Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
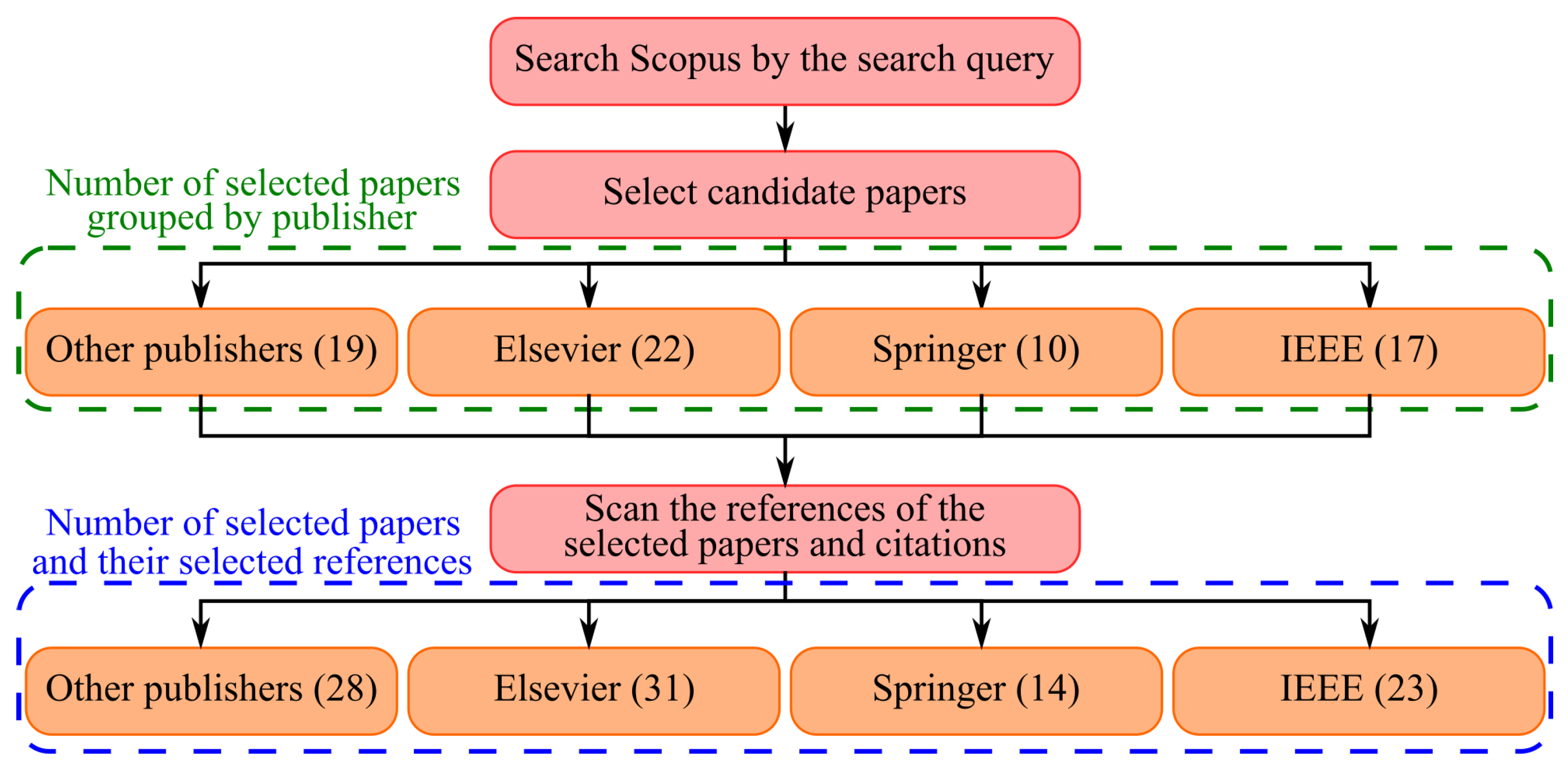
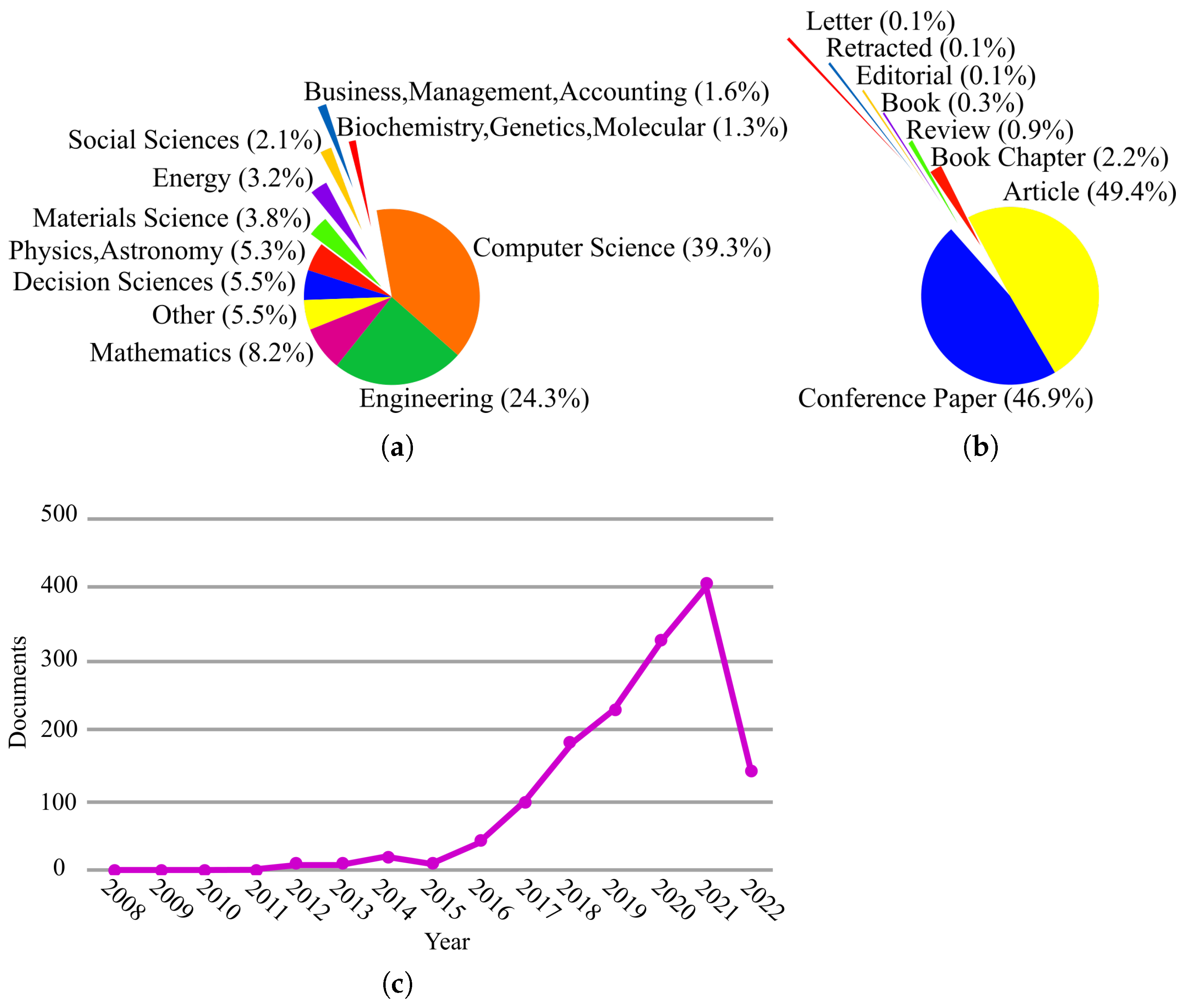
1.1. Search Strategy
1.2. Contributions
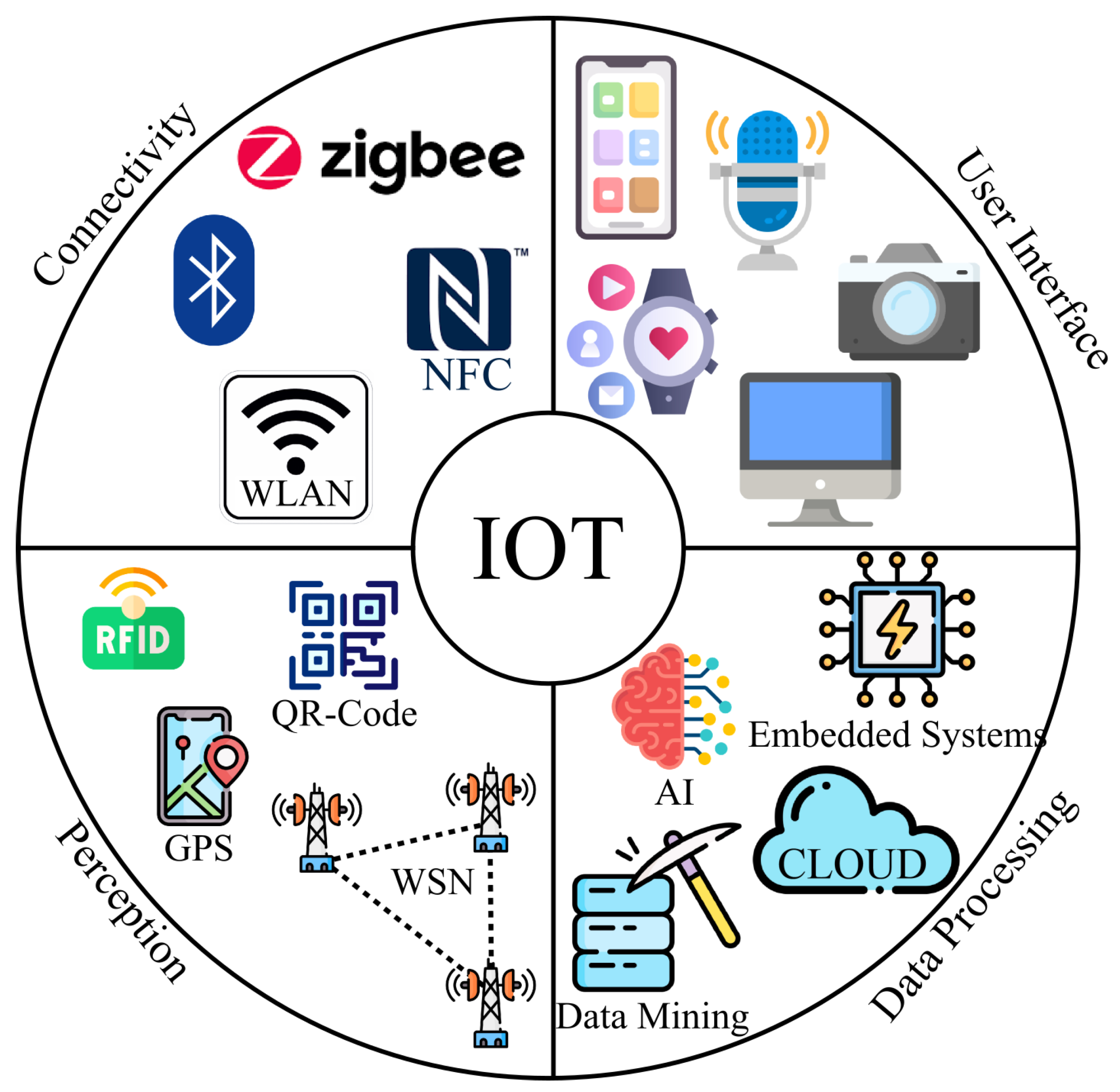
2. IoT Overview
2.1. IoT Prerequisite
2.1.1. Wireless Sensor Network
2.1.2. WSN Routing Protocols
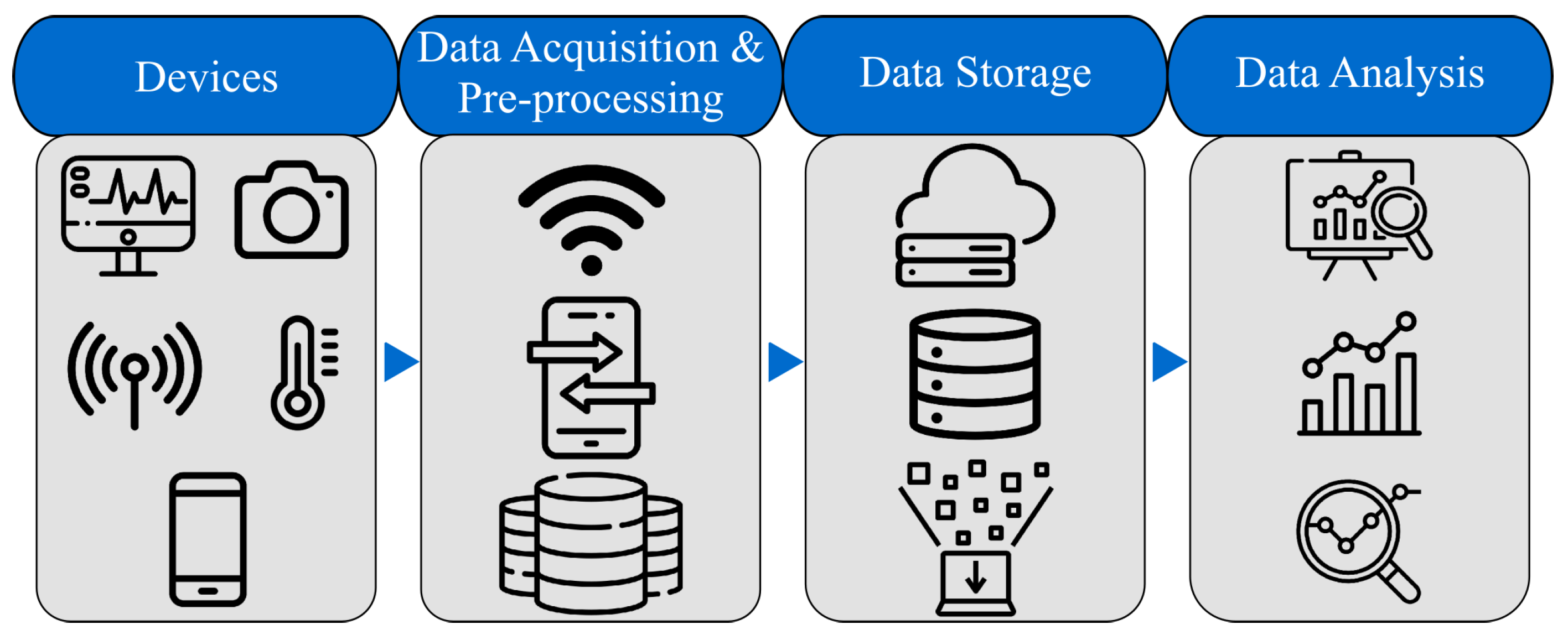
2.2. IoMT Overview
Benefits
- Improved drug management
- Decreased treatment cost
- Enhanced patient experience
- Improved patient outcome
- Improved diagnosis and treatment
- Remote monitoring of chronic diseases
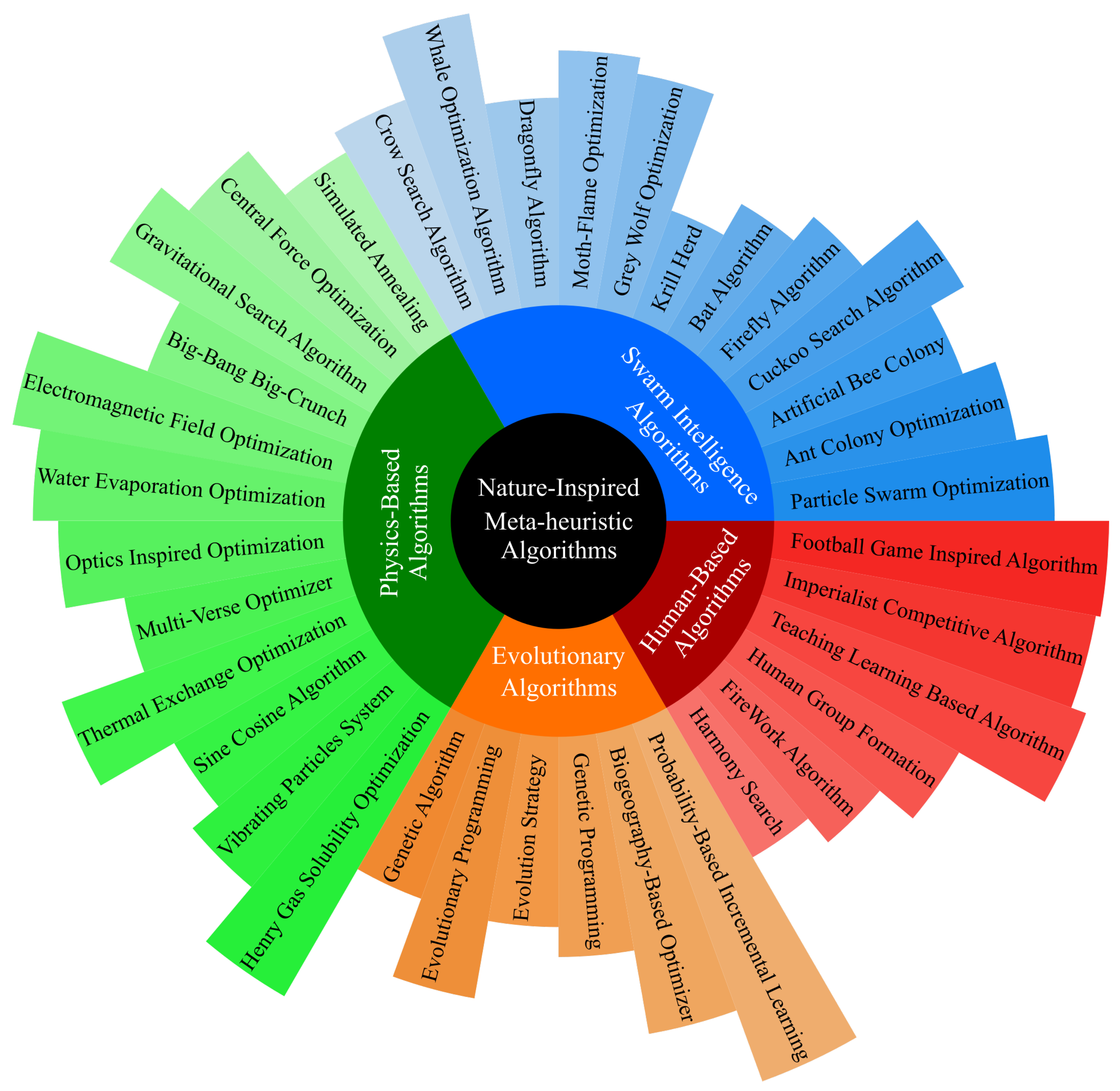
3. SI Algorithms
4. Application of SI in IoT/IoMT
4.1. PSO in IoT/IoMT
4.2. ACO in IoT/IoMT
4.3. ABC in IoT/IoMT
4.4. Other SI Algorithms in IoT/IoMT
5. Current and Future Trends
5.1. Current Trends on Using SI Methods in IoT/IoMT
5.2. SI Challenges in IoT/IoMT
5.3. Future Trends
5.4. Future Trends in IoMT
5.4.1. Preserving Patient Safety
5.4.2. Supporting Connectivity in Critical Situations
5.4.3. Dynamic Routing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IoT | Internet of things |
| SI | Swarm intelligence |
| IoMT | Internet of medical things |
| WSN | Wireless sensor networks |
| RFID | Radio-frequency-identification devices |
| PSO | Particle-swarm optimization |
| ACO | Ant-colony optimization |
| ABC | Artificial bee colony |
| SIoT | Social internet of things |
| SoA | Service-oriented architecture |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ML | Machine learning |
| DL | Deep learning |
| GPS | Global positioning system |
| CH | Cluster head |
| BS | Base station |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| GNP | Genetic network programming |
| BOA | Butterfly optimization algorithm |
| GW | Grey wolf optimizer |
| HDPSO | Hybrid dimensionality-based PSO |
| VM | Virtual machine |
| MOPSO | Multi-objective PSO |
| CI | Computational intelligence |
| GO | Grasshopper optimization |
| FL | Fuzzy logic |
| ANFIS | Adaptive dynamic network-based fuzzy inference system |
| TSP | Traveling sales man |
| VANET | Vehicular ad hoc network |
| DE | Differential evolution |
| MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| WOA | Whale optimization algorithm |
| GSO | Gravitational search optimization |
| RBN | Reflection-belief network |
| QRW | Quantum random walk |
| BROA | Brainstorming optimization algorithm |
| BIM | Bio-inspired method |
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
References
- Nahavandi, D.; Alizadehsani, R.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, U.R. Application of artificial intelligence in wearable devices: Opportunities and challenges. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 213, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotomayor, M.; Pérez-Castrillo, J.D.; Castiglione, F. Complex Social and Behavioral Systems: Game Theory and Agent-Based Models; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fister Jr, I.; Yang, X.S.; Fister, I.; Brest, J.; Fister, D. A brief review of nature-inspired algorithms for optimization. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1307.4186. [Google Scholar]
- Boveiri, H.R.; Khayami, R.; Elhoseny, M.; Gunasekaran, M. An efficient Swarm-Intelligence approach for task scheduling in cloud-based internet of things applications. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019, 10, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedadra, O.; Guerrieri, A.; Jouandeau, N.; Spezzano, G.; Seridi, H.; Fortino, G. Swarm intelligence and IoT-based smart cities: A review. In The Internet of Things for Smart Urban Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 177–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Tang, M.; Zhang, L.; Huo, Z.; Shu, L. A survey of using swarm intelligence algorithms in IoT. Sensors 2020, 20, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kabir, H.D.; Khosravi, A.; Mondal, S.K.; Rahman, M.; Nahavandi, S.; Buyya, R. Uncertainty-aware decisions in cloud computing: Foundations and future directions. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.D.; Sabyasachi, A.S.; Khosravi, A.; Hosen, M.A.; Nahavandi, S.; Buyya, R. A cloud bidding framework for deadline constrained jobs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, Australia, 13–15 February 2019; pp. 765–772. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Di Caro, G.A.; Farooq, M. Swarm intelligence based routing protocol for wireless sensor networks: Survey and future directions. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 4597–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, S.; Parra, L.; Lloret, J.; Khan, S. Systems and algorithms for wireless sensor networks based on animal and natural behavior. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2015, 11, 625972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedadra, O.; Guerrieri, A.; Jouandeau, N.; Spezzano, G.; Seridi, H.; Fortino, G. Swarm intelligence-based algorithms within IoT-based systems: A review. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2018, 122, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. ant-colony optimization: Overview and recent advances. In Handbook of Metaheuristics; Springer: Berling, Germany, 2019; pp. 311–351. [Google Scholar]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahouma, K.H.; Aly, R.H.; Hamed, H.F. Challenges and Solutions of Using the Social Internet of Things in Healthcare and Medical Solutions—A Survey. In Toward Social Internet of Things (SIoT): Enabling Technologies, Architectures and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, S.S.; Hassan, W.H.; Latiff, L.A.; Ghabban, F. A systematic review of security and privacy issues in the internet of medical things; the role of machine learning approaches. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rbah, Y.; Mahfoudi, M.; Balboul, Y.; Fattah, M.; Mazer, S.; Elbekkali, M.; Bernoussi, B. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods for Intrusion Detection Systems in IoMT: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), Meknes, Morocco, 3–4 March 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Si-Ahmed, A.; Al-Garadi, M.A.; Boustia, N. Survey of Machine Learning Based Intrusion Detection Methods for Internet of Medical Things. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.09657. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, A.; Curry, E. A survey on object detection for the internet of multimedia things (IoMT) using deep learning and event-based middleware: Approaches, challenges, and future directions. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 106, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madakam, S.; Lake, V.; Lake, V.; Lake, V. Internet of Things (IoT): A literature review. J. Comput. Commun. 2015, 3, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghavendra, C.S.; Sivalingam, K.M.; Znati, T. Wireless Sensor Networks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yick, J.; Mukherjee, B.; Ghosal, D. Wireless sensor network survey. Comput. Netw. 2008, 52, 2292–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, P.S.; Singh, S. Energy-efficient hierarchical routing for wireless sensor networks: A swarm intelligence approach. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 92, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasymov, O. Internet of Things in Healthcare. 2020. Available online: https://codeit.us/blog/internet-of-things-in-healthcare (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Al-Turjman, F.; Nawaz, M.H.; Ulusar, U.D. Intelligence in the Internet of Medical Things era: A systematic review of current and future trends. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How the Internet of Things is Transforming the Health Industry. 2020. Available online: https://www.cr-t.com/blog/how-the-internet-of-things-is-transforming-the-health-industry/ (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Dunn, J.; Runge, R.; Snyder, M. Wearables and the medical revolution. Pers. Med. 2018, 15, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comstock, J. Amiko Raises Undisclosed Round to Support Smart Inhaler Platform. 2018. Available online: https://www.mobihealthnews.com/content/amiko-raises-undisclosed-round-support-smart-inhaler-platform (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Haughey, J.; Taylor, K.; Dohrmann, M.; Snyder, G. Medtech and the Internet of Medical Things: How Connected Medical Devices Are Transforming Health Care. Deloitte. 