Rapid Identification of Beached Marine Plastics Pellets Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: A Promising Tool for the Quantification of Coastal Pollution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. LIBS Classification of the Plastic Samples
3.2. Metal Analysis
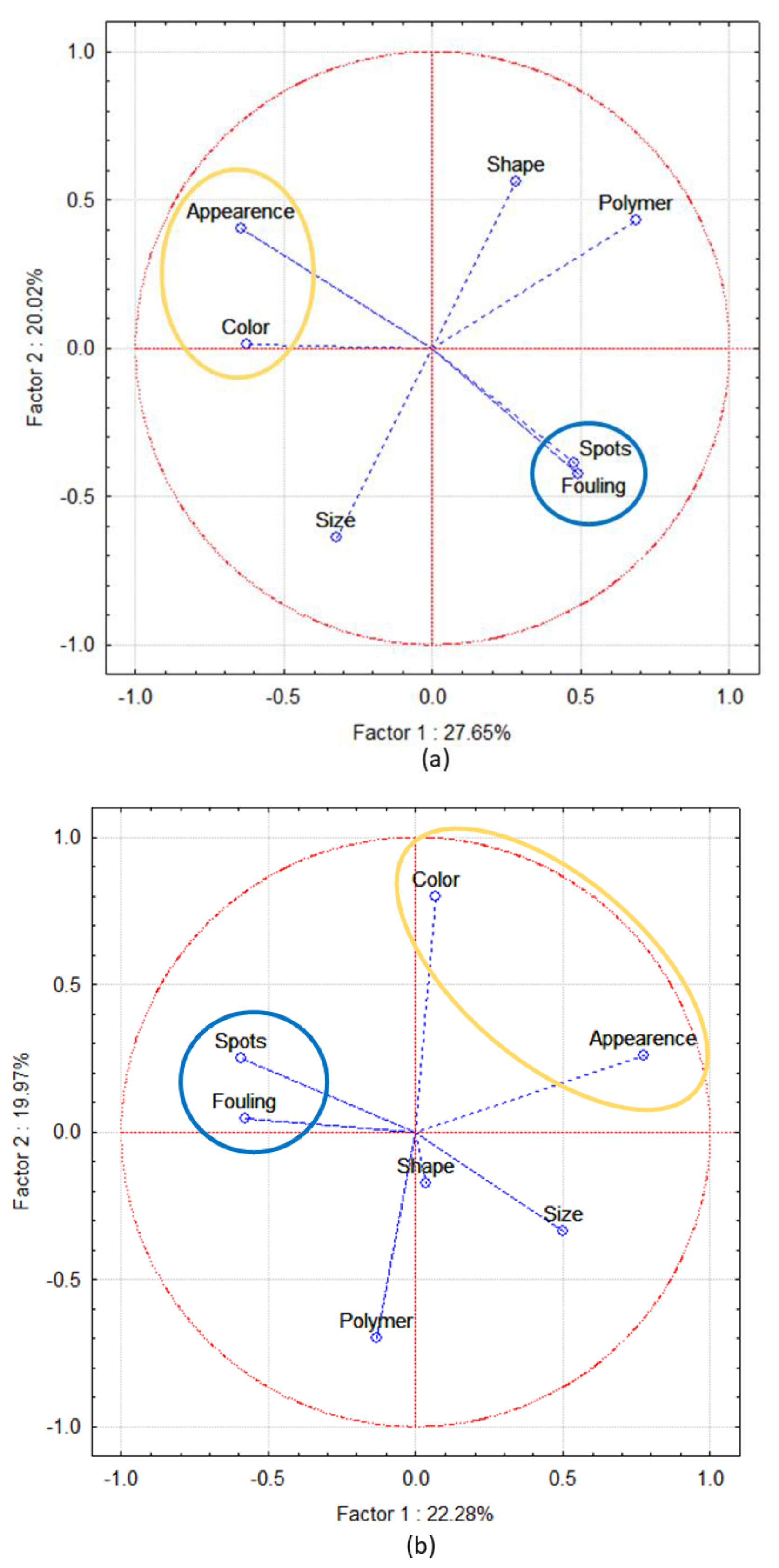
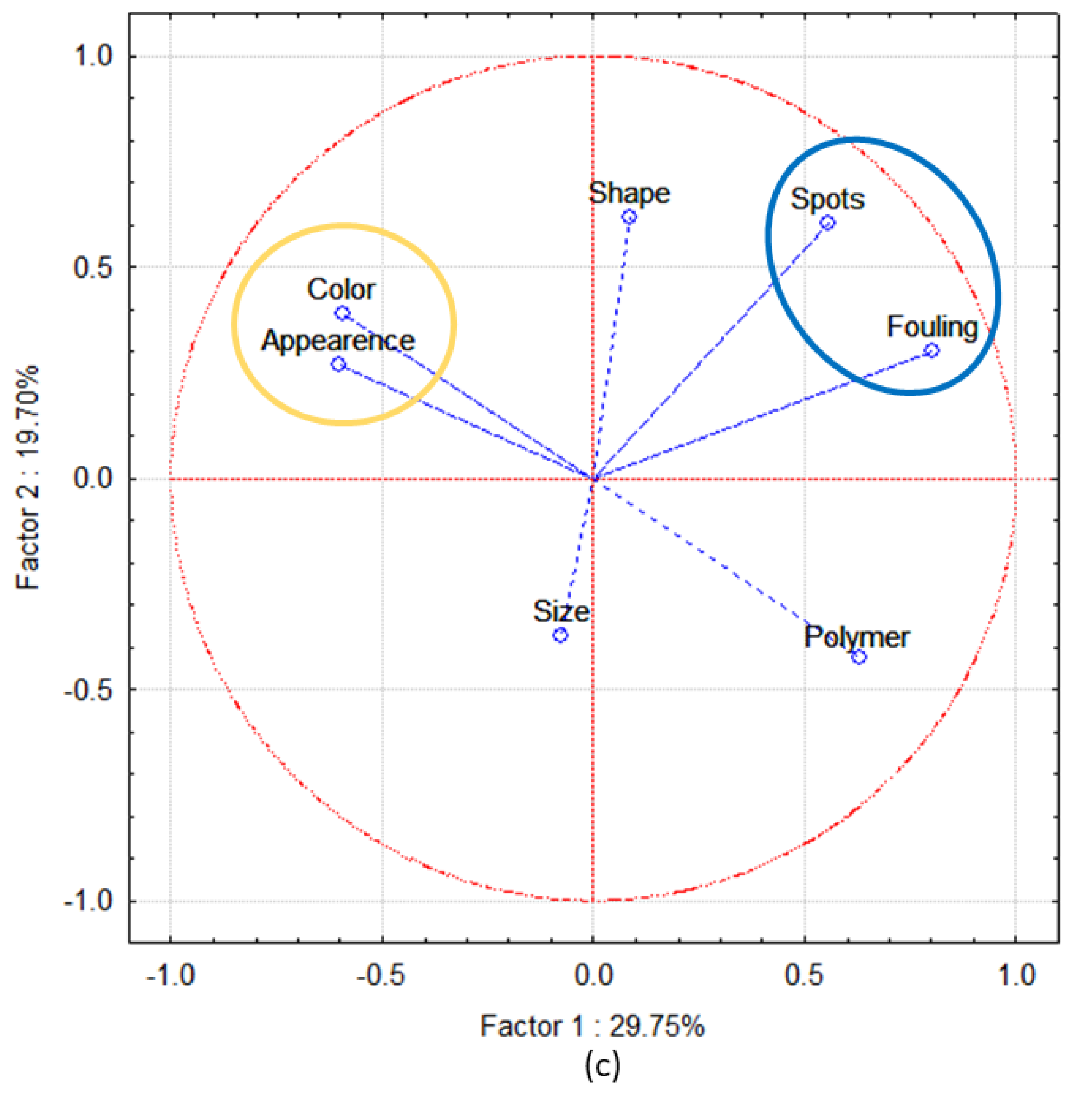
3.3. PE and PP Resin Pellets Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP Annual Report 2021. Available online: https://www.unep.org/annualreport/2021/index.php (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- McCoy, F.W. Floating Megalitter in the Eastern Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1988, 19, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liubartseva, S.; Coppini, G.; Lecci, R.; Clementi, E. Tracking Plastics in the Mediterranean: 2D Lagrangian Model. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Rowland, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Potential for Plastics to Transport Hydrophobic Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7759–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino, S.; Locritani, M.; Bernardi, G.; Como, C.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; Abbate, M. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Chemically Characterized Microplastics within the Protected Area of Pelagos Sanctuary (NW Mediterranean Sea): Focus on Natural and Urban Beaches. Water 2020, 12, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F.; Fossi, C.; Weber, R.; Santillo, D.; Sousa, J.; Ingram, I.; Nadal, A.; Romano, D. Marine Litter Plastics and Microplastics and Their Toxic Chemicals Components: The Need for Urgent Preventive Measures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, T.M.; Arneborg, L.; Broström, G.; Almroth, B.C.; Gipperth, L.; Hassellöv, M. The Unaccountability Case of Plastic