Validation of Scolioscan Air-Portable Radiation-Free Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Assessment System for Scoliosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
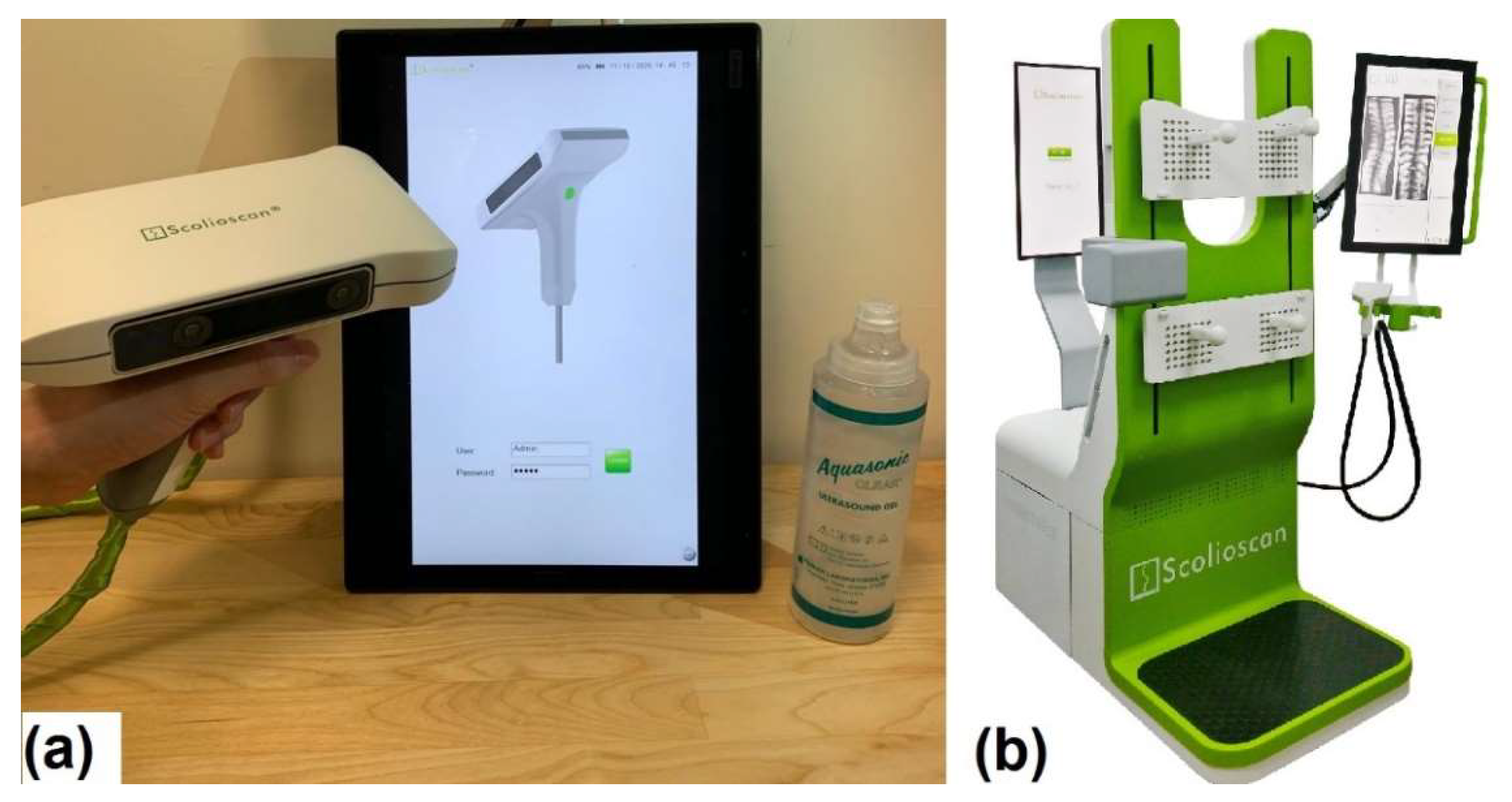
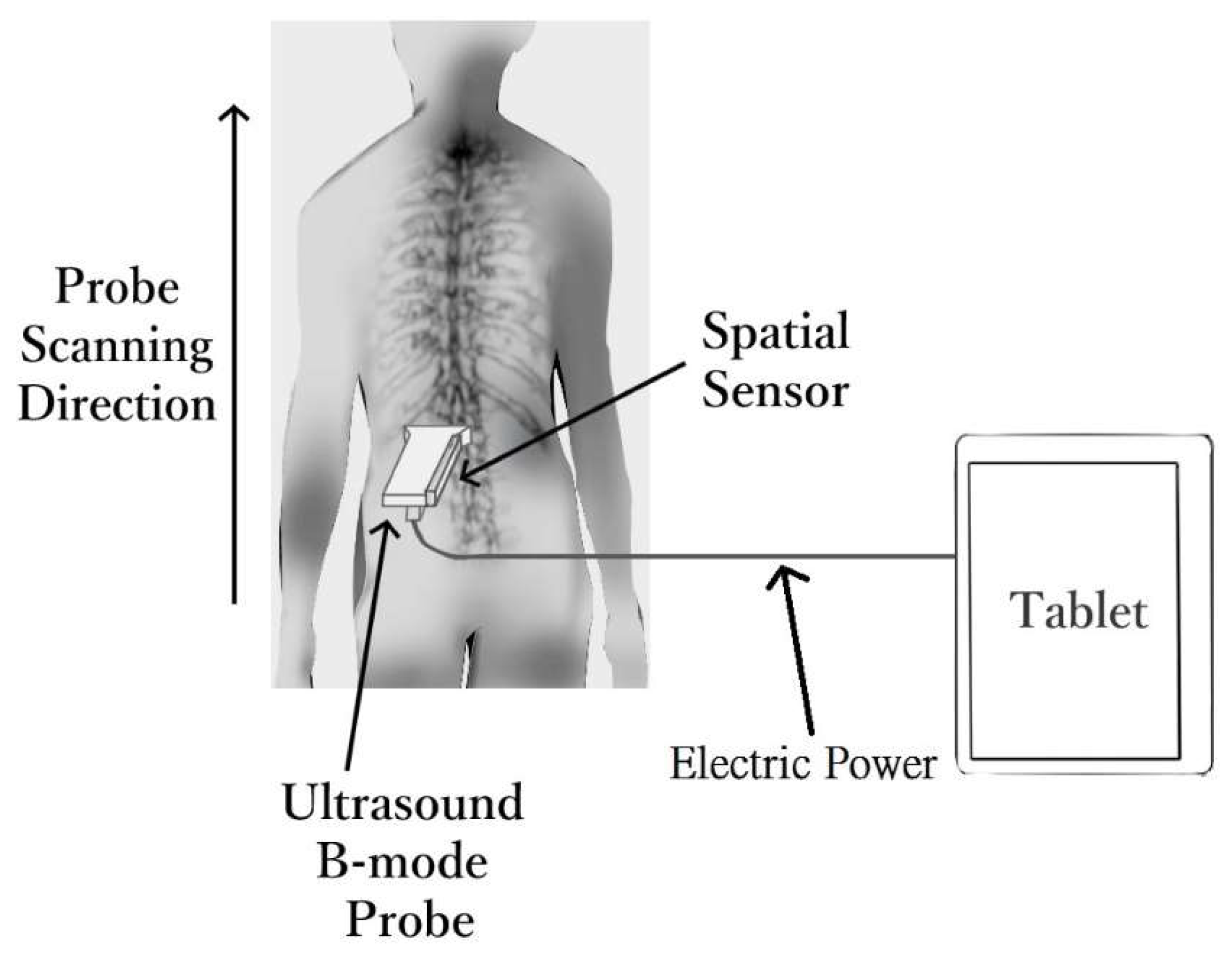
2.1. Scolioscan Air System
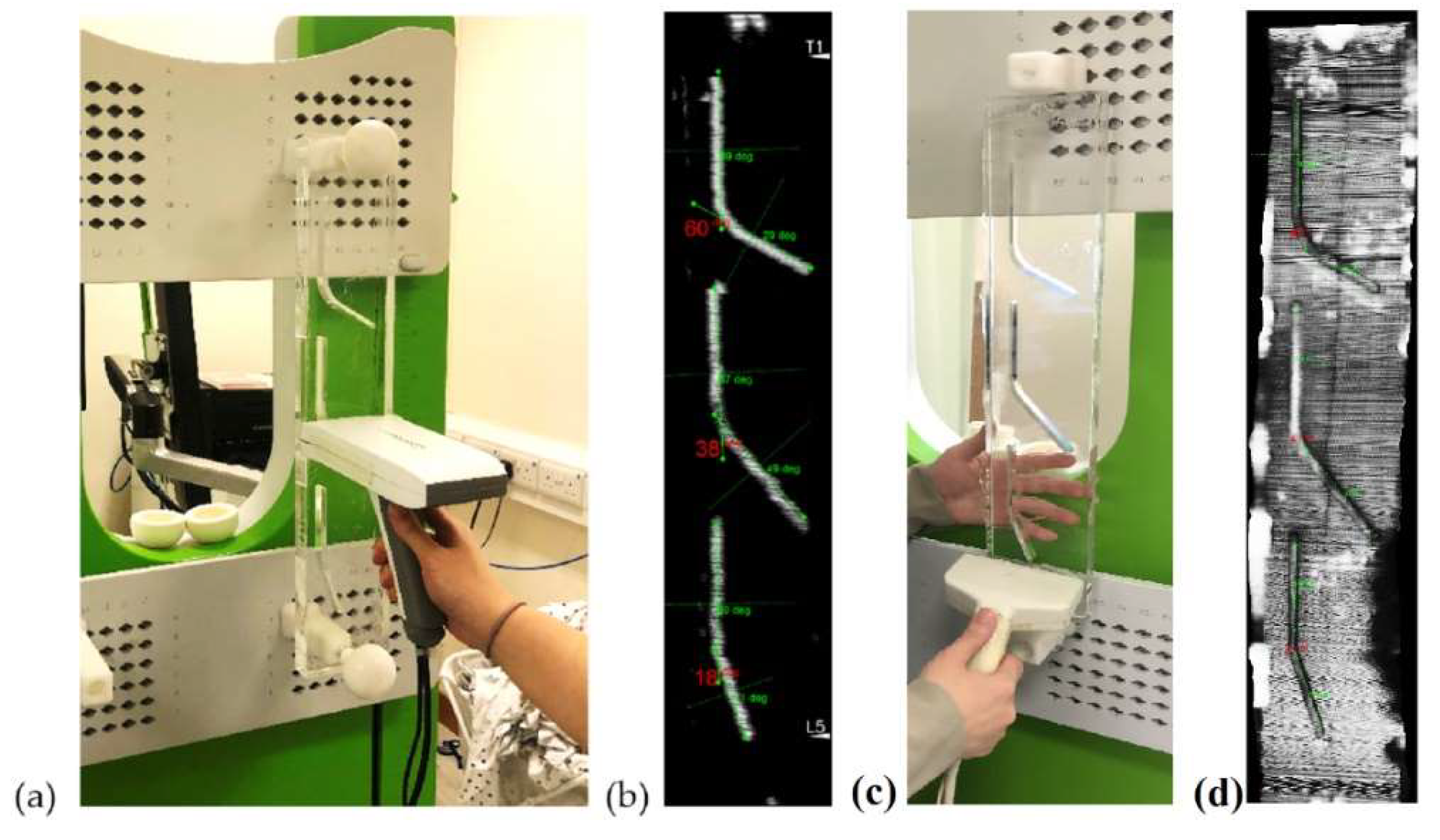
2.2. Tests for Angle Phantom
2.3. Subjects
2.4. Preparation for Subject
2.5. Subject Examination
2.6. Data Processing
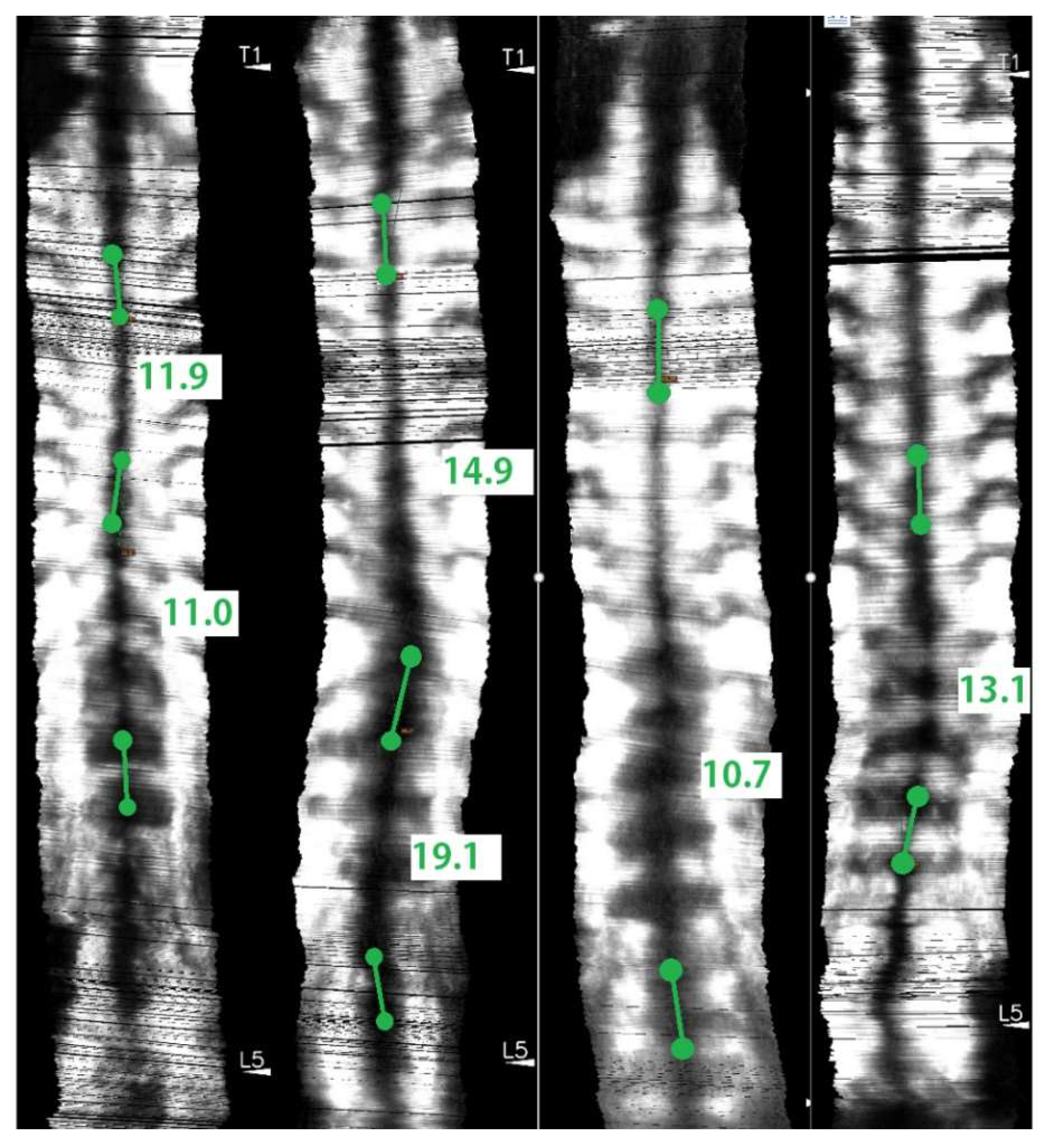
2.7. Angle Measurements and Study Design
2.8. Statistical Analysis
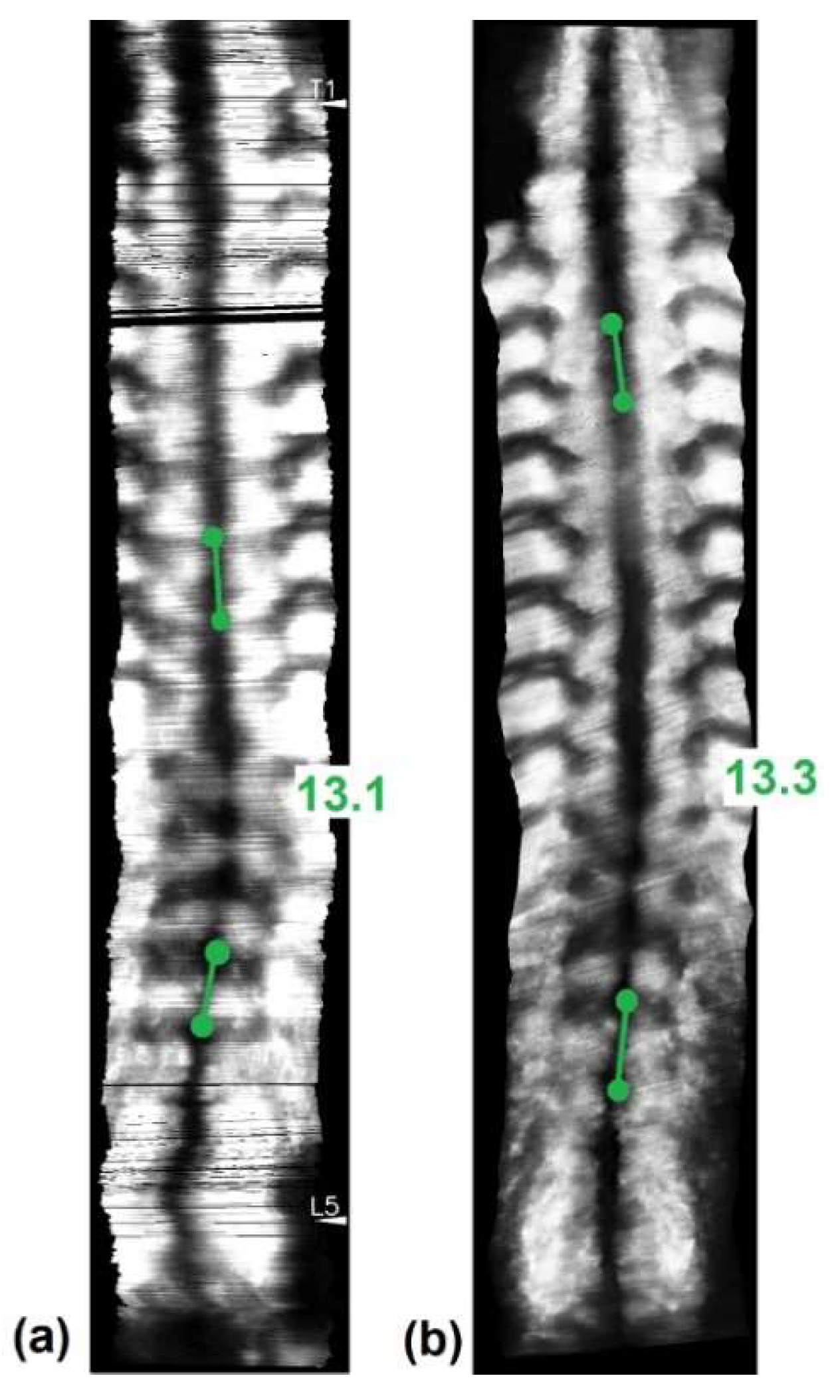
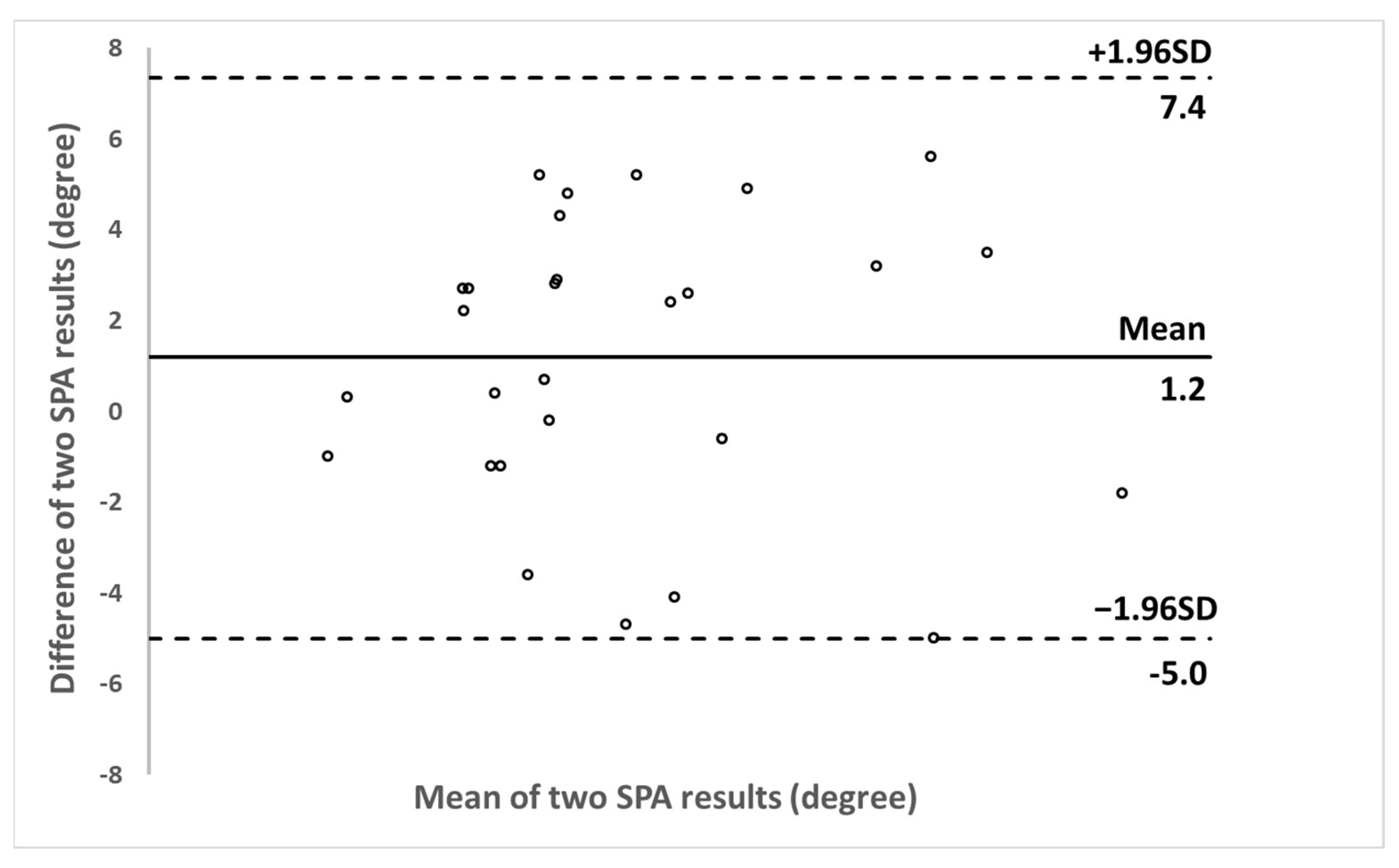
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brink, R.C.; Colo, D.; Schlösser, T.P.C.; Vincken, K.L.; Stralen, M.V.; Hui, S.C.N.; Shi, L.; Chu, W.C.W.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Castelein, R.M. Upright, prone, and supine spinal morphology and alignment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassella, M.C.; Hall, J.E. Current Treatment Approaches in the Nonoperative and Operative Management of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Phys. Ther. 1991, 71, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, M.R.; Senyurt, H.; Krauspe, R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, D.Y.T.; Cheung, K.M.C.; Wong, Y.W.; Wan, Y.Y.; Lee, C.F.; Lam, T.P.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Ng, B.K.W.; Luk, K.D.K. A population-based cohort study of 394,401 children followed for 10 years exhibits sustained effectiveness of scoliosis screening. Spine J. 2015, 15, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fok, Q.; Liu, P.Y.; Yip, J.; Cheung, M.; Yick, K.L.; Ng, S.P.; Tse, C.Y. School scoliosis screening in Hong Kong: Trunk asymmetry of girls with scoliosis. MOJOR 2020, 12, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.C.; Castelein, R.M.; Chu, W.C.C.; Danielsson, A.J.; Dobbs, M.B.; Grivas, T.B.; Gurnett, C.A.; Luk, K.D.; Moreau, A.; Newton, P.O.; et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer. 2015, 1, 15068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reamy, B.V.; Slakey, J.B. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Review and Current Concept. Am. Fam. Phys. 2001, 64, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huang, V.W.Y.; Yu, F.W.P.; Hung, A.L.H.; Ng, B.K.W.