.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ye, Z.Z.; Zhu, L.P.; Wang, L.; Zhao, B.H.; Liang, Q.L. Low-resistivity, stable p-type ZnO thin films realized using a Li–N dual-acceptor doping method. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 222114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Balamurugan, C.; Lee, D.W. Enhanced CO2 gas-sensing performance of ZnO nanopowder by La loaded during simple hydrothermal method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantò, F.; Leonardi, S.G.; Fazio, E.; Frontera, P.; Bonavita, A.; Neri, G.; Antonucci, P.; Neri, F.; Santangelo, S. CO2 sensing properties of electro-spun Ca-doped ZnO fibres. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 305501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttner, W.J.; Post, M.B.; Burgess, R.; Rivkin, C. An overview of hydrogen safety sensors and requirements. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, C. Hydrogen sensing properties of multiple networked Nb2O5/ZnO core–shell nanorod sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Hydrogen Gas Sensors Based on Semiconductor Oxide Nanostructures. Sensors 2012, 12, 5517–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Luca, L.; Donato, A.; Santangelo, S.; Faggio, G.; Messina, G.; Donato, N.; Neri, G. Hydrogen sensing characteristics of Pt/TiO2/MWCNTs composites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, S.; Faggio, G.; Messina, G.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Neri, G. On the hydrogen sensing mechanism of Pt/TiO2/CNTs based devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chen, Z. High-temperature resistive hydrogen sensor based on thin nanoporous rutile TiO2 film on anodic aluminum oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Chen, W.; Zeng, M. Carbon nanotube/titania composites prepared by a micro-emulsion method exhibiting improved photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 427–428, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpel, W.; Rocker, G.; Feierabend, R. Intrinsic defects of TiO2 (110): Interaction with chemisorbed O2, H2, CO, and CO2. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 28, 3427–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T. Photocatalysis on TiO2 Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and Selected Results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, P.; Malara, A.; Stelitano, S.; Leonardi, S.G.; Bonavita, A.; Fazio, E.; Antonucci, P.; Neri, G.; Neri, F.; Santangelo, S. Characterisation and H2O2 sensing properties of TiO2-CNTs/Pt electro-catalysts. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 170, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Sekar, C.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Development of a selective hydrogen leak sensor based on chemically doped SnO2 for automotive applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 10645–10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Lee, J.M.; Koo, J.H.; Lee, W.; Lee, T. Hysteresis behavior of electrical resistance in Pd thin films during the process of absorption and desorption of hydrogen gas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6984–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Taggart, D.K.; Penner, R.M. Fast, Sensitive Hydrogen Gas Detection Using Single Palladium Nanowires That Resist Fracture. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Kung, S.-C.; Cheng, M.; Hemminger, J.C.; Penner, R.M. Smaller is Faster and More Sensitive: The Effect of Wire Size on the Detection of Hydrogen by Single Palladium Nanowires. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5233–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsafi, F.; Hashemi, B.; Mirzaei, A.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Donato, N.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Sm-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: A novel sensing material for conductometric hydrogen leak sensor. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, C.; Moulaee, K.; Donato, N.; Iannazzo, D.; Lavanya, N.; Neri, G.; Sekar, C. Temperature modulated Cu-MOF based gas sensor with dual selectivity to acetone and NO2 at low operating temperatures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 329, 129053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Leonardi, S.G.; Marini, S.; Espro, C.; Kanagaraj, M.; Reddy, S.L.; Sekar, C.; Neri, G. MgNi2O3 nanoparticles as novel and versatile sensing material for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose and conductometric determination of acetone. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 152787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Veerapandi, G.; Leonardi, S.G.; Donato, N.; Neri, G.; Sekar, C. Fast and selective detection of volatile organic compounds using a novel pseudo spin-ladder compound CaCu2O3. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichy, C.; Donato, N.; Latino, M.; Georg Willinger, M.; Tessonnier, J.-P.; Neri, G.; Pinna, N. Gas sensing properties and p-type response of ALD TiO2coated carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2014, 26, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavanya, N.; Anithaa, A.C.; Sekar, C.; Asokan, K.; Bonavita, A.; Donato, N.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Effect of gamma irradiation on structural, electrical and gas sensing properties of tungsten oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Sekar, C.; Anithaa, A.C.; Sudhan, N.; Asokan, K.; Bonavita, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Investigations on the effect of gamma-ray irradiation on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 385502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, F.R.; Xavier, M.G. 6—Electrochemica Sensors. In Nanoscience and Its Applications; Da Róz, A.L., Ferreira, M., de Lima Leite, F., Oliveira, O.N., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemhöfer, H.-D.; Cammann, K. Specific Features of Electrochemical Sensors. In Sensors Set; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Weinhei, Germany, 1995; pp. 159–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, M.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J. Highly selective and stable glucose biosensor based on incorporation of platinum nanoparticles into polyaniline-montmorillonite hybrid composites. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, W. Label-free polygonal-plate fluorescent-hydrogel biosensor for ultrasensitive microRNA detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 306, 127554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, V.; Antonacci, A.; Arduini, F.; Moscone, D.; Campos, E.V.R.; Fraceto, L.F.; Palleschi, G. An eco-designed paper-based algal biosensor for nanoformulated herbicide optical detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Cheong, Y.H.; Ahamed, A.; Lisak, G. Heavy Metals Detection with Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Miranda Ferrari, A.; Carrington, P.; Rowley-Neale, S.J.; Banks, C.E. Recent advances in portable heavy metal electrochemical sensing platforms. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2676–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.-J. Fabrication of Ultrasensitive Field-Effect Transistor DNA Biosensors by a Directional Transfer Technique Based on CVD-Grown Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16953–16959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chand, R.; Kim, Y.-S. Microscale loop-mediated isothermal amplification of viral DNA with real-time monitoring on solution-gated graphene FET microchip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.-j.; Gu, B.; An, Q.-F.; Yang, C.; Guan, Y.L.; Yong, K.-T. Recent development of fiber-optic chemical sensors and biosensors: Mechanisms, materials, micro/nano-fabrications and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 376, 348–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lei, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W. Photoelectrochemical biosensor for acetylcholinesterase activity study based on metal oxide semiconductor nanocomposites. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.-P.; Hu, H.-M.; Liang, R.-P.; Qiu, J.-D. An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer biosensor for divalent mercury monitoring. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 856, 113494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, T.; Lim, K.; Sultan, M.T.