A Soluble Porous Coordination Polymer for Fluorescence Sensing of Explosives and Toxic Anions under Homogeneous Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials and Methods
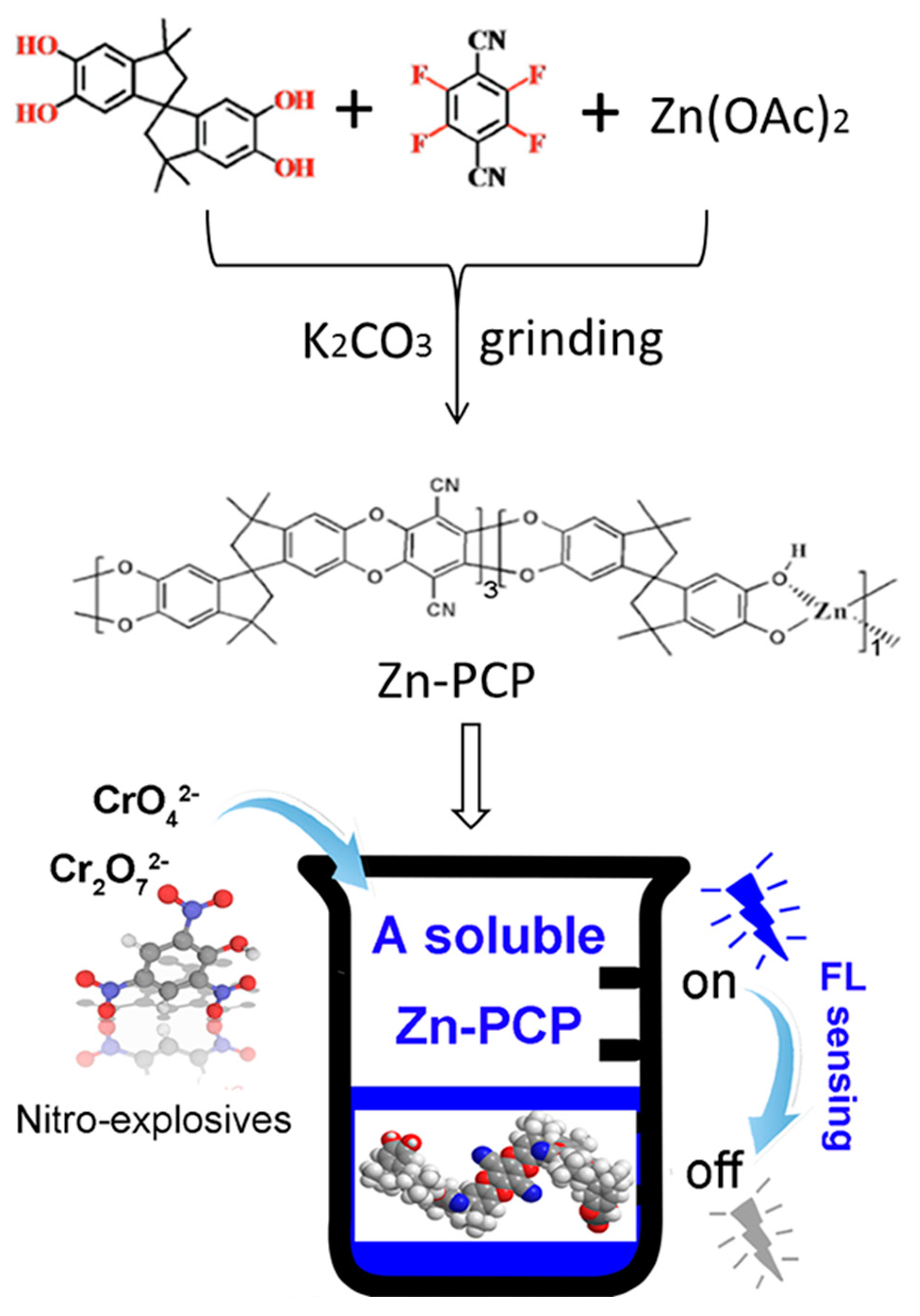
2.2. Syntheses of Zn-PCP
2.3. Fluorescence Sensing Measurements
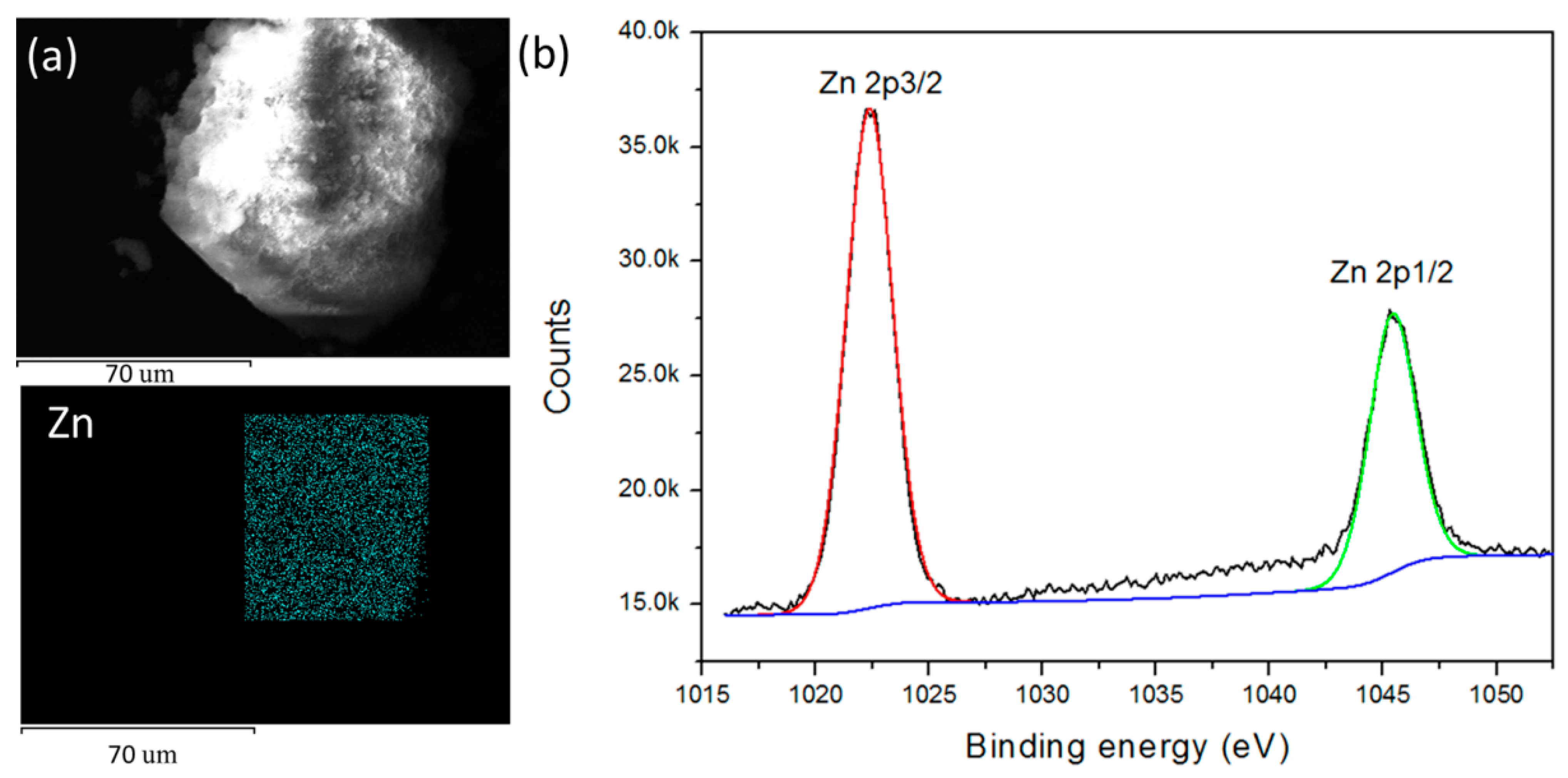
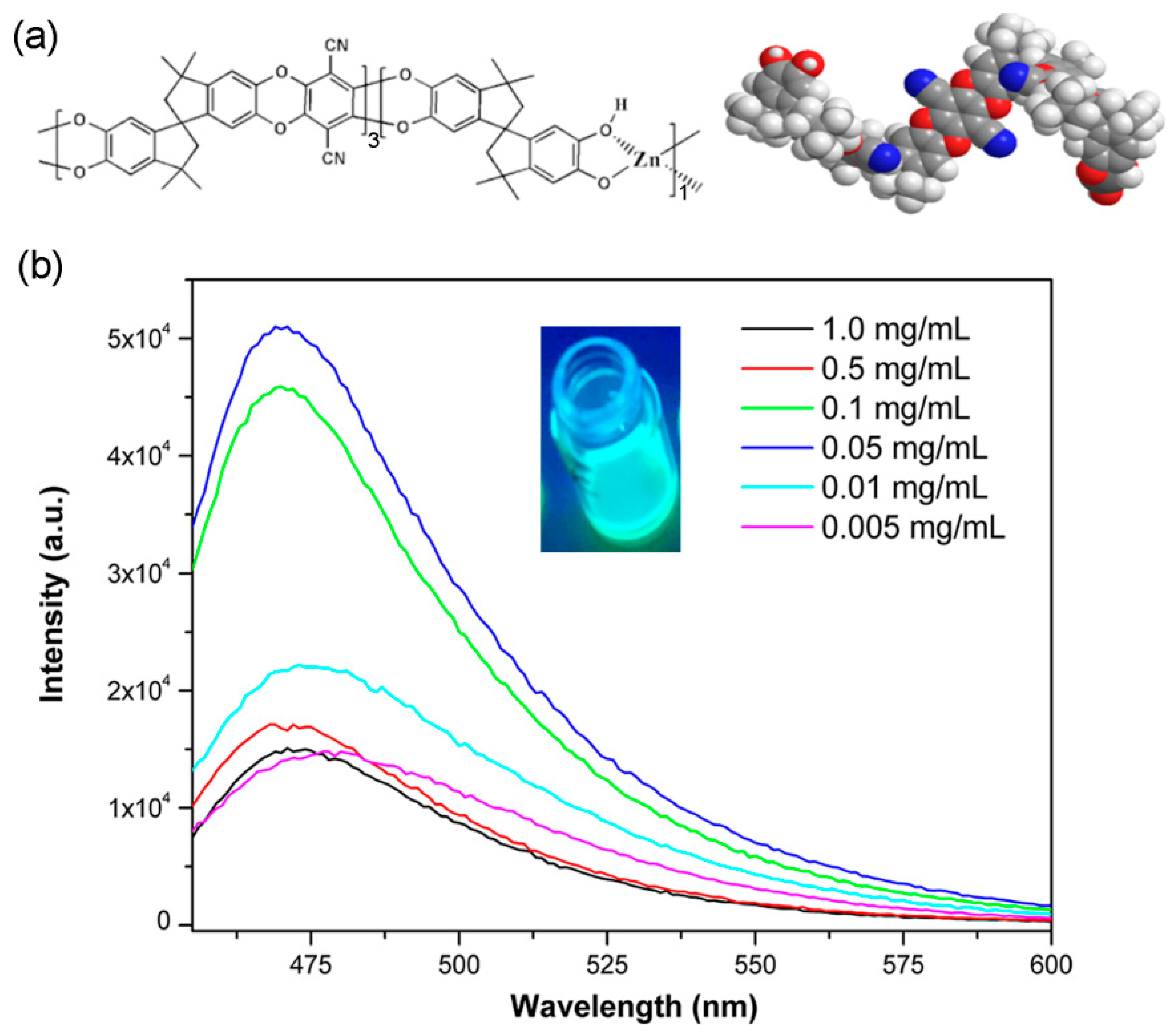
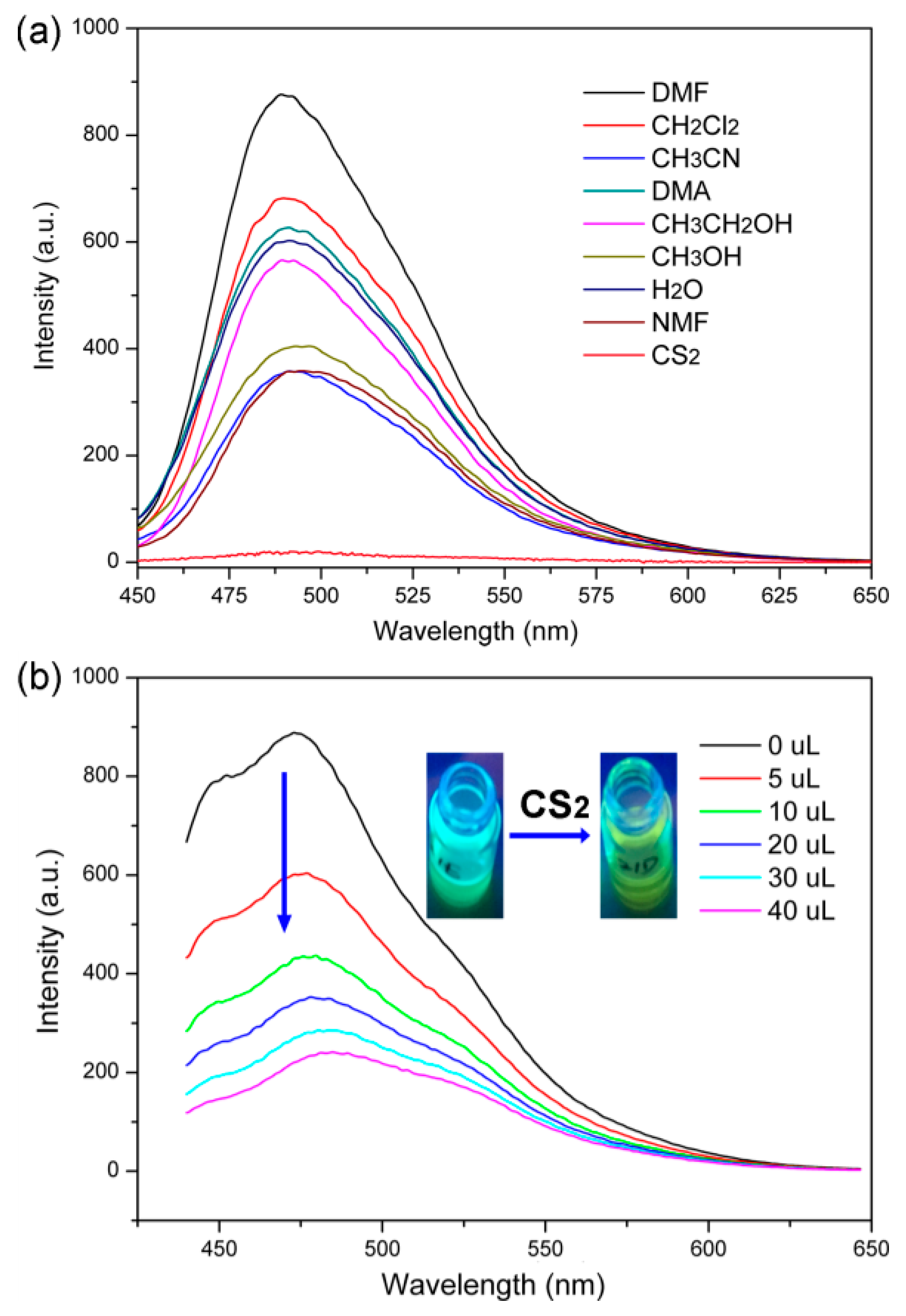
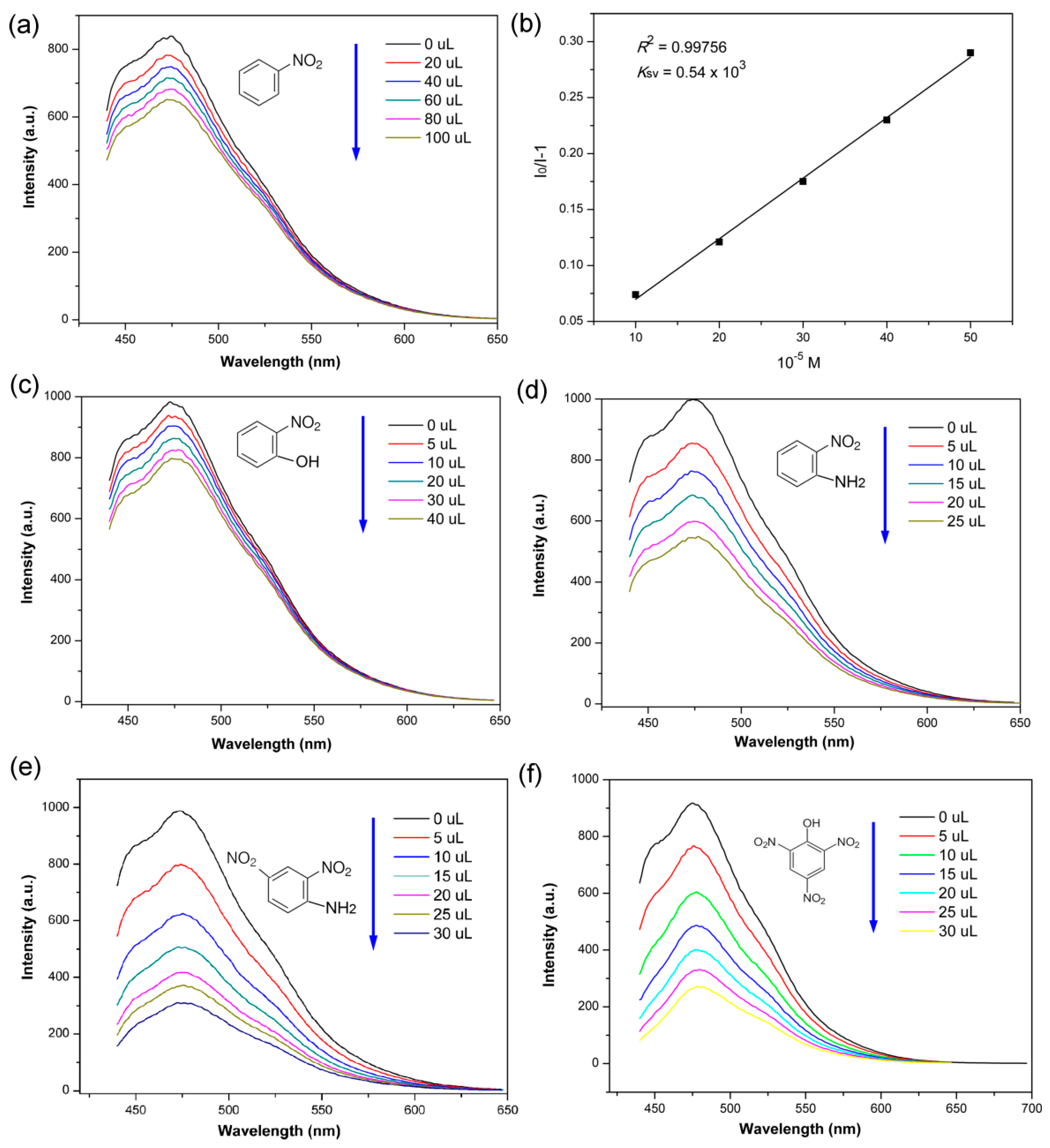
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent Functional Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–Organic Framework Materials as Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, W.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Rudd, N.D.; Desai, A.V.; Li, J.; Ghosh, S.K. Metal–organic frameworks: Functional luminescent and photonic materials for sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3242–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Qian, G. Photonic functional metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5740–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Liao, W.-M.; Yin, S.-Y.; Sun, S.-S.; Su, C.-Y. Single-Phase White-Light-Emitting and Photoluminescent Color-Tuning Coordination Assemblies. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 8889–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.; Carlos, L.D.; Paz, F.A.A.; Ananias, D. Luminescent multifunctional lanthanides-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 40, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahata, P.; Mondal, S.K.; Singha, D.K.; Majee, P. Luminescent rare-earth-based MOFs as optical sensors. Dalton Trans. 2016, 46, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraci, F.; Quezada-Novoa, V.; Donnarumma, P.R.; Howarth, A.J. Rare-earth metal–organic frameworks: From structure to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7949–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, D. Lanthanide-functionalized metal–organic frameworks as ratiometric luminescent sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12739–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Masoomi, M.Y.; Morsali, A. Highly sensitive and selective ratiometric fluorescent metal–organic framework sensor to nitroaniline in presence of nitroaromatic compounds and VOCs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Tan, B.; Gong, L.