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Lam, T.P.; Yip, B.H.K. Persistent low-normal bone mineral density in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with different curve severity: A longitudinal study from presentation to beyond skeletal maturity and peak bone mass. Bone 2020, 133, 115217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.T.Y.; Lai, K.K.L.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Castelein, R.M.; Lam, T.P.; Zheng, Y.P. Investigation of the Phenomenon of Coronal-sagittal Curvature Coupling on Curve Progression: An Exploratory Study using Three-dimensional Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021. in print. [Google Scholar]
- Lonstein, J.E.; Carlson, J.M. The Prediction of Curve Progression in Untreated Idiopathic Scoliosis during Growth. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1984, 66, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Wu, Z.H.; Han, J.N. Scoliosis on Pulmonary Function. Acta Acad. Med. Sin. 2011, 33, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H. Left Ventricular Mechanics Assessed by 2-dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in Children and Adolescents With Idiopathic Scoliosis. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E381–E389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Xuan, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z. Effects of Specific Exercise Therapy on Adolescent Patients With Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Prospective Controlled Cohort Study. Spine 2020, 45, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, T.; Astur, N.; Jones, T.L.; Perake, V.; Moisan, A.; Warner, W.C.; Sawyer, J.R.; Kelly, D.M. The Risk of Curve Progression and Surgery in African Americans with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2017, 5, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, T.L.; Hierholzer, E.; Boerke, A.; Lerner, T.; Liljenqvist, U.; Bullmann, V.; Hackenberg, L. Raster Stereography versus Radiography in the Long-term Follow-up of Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2008, 21, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Lu, X.; Qiu, Q.; Nie, G.; Huang, Y. Association between Incorrect Posture and Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Among Chinese Adolescents: Findings From a Large-Scale Population-Based Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, E.S.; Yoon, C.S.; Chung, T.S.; Song, H.T.; Suh, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S. Scoliosis Imaging: What Radiologists Should Know. Radiographics 2010, 30, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, J.R. The problem of the primary curve. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1960, 42A, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucacos, P.N.; Zacharis, K.; Gelalis, J.; Soultanis, K.; Kalos, N.; Beris, A.; Xenakis, T.; Johnson, E.O. Assessment of curve progression in Idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 1998, 7, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.A.; Lonstein, J.E.; Morin, M.M.; Visscher, W.; Harris, B.S., 3rd; Boice, J.D., Jr. Breast cancer in women with scoliosis exposed to multiple diagnostic x rays. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, M.M.; Lonstein, J.E.; Stovall, M.; Hacker, D.G.; Luckyanov, N.; Land, C.E. Breast cancer mortality after diagnostic radiography: Findings from the U.S. Scoliosis Cohort Study. Spine 2000, 25, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simony, A.; Hansen, E.J.; Christensen, S.B.; Carreon, L.Y.; Andersen, M.O. Incidence of cancer in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients treated 25 years previously. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3366–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Feuerhake, I.; Pflugbeil, S. Lifestyle’ and cancer rates in former East and West Germany: The possible contribution of diagnostic radiation exposures. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2011, 147, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijer, H.; Beckman, K.W.; Jonsson, B.; Andersson, T.; Persliden, J. Digital radiography of scoliosis with a scanning method: Initial evaluation. Radiography 2001, 218, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.R.; Goldberg, M.S.; Hanley, J.A.; Mayo, N.E.; Poitras, B. Projecting the Lifetime Risk of Cancer from Exposure to Diagnostic Ionizing Radiation for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Health Phys. 1994, 66, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, C.; Wade, R.; Faria, R.; Yang, H.; Stirk, L.; Gummerson, N.; Woolacott, N. EOS 2D/3D X-ray imaging system: A systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. Rep. 2012, 16, 1–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, J.; Germann, T.; Akbar, M.; Pepke, W.; Kauczor, H.U.; Weber, M.A.; Spira, D. 3D-modeling of the spine using EOS imaging system: Inter-reader reproducibility and reliability. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergari, C.; Gajny, L.; Courtois, I.; Ebermeyer, E.; Abelin-Genevois, K.; Kim, Y.; Langlais, T.; Vialle, R.; Assi, A.; Ghanem, I.; et al. Quasi-automatic early detection of progressive idiopathic scoliosis from biplanar radiography: A preliminary validation. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.J.; Kaliszer, M.; Moore, D.P.; Fogarty, E.E.; Dowling, F.E. Surface topography, Cobb angles, and cosmetic change in scoliosis. Spine 2001, 26, E55–E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Y.; Bettany-Saltikov, J. Imaging in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Children with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Open Orthop. J. 2017, 11, 1500–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adankon, M.M.; Chihab, N.; Dansereau, J.; Labelle, H.; Cheriet, F. Scoliosis follow-up using noninvasive trunk surface acquisition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komeili, A.; Westover, L.; Parent, E.C.; El-Rich, M.; Adeeb, S. Monitoring for idiopathic scoliosis curve progression using surface topography asymmetry analysis of the torso in adolescents. Spine J. 2015, 15, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, P.; Sturm, P.; Lonner, B.; Cahill, P.; Betsch, M.; McCarthy, R.; Kelly, M.; Lenke, L.; Betz, R. Multicenter Comparison of 3D Spinal Measurements Using Surface Topography With Those From Conventional Radiography. Spine Deform. 2016, 4, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betsch, M.; Wild, M.; Rath, B.; Tingart, M.; Schulze, A.; Quack, V. Radiation-free diagnosis of scoliosis: An overview of the surface and spine topography. Der Orthopäde 2015, 44, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girdler, S.; Cho, B.; Mikhail, C.M.; Cheung, Z.B.; Maza, N.; Kang-Wook, C.S. Emerging Techniques in Diagnostic Imaging for Idiopathic Scoliosis in Children and Adolescents: A Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2020, 136, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, T.; Baker, M.; Breakwell, L.L.; Cole, A.; Hughes-Lawson, C.; Naylor, B.; Michael, A. Correlation of rotation parameters in scoliosis between radiographs and DIERS Formetric Scans. Bone Joint J. 2014, 96B, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bassani, T.; Stucovitz, E.; Galbusera, F.; Brayda-Bruno, M. Is rasterstereography a valid noninvasive method for the screening of juvenile and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizah, M.Z.; Ng, K.L.; Te, B.C.; Mohd-Hafizuddin, A.; Nur-Aifaa, L.; Nurhanisah, M.R.; Azmi, B.; Hamzaini, A.H. Association of Cobb angle progression and neuraxial abnormality on MRI in asymptomatic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Med. J. Malays. 