Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Adaptive estimation of the unknown variables as known quantities that can be controlled directly.
- (2)
- Adaptive estimation of the SMC parameters to obtain control parameters that can achieve optimal control performance.
2. Numerical Control Machine Tool Dynamics Model
2.1. Mechanical Transmission Model
2.2. LuGre Friction Model
3. Integrated Control Design of CNC Machine Tool Servo System Based on MRAC and ASMC
3.1. Structural Framework for ASMC Based on MRAC
3.2. Sliding Mode Controller Design
3.3. Design of Sliding Mode Controller Based on Parametric Adaptive Control
- (1)
- is positive definite;
- (2)
- is negative definite.
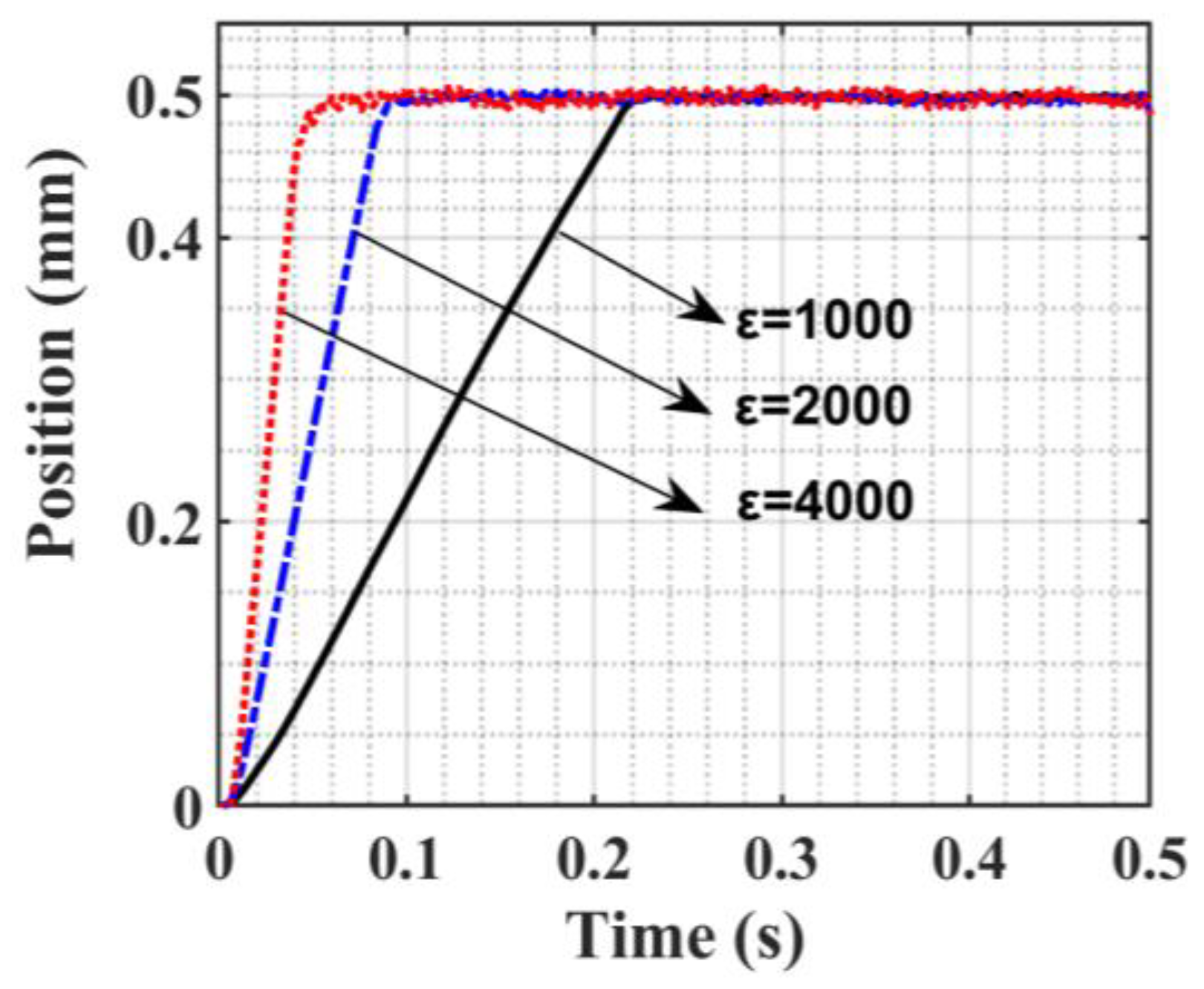
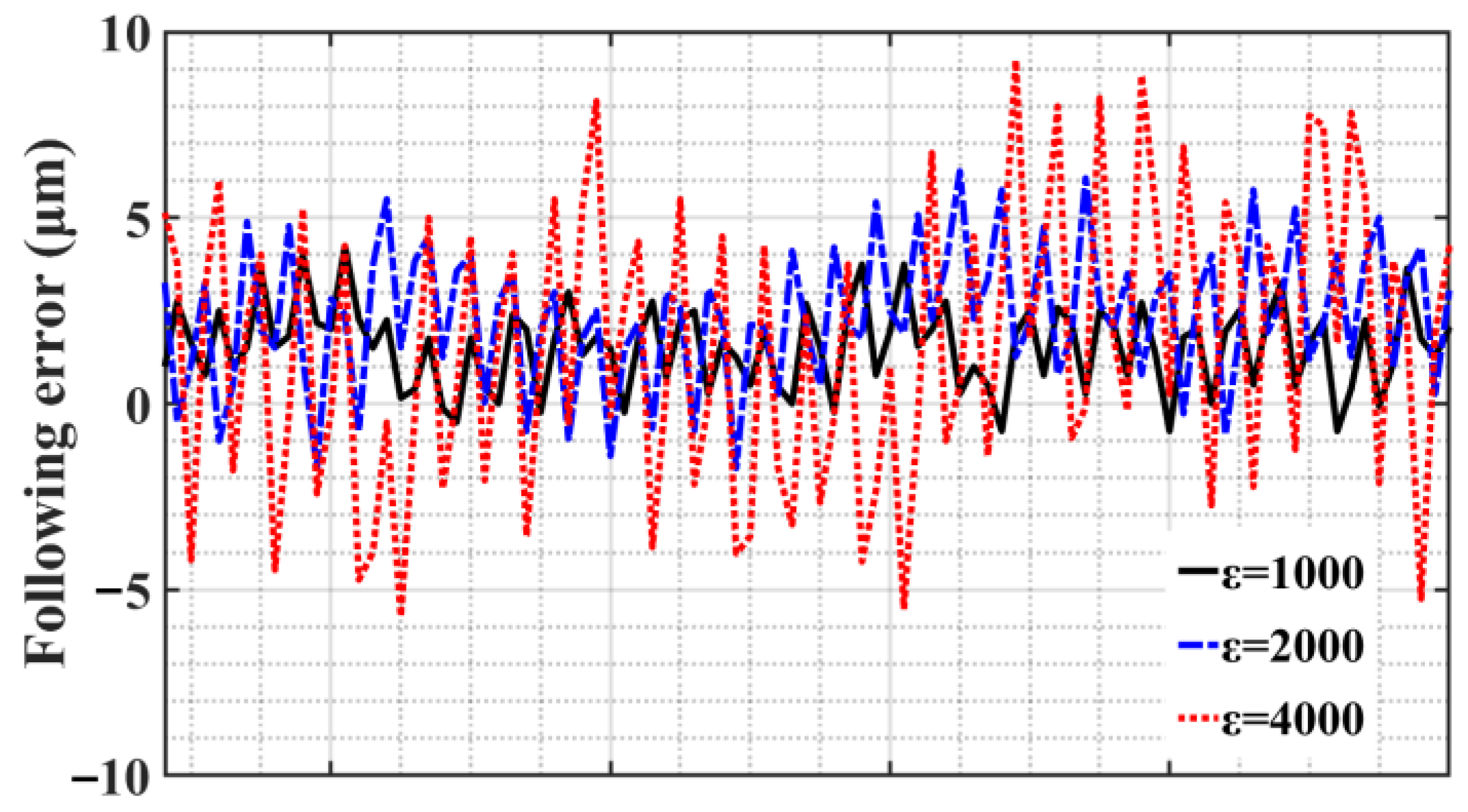
4. Simulation Analysis and Sliding Mode Control Parameters Adaptive Optimization
- (1)
- The V function represented by Equation (23) is positive definite;
- (2)
- Substituting Equation (25) into (24) gives , and the equality sign holds only at and .
