Quad Element MIMO Antenna for C, X, Ku, and Ka-Band Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
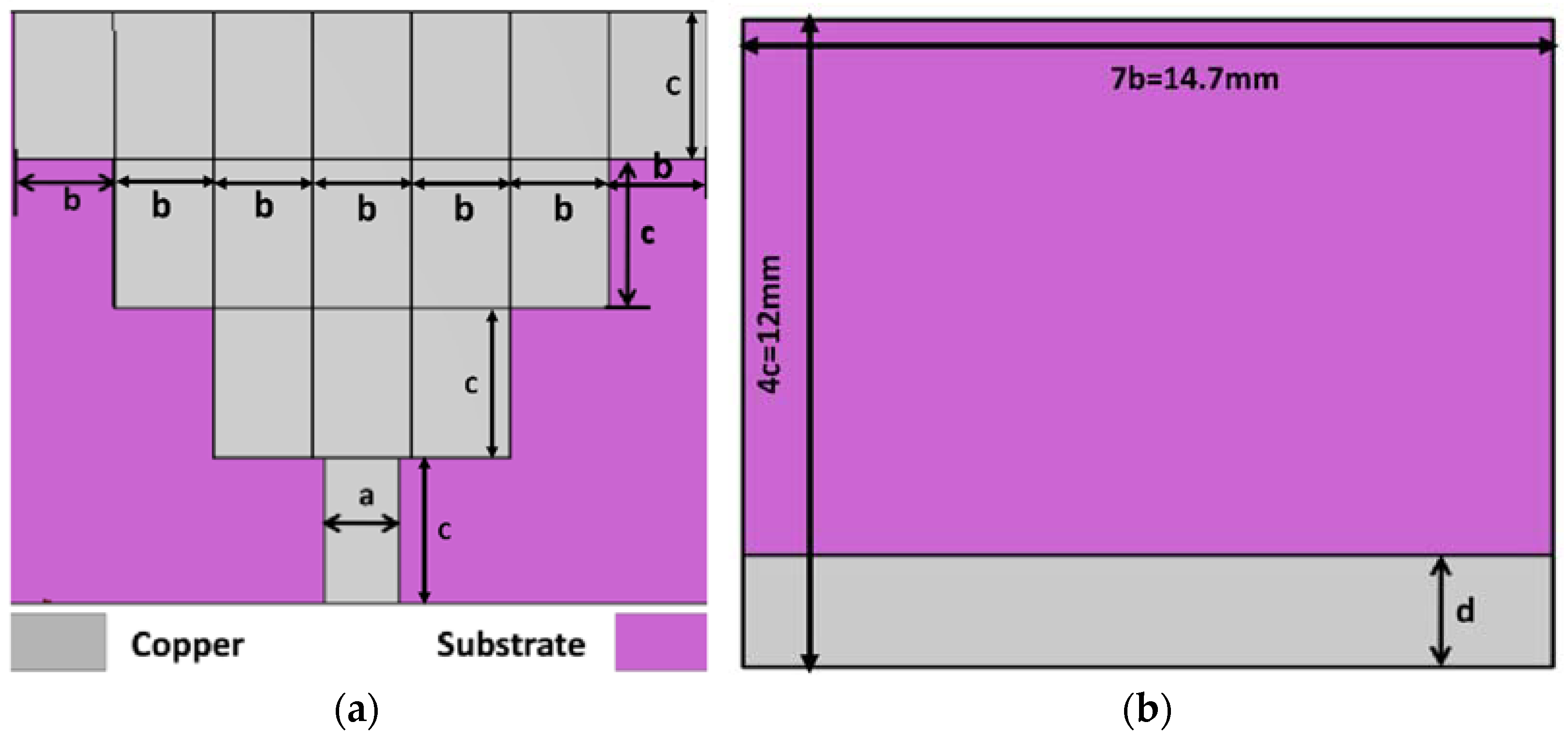
2. Antenna Geometry
2.1. Antenna Operating Principle
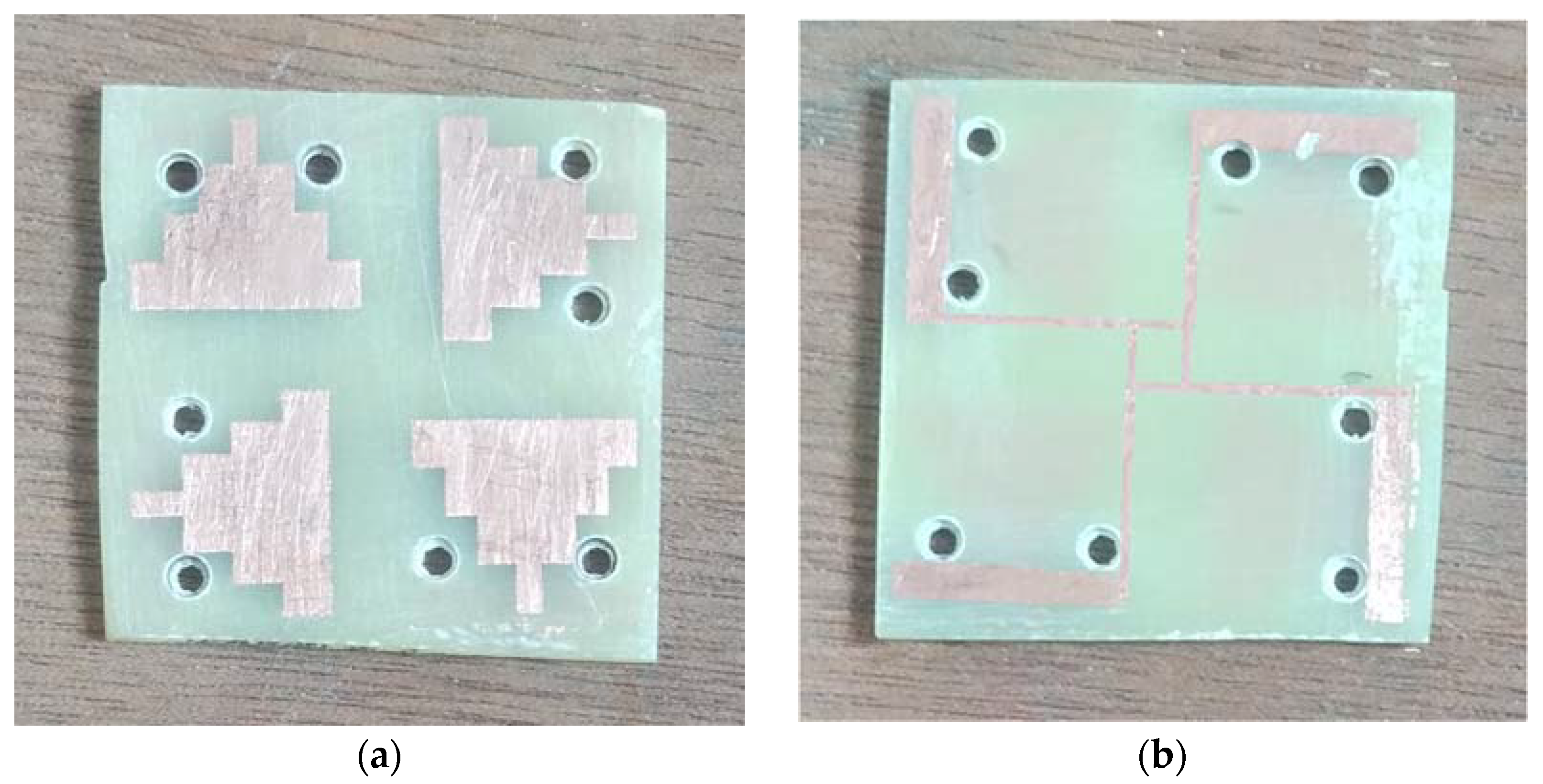
2.2. Proposed MIMO Antenna
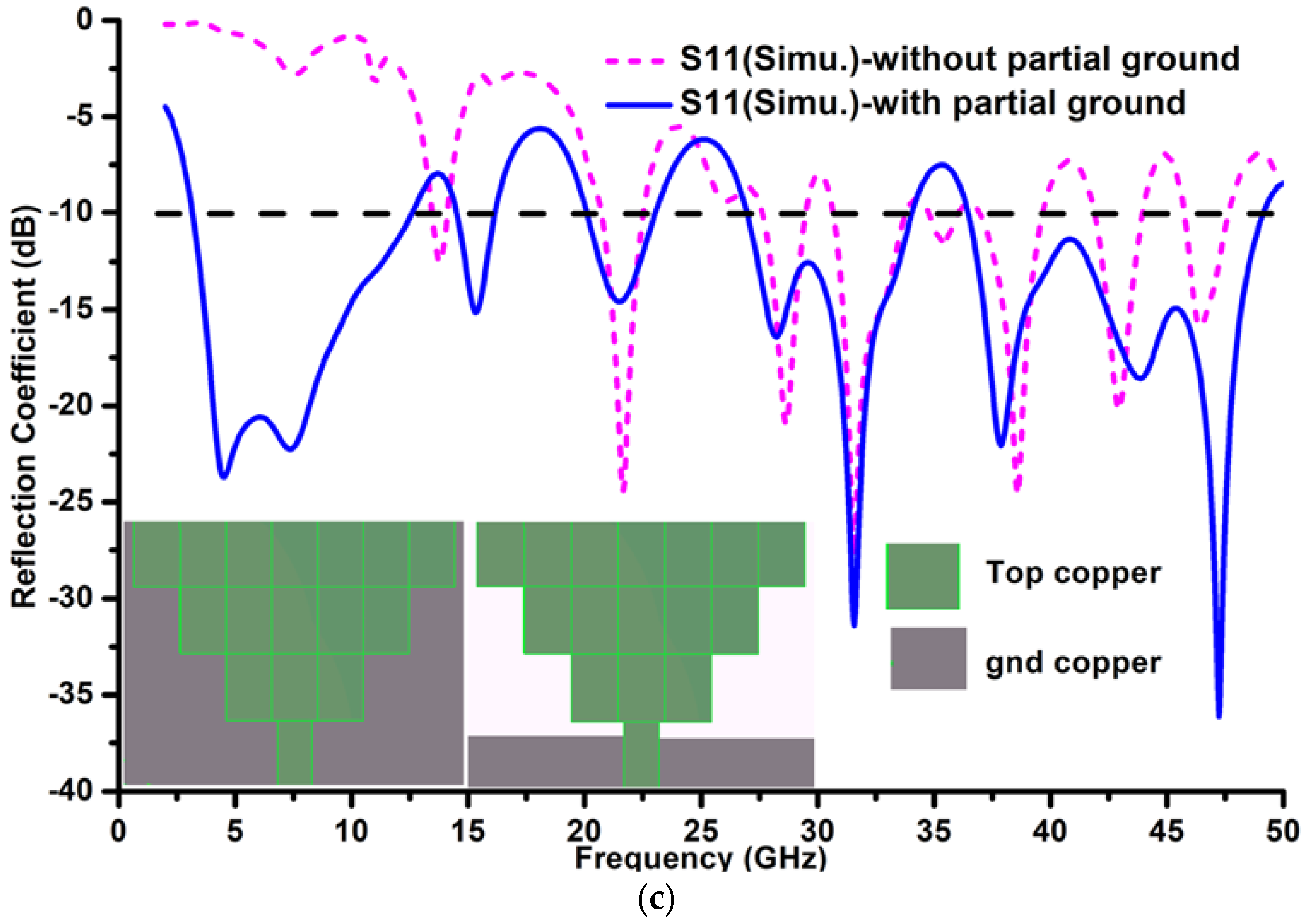
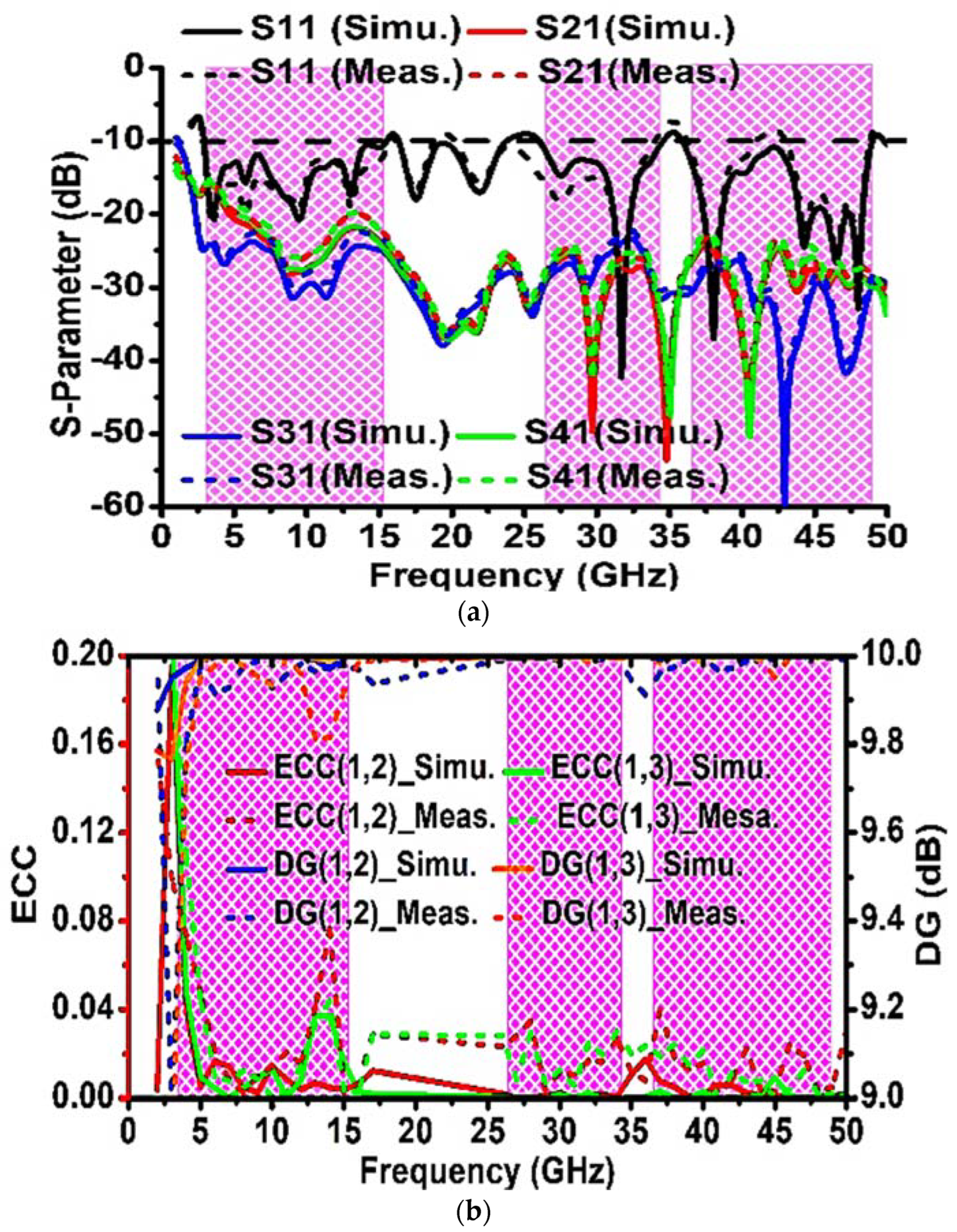
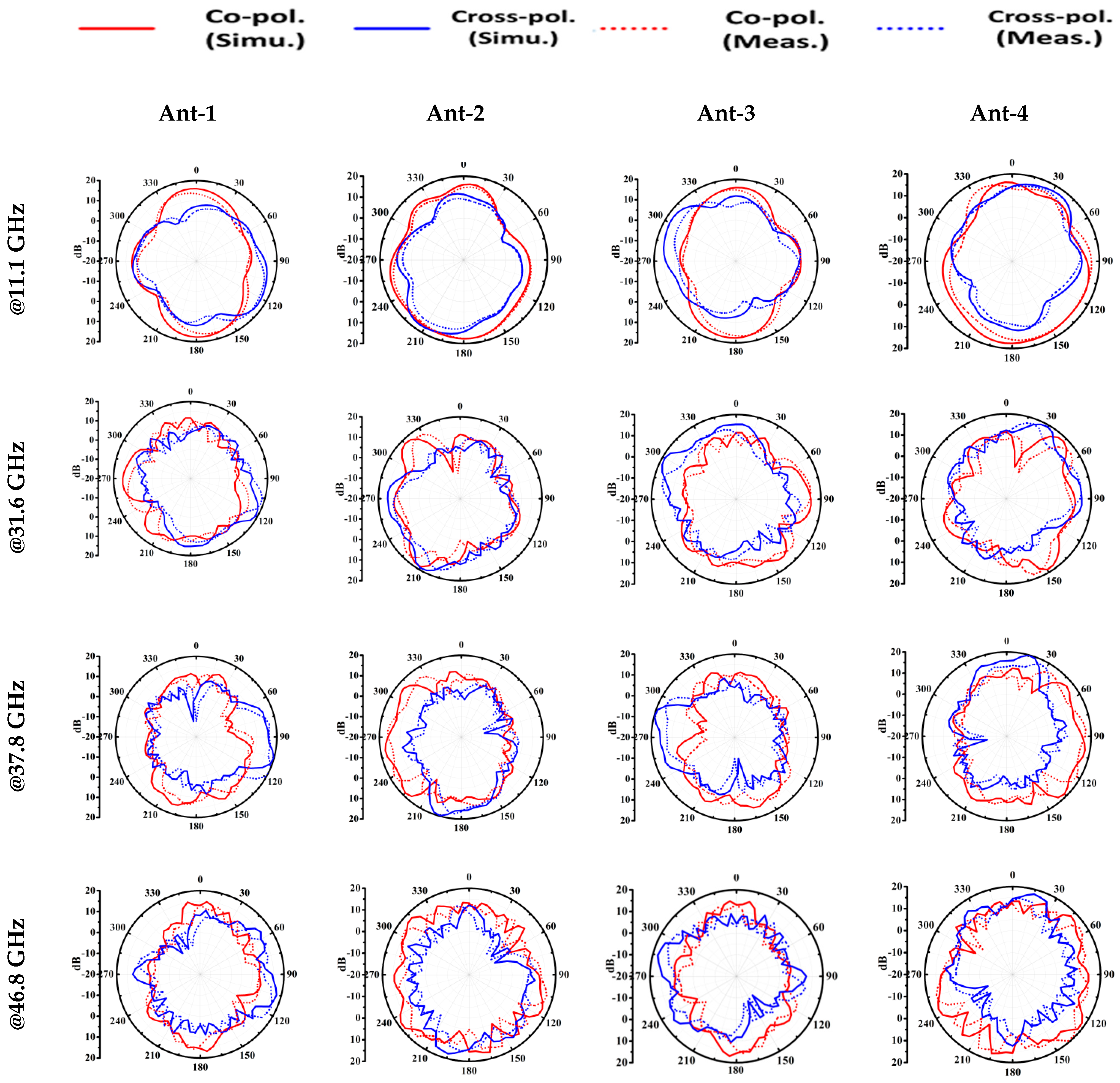
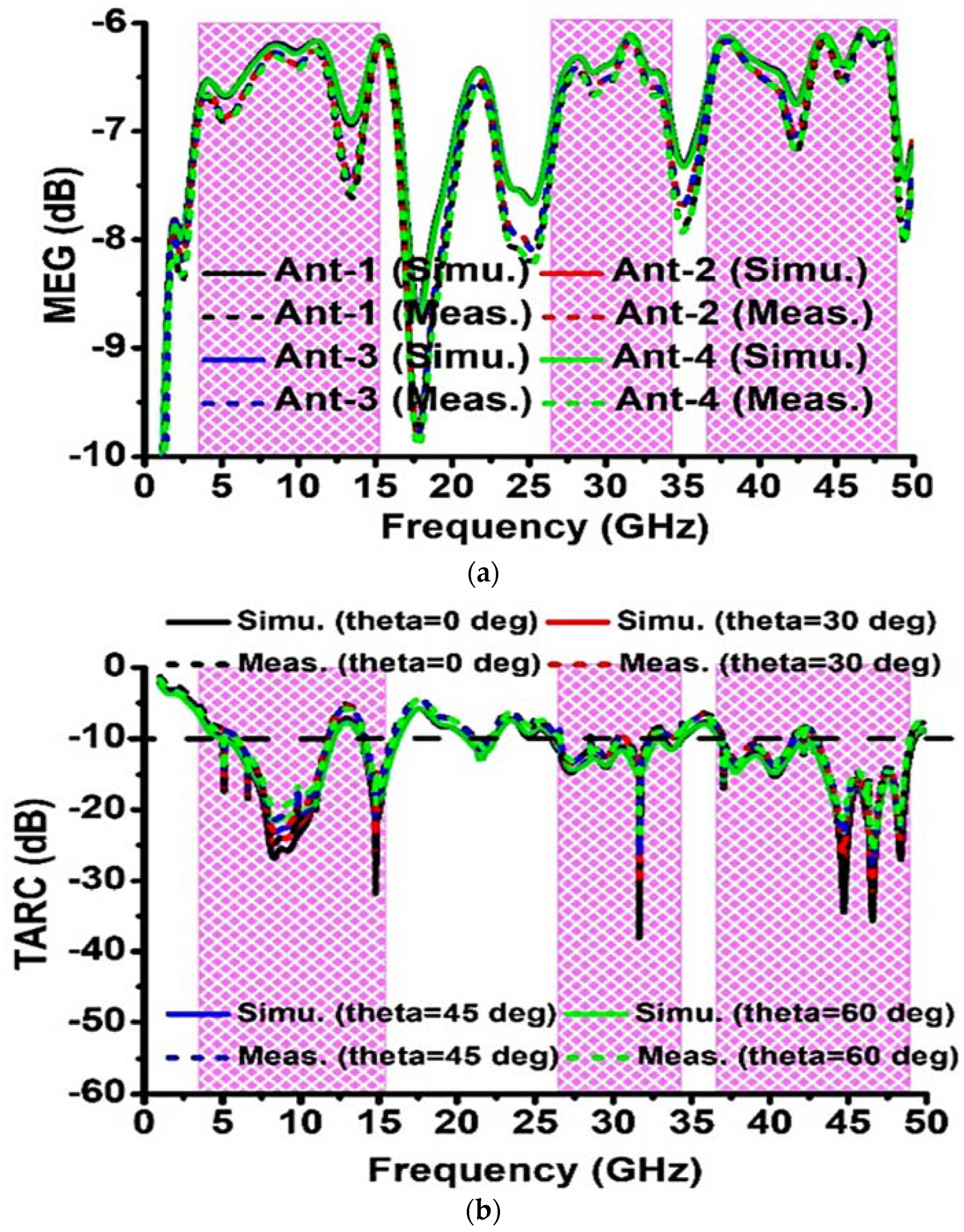
3. MIMO Performance of the Proposed Antenna
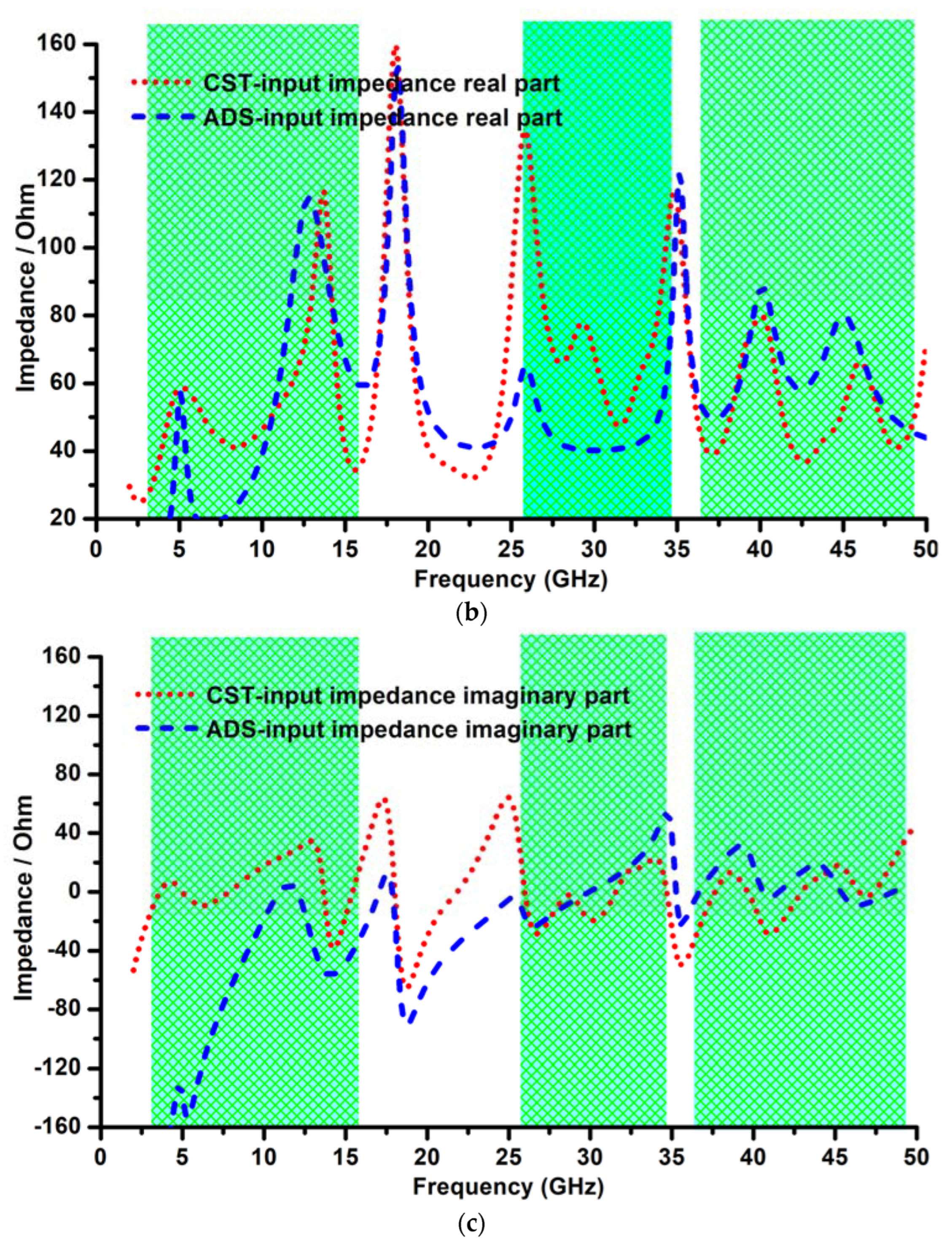
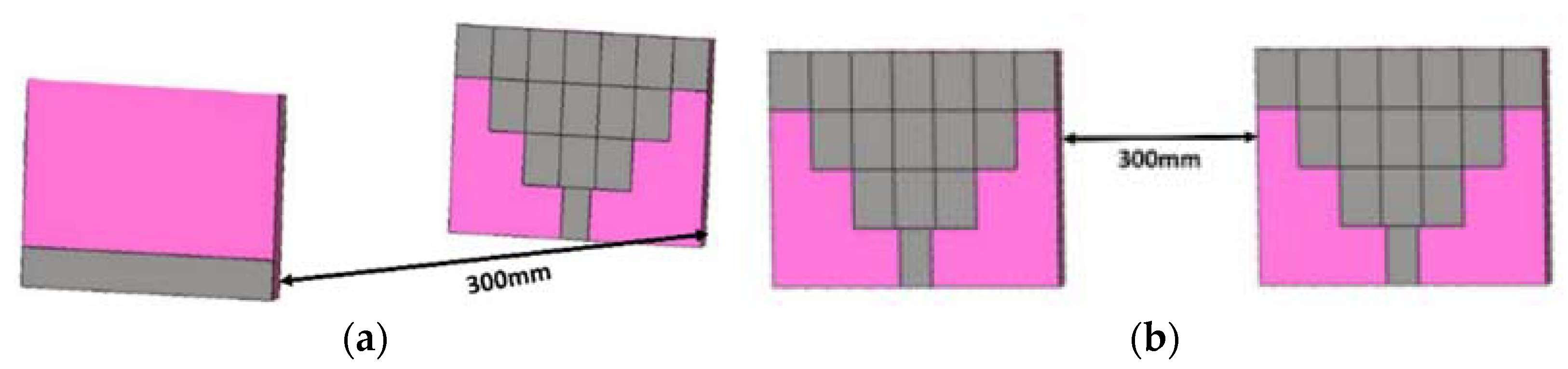
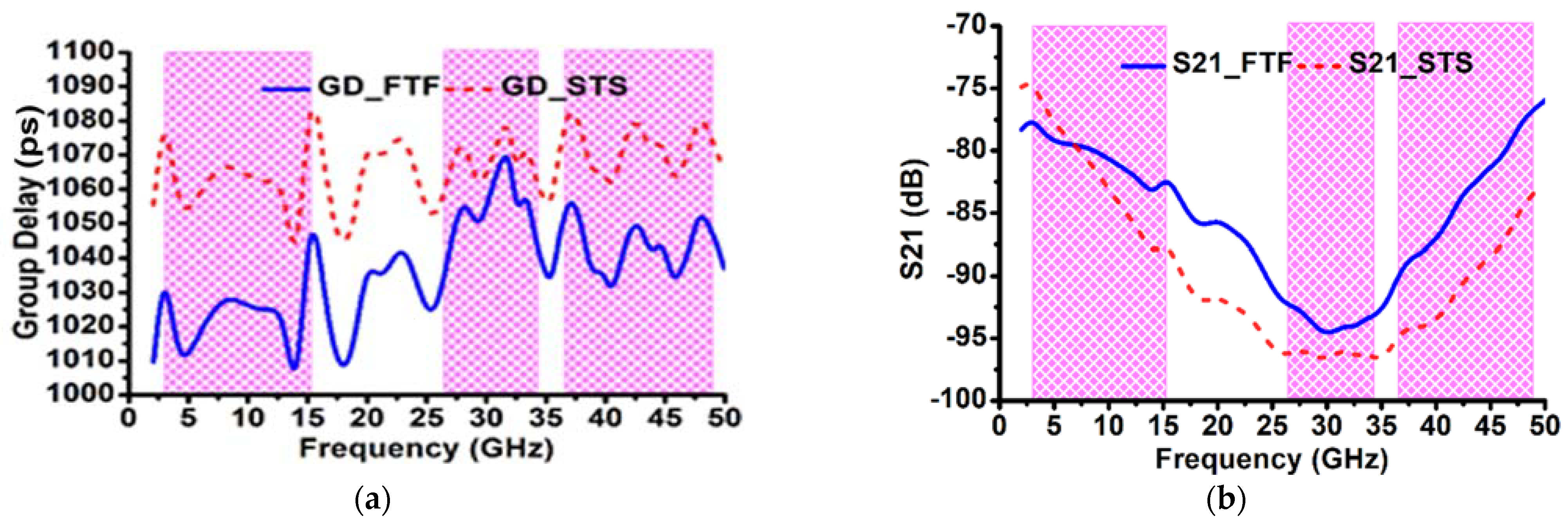
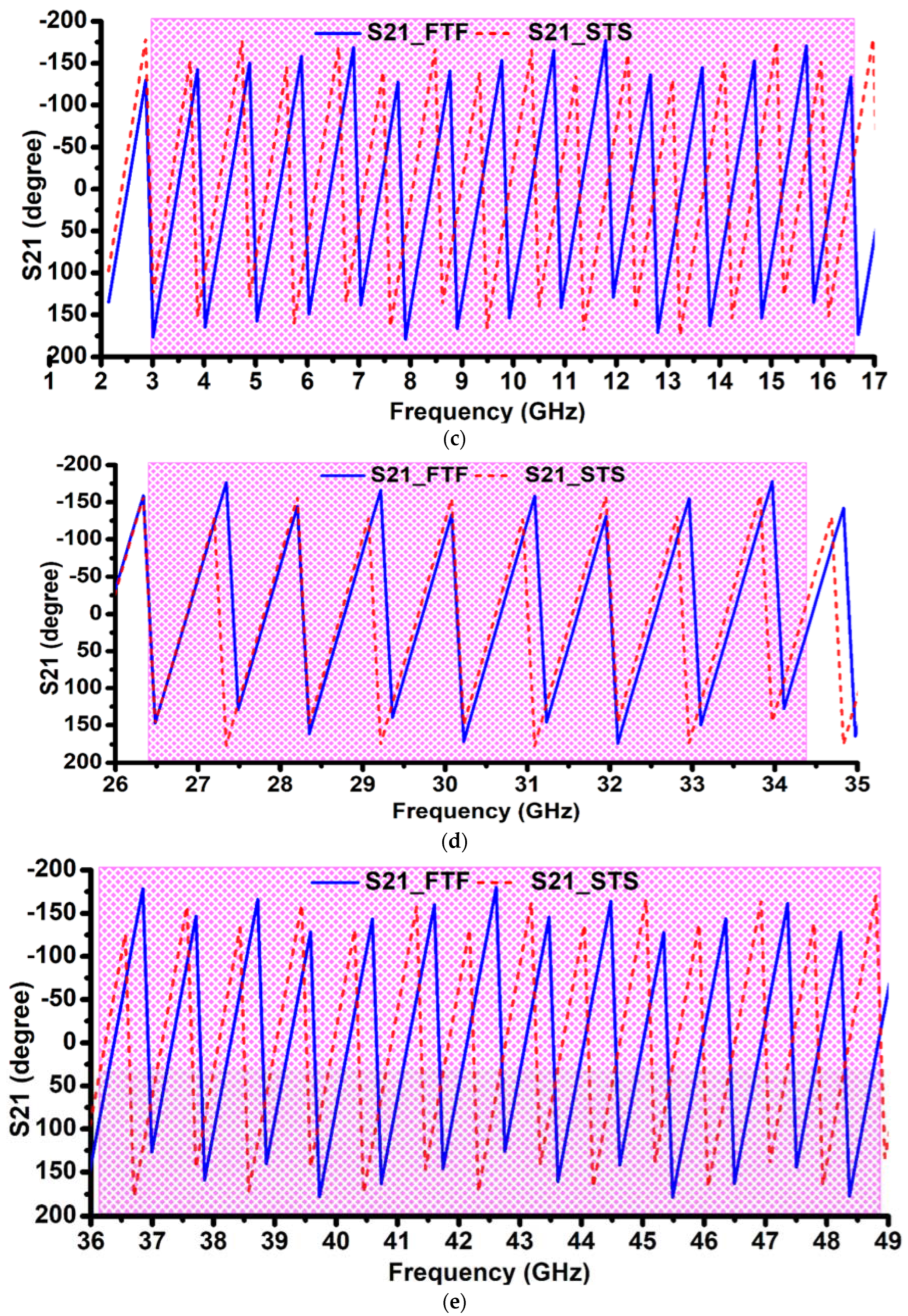
4. Simulated Time-Domain Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.; Yu, Z.; Lan, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Hong, W. Digital Beamforming-Based Massive MIMO Transceiver for 5G Millimeter-Wave Communications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 3403–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornson, E.; Van der Perre, L.; Buzzi, S.; Larsson, E.G. Massive MIMO in sub-6 GHz and mmWave: Physical, practical, and use-case differences. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehangir, S.S.; Sharawi, M.S. A Single Layer Semi-Ring Slot Yagi-Like MIMO Antenna System with High Front-to-Back Ratio. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawi, M.S.; Ikram, M.; Shamim, A. A Two Concentric Slot Loop Based Connected Array MIMO Antenna System for 4G/5G Terminals. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6679–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Hussain, R.; Sharawi, M.S. 4G/5G antenna system with dual function planar connected array. IET Microwaves, Antennas Propag. 2017, 11, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Alreshaid, A.T.; Podilchak, S.K.; Sharawi, M.S. Compact 4G MIMO antenna integrated with a 5G array for current and future mobile handsets. IET Microwaves, Antennas Propag. 2017, 11, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.M.S.; Abdipour, A.; Zhang, S.; Pedersen, G.F. Integrated Millimeter-Wave Wideband End-Fire 5G Beam Steerable Array and Low-Frequency 4G LTE Antenna in Mobile Terminals. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4042–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Nguyen-Trong, N.; Abbosh, A. Multiband MIMO microwave and millimeter antenna system employing dual-function tapered slot structure. