An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors
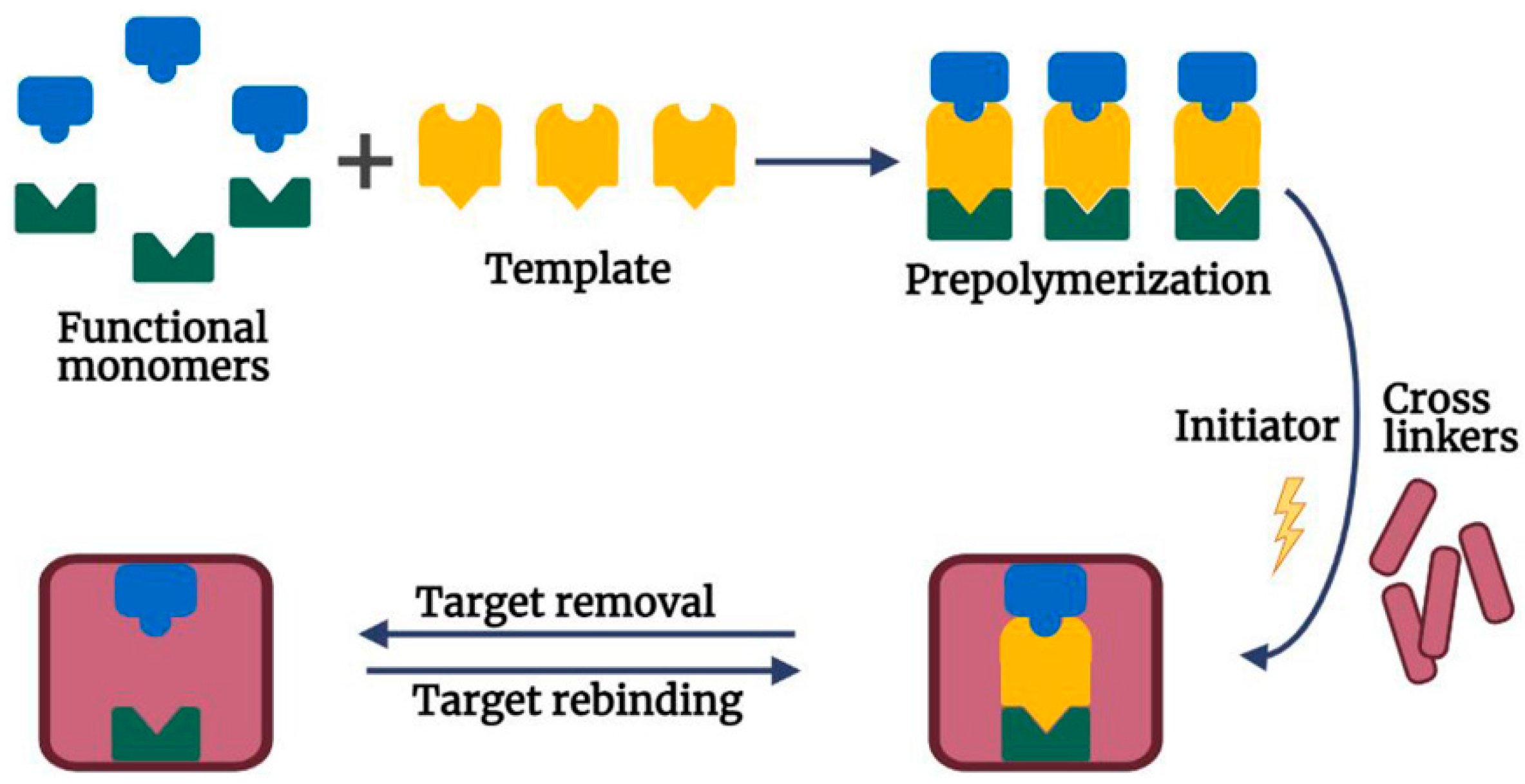
2.1. Principle of MIES for BPA Detection
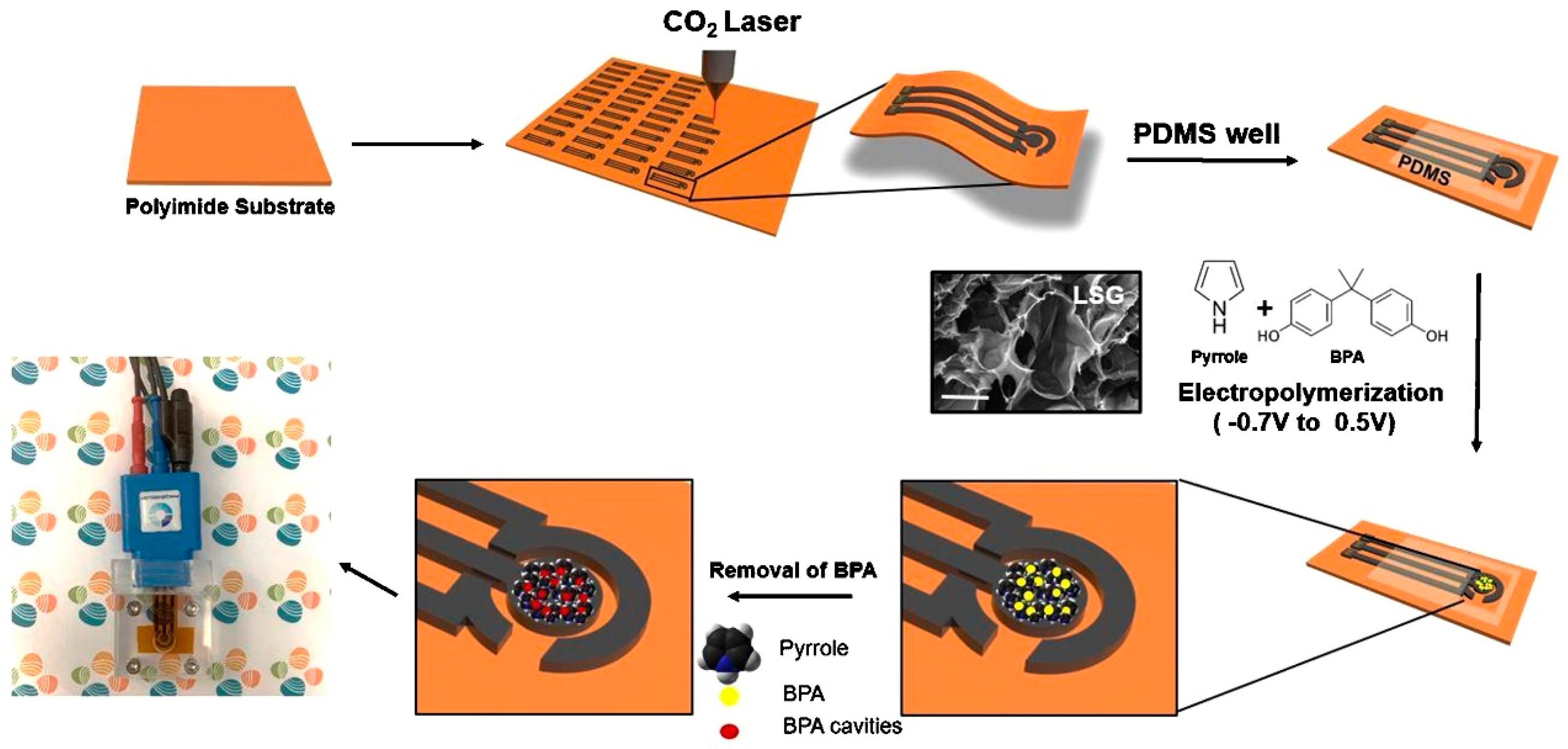
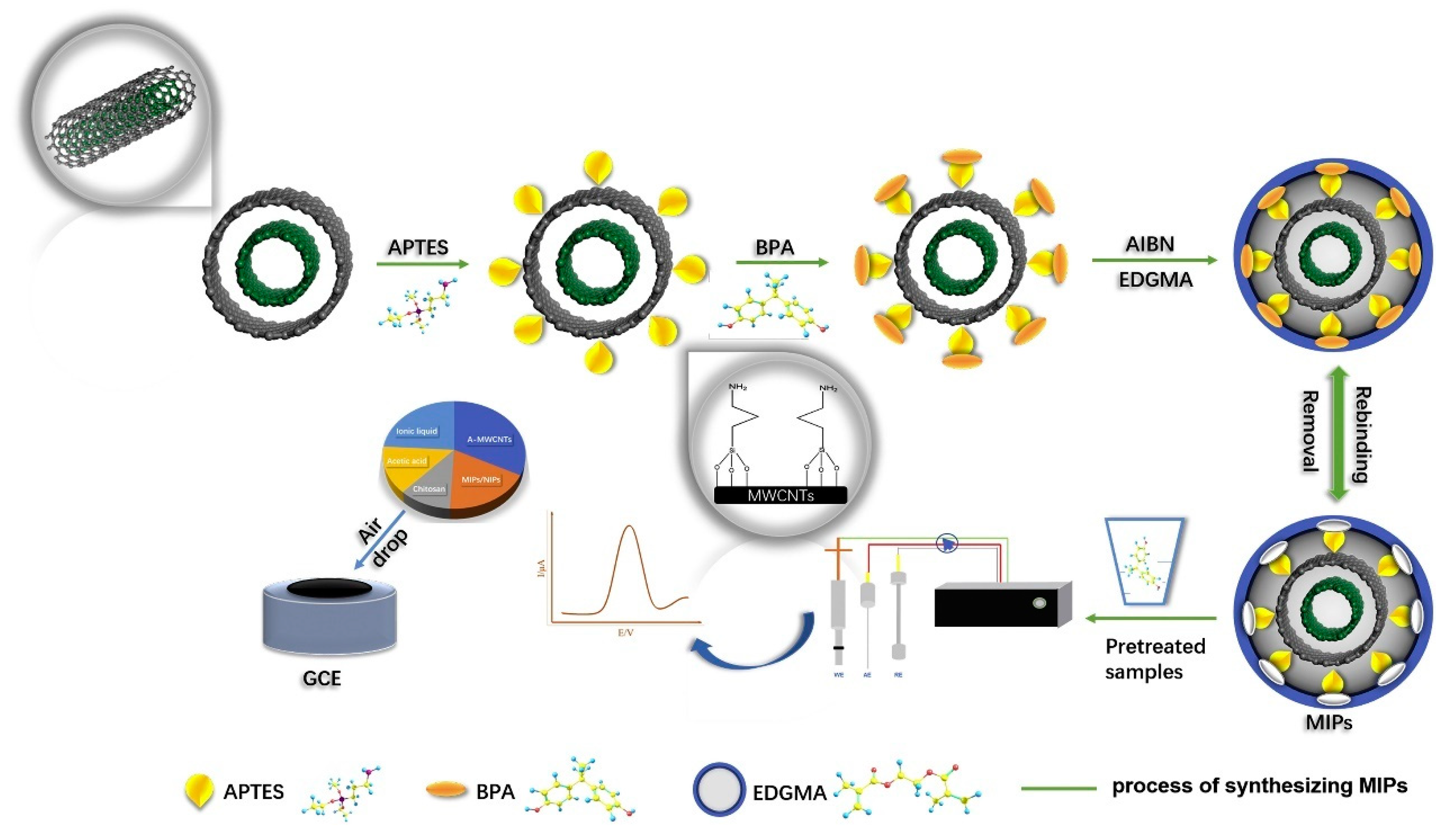
2.2. Fabrication Process
2.3. Extraction of BPA Templates
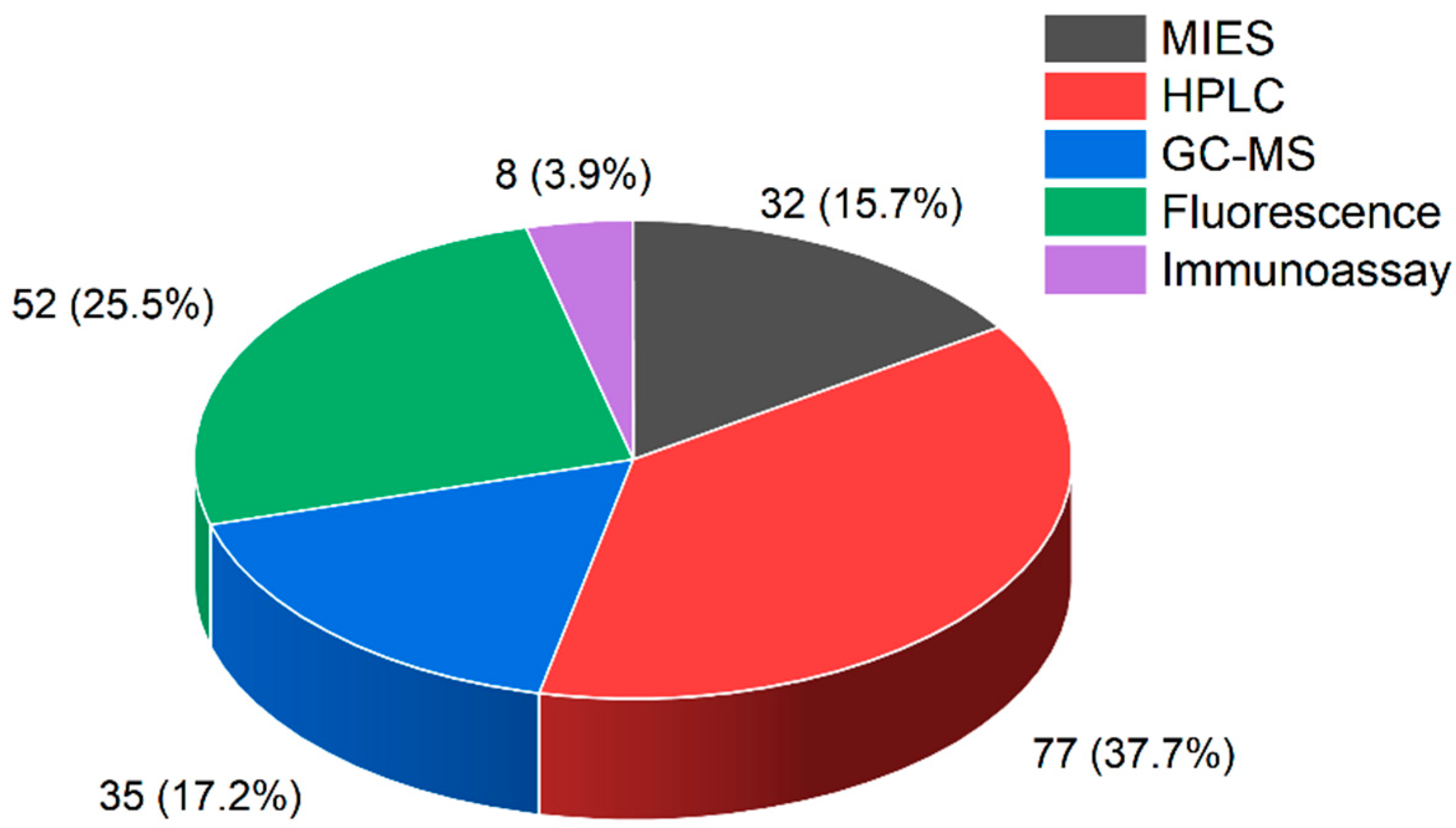
2.4. Types of MIES for BPA Detection
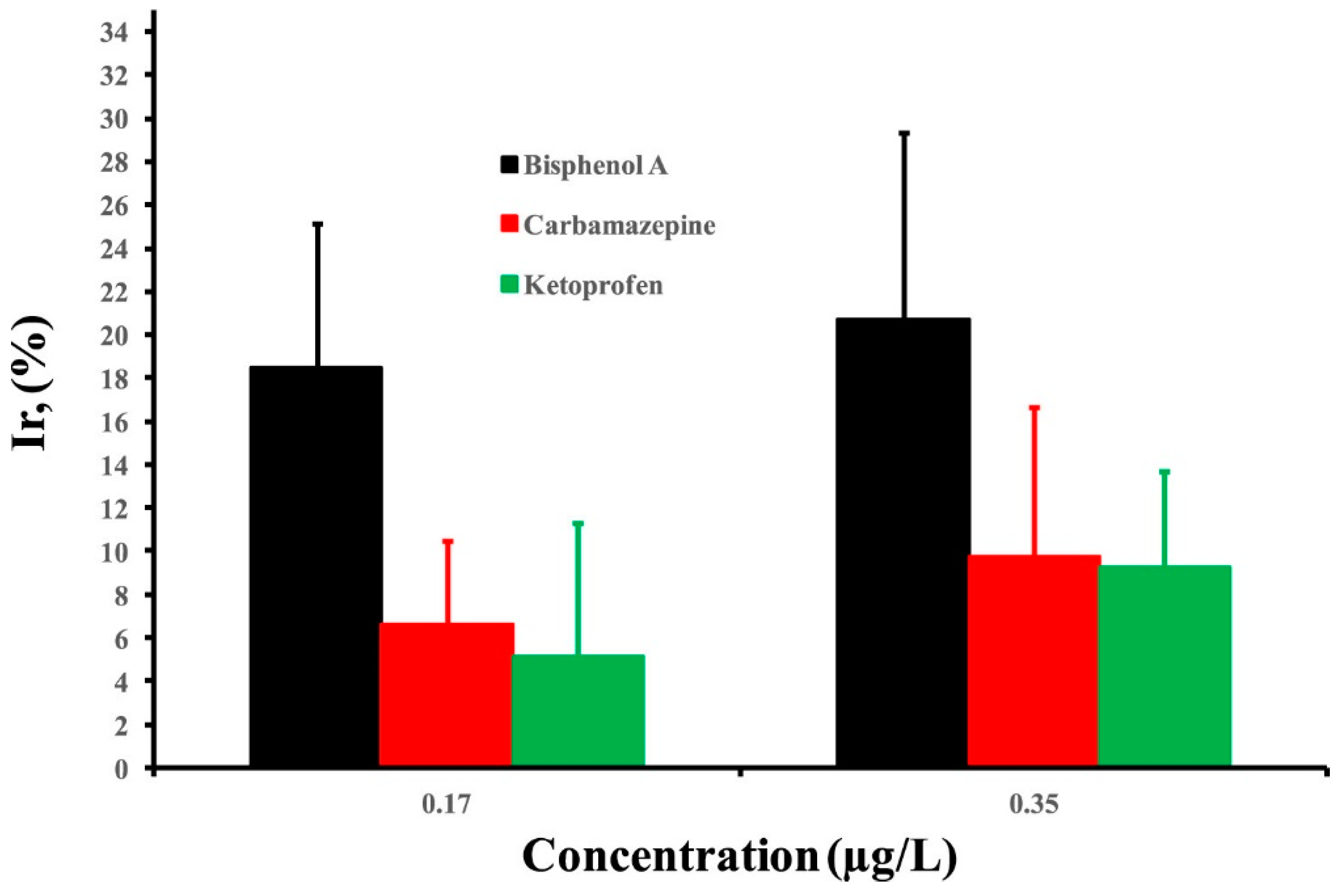
3. Performance Evaluation of Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for BPA Detection
| Sensor | Method | LDR | LOD | Real Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP/AuNPs/MWCNTs | Amperometry | 0.11 μM to 8.2 mM | 3.6 nM | Honey; Grape juice | [61] |
| MIP/AuNPs/GCE | Amperometry | 8 μM to 60 mM | 0.14 μM | Water bottles | [42] |
| MMIP/SPIONPs/SPCE | Amperometry | 25 nM to 0.1 mM | 0.16 μM | Saline; Tap water; Mineral water | [65] |
| MIP/TiO2NTs/Ti | Amperometry | 4.5 nM to 0.11 μM | 2 nM | Water | [66] |
| MIP/Au/N-MWCNT/GONRs | Amperometry | 0.44 μM to 87 μM | 8.7 nM | Serum | [67] |
| MMIP/CTAB/CPE | CV | 0.6 μM to 0.1 mM | 1 μM | Water bottles; Lake water | [68] |
| Fe3O4@TiO2/Au/TiMIF | CV | 13 nM to 6.6 μM | 1.2 nM | Chicken; Pork | [69] |
| MIP/ABPE | CV | 80 nM to 10 μM | 60 nM | Plastic | [70] |
| MIP/GO/GCE | CV | 6 nM to 0.1 μM; 0.2 μM to 20 μM | 3 nM | Milk; Mineral water | [48] |
| MIP-AuNPs-MCA-rGO/CILE | CV | 4 nM to 15 μM | 1 nM | Plastics | [71] |
| MIP/Au | CV | 10 μM to 100 μM | - | - | [72] |
| MIPMSs/CPE | CV | 10 pM to 0.1 μM | 2.8 pM | Tap water; Milk | [73] |
| MIP/graphitic-C3N4/FTO | CV | 5 μM to 0.2 mM | 1.3 μM | Bottled water | [74] |
| MIP(ANI)/GCE | CV | 1 fM to 8 fM | 0.193 fM | Serum | [75] |
| MIP/NMWCNT/CPE | CV | 0.05 μM to 90 μM | 11.8 nM | Plastic bottle leaching | [49] |
| MIP/PPy@LSG | DPV | 80 nM to 5 μM | 8 nM | Mineral water; Plastics | [56] |
| MIM(MIPs)/MWCNTs/GCE | DPV | 0.2 μM to 8 μM | 8 nM | Tap water; Mineral water | [76] |
| PEDOT/GQDs/AuNPs/GCE | DPV | 1 nM to 50 µM | 0.19 nM | Tap water. | [77] |
| MagMIP-based SPE | DPV | 0.1 µM to 10 µM | 66 nM | - | [31] |
| MIPs @ QDs-MWCNTs | DPV | 0.025 nM to 50 nM | 0.015 nM | Tap water; River water; Drinking water. | [26] |
| MIP/MWCNT/CPE | DPV | 0.1 nM to 0.1 mM | 80 pM | Tap water; Baby bottle; Soft drinks; Household filtered water | [45] |
| MIP/GC | DPV | 0.1 nM to 400 μM | 0.02 nM | Baby feeding bottle | [62] |
| MMIP/MGCE | DPV | 0.8 μM to 8 μM | 0.13 μM | Tea; Milk; Soil; Water | [46] |
| MIP|ERGO|GCE | DPV | 0.5 nM to 750 nM | 0.2 nM | Potable water; PC bottled water; Bovine milk; | [57] |
| rGO-Fe3O4-ZnOMIP/CPE | DPV | 0.008 μM to 15 μM; 15 μM to 95 μM | 4 nM | Tap water; Food storage container; Cured vinyl ester resin | [78] |
| MIP/MWCNTs/CPE | DPV | 80 nM to 0.1 mM | 22 nM | River water; Tap water | [50] |
| MIP/rGO/GCE | DPV | 5 nM to 0.75 μM | 2 nM | Bottled water; Bovine milk | [79] |
| MIP/PPy/GQDs/GCE | DPV | 0.1 μM to 50 μM | 40 nM | Sea water; Tap water | [80] |
| MIP/SPCE | DPV | 4.7 nM to 8 nM | 3.2 nM | - | [47] |
| MIP/SPCE | DPV | 0.19 nM to 1.8 nM | 60 pM | - | [30] |
| MIP–graphene–Ag/CE | DPV | 50 pM to 10 nM | 3.2 pM | Plastics | [63] |
| MIP/Pt/GCE | DPV | 7 nM to 0.7 μM | 3.2 nM | Serum; Plastics | [81] |
| MIP/AB/GCE | DPV | 5 nM to 0.2 μM; 0.5 μM to 10 μM | 2 nM | Bottled water | [82] |
| MMIP/AuNPs/CNPs/SPCE | DPV | 70 nM to 10 μM | 8.8 nM | Tap water; Mineral water | [83] |
| MIP/CNTs/AuNPs/GCE | DPV | 10 nM to 10 μM | 5 nM | Milk | [84] |
| β-CD/GO/GCE | DPV | 20 nM to 1 μM | 8 nM | Drinking water; Lake water | [85] |
| MIP/MWCNTs/GCE | DPV | 0.2 μM to 45 μM | 30 nM | Tap water | [86] |
| MIP/Au-pTH/pABSA/GCE | DPV | 80 nM to 0.1 mM | 38 nM | River water; Tap water | [87] |
| MIP/MWCNT/GCE | DPV | 0.1 nM to 10 μM | 15.7 pM | Plastic bottles; Disposable food boxes;Mobile phone shell | [88] |
| MIP/GQDs/B-g-C3N4/GCE | DPV | 10 fM to 1 nM | 3 fM | Orange juice | [89] |
| MIP-μPAD | DPV | 1 μg/L to 200 μg/L | 0.47 μg/L | Water; Plastic bottle water | [90] |
| CMOF-MIPIL | DPV | 5 nM to 5.0 μM | 4 nM | Lake water; Plastic bottle; River water; Fresh liquid milk | [91] |