2018. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/life-sciences-and-health-care/articles/medtech-internet-of-medical-things.html (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Kakhi, K.; Alizadehsani, R.; Kabir, H.D.; Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S.; Acharya, U.R. The internet of medical things and artificial intelligence: Trends, challenges, and opportunities. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 42, 749–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razdan, S.; Sharma, S. Internet of medical things (IoMT): Overview, emerging technologies, and case studies. IETE Tech. Rev. 2022, 39, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraihi, Y.; Gabis, A.B.; Ramdane-Cherif, A.; Acheli, D. A comprehensive survey of Crow Search Algorithm and its applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 2669–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J. Handbook of nature-inspired and innovative computing. In Swarm intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 187–219. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant-colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2006, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- AbdelAziz, A.M.; Ghany, K.K.A.; Soliman, T.H.A.; Sewisy, A.A.E.M. A parallel multi-objective swarm intelligence framework for Big Data analysis. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2020, 63, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, Z.M.; Akbari, R.; Shokouhifar, M.; Safaei, F.; Jalali, A. Swarm intelligence based fuzzy routing protocol for clustered wireless sensor networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 55, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passino, K.M. Bacterial foraging optimization. Int. J. Swarm Intell. Res. (IJSIR) 2010, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L. An optimizing method based on autonomous animats: Fish-swarm algorithm. Syst.-Eng.-Theory Pract. 2002, 22, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Stochastic Algorithms, Sapporo, Japan, 26–28 October 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S.; He, X. Firefly algorithm: Recent advances and applications. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1308.3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.; Qiao, P. Pigeon-inspired optimization: A new swarm intelligence optimizer for air robot path planning. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 2014, 7, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, S. Butterfly optimization algorithm: A novel approach for global optimization. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Vanoye, J.A.; Díaz-Parra, O.; Cocón, F.; Soto, A.; Arias, M.D.L.Á.B.; Verduzco-Reyes, G.; Alberto-Lira, R. Meta-heuristics algorithms based on the grouping of animals by social behavior for the traveling salesman problem. Int. J. Comb. Optim. Probl. Inform. 2012, 3, 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, B.C.; Baskaran, R. A survey: Ant-colony optimization based recent research and implementation on several engineering domain. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 4618–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Niu, P.; Xiao, X. Development and investigation of efficient artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2012, 12, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Anandan, P. A multi objective Tabu particle swarm optimization for effective cluster-head selection in WSN. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 12275–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, B.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S. Particle swarm optimization based clustering algorithm with mobile sink for WSNs. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.Z.; Al-Turjman, F. Optimizing multipath routing with guaranteed fault tolerance in Internet of Things. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 6463–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ju, C.; Gao, Y.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Kim, G.J. A PSO based energy efficient coverage control algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2018, 56, 433–446. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, W.C.; Liu, B.H.; Tsai, M.J. Constructing a wireless sensor network to fully cover critical grids by deploying minimum sensors on grid points is NP-complete. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2007, 56, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Kim, H.J. An improved routing schema with special clustering using PSO algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor network. Sensors 2019, 19, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.; Jana, P.K.; Banka, H. A particle swarm optimization based energy efficient cluster head selection algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 2017, 23, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Xiang, W. Clustering hierarchy protocol in wireless sensor networks using an improved PSO algorithm. IEEE Access 2016, 5, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, N.T.; Hai, D.T.; Son, L.H.; Vinh, L.T. Improving lifetime and network connections of 3D wireless sensor networks based on fuzzy clustering and particle swarm optimization. Wirel. Netw. 2018, 24, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguraman, P.; Ramasundaram, M.; Balakrishnan, V. Localization in wireless sensor networks: A dimension based pruning approach in 3D environments. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 68, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshkumar, K.; Suresh, R.; Mohanasundaram, K. Discrete particle swarm optimization (DPSO) algorithm for permutation flowshop scheduling to minimize makespan. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Computation, Guiyang, China, 24–26 July 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 572–581. [Google Scholar]
- Kashan, A.H.; Karimi, B. A Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Scheduling Parallel Machines. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhoseny, M.; Abdelaziz, A.; Salama, A.S.; Riad, A.M.; Muhammad, K.; Sangaiah, A.K. A hybrid model of internet of things and cloud computing to manage big data in health services applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 86, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.W.; Wu, J.M.T.; Fournier-Viger, P.; Djenouri, Y.; Chen, C.H.; Zhang, Y. A sanitization approach to secure shared data in an IoT environment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 25359–25368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumrai, T.; Ota, K.; Dong, M.; Kishigami, J.; Sung, D.K. Multiobjective optimization in cloud brokering systems for connected Internet of Things. IEEE Int. Things J. 2016, 4, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banyal, S.; Mehra, D.; Banyal, S.; Sharma, D.K.; Ghosh, U. Computational Intelligence in Healthcare with Special Emphasis on Bioinformatics and Internet of Medical Things. In Intelligent Internet of Things for Healthcare and Industry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 145–170. [Google Scholar]
- Bharti, V.; Biswas, B.; Shukla, K.K. A novel multiobjective gdwcn-pso algorithm and its application to medical data security. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. (TOIT) 2021, 21, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, K.; Mandal, B.; Dutta, P.; Mandal, J.K.; Dam, S. A genetic algorithm (ga) based load balancing strategy for cloud computing. Procedia Technol. 2013, 10, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elhoseny, M.; Shankar, K.; Lakshmanaprabu, S.; Maseleno, A.; Arunkumar, N. Hybrid optimization with cryptography encryption for medical image security in Internet of Things. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 10979–10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.Z.; Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I. Grasshopper optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turabieh, H.; Mafarja, M.; Mirjalili, S. Dynamic adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (D-ANFIS) for the imputation of missing data for Internet of medical Things applications. IEEE Int. Things J. 2019, 6, 9316–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, D. EACO and FABC to multi-path data transmission in wireless sensor networks. IET Commun. 