Low-Frequency Ground Vibrations Generated by Debris Flows Detected by a Lab-Fabricated Seismometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lab-Fabricated Seismometer
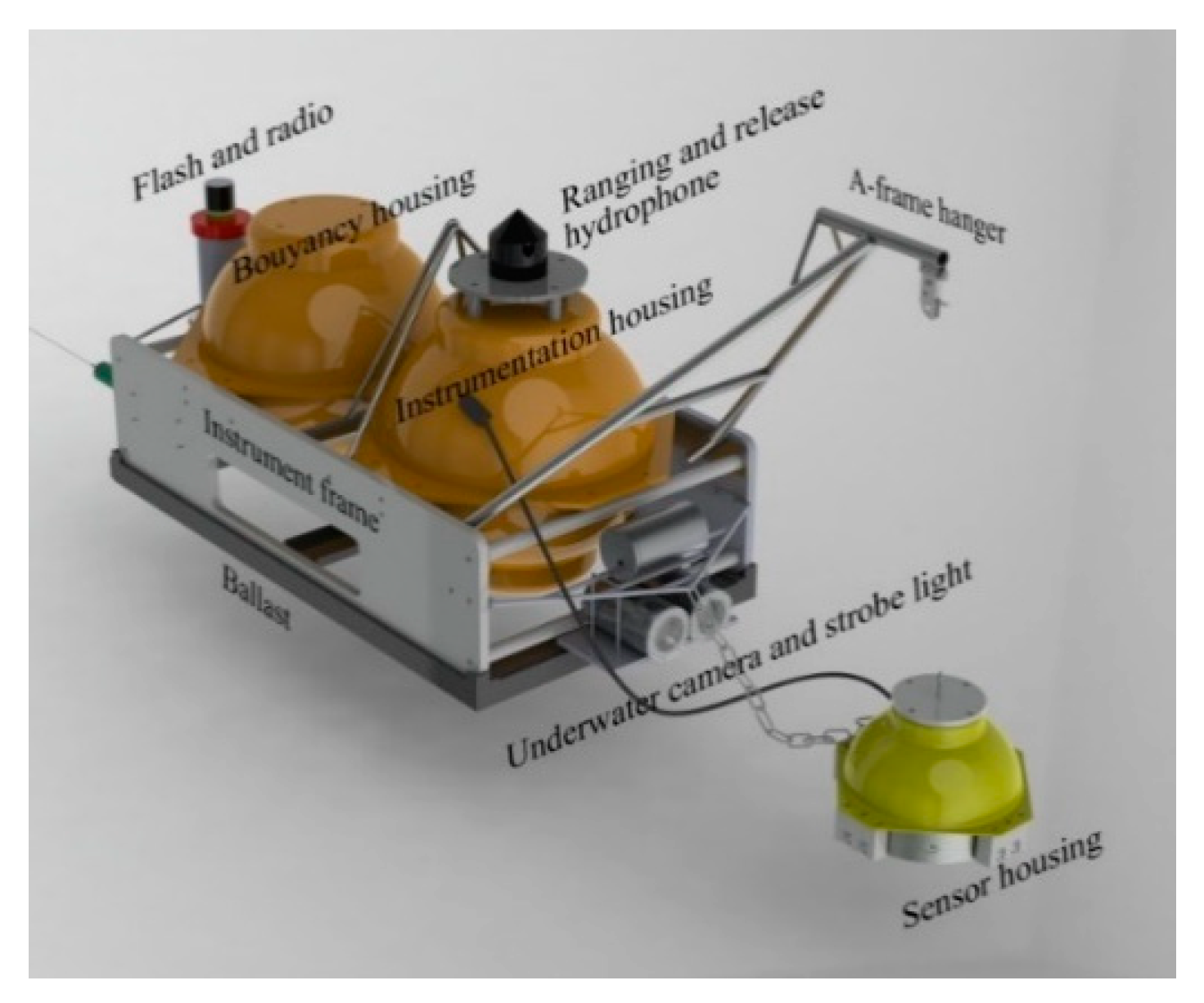
2.1. Yardbird OBS
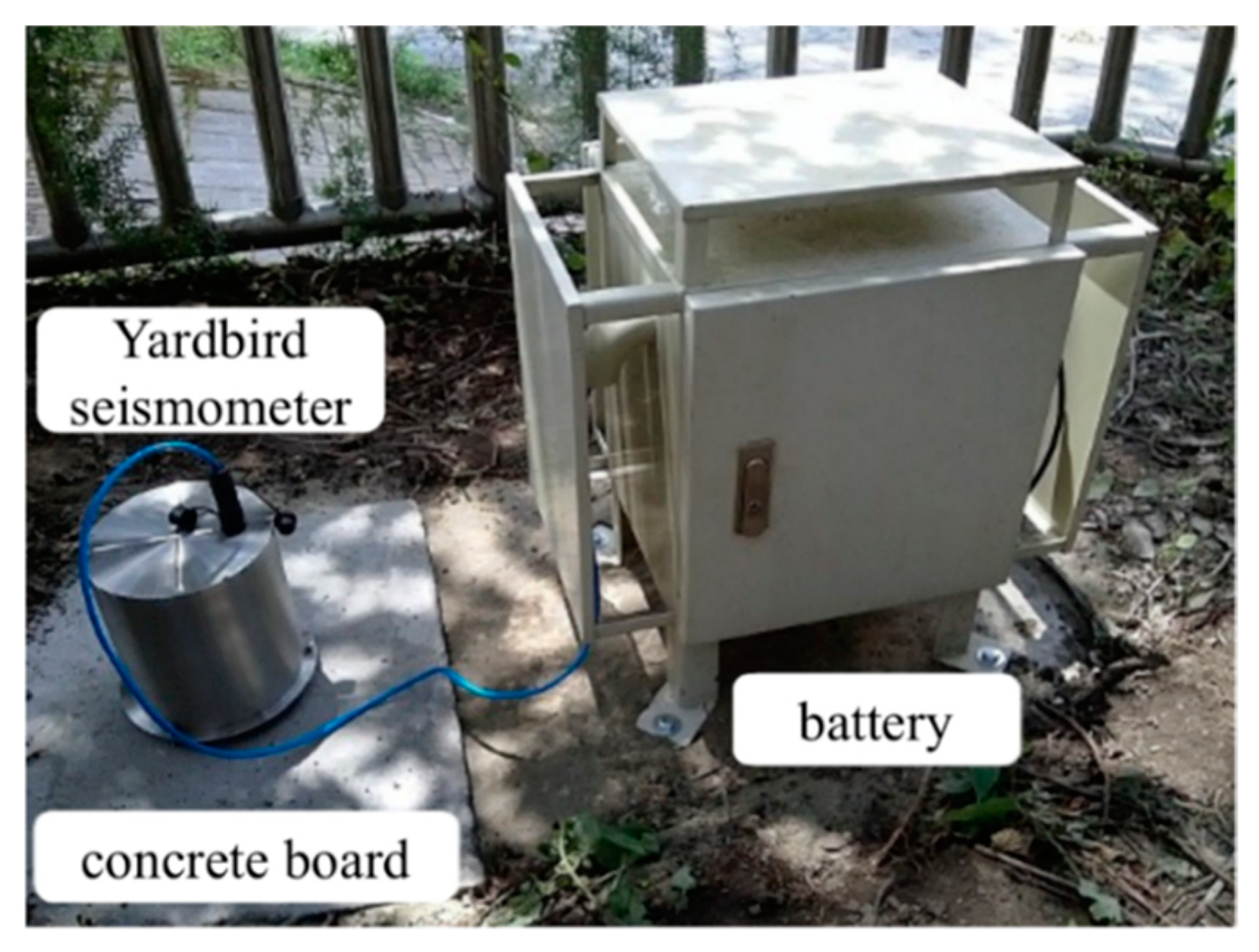
2.2. Yardbird Seismometer
2.3. Frequency Response of the Yardbird Seismometer
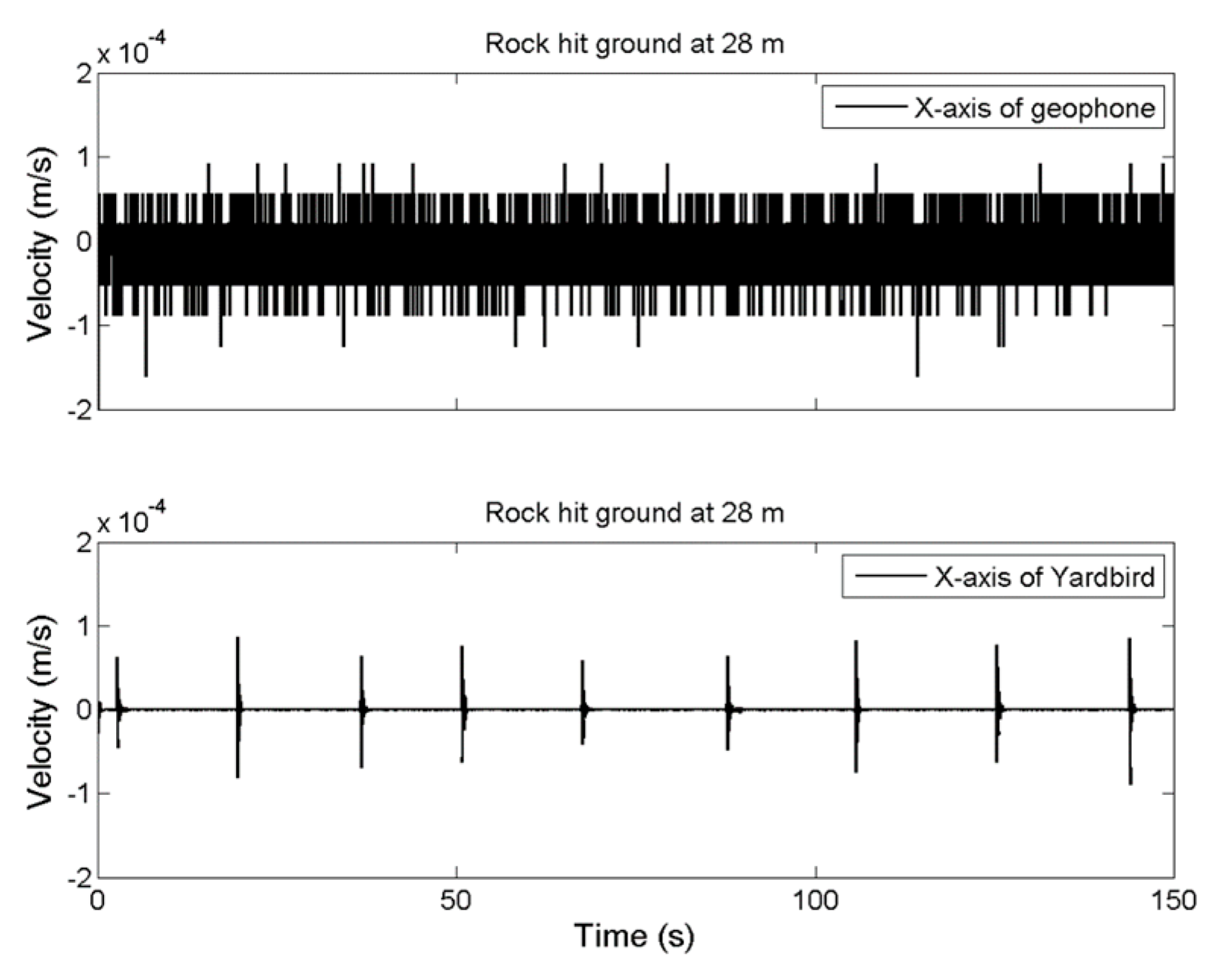
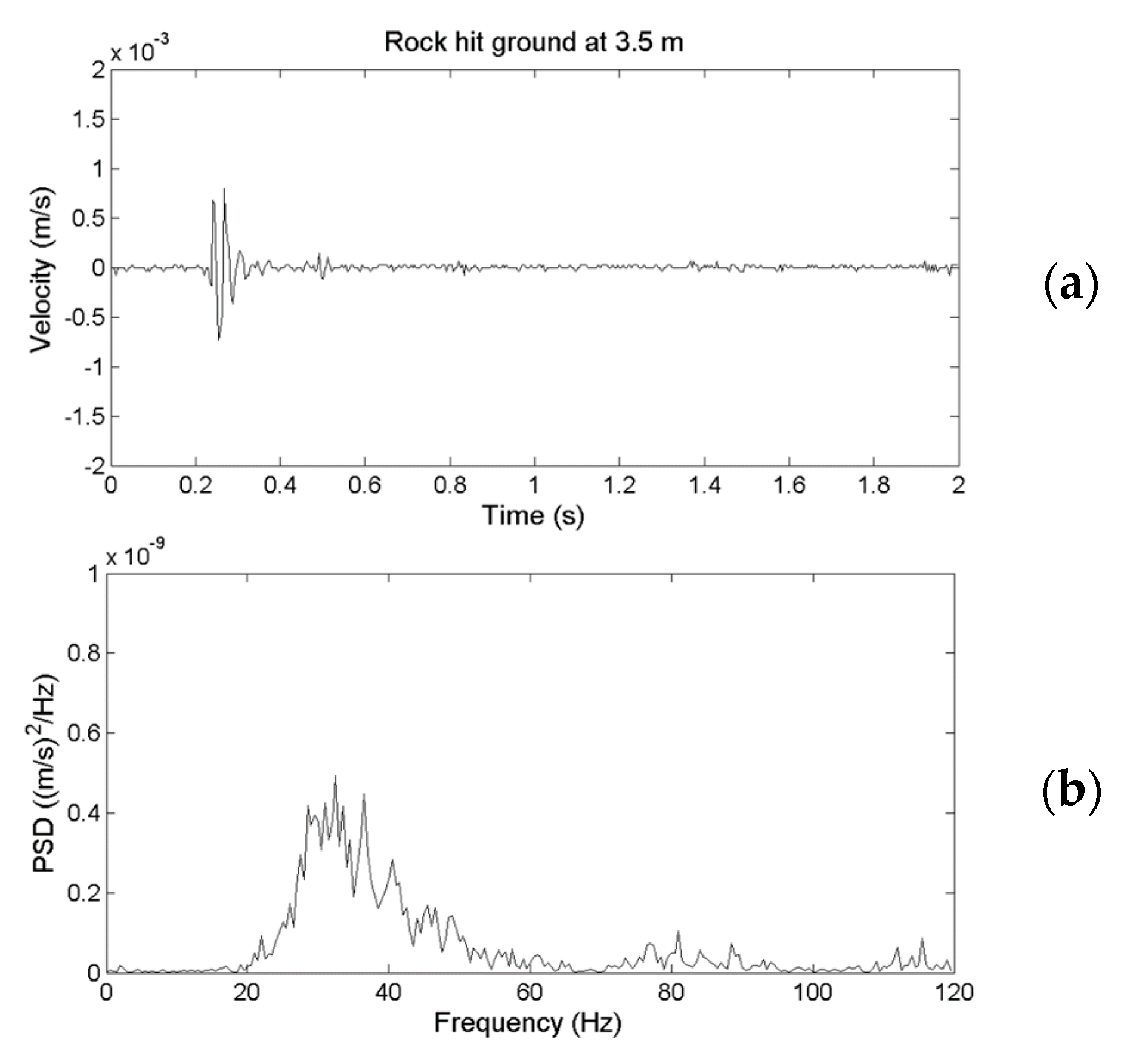
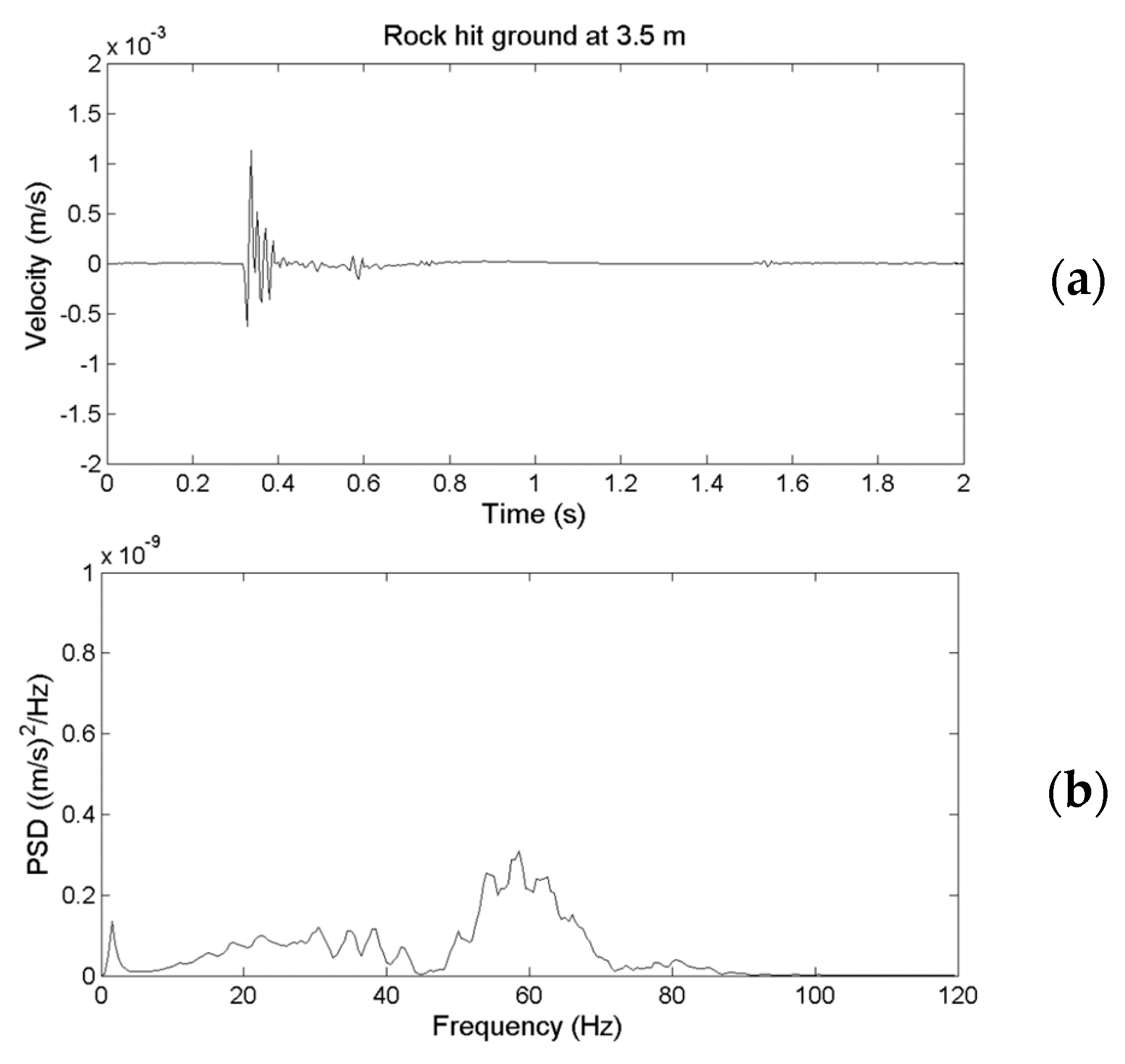
2.4. Performance Comparison of an Yardbird Seismometer and A Geophone
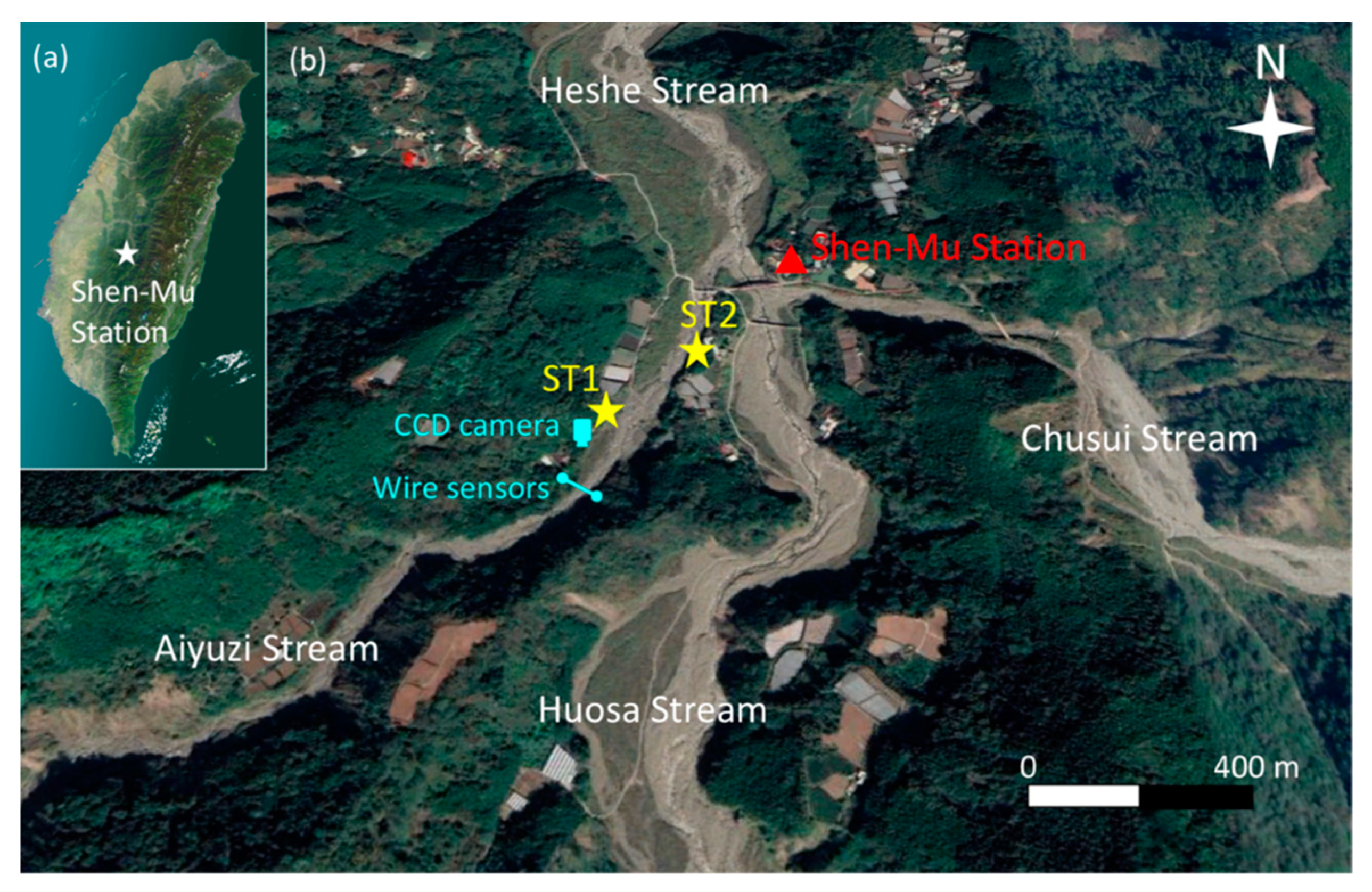
3. Deployment of Yardbird Seismometer for Monitoring Debris Flows
4. Seismic Signals of Local and Distant Earthquakes Detected by the Yardbird Seismometer
4.1. Local and Distant Earthquakes Detection in 2013
4.2. Local and Distant Earthquakes in 2014
5. Debris Flow Events
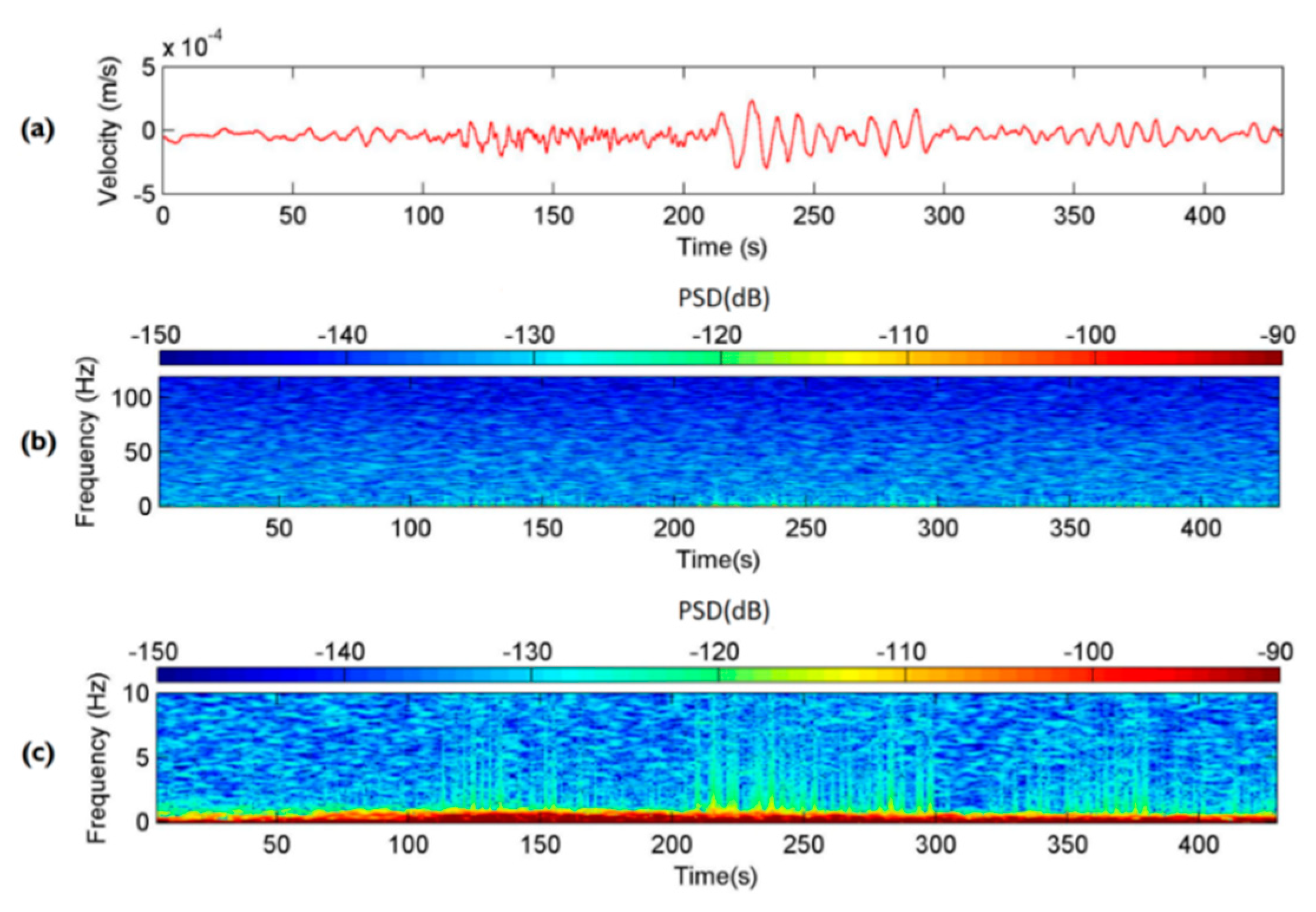
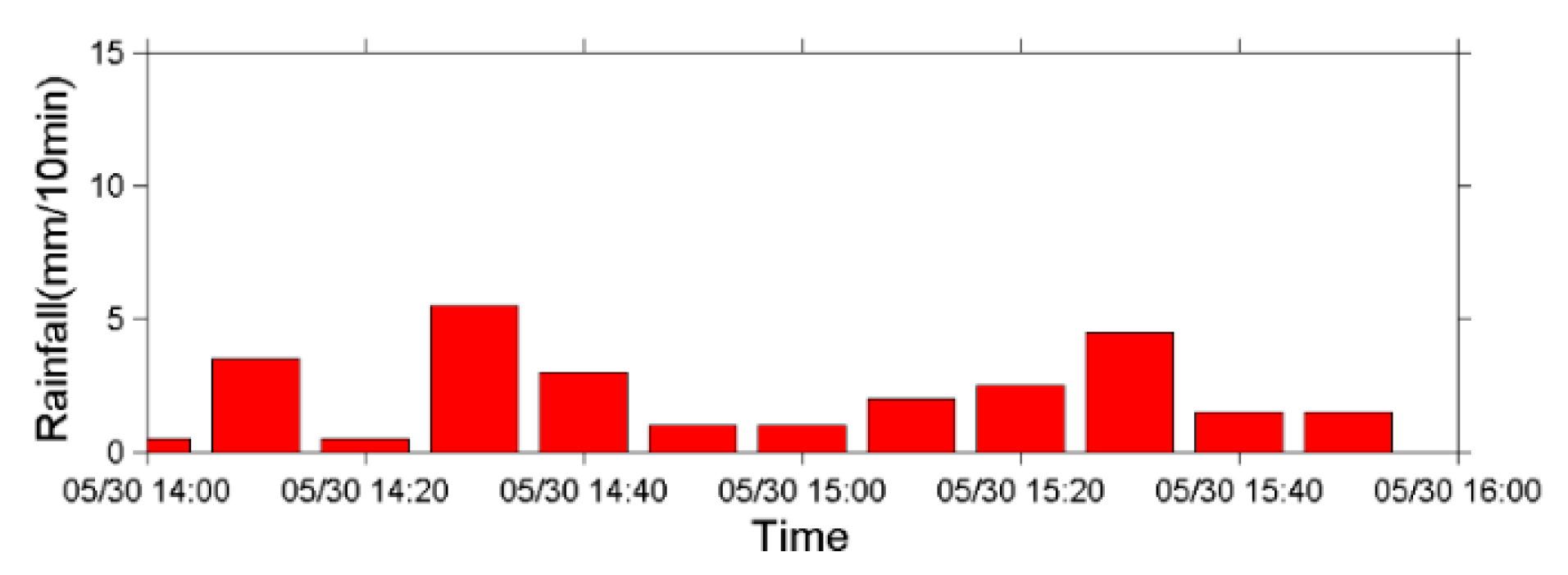
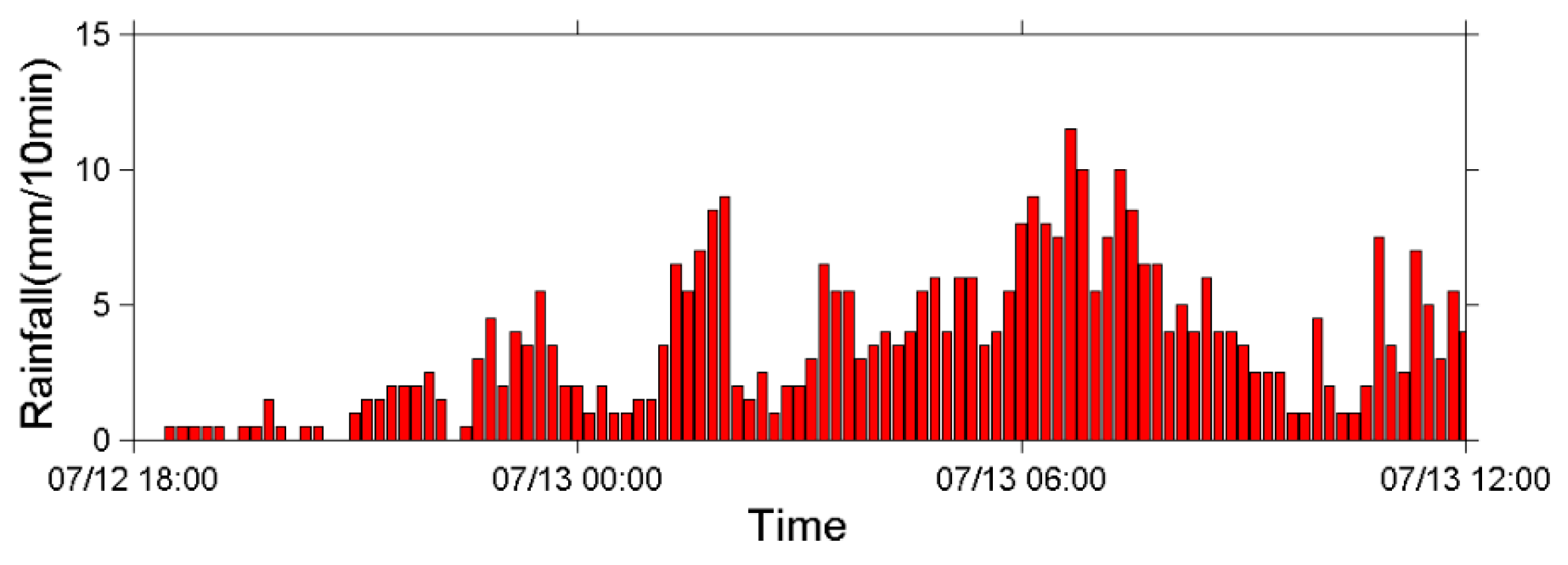
5.1. Debris Flow Triggered by Torrential Rains in 2013 and 2014
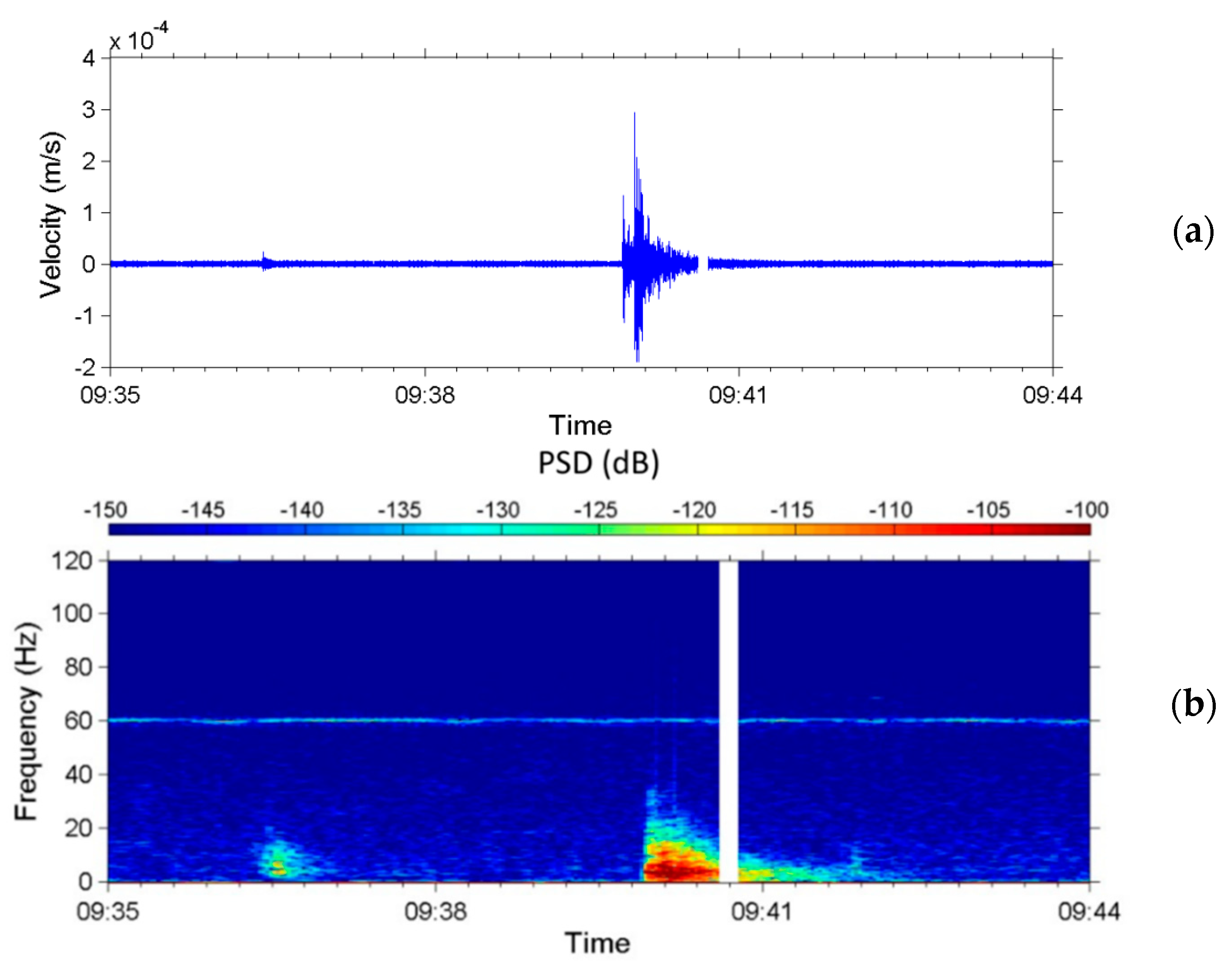
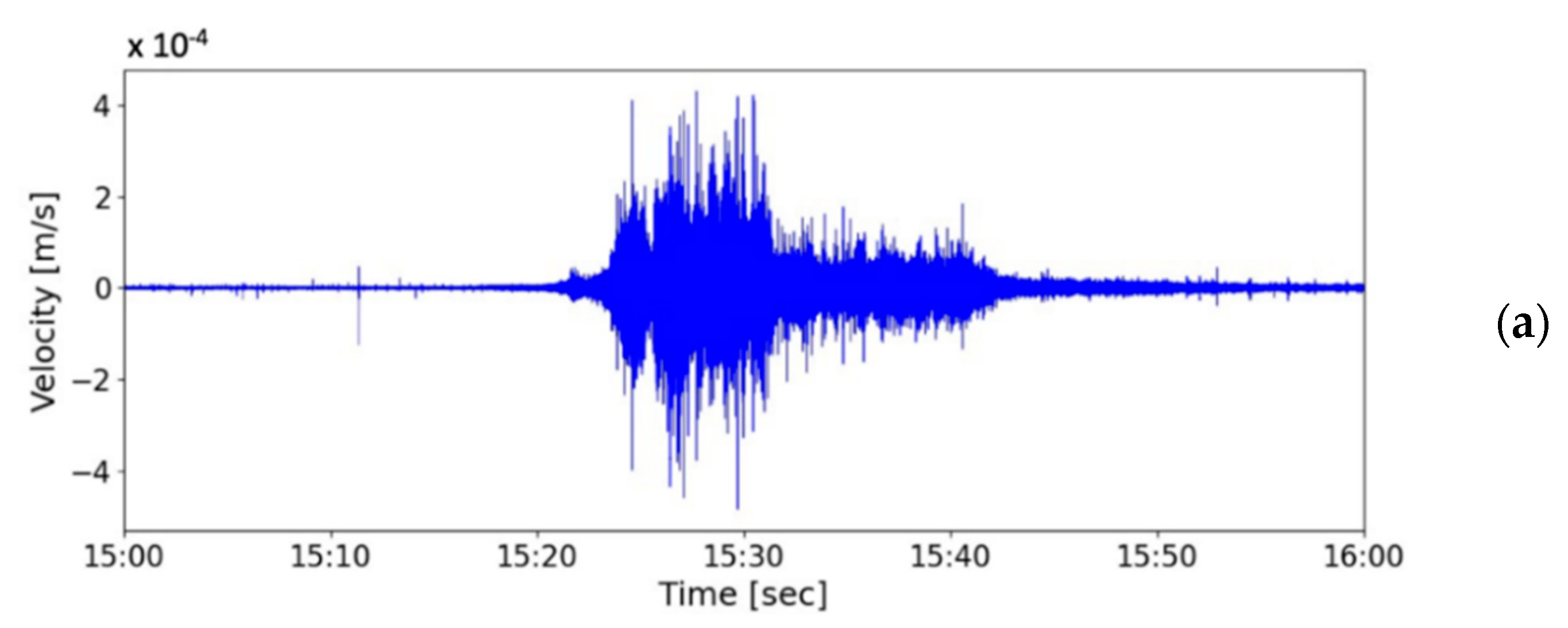
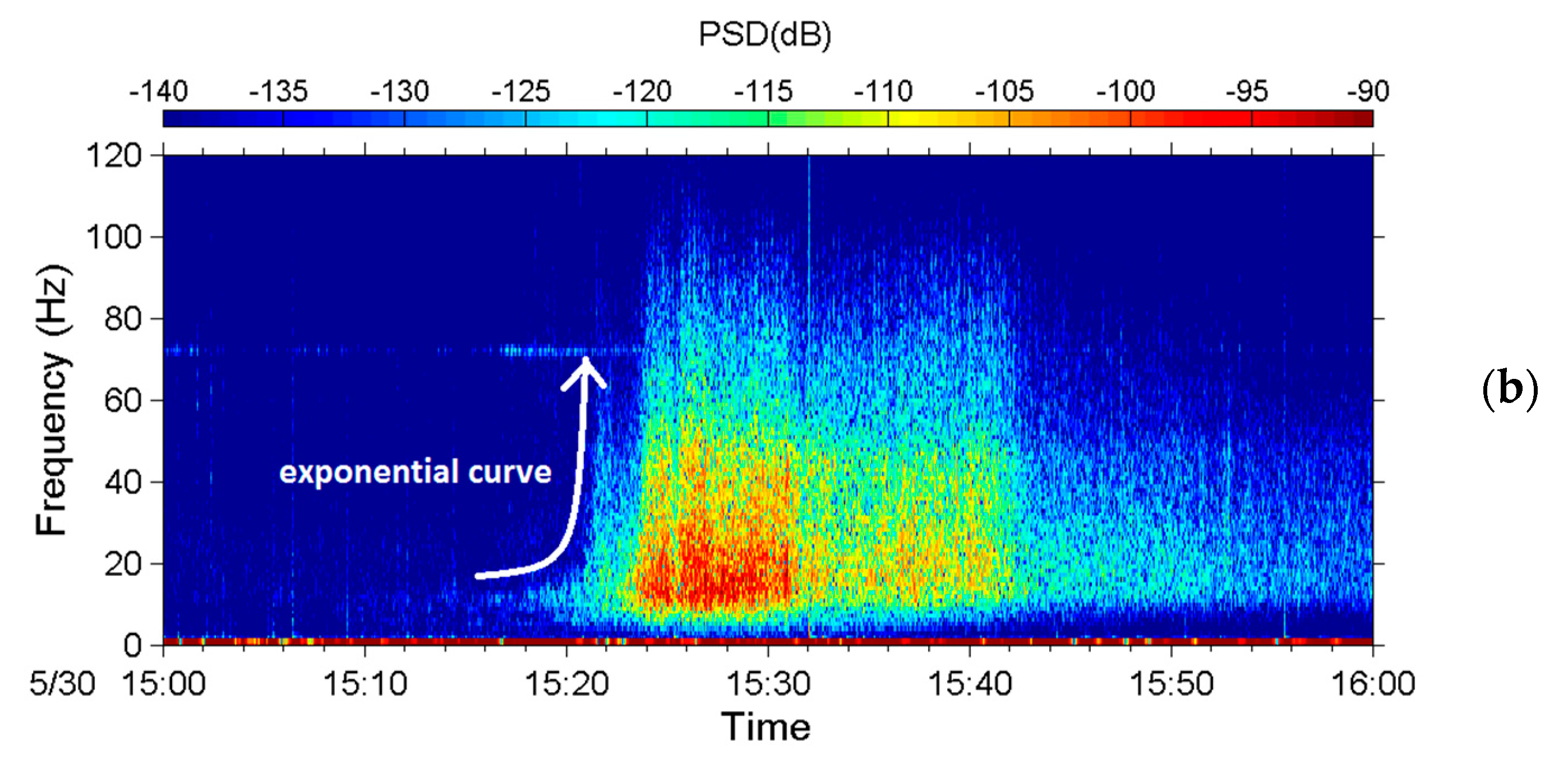
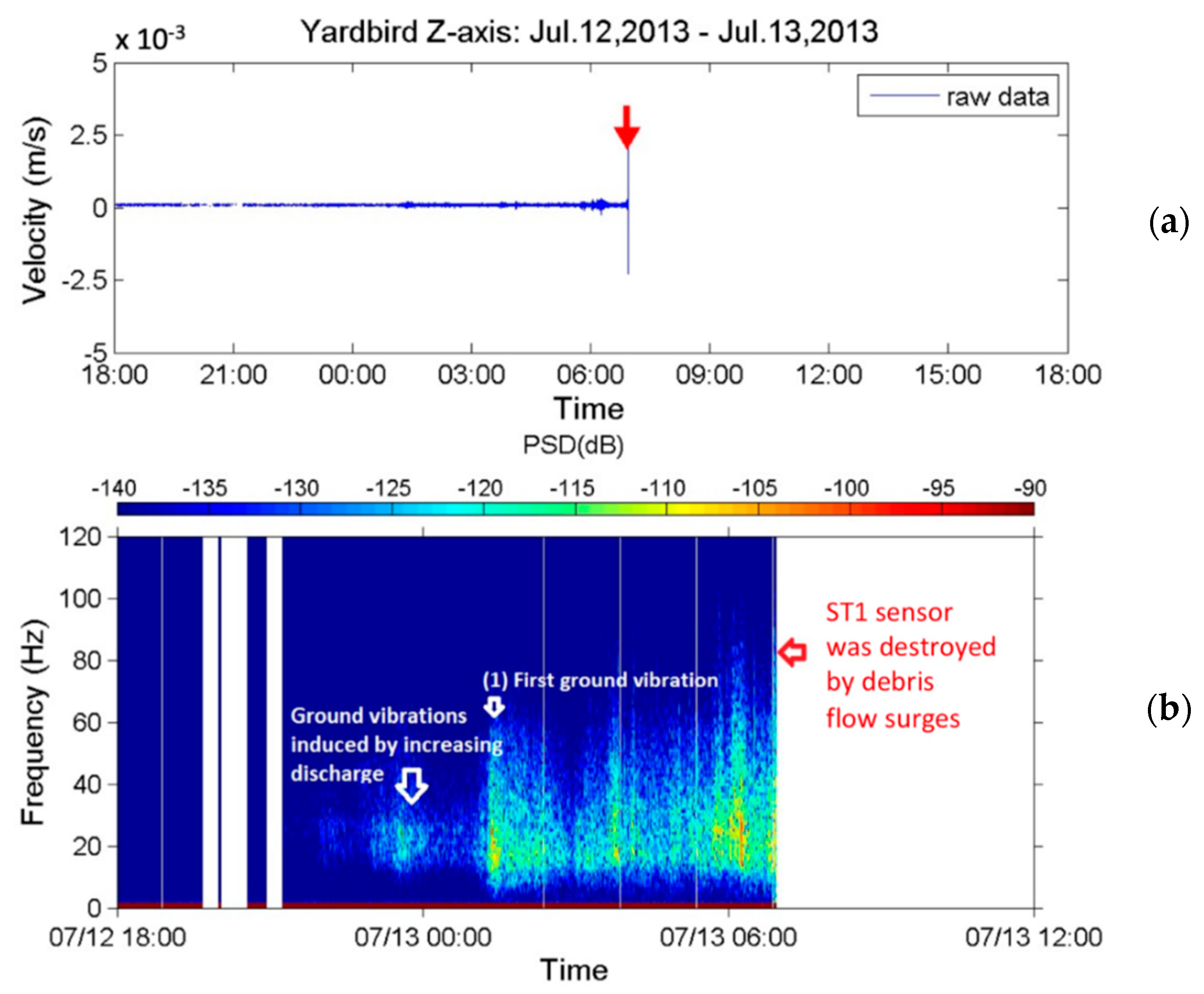
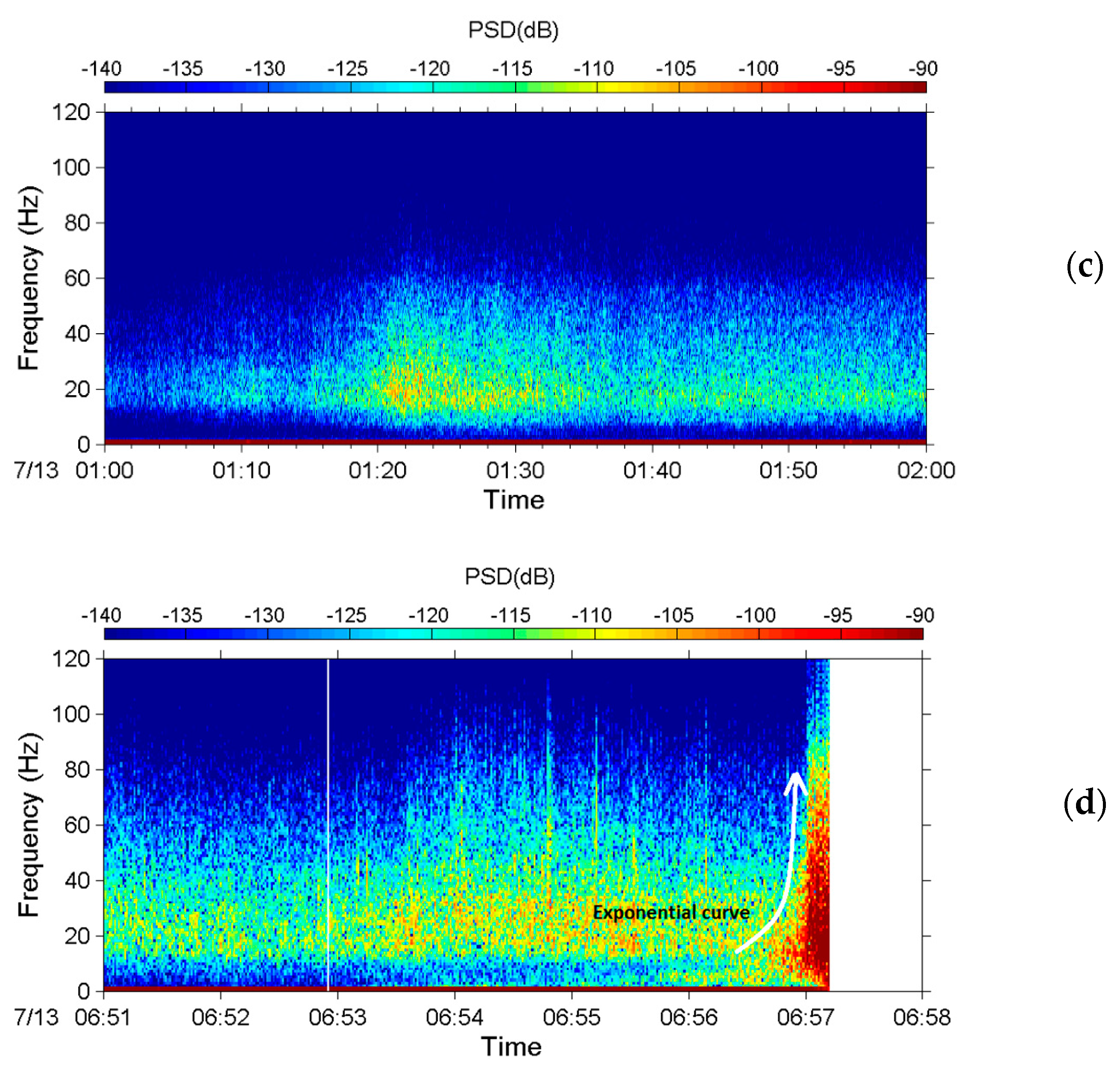
5.2. Debris Flow during Typhoon Soulik in 2013
5.3. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, A.M.; Rodine, J.R. Debris flows. In Slope Instability; Brunsden, D., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984; pp. 257–361. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, R.M. The physics of debris flows. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, T. Debris flow. In IAHR Monograph; AA Balkema Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Arattano, M.; Marchi, L. Systems and sensors for debris-flow monitoring and warning. Sensors 2008, 8, 2436–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieczorek, G.F. Effect of rainfall intensity