-K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Hei, X.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Huang, X.-Y.; et al. A CuI modified Mg-coordination polymer as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for toxic thiol molecules. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 13367–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ni, J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Liu, S.-Q.; Sun, Y.-J.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.-Q.; Duan, C.-Y. A trichromatic MOF composite for multidimensional ratiometric luminescent sensing. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Shukla, P.; Lama, P.; Das, S.; Pal, T.K. Engineering of Metal–Organic Frameworks as Ratiometric Sensors. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 3518–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lustig, W.P.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; Wang, H.; Teat, S.J.; Gong, Q.; Rudd, N.D.; Li, J. Effective Detection of Mycotoxins by a Highly Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 16209–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yuan, S.; Qin, J.; Pang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Drake, H.F.; Liu, W.R.; Zhou, H. Stepwise Assembly of Turn-on Fluorescence Sensors in Multicomponent Metal–Organic Frameworks for in Vitro Cyanide Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9319–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargurevich, I.A. Hydrogen Sulfide Combustion: Relevant Issues under Claus Furnace Conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 7706–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; de Jong, W.; Pal, R.; Verkooijen, A.H. In bed and downstream hot gas desulphurization during solid fuel gasification: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 964–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glarborg, P.; Halaburt, B.; Marshall, P.; Guillory, A.; Troe, J.; Thellefsen, M.; Christensen, K. Oxidation of Reduced Sulfur Species: Carbon Disulfide. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 6798–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, P.S.; Gupta, S. Hybrid reactor for priority pollutant nitrobenzene removal. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4331–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y. Fluorescence based explosive detection: From mechanisms to sensory materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8019–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaffoni, L.; Peverall, R.; Ritchie, G.A.D. Breath ammonia levels in a normal human population study as determined by photoacoustic laser spectroscopy. J. Breath Res. 2011, 5, 037101. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, A.G.; Burnett, A.D.; Fan, W.; Linfield, E.H.; Cunningham, J.E. Terahertz spectroscopy of explosives and drugs. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Veith, G.M.; Dai, S. Soluble Porous Coordination Polymers by Mechanochemistry: From Metal-Containing Films/Membranes to Active Catalysts for Aerobic Oxidation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 27, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-B.; Wang, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, R. Soluble Metal-Nanoparticle-Decorated Porous Coordination Polymers for the Homogenization of Heterogeneous Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10104–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M. Detection of carbon disulfide in breath and air: A possible new risk factor for coronary artery disease. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1992, 64, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMartino, A.W.; Zigler, D.F.; Fukuto, J.M.; Ford, P.C. Carbon disulfide. Just toxic or also bioregulatory and/or therapeutic? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Moore, R.M. Carbon Disulfide Measurement in Marine Waters Using Oxygen-Doped Electron Capture Detection with Purge−Trap Preconcentration. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 1753–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Li, Y.; Qian, B.; He, Y.; Peng, L.; Yu, H. A novel liquid chromatography detector based on a dielectric barrier discharge molecular emission spectrometer with online microwave-assisted hydrolysis for determination of dithiocarbamates. Analyst 2018, 143, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, C.; Shi, Q. Molecular Characterization of Lignite Extracts of Methanol and Carbon Disulfide/N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31085–31091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Tan, B.; Feng, M.