2017, 11, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Sherratt, R.S.; Park, J.H. An improved ant-colony optimization-based approach with mobile sink for wireless sensor networks. J. Supercomput. 2018, 74, 6633–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajjar, S.; Sarkar, M.; Dasgupta, K. FAMACROW: Fuzzy and ant-colony optimization based combined mac, routing, and unequal clustering cross-layer protocol for wireless sensor networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 43, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrioui, S.; Lorenz, P. Bio inspired routing algorithm and efficient communications within IoT. IEEE Netw. 2017, 31, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Hao, B.; Li, J. A survey on routing protocols for large-scale wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2011, 11, 3498–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, V.; Paulo, M.A.; Cespedes, J.G.; Nascimento, M.C. Enhancing the reliability on data delivery and energy efficiency by combining swarm intelligence and community detection in large-scale WSNs. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 78, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Dong, W.; Chen, Y. An improved routing algorithm based on ant-colony optimization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, G. Secure routing protocol based on multi-objective ant-colony-optimization for wireless sensor networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 77, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deif, D.S.; Gadallah, Y. An ant-colony optimization approach for the deployment of reliable wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 10744–10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrazgan, M. Internet of medical things and edge computing for improving healthcare in smart cities. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5776954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, H.; Arfaoui, N.; Mashhour, Y.A.; Akaichi, J. Ambulance Fastest Path Using ant-colony optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and Services, Gold Coast, Australia, 20–22 May 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 400–409. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, P.; Kaur, J. ant-colony optimization based routing in IoT for healthcare services. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 1155–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Shokouhifar, M.; Jalali, A. Optimized sugeno fuzzy clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 60, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, P.S.; Singh, S. Improved metaheuristic based energy-efficient clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 57, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Gu, C. A micro-artificial bee colony based multicast routing in vehicular ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2017, 58, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.L.; Gomes, D.; Silva, F.A.; Endo, P.T.; Lynn, T. Maximising the availability of an internet of medical things system using surrogate models and nature-inspired approaches. Int. J. Grid Util. Comput. 2022, 13, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Soosai Anandaraj, A.; Gomathy, V.; Amali Angel Punitha, A.; Abitha Kumari, D.; Sheeba Rani, S.; Sureshkumar, S. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Enabled Skin Lesion Detection and Classification Using Optimal Segmentation and Restricted Boltzmann Machines. In Cognitive Internet of Medical Things for Smart Healthcare; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 195–209. [Google Scholar]
- El-shafeiy, E.; Sallam, K.M.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Abohany, A.A. A clustering based Swarm Intelligence optimization technique for the Internet of Medical Things. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 173, 114648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo, D.; Amaro, F.; Hruschka, E.R., Jr.; Costa, A.S.d.M. Ward2icu: A vital signs dataset of inpatients from the general ward. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.00752. [Google Scholar]
