A Smart Alcoholmeter Sensor Based on Deep Learning Visual Perception
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Traditional Alcoholmeter
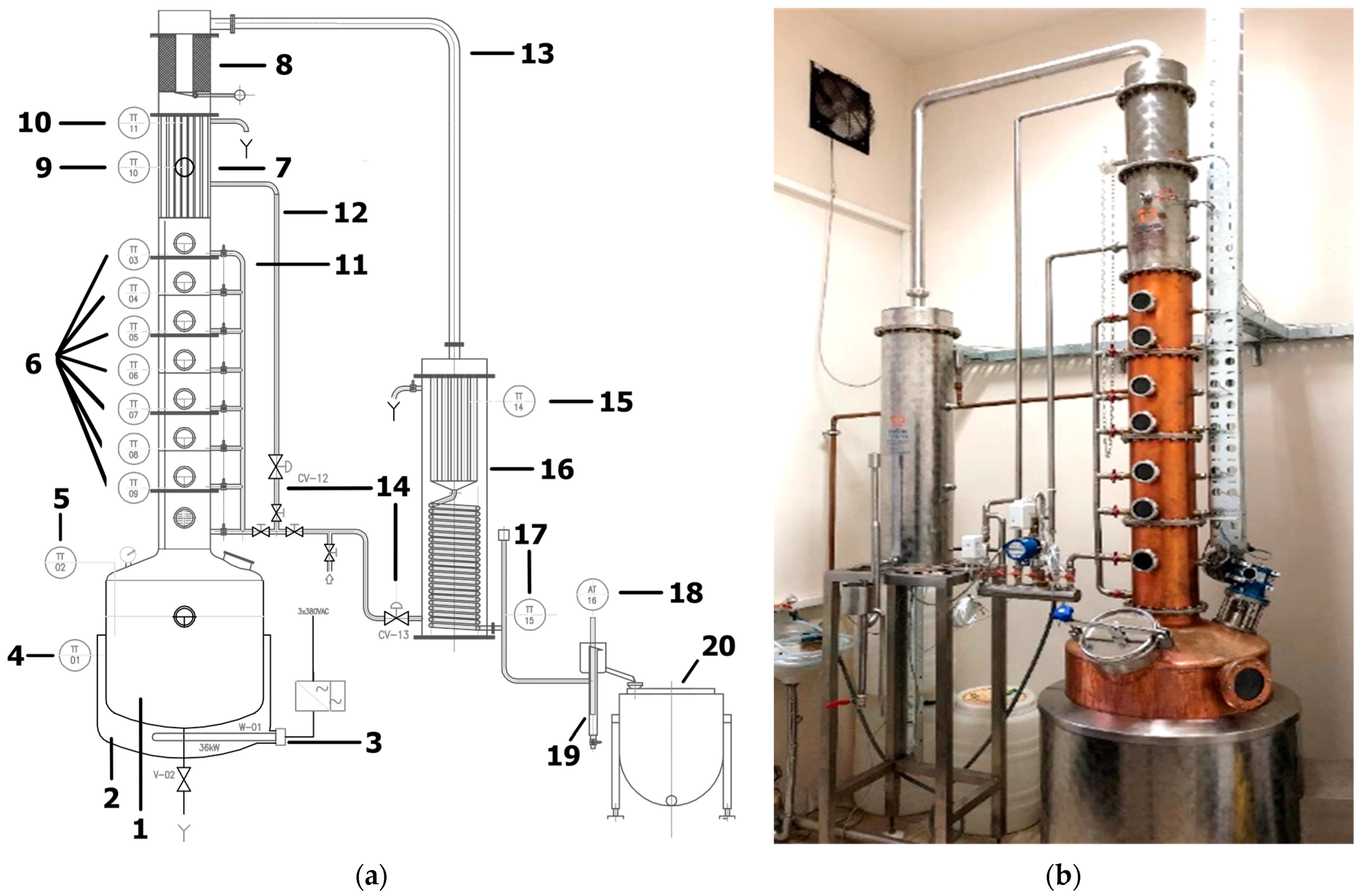
2.2. Alcoholmeter Reading System Description
2.3. Dataset
2.3.1. Acquisition Setup
2.3.2. Image and Label Pre-Processing
2.4. DNN Models
2.4.1. Regression
2.4.2. Classification
2.4.3. Implementation
3. Results
3.1. Dataset Samples
3.2. DNN Training Performance
3.2.1. Regression Performance
3.2.2. Classification Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alcarde, A.R.; Souza, P.A.; Belluco, A.E.S. Chemical profile of sugarcane spirits produced by double distillation methodologies in rectifying still. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 31, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerek, M.; Pielech-Przybylska, K.; Patelski, P.; Dziekońska-Kubczak, U.; Strąk, E. The effect of distillation conditions and alcohol content in ‘heart’ fractions on the concentration of aroma volatiles and undesirable compounds in plum brandies. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tunca, E.; Saribas, H.; Kafali, H.; Kahvecioglu, S. Determining the pointer positions of aircraft analog indicators using deep learning. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2022, 94, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Ding, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.; Zeng, M. Image-Based Automatic Watermeter Reading under Challenging Environments. Sensors 2021, 21, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, G.; Laroca, R.; Menotti, D. Deep Learning for Image-based Automatic Dial Meter Reading: Dataset and Baselines. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Chen, K.; Huang, J. A High-Robust Automatic Reading Algorithm of Pointer Meters Based on Text Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kanno, J.; Zhao, Q. A Two-Stage Deep Learning-Based Approach for Automatic Reading of Analog Meters. In Proceedings of the 2020 Joint 11th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems and 21st International Symposium on Advanced Intelligent Systems (SCIS-ISIS), Online, 5–7 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Gan, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y. Intelligent Ammeter Reading Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 24–26 May 2019; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa da Silva Marques, R.; Costa Serra, A.; Ferreira Franca, J.V.; Bandeira Diniz, J.O.; Braz Junior, G.; Sousa de Almeida, J.D.; Garros Monteiro, E.M. Image-Based Electric Consumption Recognition via Multi-Task Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems (BRACIS), Salvador, Brazil, 15–18 October 2019; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Perez, L.M.; Pedraza-Ortega, J.C.; Ramos-Arreguin, J.M.; Tovar-Arriaga, S.; Aceves-Fernandez, M.A.; Becerra, L.O.; Gorrostieta-Hurtado, E.; Vargas-Soto, J.E. Alignment of the Measurement Scale Mark during Immersion Hydrometer Calibration Using an Image Processing System. Sensors 2013, 13, 