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5705–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, S.; Khan, Q.U. An integrated MIMO antenna design for Sub-6 GHz & millimeter-wave applications with high isolation. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 153, 154247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Al Abbas, E.; Nguyen-Trong, N.; Sayidmarie, K.H.; Abbosh, A. Integrated Frequency-Reconfigurable Slot Antenna and Connected Slot Antenna Array for 4G and 5G Mobile Handsets. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 7225–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Zada, M.; Yoo, H. Low-Pass Filter Based Integrated 5G Smartphone Antenna for Sub-6-GHz and mm-Wave Bands. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 5424–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zada, M.; Shah, I.A.; Yoo, H. Integration of Sub-6-GHz and mm-Wave Bands with a Large Frequency Ratio for Future 5G MIMO Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 11241–11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xi, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, L.; Gan, L. A compact four-band high-isolation quad-port MIMO antenna for 5G and WLAN applications. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 153, 154294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K. Dual-band trident shaped MIMO antenna with novel ground plane for 5G applications. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 155, 154364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhong, T. Isolation Enhancement for 1 × 3 Closely Spaced E-Plane Patch Antenna Array Using Defect Ground Structure and Metal-Vias. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 119375–119383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kishk, A.A. Enhancing Isolation in Dual-Band Meander-Line Multiple Antenna by Employing Split EBG Structure. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A.E.; Hussein, K.F.A. Dual-Band (28/38 GHz) Wideband MIMO Antenna for 5G Mobile Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 32213–32223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabek, A.R.; Ali, W.A.E.; Ibrahim, A.A. Minimally Coupled Two-Element MIMO Antenna with Dual Band (28/38 GHz) for 5G Wireless Communications. J. Infrared, Millimeter, Terahertz Waves 2022, 43, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Bashir, S.; Chu, S. Dual band omnidirectional millimeter wave antenna for 5G communications. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2019, 33, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Awasthi, Y.K.; Singh, H.; Kumar, R.; Kumari, S. Design of Compact Flower Shape Dual Notched-Band Monopole Antenna for Extended UWB Wireless Applications. J. RF Eng. Telecommun. 2016, 3, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addepalli, T.; Kamili, J.B.; Bandi, K.K.; Nella, A.; Sharma, M. Lotus flower-shaped 4/8-element MIMO antenna for 5G n77 and n78 band applications. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2022, 36, 1404–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, M.K.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kumar, S. Defected Ground Structure: Fundamentals, Analysis, and Applications in Modern Wireless Trends. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2017, 2017, 2018527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysight Inc. Advanced Design System (ADS). Santa Rosa, CA, USA. 2022. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Jangid, S.; Rama, V.S.B. An Equivalent Circuit Modeling of UWB Patch Antenna with Band Notched Characteristics. Eur. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2014, 1, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Koohestani, M.; Azadi-Tinat, N.; Skrivervik, A.K. Compact slit-loaded ACS-Fed monopole antenna for Bluetooth and UWB systems with WLAN band-stop capability. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 7540–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Guizani, M. Millimeter-wave multimedia communications: Challenges, methodology, and applications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, R.; Zhang, M.; Mezzavilla, M.; Dutta, S.; Rangan, S.; Zorzi, M. Achieving ultra-low latency in 5G millimeter wave cellular networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, Z. Advanced Obstacles Detection and Tracking by Fusing Millimeter Wave Radar and Image Sensor Data; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2010; pp. 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, M.T.; Di Meo, S.; Crocco, L.; Isernia, T.; Pasian, M. Millimeter-waves breast cancer imaging via inverse scattering techniques. IEEE J. Electromagn. Rf Microw. Med. Biol. 2021, 5, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E.; Shay, O.; Kim, C.; Liao, C. Wearable millimeter-wave device for contactless measurement of arterial pulses. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 13, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.F.; Steer, M.B.; Rappaport, T.S. Exploiting High Millimeter Wave Bands for Military Communications, Applications, and Design. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 52350–52359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yi, P.; Zhang, R.; Xia, X.-G.; Schober, R. A Survey on millimeter-wave beamforming enabled UAV communications and networking. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2021, 24, 557–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, M.H.; Ameli, S.; Abedi, A.; Abari, O. A millimeter wave network for billions of things. In Proceedings of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Beijing China, 19 August 2019; pp. 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, M.H.; Zaki, A.I.; Hamad, R.K.; Omar, M.M. A novel dual-band (38/60 GHz) patch antenna for 5G mobile handsets. Sensors 2020, 20, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Zhao, A. High performance 5G millimeter-wave antenna array for 37–40 GHz mobile application. In 2018 International Workshop on Antenna Technology (iWAT); IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Choi, D.; Hong, W. GHz vertically-polarized end-fire 5G antenna array featuring electrically small profile. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 8–13 July 2018; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea; pp. 637–638. [Google Scholar]
- Malekar, R.R.; Shevada, L.K.; Raut, H.D.; Dixit, A.S.; Kumar, S. MIMO antenna for fifth generation mm-wave applications: A bibliometric survey. Libr. Philos. Pract. 2020, 4854, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, W.; Das, S.; Medkour, H.; Lakrit, S. Planar dual-band 27/39 GHz millimeter-wave MIMO antenna for 5G applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Iffat Naqvi, S.; Hussain, N.; Rahman, M.; Fawad; Mirjavadi, S.S.; Khan, M.J.; Amin, Y. 4-Port MIMO antenna with defected ground structure for 5G millimeter wave applications. Electronics 2020, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, N.; Seo, C. A 28-GHz wideband 2× 2 U-slot patch array antenna. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2017, 17, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A.; Allam, A.; Gaafar, A.; Elhennawy, H.M.; Sree, M.F.A. Compact UWB MIMO antenna for 5G millimeter-wave applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.T.; Shakir, S.; Durani, M.H.; Ahmed, U.; Bilal, M. December. Miniaturized four port MIMO antenna system for 5G mm-wave applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Microwave, Antennas & Circuits (ICMAC), Islamabad, Pakistan, 21–22 December 2021; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, J.; Let, G.S.; Pratap, C.B.; Winston, J.J. A miniaturized uniplanar MIMO antenna for n79/n46/millimeter-wave applications. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2023, 36, e5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Duan, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, Y. High isolation millimeter-wave wideband MIMO antenna for 5G communication. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2019, 2019, 4283010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawi, M.S.; Hassan, A.T.; Khan, M.U. Correlation coefficient calculations for MIMO antenna systems: A comparative study. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2017, 9, 1991–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Mahto, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Mistri, R.K.; Sinha, R. Reconfigurable circular patch MIMO antenna for 5G (sub-6 GHz) and WLAN applications. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2022, 35, 5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.K.; Das, G.; Gangwar, R.K. Dual polarized triple-band dielectric resonator based hybrid MIMO antenna for WLAN/WiMAX applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz-Andrade, E.; Jardon-Aguilar, H.; Tirado-Mendez, J.A. The correct application of total active reflection coefficient to evaluate MIMO antenna systems and its generalization to N ports. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2019, 30, e22113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Cui, L.; Li, C.; Sun, B. Side-Edge Frame Printed Eight-Port Dual-Band Antenna Array for 5G Smartphone Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 7412–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistri, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Mahto, S.K.; Sinha, R. Quad element millimetre-wave MIMO antenna for 5G communication. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2023, 37, 1258–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.X.; Vaughan, R.G. Multiple Element Antenna Efficiency and its Impact on Diversity and Capacity. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistri, R.K.; Mahto, S.K.; Sinha, R. Dual band 8 × 8 MIMO antenna system for DCS 1800 and 5G mobile applications. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2022, 36, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Sim, C.; Yang, G. D esign of 8 × 8 dual-band MIMO antenna array for 5 G smartphone applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2018, 28, 21420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, G.; Zurcher, J.F.; Skrivervik, A.K. System fidelity factor: A new method for comparing UWB antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar]
- Koohestani, M.; Zürcher, J.F.; Moreira, A.A.; Skrivervik, A.K. A novel, low-profile, vertically-polarized UWB antenna for WBAN. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 1888–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollipara, V.; Peddakrishna, S. Quad-Port Circularly Polarized MIMO Antenna with Wide Axial Ratio. Sensors 2022, 22, 7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nej, S.; Ghosh, A.; Ahmad, S.; Ghaffar, A.; Hussein, M. Compact Quad Band MIMO Antenna Design with Enhanced Gain for Wireless Communications. Sensors 2022, 22, 7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, K.C.; Kumar, J. Miniaturized Parasitic Loaded High-Isolation MIMO Antenna for 5G Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, S.H.; Altaf, A.; Anjum, M.R.; Afridi, S.; Arain, Z.A.; Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Lalbakhsh, A.; Khan, M.A.; et al. MIMO Antenna System for Modern 5G Handheld Devices with Healthcare and High Rate Delivery. Sensors 2021, 21, 7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
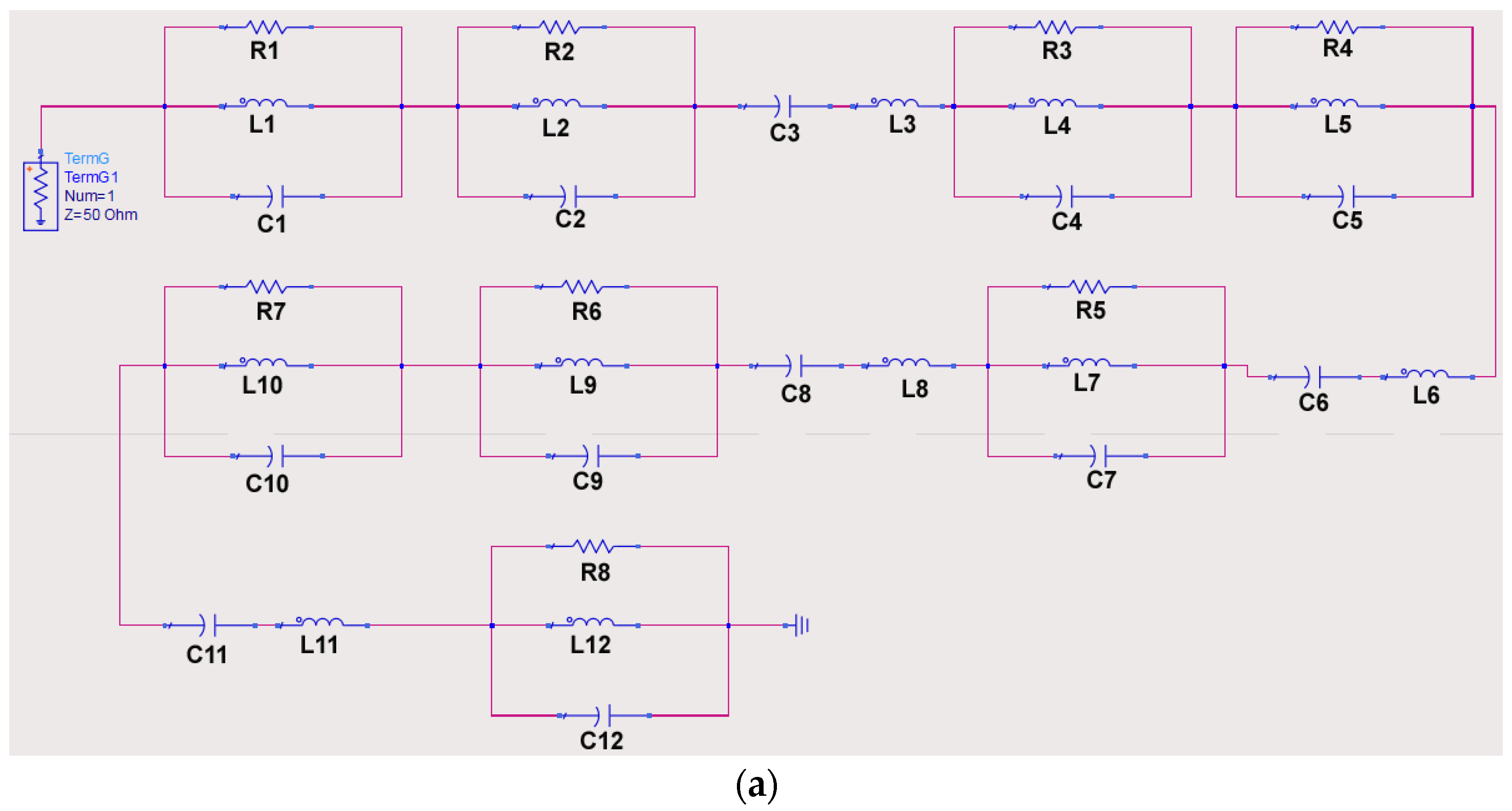




| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 |
| 3.952 | 1.098 | 0.77 | 0.001 | 0.517 | 0.53 | 1.247 | 0.68 | 2.05 | 1.575 | 1.09 | 3.78 |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | L8 | L9 | L10 | L11 | L12 |
| 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.558 | 0.299 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | C1-C12 in pF, L1-L12 in nH, and R1-R8 in ohm | |||