- ME, A.T.; ME, J.J.S.; Priya, A.K.; Maarlin, R.; Harinetha, M. Energy aware heuristic approach for cluster-head selection in wireless sensor networks. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2017, 6, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, S. Node localization in wireless sensor networks using butterfly optimization algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 3325–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, A.; Tesfayohani, M.; Shandilya, S.K.; Goyal, S.; Shaukat Jamal, S.; Shukla, P.K.; Bedi, P.; Albeedan, M. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and Reflective Belief Design-Based Big Data Analytics with Convolution Neural Network-Metaheuristic Optimization Procedure (CNN-MOP). Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2898061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, M. Energy-aware task scheduling using hybrid firefly-bat (ffabat) in big data. Cybern Inf. Technol. 2018, 18, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.S.; Slowik, A. Firefly algorithm. In Swarm Intelligence Algorithms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S. Bat algorithm: Literature review and applications. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1308.3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Ilango, P. Energy aware task scheduling using hybrid firefly-GA in big data. Int. J. Adv. Intell. Paradig. 2020, 16, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, L.; Fong, S.; Xu, Q.; Wen, T.; Liu, Z. Comparative research of swarm intelligence clustering algorithms for analyzing medical data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 137560–137569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabioun, R. Cuckoo optimization algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 5508–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogananda, P.; Babu, L.A.; Giri, A.A. Oppositional butterfly optimization algorithm with multilayer perceptron for medical data classification. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 2021, 12, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Huang, H.; Yu, X. A multi-watermarking scheme for verifying medical image integrity and authenticity in the Internet of Medical Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8885–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Brain storm optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference in Swarm Intelligence, Chongqing, China, 12–15 June 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Awotunde, J.B.; Abiodun, K.M.; Adeniyi, E.A.; Folorunso, S.O.; Jimoh, R.G. A deep learning-based intrusion detection technique for a secured IoMT system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Informatics and Intelligent Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–26 February 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Ibrahim, D.A.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Bio-inspired robotics enabled schemes in blockchain-fog-cloud assisted IoMT environment. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreano, D.; Mattiussi, C. Bio-Inspired Artificial Intelligence: Theories, Methods, and Technologies; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Anguraj, D.K.; Thirugnanasambandam, K.; RS, R.; SV, S. Enriched cluster-head selection using augmented bifold cuckoo search algorithm for edge-based internet of medical things. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mayilvahanan, P.; Govindaraj, R. Optimal feature extraction and classification-oriented medical insurance prediction model: Machine learning integrated with the internet of things. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2022, 44, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, N.; Latiff, M.S.A.; Abdulhamid, S.M.; Chiroma, H. Whale optimization algorithm: A systematic review of contemporary applications, modifications and developments. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 16245–16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, Y.; Alshayeji, M.; Ahmad, I. Distributed whale optimization algorithm based on MapReduce. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2019, 31, e4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.S.; McLoone, S.; Byeon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Liu, H. Cognitively inspired artificial bee colony clustering for cognitive wireless sensor networks. Cogn. Comput. 