A Systematic Review on Commercially Available Integrated Systems for Forensic DNA Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
Terminology
- An allelic drop-out is a failure to determine an allele within a sample. This occurs when one or both allelic copies are not amplified during PCR.
- PCR inhibitors are chemical or physical obstacles that block amplification and, as such, ultimately fail the PCR reaction.
- Rapid DNA systems are fully integrated platforms that can generate STR profiles from (reference) samples within two hours [32].
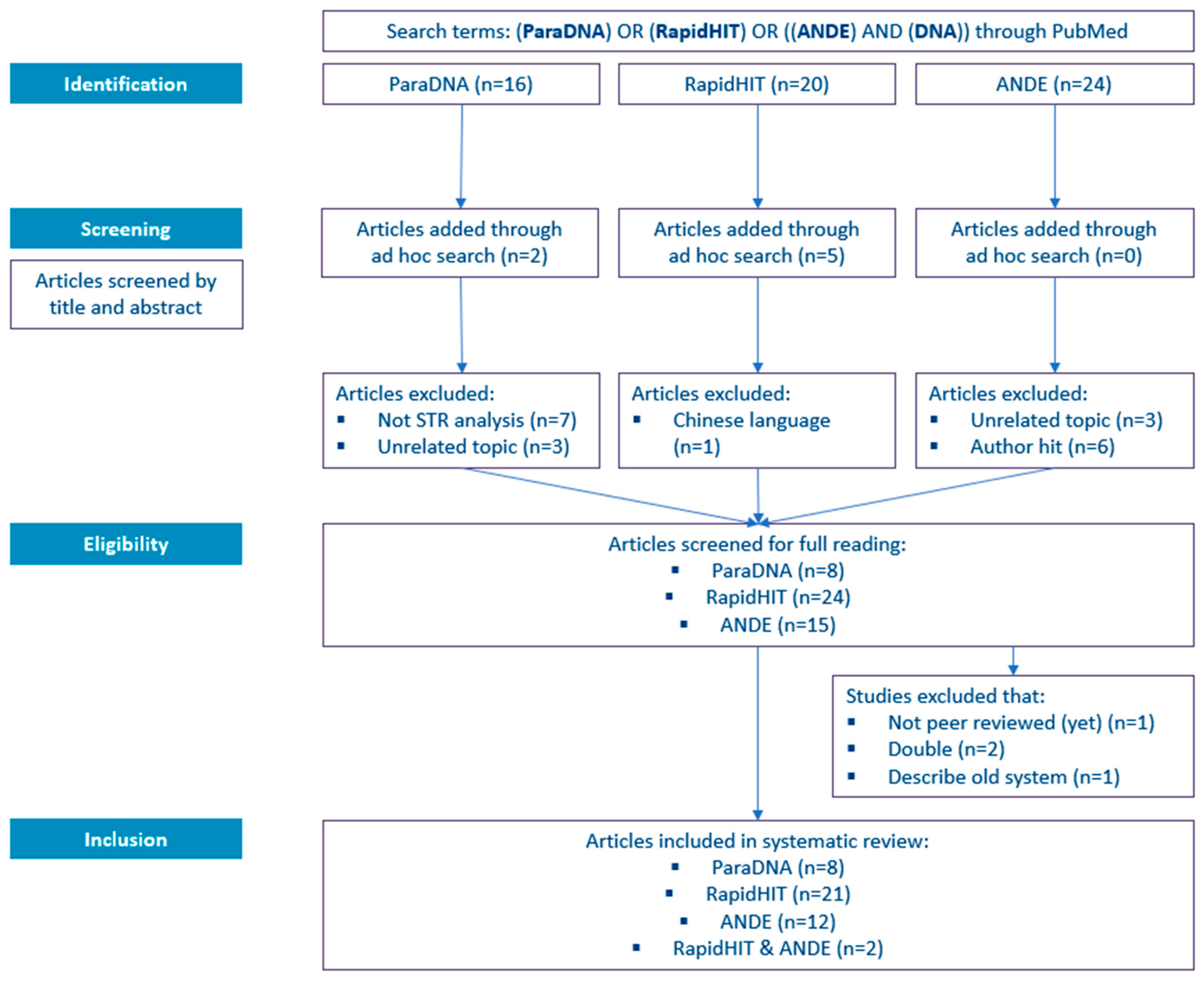
2. Literature Search
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Search Results
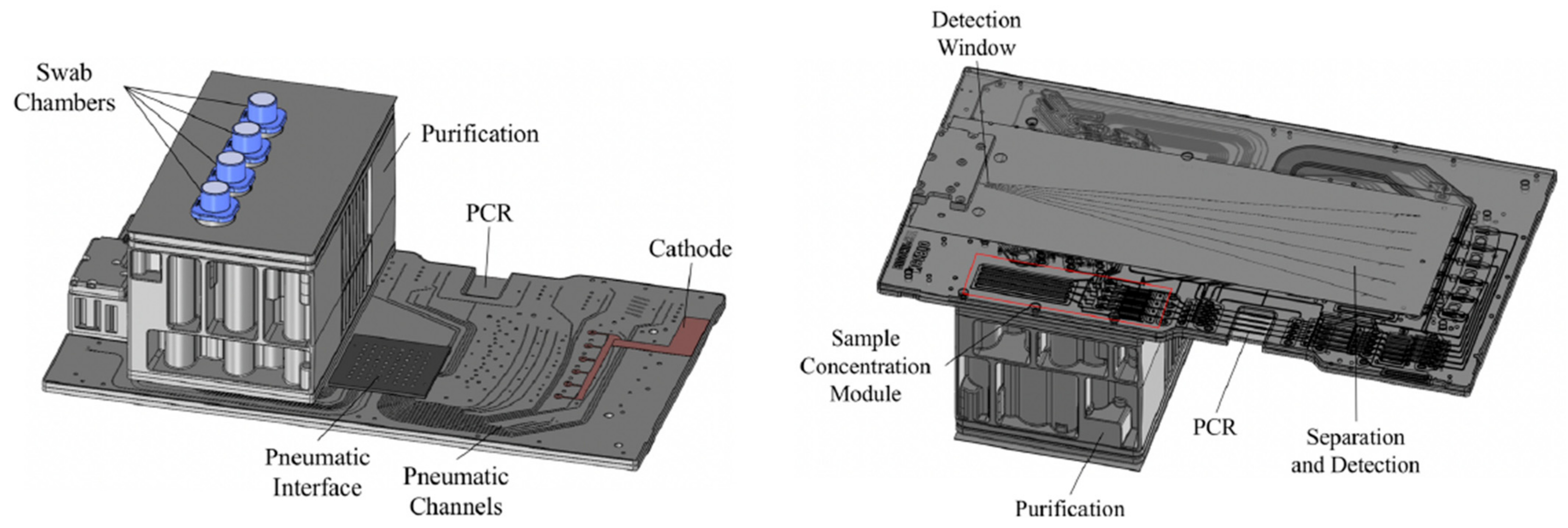
3. Rapid DNA Systems
3.1. ParaDNA
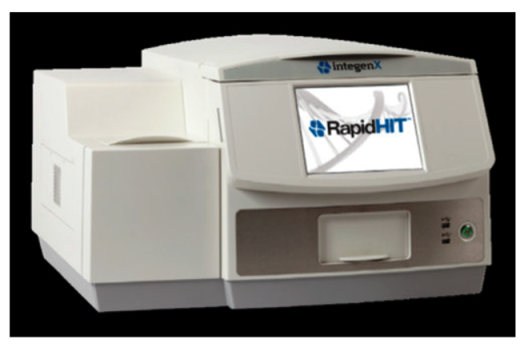
3.2. RapidHIT
3.2.1. RapidHIT 200
3.2.2. RapidHit ID
3.3. ANDE
3.3.1. ANDE 4C
3.3.2. ANDE 6C
3.4. Other Systems
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance
4.2. Direct Comparison
4.3. Portability, Time-to-Result, and Throughput
4.4. Sensitivity
4.5. Costs
4.6. Practical Challenges
4.7. Jurisdiction and Legislation
4.8. Indicative Testing
5. Conclusions
- Ease-of-use: although the rapid DNA systems themselves can be operated by minimally trained people, the interpretation of the DNA profiles gives a higher success rate when this is done by an expert (i.e., modified rapid DNA), especially for the RapidHIT.
- Use of disposable cartridges for single use: All (modified) rapid DNA systems make use of sample cartridges that are single-use cartridges.