14367–14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonezzer, M.; Bazzanella, N.; Gasperi, F.; Biasioli, F. Nanosensor Based on Thermal Gradient and Machine Learning for the Detection of Methanol Adulteration in Alcoholic Beverages and Methanol Poisoning. Sensors 2022, 22, 5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, H.G.J.; Mendes Júnior, J.J.A.; Farinelli, M.E.; Stevan, S.L., Jr. A Prototype to Detect the Alcohol Content of Beers Based on an Electronic Nose. Sensors 2019, 19, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswandi, B.; Irmawati, T.; Hidayat, M.A.; Jayus; Ahmad, M. A Simple Visual Ethanol Biosensor Based on Alcohol Oxidase Immobilized onto Polyaniline Film for Halal Verification of Fermented Beverage Samples. Sensors 2014, 14, 2135–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfkamp, J.; Guenther, M.; Gerlach, G. Hydrogel-Based Sensors for Ethanol Detection in Alcoholic Beverages. Sensors 2019, 19, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyaci, I.H.; Genis, H.E.; Guven, B.; Tamer, U.; Alper, N. A novel method for quantification of ethanol and methanol in distilled alcoholic beverages using Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Corbo, D.; Bertotti, M. Amperometric determination of ethanol in beverages at copper electrodes in alkaline medium. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 472, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, A.; Rogach, A.L. Utilizing Deep Learning to Enhance Optical Sensing of Ethanol Content Based on Luminescent Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 11208–11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaywant, S.A.; Singh, H.; Arif, K.M. Sensors and Instruments for Brix Measurement: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ling, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yan, Y. Ship detection from coastal surveillance videos via an ensemble Canny-Gaussian-morphology framework. J. Navig. 2021, 74, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qu, X.; Ma, X. Improving flex-route transit services with modular autonomous vehicles. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 149, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechliński, Ł.; Siemiątkowska, B.; Majewski, M. A System for Weeds and Crops Identification—Reaching over 10 FPS on Raspberry Pi with the Usage of MobileNets, DenseNet and Custom Modifications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B Specifications—Raspberry Pi. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.com/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/specifications/ (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- Raspberry Pi Documentation—Camera. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/accessories/camera.html (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- Leuze.com ODSL 9/V6-450-S12 Optical Distance Sensor Technical Features. Available online: https://www.leuze.com/en-int/odsl-9-v6-450-s12/50111158 (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- MCP3564R|Microchip Technology. Available online: https://www.microchip.com/en-us/product/MCP3564R (accessed on 16 August 2022).