2017, 9, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdi, M.; Zaied, M. Resource allocation based on hybrid genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for D2D multicast communications. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 83, 105605–105618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Haseeb, K.; Alam, T.; Jeon, G. Cloud-edge load balancing distributed protocol for IoE services using swarm intelligence. In Cluster Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz, M. The top 3 IoMT Challenges Keeping Healthcare IT up at Night. 2019. Available online: https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/blog/IoT-Agenda/The-top-3-IoMT-challenges-keeping-healthcare-IT-up-at-night (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Lewandowski, M.; Płaczek, B. An event-aware cluster-head rotation algorithm for extending lifetime of wireless sensor network with smart nodes. Sensors 2019, 19, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almesaeed, R.; Jedidi, A. Dynamic directional routing for mobile wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021, 110, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Survey | Topics|Methods | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|
| [10], 2011 | WSN Routing|SI | A recipe to define sound experiments and evaluation; anticipated growing application of SI in WSNs |
| [11], 2015 | WSN|SI | Percentage of SI methods application for addressing WSNs different issues |
| [16], 2020 | SIoT|DL | Importance of SIoT in various applications, especially diagnosis methods for heart diseases and brain tumors; high accuracy is achievable in disease diagnosis due to big-data methods used in SIoT |
| [7], 2020 | IoT|SI | Important challenges in WSN applications and SI methods capabilities to deal with them; analyzed three categories of the wireless network aided with UAV and role of SI in their applications; combining UAV with 5G, IoT, etc. is a worthy direction for future works |
| [17], 2021 | IoMT|ML | Without special considerations, e.g., resource and time complexity, etc., traditional ML fails to address IoMT security and privacy issues; the majority of reviewed studies ignore these considerations; and future ML-based approaches should comply with these considerations. |
| [18], 2022 | IoMT|ML, DL | Investigated different ML/DL-based attack detection techniques; future works on enforcing IoMT security using defensive techniques. |
| [19], 2022 | IoMT|ML | Investigated ML-based intrusion detection for IoMT; presented requirements and threats affecting IoMT security; and presented advantages and disadvantages of ML-based solutions and their ability for IoMT security |
| [20], 2021 | IoMT|DL | Reviewed characteristics and challenges of IoMT for the multimedia event processing based on IoT service-oriented architecture (SoA) of IoT; current approaches are robust but not adaptable due to their user interface shortcomings and limited vocabulary; challenges of using DL for multimedia event processing; and the inability of existing object detection approaches for achieving a minimum time of response while keeping the accuracy high |
| [12], 2018 | IoT|SI | Highly popular SI methods in IoT: ACO, PSO, and ABC |
| Our paper, 2022 | IoT, IoMT|SI | Investigation of SI algorithms used in the IoT with a special emphasis on their application for improving IoMT technology |
| Ref. | System|Method | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| [49], 2019 | IoT|PSO | Optimizing WSN routing |
| [50], 2017 | IoT|PSO | Optimizing WSN routing |
| [51], 2017 | IoT|PSO | Finding fault-tolerant routing methods |
| [52], 2018 | IoMT|PSO | Covering a specific area with a network of sensors |
| [54], 2019 | IoT|PSO | Preventing energy-hole generation and performing CHs selection |
| [56], 2016 | IoT|PSO | Lowering the transmission distance by enhancing the nodes in the cluster and optimizing the energy consumption of the network |
| [57], 2018 | IoT|PSO+GA | Reducing interruptions in networks |
| [58], 2018 | IoT|PSO | Locating the position of the target nodes |
| [61], 2018 | IoT|PSO+GA | VM selection |