| GCE/Au/Au@MIP | DPV | 0.5 μM to 100 μM | 52 nM | Tap water; Milk; Orange juice; Mineral water bottle | [92] |
| LSG-MIP | DPV | 0.01 μM to 10 µM | 3.97 nM | Water; Milk; Baby formula; Plastic bottle | [27] |
| MIP/MWCNTs/CPE | DPV | 4 nM to 100 nM; 0.5 μM to 50 μM | 4.4 nM | Bottled water | [93] |
| MIP@CF | DPV | 0.5 nM to 8.0 nM; 10 nM to 300 nM | 0.36 nM | Milk | [32] |
| Gr/MIPs/ABPE | DPV | 0.321 ng/L to 0.28 ng/L | 96.3 pg/L | Plastic pacifier | [94] |
| PPY/-@p-63/AuNP/GCE | EIS | 0.5 fM to 5 pM | 0.08 fM | Fresh milk; Milk powder; Tap water | [64] |
| E-MIP | EIS | 1 mM to 12 mM | 0.42 mM | - | [60] |
| MIP/Graphene/ABPE | LSV | 8 nM to 1 μM | 6 nM | Water bottles; Canned beverages | [95] |
| MIP/AuNPs/GCE | LSV | 15 nM to 55 μM | 1.1 nM | Plastic; Milk | [51] |
| MIP/C-ink/W1C-papes | Potentiometry | 0.5 μM to 13 μM | 0.15 μM | Plastics | [58] |
4. Recent Advances
5. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, A.; Chakraborty, P. A review on sources and health impacts of bisphenol A. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousoumah, R.; Leso, V.; Iavicoli, I.; Huuskonen, P.; Viegas, S.; Porras, S.P.; Santonen, T.; Frery, N.; Robert, A.; Ndaw, S. Biomonitoring of occupational exposure to bisphenol A, bisphenol S and bisphenol F: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenza, C.J.; Farooq, A.; Shubear, N.S.; Donkor, K.K. A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health implications of bisphenol analogues. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Jiang, R.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y. Occurrence, toxicity and ecological risk of Bisphenol A analogues in aquatic environment—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, O. Electrochemical sensors based on carbon nanostructures for the analysis of bisphenol A—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustieles, V.; D’Cruz, S.C.; Couderq, S.; Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Fini, J.-B.; Hofer, T.; Steffensen, I.-L.; Dirven, H.; Barouki, R.; Olea, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and its analogues: A comprehensive review to identify and prioritize effect biomarkers for human biomonitoring. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hou, J. A critical review of presence, removal and potential impacts of endocrine disruptors bisphenol A. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 254, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Rocha, L.; Ribeiro-Gonçalves, L.; Henriques, B.; Özcan, M.; Tiritan, M.E.; Souza, J.C.M. An integrative review on the toxicity of Bisphenol A (BPA) released from resin composites used in dentistry. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Park, B.J. Removal of bisphenol A from wastewater by physical, chemical and biological remediation techniques. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1801–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-García, J.L.; Ahuactzin-Pérez, M.; Fernández, F.J.; Cortés-Espinosa, D.V. Bisphenol A in the environment and recent advances in biodegradation by fungi. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornoy, A. Prenatal origin of obesity and their complications: Gestational diabetes, maternal overweight and the paradoxical effects of fetal growth restriction and macrosomia. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 32, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornoy, A.; Reece, E.A.; Pavlinkova, G.; Kappen, C.; Miller, R.K. Effect of maternal diabetes on the embryo, fetus, and children: Congenital anomalies, genetic and epigenetic changes and developmental outcomes. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2015, 105, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Sun, B.; Li, W.; Gou, X.; Gou, Y.; Li, D.; Hu, F. Novel nanomaterial of porous graphene functionalized black phosphorus as electrochemical sensor platform for bisphenol A detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 835, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, L.; He, L.; Liu, N.; Piao, Y. Electrochemical enzyme biosensor bearing biochar nanoparticle as signal enhancer for bisphenol a detection in water. Sensors 2019, 19, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, C.; Tan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhou, J.; Peng, X. Multi-residue determination of bisphenol analogues in organism tissues by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1682, 463489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodur, S.; Erarpat, S.; Dalgıç Bozyiğit, G.; Selali Chormey, D.; Öz, E.; Özdoğan, N.; Bakırdere, S. A sensitive determination method for trace bisphenol A in bottled water and wastewater samples: Binary solvent liquid phase microextraction-quadrupole isotope dilution-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raysyan, A.; Schneider, R.J. Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) to Screen for the Release of the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A from Polymer Materials and Products. Biosensors 2021, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, D.; Venkatachalam, K.; Periasamy, V. A bisphenol based fluorescence chemosensor for the selective detection of Zn2+ and PPi ions and its bioluminescence imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 242, 118730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pan, G. Molecularly Imprinted Nanomaterials with Stimuli Responsiveness for Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, S.M.M.; Abd El-Aziz, M.E.; Mohamed, H.A. Smart polymers as molecular imprinted polymers for recognition of target molecules. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2023, 72, 612–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, M. Design and development of molecularly imprinted biodegradable polymers for nanomedicine. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2023, 6, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, S.M.M.; Youssef, A.M.; Kamal, K.H.; Abd El-Aziz, M.E. Molecular imprinted polymer for tramadol: Absorption and drug release studies. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, W.; Guo, C.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Fang, G.; Sun, D. Magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1106, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, T.; Zeng, W.; Hu, B.; Zhou, S.; Wu, L. A review of current status of ratiometric molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors: From design to applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1230, 340273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çorman, M.E.; Ozcelikay, G.; Cetinkaya, A.; Kaya, S.I.; Armutcu, C.; Özgür, E.; Uzun, L.; Ozkan, S.A. Metal-organic frameworks as an alternative smart sensing platform for designing molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 150, 116573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Song, G.; Wang, N.; Xu, W.; Huang, W. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical BPA sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified by CdTe quantum dots for the detection of bisphenol A. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beduk, T.; Gomes, M.; De Oliveira Filho, J.I.; Shetty, S.S.; Khushaim, W.; Garcia-Ramirez, R.; Durmus, C.; Ait Lahcen, A.; Salama, K.N. A Portable Molecularly Imprinted Sensor for On-Site and Wireless Environmental Bisphenol A Monitoring. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 833899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Barton, S.J.; Wren, S.P.; Barker, J. Review on molecularly imprinted polymers with a focus on their application to the analysis of protein biomarkers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qi, L.; Liang, R.; Qin, W. Multifunctional Molecularly Imprinted Receptor-Based Polymeric Membrane Potentiometric Sensor for Sensitive Detection of Bisphenol A. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7795–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekomo, V.M.; Branger, C.; Bikanga, R.; Florea, A.-M.; Istamboulie, G.; Calas-Blanchard, C.; Noguer, T.; Sarbu, A.; Brisset, H. Detection of Bisphenol A in aqueous medium by screen printed carbon electrodes incorporating electrochemical molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaoui, A.; María Palacios-Santander, J.; Amine, A.