Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation Method Based on KASPICE-STAP
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Echo Signal Model
2.1. Low-Altitude Windshear Echo Signal Model
2.2. Ground Clutter Echo Signal Model
3. Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation Using KASPICE-STAP Method
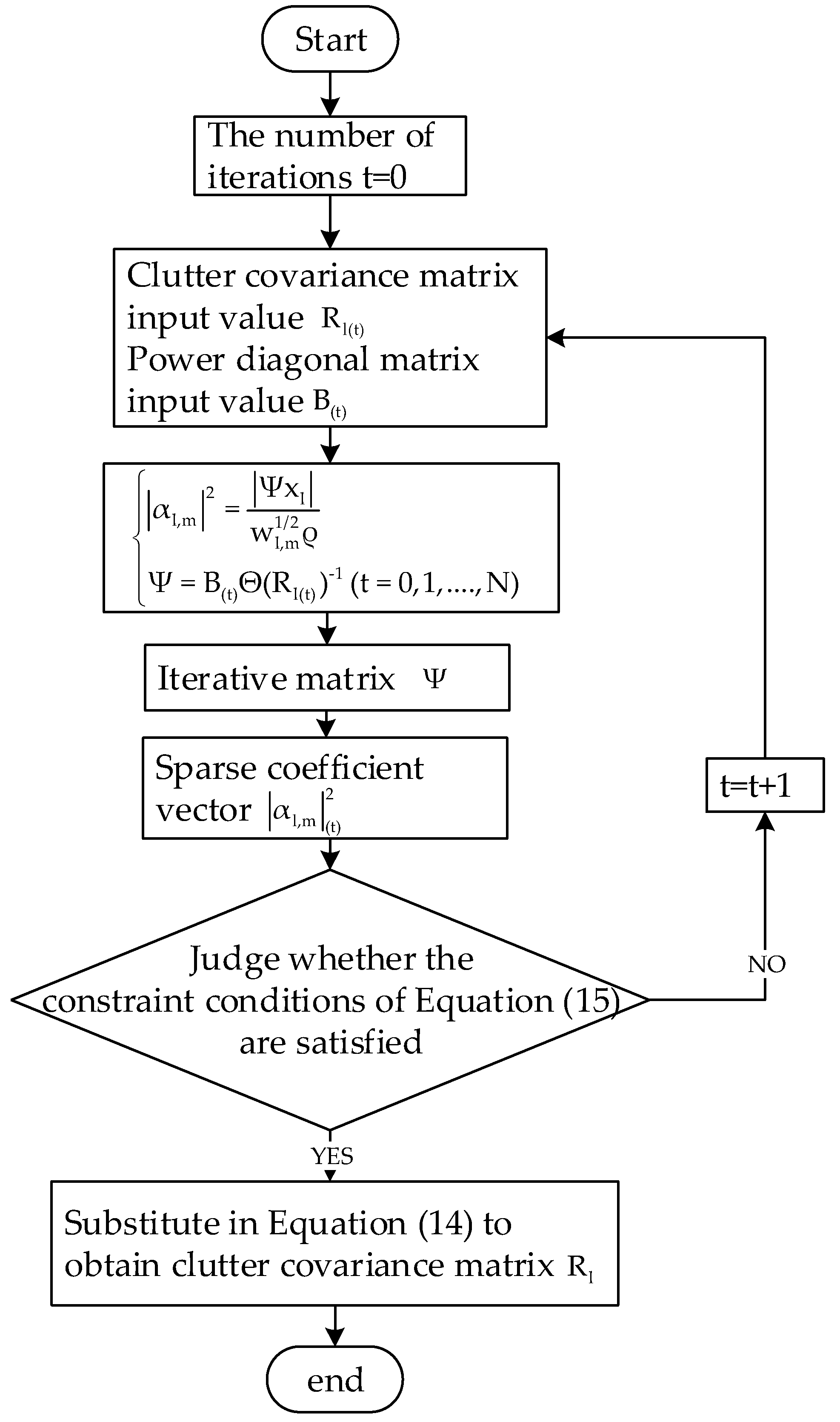
3.1. Estimation of Clutter Covariance Matrix Based on SPICE Algorithm
3.1.1. Construction of Clutter Dictionary
3.1.2. Estimation of Clutter Covariance Matrix Using SPICE Algorithm
3.2. Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation
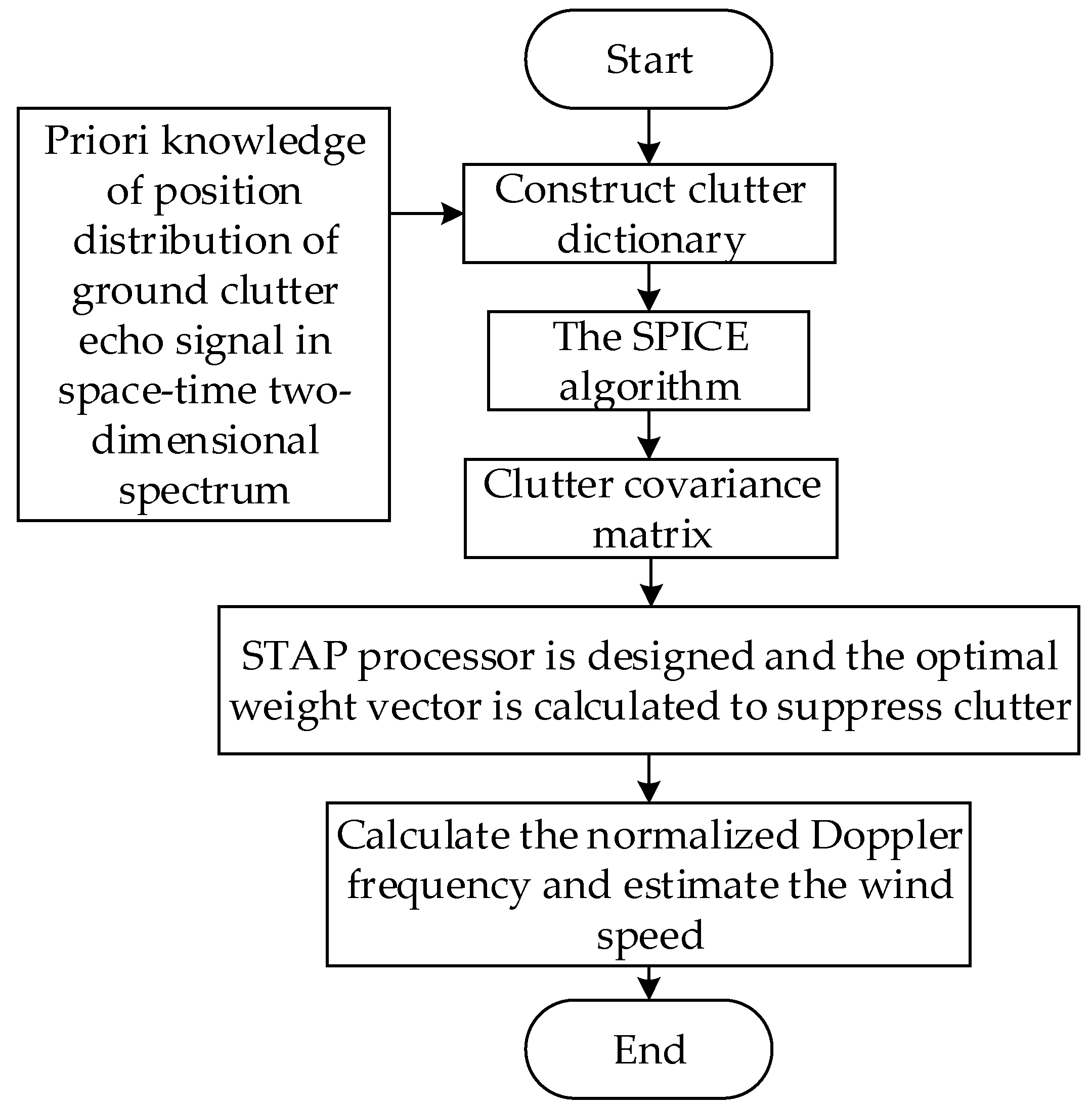
4. Process of the Method
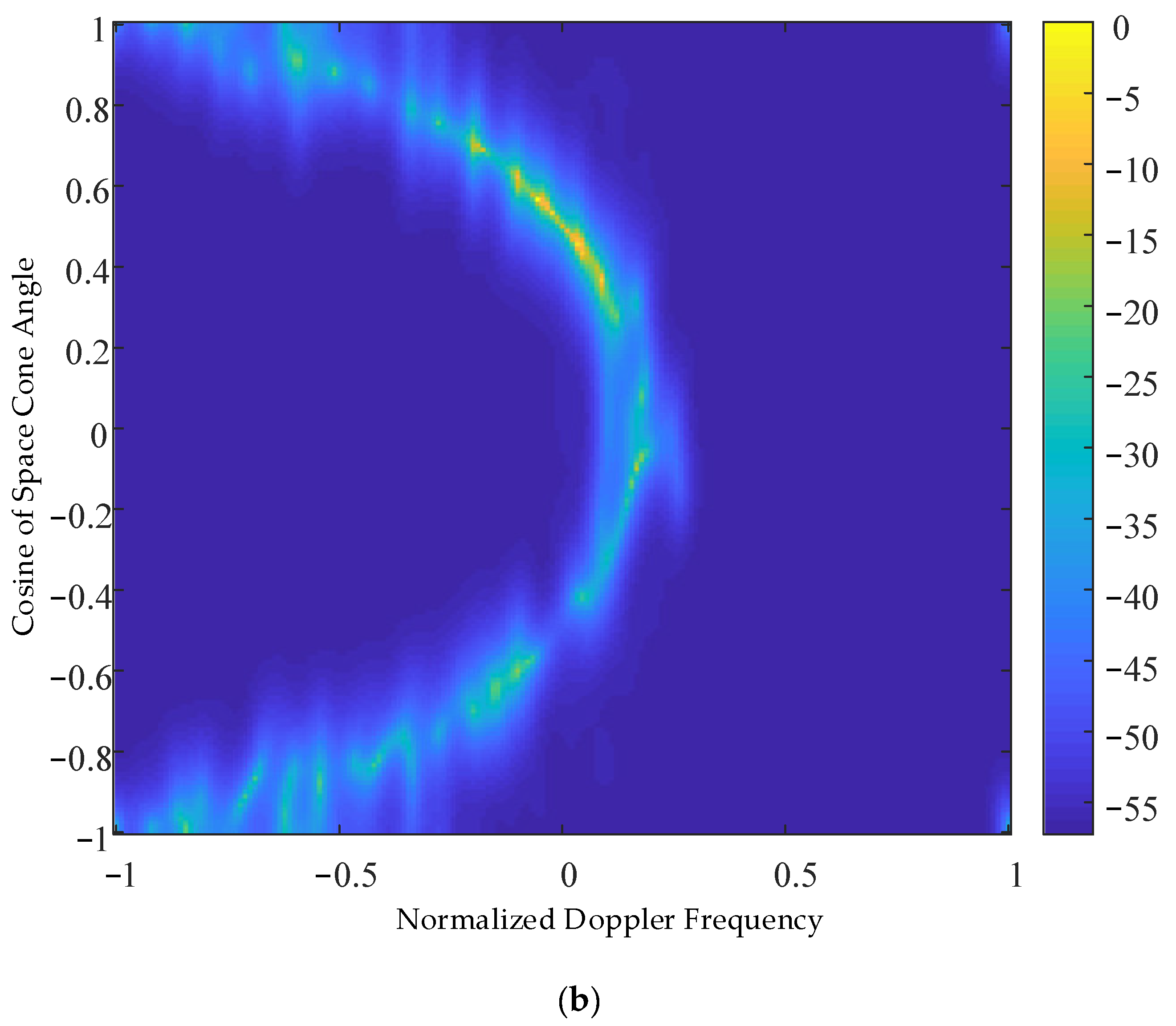
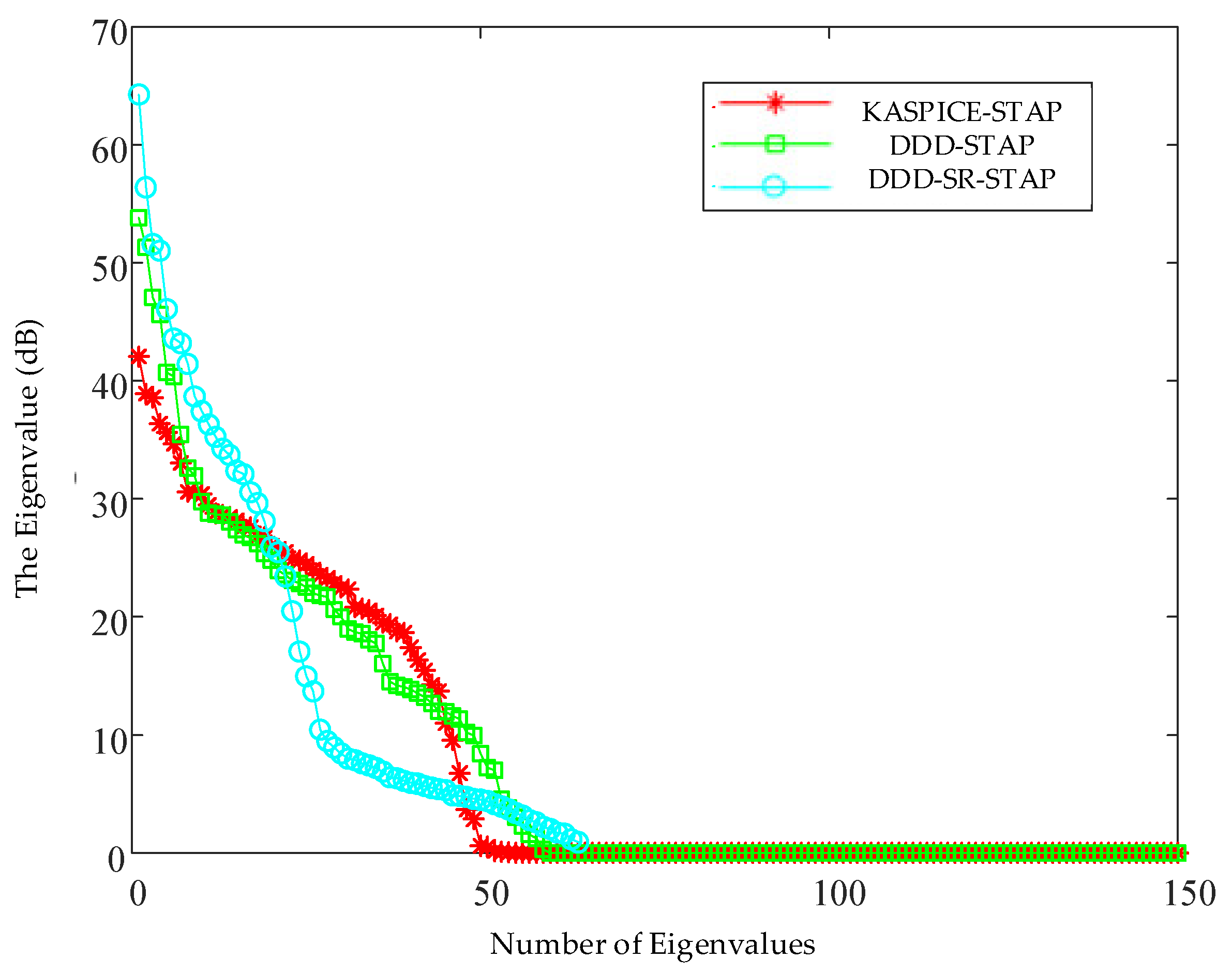
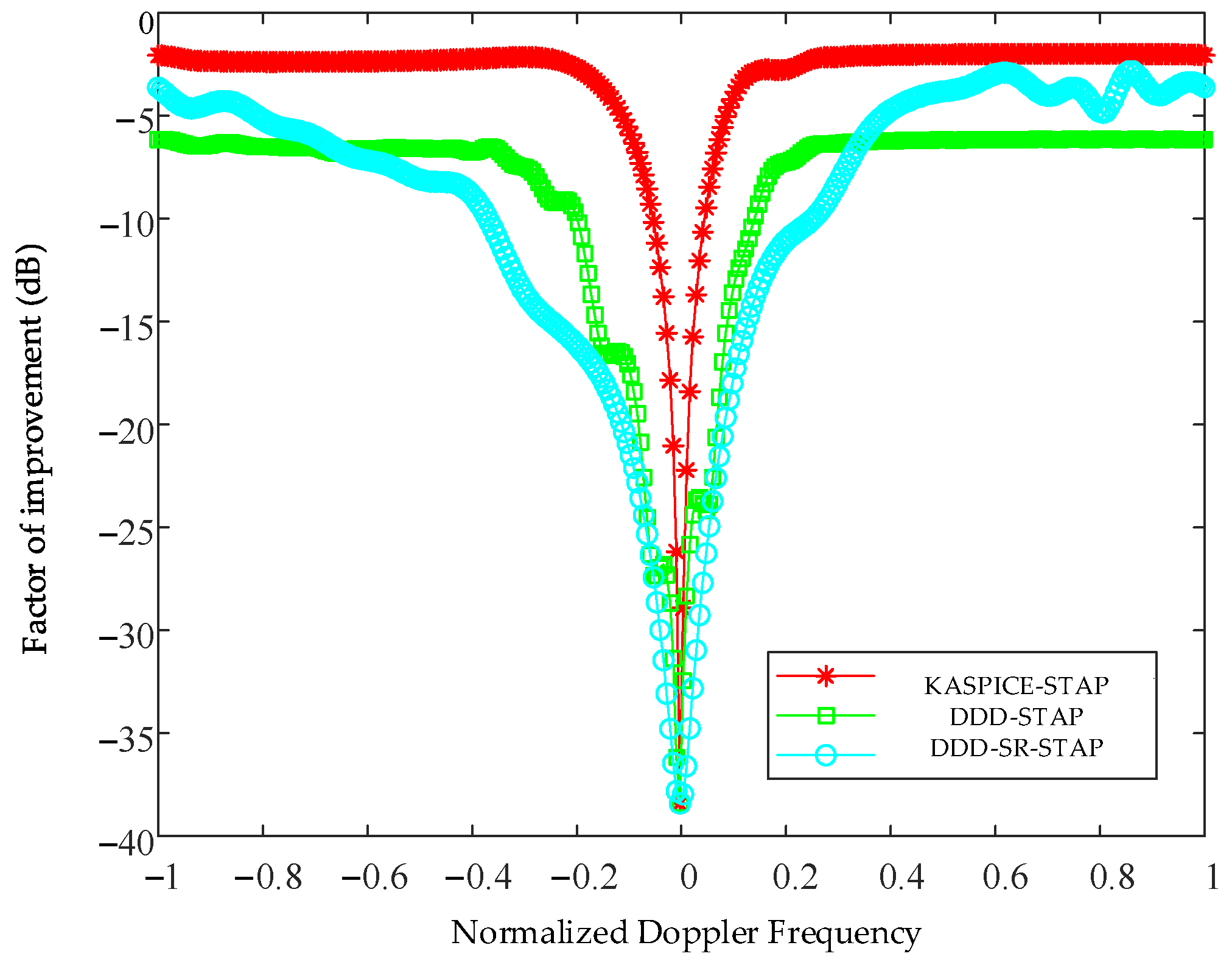
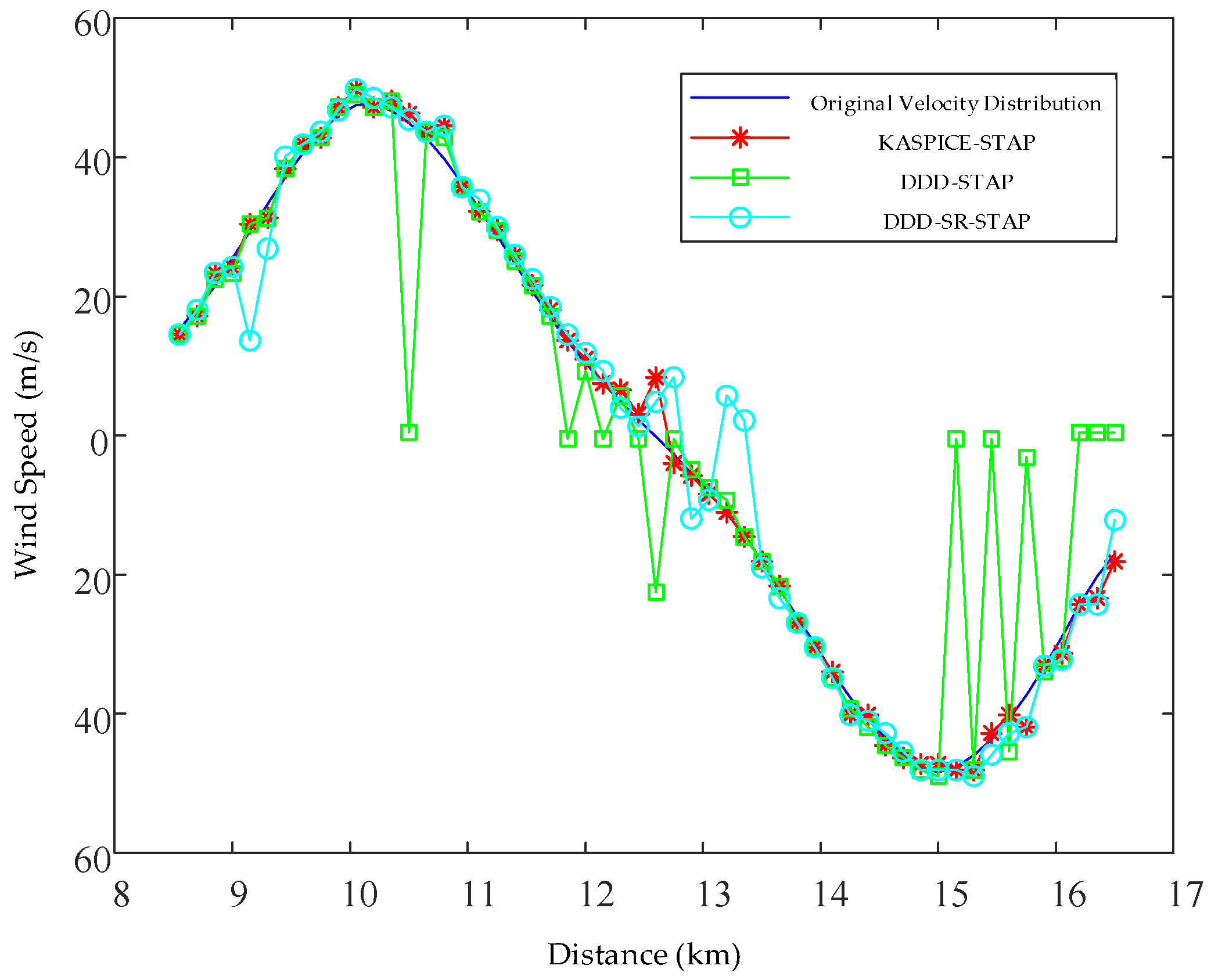
5. Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Wang, J. Low-altitude wind-shear wind speed estimation based on CMCAP. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2019, 41, 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- RTCA/DO-220; Minimum Operational Performance Standards for Airborne