Advances in Silicon-Based Integrated Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LIDAR Ranging Methods
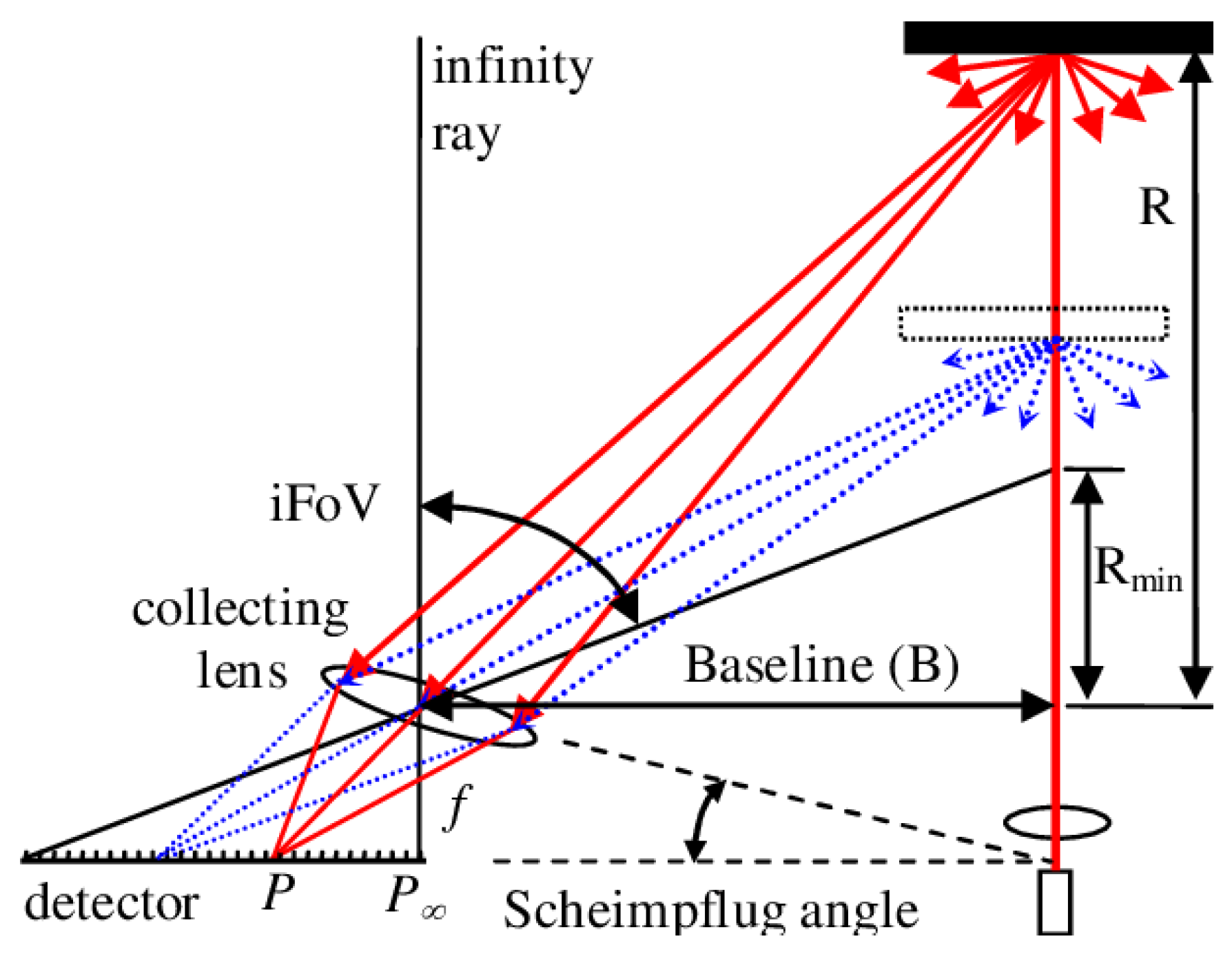
2.1. Triangular Ranging
2.2. Time of Flight

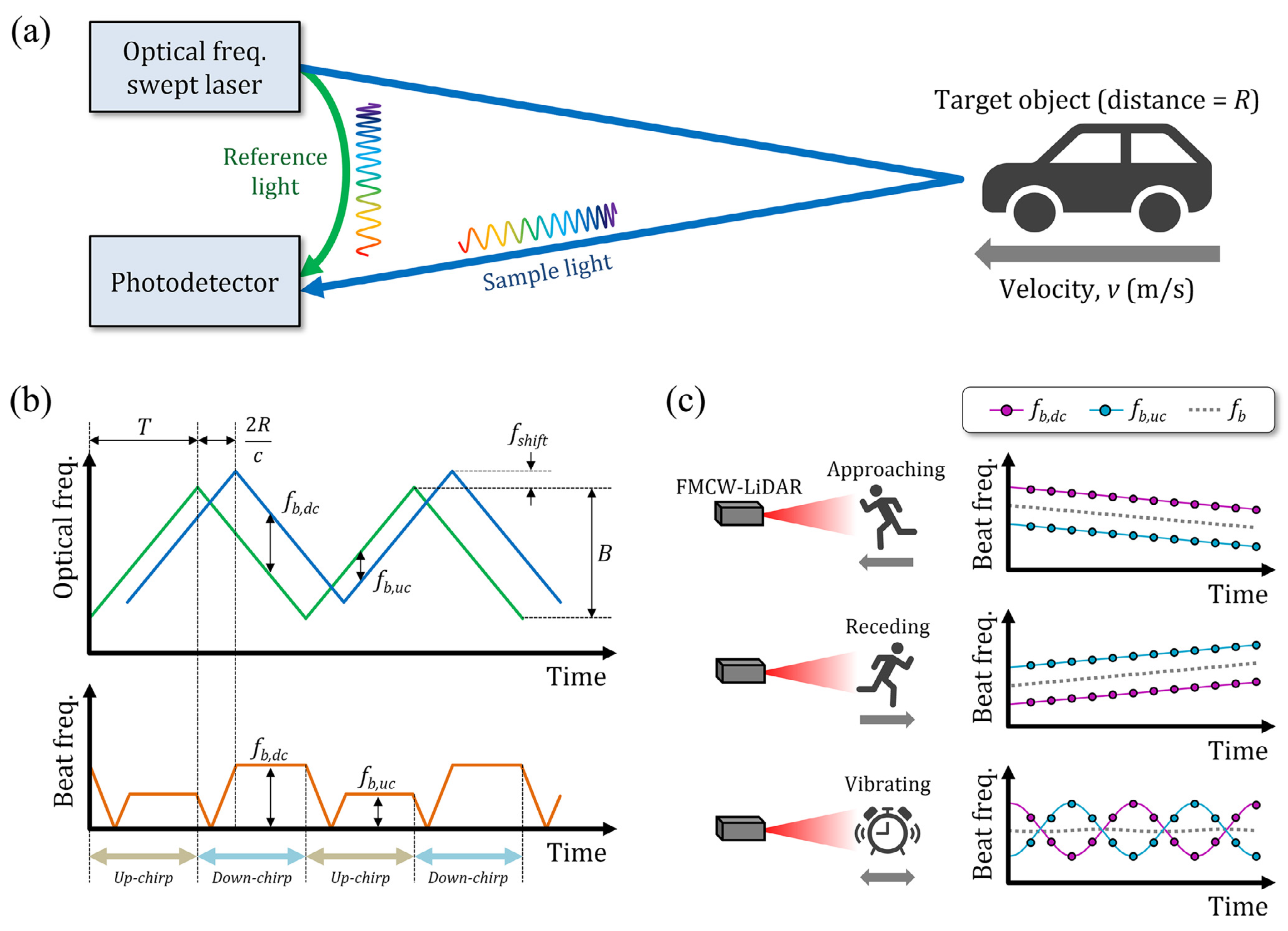
2.3. Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave
3. Silicon-Based Optical Phased Array Lidar
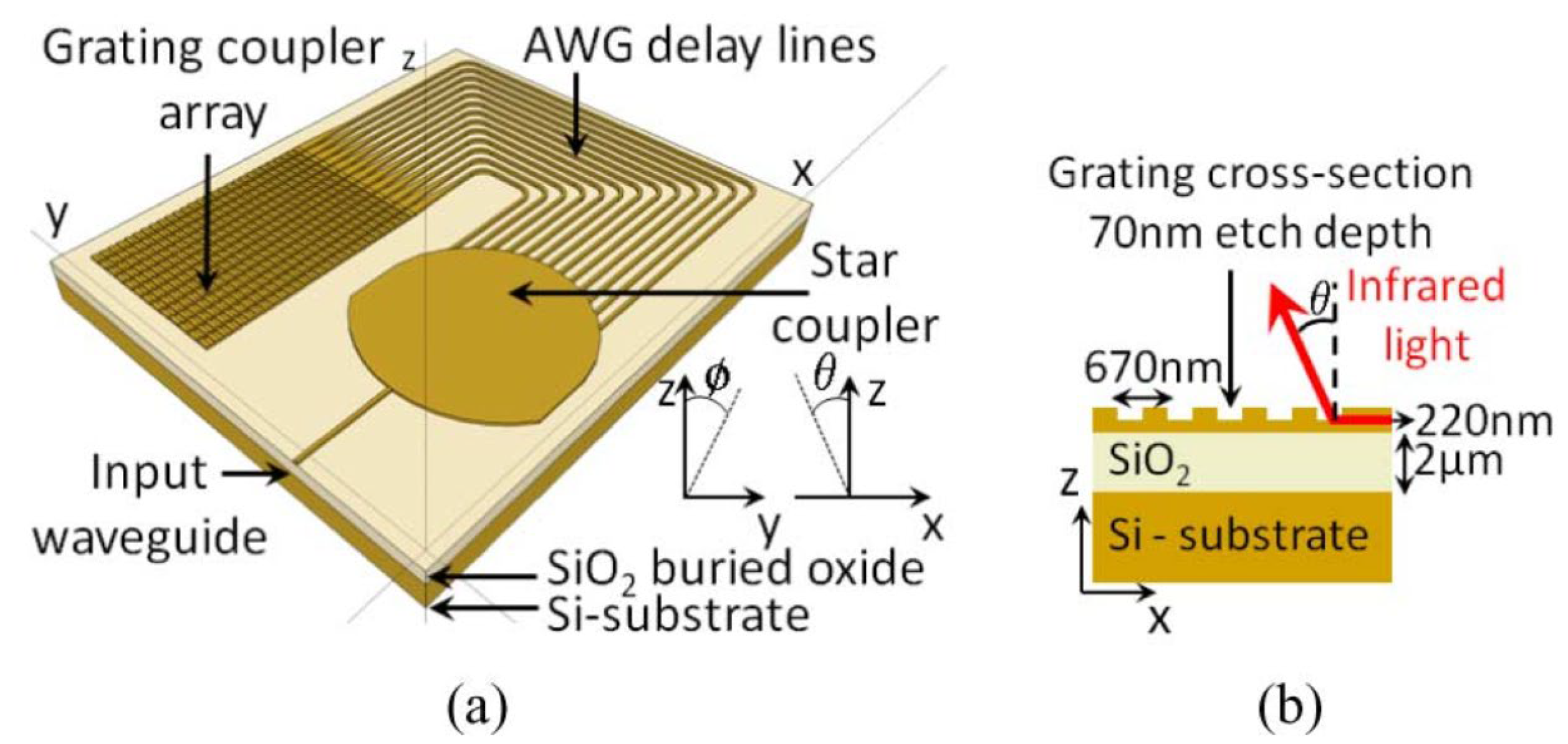
3.1. OPA Lidar Based on Silicon on Insulator
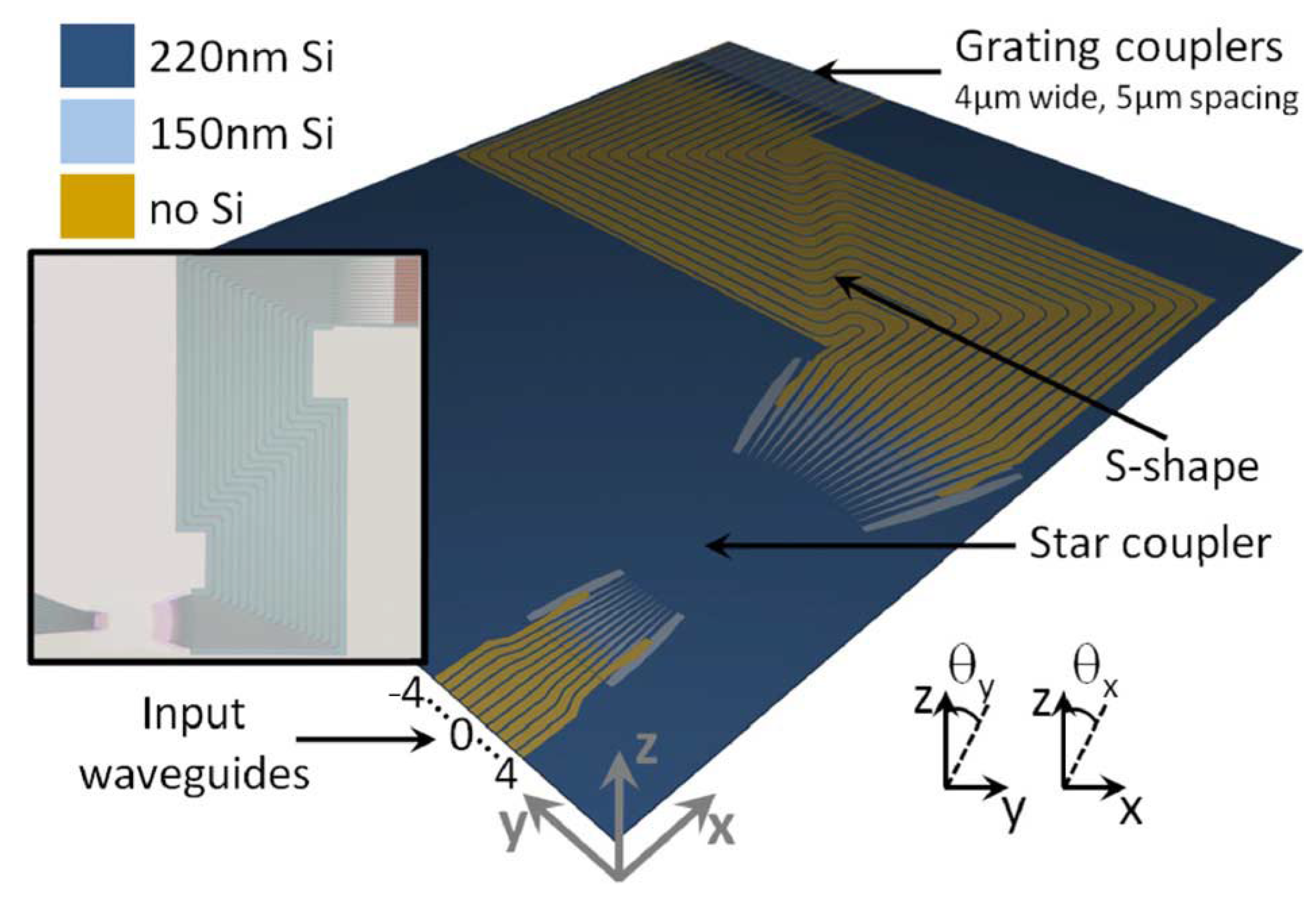
3.2. OPA Lidar Based on Hybrid Material
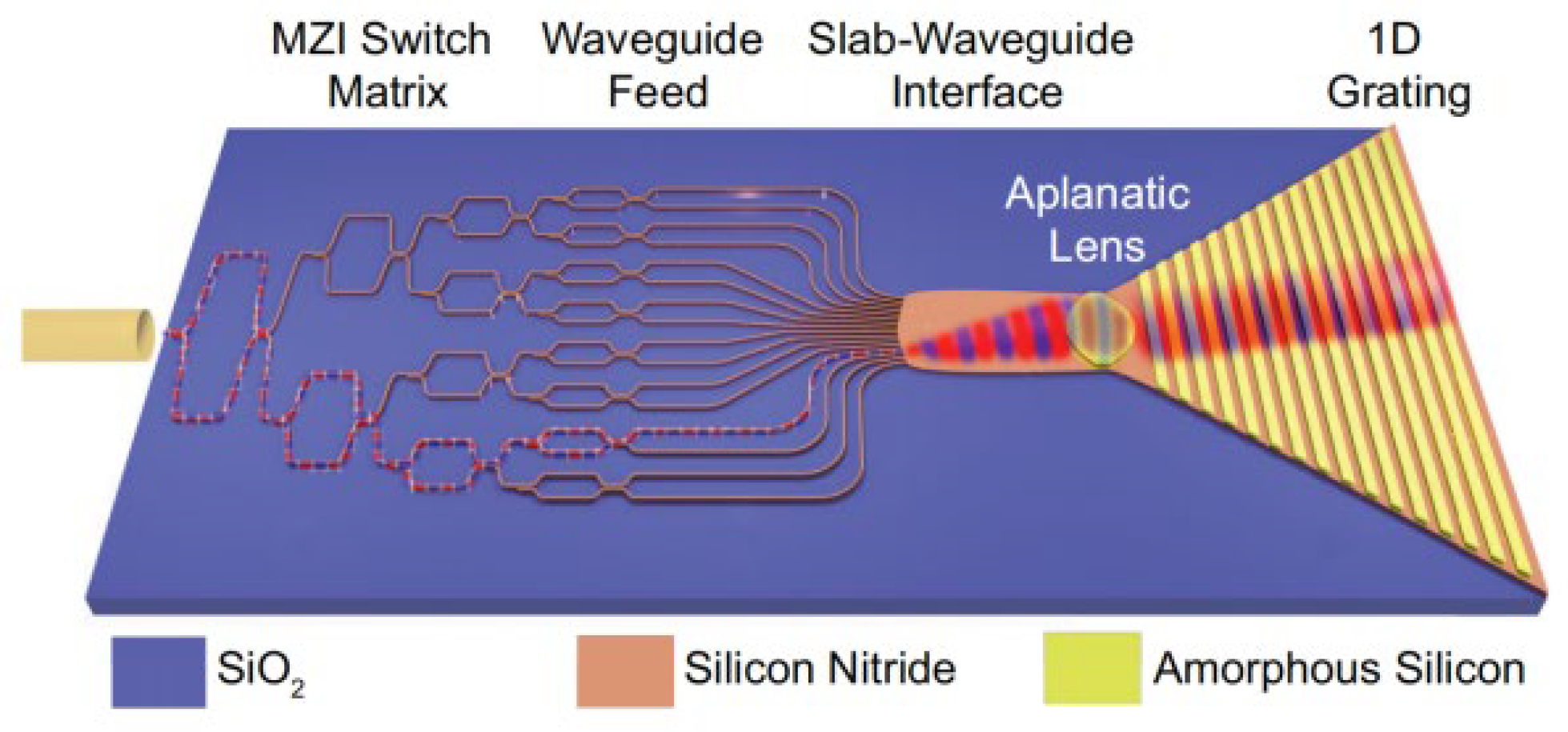
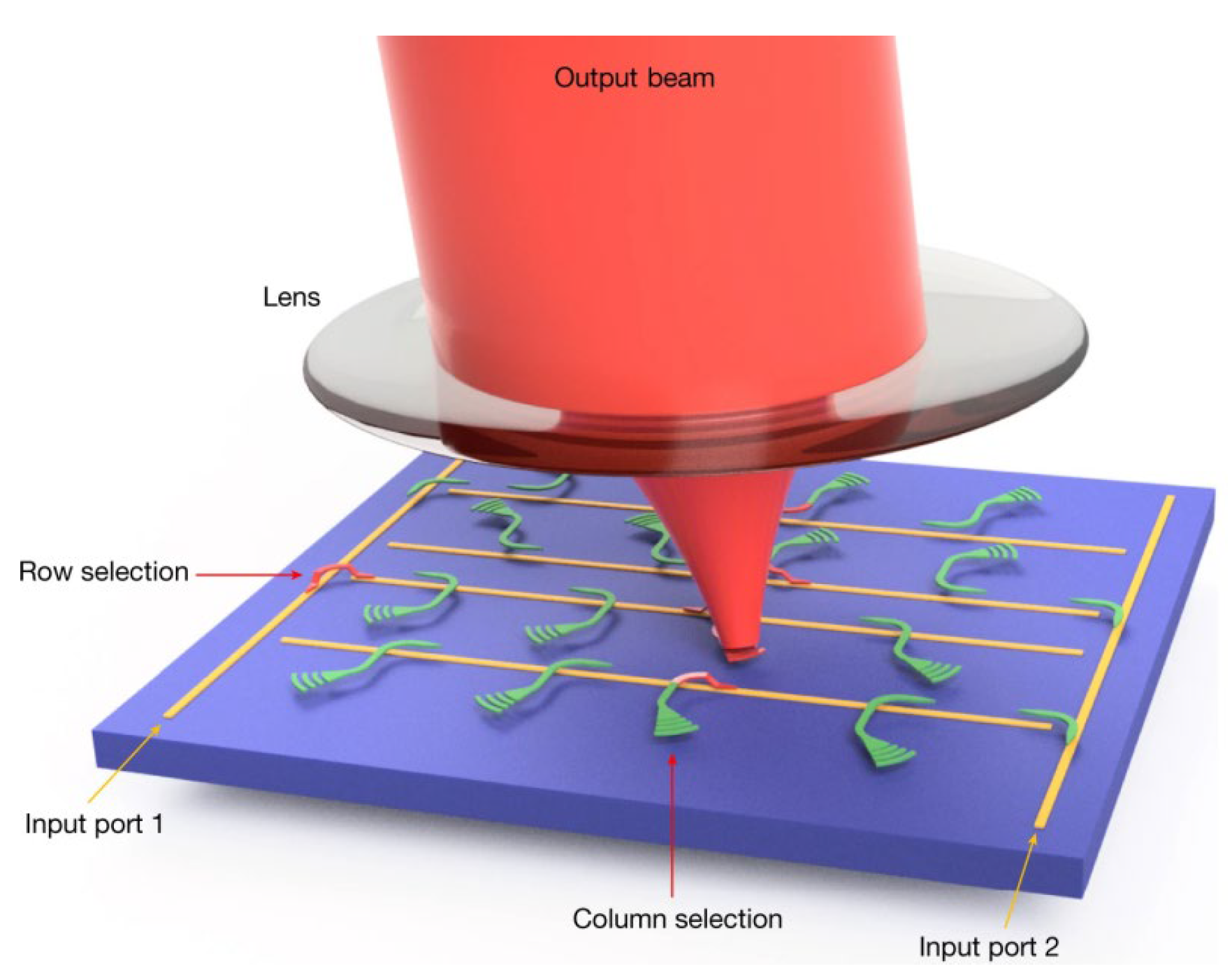
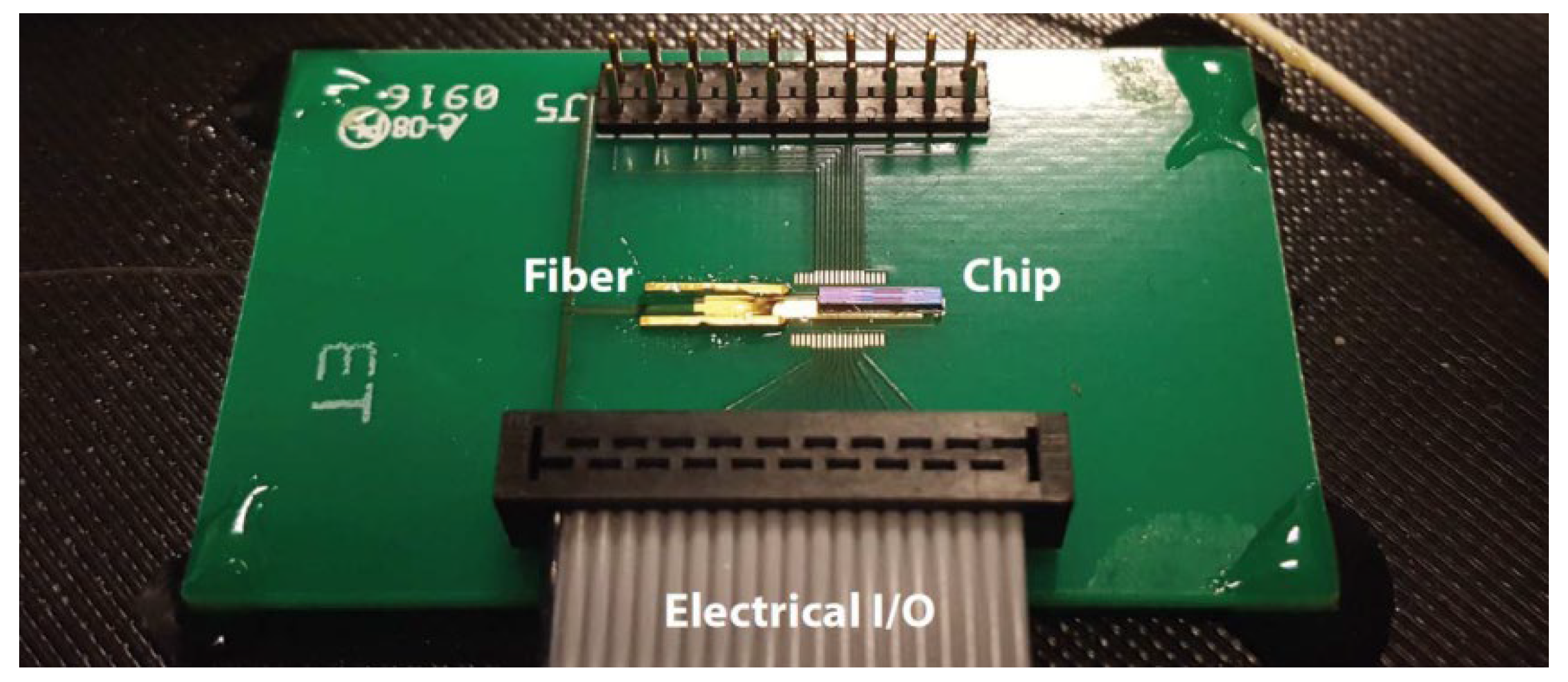
4. Silicon-Based Optical Switch Array Lidar
4.1. Low-Consumption Optical Switch Array Lidar
4.2. Wide-FoV Optical Switch Array Lidar
5. Integrated FMCW Lidar
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maiman, T.H. Stimulated Optical Radiation in Ruby. Nature 1960, 187, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, D.; Jang, B.; Byun, H.; Lee, C.; Shin, C.; Hwang, I.; Shim, D.; Lee, E.; Kim, J. Single-Chip Beam Scanner with Integrated Light Source for Real-Time Light Detection and Ranging. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–18 December 2020; pp. 7.2.1–7.2.4. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Cho, Y.; Pigniczki, M.; Köhler, M.H.; Haas, L.; Kastner, L.; Fink, M.; Schardt, M.; Cichy, Y.; Koyama, S.; et al. Performance Evaluation of MEMS-Based Automotive LiDAR Sensor and Its Simulation Model as per ASTM E3125-17 Standard. Sensors 2023, 23, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, V.; Schardt, M.; Fink, M.; Jakobi, M.; Koch, A.W. MEMS-Scanner Testbench for High Field of View LiDAR Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Hang, Y. Lidar/Mems Imu Integrated Navigation (Slam) Method for a Small Uav in Indoor Environments. In Proceedings of the 2014 DGON inertial sensors and systems (ISS), Karlsruhe, Germany, 16–17 September 2014; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Stann, B.L.; Dammann, J.F.; Giza, M.M.; Jian, P.S.; Lawler, W.B.; Nguyen, H.M.; Sadler, L.C. Mems-Scanned Ladar Sensor for Small Ground Robots. In Proceedings of the Laser Radar Technology and Applications XV, Orlando, FL, USA, 29 April 2010; pp. 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Hälker, J.; Barth, H. Lidar as a Key Technology for Automated and Autonomous Driving. ATZ Worldw. 2018, 120, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ho, C.P.; Xue, J.; Lim, L.W.; Chen, G.; Fu, Y.H.; Lee, L.Y.T. A Progress Review on Solid-State Lidar and Nanophotonics-Based Lidar Sensors. Laser Photonics Rev. 2022, 16, 2100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gómez, P.; Royo, S.; Rodrigo, N.; Casas, J.R. Geometric Model and Calibration Method for a Solid-State LiDAR. Sensors 2020, 20, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ibanez-Guzman, J. Lidar for Autonomous Driving: The Principles, Challenges, and Trends for Automotive Lidar and Perception Systems. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Advances of Flash Lidar Development Onboard Uav. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 39, B3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosby, F.; Kang, S.H. Object Identification in 3d Flash Lidar Images. J. Pattern Recognit. Res. 2011, 2, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, T.; Hashim, F.H.; Huddin, A.B.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Hussain, A. A Survey on Lidar Scanning Mechanisms. Electronics 2020, 9, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, C.V.; Byrd, M.J.; Timurdogan, E.; Russo, P.; Vermeulen, D.; Watts, M.R. Optical Phased Arrays for Integrated Beam Steering. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Group IV Photonics (GFP), Cancun, Mexico, 29–31 August 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison, D.N.; Sun, J.; Doylend, J.K.; Kumar, R.; Heck, J.; Kim, W.; Phare, C.T.; Feshali, A.; Rong, H. High-Resolution Aliasing-Free Optical Beam Steering. Optica 2016, 3, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, K. A Review of Silicon-Based Integrated Optical Switches. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; He, S.; Dai, D. Low-Loss and Broadband 2 × 2 Silicon Thermo-Optic Mach–Zehnder Switch with Bent Directional Couplers. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goh, T.; Himeno, A.; Okuno, M.; Takahashi, H.; Hattori, K. High-Extinction Ratio and Low-Loss Silica-Based 8 × 8 Strictly Nonblocking Thermooptic Matrix Switch. J. Light. Technol. 1999, 17, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J. Silicon Non-Blocking 4 × 4 Optical Switch Chip Integrated with Both Thermal and Electro-Optic Tuners. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 6603209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M.C.; Bosch, T.M.; Lescure, M.; Myllylae, R.A.; Rioux, M. Laser Ranging: A Critical Review of Unusual Techniques for Distance Measurement. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- English, C.; Zhu, S.; Smith, C.; Ruel, S.; Christie, I. Tridar: A Hybrid Sensor for Exploiting the Complimentary Nature of Triangulation and Lidar Technologies. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space, Munich, Germany, 5–8 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Q.; Fan, Z.; Jia, Y. TOF Lidar Development in Autonomous Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 3rd Optoelectronics Global Conference (OGC), Shenzhen, China, 4–7 September 2018; pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Rablau, C. LIDAR–A new (self-driving) vehicle for introducing optics to broader engineering and non-engineering audiences. Educ. Train. Opt. Photonics. 2019, 11143, 111430C. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, R.; Seitz, P. Solid-State Time-of-Flight Range Camera. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2001, 37, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whyte, R.; Streeter, L.; Cree, M.J.; Dorrington, A.A. Application of Lidar Techniques to Time-of-Flight Range Imaging. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9654–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, T.; An, D.; Sun, L.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Yue, Y. Face Mask Identification Using Spatial and Frequency Features in Depth Image from Time-of-Flight Camera. Sensors 2023, 23, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, K.; Dou, D.; Xu, C.; Kong, H. Learning Moving-Object Tracking with Fmcw Lidar. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 3747–3753. [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann, A.; Amann, M.C. Fmcw-Lidar with Tunable Twin-Guide Laser Diode. In Proceedings of the Industrial Applications of Laser Radar, San Diego, CA, USA, 23 September 1994; pp. 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Behroozpour, B.; Sandborn, P.A.M.; Wu, M.C.; Boser, B.E. Lidar System Architectures and Circuits. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, G.H.; Park, C.H.; Jun, S.W.; Jo, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.S. Simultaneous Distance and Vibration Mapping of Fmcw-Lidar with Akinetic External Cavity Diode Laser. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 160, 107283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.P.; Li, B.; Solano-Rivas, B.; Gohil, A.R.; Chan, P.H.; Moore, A.D.; Donzella, V. A Review and Perspective on Optical Phased Array for Automotive Lidar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2020, 27, 8300416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, M.J. Highly Integrated Optical Phased Arrays: Photonic Integrated Circuits for Optical Beam Shaping and Beam Steering. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, A. Fabrication of Irregular Optical Phased Arrays on Silicon-on-Insulator Wafers. Opt. Eng. 2008, 47, 040503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Acoleyen, K.; Bogaerts, W.; Jágerská, J.; Le Thomas, N.; Houdré, R.; Baets, R. Off-Chip Beam Steering with a One-Dimensional Optical Phased Array on Silicon-on-Insulator. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acoleyen, K.; Rogier, H.; Baets, R. Two-Dimensional Optical Phased Array Antenna on Silicon-on-Insulator. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 13655–13660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doylend, J.K.; Heck, M.J.R.; Bovington, J.T.; Peters, J.D.; Coldren, L.A.; Bowers, J.E. Two-Dimensional Free-Space Beam Steering with an Optical Phased Array on Silicon-on-Insulator. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 21595–21604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwong, D.; Hosseini, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.T. 1 × 12 Unequally Spaced Waveguide Array for Actively Tuned Optical Phased Array on a Silicon Nanomembrane. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 051104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Acoleyen, K.; Komorowska, K.; Bogaerts, W.; Baets, R. One-Dimensional Off-Chip Beam Steering and Shaping Using Optical Phased Arrays on Silicon-on-Insulator. J. Light. Technol. 2011, 29, 3500–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Acoleyen, K.; Bogaerts, W.; Baets, R. Two-Dimensional Dispersive Off-Chip Beam Scanner Fabricated on Silicon-on-Insulator. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 1270–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaacobi, A.; Sun, J.; Moresco, M.; Leake, G.; Coolbaugh, D.; Watts, M.R. Integrated Phased Array for Wide-Angle Beam Steering. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4575–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
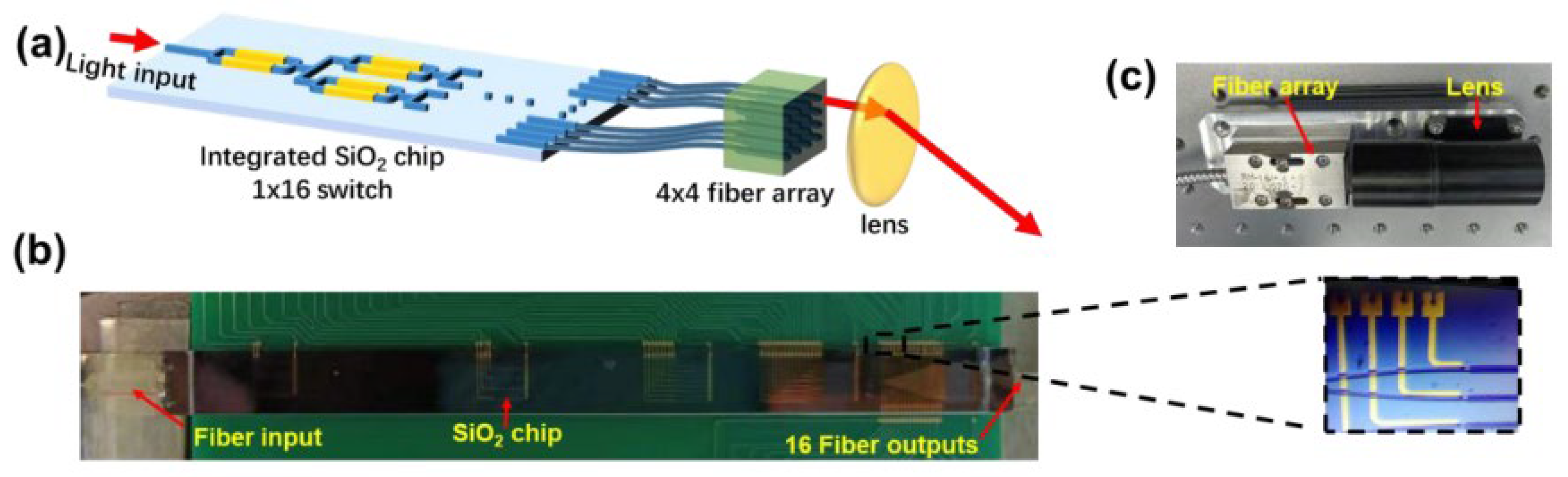
- Poulton, C.V.; Yaacobi, A.; Su, Z.; Byrd, M.J.; Watts, M.R. Optical Phased Array with Small Spot Size, High Steering Range and Grouped Cascaded Phase Shifters. In Proceedings of the Integrated Photonics Research, Silicon and Nanophotonics, Vancouver, Canada, 18–20 July 2016; p. IW1B.2. [Google Scholar]
- Poulton, C.V.; Byrd, M.J.; Russo, P.; Timurdogan, E.; Khandaker, M.; Vermeulen, D.; Watts, M.R. Long-Range Lidar and Free-Space Data Communication with High-Performance Optical Phased Arrays. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019, 25, 7700108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Kim, T.; Poulton, C.V.; Notaros, J.; Yaacobi, A.; Timurdogan, E.; Baiocco, C.; Fahrenkopf, N.; Kruger, S.; Ngai, T. Fully Integrated Coherent Lidar in 3d-Integrated Silicon Photonics/65nm Cmos. In Proceedings of the 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 9–14 June 2019; pp. C262–C263. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Chang, Y.C.; Phare, C.T.; Shin, M.C.; Zadka, M.; Roberts, S.P.; Stern, B.; Ji, X.; Mohanty, A.; Gordillo, O.A.J.; et al. Large-Scale Optical Phased Array Using a Low-Power Multi-Pass Silicon Photonic Platform. Optica 2020, 7, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y. Dual Polarization and Bi-Directional Silicon-Photonic Optical Phased Array with Large Scanning Range. IEEE Photonics J. 2022, 14, 6620905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadka, M.; Chang, Y.C.; Mohanty, A.; Phare, C.T.; Roberts, S.P.; Lipson, M. On-Chip Platform for a Phased Array with Minimal Beam Divergence and Wide Field-of-View. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2528–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Komljenovic, T.; Huang, J.; Tran, M.; Davenport, M.; Torres, A.; Pintus, P.; Bowers, J. Heterogeneous Silicon Photonics Sensing for Autonomous Cars. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 3642–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Luo, G.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Design and Fabrication of a Sin-Si Dual-Layer Optical Phased Array Chip. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