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. Computational approach and ultrasound Probe–Assisted synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the electrochemical detection of bisphenol A. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 277, 115568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-Y.; Ning, K.-P.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X.-Y. Flexible Electrochemical Platform Coupled with In Situ Prepared Synthetic Receptors for Sensitive Detection of Bisphenol A. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Zhong, A.; Sun, R.; Jin, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Niu, J.; Lu, S. Tuning Photophysical Properties via Positional Isomerization of the Pyridine Ring in Donor–Acceptor-Structured Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens Based on Phenylmethylene Pyridineacetonitrile Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zou, J.; Han, Y.; Liao, Z.; Lu, P.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y. Recent advances in Al(III)/In(III)-based MOFs for the detection of pollutants. N. J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19577–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Diao, Y.; He, Q.; Lu, C.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J.; Lan, Q. Recent advances in the electrochemical applications of Ni-based metal organic frameworks (Ni-MOFs) and their derivatives. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R. Detection and analysis of electrochemical signals in wine fermentation process. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5103–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Song, D. Detection of sugar content in food based on the electrochemical method with the assistance of partial least square method and deep learning. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 4864–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. Electrochemical evaluation of total antioxidant properties in red wine. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, C.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, J. Monitoring and management of sunset yellow in sports drinks by electrochemical sensor. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 4843–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Darabi, R.; Orooji, Y.; Karaman, C.; Karimi, F.; Baghayeri, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; et al. Calf thymus ds-DNA intercalation with pendimethalin herbicide at the surface of ZIF-8/Co/rGO/C3N4/ds-DNA/SPCE; A bio-sensing approach for pendimethalin quantification confirmed by molecular docking study. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ghalkhani, M.; Saberi Dehkordi, Z.; Mohsenpour Tehran, M.; Singh, J.; Wen, Y.; Baghayeri, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Rajendran, S. MOF-enabled pesticides as developing approach for sustainable agriculture and reducing environmental hazards. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, Q.; He, X.; Xing, X.; Lian, W. Electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A detection based on molecularly imprinted polymers and gold nanoparticles. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Darabi, R.; Karimi, F.; Karaman, C.; Shahidi, S.A.; Zare, N.; Baghayeri, M.; Fu, L.; Rostamnia, S.; Rouhi, J.; et al. State-of-art advances on removal, degradation and electrochemical monitoring of 4-aminophenol pollutants in real samples: A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Darabi, R.; Baghayeri, M.; Karimi, F.; Fu, L.; Rouhi, J.; Niculina, D.E.; Gündüz, E.S.; Dragoi, E.N. Recent developments in carbon nanomaterials-based electrochemical sensors for methyl parathion detection. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5371–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.G.; Shehab, O.R.; Ibrahim, H.; El Nashar, R.M. Electrochemical detection of Bisphenol A in plastic bottled drinking waters and soft drinks based on molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Xiao, W.