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.; Ju, H.W.; Park, C.; Jang, M. The real-time monitoring of drug reaction in HeLa cancer cell using temperature/impedance integrated biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, D.; Ding, L.; Wen, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ding, C.; Wang, K. Oxygen vacancy enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of Bi2MoO6/B, N co-doped graphene for fabricating lincomycin aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, A.; Malhotra, B.D. Mediated biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, D.A.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 6th ed.; Thomson Brooks/Cole: Belmont, CA, USA, 2007; Available online: http://lib.ugent.be/catalog/rug01:001256198 (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- D’Orazio, P. Biosensors in clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 334, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, A.Q.; Sureshkumar, T.N.; Narayanan, R.; Sukeerthi, S.; Lal, R.; Srinivasa, R.S. Conducting polymer-based biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Städler, B.; Solak, H.H.; Frerker, S.; Bonroy, K.; Frederix, F.; Vörös, J.; Grandin, H.M. Nanopatterning of gold colloids for label-free biosensing. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggins, B.R. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Panneer Selvam, S.; Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Cho, S.; Yun, K. Differential Pulse Voltammetric Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Etidronic Acid in Pharmaceutical Samples by Using rGO-Ag@SiO2/Au PCB. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiseppi-Elie, A.; Lingerfelt, L. Impedimetric Detection of DNA Hybridization: Towards Near-Patient DNA Diagnostics. In Immobilisation of DNA on Chips I; Wittmann, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, D.; Hu, T.; Ni, Z. Screen-printed electrochemical biosensor based on a ternary Co@MoS2/rGO functionalized electrode for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.-A.; Chen, W.-Y. Field-Effect Transistor Biosensors for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Sensors 2019, 19, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, K.; Feng, Q.; Wang, C.; He, P. Acetylcholinesterase modified AuNPs-MoS2-rGO/PI flexible film biosensor: Towards efficient fabrication and application in paraoxon detection. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 131, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elugoke, S.E.; Adekunle, A.S.; Fayemi, O.E.; Mamba, B.B.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Carbon-Based Quantum Dots for Electrochemical Detection of Monoamine Neurotransmitters—Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqarni, S.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Ganash, A.A.; Khan, A. Composite Material–Based Conducting Polymers for Electrochemical Sensor Applications: A Mini Review. BioNanoScience 2020, 10, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.K.; Shiprath, K.; Ratnam, K.V.; Manjunatha, H.; Janardan, S.; Ratnamala, A.; Naidu, K.B.; Ramesh, S.; Babu, K.S. Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Tyrosine using Metal oxide (MO, M = Cu and Ni) Modified Graphite Electrode: A Comparative Study. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 6460–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Leonardi, S.G.; Sekar, C.; Ficarra, S.; Galtieri, A.; Tellone, E.; Neri, G. Detection of Catecholamine Neurotransmitters by Nanostructured SnO2-Based Electrochemical Sensors: A Review of Recent Progress. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2018, 15, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Bonavita, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G.; Sekar, C. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of epinephrine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using SnO2/graphene nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, N.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Bonavita, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G.; Sekar, C. Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, uric acid and folic acid based on Mn-SnO2 nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 770, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Spadaro, S.; Bonsignore, M.; Lavanya, N.; Sekar, C.