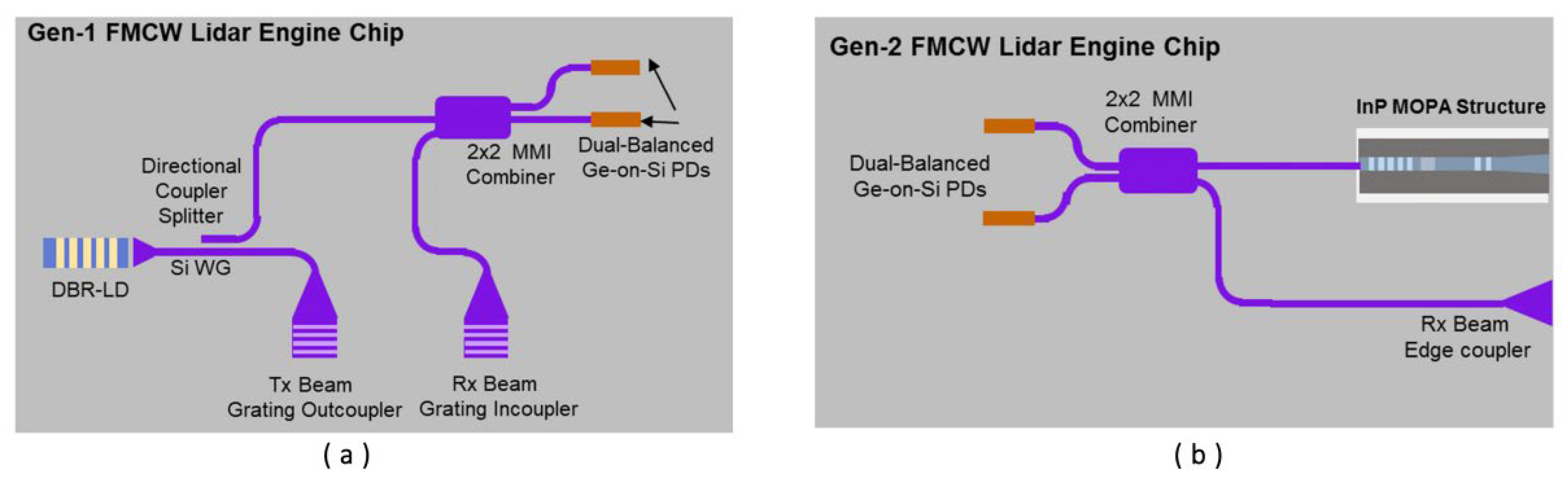
- Im, C.S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, K.P.; Ju, S.H.; Hong, J.H.; Yoon, S.W.; Kim, T.; Lee, E.S.; Bhandari, B.; Zhou, C.; et al. Hybrid Integrated Silicon Nitride–Polymer Optical Phased Array for Efficient Light Detection and Ranging. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 4402–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Tao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhi, Z.; Liu, X.; et al. Two-Dimensional Multi-Layered Sin-on-Soi Optical Phased Array with Wide-Scanning and Long-Distance Ranging. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 5008–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, P.; Yegnanarayanan, S.; Coppinger, F.; Jalali, B. Silicon-on-Insulator (Soi) Phased-Array Wavelength Multi/Demultiplexer with Extremely Low-Polarization Sensitivity. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1997, 9, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Hu, W.; Xu, A. Optical Phased-Array Beam Steering Controlled by Wavelength. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 5429–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, F.; Li, G.; Xu, A. Cascade Arrangement of Irregular Optical Phased Arrays. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 1945–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelkens, G.; Van Thourhout, D.; Baets, R. High Efficiency Silicon-on-Insulator Grating Coupler Based on a Poly-Silicon Overlay. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 11622–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Timurdogan, E.; Yaacobi, A.; Hosseini, E.S.; Watts, M.R. Large-Scale Nanophotonic Phased Array. Nature 2013, 493, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Densmore, A.; Janz, S.; Ma, R.; Schmid, J.H.; Xu, D.-X.; Delâge, A.; Lapointe, J.; Vachon, M.; Cheben, P. Compact and Low Power Thermo-Optic Switch Using Folded Silicon Waveguides. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 10457–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaintoutis, C.; Shariati, B.; Bogris, A.; Dijk, P.V.; Roeloffzen, C.G.; Bourderionnet, J.; Tomkos, I.; Syvridis, D. Free Space Intra-Datacenter Interconnects Based on 2d Optical Beam Steering Enabled by Photonic Integrated Circuits. Photonics 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Cao, X.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Chen, J. A Switch-Based Integrated 2d Beam-Steering Device for Lidar Application. In Proceedings of the CLEO: QELS_Fundamental Science, San Jose, CA, USA, 5–10 May 2019; p. JTh2A.73. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, C.; Piggott, A.Y.; Thomson, D.J.; Wiser, R.F.; Opris, I.E.; Fortune, S.A.; Compston, A.J.; Gondarenko, A.