Pellet Pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, L.M.; Moore, C.; Jones, P.R. Persistent Organic Pollutants Carried by Synthetic Polymers in the Ocean Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-Term Field Measurement of Sorption of Organic Contaminants to Five Types of Plastic Pellets: Implications for Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of Trace Metals to Plastic Resin Pellets in the Marine Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Cao, W.; Zheng, L. Study on the Capability and Characteristics of Heavy Metals Enriched on Microplastics in Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komoroske, L.M.; Lewison, R.L.; Seminoff, J.A.; Deustchman, D.D.; Deheyn, D.D. Trace Metals in an Urbanized Estuarine Sea Turtle Food Web in San Diego Bay, CA. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Fu, D.; Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Peng, L. Microplastics Aged in Various Environmental Media Exhibited Strong Sorption to Heavy Metals in Seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hentschel, B.T.; The, S.J. Long-Term Sorption of Metals Is Similar among Plastic Types: Implications for Plastic Debris in Aquatic Environments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y.; Takada, H.; Mizukawa, K.; Hirai, H.; Iwasa, S.; Endo, S.; Mato, Y.; Saha, M.; Okuda, K.; Nakashima, A.; et al. International Pellet Watch: Global Monitoring of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Coastal Waters. 1. Initial Phase Data on PCBs, DDTs, and HCHs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, D.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Schernewski, G.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.J.; Voit, B. Analysis of Environmental Microplastics by Vibrational Microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or Both? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8377–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Thomas, K.V.; Luo, Z.; Gowen, A.A. FTIR and Raman Imaging for Microplastics Analysis: State of the Art, Challenges and Prospects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, C.; Blasi, M.F.; Mattei, D.; Martellone, L.; Brancaleone, E.; Savoca, S.; Favero, G. Polymer Composition Analysis of Plastic Debris Ingested by Loggerhead Turtles (Caretta Caretta) in Southern Tyrrhenian Sea through ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 179, 105676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltynkova, A.; Johnsen, G.; Wagner, M. Hyperspectral Imaging as an Emerging Tool to Analyze Microplastics: A Systematic Review and Recommendations for Future Development. Microplastics Nanoplastics 2021, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Carelli, G.; Francesconi, F.; Francesconi, M.; Marchesini, L.; Marsili, P.; Sorrentino, F.; Cristoforetti, G.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; et al. Modì: A New Mobile Instrument for in Situ Double-Pulse LIBS Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzano, J.; Bello-Gálvez, C.; Lasheras, R. Identification of Polymers by Means of LIBS. In Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 421–438. [Google Scholar]
- Lasheras, R.J.; Bello-Gálvez, C.; Anzano, J. Identification of Polymers by Libs Using Methods of Correlation and Normalized Coordinates. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.N.; Gondal, M.A.; Redhwi, H.H. Identification of Different Type of Polymers in Plastics Waste. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junjuri, R.; Zhang, C.; Barman, I.; Gundawar, M.K. Identification of Post-Consumer Plastics Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Choi, W.Z. Real-Time Identification of Plastics by Types Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tian, D.