A Mantle Plume Beneath South China Revealed by Electrical Conductivity Obtained from Three-Dimensional Inversion of Geomagnetic Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. GDS Theory
2.2. L-BFGS Inversion
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Influence of the Ocean
3. Inversion Results and Stability
3.1. Electrical Conductivity Model
3.2. Robustness of Anomaly A
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torsvik, T.H.; Van Der Voo, R.; Doubrovine, P.V.; Burke, K.; Steinberger, B.; Ashwal, L.D.; Trønnes, R.G.; Webb, S.J.; Bull, A.L. Deep mantle structure as a reference frame for movements in and on the Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8735–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobolev, S.V.; Sobolev, A.V.; Kuzmin, D.V.; Krivolutskaya, N.A.; Petrunin, A.G.; Arndt, N.T.; Radko, V.A.; Vasiliev, Y.R. Linking Mantle Plumes, Large Igneous Provinces and Environmental Catastrophes. Nature 2011, 477, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koppers, A.A.P.; Becker, T.W.; Jackson, M.G.; Konrad, K.; Müller, R.D.; Romanowicz, B.; Steinberger, B.; Whittaker, J.M. Mantle Plumes and Their Role in Earth Processes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 382–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.W.; Romanowicz, B. Broad Plumes Rooted at the Base of the Earth’s Mantle beneath Major Hotspots. Nature 2015, 525, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D. Global Tomographic Images of Mantle Plumes and Subducting Slabs: Insight into Deep Earth Dynamics. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2004, 146, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, C.J.; Solomon, S.C.; Laske, G.; Collins, J.A.; Detrick, R.S.; Orcutt, J.A.; Bercovici, D.; Hauri, E.H. Mantle P-Wave Velocity Structure beneath the Hawaiian Hotspot. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 303, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kind, R.; Priestloy, K.; Sobolev, S.V.; Tilmann, F.; Yuar, X.; Weber, M. Mapping the Hawaiian Plume Conduit with Converted Seismic Waves. Nature 2000, 405, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D. Seismic Images under 60 Hotspots: Search for Mantle Plumes. Gondwana Res. 2007, 12, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhao, D.; Steinberger, B.; Wu, B.; Shen, F.; Li, Z. New Seismic Constraints on the Upper Mantle Structure of the Hainan Plume. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2009, 173, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Huang, H. Teleseismic Imaging of the Mantle beneath Southernmost China: New Insights into the Hainan Plume. Gondwana Res. 2016, 36, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.M.; Yang, T.; Gu, S. Upper Mantle and Transition Zone Structure beneath Leizhou-Hainan Region: Seismic Evidence for a Lower-Mantle Origin of the Hainan Plume. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.P.S. Wave Tomography of the Hainan and Surrounding Regions: Insight into the Hainan Plume. Tectonophysics 2014, 633, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.S.; Chen, Y.J. Seismic Evidence of the Hainan Mantle Plume by Receiver Function Analysis in Southern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 8978–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Tosi, N.; Chang, S.-J.; Xia, S.; Qiu, X. Receiver Function Imaging of the Mantle Transition Zone beneath the South China Block. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 16, 3666–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Lian, X.; Wang, X. Electrical Conductivity Evidence for the Existence of a Mantle Plume beneath Tarim Basin. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquart, G.; Schmeling, H.; Ito, G.; Schott, B. Conditions for Plumes to Penetrate the Mantle Phase Boundaries. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 5679–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, R.J. Geomagnetic Variations and the Electrical Conductivity of the Upper Mantle. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1969, 17, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grayver, A.V.; Munch, F.D.; Kuvshinov, A.V.; Khan, A.; Sabaka, T.J.; Tøffner-Clausen, L. Joint Inversion of Satellite-Detected Tidal and Magnetospheric Signals Constrains Electrical Conductivity and Water Content of the Upper Mantle and Transition Zone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6074–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munch, F.D.; Grayver, A.V.; Kuvshinov, A.; Khan, A. Stochastic Inversion of Geomagnetic Observatory Data Including Rigorous Treatment of the Ocean Induction Effect With Implications for Transition Zone Water Content and Thermal Structure. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeshima, M.; Schultz, A. Geoelectromagnetic Induction in a Heterogeneous Sphere: A New Three-Dimensional Forward Solver Using a Conservative Staggered-Grid Finite Difference Method. Geophys. J. Int. 2000, 140, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Weng, A.; Zhang, Y.; Schultz, A.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, Z. Evidence of Bermuda Hot and Wet Upwelling from Novel Three-Dimensional Global Mantle Electrical Conductivity Image. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2020, 21, e2020GC009016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelbert, A.; Egbert, G.D.; Schultz, A. Non-Linear Conjugate Gradient Inversion for Global EM Induction: Resolution Studies. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeev, D.; Avdeeva, A. 3D Magnetotelluric Inversion Using a Limited-Memory Quasi-Newton Optimization. Geophysics 2009, 74, F45–F57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Thomas, V.M., Resnick, S.I., Robinson, S.M., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 17, ISBN 0196-0202. [Google Scholar]
- Egbert, G.D.; Kelbert, A. Computational Recipes for Electromagnetic Inverse Problems. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 189, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chave, A.D.; Thomson, D.J. Bounded Influence Magnetotelluric Response Function Estimation. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 157, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.; Kuvshinov, A. Global 3-D Imaging of Mantle Conductivity Based on Inversion of Observatory C-Responses-II. Data Analysis and Results. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 965–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Kruglyakov, M.; Kuvshinov, A. A New Method for Accurate and Efficient Modeling of the Local Ocean Induction Effects. Application to Long-Period Responses from Island Geomagnetic Observatories. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Ren, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, K. A Multi-Resolution Finite-Element Approach for Global Electromagnetic Induction Modeling With Application to Southeast China Coastal Geomagnetic Observatory Studies. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kuvshinov, A.; Kruglyakov, M.; Munch, F.; Rafeal, R. Constraining the Crustal and Mantle Conductivity Structures Beneath Islands by a Joint Inversion of Multi-Source Magnetic Transfer Functions Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2023, 128, e2022JB024106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuvshinov, A.; Olsen, N. A Global Model of Mantle Conductivity Derived from 5 Years of CHAMP, Ørsted, and SAC-C Magnetic Data.Pdf. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, G.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.J. Three-Dimensional Conductivity Model of Crust and Uppermost Mantle at the Northern Trans North China Orogen: Evidence for a Mantle Source of Datong Volcanoes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 453, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.S.; Egbert, G.D. Electrical Conductivity Structure of Southeastern North America: Implications for Lithospheric Architecture and Appalachian Topographic Rejuvenation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 462, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egbert, G.D.; Yang, B.; Bedrosian, P.A.; Key, K.; Livelybrooks, D.W.; Schultz, A.; Kelbert, A.; Parris, B. Fluid Transport and Storage in the Cascadia Forearc Influenced by Overriding Plate Lithology. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuvshinov, A.V. Electromagnetic Induction in the Oceans and the Anomalous Behaviour of Coastal C-Responses for Periods up to 20 Days. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Khan, A.; Kuvshinov, A. Three-Dimensional Electrical Conductivity Structure beneath Australia from Inversion of Geomagnetic Observatory Data: Evidence for Lateral Variations in Transition-Zone Temperature, Water Content and Melt. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 1330–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Key, K.; Constable, S.; Liu, L.; Pommier, A. Electrical Image of Passive Mantle Upwelling beneath the Northern East Pacific Rise. Nature 2013, 495, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Manthilake, G.; Matsuzaki, T.; Katsura, T. Dry Mantle Transition Zone Inferred from the Conductivity of Wadsleyite and Ringwoodite. Nature 2008, 451, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karato, S.I. Water Distribution across the Mantle Transition Zone and Its Implications for Global Material Circulation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T. Laboratory Electrical Conductivity Measurement of Mantle Minerals. Surv. Geophys. 2010, 31, 163–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Santosh, M. Mantle Upwelling Beneath the Cathaysia Block, South China. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2020TC006447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litasov, K.D.; Ohtani, E.; Sano, A.; Suzuki, A.; Funakoshi, K. Wet Subduction versus Cold Subduction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shankland, T.J.; Poe, B.T. Laboratory-Based Electrical Conductivity in the Earth’s Mantle. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 27865–27875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercovici, D.; Karato, S.-I. Whole-Mantle Convection and the Transition-Zone Water Filter. Nature 2003, 425, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschmann, M.M. Water, Melting, and the Deep Earth H2O Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006, 34, 629–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardés, E.; Gaillard, F.; Tarits, P. Toward a Unified Hydrous Olivine Electrical Conductivity Law. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 4984–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maguire, R.; Ritsema, J.; Bonnin, M.; van Keken, P.E.; Goes, S. Evaluating the Resolution of Deep Mantle Plumes in Teleseismic Traveltime Tomography. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, D. High-Resolution Mantle Tomography of China and Surrounding Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, D. Intraplate Volcanism and Mantle Dynamics of Mainland China: New Constraints from Shear-Wave Tomography. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 188, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, G.; Zhao, D.; Kurata, K. Whole-Mantle Tomography of Southeast Asia: New Insight Into Plumes and Slabs. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
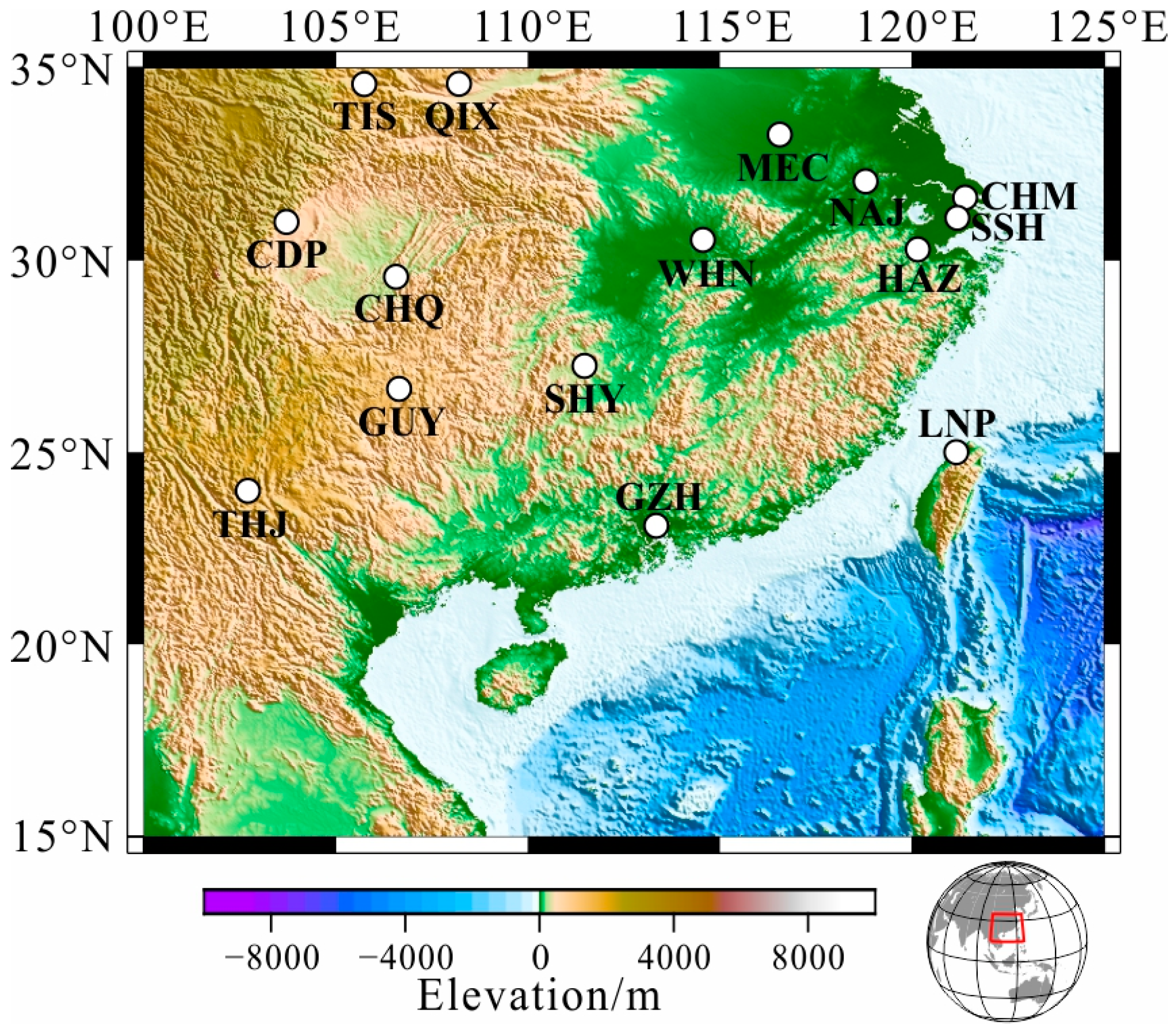










| Code | Name | Longitude | Latitude | Gm_Long | Gm_Lat | Data Length | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDP | Chengdu | 103.7 | 31 | 176.11 | 20.89 | 1995–2017 | WDC |
| CHM | Chongming | 121.4 | 31.63 | 192.14 | 21.74 | 1995–2016 | GNC |
| CHQ | Chongqing | 106.56 | 29.57 | 178.72 | 19.44 | 1995–2001 | GNC |
| GUY | Guiyang | 106.64 | 26.65 | 178.78 | 16.52 | 1995–2013 | GNC |
| GZH | Guangzhou | 113.34 | 23.09 | 184.91 | 12.99 | 1960–2017 | WDC |
| HAZ | Hangzhou | 120.16 | 30.28 | 191.06 | 20.35 | 1995–2001 | GNC |
| LNP | Lunping | 121.17 | 25 | 192.22 | 15.11 | 1980–2000 | WDC |
| MEC | Mengcheng | 116.56 | 33.27 | 187.66 | 23.23 | 1995–2001 | GNC |
| NAJ | Nanjing | 118.8 | 32.06 | 189.74 | 22.09 | 1995–2001 | GNC |
| QIX | Qianxian | 108.2 | 34.6 | 180.05 | 24.46 | 1995–2015 | WDC |
| SHY | Shaoyang | 111.47 | 27.24 | 183.1 | 17.13 | 1995–2016 | GNC |
| SSH | Sheshan | 121.19 | 31.1 | 191.97 | 21.2 | 1932–2006 | WDC |
| THJ | Tonghai | 102.7 | 24 | 175.07 | 13.91 | 1995–2017 | WDC |
| TIS | Tianshui | 105.73 | 34.59 | 178 | 24.46 | 1995–2001 | GNC |
| WHN | Wuhan | 114.56 | 30.53 | 185.9 | 20.45 | 1995–2017 | WDC |
| Mineral | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wadsleyite | 399 (311) | 1.49 (10) | 7.74 (4.08) | 0.68 (3) | 0.02 (2) |
| Ringwoodite | 838 (442) | 1.36 (5) | 27.7 (9.6) | 1.12 (3) | 0.67 (3) |
| α | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 239 46 | 5.07 1.32 | 144 16 | 2.34 0.67 | 89 9 | −1.37 0.45 | 1.79 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. A Mantle Plume Beneath South China Revealed by Electrical Conductivity Obtained from Three-Dimensional Inversion of Geomagnetic Data. Sensors 2023, 23, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031249
Li S, Liu Y, Li J. A Mantle Plume Beneath South China Revealed by Electrical Conductivity Obtained from Three-Dimensional Inversion of Geomagnetic Data. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031249
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shiwen, Yunhe Liu, and Jianping Li. 2023. "A Mantle Plume Beneath South China Revealed by Electrical Conductivity Obtained from Three-Dimensional Inversion of Geomagnetic Data" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031249
APA StyleLi, S., Liu, Y., & Li, J. (2023). A Mantle Plume Beneath South China Revealed by Electrical Conductivity Obtained from Three-Dimensional Inversion of Geomagnetic Data. Sensors, 23(3), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031249








