Stereo Image Matching Using Adaptive Morphological Correlation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Stereo Matching with Adaptive Morphological Correlation
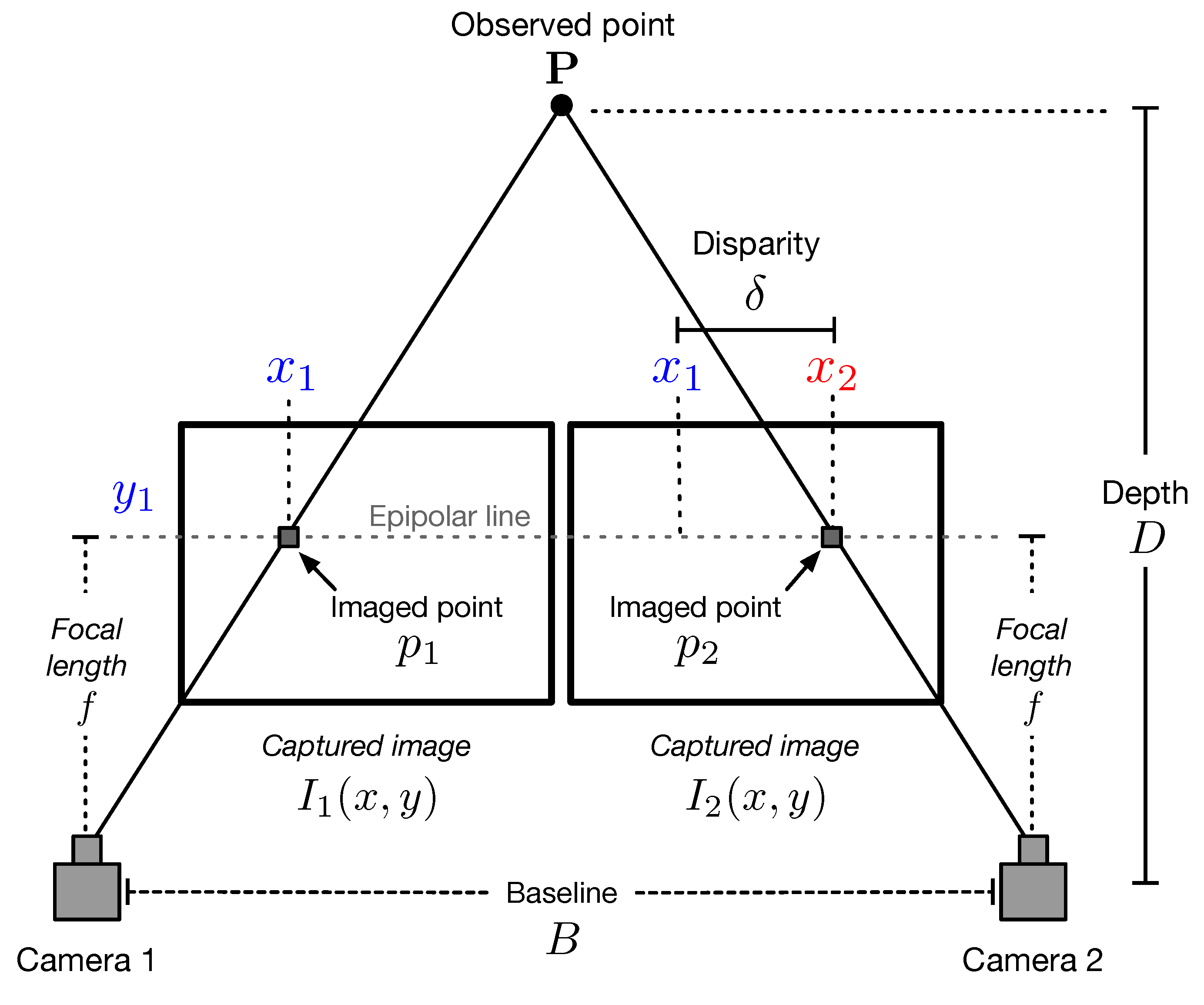
2.1. Stereo Vision
2.2. Proposed Method for Stereo Matching
2.3. Disparity Post-Processing
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Liu, X.; Ullah, Z.; Cheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q. Eye Gaze Based 3D Triangulation for Robotic Bionic Eyes. Sensors 2020, 20, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.E.; Rojas, J.F.; Goberville, N.A.; Alzubi, H.; AlRousan, Q.; Wang, C.; Huff, S.; Rios-Torres, J.; Ekti, A.R.; LaClair, T.J.; et al. Development of an energy efficient and cost effective autonomous vehicle research platform. Sensors 2022, 22, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 47, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, R.A.; Ibrahim, H. Literature survey on stereo vision disparity map algorithms. J. Sensors 2016, 2016, 8742920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirschmuller, H.; Scharstein, D. Evaluation of stereo matching costs on images with radiometric differences. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 1582–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.; Corke, P. Quantitative evaluation of matching methods and validity measures for stereo vision. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 512–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhyapak, S.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Nadin, M. Stereo matching via selective multiple windows. J. Electron. Imaging 2007, 16, 013012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusiello, A.; Roberto, V.; Trucco, E. Symmetric stereo with multiple windowing. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2001, 14, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.J.; Kweon, I.S. Adaptive support-weight approach for correspondence search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, C.; Hu, K. Accurate Image-Guided Stereo Matching with Efficient Matching Cost and Disparity Refinement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 26, 1632–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Dong, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, W. Local stereo matching with improved matching cost and disparity refinement. IEEE Multimed. 2014, 21, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, X.; Fan, A.; Jiang, J.; Yan, J. Image matching from handcrafted to deep features: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 23–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabih, R.; Woodfill, J. Non-Parametric Local Transforms for Computing Visual Correspondence. In Proceedings of the Third European Conference-Volume II on Computer Vision-Volume II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Fife, W.S.; Archibald, J.K. Improved census transforms for resource-optimized stereo vision. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jun, D.; Eem, C.; Hong, H. Improved census transform for noise robust stereo matching. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. S-census transform algorithm with variable cost. Comput. Eng. Des. 2018, 39, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Liu, C.; An, B.; Liu, Y. Stereo matching algorithm based on improved census transform and texture filtering. Optik 2022, 249, 168186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Y. Improvement of AD-Census Algorithm Based on Stereo Vision. Sensors 2022, 22, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharstein, D.; Pal, C. Learning conditional random fields for stereo. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschmuller, H.; Scharstein, D. Evaluation of cost functions for stereo matching. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Scharstein, D.; Hirschmüller, H.; Kitajima, Y.; Krathwohl, G.; Nešić, N.; Wang, X.; Westling, P. High-resolution stereo datasets with subpixel-accurate ground truth. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Juarez-Salazar, R.; Rios-Orellana, O.I.; Diaz-Ramirez, V.H. Stereo-phase rectification for metric profilometry with two calibrated cameras and one uncalibrated projector. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 6097–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusiello, A.; Trucco, E.; Verri, A. A compact algorithm for rectification of stereo pairs. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2000, 12, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragos, P. Optimal morphological approaches to image matching and object detection. In Proceedings of the 1988 Second International Conference on Computer Vision, Computer Society, Tampa, FL, USA, 5–8 December 1988; pp. 695–696. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Diaz, S.; Kober, V.I. Nonlinear synthetic discriminant function filters for illumination-invariant pattern recognition. Opt. Eng. 2008, 47, 067201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martinez, P.; Ferreira, C.; Garcia, J.; Arsenault, H.H. Nonlinear rotation-invariant pattern recognition by use of the optical morphological correlation. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, D.; Choi, S.; Lu, J.; Ham, B.; Sohn, K.; Do, M.N. Fast global image smoothing based on weighted least squares. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 5638–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Stereo Matching Non-Occluded Points | Proposed Post-Processing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP | RMS | BMP | RMS | |||||
| Method | Mean | St. Dev. | Mean | St. Dev. | Mean | St. Dev. | Mean | St. Dev. |
| IWCT | 10.69 | 4.41 | 8.44 | 2.51 | 14.46 | 6.07 | 10.99 | 3.57 |
| AD-C | 6.65 | 2.33 | 6.10 | 1.69 | 10.11 | 3.28 | 8.77 | 2.45 |
| Proposed | 3.42 | 2.20 | 4.11 | 1.62 | 6.15 | 3.28 | 7.29 | 2.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diaz-Ramirez, V.H.; Gonzalez-Ruiz, M.; Kober, V.; Juarez-Salazar, R. Stereo Image Matching Using Adaptive Morphological Correlation. Sensors 2022, 22, 9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239050
Diaz-Ramirez VH, Gonzalez-Ruiz M, Kober V, Juarez-Salazar R. Stereo Image Matching Using Adaptive Morphological Correlation. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239050
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiaz-Ramirez, Victor H., Martin Gonzalez-Ruiz, Vitaly Kober, and Rigoberto Juarez-Salazar. 2022. "Stereo Image Matching Using Adaptive Morphological Correlation" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239050
APA StyleDiaz-Ramirez, V. H., Gonzalez-Ruiz, M., Kober, V., & Juarez-Salazar, R. (2022). Stereo Image Matching Using Adaptive Morphological Correlation. Sensors, 22(23), 9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239050