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Ding, Y. A Review of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Plastic Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.N. Identification of Different Kinds of Plastics Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Waste Management. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2007, 42, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzano, J.; Bonilla, B.; Montull-Ibor, B.; Casas-González, J. Plastic Identification and Comparison by Multivariate Techniques with Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 2710–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, V.K.; Choudhari, K.S.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Nayak, R.; Kartha, V.B.; Santhosh, C. Analytical Predictive Capabilities of Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) with Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for Plastic Classification. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, S.; Perrier, S.; Freyermuth, P.; Perrin, D.; Gallard, B.; Gilon, N. Plastic Identification Based on Molecular and Elemental Information from Laser Induced Breakdown Spectra: A Comparison of Plasma Conditions in View of Efficient Sorting. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2013, 88, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, S.-B.; Park, S.-B.; Oh, S.-K.; Park, E.-K.; Choi, W.Z. Development of Intelligent Sorting System Realized with the Aid of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Hybrid Preprocessing Algorithm-Based Radial Basis Function Neural Networks for Recycling Black Plastic Wastes. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 1934–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, B.; Grifoni, E.; Legnaioli, S.; Lorenzetti, G.; Pagnotta, S.; Sorrentino, F.; Palleschi, V. Classification of Wrought Aluminum Alloys by ANN Evaluation of LIBS Spectra from Aluminum Scrap Samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2017, 134, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Takizawa, R.; Okuda, K.; Takada, H.; Chiba, K.; Kanehiro, H.; Ogi, H.; Yamashita, R.; Date, T. Concentration of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Beached Resin Pellets: Variability among Individual Particles and Regional Differences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanini, L.; Bozzeda, F. Dynamics of Plastic Resin Pellets Deposition on a Microtidal Sandy Beach: Informative Variables and Potential Integration into Sandy Beach Studies. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, J.; Goldstein, M.; Ohman, M.D. Long-Term Aging and Degradation of Microplastic Particles: Comparing in Situ Oceanic and Experimental Weathering Patterns. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.J.; Ma, Y.H.; Shimidzu, T. Terminology for Membranes and Membrane Processes (IUPAC Recommendation 1996). J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 120, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pořízka, P.; Klus, J.; Képeš, E.; Prochazka, D.; Hahn, D.W.; Kaiser, J. On the Utilization of Principal Component Analysis in Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Data Analysis, a Review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2018, 148, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic Resin Pellets as a Transport Medium for Toxic Chemicals in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decho, A.W. Microbial Biofilms in Intertidal Systems: An Overview. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compa, M.; Alomar, C.; Wilcox, C.; van Sebille, E.; Lebreton, L.; Hardesty, B.D.; Deudero, S. Risk Assessment of Plastic Pollution on Marine Diversity in the Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanagioti, H.K.; Endo, S.; Ogata, Y.; Takada, H. Diffuse Pollution by Persistent Organic Pollutants as Measured in Plastic Pellets Sampled from Various Beaches in Greece. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskett, M.; Takada, H.; Yamashita, R.; Yuyama, M.; Ito, M.; Geok, Y.B.; Ogata, Y.; Kwan, C.; Heckhausen, A.; Taylor, H.; et al. Measurement of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Plastic Resin Pellets from Remote Islands: Toward Establishment of Background Concentrations for International Pellet Watch. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, R. Critical Review of Low-Density Polyethylene’s Partitioning and Diffusion Coefficients for Trace Organic Contaminants and Implications for Its Use as a Passive Sampler. Environ. Sci Technol 2012, 46, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.F.; Manomanii, K.; Mortimer, M.R.; McLachlan, M.S. Partitioning of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Polyethylene/Water System. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 371, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedes, F.; Geertsma, R.W.; van der Zande, T.; Booij, K. Polymer-Water Partition Coefficients of Hydrophobic Compounds for Passive Sampling: Application of Cosolvent Models for Validation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7047–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P.; Nunes, A.R.; Santos, P.S.M.; Girão, A.V.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Degradation of Polyethylene Microplastics in Seawater: Insights into the Environmental Degradation of Polymers. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2018, 53, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Yuan, L.M.; Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Shi, W. Degradation Degree Analysis of Environmental Microplastics by Micro FT-IR Imaging Technology. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, X.; Ma, J. Adsorption Behavior of Organic Pollutants and Metals on Micro/Nanoplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.S.; Christensen, P.A.; Egerton, T.A.; White, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Evolution and Carbonyl Group Development during Photodegradation of Polyethylene and Polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The Plastic in Microplastics: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.U.; Lin, S.; Yousaf, B.; Abbas, Q.; Munir, M.A.M.; Ali, M.U.; Rasihd, A.; Zheng, C.; Kuang, X.; Wong, M.H. Environmental Emission, Fate and Transformation of Microplastics in Biotic and Abiotic Compartments: Global Status, Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaroa-Pérez, B.; Ortiz-Montosa, S.; Hernández-Brito, J.J.; Vega-Moreno, D. Yellowing, Weathering and Degradation of Marine Pellets and Their Influence on the Adsorption of Chemical Pollutants. Polymers 2022, 14, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Monte, C.; Locritani, M.; Merlino, S.; Ricci, L.; Pistolesi, A.; Bronco, S. An In Situ Experiment to Evaluate the Aging and Degradation Phenomena Induced by Marine Environment Conditions on Commercial Plastic Granules. Polymers 2022, 14, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
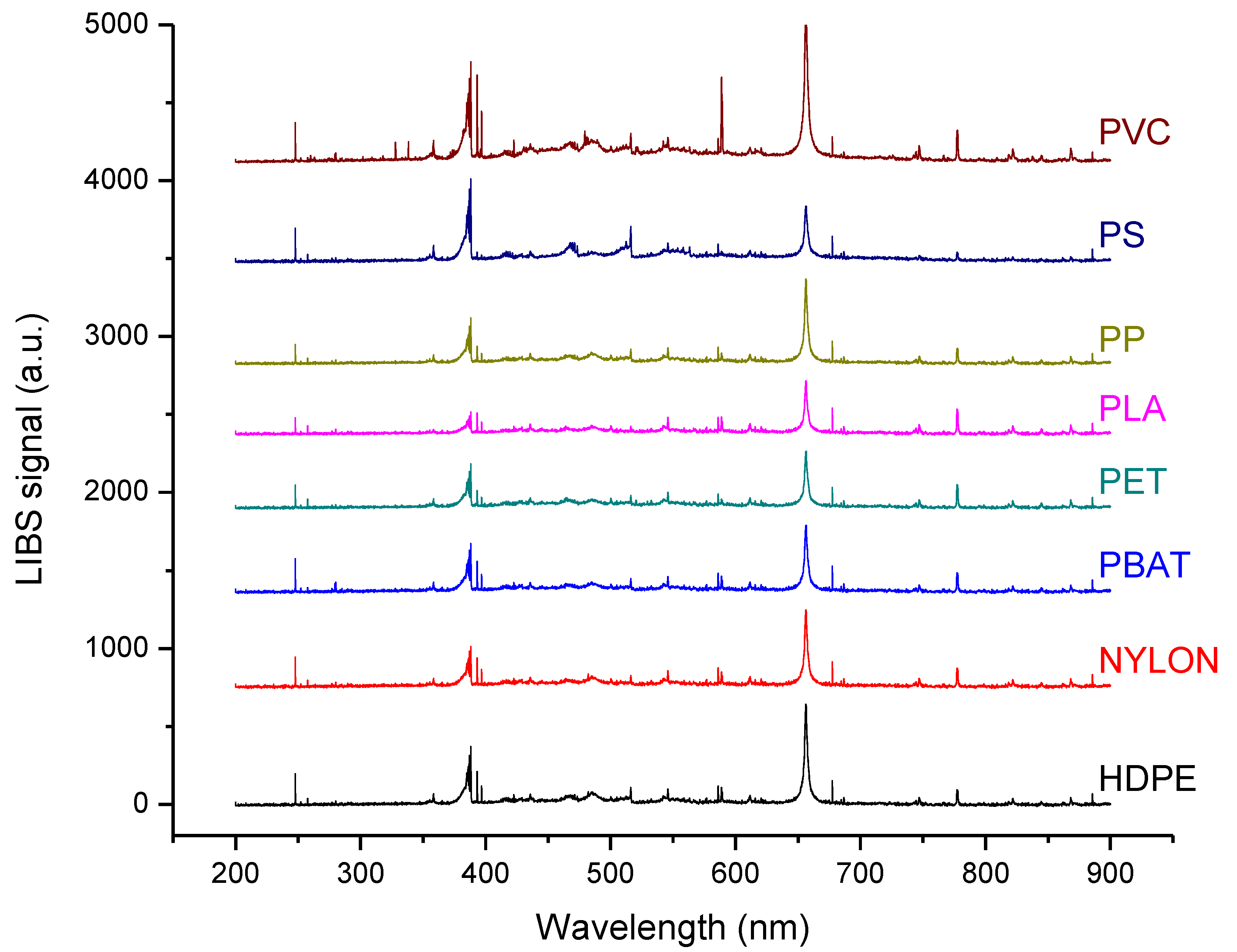
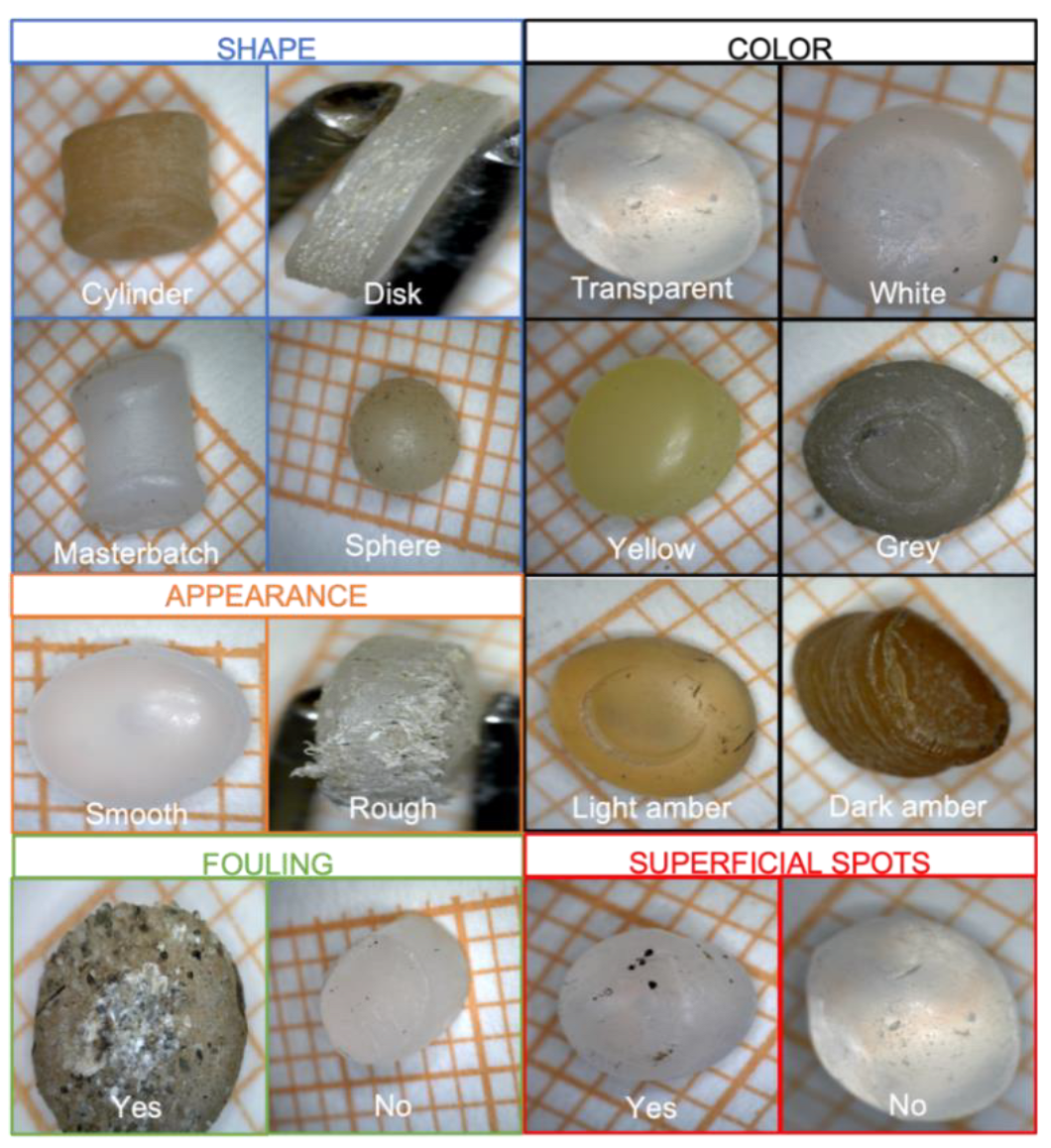
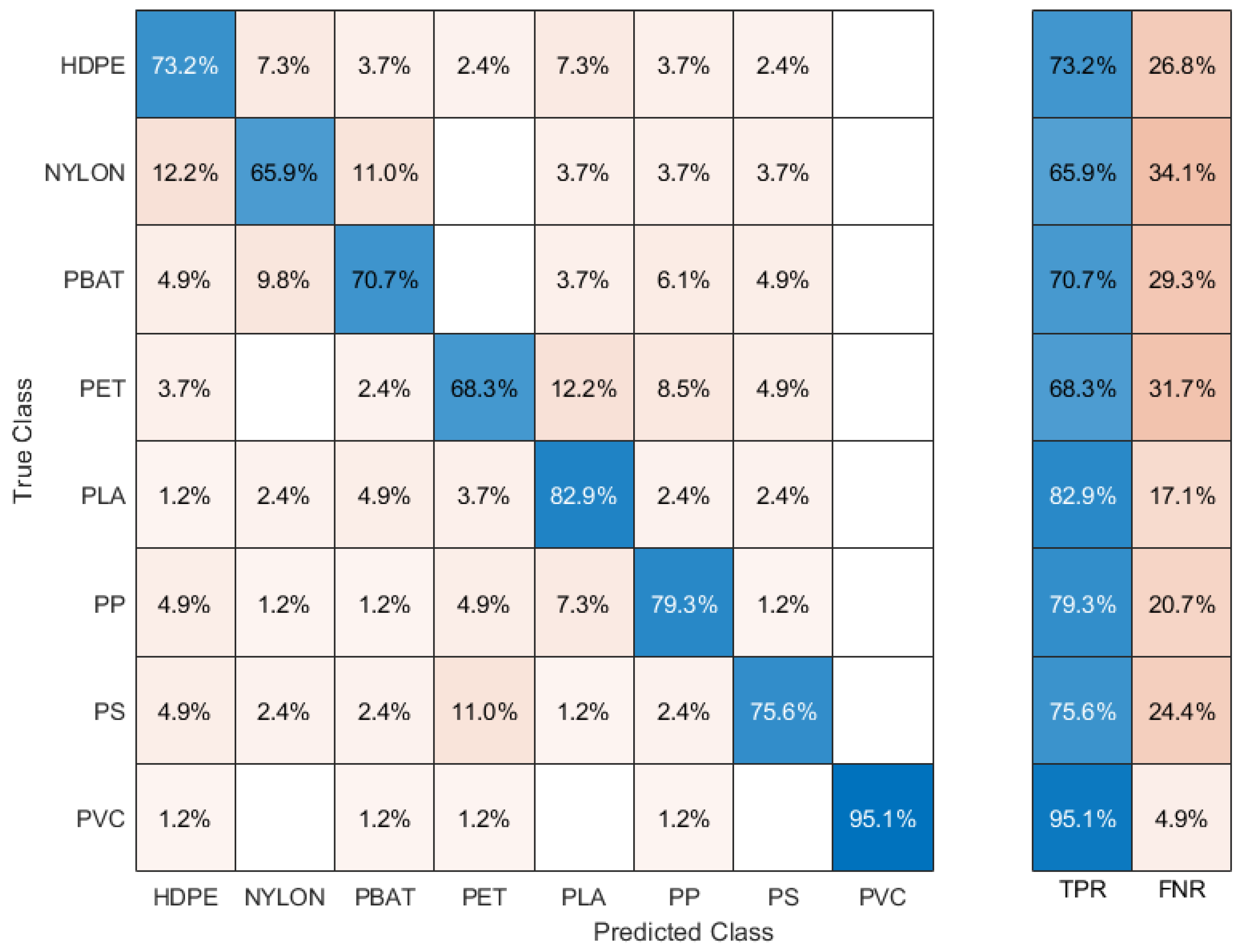
| Material | Number of Samples Analyzed |
|---|---|
| HDPE (high-density polyethylene) | 85 |
| NYLON | 148 |
| PBAT (polybutylene adipate terephthalate) | 99 |
| PET (polyethylene terephthalate) | 82 |
| PLA (polylactide) | 117 |
| PP (polypropylene) | 111 |
| PS (polystyrene) | 101 |
| PVC (polyvinyl chloride) | 85 |
| Number | Parameter | Numerical Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Polymer | PE → 0 PP →1 |