| Single Board Computer Data | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Raspberry Pi Foundation, Cambridge, England, UK |
| Model | Raspberry Pi 4 model B |
| CPU | Broadcom BCM2711, Quad core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.5 GHz |
| RAM | 4 GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM |
| Camera Interface | 2-lane MIPI CSI camera port |
| Power requirements | 5 V 3 A |
| Camera Data | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Raspberry Pi Foundation, Cambridge, England, UK |
| Model | Raspberry Pi Camera Module 2 |
| Sensor | Sony IMX219 |
| Still resolution | 8 megapixels |
| Sensor resolution | 3280 × 2464 pixels |
| Sensor image area | 3.68 × 2.76 mm (4.6 mm diagonal) |
| Pixel size | 1.12 µm × 1.12 µm |
| Optical size | 1/4″ |
| Horizontal Field of View | 62.2 degrees |
| Vertical Field of View | 48.8 degrees |
| Focal length | 3.04 mm |
| Communication interface | CSI |
| Laser Distance Sensor Data | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Leuze electronic GmbH + Co. KG, Owen, Germany | / |
| Model | ODSL 9/V6-450-S12 | / |
| Range | 50–450 | mm |
| Resolution | 0.1 | mm |
| Accuracy | 1 | % |
| Repeatability | 0.5 | % |
| Analog-to-Digital Converter Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Microchip Technology Inc; Chandler, AZ, USA | / |
| Model | MCP3564R | / |
| Resolution | 24 | bit |
| SINAD | 106.7 | dB |
| RMS Effective Resolution (max) | 23.3 | bit |
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Optimization method | ADAM |
| Mini-batch size | 32 |
| Max Epochs | 10 |
| Initial Learn Rate | 5 × 10−4 |
| Learn Rate Drop Factor | 0.1 |
| Learn Rate Drop Period | 20 |
| Statistical Parameter | Value on Test Dataset |
|---|---|
| ) | 0.7493 |
| Bias (μ) | −0.0877 |
| ) | 0.9531 |
| R-squared (R2) | 0.9988 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Icagic, S.D.; Kvascev, G.S. A Smart Alcoholmeter Sensor Based on Deep Learning Visual Perception. Sensors 2022, 22, 7394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197394
Icagic SD, Kvascev GS. A Smart Alcoholmeter Sensor Based on Deep Learning Visual Perception. Sensors. 2022; 22(19):7394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197394
Chicago/Turabian StyleIcagic, Savo D., and Goran S. Kvascev. 2022. "A Smart Alcoholmeter Sensor Based on Deep Learning Visual Perception" Sensors 22, no. 19: 7394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197394
APA StyleIcagic, S. D., & Kvascev, G. S. (2022). A Smart Alcoholmeter Sensor Based on Deep Learning Visual Perception. Sensors, 22(19), 7394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197394






