A Wireless 2-Channel Layered EMG/NIRS Sensor System for Local Muscular Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
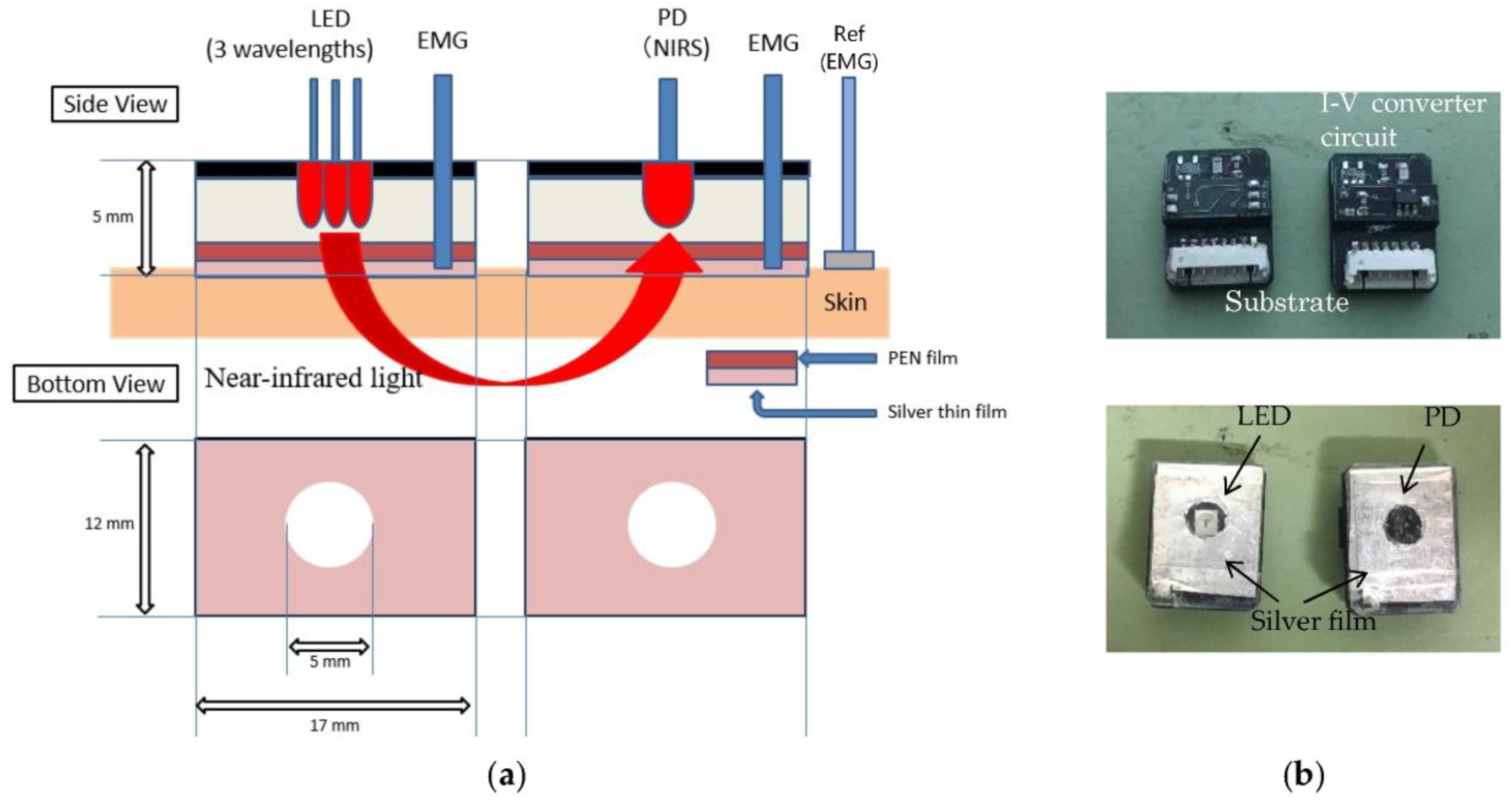
2.1. Sensing System
2.2. Signal Processing Method
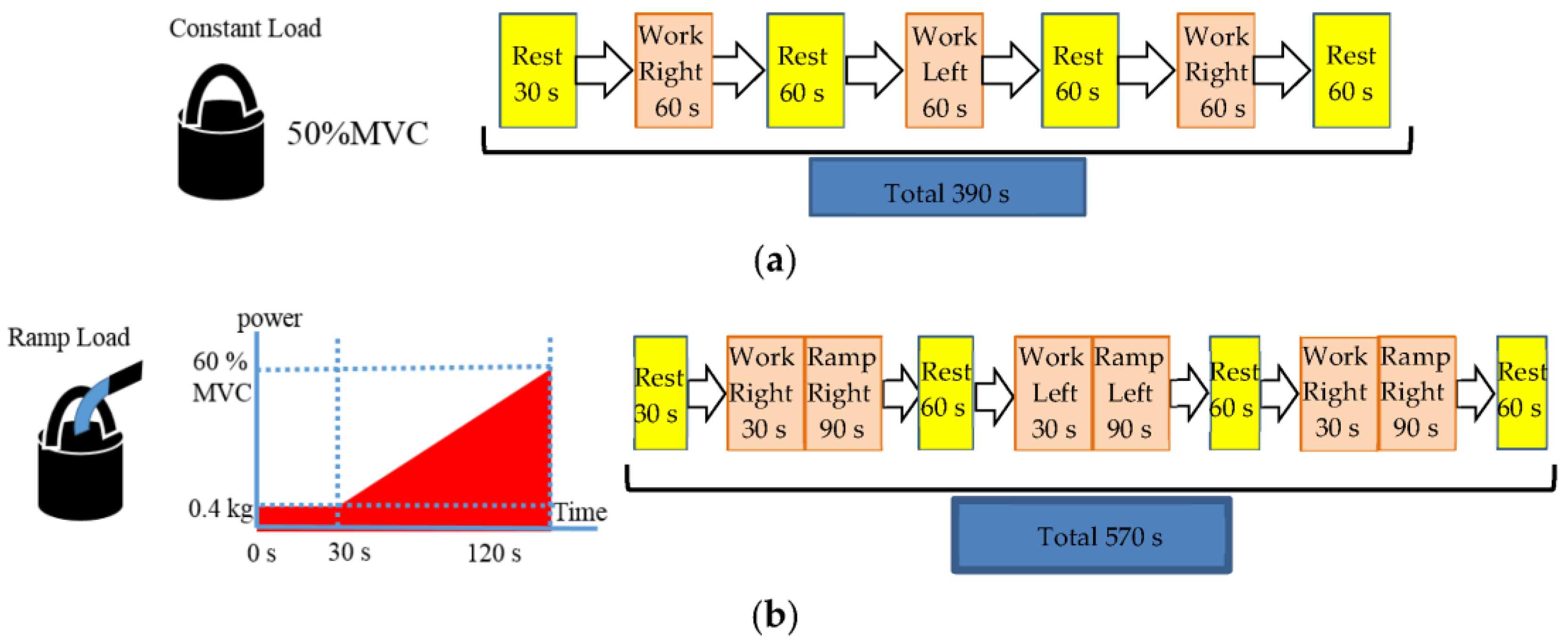
3. Experiments
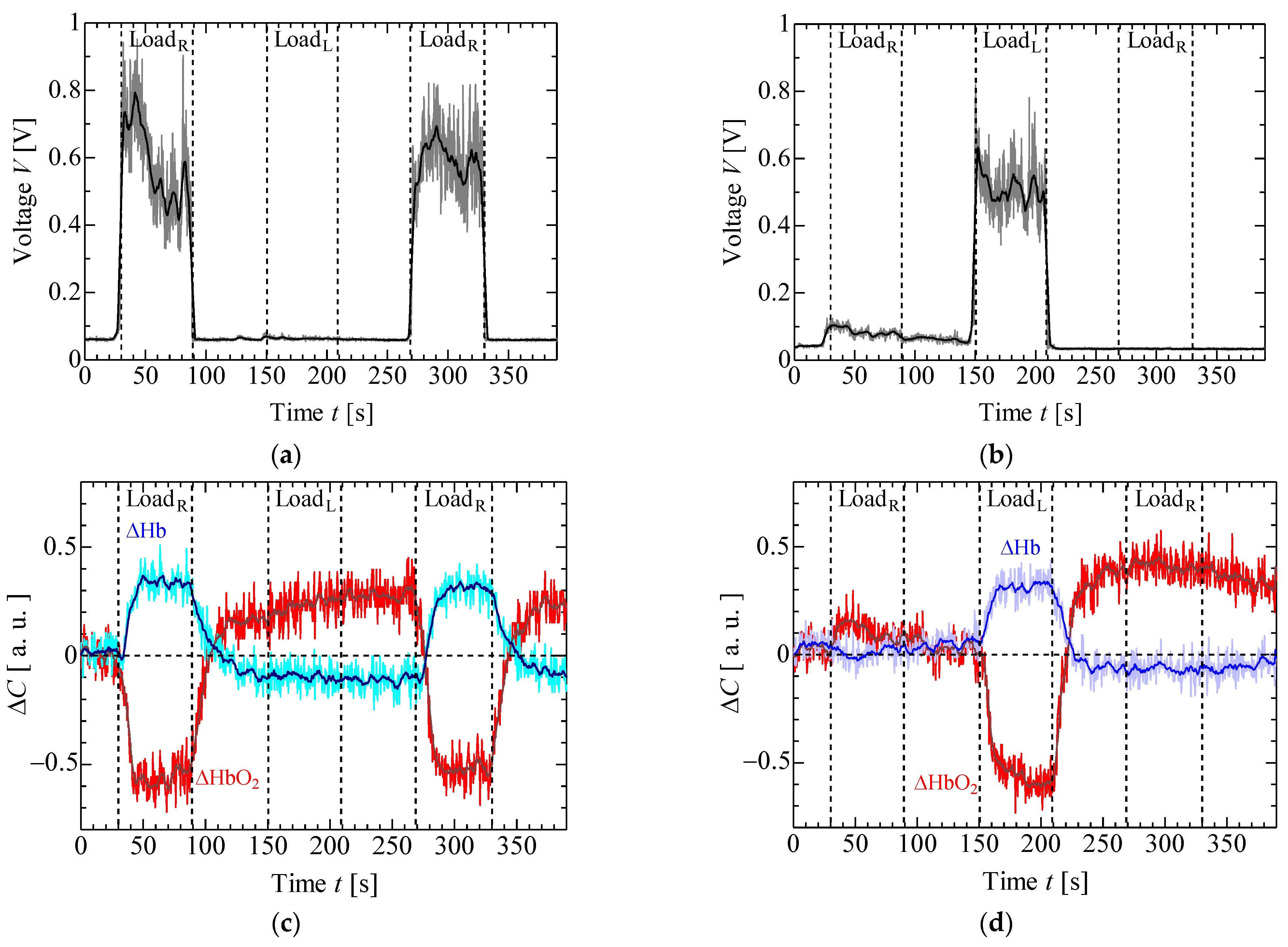
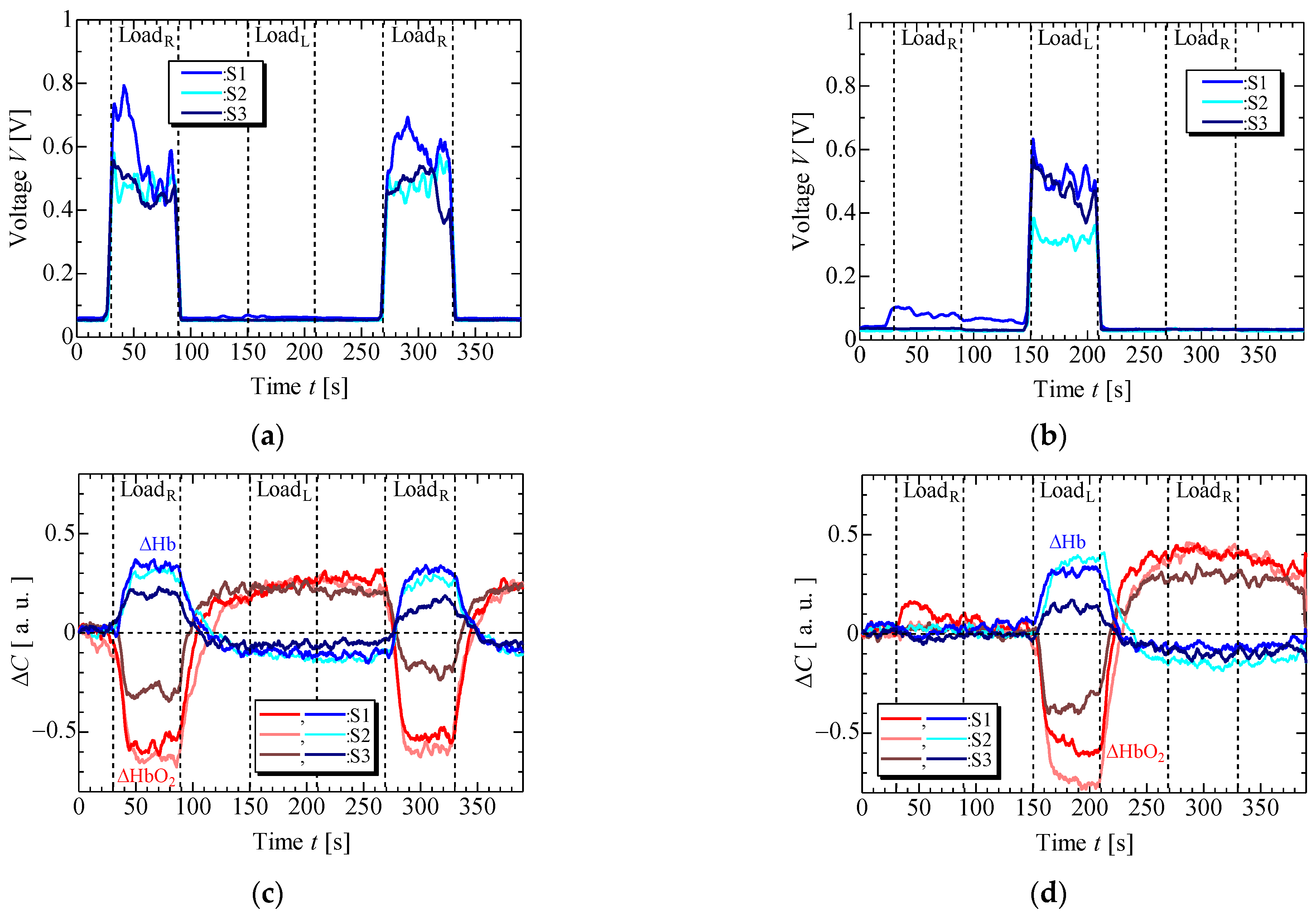
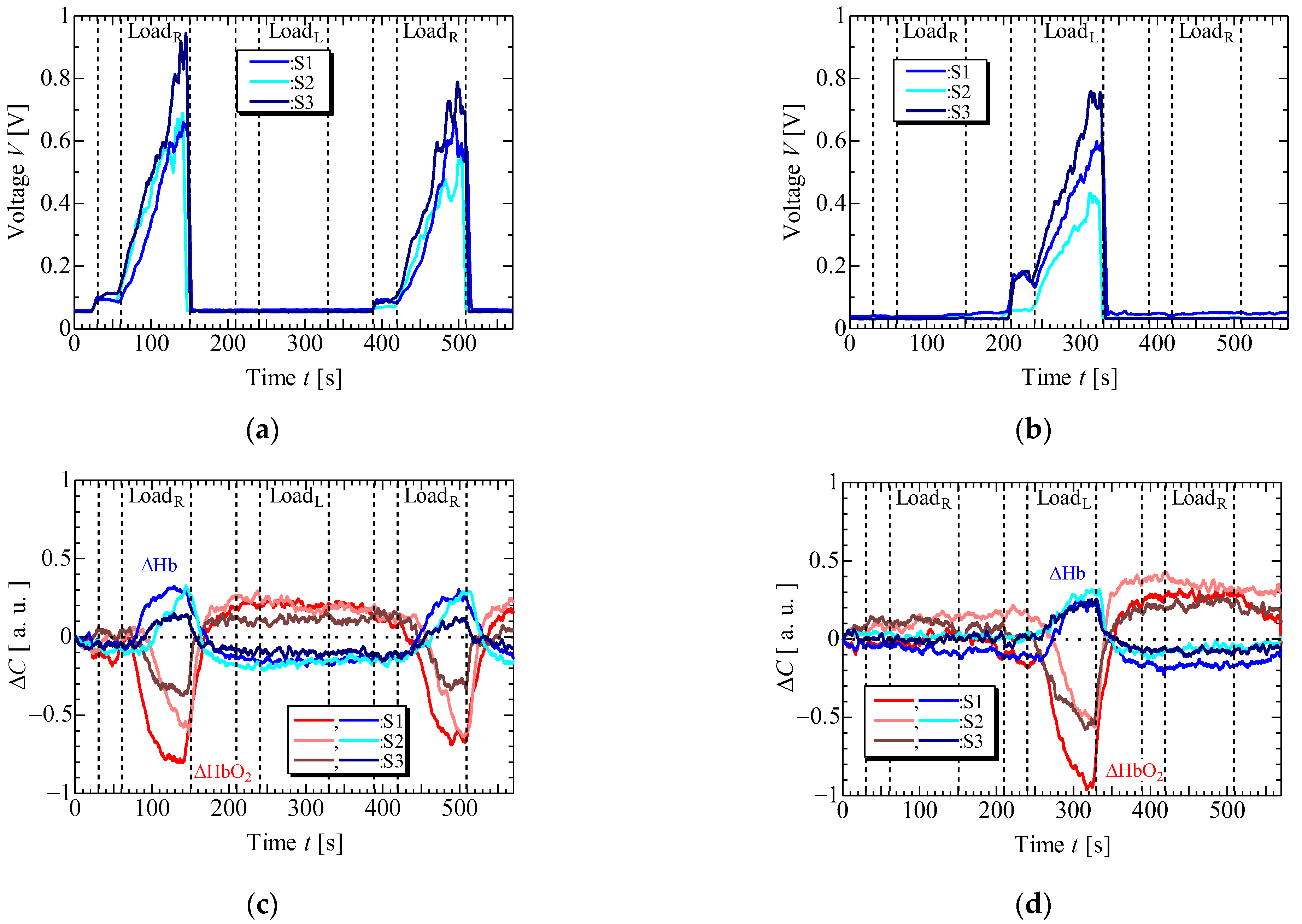
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staudenmann, D.; Kingma, I.; Daffertshofer, A.; Stegeman, D.F.; Van Dieën, J.H. Improving EMG-Based Muscle Force Estimation by Using a Hig-Density EMG Grid and Principal Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzoni, M.; Botter, A.; Vieira, T. Surface EMG and muscle fatigue: Multi-channel approaches to the study of myoelectric manifestations of muscle fatigue. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 27–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rampichini, S.; Vieira, T.M.; Castiglioni, P.; Merati, G. Complexity Analysis of Surface Electromyography for Assessing the Myoelectric Manifestation of Muscle Fatigue: A Review. Entropy 2020, 22, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, C.R.; Housh, J.T.; Johnson, G.O.; Weir, J.P.; Beck, W.; Malek, M.H.; Mielke, M.; Schmidt, R.J. A comparison of critical force and electromyographic fatigue threshold for isometric muscle actions of the forearm flexors. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 105, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fahoum, A.; Gharaibeh, K.H. Feasibility study for ANFIS and EMG utilization in modeling prosthesis for trans-femoral cut rehabilitation and gait cycle restoration. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2015, 27, 1550023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orizio, C.; Gobbo, M.; Diemont, B.; Espositi, F.; Veicsteinas, A. The surface mechanomyogram as a tool to describe the influence of fatigue on biceps brachii motor unit activation strategy. Historical basis and novel evidence. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 90, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akitaki, K.; Mita, K.; Watakabe, M. Mechanomyogram and force relationship during voluntary isometric ramp contractions of the biceps branchii muscle. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 84, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cescon, C.; Frina, D.; Gobbo, M.; Merletti, R.; Orizio, C. Effect of accelerometer location on mechanomyogram variables during voluntary, constant-force contractions in three human muscles. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2004, 42, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosvic, D.; Than, C.; Brown, J.M.M. The effect of accumulated muscle fatigue on the mechanomyographic waveform: Implications for injury prediction. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, T.W.; Housh, T.J.; Cramer, J.T.; Weir, J.P.; Johnson, G.O.; Coburn, J.W.; Malek, M.H.; Mielke, M. Mechanomyographic amplitude and frequency responses during dynamic muscle actions: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, D.; Andreozzi, E.; Fratini, A.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Savino, S.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. A Piezoresistive Sensor to Measure Muscle Contraction and Mechanomyography. Sensors 2018, 18, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matcher, S.J.; Elwell, C.E.; Cooper, C.E.; Cope, M.; Delpy, D.T. Performance Comparison of Several Published Tissue Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Algorithms. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 227, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogev, A.; Arnold, J.; Clarke, D.; Guenette, J.A.; Sporer, B.C.; Koehle, M.S. Comparing the Respiratory Compensation Point with Muscle Oxygen Saturation in Locomotor and Non-locomotor Muscles Using Wearable NIRS Spectroscopy During Whole-Body Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 818733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binzoni, T.; Cooper, C.E.; Wittekind, A.L.; Beneke, R.; Elwell, C.E.; Van De Ville, D.; Leung, T.S. A new method to measure local oxygen consumption in human skeletal muscle during dynamic exercise using near-infrared spectroscopy. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, D.A.; Fontana, F.Y.; Robertson, T.C.; Murias, J.M.; Paterson, D.M.; Kowalchuk, J.M.; Pogliaghi, S. Exercise Intensity Thresholds: Identifying the Boundaries of Sustainable Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 47, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöggl, T.; Born, D. Near Infrared Spectroscopy for Muscle Specific Analysis of Intensity and Fatigue during Cross-Country