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G.; Neri, F. Molybdenum oxide nanoparticles for the sensitive and selective detection of dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 814, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Wang, C. A novel dopamine sensor based on Mo doped reduced graphene oxide/polyimide composite membrane. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 685, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Gökce, B.; De Giacomo, A.; Meneghetti, M.; Compagnini, G.; Tommasini, M.; Waag, F.; Lucotti, A.; Zanchi, C.G.; Ossi, P.M.; et al. Nanoparticles Engineering by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Concepts and Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehru, L.; Chinnathambi, S.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Leonardi, S.G.; Bonavita, A.; Neri, G. Electrochemical Sensing of Serotonin by a Modified MnO2-Graphene Electrode. Biosensors 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Zhu, S.J.; Liu, X.; Fu, X.; Huo, W.C.; Liu, X.L.; Chen, Y.X.; Shan, Q.Y.; Yao, H.-C.; Zhang, Y.X. Phase and morphology controlled polymorphic MnO2 nanostructures for electrochemical energy storage. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 5322–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S.; Wu, Y.; Holze, R. Electrochemical Performance of MnO2 Nanorods in Neutral Aqueous Electrolytes as a Cathode for Asymmetric Supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14020–14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napi, M.L.M.; Sultan, S.M.; Ismail, R.; How, K.W.; Ahmad, M.K. Electrochemical-Based Biosensors on Different Zinc Oxide Nanostructures: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Ma, L.-X. One-pot facile fabrication of graphene-zinc oxide composite and its enhanced sensitivity for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Saha, S.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E.; Gupta, V.; Bhansali, S.; Singh, S.P. Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, M.; Mandal, S.; Manasreh, O. An Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Zinc Oxide Nanorods. Sensors 2015, 15, 18714–18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-H.; Chen, X.-J.; Li, W.-T.; Zhou, W.-H.; Guo, X.-C.; Kang, W.-Y.; Kou, D.-X.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Meng, Y.-N.; Tian, Q.-W.; et al. ZnO nanotubes supported molecularly imprinted polymers arrays as sensing materials for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Talanta 2018, 176, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Q.; Komori, K.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y.; Sakai, Y. Electrochemical biosensor for the detection of H2O2 from living cancer cells based on ZnO nanosheets. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 670, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychoyios, V.N.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Tzamtzis, N.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Psaroudakis, N.; Danielsson, B.; Israr, M.Q.; Willander, M. Potentiometric Cholesterol Biosensor Based on ZnO Nanowalls and Stabilized Polymerized Lipid Film. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, G. Synthesis of CuO/g-C3N4 composites, and their application to voltammetric sensing of glucose and dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2018, 186, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, K.V.; Manjunatha, H.; Janardan, S.; Babu Naidu, K.C.; Ramesh, S. Nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor based on metal oxide, MO (M = Cu, Ni, Zn, and Fe) nanomaterials for neurotransmitters: An abridged review. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandikumar, A.; Soon How, G.T.; See, T.P.; Omar, F.S.; Jayabal, S.; Kamali, K.Z.; Yusoff, N.; Jamil, A.; Ramaraj, R.; John, S.A.; et al. Graphene and its nanocomposite material based electrochemical sensor platform for dopamine. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 63296–63323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergman, J.; Mellander, L.; Wang, Y.; Cans, A.