2016, 71, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Labrom, F.R.; Izatt, M.T.; Contractor, P.; Grant, C.A.; Pivonka, P.; Askin, G.N.; Labrom, R.D.; Little, J.P. Sequential MRI reveals vertebral body wedging significantly contributes to coronal plane deformity progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Spine Deform. 2020, 8, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jada, A.; Mackel, C.E.; Hwang, S.W.; Samdani, A.F.; Stephen, J.H.; Bennett, J.T.; Baaj, A.A. Evaluation and management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A review. Neurosurg. Focus. 2017, 43, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungi, T.; King, F.; Kempston, M.; Keri, Z.; Lasso, A.; Mousavi, P.; Rudan, J.; Borschneck, D.P.; Fichtinger, G. Spinal Curvature Measurement by Tracked Ultrasound Snapshots. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Yamamuro, T.; Shikata, J.; Shimizu, K.; Iida, H. Ultrasound measurement of vertebral rotation in idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1989, 71, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.H.; Zheng, Y.P.; Li, R.; Lu, M.H. 3-D measurement of body tissues based on ultrasound images with 3D spatial information. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2005, 31, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, Q.H.; Zheng, Y.P.; Lu, M.H.; Chi, Z.R. Development of a porTable 3D ultrasound imaging system for musculoskeletal tissues. Ultrasonics 2005, 43, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, J.; Ying, M.; Ng, B.; Zheng, Y.P.; Lam, T.P.; Wong, W.Y.; Wong, M.S. Could clinical ultrasound improve the fitting of spinal orthosis for the patients with AIS? Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lou, E.H.M.; Zhang, P.Q.; Le, L.H.; Hill, D. Reliability of assessing the coronal curvature of children with scoliosis by using ultrasound images. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.W.; Law, S.Y.; Zheng, Y.P. Development of 3-D ultrasound system for assessment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): And system validation. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6474–6477. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, C.W.J.; Zhou, G.Q.; Law, S.Y.; Lai, K.L.; Jiang, W.W.; Zheng, Y.P. Freehand three-dimensional ultrasound system for assessment of scoliosis. J. Orthop. Translat. 