-L.; Lan, A.-J.; Huang, X.-Y. A magnesium MOF as a sensitive fluorescence sensor for CS2 and nitroaromatic compounds. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6426–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Huang, X.-Y. A series of Mg–Zn heterometallic coordination polymers: Synthesis, characterization, and fluorescence sensing for Fe3+, CS2, and nitroaromatic compounds. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12597–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, E.; Osumi, Y.; Teat, S.J.; Jensen, S.; Tan, K.; Thonhauser, T.; Li, J. Fluorescent Detection of Carbon Disulfide by a Highly Emissive and Robust Isoreticular Series of Zr-Based Luminescent Metal Organic Frameworks (LMOFs). Chemistry 2021, 3, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, P.; Nesterenko, P.N. Application of photo degradation for remediation of cyclic nitramine and nitroaromatic explosives. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 77603–77621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatwal, M.; Mittal, R.; Gupta, R.D.; Awasthi, S.K. Sensing ensembles for nitroaromatics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12142–12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Yusuf, M.; Malik, A.K. Synthesis of Copper Metal Organic Framework Based on Schiff Base Tricarboxylate Ligand for Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol in Aqueous Medium. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 1959–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.-Z.; Song, S.-Y.; Zhao, S.-N.; Hao, Z.-M.; Zhu, M.; Meng, X.; Wu, L.-L.; Zhang, H.-J. Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Transformation of a Europium(III) Metal–Organic Framework Producing a Multi-responsive Luminescent Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4034–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. A fluorescent metal–organic framework for highly selective detection of nitro explosives in the aqueous phase. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8915–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.-L.; Huang, P.; Qin, C.; Shao, K.-Z.; Su, Z.-M. A stable luminescent anionic porous metal–organic framework for moderate adsorption of CO2 and selective detection of nitro explosives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7224–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Joarder, B.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Highly Selective Detection of Nitro Explosives by a Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2881–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-Q.; Qin, C.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Wu, X.-S.; Yang, L.; Shao, K.-Z.; Su, Z.-M. Spontaneous chiral resolution of a rare 3D self-penetration coordination polymer for sensitive aqueous-phase detection of picric acid. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 18386–18394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joarder, B.; Desai, A.V.; Samanta, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Selective and Sensitive Aqueous-Phase Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) by an Amine-Functionalized Metal–Organic Framework. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhankhar, S.S.; Sharma, N.; Nagaraja, C.M. Construction of bifunctional 2-fold interpenetrated Zn(ii) MOFs exhibiting selective CO2 adsorption and aqueous-phase sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Karmaker, P.G.; Zhang, L.; Huo, F.; Yang, X.; Zhao, B. Mechanistic insights into the luminescent sensing of nitrophenol compounds by a cationic Zn-based metal-organic framework. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 199, 110099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Desai, A.V.; Samanta, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Aqueous phase selective detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol using a fluorescent metal–organic framework with a pendant recognition site. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 15175–15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Saha, S.K.; Roychowdhury, A.; Banerjee, P. Recognition of an Explosive and Mutagenic Water Pollutant, 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol, by Cost-Effective Luminescent MOFs. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.-S.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Yang, X.-Q.; Mu, X.-G. Three metal organic frameworks based on mixed ligands: Synthesis, crystal structures and luminescent sensing of nitro explosives. Transit. Met. Chem. 2023, 48, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.-H.; Shi, F.; Zhang, W.-M.; Zang, S.-Q.; Mak, T.C.W. Selective Sensing of Fe3+ and Al3+ Ions and Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol by a Water-Stable Terbium-Based Metal–Organic Framework. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15705–15712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, T.; Zhang, X. An NH2-modified {EuIII2}–organic framework for the efficient chemical fixation of CO2 and highly selective sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4376–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Desai, A.V.; Manna, B.; Inamdar, A.I.; Ghosh, S.K. Exploitation of Guest Accessible Aliphatic Amine Functionality of a Metal–Organic Framework for Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) in Water. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2015, 15, 4627–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, X.; Qin, D.; Zhao, B. Tetraphenylpyrazine-Based Manganese Metal–Organic Framework as a Multifunctional Sensor for Cu2+, Cr3+, MnO4–, and 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol and the Construction of a Molecular Logical Gate. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 11222–11230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Vajpayee, P.; Singh, S.N.; Mehrotra, S. Effect of chromium accumulation on photosynthetic pigments, oxidative stress defense system, nitrate reduction, proline level and eugenol content of Ocimum tenuiflorum L. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Pan, Z.-Y.; Lang, J.-M.; Xu, J.-M.; Zheng, Y.-G. Bioleaching of chromium from tannery sludge by indigenous Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Liao, S.; Gu, W.; Liu, X. An amino-decorated dual-functional metal–organic framework for highly selective sensing of Cr(iii) and Cr(vi) ions and detection of nitroaromatic explosives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15494–15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.