Secondary Interface Echoes Suppression for Immersion Ultrasonic Imaging Based on Phase Circular Statistics Vector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
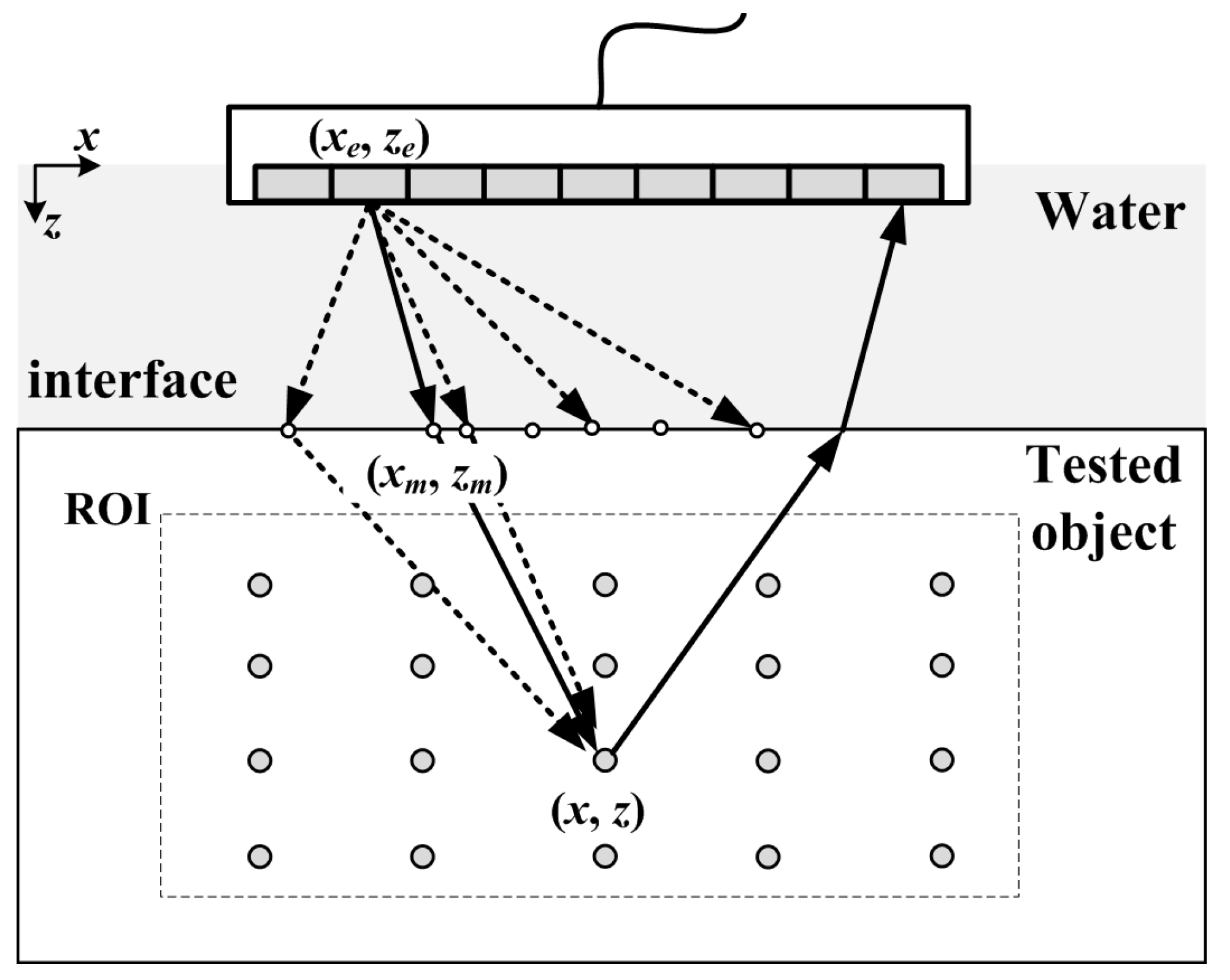
2.1. Total Focusing Method in the Layered Object
2.2. Phase Circular Statistics Vector Weighting Methodology
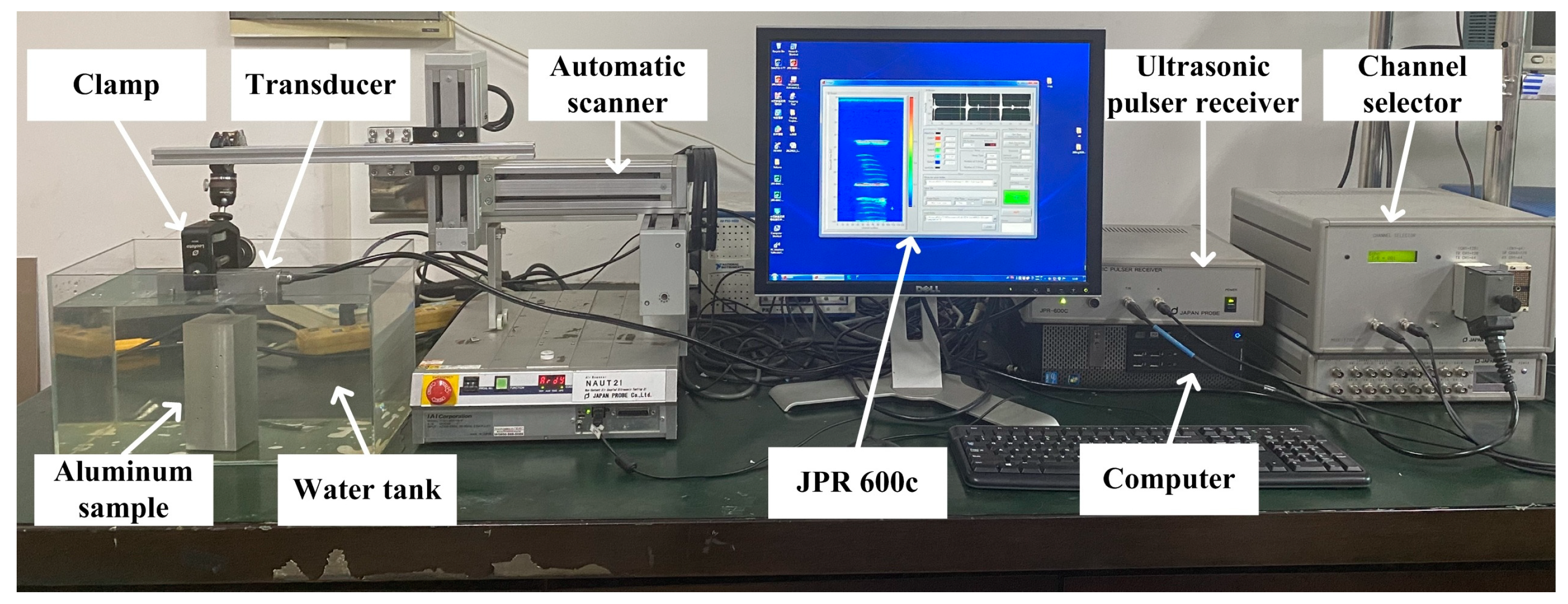
3. Experiments
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Consistency of the Phase Distribution
4.2. The TFM Imaging Results after Weighting by PCSV Factor
4.3. The Analysis of Image Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wuest, M.; Schwarz, M.; Eisenhart, J.; Nierla, M.; Rupitsch, S.J. A matched model-based synthetic aperture focusing technique for acoustic microscopy. NDT E Int. 2019, 104, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanekar, P.; Jothilakshmi, N.; Kumar, A.; Jayakumar, T. Characterization of planar flaws by an integrated approach using phased array and synthetic aperture focusing technique. Measurement 2019, 147, 106845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Wilcox, P.D. Post-processing of the full matrix of ultrasonic transmit–receive array data for non-destructive evaluation. NDT E Int. 2005, 38, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Cao, H.Q.; Luo, Z.B. Dijkstra’s algorithm-based ray tracing method for total focusing method imaging of CFRP laminates. Compos. Struct. 2019, 215, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Phased array ultrasonic imaging using angle beam virtual source full matrix capture-total focusing method. NDT E Int. 2020, 116, 102324. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.; Long, R.; Cawley, P.; Duxbury, D.J. Development and implementation of a membrane-coupled conformable array transducer for use in the nuclear industry. Insight-Non-Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2012, 54, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Wilcox, P.D. Efficient immersion imaging of components with nonplanar surfaces. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruza, J.F.; Camacho, J. Total Focusing Method with Virtual Sources in the Presence of Unknown Geometry Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, M.; Gachagan, A.; Mulholland, A.J.; Nordon, A.; Hegarty, M. Ultrasonic Array Imaging Through Reverberating Layers for Industrial Process Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Kobe, Japan, 22–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout, A.J.; Verschuur, D.J. Estimation