2015, 3, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.W.J.; Zhou, G.Q.; Law, S.Y.; Mak, T.M.; Lai, K.L.; Zheng, Y.P. Ultrasound Volume Projection Imaging for Assessment of Scoliosis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, J.; Ying, M.; Ng, B.; Lam, T.P.; Wong, M.S. A Preliminary Study of Estimation of Cobb’s Angle From the Spinous Process Angle Using a Clinical Ultrasound Method. Spine Deform. 2015, 3, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Deng, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Scoliotic imaging with a novel double-sweep 2.5-dimensional extended field-of-view Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2019, 66, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Sakaura, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Nagamoto, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Sugamoto, K. In vivo three-dimensional segmental analysis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.P.; Lee, T.T.Y.; Lai, K.K.L.; Yip, B.H.; Zhou, G.Q.; Jiang, W.W.; Cheung, J.C.W.; Wong, M.S.; Ng, B.K.W.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; et al. A reliability and validity study for Scolioscan: A radiation-free scoliosis assessment system using 3D ultrasound imaging. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2016, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, R.C.; Wijdicks, S.P.J.; Tromp, I.N.; Schlösser, T.P.C.; Kruyt, M.C.; Beek, F.J.A.; Castelein, R.M. A reliability and validity study for different coronal angles using ultrasound imaging in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2018, 18, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.S.; Lai, K.K.L.; Zheng, Y.P.; Wong, L.L.; Ng, B.K.W.; Hung, A.L.H.; Yip, B.H.K.; Chu, W.C.W.; Ng, A.W.H.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Is Radiation-Free Ultrasound Accurate for Quantitative Assessment of Spinal Deformity in Idiopathic Scoliosis (IS): A Detailed Analysis With EOS Radiography on 952 Patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2866–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.T.Y.; Jiang, W.W.; Cheng, C.L.K.; Lai, K.K.L.; Castelen, R.M.; To, M.K.T.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; Zheng, Y.P. A novel method to measure the sagittal curvature in spinal deformities: The reliability and feasibility of 3D ultrasound Imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.W.; Cheng, C.L.K.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; Samartzis, D.; Lai, K.K.L.; To, M.K.T.; Zheng, Y.P. Patterns of coronal curve change in forward bending posture: A 3D ultrasound study of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lee, T.T.Y.; Lai, K.K.L.; Wong, Y.S.; Wong, L.N.; Yang, J.L.; Lam, T.P.; Castelein, R.M.