5. Experimental Verification
5.1. Experimental Platform
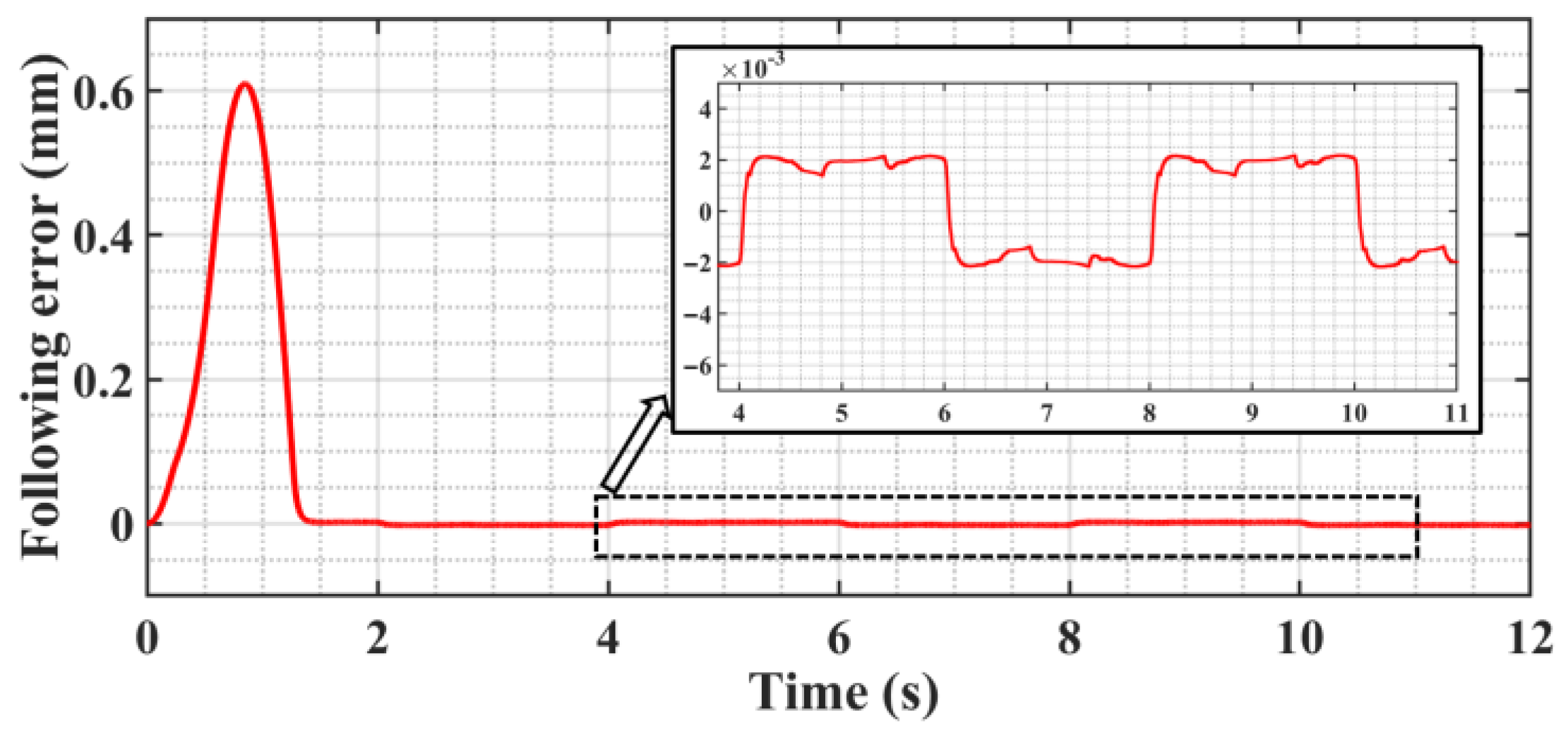
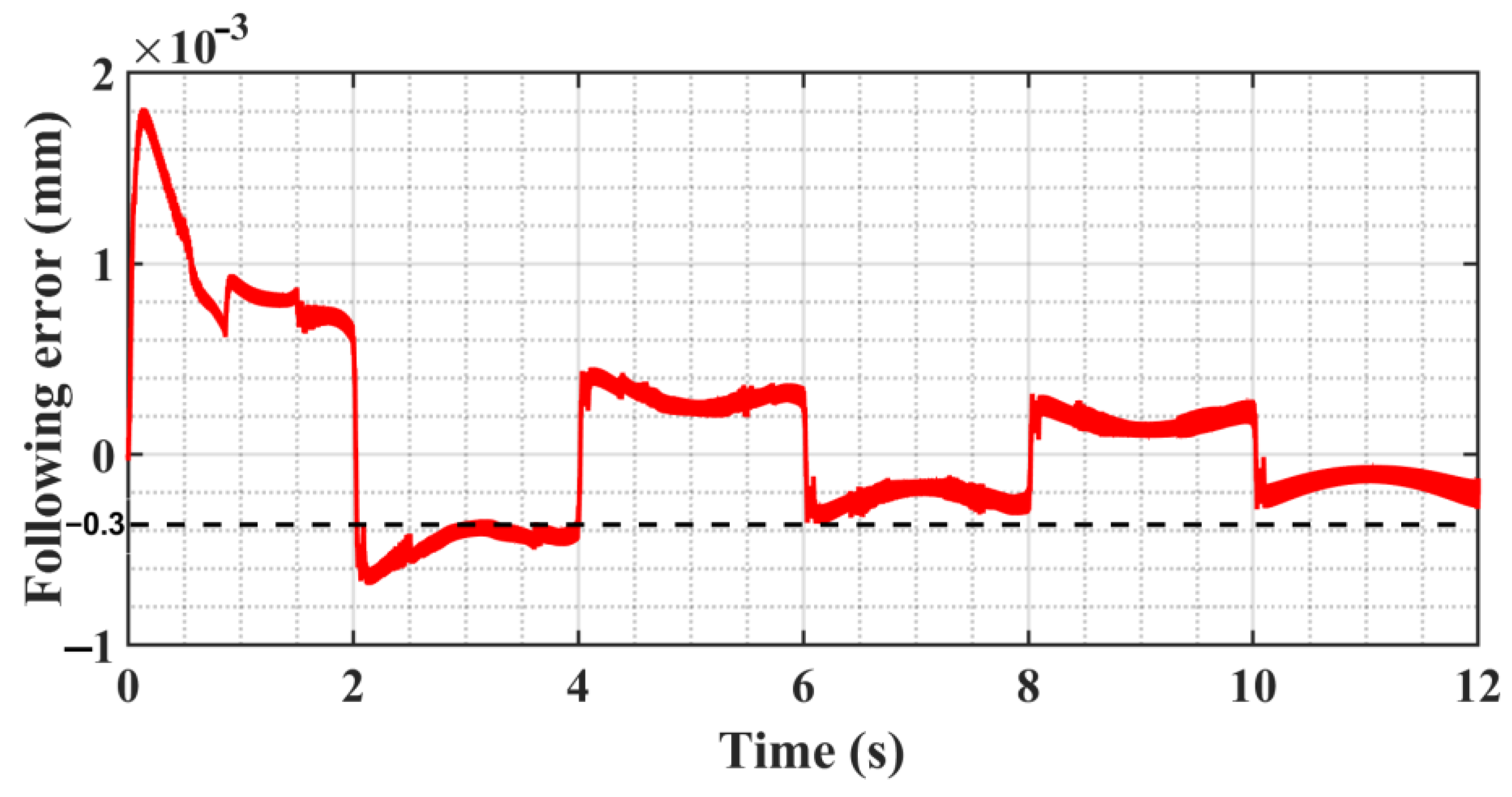
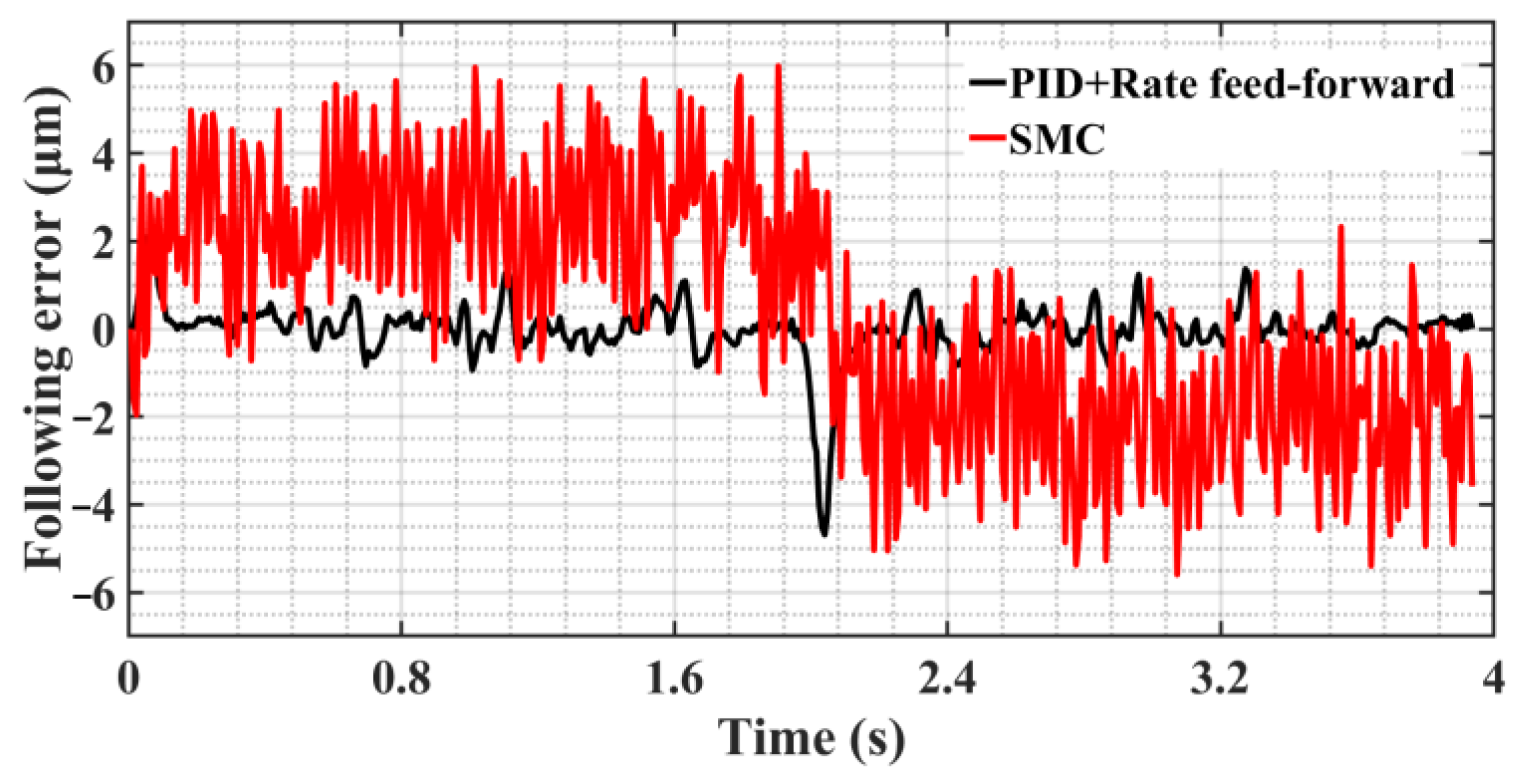
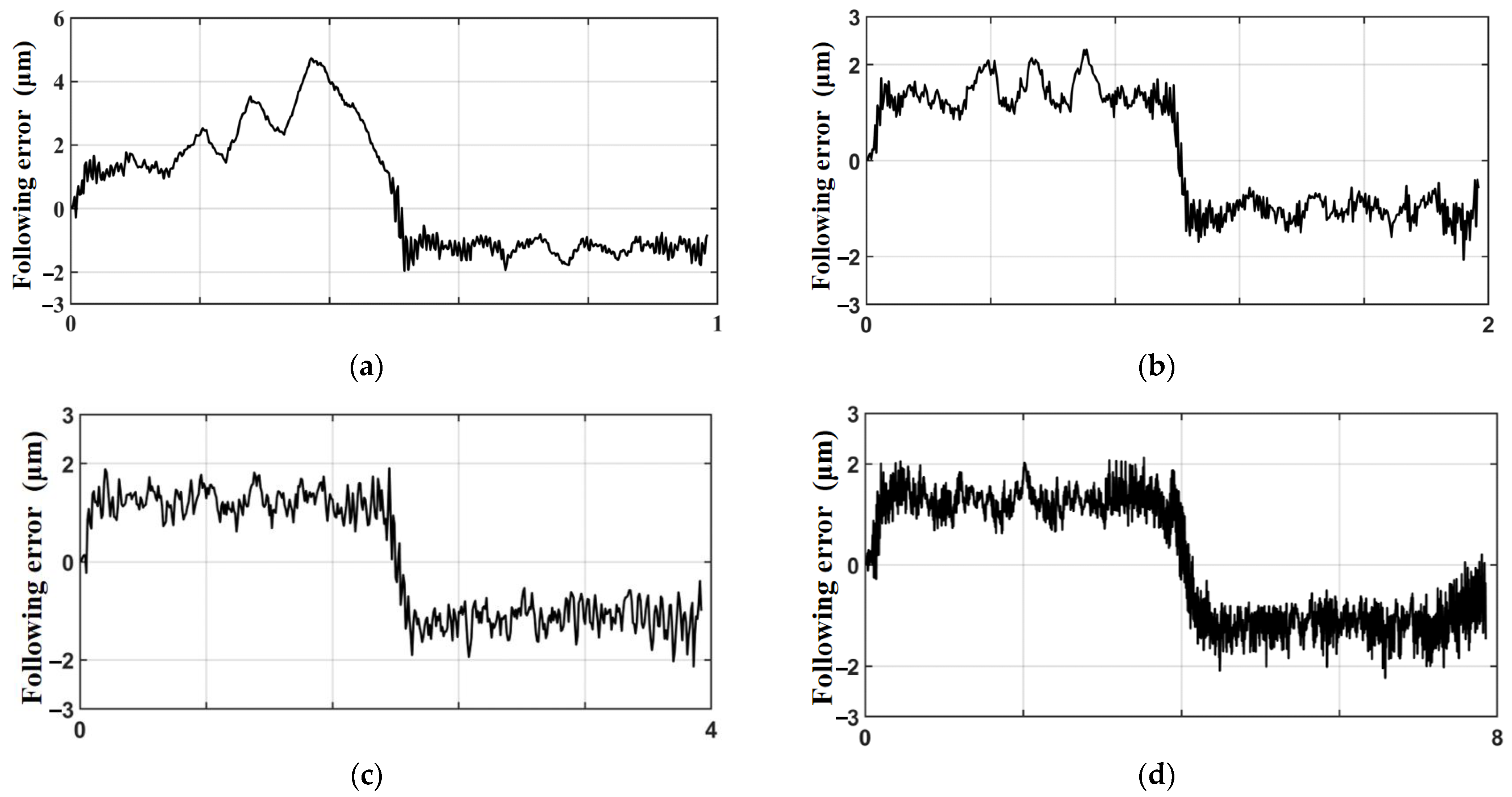
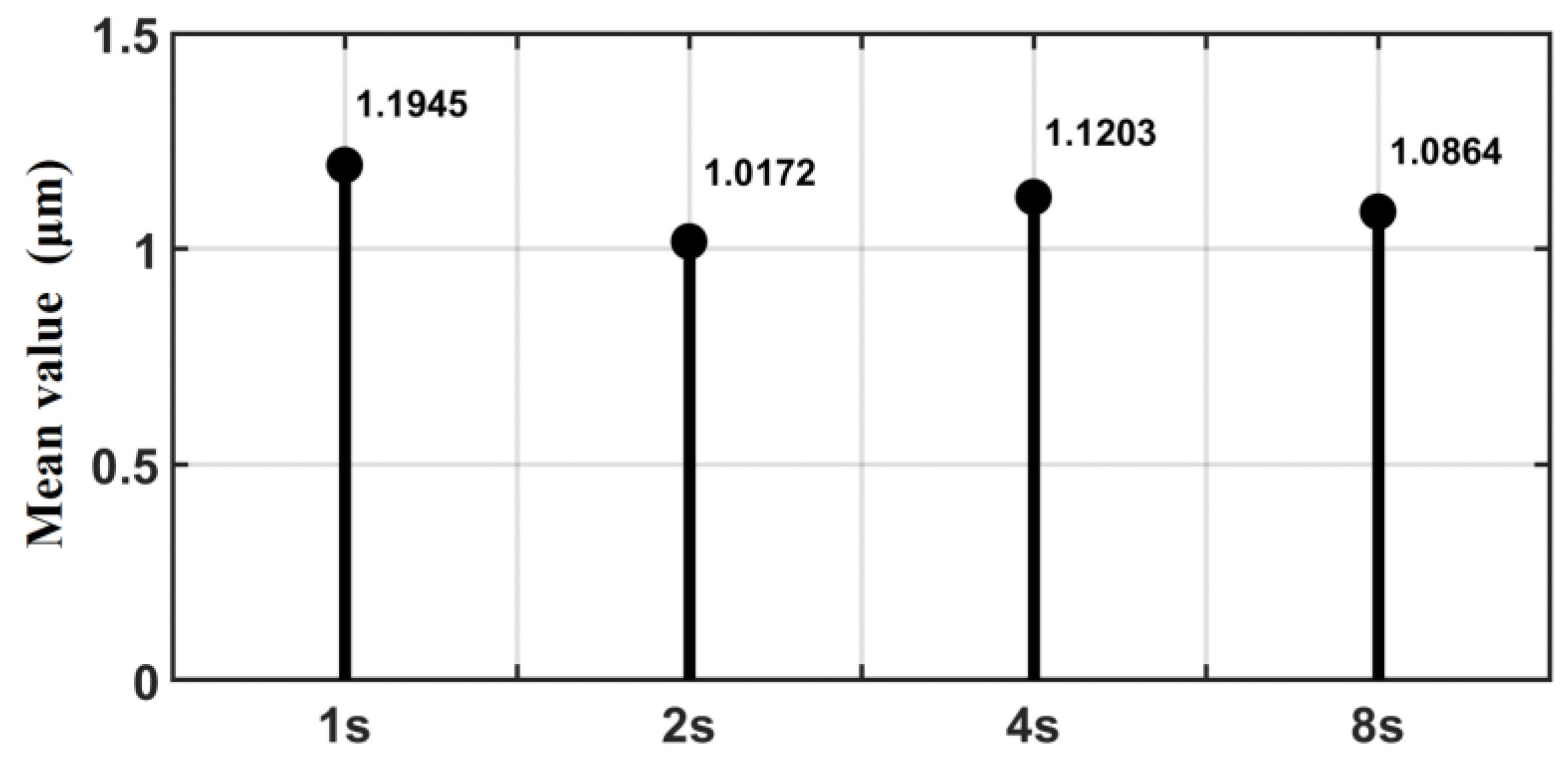
5.2. SMC of Trajectory Motion Experiments
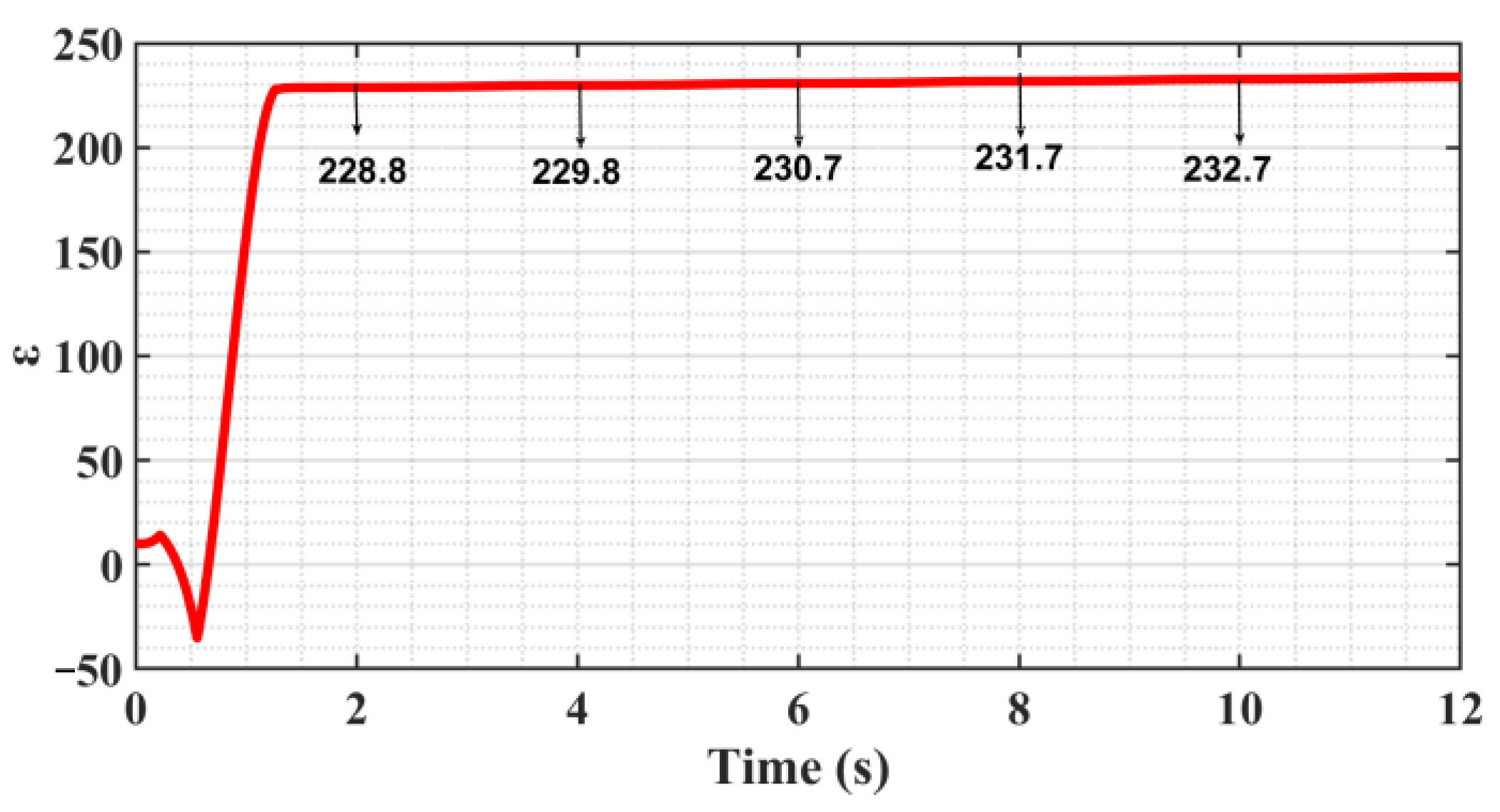
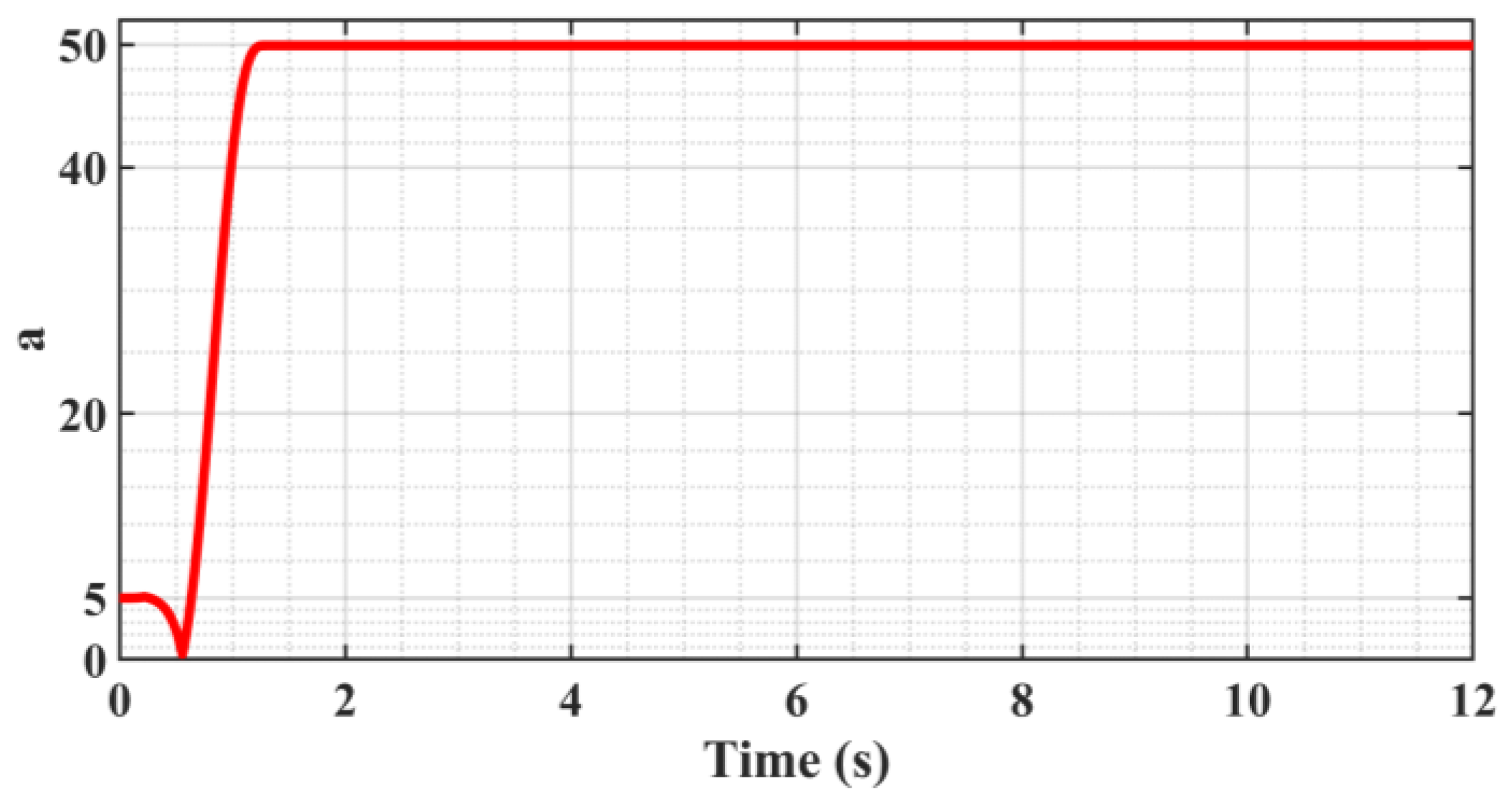
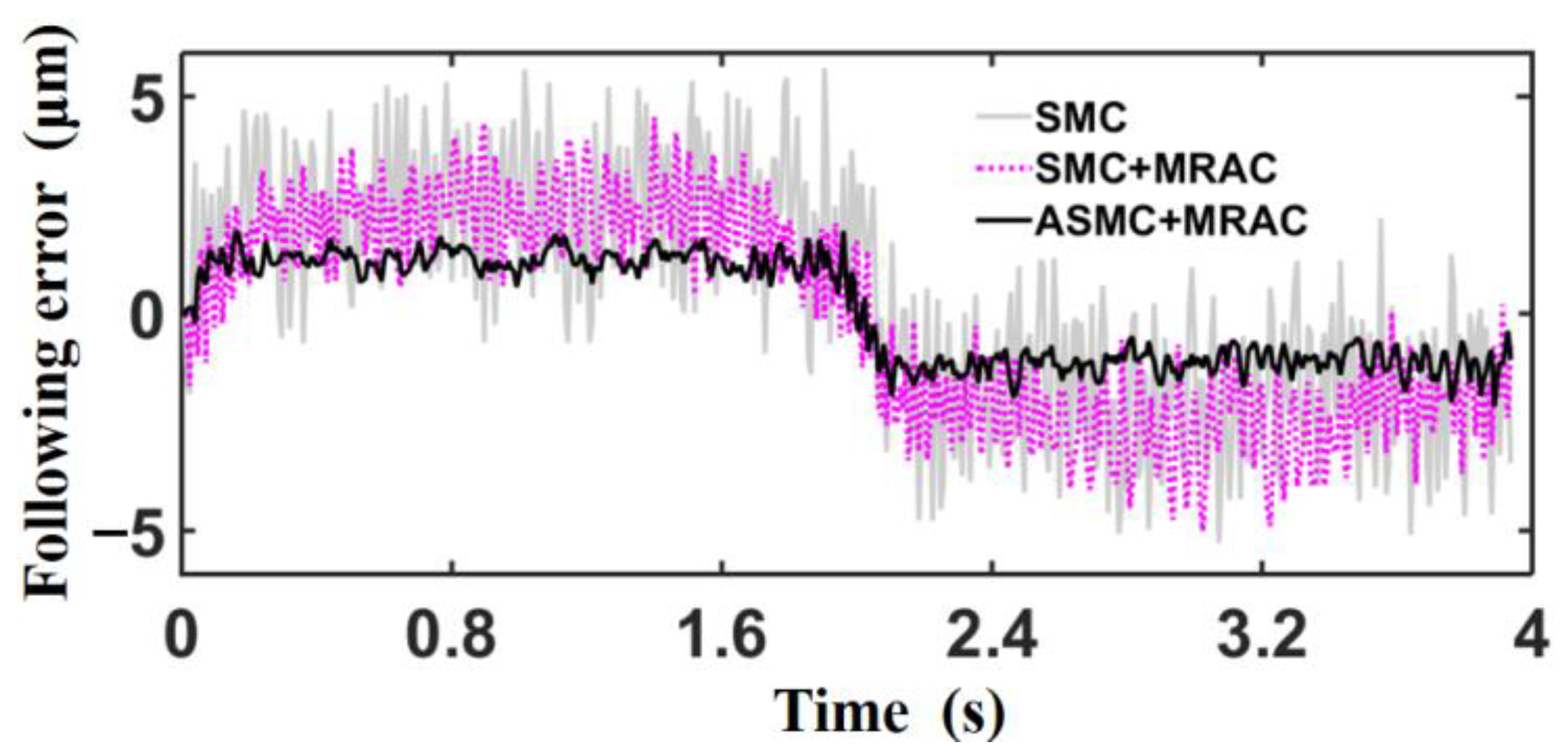
5.3. ASMC of Trajectory Motion Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Åström, K.J.; Hägglund, T. The future of PID control. Control Eng. Pract. 2001, 9, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesmin, A.; Bera, M.K. Design of event-triggered sliding mode controller based on reaching law with time varying event generation approach. Eur. J. Control 2019, 48, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, Y. Sliding mode control with a second-order switching law for a class of nonlinear fractional order systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 85, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Sensorless Control Method for SPMSMs Based on Improved Sliding Mode Reaching Rate. Electronics 2023, 12, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, M.; Plestan, F.; Bououlid, B. Higher order sliding mode control based on adaptive first order sliding mode controller. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levant, A. Homogeneous High-Order Sliding Modes. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2008, 41, 3799–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Chen, W.-H.; Lu, X. Sliding mode control with integral sliding surface for linear uncertain impulsive systems with time delays. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 113, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, Y. Chaotic synchronization based on improved global nonlinear integral sliding mode control☆. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 96, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, C.C. Integral sliding mode control with a disturbance observer for next-generation servo track writing. Mechatronics 2016, 40, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Z.-Q.; Yang, H.; Fu, Y.-T.; Wang, H. Data-driven integral sliding mode control based on disturbance decoupling technology for electric multiple unit. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 9399–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, D.; Zhu, W. Implementation of integral fixed-time sliding mode controller for speed regulation of PMSM servo system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 102, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; You, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W. Nonlinear sliding mode controller using disturbance observer for permanent magnet synchronous motors under disturbance. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 214, 119085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, S.; Arai, Y.; Gao, W. Dynamic compensation of modeling uncertainties and disturbances of a precision planar motion stage based on sliding mode observer. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 46, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; De León, J.; Fridman, L. Synchronization in reduced-order of chaotic systems via control approaches based on high-order sliding-mode observer. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 3219–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barambones, O.; Alkorta, P. A robust vector control for induction motor drives with an adaptive sliding-mode control law. J. Frankl. Inst. 2011, 348, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, L. Adaptive sliding mode trajectory tracking control of robotic airships with parametric uncertainty and wind disturbance. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.; Shu, F.; Xu, Y.; Ding, R.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Iterative learning based neural network sliding mode control for repetitive tasks: With application to a PMLSM with uncertainties and external disturbances. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 172, 108950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Song, Q.; Ma, S.; Ma, W.; Yin, C.; Cao, D.; Yu, H. A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kee, S.-C. Neural Network Approach Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Control for Path-Tracking of Autonomous Vehicles. Electronics 2023, 12, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wei, M. Fuzzy sliding mode control design for the stabilization of wind power generation system with permanent magnet synchronous generator. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, H. Design of Sensorless Speed Control System for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Based on Fuzzy Super-Twisted Sliding Mode Observer. Electronics 2022, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B. Adaptive super-twisting fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control with ESO for high-pressure electro-pneumatic servo valve. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 134, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Kuo, T.C.; Chang, S.H. Adaptive sliding-mode control for nonlinear systems with uncertain parameters. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. B Cybern. 2008, 38, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.-P.; Zhou, R.; Li, J. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode tracking control for DC motor servo system. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 5090–5095. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Pan, S. Adaptive sliding mode control of electro-hydraulic system with nonlinear unknown parameters. Control Eng. Pract. 2008, 16, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Fan, X.; Dai, W.; Shen, J.; Hua, M. Robust tracking control of triaxial angular velocity sensors using adaptive sliding mode approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 52, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, A.; Luo, X.; Tang, Q.; Li, Z. The path following of intelligent unmanned vehicle scheme based on adaptive sliding mode-model predictive control. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 5658–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, H.; Li, X.; Jiao, F.; Cheng, X.; Yang, X.; Zheng, G. Application of a New Model Reference Adaptive Control Based on PID Control in CNC Machine Tools. Machines 2021, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong-Hélouvry, B.; Dupont, P.; De Wit, C.C. A survey of models, analysis tools and compensation methods for the control of