Explainable Machine-Learning-Based Characterization of Abnormal Cortical Activities for Working Memory of Restless Legs Syndrome Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Methods
2.2. Data Analysis Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Input Data
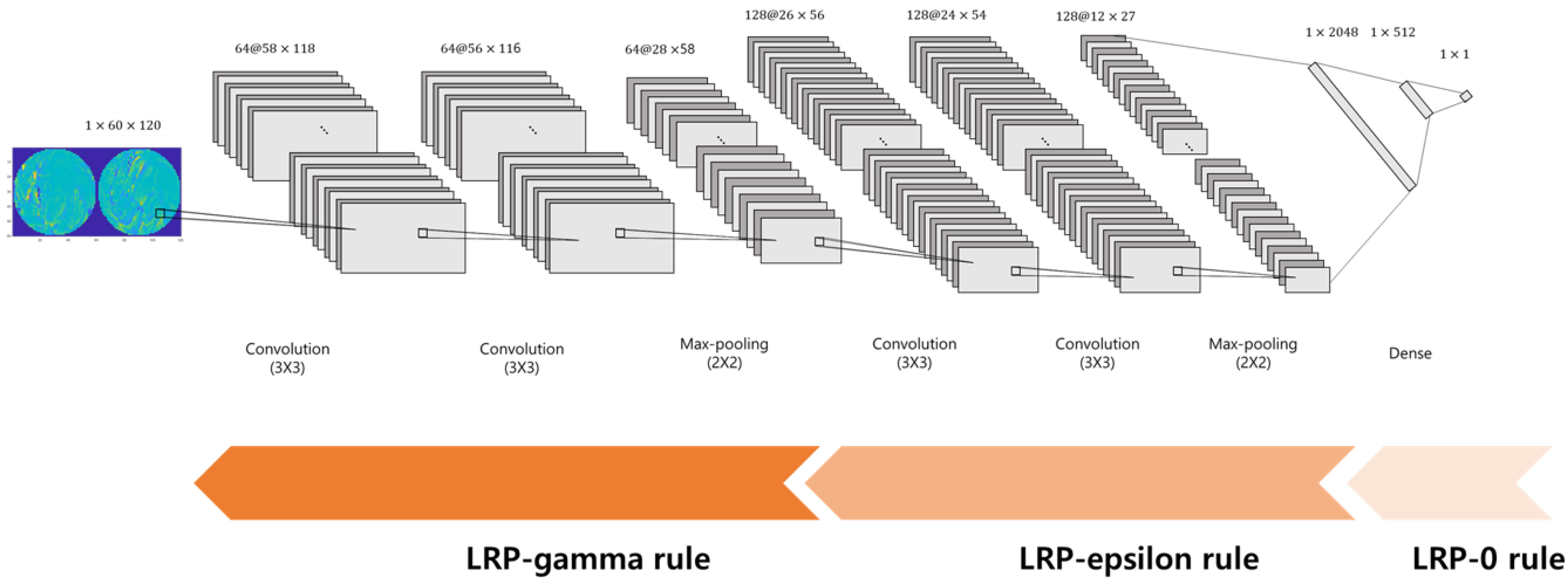
2.2.2. Convolutional Neural Network Classifier
2.2.3. Training and Test of the Classifier
2.2.4. Determination of Critical Input Features by LRP
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Responses
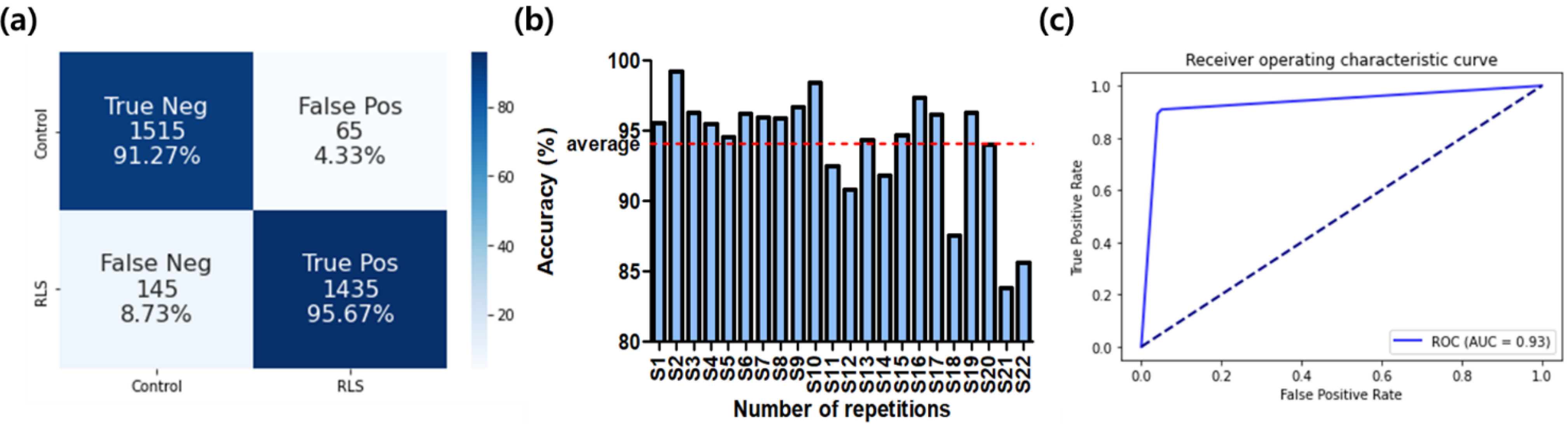
3.2. Classifier Performance
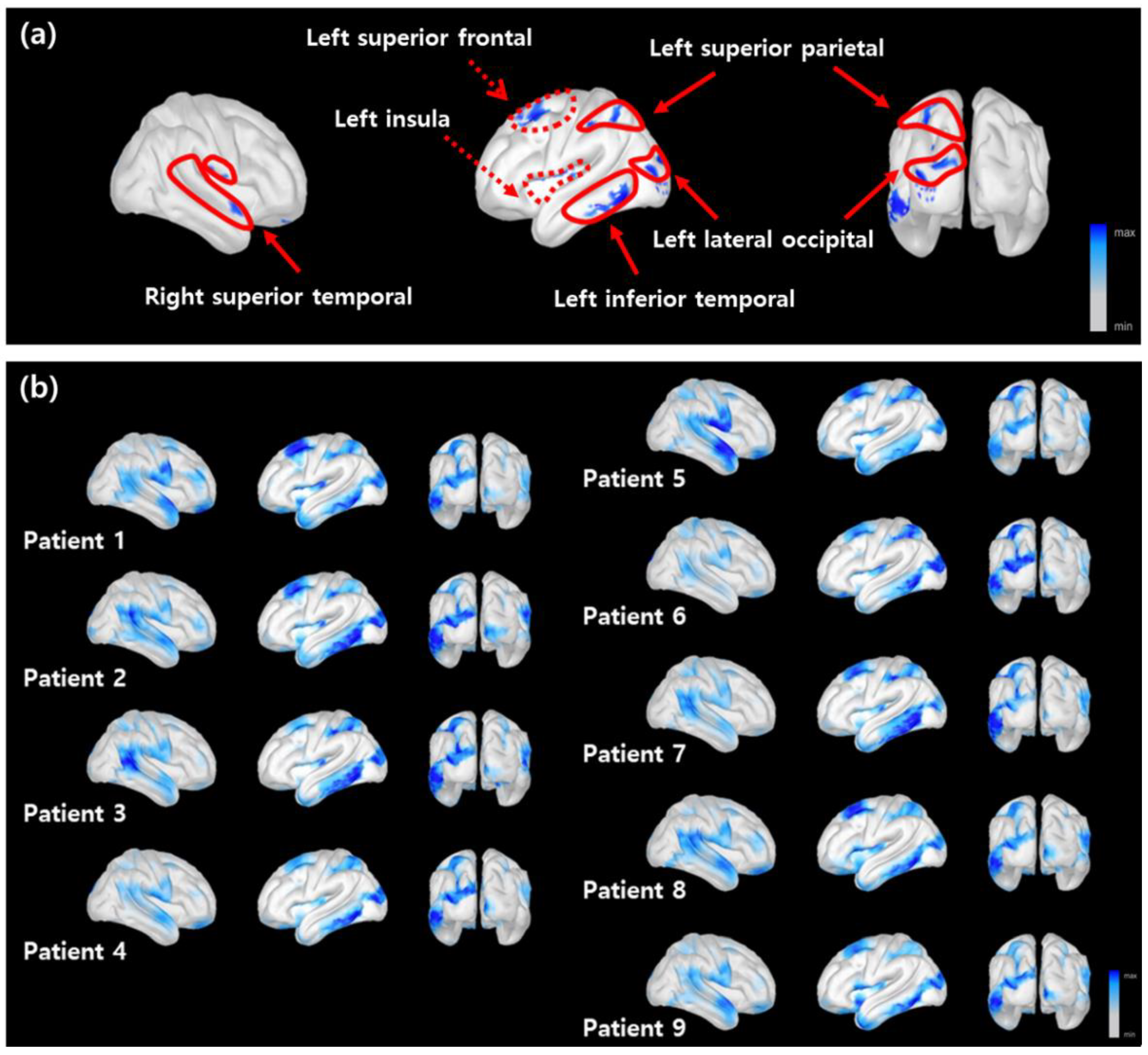
3.3. Distribution of Critical Features on the Cortical Surface
3.4. Correlations of the Critical Region’s Activities and Clinical Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RLS | Restless legs syndrome |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| WM | Working memory |
| ERP | Event-related potential |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CNNs | Convolutional neural networks |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| IRLS | International RLS severity scale |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| ESS | Epworth Sleepiness Scale |
| ISI | Insomnia Severity Index |
| BDI | Back Depression Inventory II |
| HADS | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale |
| LRP | Layer-wise relevance propagation |
| sLORETA | Standardized low resolution brain electromagnetic tomography |
| ReLU | Rectified linear unit |
| LOOCV | Leave-one-subject-out cross-validation |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
References
- Allen, R.P.; Picchietti, D.L.; Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Ondo, W.G.; Walters, A.S.; Winkelman, J.W.; Zucconi, M.; Ferri, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Lee, H.B. Restless legs syndrome/Willis–Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: Updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria—History, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelman, J.W.; Redline, S.; Baldwin, C.M.; Resnick, H.E.; Newman, A.B.; Gottlieb, D.J. Polysomnographic and Health-related Quality of Life Correlates of Restless Legs Syndrome in the Sleep Heart Health Study. Sleep 2009, 32, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, V.E.; Allen, R.P.; Dean, T.; Gamaldo, C.; Lesage, S.R.; Earley, C.J. Cognitive deficits associated with restless legs syndrome (RLS). Sleep Med. 2006, 7, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Msc, M.E.B.; Reppermund, S.; Winkelmann, J.; Wetter, T.C. Short-term attention and verbal fluency is decreased in restless legs syndrome patients. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, C.; Lee, B.U.; Koo, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Jung, K.-Y. Working memory deficit in patients with restless legs syndrome: An event-related potential study. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.S.; Sunwoo, J.-S.; Byun, J.-I.; Kim, T.-J.; Shin, J.