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; Zheng, Y.P. A novel classification method for mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using 3D ultrasound imaging. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2021. in print. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Wong, Y.S.; Yip, B.H.H.; Hung, A.L.H.; Chu, W.C.W.; Lai, K.K.L.; Zheng, Y.P.; Chung, T.W.H.; Sharma, G.; Cheng, J.C.Y.; et al. Using ultrasound for screening scoliosis to reduce unnecessary radiographic radiation-A prospective diagnostic accuracy study on 442 schoolchildren. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021. in print. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, R.; Lou, E.; Le, L.H. Compact and Wireless Freehand 3D Ultrasound Real-time Spine Imaging System: A pilot study. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 2105–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Desain, C. Validation for Medical Device and Diagnostic Manufacturers. J. Clin. Eng. 1996, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, D.; Hüske, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Cui, X.W.; Dong, Y.; Lim, A.; Jenssen, C.; Löwe, A.; Koch, J.; Dietrich, C.F. Ultrasound Image Optimization (“Knobology”): B-Mode. Ultrasound Int. Open 2020, 6, E14–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, N.; di Bernardo, E.; Ostrowski, J.; Goncalves, L.; Pirjanian, P.; Munich, M.E. The vSLAM Algorithm for Robust Localization and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, H.R.; Negrini, S.; Rigo, M.; Kotwicki, T.; Hawes, M.C.; Grivas, T.B.; Maruyama, T.; Landauer, F. Indications for conservative management of scoliosis (guidelines). Scoliosis 2006, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiligiannis, T.; Grivas, T. Pulmonary function in children with idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis 2012, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Ling, S.H.; Banerjee, S.; Zheng, J.J.Y.; Lai, K.L.; Yang, D.; Zheng, Y.P.; Su, S. 3D Ultrasound Spine Image Selection Using Convolution Learning-to-Rank Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 4799–4802. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, B.; Trapp, R.G. Basic and Clinical Biostatistics, 4th ed.; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- De Reuver, S.; Brink, R.C.; Lee, T.T.Y.; Zheng, Y.P.; Beek, F.J.A.; Castelein, R.M. Cross-validation of ultrasound imaging in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2020. in print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, C.