and duration on debris flows in the central Santa Cruz Mountains, California. In Debris Flows/Avalanches: Process, Recognition, and Mitigation; Costa, J.E., Wieczorek, G.F., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1987; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, C.D.; Lee, M.H.; Huang, T.H. Effect of rainfall on debris flows in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Slope Engineering, Hong Kong, China, 8–10 December 2003; Volume 2, pp. 741–751. [Google Scholar]
- Bänziger, R.; Burch, H. Acoustic sensors (hydrophones) as indicators for bed load transport in a mountain torrent. In Hydrology in Mountainous Regions, 1-Hydrological Measurements, the Water Cycle; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 1990; Volume 193, pp. 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-J.; Shieh, C.-L.; Yin, H.-Y. Laboratory study of the underground sound generated by debris flows. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2004, 109, F01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, M.; Genevois, R.; LaHusen, R.; Simoni, A.; Tecca, P.R. Debris flow monitoring in the Acquabona watershed on the Dolomites (Italian Alps). Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hürlimann, M.; Rickenmann, D.; Graf, C. Field and monitoring data of debris-flow events in the Swiss Alps. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; Yin, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yeh, C.-H.; Wang, C.-L. Ground vibrations produced by rock motions and debris flows. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, F02014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kogelnig, A.; Hübl, J.; Suriñach, E.; Vilajosana, I.; McArdell, B.W. Infrasound produced by debris flow: Propagation and frequency content evolution. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 1713–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, A.; Hübl, J. Automatic detection of debris flows and debris floods based on a combination of infrasound and seismic signals. Landslides 2016, 13, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, A.; Hübl, J.; McArdell, B.W.; Walter, F. Automatic identification of alpine mass movements by a combination of seismic and infrasound sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arattano, M. On the use of seismic detectors as monitoring and warning systems for debris flows. Nat. Hazards 1999, 20, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arattano, M.; Moia, F. Monitoring the propagation of a debris flow along a torrent. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1999, 44, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Arattano, M.; Deganutti, A. Ten years of debris-flow monitoring in the Moscardo Torrent (Italian Alps). Geomorphology 2002, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, V.H.; Tsai, V.C.; Lamb, M.P.; Ulizio, T.P.; Beer, A.R. The seismic signature of debris flows: Flow mechanics and early warning at Montecito, California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5528–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, E.; Walter, F.; Barfucci, G.; Genco, R.; Wenner, M.; Ripepe, M.; McArdell, B.; Price, C. Infrasound array analysis of debris flow activity and implication for early warning. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belli, G.; Walter, F.; McArdell, B.; Gheri, D.; Marchetti, E. Infrasound and seismic analysis of debris-flow events at Illgraben (Switzerland): Relating signal features to flow parameters and to the seismo-acoustic mechanism. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2022, 127, e2021JF006576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; Chu, C.-R.; Tien, T.-M.; Yin, H.-Y.; Chen, P.