| 48.79 | 112.8 | 38.62 | 90.25 | 38.62 | 80.67 | 45.64 | 26.74 | ||||
| Orientation | FF | SFF |
|---|---|---|
| face to face | 0.9359 | 0.7584 |
| side by side | 0.9477 | 0.7583 |
| Ref | Bands | No. of Ports | Antenna Size/Substrate | Peak Gain | Peak Efficiency (%) | Isolation (dB) | ECC | TARC | CC (at −20 dB SNR) [bps/Hz] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | dual band | 1.87–2.53 GHz (6 dB) | 2 | 0.44 × 0.73 × 0.007 (-) | 4 dBi | 75 | 15 | 0.18 | - | - |
| 26–28.4 GHz (10 dB) | 8 dBi | 83 | 25 | - | - | - | ||||
| [7] | triple band | 0.74–0.96 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 0.19 × 0.34 × 0.002 (Nelco N9000) | 8 dBi | 80 | 13 | - | - | - |
| 1.7–2.2 GHz (10 dB) | 1 | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | |||
| 22–31 GHz (10 dB) | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | ||||
| [8] | triple band | 2.4–5.1 GHz (10 dB) | 8 | 1.3 × 1.3 × 0.006 (RT/duroid 5880) | 5 dBi | 70 | 16 | 0.16 | - | - |
| 5.1–5.6 GHz (10 dB) | 5 dBi | 70 | 16 | 0.16 | - | - | ||||
| 23–30 GHz (10 dB) | 11 dBi | 70 | 16 | 0.16 | - | - | ||||
| [9] | triple band | 2.38–4.13 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 0.87 × 0.87 × 0.006 (RO5880) | 3.47 dBi | 93.58 | >22 | 0.284 | <−10 dB | - |
| 5.04–6.12 GHz (10 dB) | 5.64 dBi | 94.64 | >22 | - | <−10 dB | - | ||||
| 22.28–29.28 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 11.4 dBi | 93.26 | >22 | - | <−10 dB | - | |||
| [10] | dual band | 2.05–2.7 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 0.55 × 0.47 × 0.003 (Rogers 5880) | 4.5 dBi | 70 | 20 | 0.01 | - | - |
| 23–29 GHz (10 dB) | 12.5 dBi | 95 | 20 | 0.01 | - | - | ||||
| [11] | triple band | 3.3–3.75 GHz (10 dB) | 8 | 1.85 × 0.82 × 0.006 (Rogers RT/duroid 5880) | 4 dBi | 45 | 15 | 0.3 (AVG) | - | - |
| 27.15–28.77 GHz (10 dB) | 6 dBi | 60 | >25 | <<0.3 (AVG) | - | - | ||||
| 37.59–38.49 GHz (10 dB) | 6 dBi | 60 | >25 | <<0.3 (AVG) | - | - | ||||
| [13] | quad band | 2.54–2.64 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 0.33 × 0.33 × 0.014 (FR4) | 1 dBi | - | >21.5 | <0.012 | - | - |
| 3.4–3.62 GHz (10 dB) | 3 dBi | - | >21.5 | <0.012 | - | - | ||||
| 4.4–5.28 GHz (10 dB) | 3.5 dBi | - | >21.5 | <0.012 | - | - | ||||
| 5.6–6 GHz (10 dB) | 1.6 dBi | - | >21.5 | <0.012 | - | - | ||||