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; et al. A universal 3D imaging sensor on a silicon photonics platform. Nature 2021, 590, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Skirlo, S.A.; Kharas, D.; Sloan, J.; Herd, J.; Juodawlkis, P.; Soljačić, M.; Sorace-Agaskar, C. Planar-Lens Enabled Beam Steering for Chip-Scale Lidar. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), San Jose, CA, USA, 13–18 May 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, H.; Kusunoki, Y.; Maeda, J.; Akiyama, D.; Kodama, N.; Abe, H.; Tetsuya, R.; Baba, T. Wide beam steering by slow-light waveguide gratings and a prism lens. Optica 2020, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kwon, K.; Henriksson, J.; Luo, J.; Wu, M.C. A Large-Scale Microelectromechanical-Systems-Based Silicon Photonics Lidar. Nature 2022, 603, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, C.V.; Yaacobi, A.; Cole, D.B.; Byrd, M.J.; Raval, M.; Vermeulen, D.; Watts, M.R. Coherent Solid-State Lidar with Silicon Photonic Optical Phased Arrays. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4091–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Dodane, D.; Leviandier, L.; Dolfi, D.; Naughton, A.; O’Brien, P.; Spuessens, T.; Baets, R.; Lepage, G.; Verheyen, P.; et al. Photonic Integrated Circuit-Based Fmcw Coherent Lidar. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 4640–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pouls, J.; Wu, M.C. Laser Frequency Sweep Linearization by Iterative Learning Pre-Distortion for Fmcw Lidar. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 9965–9974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
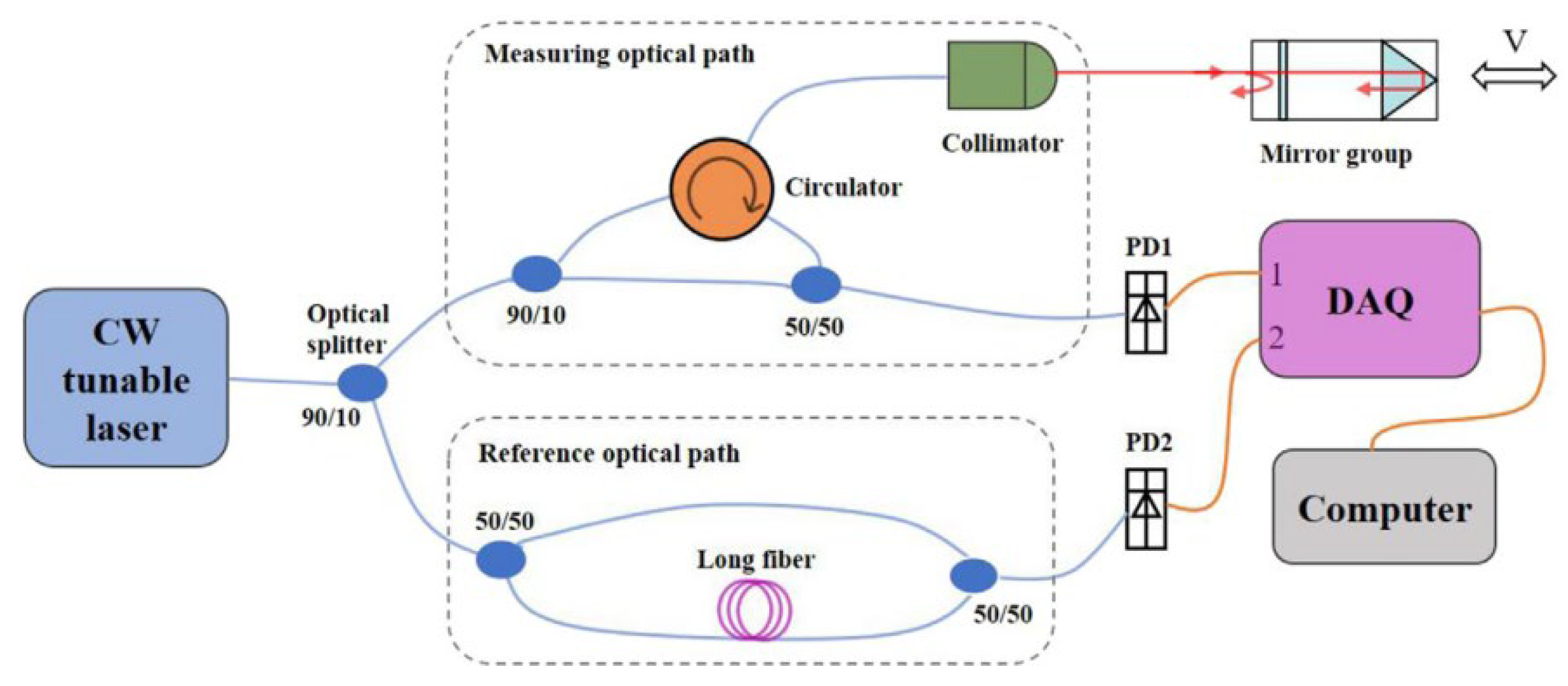
- Zhang, F.; Yi, L.; Qu, X. Simultaneous Measurements of Velocity and Distance via a Dual-Path Fmcw Lidar System. Opt. Commun. 2020, 474, 126066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zang, Z.; Han, Y.; Wu, L.; Fu, H. Solid-State Fmcw Lidar with Two-Dimensional Spectral Scanning Using a Virtually Imaged Phased Array. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 16547–16562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
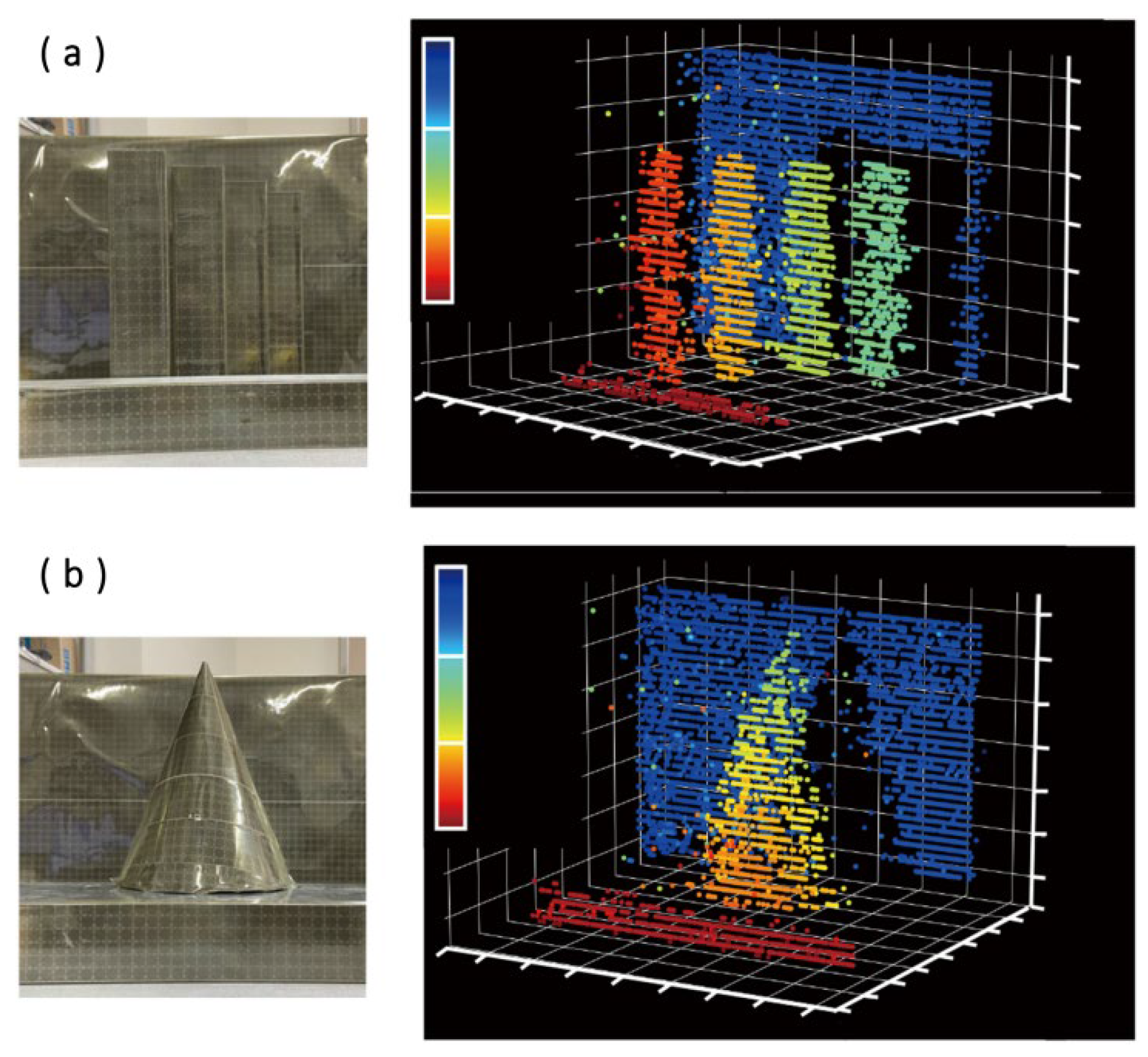
- Cao, X.; Wu, K.; Li, C.; Long, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J. All Solid-State Lidar Based on Lens Assisted Beam Steering and Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave Ranging. In Proceedings of the Asia Communications and Photonics Conference, Shanghai, China, 24–27 October 2021; p. T4A.218. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, T.; Tamanuki, T.; Ito, H.; Kamata, M.; Tetsuya, R.; Suyama, S.; Abe, H.; Kurahashi, R. Silicon Photonics Fmcw Lidar Chip with a Slow-Light Grating Beam Scanner. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2022, 28, 8300208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyah, K.; Sarkissian, R.; Patterson, P.; Huang, B.; Efimov, O.; Kim, D.; Elliott, K.; Yang, L.; Hammon, D. Fully Integrated Fmcw Lidar Optical Engine on a Single Silicon Chip. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 40, 2763–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemensberger, J.; Lukashchuk, A.; Karpov, M.; Weng, W.; Lucas, E.; Liu, J.; Kippenberg, T.J. Massively Parallel Coherent Laser Ranging Using a Soliton Microcomb. Nature 2020, 581, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
