Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control of DC-DC Cuk Converter for Low-Cost Industrial Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
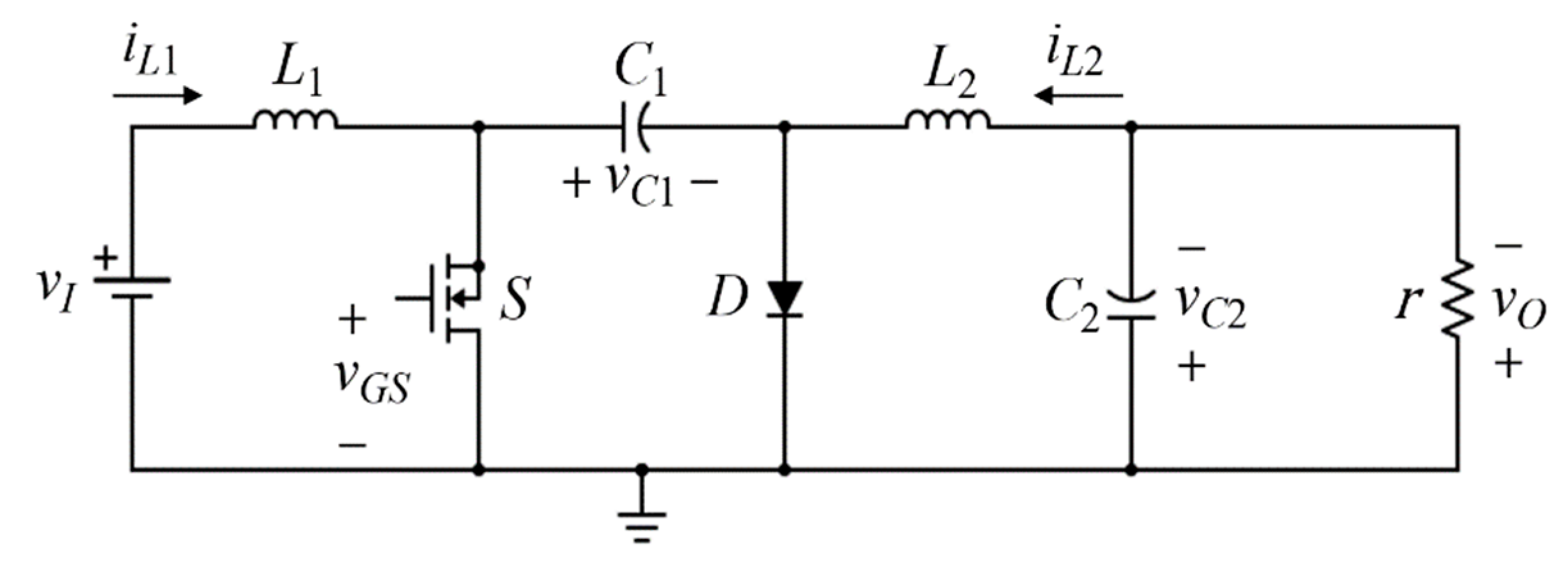
2. Modeling of DC-DC Cuk Converter
2.1. Ideal Switched Model
2.2. Control-Oriented Model
3. Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control Design
3.1. Derivation of Equivalent Control Law
3.2. Existence and Stability Conditions
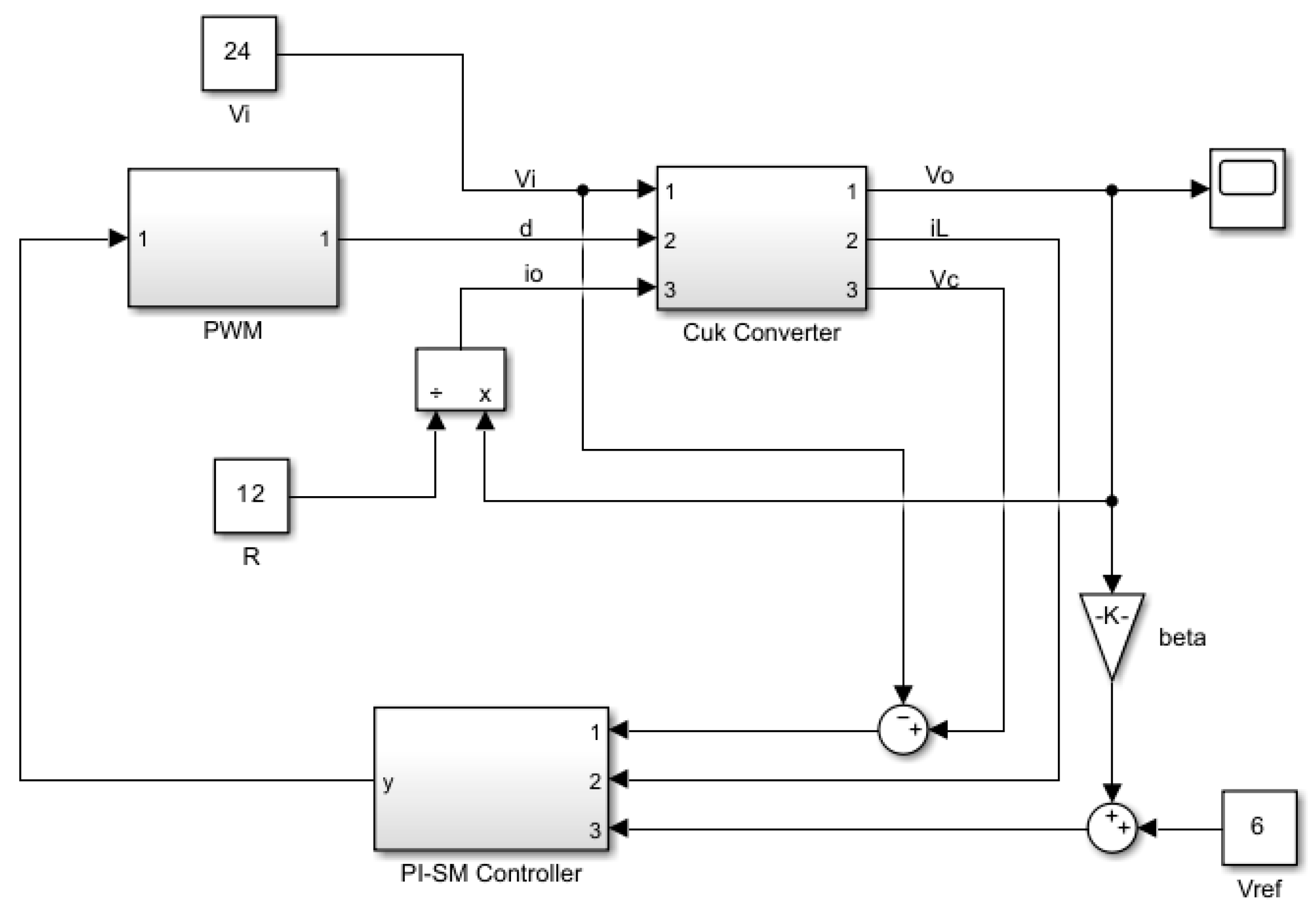
4. Realization of Simplified Current-Mode Control Circuit
- Voltage sensor gain : The desired output voltage in this research is 36 V. Hence, if the reference voltage is set to 6 V, then the voltage sensor gain .
- Summing and inverting op-amps: The resistors , , , and for the summing op-amp, and and for the inverting op-amp, can be set to 5.1 kΩ.
- Pulse-width modulator: The peak ramp voltage and the switching frequency of the pulse-width modulator are chosen to be 6 V and 200 kHz, respectively.
- Proportional gain: As detailed in [24], the proportional gain of the PI compensator in the analog control circuit is defined as . Thus, if the gain is set to 1, as in (23), then the resistors and are 5.1 kΩ.
- Integral gain: According to [24], the integral gain is . Since the gain and the resistor are chosen to be 170 and 5.1 kΩ, respectively, the capacitor C is 5.6 µF.
- Input inductor gain: The gain of the input inductor . If the gain value is set to 0.4 and the resistor is 10 kΩ, then the value of the resistor is 4 kΩ.
- Differential amplifier: The resistors and of the differential amplifier in the control circuit are set to 10 kΩ.
5. Framework of Developing Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control Circuit
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Steady-State Performance
6.2. Large Disturbance Rejection Capability
6.3. Comparison with Classical Sliding-Mode Current Controller
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, S.C.; Lai, Y.M.; Tse, C.K. Sliding Mode Control of Switching Power Converters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Baidhani, H.; Salvatierra, T.; Ordonez, R.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Simplified nonlinear voltage-mode control of PWM DC-DC buck converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers 2021, 36, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kashif, S.A.R.; Ain, N.U.; Rasool, A.; Shahid, M.S.; Padmanaban, S.; Ozsoy, E.; Saqib, M.A. Mitigation of Complex Non-Linear Dynamic Effects in Multiple Output Cascaded DC-DC Converters. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54602–54612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.; Holliday, D.; Ahmed, S.; Massoud, A.M.; Williams, B.W. A Single-Stage Three-Phase Inverter Based on Cuk Converters for PV Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2014, 2, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.S.; Berzoy, A.; Mohammed, O.A. Design and Hardware Implementation of FL-MPPT Control of PV Systems Based on GA and Small-Signal Analysis. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.L.; Avalos, J.L.B.; Espinoza, C.A.B. Passivity-Based Controller and Online Algebraic Estimation of the Load Parameter of the DC-to-DC power converter Cuk Type. IEEE Latin Am. Trans. 