-S. Calibration and deployment of a fiber-optic sensing system for monitoring debris flows. Sensors 2012, 12, 5835–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuda, S.; Okunishi, K.; Suwa, H. Observation of debris flow at Kamikamihori Valley of Mt. Yakedade. In Excursion Guidebook, Proceedings of the 3rd Meeting of IGU commission on Field Experiment in Geomorphology, Kyoto, Japan, 24–30 August 1980; Disaster Prevention Research Institute: Kyoto, Japan, 1980; pp. 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel, A.; Coviello, V.; Comiti, F. Debris flow velocity and volume estimations based on seismic data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haas, T.; Åberg, A.S.; Walter, F.; Zhang, Z. Deciphering seismic and normal-force fluctuation signatures of debris flows: An experimental assessment of effects of flow composition and dynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 2195–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, Y.; Inaba, H.; Sawada, T. A debris-flow monitoring devices and methods bibliography. Nat. Hazards. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutzmann, E.; Roult, G.; Astiz, L. Geoscope station noise levels. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2000, 90, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, P.M. Introduction to Seismology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Udias, A. Principles of Seismology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.; Sain, K.; Kumar, A.; Tiwari, J.; Paul, A.; Kumar, N.; Haldar, C.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, C.P. Potential seismic precursors and surficial dynamics of a deadly Himalayan disaster: An early warning approach. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.L.; Rekapalli, R.; Dietze, M.; Pilz, M.; Cesca, S.; Purnachandra Rao, N.; Srinagesh, D.; Paul, H.; Metz, M.; Mandal, P.; et al. Detection and potential early warning of catastrophic flow events with regional seismic networks. Sciences 2021, 374, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hong, Y.; Yu, B. Detecting infrasound emission of debris flow for warning purposes. In Proceedings of the International Symposium Interpraevent, Taipei, Taiwan, 26–30 April 2004; Volume VII, pp. 