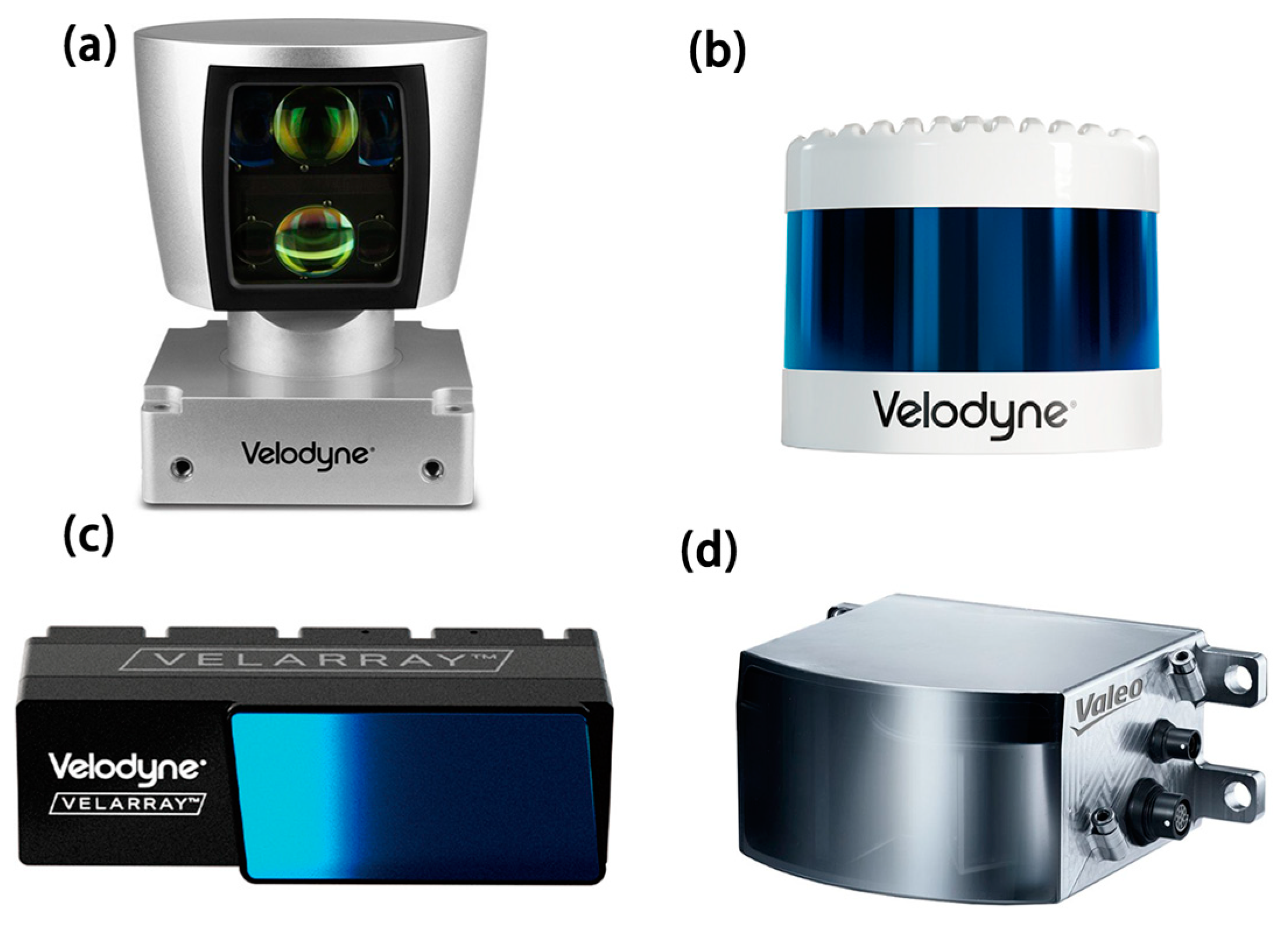



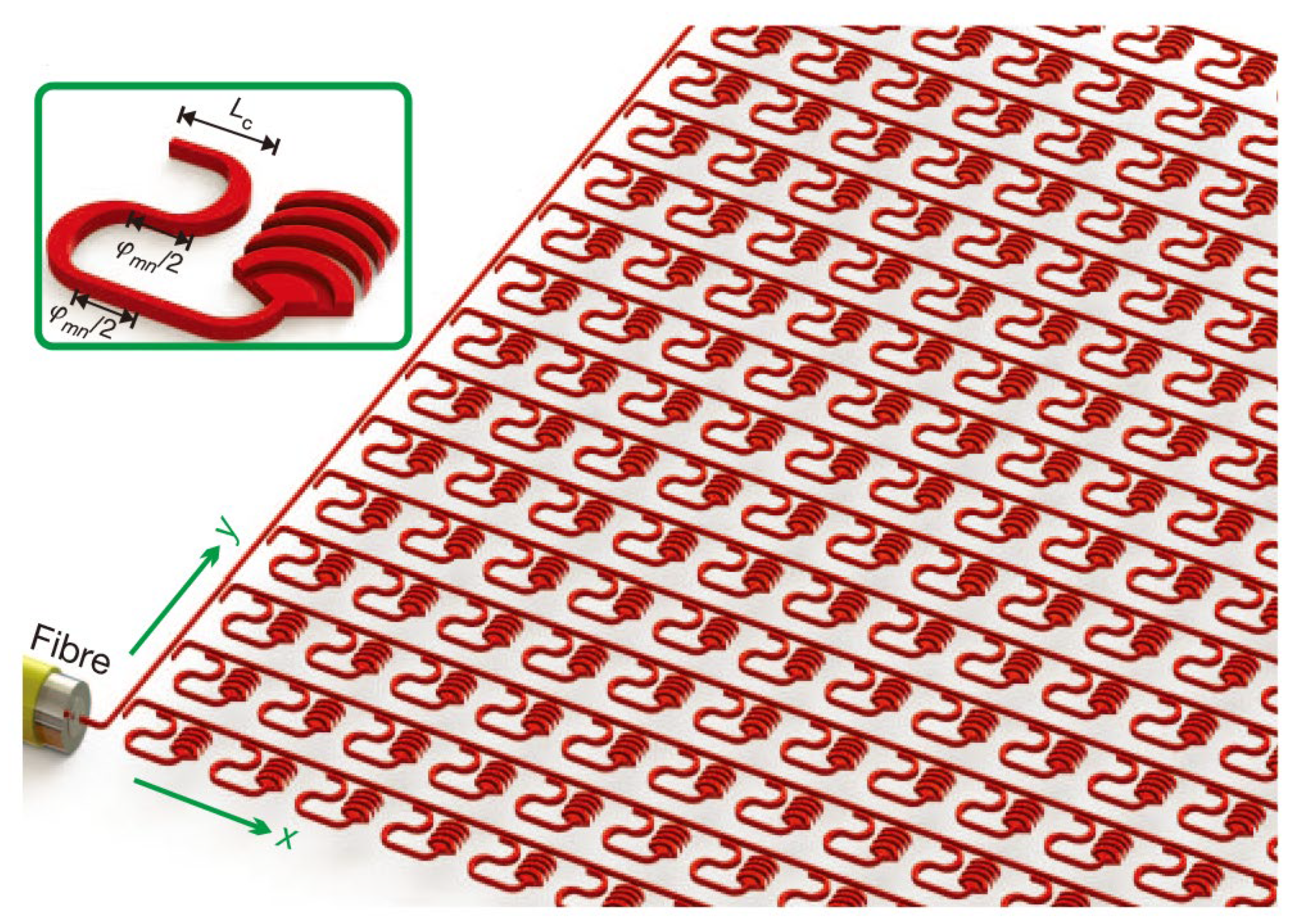



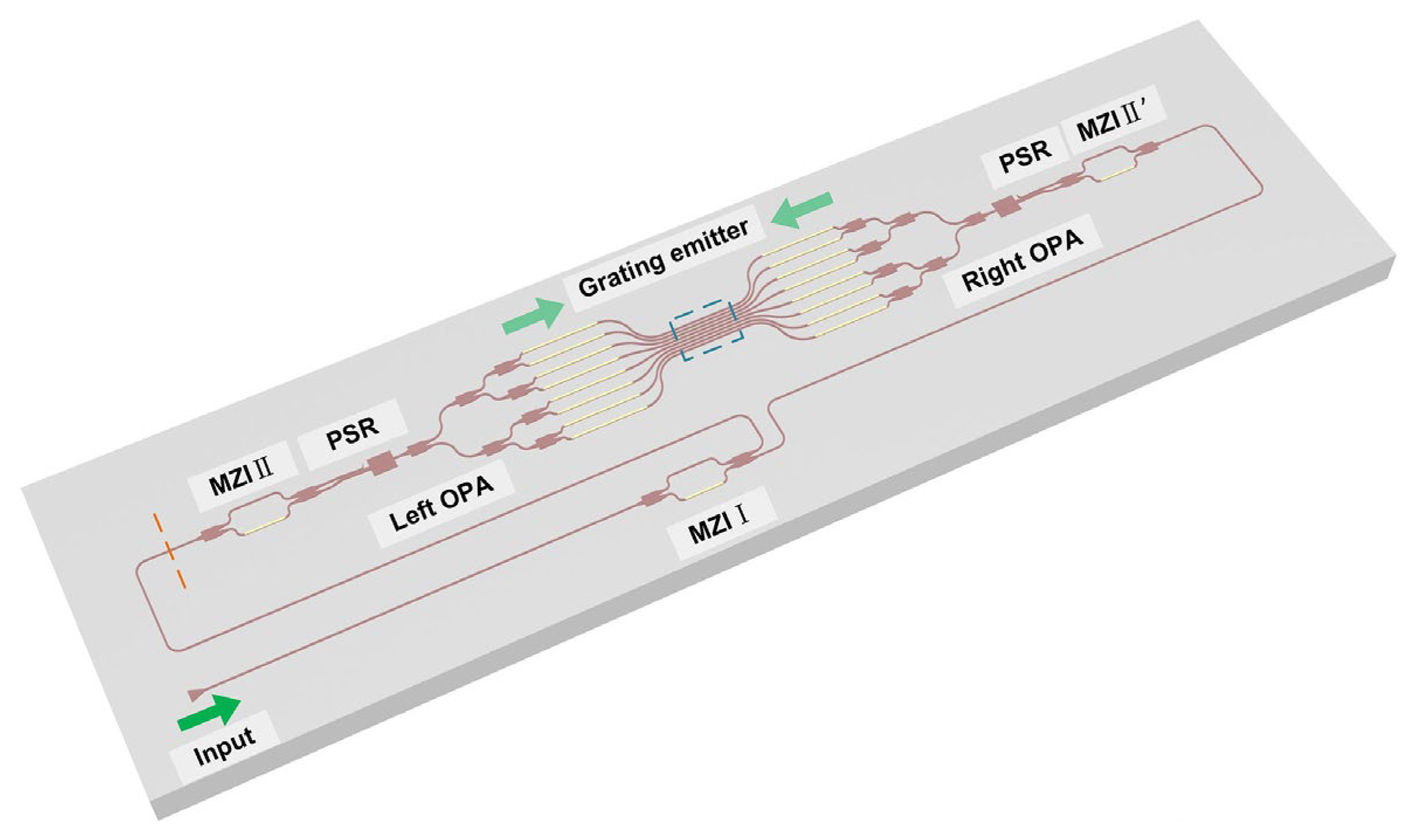


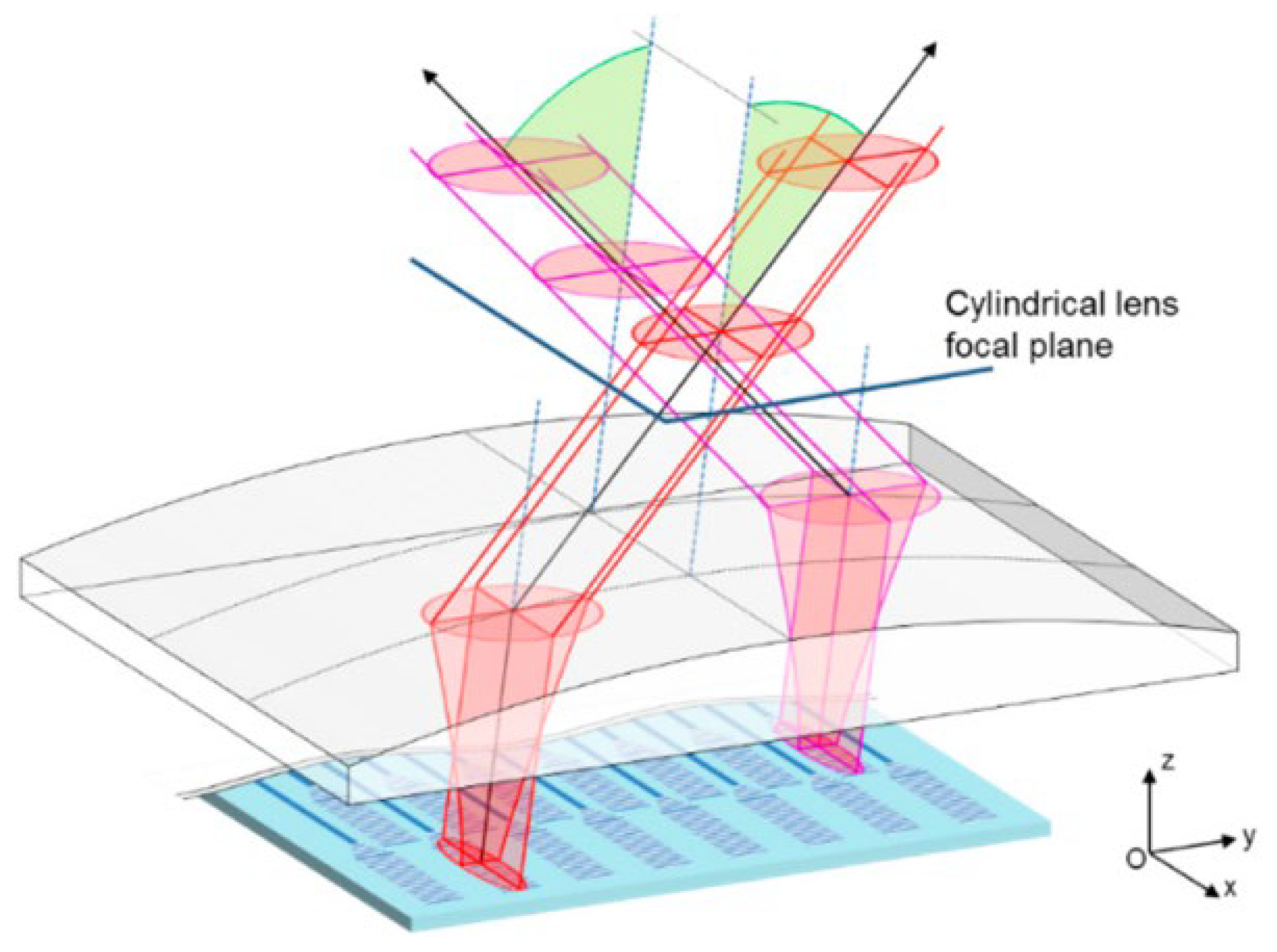
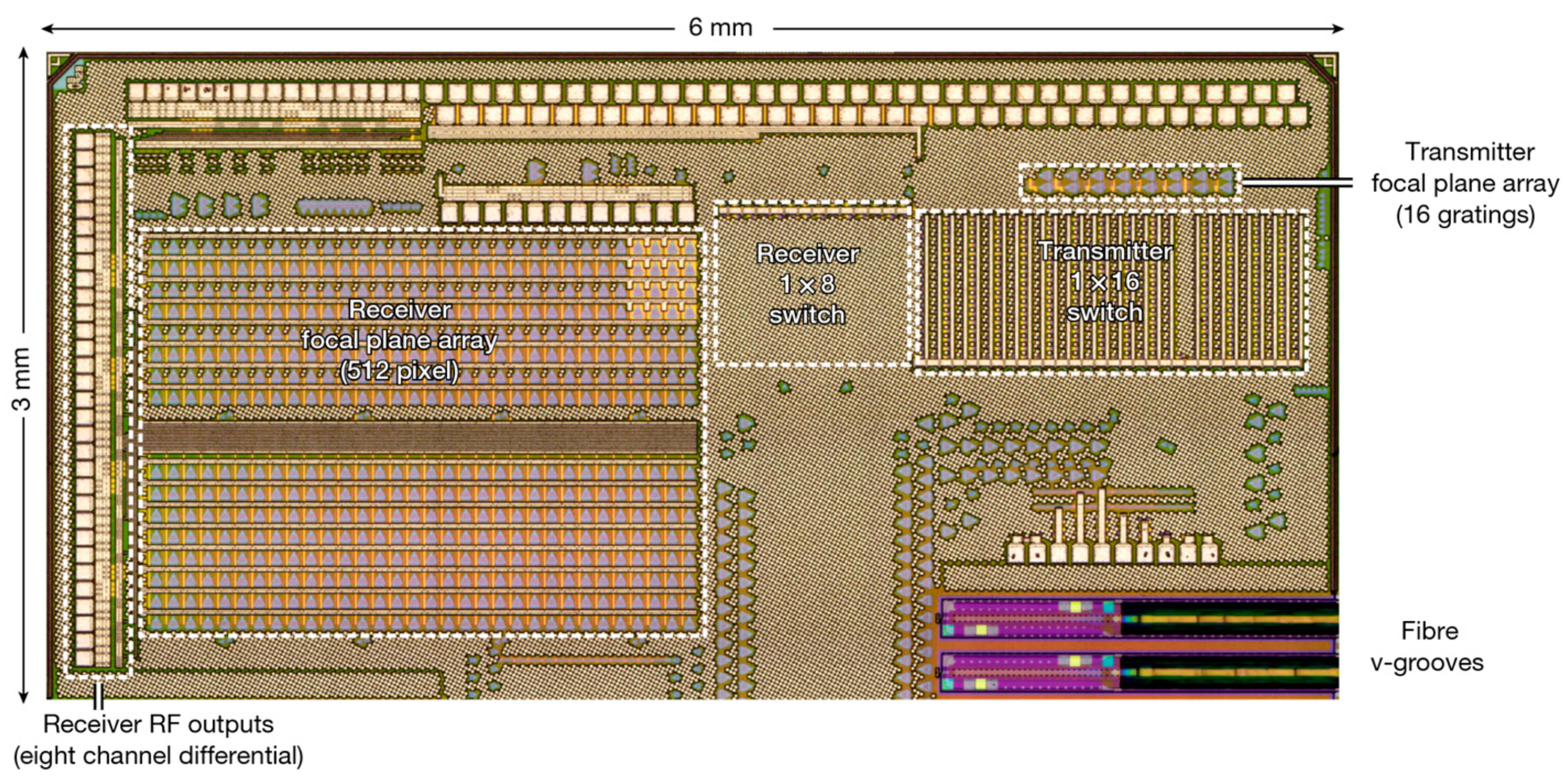


| Variety | Advantage | Shortcoming | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Lidar | Mature technology 360° horizontal FoV | Bulky [2] Poor stability High consumption | HDL-64E FoV: 360° × 26.8° resolution: 0.4° × 0.08–0.35° weight: 13.2 kg price: 28,064 $ |
| MEMS Lidar | Light Lower cost [3,4] Simple in structure | Limited FoV Lack of stability | Velarray M1600 FoV: 120° × 32° resolution: 0.2° × 0.2–0.5° weight: <1 kg |
| Flash Lidar | Inexpensive Non-mechanical device | Susceptible to environment Limited FoV [10] | OUSTER-ES2 FoV: 13° × 26° resolution: 0.1° × 0.1° price: 100 $ |
| Silicon-based OPA Lidar | Light Low cost High stability Compatible with CMOS process [12] | Still under development | - |
| Silicon-based Optical Switch Lidar | Simple construction Fast response speed [15] Compatible with silicon process | Still under development | - |
| Reference | FoV (Degree) | Beam Width (Degree) | Platform Materials | New Finding (s) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | 0~3 | 0.25 | SOI | irregular phased array | 1550 |
| [34] | 2.3 × 14.1 | - | SOI | thermo-optical and wavelength tuning | 1550 |
| [35] | - | - | SOI | high wavelength steering low antenna loss | 1550 |
| [36] | 20 × 14 | <1 | SOI | Small phase error and background peak noise | 1500 1550 1600 |
| [37] | 31.9 | - | SOI | silicon nanomembrane with off-chip laser source | 1550 |
| [38] | 23 | 1.27 | SOI | waveguides of special structure to minimize the damage in sharp turns | 1550 |
| [39] | 15 × 50 | 4.0 | SOI | high steering efficiency | 1500–1600 |
| [40] | 51 | - | SOI | high speed beam steering | 1550 |
| [41] | 46 × 36 | - | SOI | utilize grouped cascaded phase shifters | 1550 |
| [15] | 80 × 17 | 0.14 | SOI | high resolution and wide beam steering angle | 1260–1360 |
| [42] | 56 × 15 | - | SOI | low power consumption and high directivity | 1450–1640 |
| [43] | 18.5 | 0.15 | SOI | the first Lidar system based on OPA | 1550 |
| [44] | 70 × 6 | - | SOI | cycle the light to achieve phase shifting | 1525–1600 |
| [45] | 54.5 × 77.8 | - | SOI | the bi-directional OPA with only one grating antenna array | 1500–1600 |
| [46] | - | 0.089 | SiN-Si | a solution to solve the trade-off between FoV and beam divergence | 1550 |
| [47] | 51 × 28 | 0.02 | hybrid III-V/Si waveguides | wide optical bandwidth high operating speed(1 GHz) | 1550 |
