A Comprehensive Analysis of Smartphone GNSS Range Errors in Realistic Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
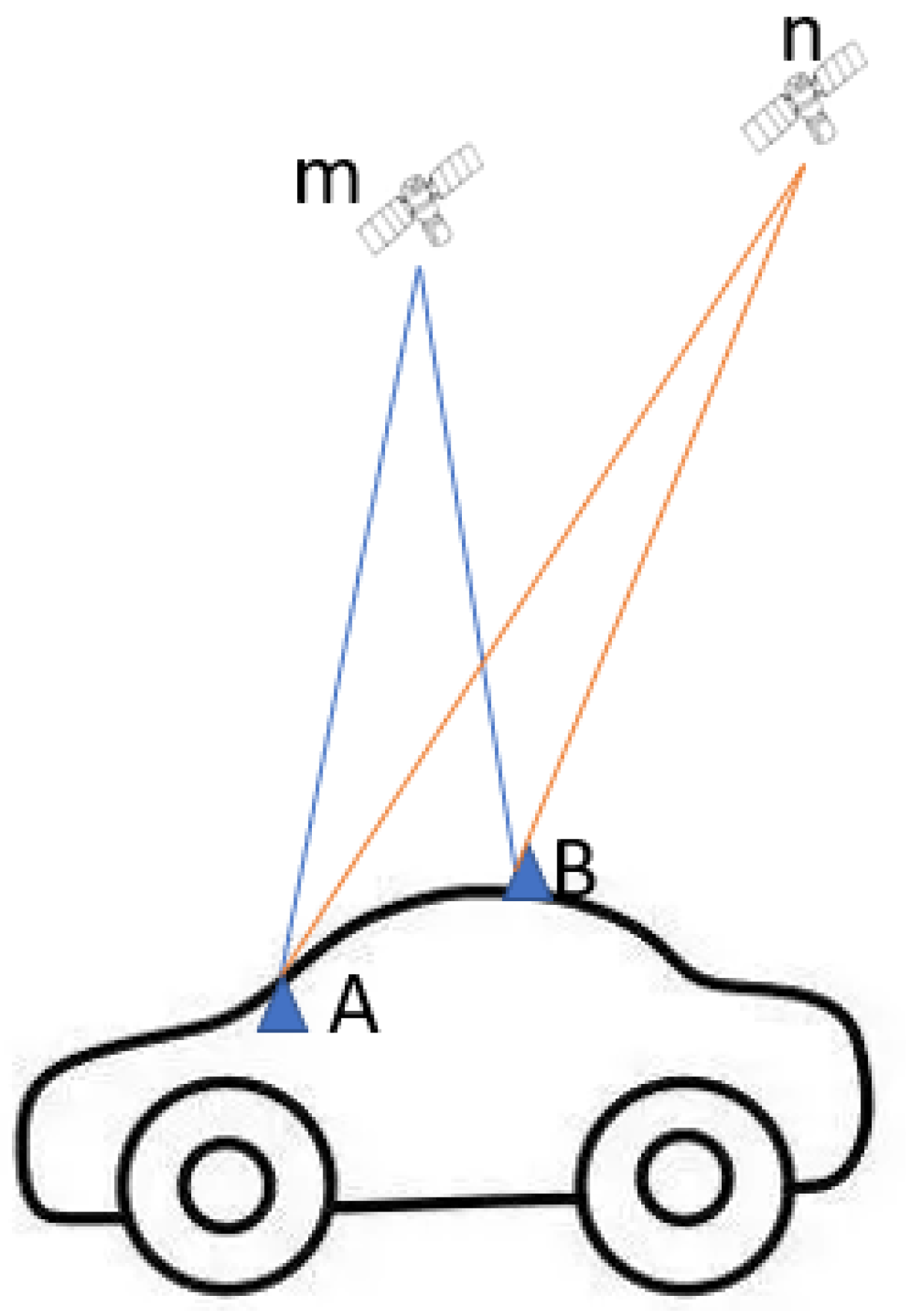
2. Methodology
3. Measurement Campaigns and Experimental Setup
4. Results
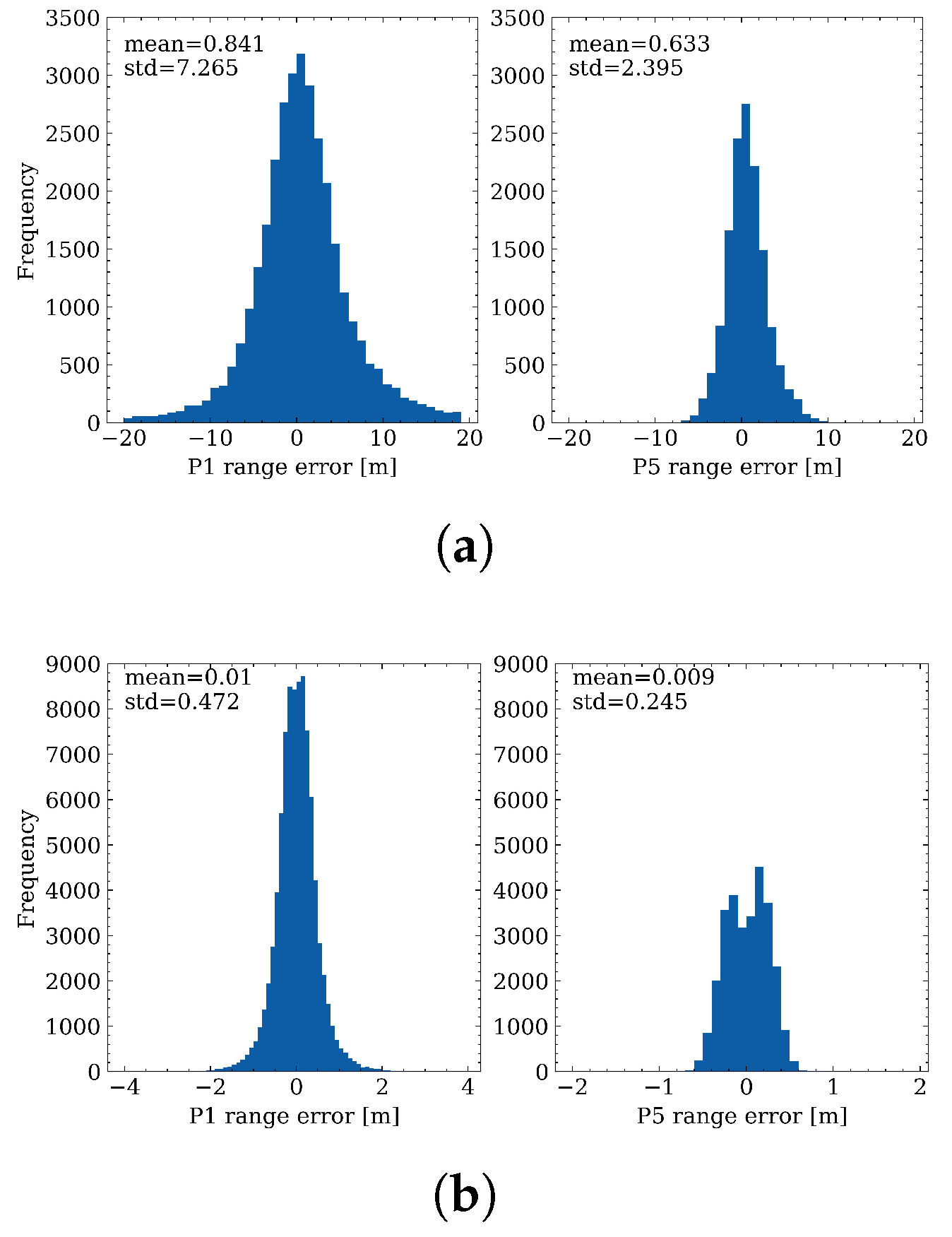
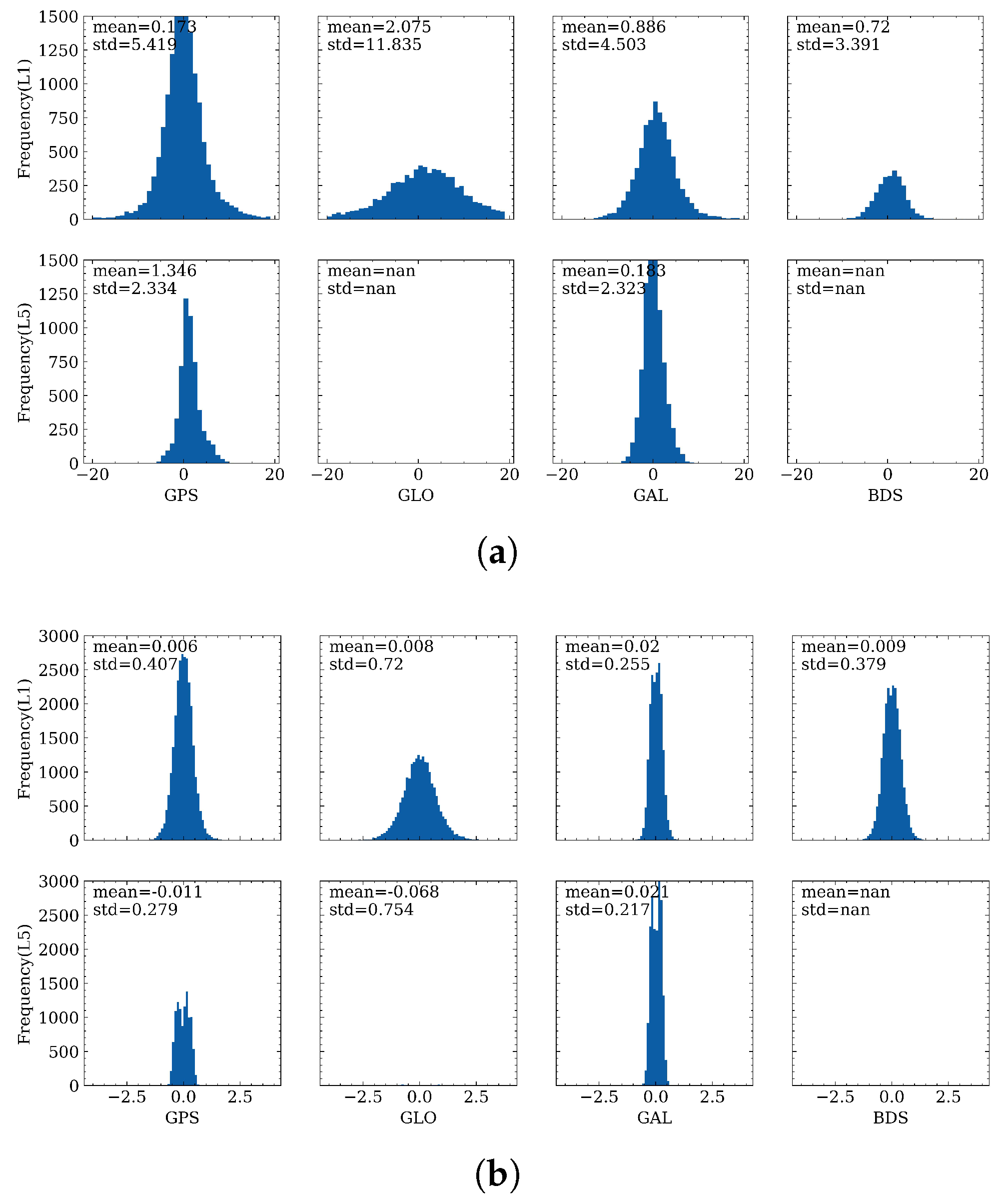
4.1. Distribution of Range Errors
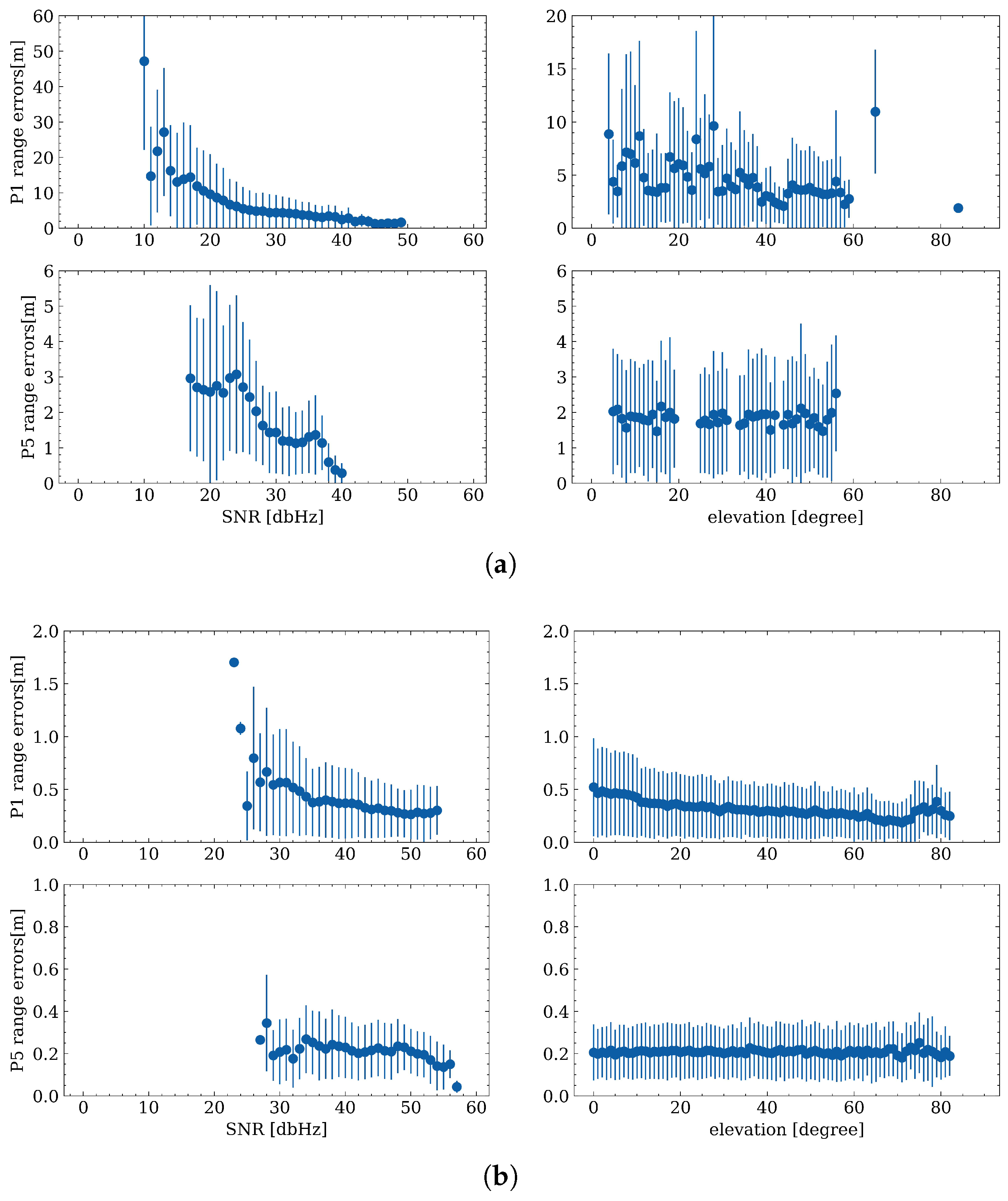
4.2. Range Errors Correlation with Elevation Angle and SNR
4.3. Range Errors under Different Environments
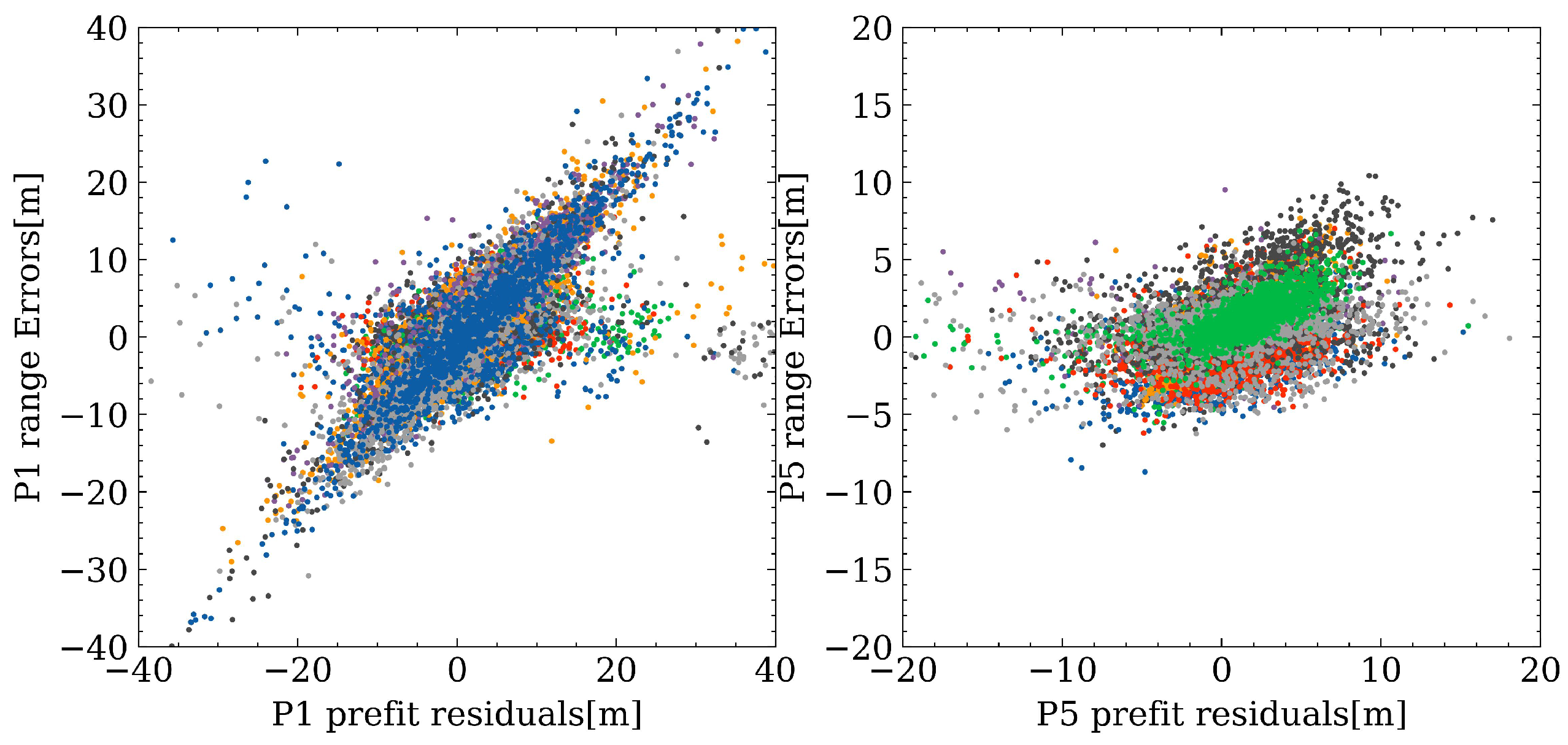
4.4. Comparison between Range Errors and Pre-Fit Residuals
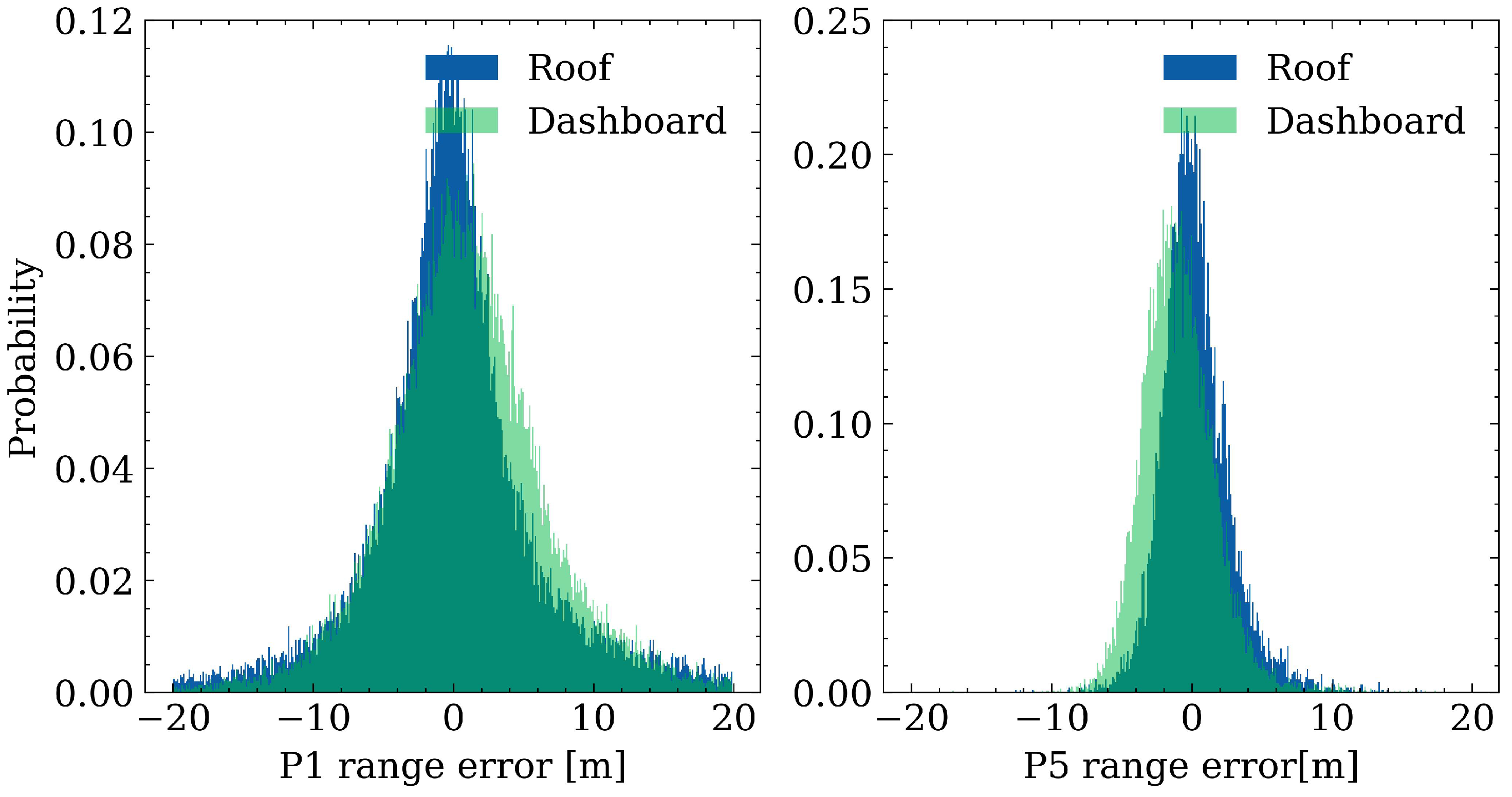
4.5. Range Errors Comparison on Car Dashboard and Roof
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malkos, S. User location takes center stage in new Android OS: Google to provide raw GNSS measurements. GPS World 2016, 27, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zangenehnejad, F.; Gao, Y. GNSS smartphones positioning: Advances, challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsubaie, N.M.; Youssef, A.A.; El-Sheimy, N. Improving the accuracy of direct geo-referencing of smartphone-based mobile mapping systems using relative orientation and scene geometric constraints. Sensors 2017, 17, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Allen, R.M.; Schreier, L.; Kwon, Y.W. MyShake: A smartphone seismic network for earthquake early warning and beyond. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J. Recent advances and perspectives for positioning and applications with smartphone GNSS observations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 091001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesyna, K.M.; Heath, R.W.; Humphreys, T.E. Centimeter positioning with a smartphone-quality GNSS antenna. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 1568–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Sikirica, N.; Malić, E.; Rumora, I.; Filjar, R. Exploitation of Google GNSS measurement API for risk assessment of GNSS applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Telecommunication Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 21–22 November 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Szot, T.; Specht, C.; Specht, M.; Dabrowski, P.S. Comparative analysis of positioning accuracy of Samsung Galaxy smartphones in stationary measurements. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Pugliano, G.; Robustelli, U. Performance assessment of GNSS single point positioning with recent smartphones. In Proceedings of the IMEKO TC-19 International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Naples, Italy, 5–7 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Realini, E.; Caldera, S.; Pertusini, L.; Sampietro, D. Precise GNSS positioning using smart devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabove, P.; Di Pietra, V. Towards high accuracy GNSS real-time positioning with smartphones. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J. An assessment of smartphone and low-cost multi-GNSS single-frequency RTK positioning for low, medium and high ionospheric disturbance periods. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Duan, S. Xiaomi Mi 8 smartphone GNSS data quality analysis and single-frequency RTK positioning performance evaluation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.; Bisnath, S.; Aggrey, J.; Seepersad, G. Precise point positioning (PPP) using low-cost and ultra-low-cost GNSS receivers. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; pp. 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Bo, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, M.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Y. Ionosphere-constrained single-frequency PPP with an Android smartphone and assessment of GNSS observations. Sensors 2020, 20, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmezayen, A.; El-Rabbany, A. Precise point positioning using world’s first dual-frequency GPS/GALILEO smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, P. Precise point positioning using dual-frequency GNSS observations on smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabove, P.; Di Pietra, V. Single-baseline RTK positioning using dual-frequency GNSS receivers inside smartphones. Sensors 2019, 19, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggrey, J.; Bisnath, S.; Naciri, N.; Shinghal, G.; Yang, S. Multi-GNSS precise point positioning with next-generation smartphone measurements. J. Spat. Sci. 2020, 65, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Real-time GNSS precise point positioning for low-cost smart devices. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robustelli, U.; Baiocchi, V.; Marconi, L.; Radicioni, F.; Pugliano, G. Precise Point Positioning with Single and Dual-Frequency Multi-GNSS Android Smartphones. In Proceedings of the ICL-GNSS (Work in Progress), Tampere, Finland, 2–4 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lachapelle, G.; Gratton, P. GNSS precise point positioning with Android smartphones and comparison with high performance receivers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, R.; Liu, A. Real-time GNSS precise point positioning with smartphones for vehicle navigation. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P. Real-time precise point positioning with a Xiaomi MI 8 android smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seepersad, G.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Yi, D.; Bisnath, S. Changing Lanes with Smartphones Technology. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 September 2021; pp. 3021–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Seepersad, G.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Yi, D.; Bisnath, S. Performance Assessment of Tightly Coupled Smartphone Sensors with Legacy and State Space Corrections. In Proceedings of the 35th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2022), Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 September 2022; pp. 2235–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yi, D.; Vana, S.; Bisnath, S. Resilient Smartphone Positioning using Native Sensors and PPP Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 September 2021; pp. 4208–4222. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, D.; Yang, S.; Bisnath, S. Native Smartphone Single-and Dual-Frequency GNSS-PPP/IMU Solution in Real-World Driving Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, T.E.; Murrian, M.; Van Diggelen, F.; Podshivalov, S.; Pesyna, K.M. On the feasibility of cm-accurate positioning via a smartphone’s antenna and GNSS chip. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Jiao, F.; Li, J. The assessment of GNSS measurements from android smartphones. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference, Harbin, China, 23–25 May 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Shi, X.; Zhu, F.; Tao, X.; Wang, F. Quality analysis of multi-GNSS raw observations and a velocity-aided positioning approach based on smartphones. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2358–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Baryla, R. Signal characterization and assessment of code GNSS positioning with low-power consumption smartphones. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinghal, G.; Bisnath, S. Conditioning and PPP processing of smartphone GNSS measurements in realistic environments. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banville, S.; Lachapelle, G.; Ghoddousi-Fard, R.; Gratton, P. Automated processing of low-cost GNSS receiver data. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2019), Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 3636–3652. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, X.; Zhu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, F. Quality assessment of GNSS observations from an Android N smartphone and positioning performance analysis using time-differenced filtering approach. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.; Lentz, W.; Clare, A. On the path to precision-observations with android GNSS observables. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; pp. 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Li, G.; Zeng, R.; Wen, Q.; Jiang, E. A comprehensive assessment of raw multi-GNSS measurements from mainstream portable smart devices. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 392–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Q.; Geng, J.; Li, G.; Guo, J. Precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using an external survey-grade antenna enhanced dual-frequency android GNSS data. Measurement 2020, 157, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Geng, J. Characteristics of raw multi-GNSS measurement error from Google Android smart devices. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, G.; Gratton, P.; Horrelt, J.; Lemieux, E.; Broumandan, A. Evaluation of a low cost hand held unit with GNSS raw data capability and comparison with an android smartphone. Sensors 2018, 18, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L.; Heßelbarth, A. GNSS code and carrier phase observations of a Huawei P30 smartphone: Quality assessment and centimeter-accurate positioning. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robustelli, U.; Pugliano, G. Code multipath analysis of Galileo FOC satellites by time-frequency representation. Appl. Geomat. 2019, 11, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robustelli, U.; Baiocchi, V.; Pugliano, G. Assessment of dual frequency GNSS observations from a Xiaomi Mi 8 Android smartphone and positioning performance analysis. Electronics 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ponte Müller, F.; Steingass, A.; Strang, T. Zero-baseline measurements for relative positioning in vehicular environments. In Proceedings of the 6th European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing, Neubiberg, Germany, 5–6 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. 2009. Available online: http://acc.igs.org/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Saleem, T.; Usman, M.; Elahi, A.; Gul, N. Simulation and performance evaluations of the new GPS L5 and L1 signals. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 7492703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, J.; Landry, R., Jr.; Botteron, C. Comparison of L1 and L5 bands GNSS signals acquisition. Sensors 2018, 18, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Bisnath, S.; Pan, L. Precise point positioning with BDS-2 and BDS-3 constellations: Ambiguity resolution and positioning comparison. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 1830–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangenehnejad, F.; Gao, Y. Application of UofC Model Based Multi-GNSS PPP to Smartphones GNSS Positioning. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 September 2021; pp. 2986–3003. [Google Scholar]