-W.; Kim, K.H.; Jung, K.Y. Working memory deficits in patients with idiopathic restless legs syndrome are associated with abnormal theta-band neural synchrony. J. Sleep Res. 2021, 30, e13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, L.K.; Pellouchoud, E.; E Smith, M.; Gevins, A. Neurophysiological signals of working memory in normal aging. Cogn. Brain Res. 2001, 11, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Nahas, Z.; Johnson, K.A.; Yamanaka, K.; Mishory, A.; Koola, J.; Hill, S.; Horner, M.D.; Bohning, D.E.; George, M.S. Decreased Cortical Response to Verbal Working Memory Following Sleep Deprivation. Sleep 2005, 28, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, B.B.; Bagai, K.; Walters, A.S. Restless Legs Syndrome: Current Concepts about Disease Pathophysiology. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2016, 6, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Li, X.; Galantucci, S.; Filippi, M.; Cho, Y.W. Brain imaging and networks in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2016, 31, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unrath, A.; Juengling, F.D.; Schork, M.; Kassubek, J. Cortical grey matter alterations in idiopathic restless legs syndrome: An optimized voxel-based morphometry study. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, A.; Marelli, S.; Giora, E.; Zucconi, M.; Oldani, A.; Ferini-Strambi, L. Neurocognitive function in patients with idiopathic Restless Legs Syndrome before and after treatment with dopamine-agonist. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 95, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieoullon, A. Dopamine and the regulation of cognition and attention. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 67, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymenko, K.; Giusiano, B.; Roehri, N.; Bénar, C.-G.; Badier, J.-M. Strategies for statistical thresholding of source localization maps in magnetoencephalography and estimating source extent. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 290, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmeister, R.T.; Springenberg, J.T.; Fiederer, L.D.J.; Glasstetter, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Tangermann, M.; Hutter, F.; Burgard, W.; Ball, T. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5391–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayor-Torres, J.M.; Medina-DeVilliers, S.; Clarkson, T.; Lerner, M.D.; Riccardi, G. Evaluation of Interpretability for Deep Learning Algorithms in EEG Emotion Recognition: A Case Study in Autism. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.13208. [Google Scholar]
- Craik, A.; He, Y.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Deep learning for electroencephalogram (EEG) classification tasks: A review. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, I.; Lapuschkin, S.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.-R. Interpretable deep neural networks for single-trial EEG classification. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 274, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubreuil-Vall, L.; Ruffini, G.; Camprodon, J.A. Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks Discriminate Adult ADHD from Healthy Individuals on the Basis of Event-Related Spectral EEG. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffini, G.; Ibañez, D.; Castellano, M.; Dubreuil-Vall, L.; Soria-Frisch, A.; Postuma, R.; Gagnon, J.-F.; Montplaisir, J. Deep Learning with EEG Spectrograms in Rapid Eye Movement Behavior Disorder. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vahid, A.; Mückschel, M.; Stober, S.; Stock, A.-K.; Beste, C. Applying deep learning to single-trial EEG data provides evidence for complementary theories on action control. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, J.; Hornyak, M.; Voderholzer, U.; Kryger, M.; Skomrow, R.; Lipinski, J.F.; Masood, A.; Phillips, B.; Oertel, W.H.; Stiasny, K.; et al. Validation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2003, 4, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI): A New Instrument for Psychiatric Research and Practice. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. A New Method for Measuring Daytime Sleepiness: The Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bastien, C.H.; Vallieres, A.; Morin, C.M. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Med. 2001, 2, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Lee, H.; Lee, K. Validation and Factor Structure of Korean Version of the Beck Depression Inventory Second Edition (BDI-II): In a University Student Sample. Korean J. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 18, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Djukanovic, I.; Carlsson, J.; Årestedt, K. Is the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) a valid measure in a general population 65–80 years old? A psychometric evaluation study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556v6. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Klauschen, F.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. On Pixel-Wise Explanations for Non-Linear Classifier Decisions by Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, X.; Herron, T.J.; Cate, A.D.; Yund, E.W.; Woods, D.L. Hemispherically-Unified Surface Maps of Human Cerebral Cortex: Reliability and Hemispheric Asymmetries. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Standardized Low-Resolution Brain Electromagnetic Tomography (SLORETA): Technical Details. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24 (Suppl. D), 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- E Crowley, K.; Colrain, I.M. A review of the evidence for P2 being an independent component process: Age, sleep and modality. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, B.R.; Sabia, M.; Langan, C. Components of working memory and visual selective attention. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2014, 40, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, S.W. A New Equal-Area Projection for World Maps. Geogr. J. 1929, 73, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.; Nash, R. An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.08458. [Google Scholar]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jemal, I.; Mezghani, N.; Abou-Abbas, L.; Mitiche, A. An Interpretable Deep Learning Classifier for Epileptic Seizure Prediction Using EEG Data. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60141–60150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilamala, A.; Madsen, K.H.; Hansen, L.K. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Interpretable Analysis of EEG Sleep Stage Scoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 27th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), Tokyo, Japan, 25–28 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauli, M.P.; Pohl, C.; Golz, M. Balanced Leave-One-Subject-Out Cross- Validation for Microsleep Classification. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 7, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechelt, L. Automatic early stopping using cross validation: Quantifying the criteria. Neural Netw. 1998, 11, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random Search for Hyper-Parameter Optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Montavon, G.; Binder, A.; Lapuschkin, S.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.R. Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation: An Overview. Explain. AI Interpret. Explain. Vis. Deep Learn. 2019, 1, 193–209. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzaley, A.; Nobre, A.C. Top-down modulation: Bridging selective attention and working memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gazzaley, A.; Rissman, J.; Cooney, J.; Rutman, A.; Seibert, T.; Clapp, W.; D’Esposito, M. Functional Interactions between Prefrontal and Visual Association Cortex Contribute to Top-Down Modulation of Visual Processing. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, i125–i135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boettcher, S.E.P.; Gresch, D.; Nobre, A.C.; van Ede, F. Output planning at the input stage in visual working memory. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, N.; Willoughby, A.; Swick, D. Effects of Working Memory Load on Visual Selective Attention: Behavioral and Electrophysiological Evidence. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.K.; Li, L.; Desimone, R. A Neural Mechanism for Working and Recognition Memory in Inferior Temporal Cortex. Science 1991, 254, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schacter, D.L.; Norman, K.A.; Koutstaal, W. The Cogntive Neuroscience of Constructive Memory. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1998, 49, 289–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillis, A.E.; Oh, S.; Ken, L. Deterioration of naming nouns versus verbs in primary progressive aphasia. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranel, D.; Kemmerer, D.; Adolphs, R.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R. Neural correlates of conceptual knowledge for actions. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2003, 20, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manes, F.; Springer, J.; Jorge, R.; Robinson, R.G. Verbal memory impairment after left insular cortex infarction. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 67, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.F. Semantic Activation and Verbal Working Memory Maintenance in Schizophrenic Thought Disorder: Insights from Electrophysiology and Lexical Amibiguity. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2008, 39, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonucci, S.M.; Reilly, J. Semantic Memory and Language Processing: A Primer. Semin. Speech Lang. 2008, 29, 005–017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, A.N.; Greer, S.M.; Saletin, J.M.; Harvey, A.G.; Nitschke, J.B.; Walker, M.P. Tired and Apprehensive: Anxiety Amplifies the Impact of Sleep Loss on Aversive Brain Anticipation. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10607–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Faber, P.; Kinoshita, T.; Kochi, K.; Milz, P.; Nishida, K.; Yoshimura, M. Comparing EEG/MEG Neuroimaging Methods Based on Localization Error, False Positive Activity, and False Positive Connectivity. bioRxiv 2018, 269753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Davey, C.; Poulsen, C.; Luu, P.; Turovets, S.; Anderson, E.; Li, K.; Tucker, D. EEG source localization: Sensor density and head surface coverage. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 256, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ESS | ISI | BDI | PSQI | HADS Anxiety | HADS Depression | IRLS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| left | Superior frontal | 0.185 | 0.353 | 0.529 | −0.218 | 0.562 | 0.458 | 0.042 |
| Inferior temporal | 0.328 | −0.529 | −0.361 | −0.644 * | −0.468 | −0.322 | −0.639 * | |
| Insular | 0.227 | 0.622 * | 0.378 | 0.628 * | 0.587 * | 0.254 | 0.630 * | |
| Superior parietal | −0.210 | −0.227 | −0.067 | 0.075 | −0.289 | −0.068 | −0.269 | |
| Lateral occipital | −0.176 | 0.235 | 0.429 | −0.276 | 0.196 | 0.509 | 0.067 | |
| right | Superior temporal | −0.672 * | −0.067 | −0.361 | −0.243 | 0.068 | −0.322 | 0.168 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Seo, P.; Jung, K.-Y.; Kim, K.H. Explainable Machine-Learning-Based Characterization of Abnormal Cortical Activities for Working Memory of Restless Legs Syndrome Patients. Sensors 2022, 22, 7792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207792
Kim M, Kim H, Seo P, Jung K-Y, Kim KH. Explainable Machine-Learning-Based Characterization of Abnormal Cortical Activities for Working Memory of Restless Legs Syndrome Patients. Sensors. 2022; 22(20):7792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207792
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minju, Hyun Kim, Pukyeong Seo, Ki-Young Jung, and Kyung Hwan Kim. 2022. "Explainable Machine-Learning-Based Characterization of Abnormal Cortical Activities for Working Memory of Restless Legs Syndrome Patients" Sensors 22, no. 20: 7792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207792
APA StyleKim, M., Kim, H., Seo, P., Jung, K.-Y., & Kim, K. H. (2022). Explainable Machine-Learning-Based Characterization of Abnormal Cortical Activities for Working Memory of Restless Legs Syndrome Patients. Sensors, 22(20), 7792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207792