| [62], 2019 | IoT|PSO | Hiding secret information |
| [63], 2016 | IoT|PSO | Optimizing resource selection |
| [64], 2022 | IoMT|PSO | Breast cancer prediction |
| [65], 2021 | IoMT|PSO+GA | Protecting patients’ sensitive and confidential data |
| [67], 2020 | IoMT| Grasshopper Optimization + PSO | Encrypting medical image |
| [69], 2019 | IoMT| ANFIS + PSO + GA | Assigning appropriate values to missing data |
| [70], 2017 | IoT|ACO+ABC | A WSN-based multi-path routing and CH selection |
| [71], 2018 | IoT|ACO | Finding an optimal path for mobile sink |
| [72], 2016 | IoT|ACO+Fuzzy Logic | Dealing with the hot-spot problem in WSNs |
| [73], 2017 | IoT|ACO | Reducing the amount of energy consumed, increasing node longevity, and improving routing algorithm |
| [75], 2017 | IoT|ACO | Keeping information transmission-level high and power consumption level low |
| [76], 2017 | IoT|ACO | Proposing an enhanced routing algorithm |
| [77], 2019 | IoT|ACO | Enforcing security in WSNs data transmission and finding better results for multi-path routing |
| [78], 2017 | IoT|ACO | Reliable deployment of WSN |
| [80], 2018 | IoMT|ACO | Choosing the optimal route for ambulances to minimize the time to reach the crash scene |
| [81], 2018 | IoMT|ACO | Finding the shortest path for data transfer |
| [82], 2017 | IoT|ABC | Proposing centralized cluster routing protocol |
| [83], 2019 | IoT|ABC | Clustering with low energy consumption in WSNs |
| [84], 2017 | IoT|ABC | Reducing the computational time |
| [85], 2022 | IoMT| ABC + DE + GA | Maximizing e-health system availability, taking into account the limited budget for redundant components |
| [86], 2021 | IoMT|ABC | Skin-lesion diagnosis and classification |
| [87], 2021 | IoMT|ABC | Offering solutions for patients’ data analysis and management; clustering data (patients) |
| [89], 2017 | IoT|BFO | Optimizing the gap between cluster members and CH and enhancing network longevity through the reduction in consumed energy |
| [90], 2017 | IoT|BOA | Finding the local node optimal position |
| [91], 2022 | IoMT|gravitational search optimization + reflection-belief networks + CNN | Optimizing data to predict diabetes |
| [96], 2019 | IoMT|Bat + cuckoo+ firefly + PSO | Clustering artificial and real medical datasets |
| [98], 2021 | IoMT|BOA + multilayer perceptron | medical data classification |
| [99], 2022 | IoMT|quantum random walk + brainstorming optimization | Embedding private medical data in private images to achieve enhanced image security and ensure their authenticity |
| [101], 2021 | IoMT|swarm NNs | Identifying intruders in the IoMT data-driven system and finding a solution to identify intruders during data transmission as well as the possibility of analyzing healthcare data efficiently and accurately |
| [102], 2021 | IoMT|bio-inspired method | Minimizing the cost of execution and blocking of applications |
| [104], 2021 | IoMT|augmented bio fold cuckoo | Selecting CH in WSNs, reducing overall energy consumption by wireless medical devices |
| [105], 2020 | IoMT|WOA + NNs | Predicting the amount of health insurance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alizadehsani, R.; Roshanzamir, M.; Izadi, N.H.; Gravina, R.; Kabir, H.M.D.; Nahavandi, D.; Alinejad-Rokny, H.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, U.R.; Nahavandi, S.; et al. Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031466
Alizadehsani R, Roshanzamir M, Izadi NH, Gravina R, Kabir HMD, Nahavandi D, Alinejad-Rokny H, Khosravi A, Acharya UR, Nahavandi S, et al. Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031466
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlizadehsani, Roohallah, Mohamad Roshanzamir, Navid Hoseini Izadi, Raffaele Gravina, H. M. Dipu Kabir, Darius Nahavandi, Hamid Alinejad-Rokny, Abbas Khosravi, U. Rajendra Acharya, Saeid Nahavandi, and et al. 2023. "Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031466
APA StyleAlizadehsani, R., Roshanzamir, M., Izadi, N. H., Gravina, R., Kabir, H. M. D., Nahavandi, D., Alinejad-Rokny, H., Khosravi, A., Acharya, U. R., Nahavandi, S., & Fortino, G. (2023). Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review. Sensors, 23(3), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031466