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Huang, Y.C. A Single-Chip High-Voltage Integrated Actuator for Biomedical Ultrasound Scanners. Sensors 2019, 19, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lam, K.H.; Zhou, D.; Yue, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Qiu, W.; Un, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, H.; et al. High Performance Relaxor-Based Ferroelectric Single Crystals for Ultrasonic Transducer Applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 13730–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amzallag-Bellenger, E.; Uyttenhove, F.; Nectoux, E.; Moraux, A.; Bigot, J.; Herbaux, B.; Boutry, N. Idiopathic scoliosis in children and adolescents: Assessment with a biplanar X-ray device. Insights Imaging 2014, 5, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.T.; Pugely, A.J.; Gao, Y.; Mendoza-Lattes, S.A.; Ilgenfritz, R.M.; Callaghan, J.J.; Weinstein, S.L. Increasing hospital charges for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in the United States. Spine 2014, 39, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Scoliosis Foundation. Available online: https://www.scoliosis.org/info.php (accessed on 9 April 2021).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, K.K.-L.; Lee, T.T.-Y.; Lee, M.K.-S.; Hui, J.C.-H.; Zheng, Y.-P. Validation of Scolioscan Air-Portable Radiation-Free Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Assessment System for Scoliosis. Sensors 2021, 21, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082858
Lai KK-L, Lee TT-Y, Lee MK-S, Hui JC-H, Zheng Y-P. Validation of Scolioscan Air-Portable Radiation-Free Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Assessment System for Scoliosis. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082858
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Kelly Ka-Lee, Timothy Tin-Yan Lee, Michael Ka-Shing Lee, Joseph Chi-Ho Hui, and Yong-Ping Zheng. 2021. "Validation of Scolioscan Air-Portable Radiation-Free Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Assessment System for Scoliosis" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082858
APA StyleLai, K. K.-L., Lee, T. T.-Y., Lee, M. K.-S., Hui, J. C.-H., & Zheng, Y.-P. (2021). Validation of Scolioscan Air-Portable Radiation-Free Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Assessment System for Scoliosis. Sensors, 21(8), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082858