| 2 | Size | 2–3 mm → 0 3–4 mm → 1 4–5 mm → 2 |
| 3 | Shape | Disk → 0 Cylinder → 1 Sphere → 2 Masterbatch → 3 |
| 4 | Appearance | Smooth → 0 Rough → 1 |
| 5 | Color | Transparent → 0 White → 1 Gray → 2 Yellow → 3 Light Amber → 4 Dark Amber → 5 |
| 6 | Fouling | Yes → 0 No → 1 |
| 7 | Superficial spots | Yes → 0 No → 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giugliano, R.; Cocciaro, B.; Poggialini, F.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; Locritani, M.; Merlino, S. Rapid Identification of Beached Marine Plastics Pellets Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: A Promising Tool for the Quantification of Coastal Pollution. Sensors 2022, 22, 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186910
Giugliano R, Cocciaro B, Poggialini F, Legnaioli S, Palleschi V, Locritani M, Merlino S. Rapid Identification of Beached Marine Plastics Pellets Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: A Promising Tool for the Quantification of Coastal Pollution. Sensors. 2022; 22(18):6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186910
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiugliano, Roberta, Bruno Cocciaro, Francesco Poggialini, Stefano Legnaioli, Vincenzo Palleschi, Marina Locritani, and Silvia Merlino. 2022. "Rapid Identification of Beached Marine Plastics Pellets Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: A Promising Tool for the Quantification of Coastal Pollution" Sensors 22, no. 18: 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186910
APA StyleGiugliano, R., Cocciaro, B., Poggialini, F., Legnaioli, S., Palleschi, V., Locritani, M., & Merlino, S. (2022). Rapid Identification of Beached Marine Plastics Pellets Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: A Promising Tool for the Quantification of Coastal Pollution. Sensors, 22(18), 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186910