| [48] | 48 × 14 | - | SiN-Si | an ideal way to long range detection | 1550 |
| [49] | 12 × 30 | - | silicon nitride mixed polymer | high thermal and optical effect | - |
| [50] | 96 × 14.4 | 1.9 | SiN-Si | power processing capacity high thermal-optical modulation efficiency | 1550 |
| Reference | FoV (Degree) | Beam Divergence (Degree) | Power Consumption | New Finding (s) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [56] | - | - | 6.5 mW | using folded waveguide to reduce the switching power | 1550 |
| [57] | 20 × 20 | - | W level | phase shifter relying on piezoelectric transducer | - |
| [58] | - | - | logN * | high wavelength steering low antenna loss | 1550 |
| [59] | - | - | 4 mW | large-scale coherent detector array with high accuracy | - |
| [60] | 38.8 × 12 | 0.15 | - | first optical planar-lens-enabled beam steering device | 1550 |
| [61] | 40 × 4.4 | 0.15 | - | designed a prism lens for beam steering and collimation | 1550 |
| [62] | 70 × 70 | 0.050 × 0.049 | - | 128 × 128-element focal plan switch array with a wide FoV | 1550 |
| Reference | Detection Range | Accuracy | FoV (Degree) | New Finding (s) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [63] | 2 m | 20 mm | 20 | the first coherent Lidar with a silicon chip using OPA | 1550 |
| [64] | 60 m | - | 70 | the scanning is accomplished by using collimation lenses | - |
| [65] | 3 m | - | 24 × 20 | propose a new method for laser frequency sweep linearization | 1550 |
| [66] | 205.595 mm | - | a dual-path system with a simple structure and good nonlinear eliminate effect | 1515–1565 | |
| [67] | 1.8 m | 0.5 mm | 1.9 × 7.7 | use the virtually imaged phased array to realize 2D beam steering | 1500–1600 |
| [68] | 80 m | - | 1.05 | the scanning points and steering angle can be easily extended | 1550 |
| [69] | 3–5 m | - | 40 × 8.8 | realize the point cloud image with 4928 pixels by slow-light gratings | 1550 |
| [70] | GEN-1 28 m GEN-2 75 m | GEN-1 28 cm GEN-2 16.7 cm | - | the first single chip-scale(include laser source) integrated FMCW Lidar | - |
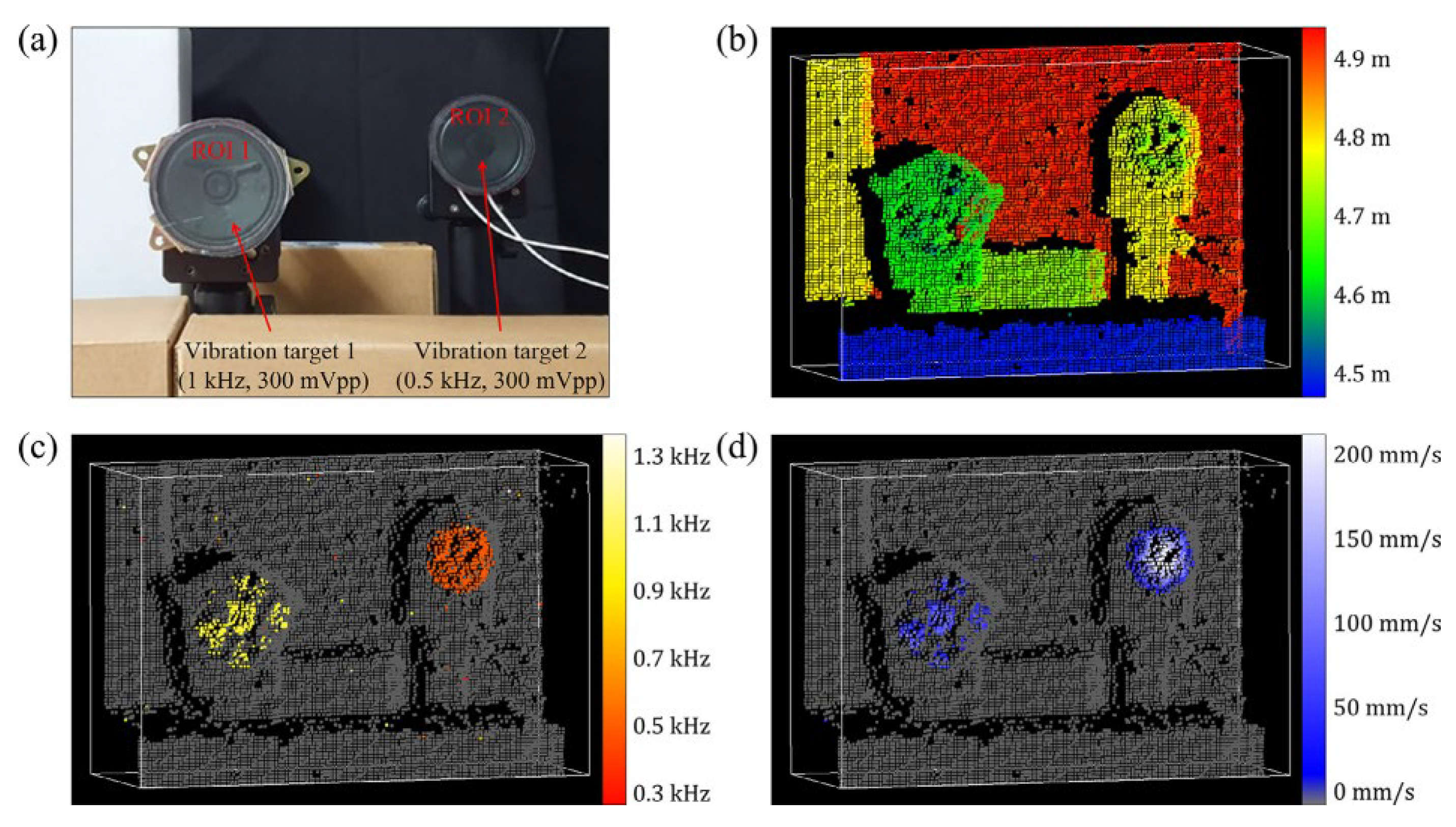
| [30] | 10 m | 20.86 cm | - | realize the 3D-mapping of distance vibration frequency and vibration velocity | 1467–1617 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Pang, Y.; Gao, L. Advances in Silicon-Based Integrated Lidar. Sensors 2023, 23, 5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135920
Hu M, Pang Y, Gao L. Advances in Silicon-Based Integrated Lidar. Sensors. 2023; 23(13):5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135920
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Mingxuan, Yajun Pang, and Long Gao. 2023. "Advances in Silicon-Based Integrated Lidar" Sensors 23, no. 13: 5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135920
APA StyleHu, M., Pang, Y., & Gao, L. (2023). Advances in Silicon-Based Integrated Lidar. Sensors, 23(13), 5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135920