-S. Co-Detection of Dopamine and Glucose with High Temporal Resolution. Catalysts 2018, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Sudha, V.; Senthil Kumar, S.M.; Thangamuthu, R. Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid using copper oxide nano-rice modified electrode. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 748, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhai, T.; Hu, M.; Zhang, C.; Huang, K. Flower-like MoS2 decorated with Cu2O nanoparticles for non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose. Talanta 2017, 167, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hsu, J.-P.; Shen Wee, A.T.; Jiang, J. An ultra-sensitive electrochemical sensor based on 2D g-C3N4/CuO nanocomposites for dopamine detection. Carbon 2018, 130, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C.; Xing, Z.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets: A low-cost, green, and highly efficient electrocatalyst toward the reduction of hydrogen peroxide and its glucose biosensing application. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8921–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, H.; Cao, W.; Wen, Z.; Wang, J.; François-Xavier, C.P.; Wintgens, T. Cu-Al2O3-g-C3N4 and Cu-Al2O3-C-dots with dual-reaction centres for simultaneous enhancement of Fenton-like catalytic activity and selective H2O2 conversion to hydroxyl radicals. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 234, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridara, T.; Upan, J.; Saianand, G.; Tuantranont, A.; Karuwan, C.; Jakmunee, J. Non-Enzymatic Amperometric Glucose Sensor Based on Carbon Nanodots and Copper Oxide Nanocomposites Electrode. Sensors 2020, 20, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.; Kumara Swamy, B.E.; Jayadevappa, H. CuO nanoparticle sensor for the electrochemical determination of dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 61, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete-Rosales, P.; Ortega, V.; Álvarez-Lueje, A.; Bollo, S.; González, M.; Ansón, A.; Martínez, M.T. Influence of size and oxidative treatments of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on their electrocatalytic properties. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 62, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.-M.; Kim, D.; Jeon, S. Electrocatalytic reduction of H2O2 by Pt nanoparticles covalently bonded to thiolated carbon nanostructures. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 65, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Bonavita, A.; Fazio, E.; Stelitano, S.; Neri, G.; Neri, F.; Santangelo, S. Origin of the different behavior of some platinum decorated nanocarbons towards the electrochemical oxidation of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 184, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, L. A novel non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on poly-melamine film modified with platinum nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45185–45190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anithaa, A.C.; Asokan, K.; Sekar, C. Highly sensitive and selective serotonin sensor based on gamma ray irradiated tungsten trioxide nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anithaa, A.C.; Asokan, K.; Sekar, C. Low energy nitrogen ion beam implanted tungsten trioxide thin films modified indium tin oxide electrode based acetylcholine sensor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 84, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anithaaa, A.C.; Asokanb, K.; Sekara, C. Swift heavy nickel ion irradiated ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid-assisted tungsten trioxide thin film for the electrocatalytic detection of guanine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uktveris, T.; Jusas, V. Development of a Modular Board for EEG Signal Acquisition. Sensors 2018, 18, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.; Jeong, W.; Kang, I.-S.; Choi, K.