Weather Radar with Forward-looking Windshear Capability. RTCA Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Li, H.; Song, D.; Huyan, Z.; Feng, Q.; Zhuang, Z. Wind speed estimation of low-altitude wind-shear based on TDPC-JDL under LFMCW system. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2020, 42, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, R. Applications of Space-Time Adaptive Processing; IEE Press: Stevenage, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Pallotta, L.; Farina, A. Covariance matrix estimation via geometric barycenters and its application to radar training data selection. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013, 7, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, I.S.; Mallett, J.D.; Brennan, L.E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1974, 10, 85–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, C.D.; Haimovich, A.M.; Ayoub, T.F.; Goldstein, J.S.; Reid, I.S. Reduced-rank STAP performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2000, 36, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Wu, R.B.; Han, Y. Wind speed estimation of low-altitude wind-shear based on multiple Doppler channels joint adaptive processing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 3116–3120. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, T.K.; Wang, H.; Park, S.; Adve, R.; Koh, J.; Kim, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wicks, M.; Brown, R. A deterministic least-squares approach to space-time adaptive processing (STAP). IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 49, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Meng, H.; Wang, X. Direct data domain STAP algorithm using sparse recovery. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 51, 972–976. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, T. Sparse Bayesian learning-based robust SR-STAP algorithm. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2022, 1–12. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20221107.1556.004.html (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Zou, B.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Zhu, H.; Lu, F. DU-CG-STAP Method Based on Sparse Recovery and Unsupervised Learning for Airborne Radar Clutter Suppression. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cheng, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Angle-Doppler Channel Selection Method via Sparse Recovery for Reduced-Dimension STAP. J. Univ. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 2022, 51, 506–513. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Hao, C. A robust STAP algorithm using two prior knowledge. J. Signal Process. 2022, 38, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Su, Y. A fast and gridless STAP algorithm based on mixed-norm minimisation and the alternating direction method of multipliers. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2021, 15, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; An, R.; He, N.; He, Z.; Li, H. Reduced Dimension STAP Based on Sparse Recovery in Heterogeneous Clutter Environments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. Off-gird STAP algorithm based on local search orthogonal matching pursuit. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2018, 40, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Yang, J.; Yue, Q.; Zhang, H. Airborne Bistatic Radar Clutter Suppression Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2018, 40, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Stoica, P.; Wong, K. Estimation of the directions of arrival of spatially dispersed signals in array processing. Radar Sonar Navig. IEEE Proc. 1996, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H. Research on parameter estimation method for distributed sources. PhD Thesis, Information Engineering University of PLA, Zhengzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J. Space-Time Adaptive Processing for Airborne Radar Data Systems; Technical Report 1015; Lincoln Laboratory of MIT: Lexington, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 25–45. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, R. Principle of Space-time Adaptive Processing, 3rd ed.; IET Publisher: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Tang, B.; Zhang, Y. Sparse Recovery Algorithm of MIMO-STAP Based on Weighted SPICE. J. Signal Process. 2019, 35, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, F.Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, J.X.; Su, Y. A knowledge aided SPICE space time adaptive processing method for airborne radar with conformal array. Signal Process. 