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H.T.; Cheung, Y.L.; Zhang, S. Calibration of infrasound monitoring system and acoustic characteristics of debris-flow movement by field studies. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment; Chen, C.-L., Major, J.J., Eds.; Millpress: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-J.; Yeh, C.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chang, S.-T. Ground vibrations and airborne sounds generated by motion of rock in a river bed. Nat. Hazrads Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-J.; Chen, S.-C.; Chao, W.-A.; Yang, C.-M. Application of Raspberry Shake 3D geophone for monitoring slope disasters. J. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 53, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Lin, C.-R.; Kuo, B.-Y. Development of a short-period ocean bottom seismometer in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Underwater Technology and Workshop on Scientific Use of Submarine Cables and Related Technologies, Tokyo, Japan, 5–8 April 2011; p. 12031721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.M. A versatile equalization circuit for increasing seismometer velocity response below the natural frequency. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1989, 79, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvino, A.; Bates, D.J. Electronic Principles, 7th ed.; The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hibert, E.; Malet, J.-P.; Bourrier, F.; Provost, F.; Berger, F.; Bornemann, P.; Tardif, P.; Mermin, E. Single-block rockfall dynamics inferred from seismic signal analysis. Earth Surf. Dynam. 2017, 5, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saló, L.; Corominas, J.; Lantada, N.; Matas, G.; Prades, A.; Ruiz-Carulla, R. Seismic energy analysis as generated by impact and fragmentation of single-block experimental rockfalls. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 1450–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.Y. Studying and Monitoring the Ground Vibration Generated by Debris Flows. Ph.D. Thesis, National Cheng Kung University, Department of Hydraulic and Ocean Engineering, Tainan, Taiwan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriñach, E.; Vilajosana, I.; Khazaradze, G.; Biescas, B.; Furdada, G.; Vilaplana, J.M. Seismic detection and characterization of landslides and other mass movements. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arattano, M. On debris flow front evolution along a torrent. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Arattano, M.; Marchi, L. Measurements of debris flow velocity through cross-correlation of instrumentation data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arattano, M.; Marchi, L.; Cavalli, M. Analysis of debris-flow recordings in an instrumented basin: Confirmations and new findings. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierson, T.C. Flow behavior of channelized debris flows, Mount St. Helens, Washington. In Hillslope Processes: Binghamton Geomorphology Symposium 16; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 1986; pp. 269–296. [Google Scholar]
- Burtin, A.; Bollinger, L.; Vergne, J.; Cattin, R.; Nabelek, J.L. Spectral analysis of seismic noise induced by rivers: A new tool to monitor spatiotemporal changes in stream hydrodynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113, B05301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burtin, A.; Cattin, R.; Bollinger, L.; Vergne, J.; Steer, P.; Robert, A.; Findling, N.; Tiberi, C. Towards the hydrologic and bed load monitoring from high-frequency seismic noise in a braided river: The “torrent de St Pierre”, French Alps. J. Hydrol. 