- Time-to-result: although it is not (yet) possible to generate a DNA profile within the targeted 60 min, obtaining a DNA profile in ~90 min is possible.
- Portability: With a weight of at least 29 kg and the present dimensions, current rapid DNA systems are not really ‘briefcase’ sized systems. When loaded into a bus or van, such systems become mobile but not portable.
- An enclosed system (no operator manipulation possible to avoid contamination): All rapid DNA systems fulfill this requirement.
- Robustness: The rapid DNA systems are robust in terms of being transportable. They can withstand, e.g., shocks while being transported from one location to another in a car or van.
- Possibility to analyze a variety of forensic samples: The RapidHIT works well with buccal swab samples, but for other types of samples, the success rate drops. While the ANDE performs somewhat better with real case samples, reference samples (i.e., buccal swabs) are the preferred sample type.
- Performance (sensitivity and selectivity): Even though the selectivity of the rapid DNA systems is not widely reported, no incidents were mentioned. Their sensitivity, on the other hand, is still substantially lower than conventional laboratory methods. It has to be mentioned that a trade-off exists between sensitivity and speed: in general, a higher analysis speed negatively influences the sensitivity that can be obtained with a system.
- Costs: About €200 per cartridge run makes the use of rapid DNA systems quite costly, especially with the low throughput/amount of sample per cartridge taken into account.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mapes, A. Rapid DNA Technologies at the Crime Scene: ‘CSI’ Fiction Matching Reality. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science (FNWI), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, Z.; Daniel, R.; Gerostamoulos, D.; Woodford, N.; Hartman, D. Rapid DNA from a Disaster Victim Identification Perspective: Is It a Game Changer? Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2022, 58, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Wilde, L.; Pitman, F. Legislative and Policy Implications for the Use of Rapid DNA Technology in the Australian Context. For. Sci. Pol. Manag. Int. J. 2017, 8, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, R.; Sage, K.; LaRue, B.; Budowle, B. Internal Validation of the RapidHIT® ID System. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 31, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roo, R.H.D.; de Poot, C.J. LocalDNA: De Ontwikkeling En Werking van Een Snelle. 2022. Available online: https://www.narcis.nl/publication/RecordID/oai:hbokennisbank.nl:amsterdam_pure%3Aoai%3Apure.hva.nl%3Apublications%2F786aa894-be74-438a-bf76-405e214db393 (accessed on 25 June 2022).
- Morgan, R.; Illidge, S.; Wilson-Wilde, L. Assessment of the Potential Investigative Value of a Decentralised Rapid DNA Workflow for Reference DNA Samples. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 294, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlich, H.; Calloway, C.; Lee, S.B. Recent Developments in Forensic DNA Technology. In Silent Witness: Forensic DNA Evidence in Criminal Investigations and Humanitarian Disasters; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 105–127. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/book/33504/chapter-abstract/287811363?redirectedFrom=fulltext&login=false (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Wai Yin Chong, K.; Thong, Z.; Kiu-Choong Syn, C.; Zhonghui Thong, C.; Wai Yin, K. Recent Trends and Developments in Forensic DNA Extraction. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Forensic Sci. 2021, 3, e1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, A.D.; Kersbergen, P. Efficacy and Limits of Genotyping Low Copy Number (LCN) DNA Samples by Multiplex PCR of STR Loci. J. Soc. Biol. 2003, 197, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijns, B.; van Asten, A.; Tiggelaar, R.; Gardeniers, H. Microfluidic Devices for Forensic DNA Analysis: A Review. Biosensors 2016, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, J.W.; DeArman Lukacs, K. Zone Electrophoresis in Open-Tubular Glass Capillaries: Preliminary Data on Performance. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 1981, 4, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, A.; Harrison, D.J.; Verpoorte, E.M.J.; Fettinger, J.C.; Paulus, A.; Lüdi, H.; Widmer, H.M. Planar Chips Technology for Miniaturization and Integration of Separation Techniques into Monitoring Systems: Capillary Electrophoresis on a Chip. J. Chromatogr. A 1992, 593, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrup, M.A.; Hadley, D.; Richards, J.; Stratton, P.; Lehew, S.; Benett, B.; Landre, P. A Miniature Analytical Instrument for Nucleic Acids Based on Micromachined Silicon Reaction Chambers. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, A.J.; Hurth, C.; Yang, J.; Cai, Z.; Moran, N.; Lee-Edghill, J.G.; Nordquist, A.; Lenigk, R.; Estes, M.D.; Haley, J.P.; et al. Integrated Microfluidic System for Rapid Forensic DNA Analysis: Sample Collection to DNA Profile. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6991–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; Yang, J.; Barrett, M.; Duane, B.; Brooks, C.; Jung, W.; Yang, J.; Barrett, M.; Duane, B.; Brooks, C.; et al. Recent Improvement in Miniaturization and Integration of A DNA Analysis System for Rapid Forensic Analysis (MiDAS). J. Forensic Investig. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hurth, C.; Smith, S.D.; Nordquist, A.R.; Lenigk, R.; Duane, B.; Nguyen, D.; Surve, A.; Hopwood, A.J.; Estes, M.D.; Yang, J.; et al. An Automated Instrument for Human STR Identification: Design, Characterization, and Experimental Validation. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3510–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienvenue, J.M.; Legendre, L.A.; Ferrance, J.P.; Landers, J.P. An Integrated Microfluidic Device for DNA Purification and PCR Amplification of STR Fragments. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2010, 4, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lounsbury, J.A.; Landers, J.P. Ultrafast Amplification of DNA on Plastic Microdevices for Forensic Short Tandem Repeat Analysis. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lounsbury, J.A.; Karlsson, A.; Miranian, D.C.; Cronk, S.M.; Nelson, D.A.; Li, J.; Haverstick, D.M.; Kinnon, P.; Saul, D.J.; Landers, J.P. From Sample to PCR Product in under 45 Minutes: A Polymeric Integrated Microdevice for Clinical and Forensic DNA Analysis. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roux, D.; Root, B.E.; Hickey, J.A.; Scott, O.N.; Tsuei, A.; Li, J.; Saul, D.J.; Chassagne, L.; Landers, J.P.; De Mazancourt, P. An Integrated Sample-in-Answer-out Microfluidic Chip for Rapid Human Identification by STR Analysis. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yeung, S.H.I.; Crenshaw, K.A.; Crouse, C.A.; Scherer, J.R.; Mathies, R.A. Real-Time Forensic DNA Analysis at a Crime Scene Using a Portable Microchip Analyzer. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2008, 2, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Greenspoon, S.A.; Yeung, S.H.; Scherer, J.R.; Mathies, R.A. Integrated Sample Cleanup and Microchip Capillary Array Electrophoresis for High-Performance Forensic STR Profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 830, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, X.; Greenspoon, S.A.; Scherer, J.R.; Mathies, R.A. Integrated DNA Purification, PCR, Sample Cleanup, and Capillary Electrophoresis Microchip for Forensic Human Identification. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gan, W.; Zhuang, B.; Sun, J.; Zhao, L.; Ye, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.X.; Liu, P. A Fully Integrated Microchip System for Automated Forensic Short Tandem Repeat Analysis. Analyst 2017, 142, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mauk, M.; Qiu, X.; Liu, C.; Kim, J.; Ramprasad, S.; Ongagna, S.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; et al. An Integrated, Self-Contained Microfluidic Cassette for Isolation, Amplification, and Detection of Nucleic Acids. Biomed. Microdevices 2010, 12, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Evaluation of Microfluidics-Based Droplet PCR Combined with Multiplex STR System in Forensic Science. Electrophoresis 2022, 43, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakaratanopas, S.; Zhuang, B.; Gan, W.; Liu, P. Integrated Microfluidic Systems for Genetic Analysis. Microfluid. Devices Biomed. Appl. 2021, 507, 511–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouwairi, R.L.; Cunha, L.L.; Turiello, R.; Scott, O.; Hickey, J.; Thomson, S.; Knowles, S.; Chapman, J.D.; Landers, J.P. Ultra-Rapid Real-Time Microfluidic RT-PCR Instrument for Nucleic Acid Analysis. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 3424–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romsos, E.L.; French, J.L.; Smith, M.; Figarelli, V.; Harran, F.; Vandegrift, G.; Moreno, L.I.; Callaghan, T.F.; Brocato, J.; Vaidyanathan, J.; et al. Results of the 2018 Rapid DNA Maturity Assessment. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, O. Bringing Science to the Scene: Novel Strategies for Portable DNA Profiling. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, R.; Jiang, H.; Turingan, R.S.; French, J.L.; Tan, E.; Selden, R.F. FlexPlex27—Highly Multiplexed Rapid DNA Identification for Law Enforcement, Kinship, and Military Applications. Int. J. Legal Med. 2017, 131, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.I.; Brown, A.L.; Callaghan, T.F. Internal Validation of the DNAscan/ANDETM Rapid DNA AnalysisTM Platform and Its Associated PowerPlex® 16 High Content DNA Biochip Cassette for Use as an Expert System with Reference Buccal Swabs. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 29, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRISMA PRISMA Flow Diagram. Available online: http://www.prisma-statement.org/PRISMAStatement/FlowDiagram (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Folch, A. Hidden in Plain Sight: The History, Science, and Engineering of Microfluidic Technology; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, C.L.; Ambers, A. Rapid DNA Analysis–Need, Technology, and Applications. In Portable Spectroscopy and Spectrometry; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 515–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Giese, H.; Hartmann, D. Microfluidic DNA Extraction and Purification from Forensic Samples: Towards Rapid, Fully Integrated STR Analysis|Office of Justice Programs. Available online: https://www.ojp.gov/library/publications/microfluidic-dna-extraction-and-purification-forensic-samples-towards-rapid (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Gold, S. RapidDNA: A Game Changer in the Law Enforcement Identification Stakes. Biometric Technol. Today 2013, 2013, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tao, R.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Meng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, L.; Bian, Y.; Li, C. Validation Studies of the ParaDNA® Intelligence System with Artificial Evidence Items. Forensic Sci. Res. 2021, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribble, N.D.; Miller, J.A.D.; Dawnay, N.; Duxbury, N.J. Applicability of the ParaDNA® Screening System to Seminal Samples. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 60, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawnay, N.; Ahmed, R.; Naif, S. The ParaDNA® Screening System—A Case Study in Bringing Forensic R&D to Market. Sci. Justice 2014, 54, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doole, S. An Investigation into the Use of the ParaDNA® Body Fluid Identification System in Forensic Examinations. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2017, 6, e492–e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, G.; Dawnay, N.; Stafford-Allen, B.; Panasiuk, M.; Rendell, P.; Blackman, S.; Duxbury, N.; Wells, S. Concordance Study between the ParaDNA® Intelligence Test, a Rapid DNA Profiling Assay, and a Conventional STR Typing Kit (AmpFlSTR® SGM Plus®). Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 16, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donachie, G.E.; Dawnay, N.; Ahmed, R.; Naif, S.; Duxbury, N.J.; Tribble, N.D. Assessing the Impact of Common Forensic Presumptive Tests on the Ability to Obtain Results Using a Novel Rapid DNA Platform. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 17, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawnay, N.; Stafford-Allen, B.; Moore, D.; Blackman, S.; Rendell, P.; Hanson, E.K.; Ballantyne, J.; Kallifatidis, B.; Mendel, J.; Mills, D.K.; et al. Developmental Validation of the ParaDNA® Screening System—A Presumptive Test for the Detection of DNA on Forensic Evidence Items. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 11, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawnay, N.; Flamson, R.; Hall, M.J.R.; Steadman, D.W. Impact of Sample Degradation and Inhibition on Field-Based DNA Identification of Human Remains. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 37, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.; Dawnay, N.; Ball, G.; Stafford-Allen, B.; Tribble, N.; Rendell, P.; Neary, K.; Hanson, E.K.; Ballantyne, J.; Kallifatidis, B.; et al. Developmental Validation of the ParaDNA® Intelligence System—A Novel Approach to DNA Profiling. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 17, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulstein, G.; Pably, P.; Fürst, A.; Wiegand, P.; Hadrys, T. “The Acid Test”—Validation of the ParaDNA® Body Fluid ID Test for Routine Forensic Casework. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 133, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.; Stafford-Allen, B.; Hanson, E.K.; Panasiuk, M.; Brooker, A.L.; Rendell, P.; Ballantyne, J.; Wells, S. Developmental Validation of the ParaDNA® Body Fluid ID System—A Rapid Multiplex MRNA-Profiling System for the Forensic Identification of Body Fluids. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 37, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, F.; Hitchcock, C. Taking the ‘Secret’ out of Secretions: Evaluation of the ParaDNA Body Fluid ID System at NSWHP FASS. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 51, S81–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cision PR Newswire Life Technologies Offers New Rapid DNA Platform. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/life-technologies-offers-new-rapid-dna-platform-200828861.html (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- CBRNE Tech Index ParaDNA. Available online: https://www.cbrnetechindex.com/p/4016/LGC-Forensics/ParaDNA (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Murakami, C.; Irie, W.; Sasaki, C.; Nakamaru, N.; Sakamoto, M.; Nagato, J.; Satoh, F. Individual Identification Using the RapidHITTM ID System for Forensic Samples. Leg. Med. 2020, 47, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tao, R.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Analytical Validation of an RI Sample Cartridge with the RapidHIT® ID System. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleton, D.; Gray, N.; Ives, L.; Malsom, S.; Vanhinsbergh, D. Development of RapidHIT® ID Using NGMSElectTM Express Chemistry for the Processing of Reference Samples within the UK Criminal Justice System. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 295, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watherston, J.; Watson, J.; Bruce, D.; Ueland, M.; McNevin, D.; Ward, J. An In-Field Evaluation of Rapid DNA Instruments for Disaster Victim Identification. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 136, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.; Wendt, F. Evaluation of the RapidHITTM 200, an Automated Human Identification System for STR Analysis of Single Source Samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 14, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlar, J.C.; Kapema, K.B.; Budowle, B. Validation of the Applied Biosystems RapidHIT ID Instrument and ACE GlobalFiler Express Sample Cartridge. Int. J. Legal Med. 2022, 136, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M.; Willis, S. Interpol Review of Forensic Biology and Forensic DNA Typing 2016–2019. Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2020, 2, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollo 200 Fully Integrated DNA HID System: Multi Channel Results in Under 2 Hours-PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3186583/ (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Rapid DNA Solutions for Crime Laboratories. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/nl/en/home/industrial/forensics/human-identification/forensic-dna-analysis/dna-analysis/rapidhit-id-system-human-identification/rapidhit-id-system-crime-labs.html (accessed on 14 August 2022).
- Amick, G.D.; Swiger, R.R. Internal Validation of RapidHIT®ID ACE Sample Cartridge and Assessment of the EXT Sample Cartridge*†. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 64, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, L.K.; Mehendale, N.; Chear, K.; Jovanovich, S.; Williams, S.; Park, C.; Gangano, S. Developmental Validation of the GlobalFiler® Express Kit, a 24-Marker STR Assay, on the RapidHIT® System. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 13, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Rapid DNA Solutions-Bacause Every Minute Counts. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/nl/en/home/industrial/forensics/human-identification/forensic-dna-analysis/dna-analysis/rapidhit-id-system-human-identification.html (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Jovanovich, S.; Bogdan, G.; Belcinski, R.; Buscaino, J.; Burgi, D.; Butts, E.L.R.; Chear, K.; Ciopyk, B.; Eberhart, D.; El-Sissi, O.; et al. Developmental Validation of a Fully Integrated Sample-to-Profile Rapid Human Identification System for Processing Single-Source Reference Buccal Samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 16, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscaino, J.; Barican, A.; Farrales, L.; Goldman, B.; Klevenberg, J.; Kuhn, M.; Lin, F.; Nguyen, P.; Salceda, S.; Schueren, R.; et al. Evaluation of a Rapid DNA Process with the RapidHIT® ID System Using a Specialized Cartridge for Extracted and Quantified Human DNA. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 34, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.; Kaesler, T.; Linacre, A. Analysis of Rapid HIT Application to Touch DNA Samples. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larue, B.L.; Moore, A.; King, J.L.; Marshall, P.L.; Budowle, B. An Evaluation of the RapidHIT® System for Reliably Genotyping Reference Samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 13, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, Z.; Phua, Y.H.; Loo, E.S.; Goh, S.K.; Ang, J.; Looi, W.F.; Syn, C.K.C. Evaluation of the RapidHITTM 200 System: A Comparative Study of Its Performance with Maxwell® DNA IQTM/Identifiler® Plus/ABI 3500xL Workflow. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 19, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, D.; Pagram, J.; Andrews, N.; Malsom, S.; Ives, L.; Vanhinsbergh, D. Development of Enhanced Sensitivity Protocols on the RapidHITTM 200 with a View to Processing Casework Material. Sci. Justice 2019, 59, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleton, D.; Pagram, J.; Ives, L.; Vanhinsbergh, D. Development and Validation of the RapidHITTM 200 Utilising NGMSElectTM Express for the Processing of Buccal Swabs. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date-Chong, M.; Hudlow, W.R.; Buoncristiani, M.R. Evaluation of the RapidHITTM 200 and RapidHIT GlobalFiler® Express Kit for Fully Automated STR Genotyping. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheij, S.; Clarisse, L.; van den Berge, M.; Sijen, T. RapidHITTM 200, a Promising System for Rapid DNA Analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 4, e254–e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, H.S.; Frank-Hansen, R.; Simonsen, B.T.; Morling, N. Performance of the RapidHITTM200. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 4, e286–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangano, S.; Elliott, K.; Anoruo, K.; Gass, J.; Buscaino, J.; Jovanovich, S.; Harris, D. DNA Investigative Lead Development from Blood and Saliva Samples in Less than Two Hours Using the RapidHITTM Human DNA Identification System. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 4, e43–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salceda, S.; Barican, A.; Buscaino, J.; Goldman, B.; Klevenberg, J.; Kuhn, M.; Lehto, D.; Lin, F.; Nguyen, P.; Park, C.; et al. Validation of a Rapid DNA Process with the RapidHIT® ID System Using GlobalFiler® Express Chemistry, a Platform Optimized for Decentralized Testing Environments. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 28, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.; Henry, J.; Taylor, D. Analysis of Mixed DNA Profiles from the RapidHITTM ID Platform Using Probabilistic Genotyping Software STRmixTM. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2022, 58, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.; Turingan, R.S.; Hogan, C.; Vasantgadkar, S.; Palombo, L.; Schumm, J.W.; Selden, R.F. Fully Integrated, Fully Automated Generation of Short Tandem Repeat Profiles. Investig. Genet. 2013, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turingan, R.S.; Vasantgadkar, S.; Palombo, L.; Hogan, C.; Jiang, H.; Tan, E.; Selden, R.F. Rapid DNA Analysis for Automated Processing and Interpretation of Low DNA Content Samples. Investig. Genet. 2016, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Manna, A.; Nye, J.V.; Carney, C.; Hammons, J.S.; Mann, M.; Al Shamali, F.; Vallone, P.M.; Romsos, E.L.; Marne, B.A.; Tan, E.; et al. Developmental Validation of the DNAscanTM Rapid DNA AnalysisTM Instrument and Expert System for Reference Sample Processing. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 25, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragazzo, M.; Melchiorri, S.; Manzo, L.; Errichiello, V.; Puleri, G.; Nicastro, F.; Giardina, E. Comparative Analysis of ANDE 6C Rapid DNA Analysis System and Traditional Methods. Genes 2020, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turingan, R.S.; Tan, E.; Jiang, H.; Brown, J.; Estari, Y.; Krautz-Peterson, G.; Selden, R.F. Developmental Validation of the ANDE 6C System for Rapid DNA Analysis of Forensic Casework and DVI Samples. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmbach, T.; Blom, J.; Hoynes, E.; Primorac, D.; Gaboury, M. Utilizing DNA Analysis to Combat the World Wide Plague of Present Day Slavery--Trafficking in Persons. Croat. Med. J. 2014, 55, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gin, K.; Tovar, J.; Bartelink, E.J.; Kendell, A.; Milligan, C.; Willey, P.; Wood, J.; Tan, E.; Turingan, R.S.; Selden, R.F. The 2018 California Wildfires: Integration of Rapid DNA to Dramatically Accelerate Victim Identification. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, N.; Springstead, T.; Wright, K.; McNamara, K.P. Evaluation of Rapid DNA Using ANDETM in a Technical Exploitation Level 2 Laboratory Workflow. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzella, A.M.; Carte, K.M.; King, S.L.; Moreno, L.I. Assessment of the ANDE 6C Rapid DNA System and Investigative Biochip for the Processing of Calcified and Muscle Tissue. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2021, 53, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, C.; Whitney, S.; Vaidyanathan, J.; Persick, R.; Noel, F.; Vallone, P.M.; Romsos, E.L.; Tan, E.; Grover, R.; Witkowski, R.S.; et al. Developmental Validation of the ANDETM Rapid DNA System with FlexPlexTM Assay for Arrestee and Reference Buccal Swab Processing and Database Searching. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2019, 40, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turingan, R.S.; Brown, J.; Kaplun, L.; Smith, J.; Watson, J.; Boyd, D.A.; Steadman, D.W.; Selden, R.F. Identification of Human Remains Using Rapid DNA Analysis. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEC NEC Tests Its Portable DNA Analyzer with Japan’s National Research Institute of Police Science. Available online: https://www.nec.com/en/press/201211/global_20121122_02.html (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Yang, J.; Hurth, C.; Nordquist, A.; Smith, S.; Zenhausern, F. Integrated Microfluidic System for Rapid DNA Fingerprint Analysis: A Miniaturized Integrated DNA Analysis System (MiDAS)—Swab Sample-in to DNA Profile-Out. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1906, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Brooks, C.; Estes, M.D.; Hurth, C.M.; Zenhausern, F. An Integratable Microfluidic Cartridge for Forensic Swab Samples Lysis. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 8, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, M.D.; Yang, J.; Duane, B.; Smith, S.; Brooks, C.; Nordquist, A.; Zenhausern, F. Optimization of Multiplexed PCR on an Integrated Microfluidic Forensic Platform for Rapid DNA Analysis. Analyst 2012, 137, 5510–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. DNA Sequencing Systems-RapidHIT. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/search/browse/category/nl/en/90220359/dna+sequencing+systems?filter=dimProductLine_dim_ss%3ARapidHIT%26trade%3B (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Wetten.Nl-Regeling-Besluit DNA-Onderzoek in Strafzaken-BWBR0012791. Available online: https://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0012791/2018-02-01 (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Staatsblad 2020, 394|Overheid.Nl > Officiële Bekendmakingen. Available online: https://zoek.officielebekendmakingen.nl/stb-2020-394.html (accessed on 17 October 2022).




 |  |  | ||
 |  |  |  | |
| ParaDNA | RapidHIT 200 | RapidHIT ID | ANDE 6C | |
| Manufacturer | LGC Forensics | IntegenX (Thermo Fisher Scientific) | ANDE | |
| Weight | 6 kg | 81.5 kg | 29 kg | 54 kg |
| Dimensions (L× W × H) | 39 × 29 × 19 cm3 | 73 × 71 × 48 cm3 | 135 × 122 × 69 cm3 | 75 × 45 × 60 cm3 |
| # STRs | 6 loci | GlobalFiler Express: 24 loci AmpFLSTR NGM SElect Express: 17 loci | A-chip: 27 loci I-chip: 27 loci | |
| Sampling | ParaDNA sample collector | GlobalFiler Express: Swab (Puritan Cotton Swab) AmpFLSTR NGM SElect Express: Swab (Whatman OmniSwab) | A-Chip: (Buccal) Swab I-Chip: Swab | |
| Technology | HyBeacons | CE | CE | |
| Time-to-result | 75 min | <2 h | 90 (−110) min | A-chip: 94 min I-chip: 106 min |
| # Samples | 4 | Up to 5 * | 1 | A-chip: 5 I-chip: 4 |
| Sensitivity | Not enough data | 50–200 ng | 40–80 ng | 250 ng-2 µg |
| Notes | Discontinued | Replaced by the RapidHIT ID | ||
| Only indicative | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruijns, B.; Knotter, J.; Tiggelaar, R. A Systematic Review on Commercially Available Integrated Systems for Forensic DNA Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031075
Bruijns B, Knotter J, Tiggelaar R. A Systematic Review on Commercially Available Integrated Systems for Forensic DNA Analysis. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031075
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruijns, Brigitte, Jaap Knotter, and Roald Tiggelaar. 2023. "A Systematic Review on Commercially Available Integrated Systems for Forensic DNA Analysis" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031075
APA StyleBruijns, B., Knotter, J., & Tiggelaar, R. (2023). A Systematic Review on Commercially Available Integrated Systems for Forensic DNA Analysis. Sensors, 23(3), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031075