2018, 152, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F. Study on Clutter and Jamming Suppression Methods for Airborne Radar with Conformal Array. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an University, Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.R.; Katselis, D.; Hjalmarsson, H. A Note on the SPICE Method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 4545–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoica, P.; Babu, P.; Li, J. SPICE: A Sparse Covariance-Based Estimation Method for Array Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Babu, P.; Li, J. New Method of Sparse Parameter Estimation in Separable Models and Its Use for Spectral Analysis of Irregularly Sampled Data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 59, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H. Underwater Target DOA Estimation Based on Sparse Covariance Matrix. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft platform height (m) | 600 | Number of array elements | 8 |
| Aircraft platform speed (m/s) | 75 | Number of coherent pulse | 32 |
| Radar wavelength (m) | 0.032 | Angle of main lobe (°) | (60,0) |
| Pulse repetition frequency (Hz) | 7000 | Range resolution (m) | 150 |
| Signal-to-noise ratio (dB) | 5 | Clutter-to-noise ratio (dB) | 40 |
| Wind Speed Estimation Method | Root Mean Square Error/(m/s) |
|---|---|
| DDD-STAP | 13.2187 |
| DDD-SR-STAP | 4.7335 |
| KASPICE-STAP | 1.8692 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Feng, K.; Jin, M. Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation Method Based on KASPICE-STAP. Sensors 2023, 23, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010054
Li H, Chen Y, Feng K, Jin M. Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation Method Based on KASPICE-STAP. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hai, Yutong Chen, Kaihong Feng, and Ming Jin. 2023. "Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation Method Based on KASPICE-STAP" Sensors 23, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010054
APA StyleLi, H., Chen, Y., Feng, K., & Jin, M. (2023). Low-Altitude Windshear Wind Speed Estimation Method Based on KASPICE-STAP. Sensors, 23(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010054