-K.; Jaffery, S.H.A.; Ali, A.; Hussain, T.; Ayaz, M.; Hussain, S.; Jung, J. Highly Fast Response of Pd/Ta2O5/SiC and Pd/Ta2O5/Si Schottky Diode-Based Hydrogen Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, F.; Danza, L.; Meroni, I.; Pollastro, M.C. A Low-Cost Environmental Monitoring System: How to Prevent Systematic Errors in the Design Phase through the Combined Use of Additive Manufacturing and Thermographic Techniques. Sensors 2017, 17, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, J.C.; Spina, F.; Lugoda, P.; Garcia-Garcia, L.; Roggen, D.; Münzenrieder, N. Flexible Sensors—From Materials to Applications. Technologies 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imbault, A.; Wang, Y.; Kruse, P.; Strelcov, E.; Comini, E.; Sberveglieri, G.; Kolmakov, A. Ultrathin Gas Permeable Oxide Membranes for Chemical Sensing: Nanoporous Ta2O5 Test Study. Materials 2015, 8, 6677–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piro, B.; Tran, H.V.; Thu, V.T. Sensors Made of Natural Renewable Materials: Efficiency, Recyclability or Biodegradability—The Green Electronics. Sensors 2020, 20, 5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekonen, A.; Bergelin, M.; Johansson, M.; Kumar Joon, N.; Bobacka, J.; Viik, J. Bioimpedance Sensor Array for Long-Term Monitoring of Wound Healing from Beneath the Primary Dressings and Controlled Formation of H2O2 Using Low-Intensity Direct Current. Sensors 2019, 19, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





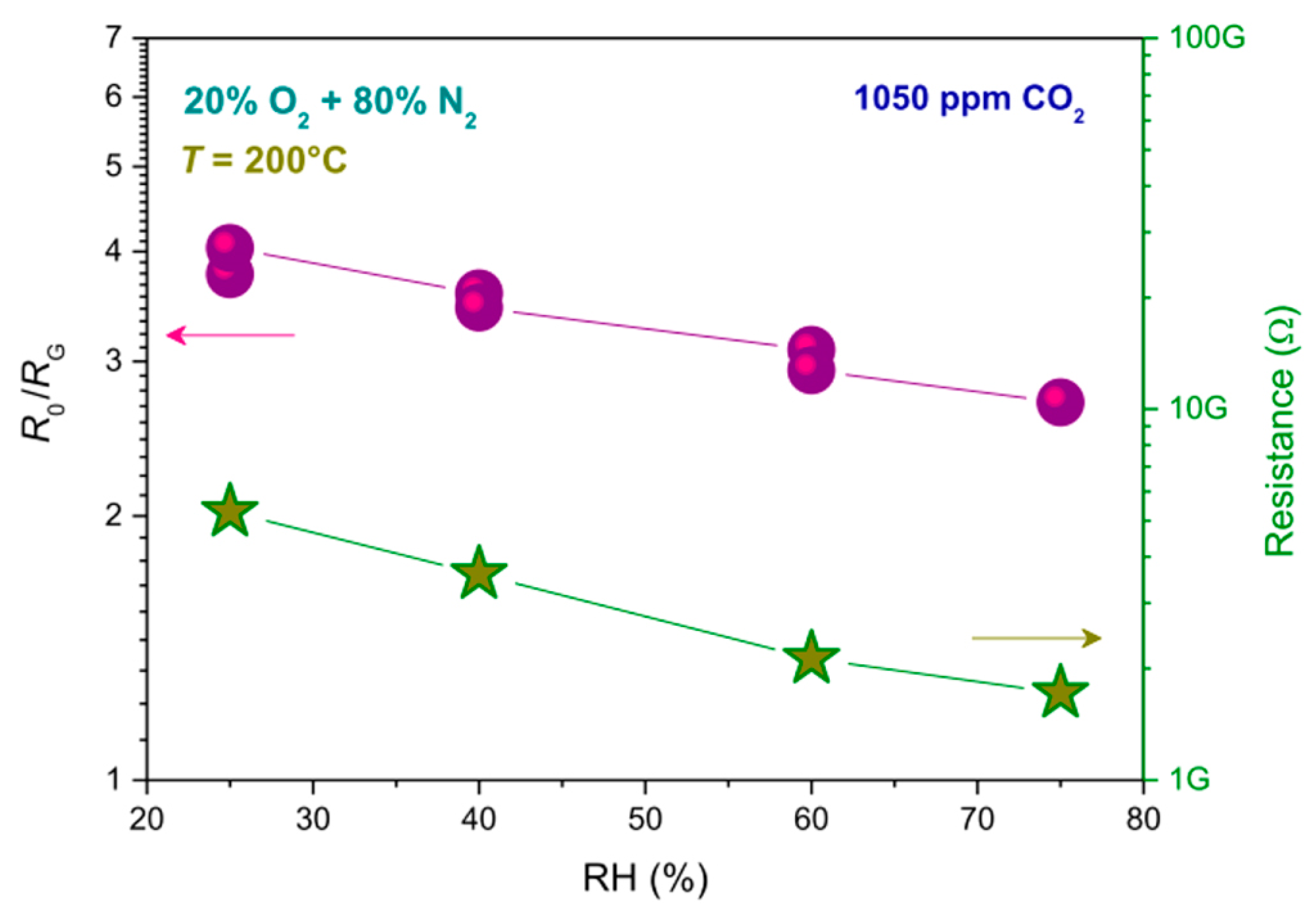










| Materials | Working Temperature (°C) | Concentration (ppm) | Response (Ra/Rg) | Response/Recovery Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnO2 nanowires | 150, 300 | 1000 | 6.5, 4.25 | -/- |
| Co-SnO2 nanofibers | 330 | 100 (1000) | 24 (~90) | 2/3 (-/-) |
| SnO2 nanowires | 300 | 1000 | 4.25 | -/- |
| SnO2 thin film | r.t. | 1000 | 26.5 | 192/95 |
| Pt/SnO2 thin film | 110 | 500 | 169 | 6/57 |
| Pd-SnO2/MoS2 composite | r.t. | 5000 | 1.22 | 30/20 |
| Pd-SnO2 thin film | 180 | 500 | 6.5 | -/- |
| Pd-SnO2 nanofibers | 280 | 100 (1000) | 8.2 (~26) | 9/9 (-/-) |
| Al-SnO2 nanofibers | 340 | 100 (1000) | 7.7 (~15) | 3/2 (-/-) |
| ZnO/SnO2 composite | 150 | 10,000 | 10 | 60/75 |
| SnO2/CNTs | 100 | 1000 | 1.55 | -/- |
| Au-SnO2 NPs | 250 | 100 (1000) | 25 (150) | 1/3 (-/-) |
| Eu-SnO2 NPs | 350 | 300 | 21 | 7/- |
| RGO-SnO2 nanofibers | 60 | 1000 | 1.3 | 119/265 |
| Co-SnO2 NPs | 250 | 2000 | 100 | 3/15 |
| Electrode | Linear Range (μM) | Detection Limit (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | UA | EP | UA | |
| Nano-diamond/graphite/PGE | 0.01–10 | 0.01–60 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| Nanofion-OMC/GCE | 0.5–200 | 0.25–100 | 0.2 | 0.07 |
| Poly(p-xylenolsulfo-nephthalein)/GCE | 2–390 | 0.1–560 | 0.1 | 0.08 |
| Electrochemically activated GCE | 1–40 | 1–55 | 0.089 | 0.16 |
| Caffeic acid/GCE | 2–80 | 5–300 | 20 | 60 |
| CNTs/Ru oxide/hexacyanoferrate/GCE | 0.1–10 | 0.90–250 | 0.087 | 0.052 |
| Graphene/SnO2/Au composite/GCE | 0.5–100 | 2–100 | 0.050 | 0.5 |
| SnO2/graphene/GCE | 0.5–200 | 0.1–200 | 0.017 | 0.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fazio, E.; Spadaro, S.; Corsaro, C.; Neri, G.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, F.; Lavanya, N.; Sekar, C.; Donato, N.; Neri, G. Metal-Oxide Based Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications in Electrical and Electrochemical Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072494
Fazio E, Spadaro S, Corsaro C, Neri G, Leonardi SG, Neri F, Lavanya N, Sekar C, Donato N, Neri G. Metal-Oxide Based Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications in Electrical and Electrochemical Sensors. Sensors. 2021; 21(7):2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072494
Chicago/Turabian StyleFazio, Enza, Salvatore Spadaro, Carmelo Corsaro, Giulia Neri, Salvatore Gianluca Leonardi, Fortunato Neri, Nehru Lavanya, Chinnathambi Sekar, Nicola Donato, and Giovanni Neri. 2021. "Metal-Oxide Based Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications in Electrical and Electrochemical Sensors" Sensors 21, no. 7: 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072494
APA StyleFazio, E., Spadaro, S., Corsaro, C., Neri, G., Leonardi, S. G., Neri, F., Lavanya, N., Sekar, C., Donato, N., & Neri, G. (2021). Metal-Oxide Based Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications in Electrical and Electrochemical Sensors. Sensors, 21(7), 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072494