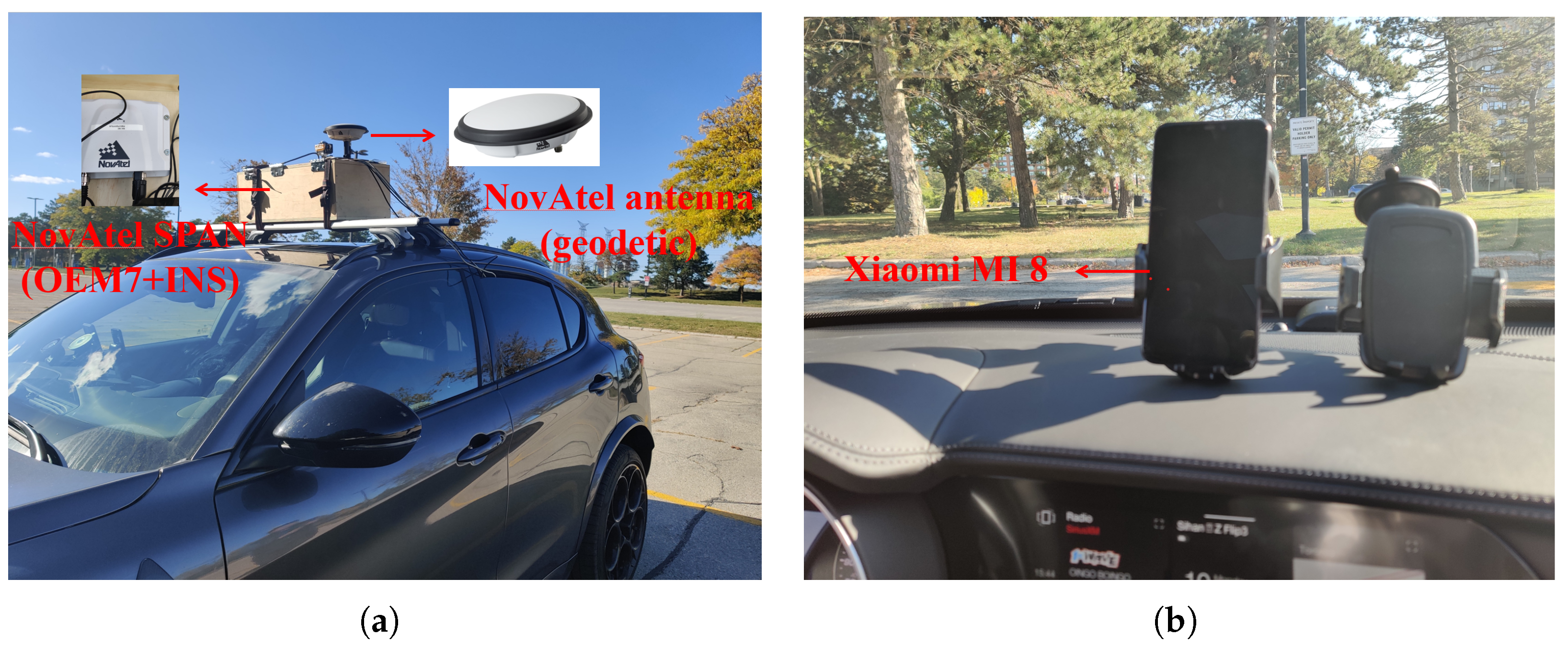



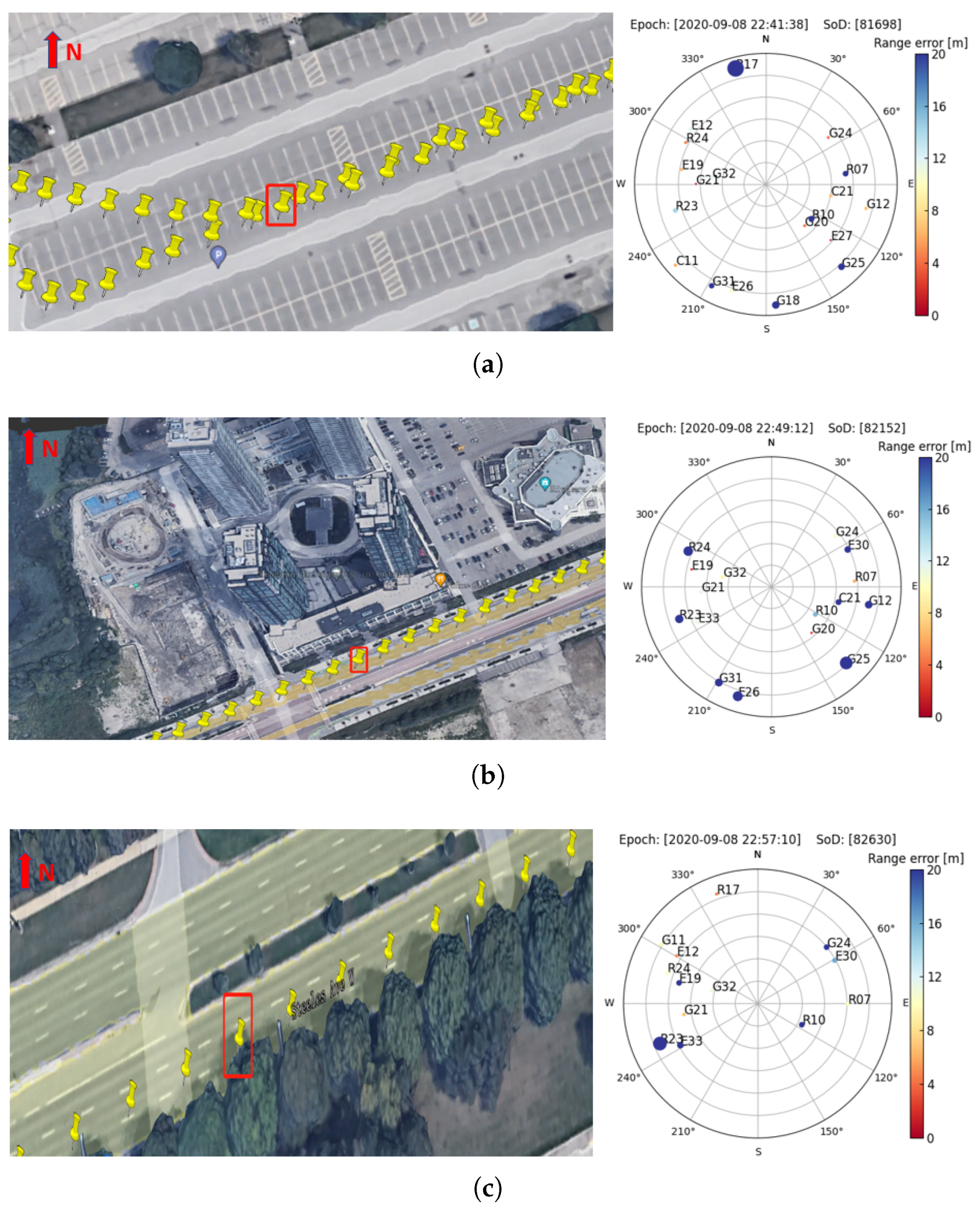

| Test # | Collection Date | Duration | Mounted Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 September 2020 | 22:29–23:00 | Roof |
| 2 | 8 August 2021 | 1:14–1:42 | Roof |
| 3 | 8 August 2021 | 1:50–2.19 | Dashboard |
| P1 | P5 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | STD | 95th per | Number | Mean | STD | 95th per | Number | |
| Open-sky | 0.8 | 7.3 | 14.5 | 32267 | 0.9 | 2.4 | 5.1 | 14198 |
| Sub-urban | 2.2 | 9.4 | 18.2 | 1443 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 5.9 | 658 |
| Vegetation | 1.5 | 7.5 | 17.1 | 354 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 176 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Yi, D.; Bisnath, S. A Comprehensive Analysis of Smartphone GNSS Range Errors in Realistic Environments. Sensors 2023, 23, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031631
Hu J, Yi D, Bisnath S. A Comprehensive Analysis of Smartphone GNSS Range Errors in Realistic Environments. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031631
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jiahuan, Ding Yi, and Sunil Bisnath. 2023. "A Comprehensive Analysis of Smartphone GNSS Range Errors in Realistic Environments" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031631
APA StyleHu, J., Yi, D., & Bisnath, S. (2023). A Comprehensive Analysis of Smartphone GNSS Range Errors in Realistic Environments. Sensors, 23(3), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031631