-X.; Yao, R.-X.; Zhang, F.-Q.; Zhang, X.-M. A Fluorescent Anionic MOF with Zn4(trz)2 Chain for Highly Selective Visual Sensing of Contaminants: Cr(III) Ion and TNP. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2690–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Hu, M. A water-stable europium-MOF as a multifunctional luminescent sensor for some trivalent metal ions (Fe3+, Cr3+, Al3+), PO43− ions, and nitroaromatic explosives. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Deibert, B.J.; Li, J. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5815–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chua, M.H.; Tang, B.Z.; Xu, J. Aggregation-induced emission (AIE)-active polymers for explosive detection. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 3822–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Singh, A.; Wang, X.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J. Luminescent sensing of nitroaromatics by crystalline porous materials. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 7736–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Zhao, S.-N.; Zang, S.-Q.; Li, J. Functional metal–organic frameworks as effective sensors of gases and volatile compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6364–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G. Sensing-functional luminescent metal–organic frameworks. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 3746–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jiang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhao, B. Applications of MOFs as Luminescent Sensors for Environmental Pollutants. Small 2021, 17, 2005327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaimoor, E.F.H.; Khan, E. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs)-Based Sensors for the Detection of Heavy Metals: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, H.; Ghasemzadeh, S.; Shakib, S.; Majidi, M.R.; Razmjou, A.; Yoon, Y.; Khataee, A. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Biosensing Platforms for the Sensitive Determination of Trace Elements and Heavy Metals: A Comprehensive Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 62, 4611–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PCPs | Ksv/M−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Zn-PCP | 0.16 × 106 | This work |