of multiple scattering by iterative inversion, Part I: Theoretical considerations. Geophysics 1997, 62, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, L. Elimination of free-surface related multiples without need of the source wavelet. Geophysics 2001, 66, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groenestijn, G.J.A.; Verschuur, D.J. Estimation of primaries and near-offset reconstruction by sparse inversion: Marine data applications. Geophysics 2009, 74, R119–R128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ypma, F.H.C.; Verschuur, D.J. Estimating primaries by sparse inversion, a generalized approach. Geophys. Prospect. 2013, 61, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, J.W. Attenuation of complex water-bottom multiples by wave-equation-based prediction and subtraction. Geophysics 1988, 53, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, E.; Belfer; Keydar, S. Multiple attenuation in the parabolic τ-p domain using wavefront characteristics of multiple generating primaries. Lead. Edge 1999, 64, 1806. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, J.; Parrilla, M.; Fritsch, C. Phase coherence imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 56, 958–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Kanai, H. Effect of subaperture beamforming on phase coherence imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, J.; Brizuela, J.; Fritsch, C. Grain noise reduction by phase coherence imaging. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 1211, pp. 855–862. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, J.; Fritsch, C. Phase coherence imaging of grained materials. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, N.S.N.; Abdullah, M.Z. Sidelobe suppression featuring the phase coherence factor in 3-D through-the-wall radar imaging. Radioengineering 2016, 25, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H. Enhancing effect of phase coherence factor for improvement of spatial resolution in ultrasonic imaging. J. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverdy, F.; Le Ber, L.; Roy, O.; Benoist, G. Real-time Total Focusing Method on a portable unit, applications to hydrogen damage and other industrial cases. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2018), Gothenburg, Sweden, 11–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hanbury, A. Circular statistics applied to colour images. In 8th Computer Vision Winter Workshop; Citeseer: University Park, PA, USA, 2003; Volume 91, pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, D.; Kanji, G.K.; Gadsden, R.J. Analysis of variance for circular data. J. Appl. Stat. 2006, 13, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.; Kanji, G.K. The development of analysis of variance for circular data. J. Appl. Stat. 2006, 15, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewsey, A.; Neuhäuser, M.; Ruxton, G.D. Circular Statistics in R; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Kong, Q.; Ma, X.; Chen, M.; Lu, C. Circular statistics vector for improving coherent plane wave compounding image in Fourier domain. Ultrasonics 2023, 128, 106856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zeng, L.T.; Fan, G.P.; Zhang, H. Instantaneous Phase Coherence Imaging for Near-Field Defects by Ultrasonic Phased Array Inspection. Sensors 2020, 20, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela, J.; Camacho, J.; Cosarinsky, G.; Iriarte, J.M. Improving elevation resolution in phased-array inspections for NDT. NDT E Int. 2019, 101, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of elements to use | 32 |
| Element width | 0.9 mm |
| Element pitch | 1 mm |
| Center frequency | 5 MHz |
| Sampling frequency | 20 MHz |
| Excitation voltage | 100 V |
| Speed of sound in water | 1480 m/s |
| Speed of sound in aluminum | 6300 m/s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Xiong, Z.; Jing, Y.; He, X.; Kong, Q.; Chen, Y. Secondary Interface Echoes Suppression for Immersion Ultrasonic Imaging Based on Phase Circular Statistics Vector. Sensors 2023, 23, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031081
Chen M, Xiong Z, Jing Y, He X, Kong Q, Chen Y. Secondary Interface Echoes Suppression for Immersion Ultrasonic Imaging Based on Phase Circular Statistics Vector. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031081
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ming, Zhenghui Xiong, Yan Jing, Xi He, Qingru Kong, and Yao Chen. 2023. "Secondary Interface Echoes Suppression for Immersion Ultrasonic Imaging Based on Phase Circular Statistics Vector" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031081
APA StyleChen, M., Xiong, Z., Jing, Y., He, X., Kong, Q., & Chen, Y. (2023). Secondary Interface Echoes Suppression for Immersion Ultrasonic Imaging Based on Phase Circular Statistics Vector. Sensors, 23(3), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031081