Skiing Competition—A Case Report. Sensors 2021, 21, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, G.; Hindistan, İ.E.; Özkaya, Y.G.; Köklükaya, E.; Polad, Ö.; Colak, Ö.H. Determination of fatigue following maximal loaded treadmill exercise by using wavelet packet transform analysis and MLPNN from MMG-EMG data combinations. J. Med. Syst. 2015, 39, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akataki, K.; Mita, K.; Watanabe, M. Electromyographic and mechanomyographic estimation of motor unit activation strategy in voluntary force production. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 44, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, C.R.; Hooush, T.J.; Camic, C.L.; Zuniga, J.M.; Johnson, G.O.; Schmidt, R.J. Comparing electromyographic and mechanomyographic frequency-based fatigue thresholds to critical torque during isometric forearm flexion. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 194, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scano, A.; Zanoletti, M.; Pirovano, I.; Spinelli, I.; Contini, D.; Torricelli, A.; Re, R. NIRS-EMG for Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geršak, V.; Geršak, G. NIRS: Measuring changes in muscle oxygenation and the detection of muscle activity. In Proceedings of the XIX IMEKO World Congress, Lisbon, Portugal, 6–11 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, S.Y.; Popov, D.V.; Borovik, A.S.; Vinogradova, O.L. Determination of aerobic anaerobic transition in the working muscle using EMG and Near-infrared spectroscopy data. Hum. Physiol. 