| [14] | dual band | 2.99–3.61 GHz (10 dB) | 2 | 0.68 × 0.28 × 0.017 (Rogers RO4003) | 3.14 dB | 80.24 (RAD) | >25 | <0.002 | <−25 dB | - |
| 4.53–4.92 GHz (10 dB) | 3.84 dB | 84.64 (RAD) | >16 | <0.002 | <−20 dB | - | ||||
| [56] | single band | 5.37–11.0 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 1.364 × 1.364 × 0.013 (FR4) | 5.6 dB | - | >21 | <0.003 | 0.0001 dB | |
| [57] | quad band | 1.21–1.24 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 0.246 × 0.246 × 0.0065 (FR4) | 1.73 dBi | - | >22 | <0.003 | - | - |
| 2.42–2.5 GHz (10 dB) | 4.83 dBi | - | >22 | <0.003 | - | - | ||||
| 3.4–3.6 GHz (10 dB) | 7.62 dBi | - | >22 | <0.003 | - | - | ||||
| 4.8–5.1 GHz (10 dB) | 9.81 dBi | - | >22 | <0.003 | - | - | ||||
| [58] | single band | 25–31.6 GHz (10 dB) | 2 | 1.01 × 1.85 × 0.154 (FR4) | 4.8 dBi | - | >25 | <0.01 | - | - |
| [59] | single band | 3.4–3.6 GHz (6 dB) | 8 | 0.233 × 0.145 × 0.0093 (FR4) | 2.87 dBi | 65 | >12 | <0.2 | - | 38 |
| This work | triple band | 3–17 GHz (10 dB) | 4 | 1.057 × 1.057 × 0.053 (FR4) | 3.03 dB | 56.7 | >15.1 | <0.21 | <−5 dB | 12.1–19.1 |
| 25.3–35.1 GHz (10 dB) | 5.87 dB | 58.8 | >22 | <0.034 | <−7.4 dB | 16.6–19.2 | ||||
| 35.5–49.4 GHz (10 dB) | 5.92 dB | 52.5 | >22.37 | <0.04 | <−6.9 dB | 16.9–18.4 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mistri, R.K.; Mahto, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, R.; Al-Gburi, A.J.A.; Alghamdi, T.A.H.; Alathbah, M. Quad Element MIMO Antenna for C, X, Ku, and Ka-Band Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 8563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208563
Mistri RK, Mahto SK, Singh AK, Sinha R, Al-Gburi AJA, Alghamdi TAH, Alathbah M. Quad Element MIMO Antenna for C, X, Ku, and Ka-Band Applications. Sensors. 2023; 23(20):8563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208563
Chicago/Turabian StyleMistri, Raj Kumar, Santosh Kumar Mahto, Ajit Kumar Singh, Rashmi Sinha, Ahmed Jamal Abdullah Al-Gburi, Thamer A. H. Alghamdi, and Moath Alathbah. 2023. "Quad Element MIMO Antenna for C, X, Ku, and Ka-Band Applications" Sensors 23, no. 20: 8563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208563
APA StyleMistri, R. K., Mahto, S. K., Singh, A. K., Sinha, R., Al-Gburi, A. J. A., Alghamdi, T. A. H., & Alathbah, M. (2023). Quad Element MIMO Antenna for C, X, Ku, and Ka-Band Applications. Sensors, 23(20), 8563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208563