2011, 408, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.L.; Dietze, M. Seismic Advances in Process Geomorphology. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2022, 50, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arámbula-Mendoza, R.; Valdés-González, C.; Varley, N.; Juarez-Garcia, B.; Alonso-Rivera, P.; Hernández-Joffre, V. Observation of vulcanian explosions with seismic and acoustic data at Popocatepetl volcano, Mexico. In Complex Monitoring of Volcanic Activity: Methods and Results; Zobin, V.M., Ed.; Nova: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 13–33. [Google Scholar]
- Matoza, R.S.; Arciniega-Ceballos, A.; Sanderson, R.W.; Mendo-Pérez, G.; Rosado-Fuentes, A.; Chouet, B.A. High-broadband seismoacoustic signature of vulcanian explosions at Popocatepetl volcano, Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z. The seismic signatures of the 2009 Shiaolin landslide in Taiwan. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Broadband Seismometer (STS-2) | Geophone (GS-20DX) | Raspberry Shake 3D | LE-3Dlite | Yardbird Seismometer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working frequency range (Hz) | 0.0083–100 | 8–250 | 0.5–40 | 1–100 | 0.3–120 |
| Sensitivity (V/m/s) | 1500 | 27.6 | 75 | 800 | 150 |
| Weight (kg) | 13 | 0.08 | 0.6 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Event | Date | Debris Flow Scale | Rock Size in the Surge Front (m) | Lowest Frequency * (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
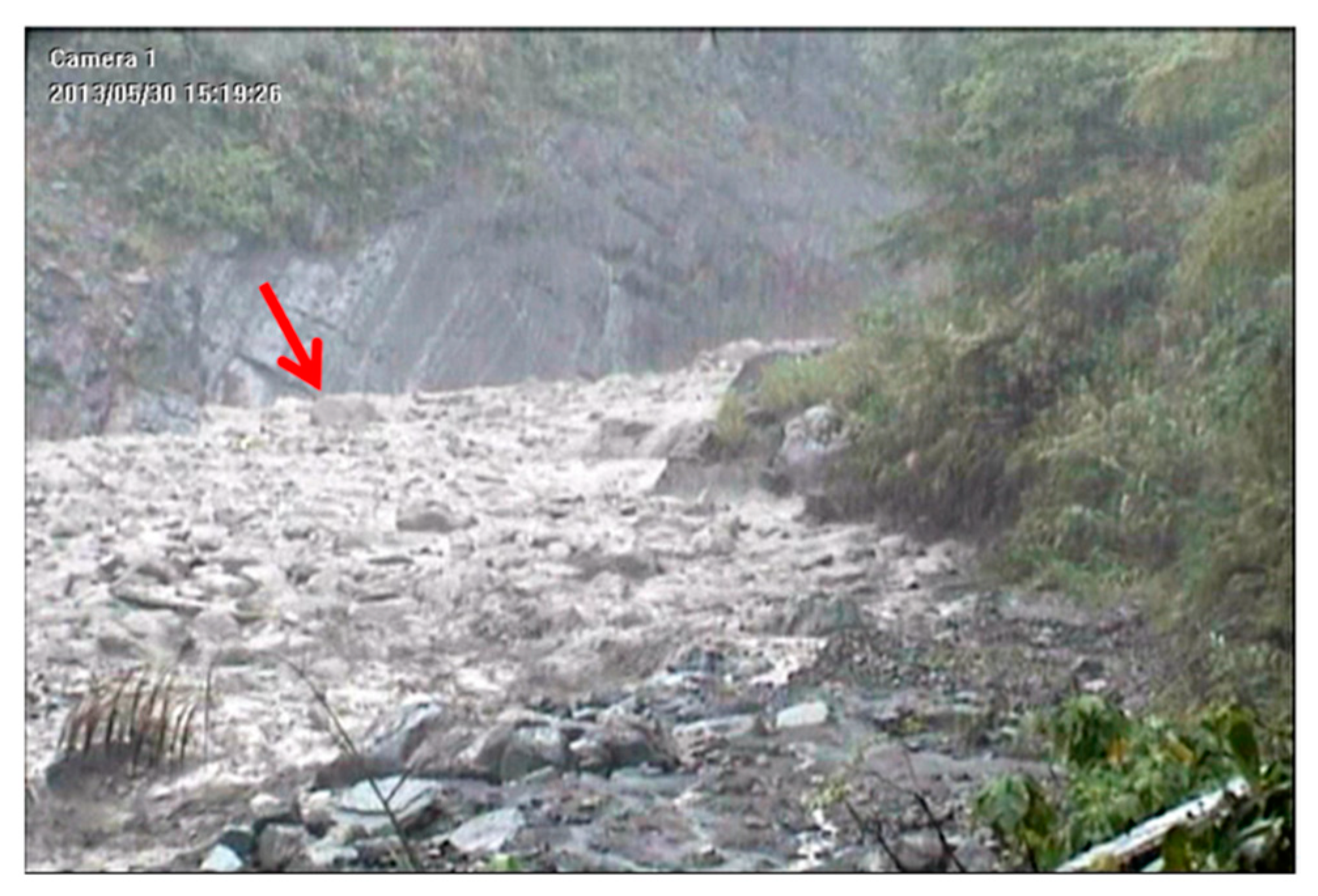
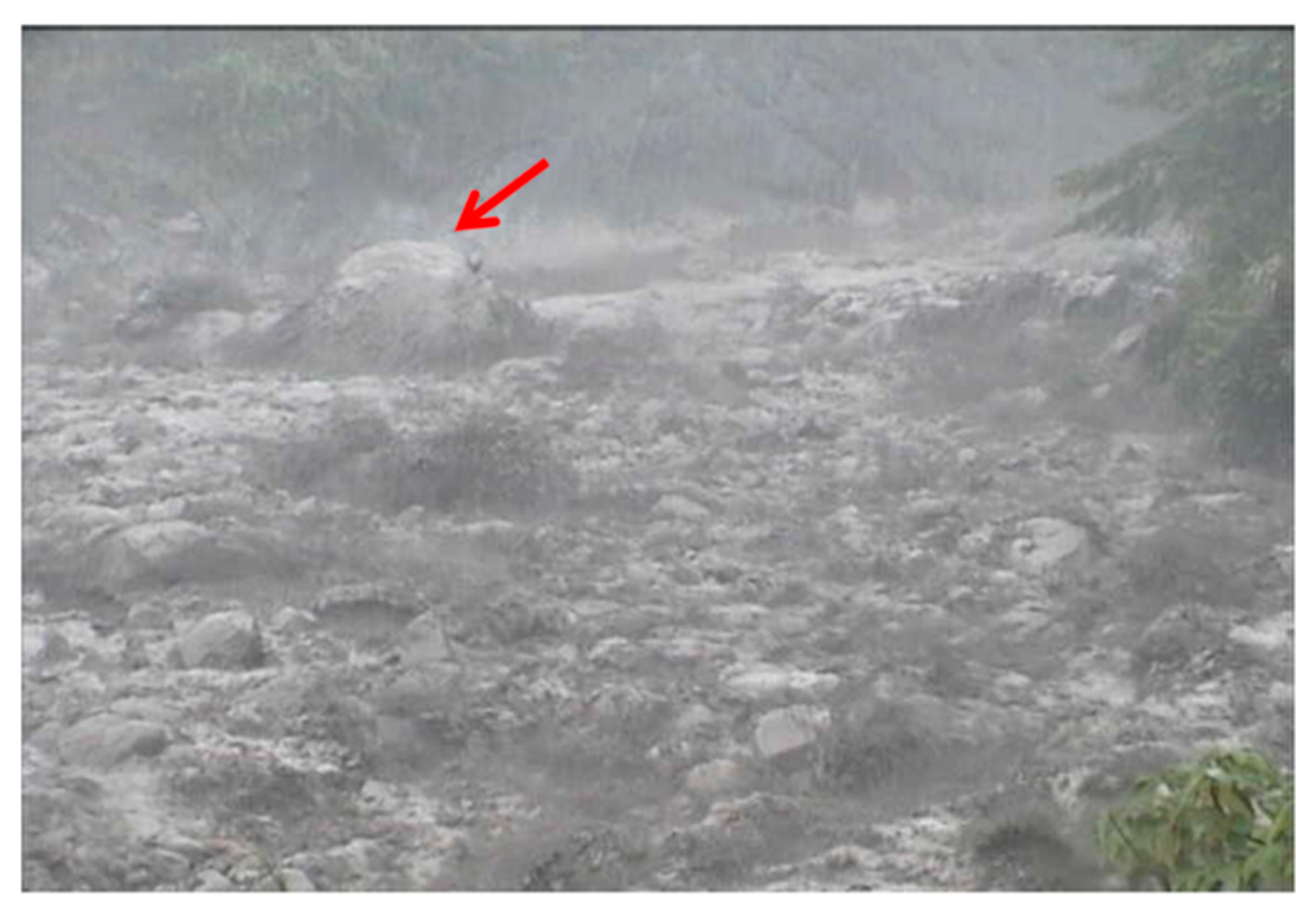
| 1 | 30 May 2013 | small | 0.5 | 11 |
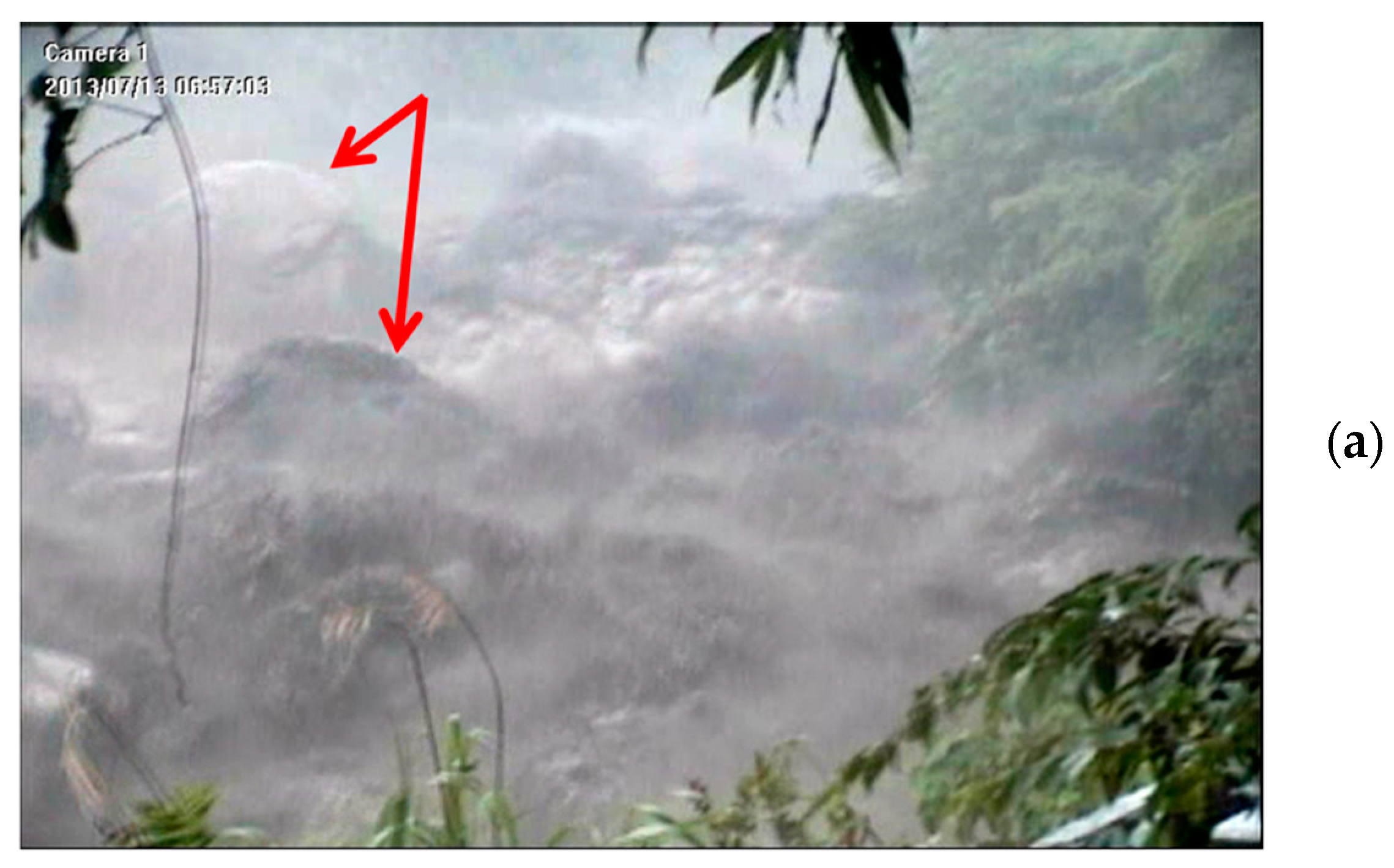
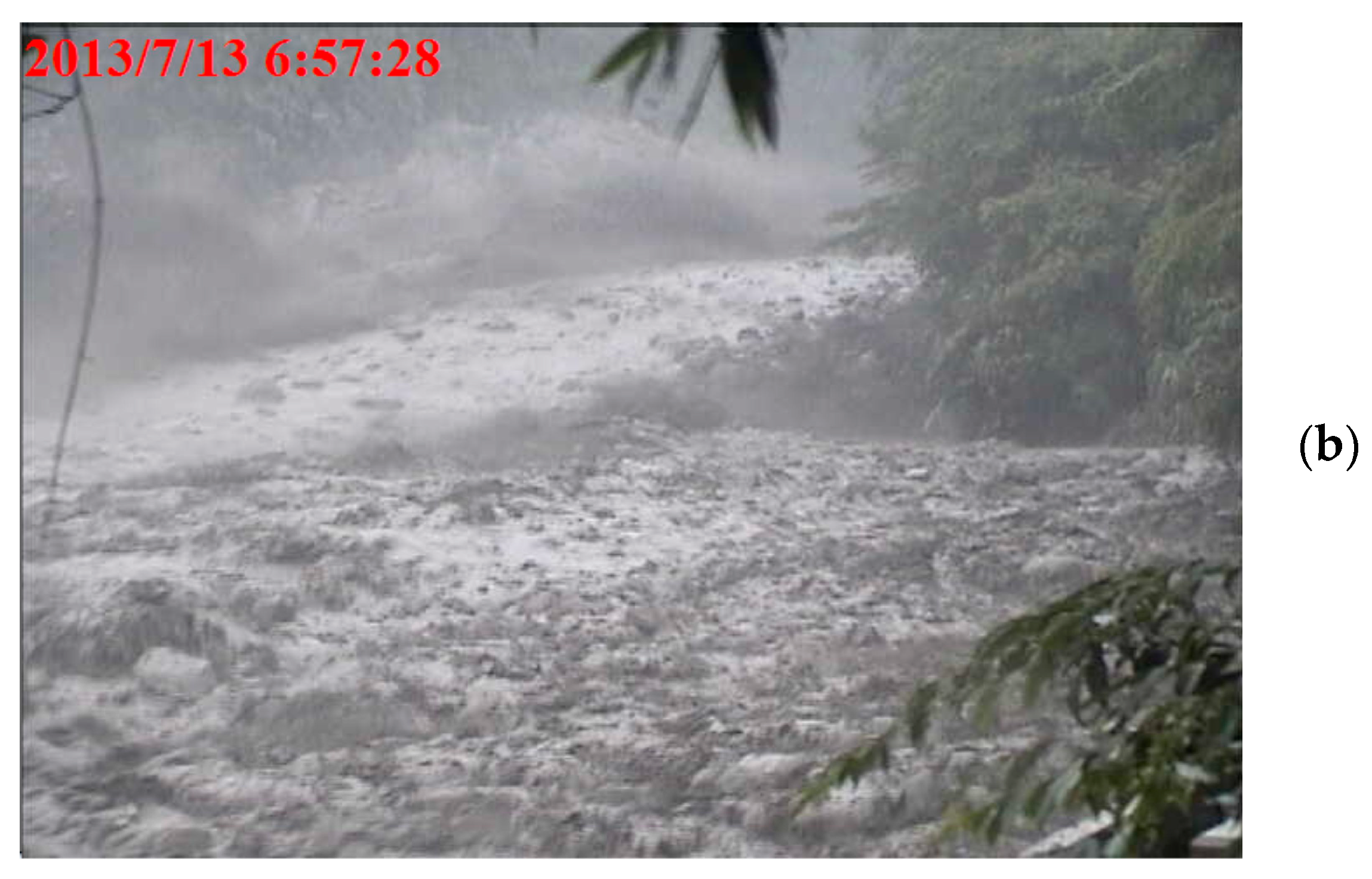
| 2 | 13 July 2013 | large | 3–5 | 2 |
| 3 | 20 May 2014 | medium | 2.0 | 5 |