2015, 41, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Lin, N.; Yin, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Qi, L. The Effects of Inter-Set Recovery Time on Explosive Power, Electromyography Activity, and Tissue Oxygenation during Plyometric Training. Sensors 2021, 21, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, K.; Korhonen, V.; Ferdinando, H.; Kallio, M.; Myllyla, T. Combined surface electromyography, near-infrared spectroscopy and acceleration recordings of muscle contraction: The effect of motion. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2017, 10, 1650056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, S.; Watanabe, S.; Oka, H. Novel Mechanomyogram/electromyogram Hybrid Transducer Measurements Reflect Muscle Strength during Dynamic Exercise—Pedaling of Recumbent Bicycle. Adv. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 7, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Misawa, H.; Takigawa, T.; Tetsunaga, T.; Yamane, K.; Oda, Y.; Ozaki, T. Quantification of patellar tendon reflex using portable mechanomyography and electromyography devices. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Development of a Multi-Channel Compact-Size Wireless Hybrid sEMG/NIRS Sensor System for Prosthetic Manipulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giminiani, R.D.; Cardinale, M.; Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. Validation of Fabric-Based Thigh-Wearable EMG Sensors and Oximetry for Monitoring Quadriceps Activity during Strength and Endurance Exercises. Sensors 2020, 20, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavrinsky, E.; Svobodova, H.; Donoval, M.; Daricek, M.; Kopani, M.; Miklovic, P.; Horinek, F.; Telek, P. Application of single wireless holter to simultaneous EMG, MMG and EIM measurement of human muscles activity. Clin. Technol. 2018, 48, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, A.; Minami, K. A multi-layered sensor for muscular activity analysis. IEEJ Trans. Sens. Micromach. 2021, 141, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, A.; Fujiyama, H.; Machida, M. A Wireless Multi-Layered EMG/MMG/NIRS Sensor for Muscular Activity Evaluation. Sensors 2023, 23, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimoto, A.; Oishi, Y.; Machida, M. A Wireless 2-Channel Layered EMG/NIRS Sensor System for Local Muscular Activity Evaluation. Sensors 2023, 23, 8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208394
Kimoto A, Oishi Y, Machida M. A Wireless 2-Channel Layered EMG/NIRS Sensor System for Local Muscular Activity Evaluation. Sensors. 2023; 23(20):8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208394
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimoto, Akira, Yuya Oishi, and Masanao Machida. 2023. "A Wireless 2-Channel Layered EMG/NIRS Sensor System for Local Muscular Activity Evaluation" Sensors 23, no. 20: 8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208394
APA StyleKimoto, A., Oishi, Y., & Machida, M. (2023). A Wireless 2-Channel Layered EMG/NIRS Sensor System for Local Muscular Activity Evaluation. Sensors, 23(20), 8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208394