| Cu-CIP | 1.07 × 104 | [36] |
| [Eu3(L)3(HCOO)(μ3-OH)2(H2O)]∙x(solv) | 2.1 × 104 | [37] |
| Zr6O4(OH)6(L)6 | 2.9 × 104 | [38] |
| [(CH3)2NH2]3[Zn4Na(BPTC)3]∙4CH3OH∙2DMF | 3.2 × 104 | [39] |
| [Cd(NDC)0.5(PCA)] | 3.5 × 104 | [40] |
| [Cd(NDC)L]2∙H2O | 3.7 × 104 | [41] |
| [Zn8(ad)4(BPDC)6O∙2Me2NH2] | 4.6 × 104 | [42] |
| [Zn(BINDI)0.5(bpa)0.5(H2O)]∙4H2O | 4.9 × 104 | [43] |
| [Zn(BINDI)0.5(bpe)]∙3H2O | 1.29 × 104 | |
| [Zn3(TIAB)2(IMDC)2]·(NO3)2·(DMF)2·(H2O)2 | 5.68 × 104 | [44] |
| Zr6O4(OH)6(L)6 | 5.8 × 104 | [45] |
| Zn(NDC)(H2O) | 6.0 × 104 | [46] |
| Cd(NDC)(H2O) | 2.38 × 104 | |
| Zn(bipa)(suc) | 6.48 × 104 | [47] |
| [Tb(L)1.5(H2O)]∙3H2O | 7.47 × 104 | [48] |
| (Me2NH2)4[Eu4(DDAC)3(HCO2)(OH2)2]·8DMF·9H2O | 8.6 × 104 | [49] |
| [Zn4(DMF)(Ur)2(NDC)4] | 1.08 × 105 | [50] |
| {Mn(Tipp)(A)2}n·2H2O | 1.18 × 105 | [51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Li, Z.-W.; Wu, Z.-F.; Huang, X.-Y. A Soluble Porous Coordination Polymer for Fluorescence Sensing of Explosives and Toxic Anions under Homogeneous Environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 9719. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249719
Jiang J, Li Z-W, Wu Z-F, Huang X-Y. A Soluble Porous Coordination Polymer for Fluorescence Sensing of Explosives and Toxic Anions under Homogeneous Environment. Sensors. 2023; 23(24):9719. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249719
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jiang, Zi-Wei Li, Zhao-Feng Wu, and Xiao-Ying Huang. 2023. "A Soluble Porous Coordination Polymer for Fluorescence Sensing of Explosives and Toxic Anions under Homogeneous Environment" Sensors 23, no. 24: 9719. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249719
APA StyleJiang, J., Li, Z.-W., Wu, Z.-F., & Huang, X.-Y. (2023). A Soluble Porous Coordination Polymer for Fluorescence Sensing of Explosives and Toxic Anions under Homogeneous Environment. Sensors, 23(24), 9719. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249719