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Xiong, X.H. Rapid isolation and determination of bisphenol A in complicated matrices by magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebocho, S.; Cordas, C.M.; Viveiros, R.; Casimiro, T. Development of a ferrocenyl-based MIP in supercritical carbon dioxide: Towards an electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 135, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, S.; Ziaei, E.; Mehdinia, A.; Baradaran Kayyal, T.; Jabbari, A. A glassy carbon electrode modified with amino-functionalized graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical sensing of bisphenol A. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, J. A molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on N-MWCNT/CPE for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Bisphenol A. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, Z.; Li, L. Determination of Bisphenol A Using an Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Modified Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Paste Electrode. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 996–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-R.; Kang, T.-F.; Lu, L.-P.; Shen, F.-X.; Cheng, S.-Y. A novel electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymer with binary functional monomers for sensitive detection of bisphenol A. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 786, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hou, J. Facile fabrication of snowman-like magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres for bisphenol A via one-step Pickering emulsion polymerization. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 164, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, B.; Nikfarjam, N.; Kazemi, S.H. Hollow molecularly imprinted microspheres made by w/o/w double Pickering emulsion polymerization stabilized by graphene oxide quantum dots targeted for determination of l-cysteine concentration. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 612, 125978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Guo, H.; Jin, H. Preparation and applications of electrochemical chemosensors based on carbon-nanomaterial-modified molecularly imprinted polymers. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 3325–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, N.; Fuchiwaki, Y.; Kubo, I. Fabrication of Bisphenol A Sensor Utilizing Electrode Modified with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. ECS Trans. 2008, 16, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beduk, T.; Ait Lahcen, A.; Tashkandi, N.; Salama, K.N. One-step electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymer on laser scribed graphene bisphenol a sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 314, 128026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, P.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Viswanathan, S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for the determination of endocrine disruptor bisphenol-A in bovine milk. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Liang, R. A paper-based potentiometric sensing platform based on molecularly imprinted nanobeads for determination of bisphenol A. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Song, Y.; Song, D.; Liang, R. Plasticizer-free polymer membrane potentiometric sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers for determination of neutral phenols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1121, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, D.C.; Pernites, R.B.; Ponnapati, R.; Del Mundo, F.R.; Advincula, R.C. Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film: EIS Sensing of Bisphenol A. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6669–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Q.; He, X.; Xing, X.; Huai, H.; Lian, W.; Zhu, H. Electrochemical sensor based on imprinted sol–gel and nanomaterials for sensitive determination of bisphenol A. Food Control 2011, 22, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Athira, V.S.; Chithra Sekhar, V. Electrochemical sensing and nano molar level detection of Bisphenol-A with molecularly imprinted polymer tailored on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2018, 146, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Rao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Long, F.; Yin, Y. An imprinted electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A determination based on electrodeposition of a graphene and Ag nanoparticle modified carbon electrode. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Amini, M.; Rezaei, B. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical aptasensor for the attomolar detection of bisphenol A. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leepheng, P.; Limthin, D.; Onlaor, K.; Tunhoo, B.; Phromyothin, D.; Thiwawong, T. Modification of selective electrode based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for bisphenol A determination. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 60, SCCJ03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ding, W.; Luan, C. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective determination of trace bisphenol A in river water by electrochemiluminescence. Can. J. Chem. 2013, 91, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Jia, R. Sensitive detection of estriol with an electrochemical sensor based on core-shell N-MWCNT/GONR-imprinted electrode. Ionics 2020, 26, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cao, Y.; Cao, G. Electrochemical sensor based on magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles at surfactant modified magnetic electrode for determination of bisphenol A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, L.; Huang, F.; Lin, Z. [Ru(bpy)3]2+-mediated photoelectrochemical detection of bisphenol A on a molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified SnO2 electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y. Acetylene black paste electrode modified with a molecularly imprinted chitosan film for the detection of bisphenol A. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, R.; Ezzatzadeh, E.; Taheri, A. A novel self-assembled gold nanoparticles-molecularly imprinted modified carbon ionic liquid electrode with high sensitivity and selectivity for the rapid determination of bisphenol A leached from plastic containers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, I.; Yokota, N.; Nakane, Y.; Fuchiwaki, Y. The Establishment of Bisphenol A Sensing System Utilizing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Receptor and Electrochemical Determination. Int. J. Electrochem. 2010, 2011, e534936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, N.; Han, Y.; Zhao, F.; Peng, Z.; Li, Y. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres based on distillation–precipitation polymerization for an ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor. Analyst 2017, 142, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. A self-powered sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer-coupled graphitic carbon nitride photoanode for selective detection of bisphenol A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.I.; Ozcelikay, G.; Armutcu, C.; Ozkan, S.A. An Ultra-Sensitive Molecularly Imprinted Poly(Aniline) Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Bisphenol A in Synthetic Human Serum Specimen and Plastic Bottled Water Samples. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 017506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zang, Y.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Xue, H. 4-Pentenoyl-isoleucyl-chitosan oligosaccharide and acrylamide functional monomer-dependent hybrid bilayer molecularly imprinted membrane for sensitive electrochemical sensing of bisphenol A. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36769–36776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, A.; Khan, R. Plastic antibodies integrated with graphene quantum dots for electrochemical sensing of bisphenol-A in real samples. Mater. Lett. 2023, 350, 134880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, H.R.; Rezaei, M.; Mohagheghzadeh, Z. Construction of Electrochemical Sensor Modified with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and rGO-Fe3O4-ZnO Nanocomposite for Determination of Bisphenol A in Polymers and Water Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2021, 8, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, P.; Costa-Rama, E.; Seguro, I.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for environmental analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Cong, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X.; Chen, J. An electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole/graphene quantum dots composite for detection of bisphenol A in water samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xiong, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Li, G.; Niu, L.; Liu, W. Electrodeposited Pt@Molecularly imprinted polymer core-shell nanostructure: Enhanced sensing platform for sensitive and selective detection of bisphenol A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Pu, W.; Yang, C. Electrochemical Determination of Bisphenol A Using a Molecularly Imprinted Chitosan-acetylene Black Composite Film Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Messaoud, N.; Ait Lahcen, A.; Dridi, C.; Amine, A. Ultrasound assisted magnetic imprinted polymer combined sensor based on carbon black and gold nanoparticles for selective and sensitive electrochemical detection of Bisphenol A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. A novel bisphenol A electrochemical sensor based on a molecularly imprinted polymer/carbon nanotubes-Au nanoparticles/boron-doped ordered mesoporous carbon composite. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4543–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Jana, N.R. Selective electrochemical detection of bisphenol A using a molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite. N. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yan, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, X. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the detection of bisphenol A. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 3610–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Kan, X. Au-polythionine nanocomposites: A novel mediator for bisphenol A dual-signal assay based on imprinted electrochemical sensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3839–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yin, X.; Sarpong, K.A.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, H.; Yang, W.; Xu, W. Computer-aided design and synthesis of molecular imprinting polymers based on doubly oriented functional multiwalled carbon nanotubes for electrochemically sensing bisphenol A. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 157, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, H.A.; Mavioğlu Kaya, M.; Kaya, İ.; Bankoğlu Yola, B.; Atar, N.; Yola, M.L. Bisphenol A Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on Graphene Quantum Dots with Boron Functionalized g-C3N4 in Food Samples. Biosensors 2023, 13, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mars, A.; Mejri, A.; Hamzaoui, A.H.; Elfil, H. Molecularly imprinted curcumin nanoparticles decorated paper for electrochemical and fluorescence dual-mode sensing of bisphenol A. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Deng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Li, L. A novel composite of conductive metal organic framework and molecularly imprinted poly (ionic liquid) for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of bisphenol A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Pan, Y.; Li, L.; Cai, J. Bisphenol A detection based on nano gold-doped molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor with enhanced sensitivity. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güney, S.; Güney, O. Development of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Covalent Molecular Imprinting for Selective Determination of Bisphenol-A. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2579–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, F.; Li, C.; Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Yin, Z.; Yang, W. Acetylene black paste electrode modified with molecularly imprinted polymers/graphene for the determination of bisphenol A. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4851–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Xu, Z.; Kuang, Y. Electrochemical determination of bisphenol A in plastic bottled drinking water and canned beverages using a molecularly imprinted chitosan–graphene composite film modified electrode. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemmeli, D.; Marcoccio, E.; Moscone, D.; Dridi, C.; Arduini, F. Highly sensitive paper-based electrochemical sensor for reagent free detection of bisphenol A. Talanta 2020, 216, 120924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Olmo, M.; Zafra, A.; Jurado, A.B.; Vilchez, J.L. Determination of bisphenol A (BPA) in the presence of phenol by first-derivative fluorescence following micro liquid–liquid extraction (MLLE). Talanta 2000, 50, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, R.; Khandaghi, J.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Combination of Vortex-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Air-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for the Extraction of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B in Canned Doogh Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahin Mohd Ali, N.; Sajid, M.; Ibrahim Thani Abd Halim, W.; Husaini Mohamed, A.; Nadhirah Mohamad Zain, N.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Suhaila Mohamad Hanapi, N.; Nazihah Wan Ibrahim, W.; Yahaya, N. Recent advances in solid phase extraction methods for the determination of bisphenol A and its analogues in environmental matrices: An updated review. Microchem. J. 2023, 184, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jiang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes as a Solid-Phase Extraction Adsorbent for the Determination of Bisphenol A, 4-n-Nonylphenol, and 4-tert-Octylphenol. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zuo, X.; He, D.; Ding, S.; Xu, F.; Yang, H.; Jin, X.; Fan, Y.; Ying, L.; Tian, C.; et al. Long-term exposure to a ‘safe’ dose of bisphenol A reduced protein acetylation in adult rat testes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, M.S.; Liao, C.; Kannan, K.; Harris, C.; Dolinoy, D.C. In utero bisphenol A concentration, metabolism, and global DNA methylation across matched placenta, kidney, and liver in the human fetus. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.C.; Pena, A.; Fernandes, J.O. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by microwave-assisted silylation and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis for simultaneous trace quantification of bisphenol A and 13 ultraviolet filters in wastewaters. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1414, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Shi, M.; Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, Y.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ye, C.; Lin, C.-T.; Fu, L. An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A. Sensors 2023, 23, 8656. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208656
Pan Y, Wu M, Shi M, Shi P, Zhao N, Zhu Y, Karimi-Maleh H, Ye C, Lin C-T, Fu L. An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A. Sensors. 2023; 23(20):8656. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208656
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Ying, Mengfan Wu, Mingjiao Shi, Peizheng Shi, Ningbin Zhao, Yangguang Zhu, Hassan Karimi-Maleh, Chen Ye, Cheng-Te Lin, and Li Fu. 2023. "An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A" Sensors 23, no. 20: 8656. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208656
APA StylePan, Y., Wu, M., Shi, M., Shi, P., Zhao, N., Zhu, Y., Karimi-Maleh, H., Ye, C., Lin, C.-T., & Fu, L. (2023). An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A. Sensors, 23(20), 8656. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23208656