2011, 9, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Namazi, M.M.; Li, T.; Ortega, R. A State Observer for Sensorless Control of Power Converters with Unknown Load Conductance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 9187–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Lai, J.S.; Kim, M. Down-Sampled Repetitive Controller for Grid-Connected Cuk CCM Inverter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2022, 10, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusair, K.; Alasali, F.; Holderbaum, W.; Vinayagam, A.; Aziz, A. High Hybrid Power Converter Performance Using Modern-Optimization-Methods Based PWM Strategy. Electronics 2022, 11, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Padmanaban, S.; Azam, F. An Ant Colony Optimized MPPT for Standalone Hybrid PV-Wind Power System with Single Cuk Converter. Energies 2019, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seguel, J.L.; Seleme, S.I., Jr.; Morais, L.M.F. Comparative Study of Buck-Boost, SEPIC, Cuk and Zeta DC-DC Converters Using Different MPPT Methods for Photovoltaic Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, M.; Elavarasu, R.; Ramesh, P.; Bharatiraja, C.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Mitolo, M. A Hybridization of Cuk and Boost Converter Using Single Switch with Higher Voltage Gain Compatibility. Energies 2020, 13, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, J.; Chen, W.; Yu, L.; Jin, X. Commutation Torque Reduction Strategy of Brushless DC Motor Based on Single-Input Dual-Output Cuk Converter. Machines 2022, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Gao, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control for DC/DC Buck Converters with Mismatched Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, X.; Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Alcaide, A.M.; Wu, L.; Franquelo, L.G. Fuzzy Sliding-Mode Control for Three-Level NPC AFE Rectifiers: A Chattering Alleviation Approach. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 11704–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shen, X.; Alcaide, A.M.; Yin, Y.; Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Wu, L.; Franquelo, L.G. Sliding Mode Control of Grid-Connected Neutral-Point-Clamped Converters Via High-Gain Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, J.; Nasiri, M.R.; Agah, A.; Emadi, A. Application of neural networks and State-space averaging to DC/DC PWM converters in sliding-mode operation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2005, 10, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. PI and Sliding Mode Control of a Cuk Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3695–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Hote, Y.V.; Garg, M.M. Comments on PI and Sliding Mode Control of a Cuk Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1551–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesani, L.; Spiazzi, R.G.; Tenti, P. Performance Optimization of Cuk Converters by Sliding-Mode Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1995, 10, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baidhani, H.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Simplified Double-Integral Sliding-Mode Control of PWM DC-AC Converter with Constant Switching Frequency. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Lai, Y.M. Constant-Frequency Reduced-State Sliding Mode Current Controller for Cuk Converters. IET Power Electron. 2008, 1, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baidhani, H. Design and Implementation of Simplified Sliding-Mode Control of PWM DC-DC Converters for CCM. Ph.D. Thesis, Wright State University, Dayton, OH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierczuk, M.K. Pulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Power Converters, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Baidhani, H.; Kazimierczuk, M.K.; Reatti, A. Modeling and Control of Bridgeless Single-Switch Non-Inverting AC-DC Cuk Converter in DCM. In Proceedings of the IECON 2022—48th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Brussels, Belgium, 17–20 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]







| Control Method | Advantages | Drawbacks | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy logic-based control |
|
| [5,11] |
| Passivity-based control | [6] | ||
| State observer-based control |
|
| [7] |
| Repetitive control |
|
| [8] |
| Modern optimization control |
|
| [9] |
| Ant colony-based control |
|
| [10] |
| Neural network-based SMC |
|
| [17] |
| Proportional-integral SMC |
|
| [18,19] |
| Hysteresis-modulated SMC |
|
| [20] |
| PWM double-integral SMC |
|
| [22] |
| Description | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Input inductance | 400 µH | |
| Internal resistance of | 0.12 Ω | |
| Output inductance | 200 µH | |
| Internal resistance of | 0.12 Ω | |
| Energy transfer capacitance | 2200 µF | |
| ESR of | 25 mΩ | |
| Output filter capacitance | 230 µF | |
| ESR of | 25 mΩ | |
| Input voltage | 24 V | |
| Output voltage | 36 V | |
| Load resistance | (12–48) Ω | |
| Switching frequency | 200 kHz |
| Line/Load Disturbance | Percentage Peak Overshoot/Undershoot (%) | Settling Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.8 | 15 | |
| 2.8 | 15 | |
| 5.6 | 20 | |
| 5.6 | 20 |
| Control Method | Required Sensors | PI Compensators | Characteristics during Load Disturbance | Characteristics during Line Disturbance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical DI-SMC | vO, vI, iL1, vC1, iC2 | Dual | PO = 3%, ts = 22 ms | PO = 5.6%, ts = 22 ms |
| Simplified DI-SMC | vO, vI, iL1, vC1 | Single | PO = 2.8%, ts = 15 ms | PO = 5.6%, ts = 20 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Baidhani, H.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control of DC-DC Cuk Converter for Low-Cost Industrial Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031462
Al-Baidhani H, Kazimierczuk MK. Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control of DC-DC Cuk Converter for Low-Cost Industrial Applications. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031462
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Baidhani, Humam, and Marian K. Kazimierczuk. 2023. "Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control of DC-DC Cuk Converter for Low-Cost Industrial Applications" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031462
APA StyleAl-Baidhani, H., & Kazimierczuk, M. K. (2023). Simplified Nonlinear Current-Mode Control of DC-DC Cuk Converter for Low-Cost Industrial Applications. Sensors, 23(3), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031462