machines with friction. Automatica 1994, 30, 1083–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, N.; Malik, F.M.; Raza, A.; Khan, R. Predefined-time control of nonlinear systems: A sigmoid function based sliding manifold design approach. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 6831–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; Chou, W.; Rong, Y.; Dong, M. Anti-disturbance attitude control for quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle manipulator via fuzzy adaptive sigmoid generalized super-twisting sliding mode observer. J. Vib. Control 2021, 28, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
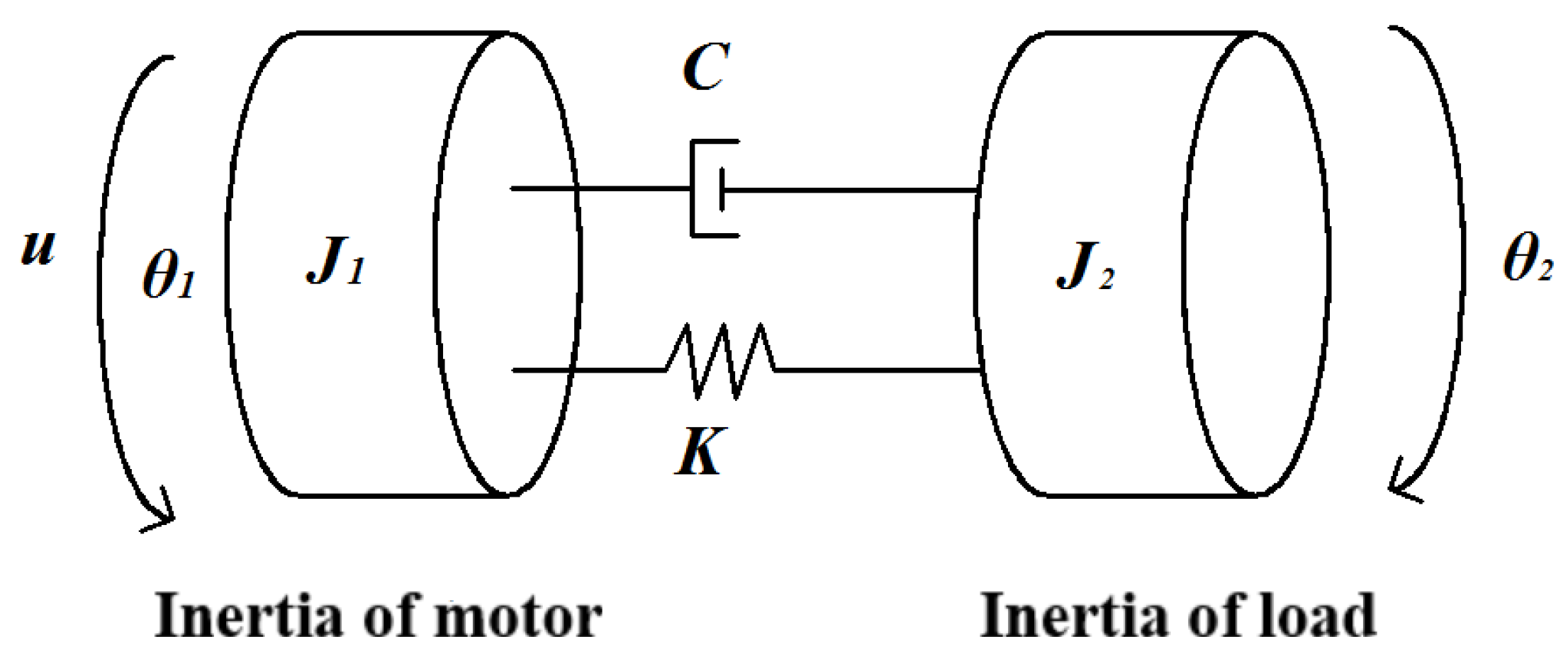
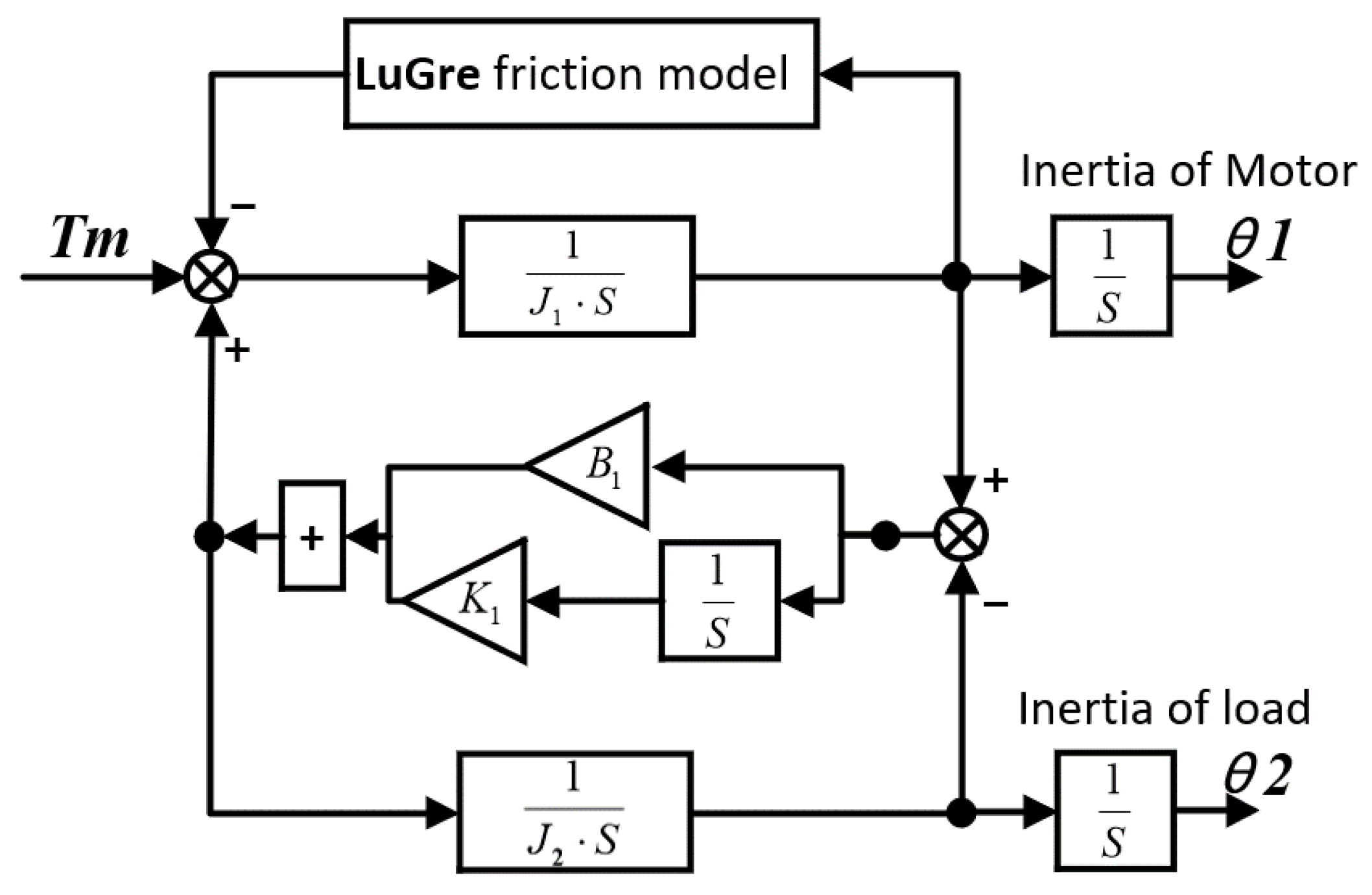
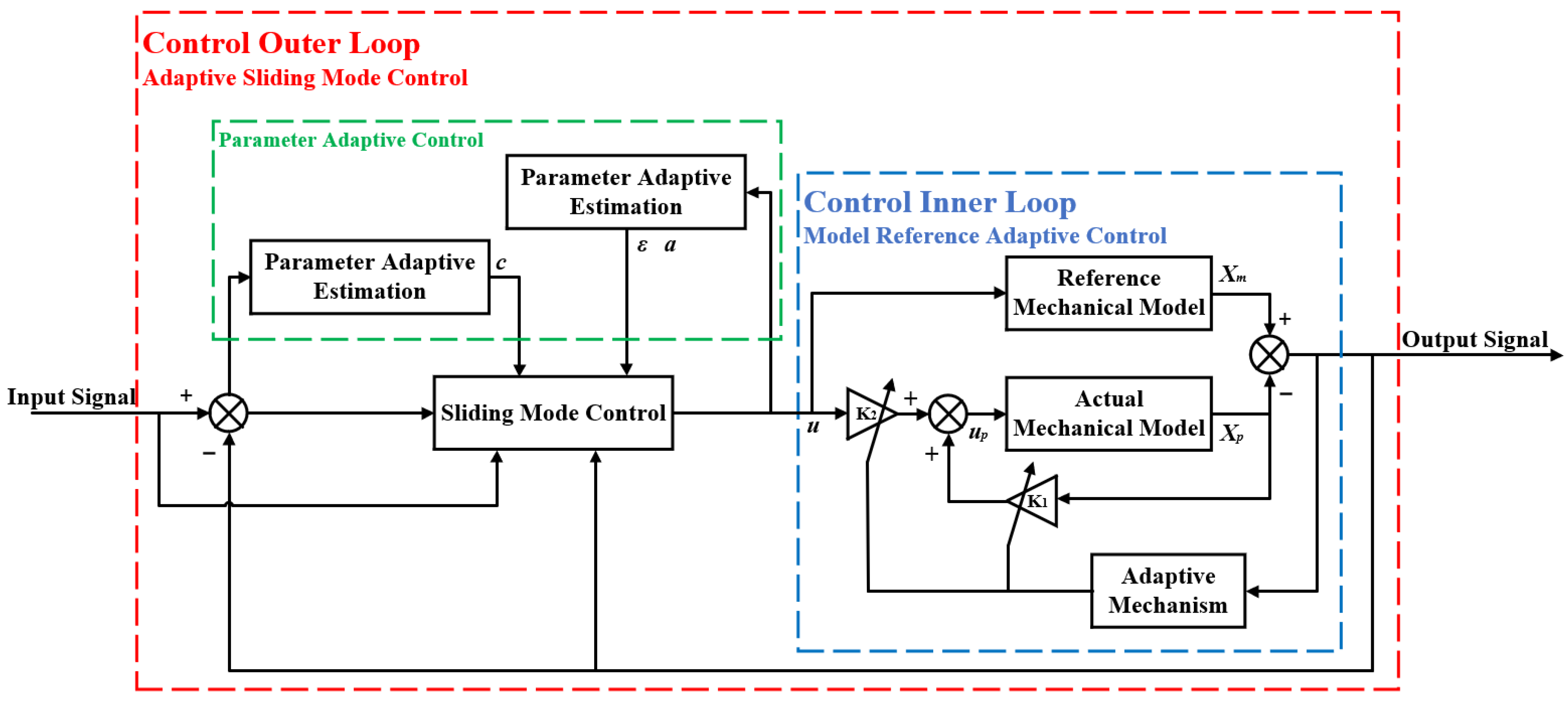
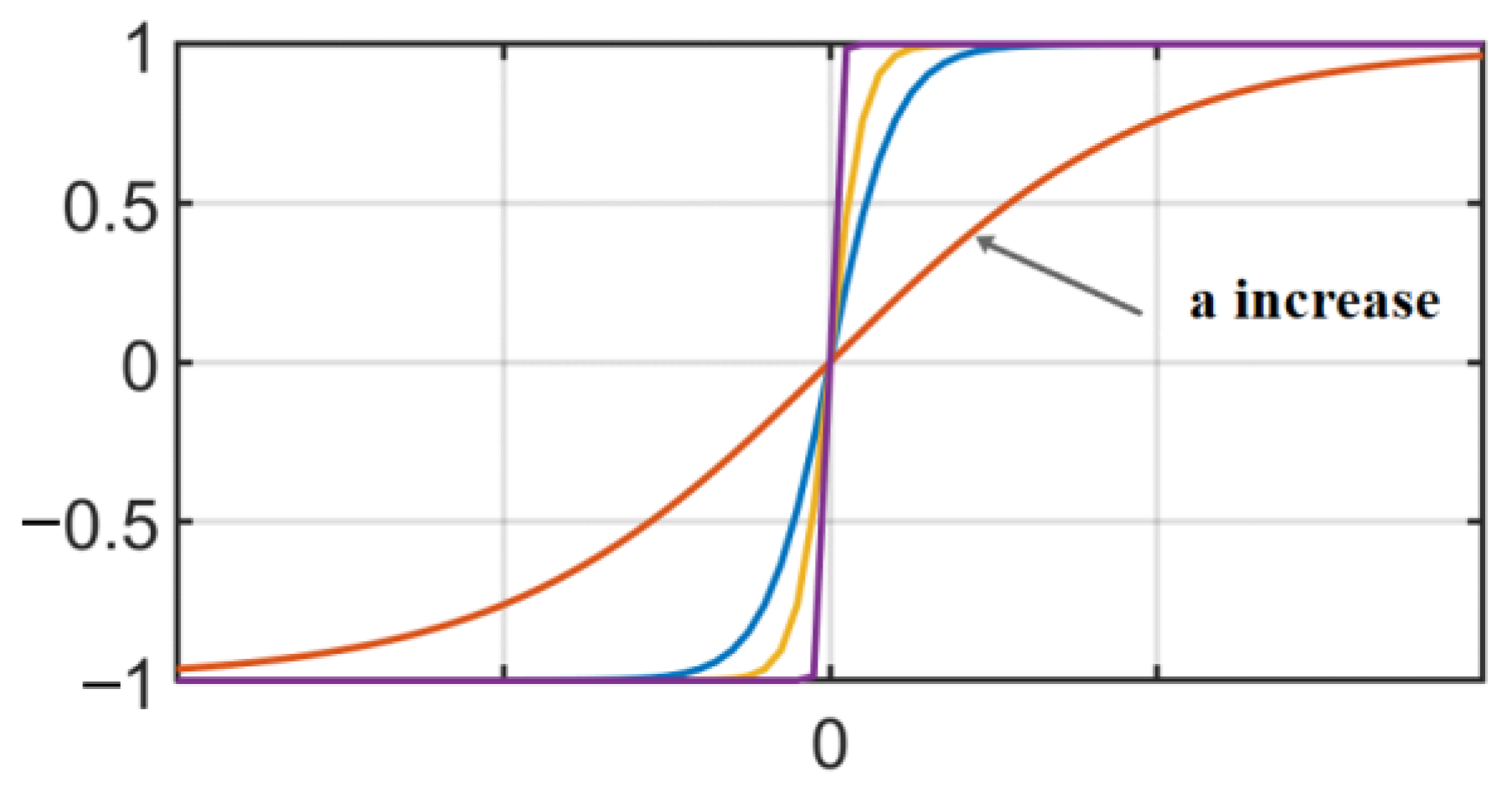




| Symbols | Name | Values |
|---|---|---|
| J1 | Inertia of motor | 2.85 × 10−4 kg·m2 |
| J2 | Inertia of load | 5.12 × 10−5 kg·m2 |
| K | Equivalent stiffness | 18.29 N·m/rad |
| C | Equivalent damping | 0.064 N·m/rad |
| Symbols | Name | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Fs | Max static friction | 0.04263 N/m |
| Fc | Coulomb friction | 0.0091 N/m |
| Vs | Stribeck velocity | 0.007353 m/s |
| σ0 | Stiffness coefficient | 8.0274 N/m |
| σ1 | Damping coefficien | 2.343 N·s/m2 |
| σ2 | Viscosity coefficient | 0.02772 N·s/m2 |
| Control Methods | Control Parameters |
|---|---|
| SMC | c = 500 |
| ε = 1500 | |
| SMC+MRAC | c = 500 |
| ε = 500 | |
| ASMC+MRAC | γε = 500 kε0 = 230 |
| γa = 10 ka0 = 50 | |
| γc = 3000 kc0 = 250 |
| Control Methods | Variance |
|---|---|
| SMC | 6.88 |
| SMC+MRAC | 5.76 |
| ASMC+MRAC | 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Gai, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, X. Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control. Sensors 2023, 23, 9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249755
Zhang T, Li X, Gai H, Zhu Y, Cheng X. Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control. Sensors. 2023; 23(24):9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249755
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Taihao, Xuewei Li, Hongdong Gai, Yuheng Zhu, and Xiang Cheng. 2023. "Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control" Sensors 23, no. 24: 9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249755
APA StyleZhang, T., Li, X., Gai, H., Zhu, Y., & Cheng, X. (2023). Integrated Controller Design and Application for CNC Machine Tool Servo Systems Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control and Adaptive Sliding Mode Control. Sensors, 23(24), 9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249755




