Path Planning for Wheeled Mobile Robot in Partially Known Uneven Terrain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Environmental Modeling and Problem Formulation
2.1. Digital Representation of 3D DEM
2.2. Information Extraction of a Partially Known Uneven Terrain Environment
2.3. Objective Function
2.4. Robot Kinematic Model
3. Path Planning Algorithm for Mobile Robot
3.1. A Algorithm for Global Path Planning
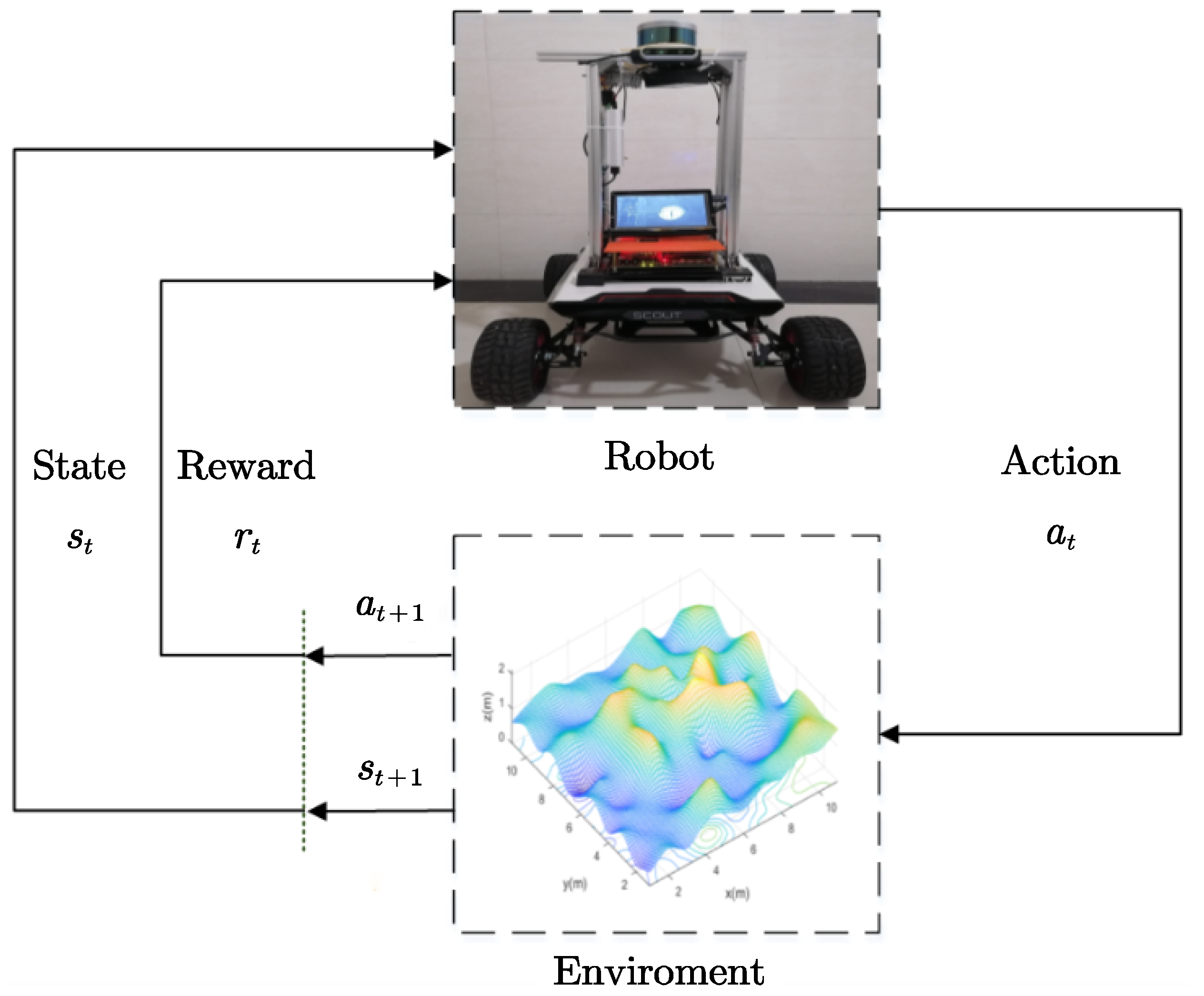
3.2. Q-Learning Based Local Path Planning Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Q-learning algorithm |
Initialize, ·
|
4. Simulation and Experimental Tests
4.1. Global Path Planning Based on A Algorithm
4.2. Local Path Planning Based on Q-Learning Algorithm
4.3. Experimental Test
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spenko, M.; Iagnemma, D.; Dubowsky, S. High speed hazard avoidance for mobile robots in rough terrain. Unmanned Ground Veh. Technol. VI 2004, 5422, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, W.; Gou, S.; Peng, M.; Liu, Z.; Di, K.; Li, L.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, X. Vision-based decision support for rover path planning in the Chang’e-4 Mission. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- [EB/OL]. Available online: http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/MPF/index1.html (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Liang, H.; Bai, H.; Sun, R.; Sun, R.; Li, C. Three-dimensional path planning based on DEM. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 5980–5987. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis, E.; Allard, P.; Bakambu, J.; Lamarche, T.; Zhu, W.H.; Rekleitis, I. Towards autonomous long-range navigation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space, Munich, Germany, 5–8 September 2005; pp. 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Vandapel, N.; Huber, D.F.; Kapuria, A.; Hebert, M. Natural terrain classification using 3-d ladar data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA’04, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 5117–5122. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, M.; Konolige, K.; Bolles, R.C. Localization and Mapping for Autonomous Navigation in Outdoor Terrains: A Stereo Vision Approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV’07), Austin, TX, USA, 20–21 February 2007; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, D.; Carmichael, O.; Hebert, M. 3D map reconstruction from range data. In Proceedings of the 2000 ICRA, Millennium Conference, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 891–897. [Google Scholar]
- Stentz, A. Optimal and efficient path planning for partially known environments. In Intelligent Unmanned Ground Vehicles; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 203–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, P.E.; Nilsson, N.J.; Raphael, B.A. Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaValle, S.M.; Kuffner, J.J. Randomized Kinodynamic Planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. In Autonomous Robot Vehicles; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Dynamic path planning algorithm for a mobile robot based on visible space and an improved genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Tian, X.; Gao, M. An improved ant colony algorithm for robot path planning. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 5829–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chou, W. Path planning for mobile robot using self-adaptive learning particle swarm optimization. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2018, 61, 052204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaradat, M.A.K.; Al-Rousan, M.; Quadan, L. Reinforcement based mobile robot navigation in dynamic environment. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2011, 27, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Xu, X. 2D and 3D Robot path planning based on the A⋆ algorithm. J. Jinggangshan Univ. (Natural Sci.) 2015, 36, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, M.; Cui, J.; Xie, S. Obstacle avoidance planning based on artificial potential field optimized by point of tangency in three-dimensional space. J. Syst. Simul. 2014, 26, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Wu, X.; Hou, X.; Feng, Y. Global path planning based on genetic-ant hybrid algorithm for AUV. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 45, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Josef, S.; Degani, A. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Safe Local Planning of a Ground Vehicle in Unknown Rough Terrain. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6748–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Peng, X.Z. Autonomous quadrotor navigation with vision based obstacle avoidance and path planning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 102450–102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, P.G.; Thinh, N.T. Real-time hybrid navigation system-based path planning and obstacle avoidance for mobile robots. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dou, W. A parallel algorithm of path planning for DEM terrain data. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Applications for Business Engineering and Science (DCABES), Wuxi, China, 19–23 October 2018; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrane, A.; Braham, A.C.; Cherki, B. UAV Path Planning Based on Dynamic Programming Algorithm On Photogrammetric DEMs. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Bandung, Indonesia, 23–24 September 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wermelinger, M.; Fankhauser, P.; Diethelm, R.; Krüsi, P.; Siegwart, R.; Hutter, M. Navigation planning for legged robots in challenging terrain. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 1184–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Rösmann, C.; Hoffmann, F.; Bertram, T. Kinodynamic trajectory optimization and control for car-like robots. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5681–5686. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Fang, X.; Wu, S. 2.5 D Navigation Graph and Improved A-Star Algorithm for Path Planning in Ship inside Virtual Environment. In Proceedings of the 2020 Prognostics and Health Management Conference (PHM-Besançon), Besancon, France, 4–7 May 2020; pp. 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, K.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R. Model based path planning using Q-Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–25 March 2017; pp. 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Fu, H. On Local Path Planning for the Mobile Robot based on QL Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; pp. 5293–5298. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D.; Li, M. Application of deep reinforcement learning in mobile robot path planning. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 7112–7116. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yao, Z.; Wu, B.; Ling, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J. Research On Path Planning Of Hull Decontamination Robot Based On Q-Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL), Chongqing, China, 10–12 July 2020; pp. 338–341. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, U.; Malmathanraj, R.; Srivastav, C. Simulation for path planning of autonomous underwater vehicle using flower pollination algorithm, genetic algorithm and Q-learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Cognitive Computing and Information Processing (CCIP), Noida, India, 3–4 March 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Triharminto, H.H.; Wahyunggoro, O.; Adji, T.B.; Cahyadi, A.I. An integrated artificial potential field path planning with kinematic control for nonholonomic mobile robot. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2016, 6, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Algorithm | Weight | Running | Path | Feasible |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w | Time (s) | Cost f | Times | |
| Classical A | 0 | 1.42 | 34.33 | 3 |
| Improved A | 0.2 | 1.31 | 28.12 | 10 |
| 0.5 | 1.73 | 31.24 | 10 | |
| 1 | 1.81 | 32.17 | 10 | |
| 2 | 1.89 | 35.27 | 10 | |
| 4 | 1.96 | 38.24 | 10 | |
| 5 | 2.15 | 39.51 | 10 |
| Scenarios | Local Path | Weight | Running | Path |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planning Algorithm | w | Time (s) | Cost f | |
| Scenario 1 | Q-learning | 1 | 3.06 | 29.95 |
| APF | - | 1.45 | 34.76 | |
| Classical A | 0 | 0.26 | 37.98 | |
| Improved A | 0.2 | 0.22 | 31.23 | |
| 0.5 | 0.24 | 31.78 | ||
| 1 | 0.28 | 32.15 | ||
| 2 | 0.33 | 33.45 | ||
| 4 | 0.45 | 34.25 | ||
| 5 | 0.58 | 35.12 | ||
| Scenario 2 | Q-learning | 1 | 2.31 | 20.36 |
| APF | - | 1.25 | 28.67 | |
| Classical A | 0 | 0.23 | 32.82 | |
| Improved A | 0.2 | 0.16 | 23.51 | |
| 0.5 | 0.16 | 24.18 | ||
| 1 | 0.17 | 24.97 | ||
| 2 | 0.19 | 25.82 | ||
| 4 | 0.21 | 26.48 | ||
| 5 | 0.25 | 27.69 | ||
| Scenario 3 | Q-learning | 1 | 3.21 | 35.25 |
| APF | - | 1.35 | 42.32 | |
| Classical A | 0 | 0.31 | 43.58 | |
| Improved A | 0.2 | 0.26 | 39.51 | |
| 0.5 | 0.26 | 40.24 | ||
| 1 | 0.28 | 40.95 | ||
| 2 | 0.31 | 41.46 | ||
| 4 | 0.42 | 43.65 | ||
| 5 | 0.49 | 44.28 | ||
| Scenario 4 | Q-learning | 1 | 2.75 | 23.59 |
| APF | - | 1.14 | 27.18 | |
| Classical A | 0 | 0.28 | 31.57 | |
| Improved A | 0.2 | 0.19 | 27.96 | |
| 0.5 | 0.20 | 28.53 | ||
| 1 | 0.22 | 29.37 | ||
| 2 | 0.24 | 30.92 | ||
| 4 | 0.28 | 32.51 | ||
| 5 | 0.31 | 33.24 |
| Exp | Start Position | Goal Position | Obstacle 1 | Obstacle 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp 1 | (7.5, 7.5, 0) | (1.5, 7.5, 0.23) | (2.5, 3.5, 0.37) | - |
| Exp 2 | (7.5, 7.5, 0) | (2.5, 3.5, 0.37) | (7, 6.5, 0.02) | (5, 5.5, 0.18) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Li, G.; Zheng, Q.; Bai, X.; Ding, Y.; Khan, A. Path Planning for Wheeled Mobile Robot in Partially Known Uneven Terrain. Sensors 2022, 22, 5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145217
Zhang B, Li G, Zheng Q, Bai X, Ding Y, Khan A. Path Planning for Wheeled Mobile Robot in Partially Known Uneven Terrain. Sensors. 2022; 22(14):5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145217
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Guobin Li, Qixin Zheng, Xiaoshan Bai, Yu Ding, and Awais Khan. 2022. "Path Planning for Wheeled Mobile Robot in Partially Known Uneven Terrain" Sensors 22, no. 14: 5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145217
APA StyleZhang, B., Li, G., Zheng, Q., Bai, X., Ding, Y., & Khan, A. (2022). Path Planning for Wheeled Mobile Robot in Partially Known Uneven Terrain. Sensors, 22(14), 5217. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145217