| Events | Specifications | Frequency Range (Hz) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earthquakes | Local (~50 km) Regional (~230 km) Teleseism (~7000 km) | 1–50 1–12 0.1–1 | Suriñach et al. [42] |
| Rockfalls | masses 76–472 kg masses 466–13,581 kg | 5–120 | Hibert et al. [38] Saló et al. [39] |
| Volcanic eruptions | Popocatépetl Volcano | 0.1–10 | Arámbula-Mendoza [50] Matoza et al. [51] |
| Debris flows | Large boulders in the surge front | 2–120 | Present Study Lai et al. [18], Schimmel et al. [14], Marchetti et al. [19], Belli et al. [20] |
| Landslides | Laguna Beach 2005 Shiaolin landslide 2009 | 1–10 0.5–1.5 | Suriñach et al. [42] Feng [52] |
| Snow avalanches | Small scale Large scale | 2–45 0.1–90 | Suriñach et al. [42] |
| River flows | 10–30, 8–70 2–80 | Present Study Burtin et al. [47,48] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chu, C.-R.; Lin, C.-R.; Yen, L.-C.; Yin, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Kuo, B.-Y. Low-Frequency Ground Vibrations Generated by Debris Flows Detected by a Lab-Fabricated Seismometer. Sensors 2022, 22, 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239310
Huang C-J, Chen H-Y, Chu C-R, Lin C-R, Yen L-C, Yin H-Y, Wang C-C, Kuo B-Y. Low-Frequency Ground Vibrations Generated by Debris Flows Detected by a Lab-Fabricated Seismometer. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239310
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ching-Jer, Hsin-Yu Chen, Chung-Ray Chu, Ching-Ren Lin, Li-Chen Yen, Hsiao-Yuen Yin, Chau-Chang Wang, and Ban-Yuan Kuo. 2022. "Low-Frequency Ground Vibrations Generated by Debris Flows Detected by a Lab-Fabricated Seismometer" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239310
APA StyleHuang, C.-J., Chen, H.-Y., Chu, C.-R., Lin, C.-R., Yen, L.-C., Yin, H.-Y., Wang, C.-C., & Kuo, B.-Y. (2022). Low-Frequency Ground Vibrations Generated by Debris Flows Detected by a Lab-Fabricated Seismometer. Sensors, 22(23), 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239310






