Integrating Bio-Sensing Array with Blood Plasma Separation on a Centrifugal Platform
Abstract
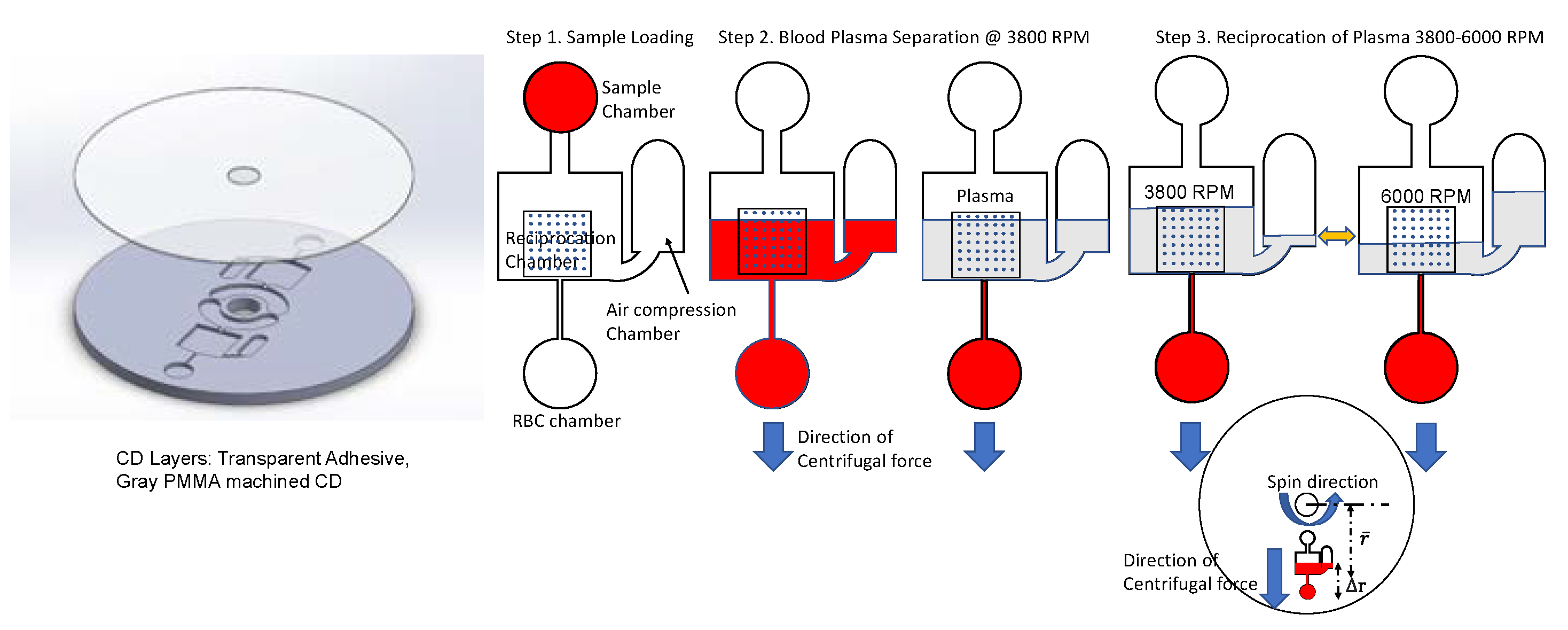
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Theory
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Blood Plasma Separation
4.2. Simulation
4.3. Efficiency of Reciprocation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amasia, M.; Madou, M. Large-Volume Centrifugal Microfluidic Device for Blood Plasma Separation. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, Z.; Kido, H.; Peytavi, R.; Nakajima-Sasaki, R.; Jasinskas, A.; Micic, M.; Felgner, P.L.; Madou, M.J. A Multiplexed Immunoassay System Based upon Reciprocating Centrifugal Microfluidics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 064303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madou, M.J.; Kellogg, G.J. LabCD: A Centrifuge-Based Microfluidic Platform for Diagnostics. In Proceedings of the Systems and Technologies for Clinical Diagnostics and Drug Discovery, San Jose, CA, USA, 10 April 1998; International Society for Optics and Photonics—SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Volume 3259, pp. 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.-K.; Lee, J.-G.; Park, J.-M.; Lee, B.-S.; Lee, Y.; Ko, C. One-Step Pathogen Specific DNA Extraction from Whole Blood on a Centrifugal Microfluidic Device. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Ye, P.; Yang, K.; Meng, J.; Guo, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Guo, J. Application of Centrifugal Microfluidics in Immunoassay, Biochemical Analysis and Molecular Diagnosis. Analyst 2021, 146, 5800–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielczarek, W.S.; Obaje, E.A.; Bachmann, T.T.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Microfluidic Blood Plasma Separation for Medical Diagnostics: Is It Worth It? Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3441–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, J.-N.; Chen, X.-F. Plasma Separation and Preparation on Centrifugal Microfluidic Disk for Blood Assays. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, Z.; Kido, H.; Micic, M.; Pan, H.; Bartolome, C.; Princevac, M.; Zoval, J.; Madou, M. Reciprocating Flow-Based Centrifugal Microfluidics Mixer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 075102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishbin, E.; Eghbal, M.; Fakhari, S.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Navidbakhsh, M. The Effect of Moment of Inertia on the Liquids in Centrifugal Microfluidics. Micromachines 2016, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, J.F.; Zehnle, S.; Juelg, P.; Hutzenlaub, T.; Zengerle, R.; Paust, N. Review on Pneumatic Operations in Centrifugal Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3745–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwu, A.T.; Madadelahi, M.; Nakajima, R.; Shamloo, E.; Perebikovsky, A.; Kido, H.; Jain, A.; Jasinskas, A.; Prange, S.; Felgner, P.; et al. Centrifugal Disc Liquid Reciprocation Flow Considerations for Antibody Binding to COVID Antigen Array during Microfluidic Integration. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 2695–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peshin, S.; George, D.; Shiri, R.; Kulinsky, L.; Madou, M. Capillary Flow-Driven and Magnetically Actuated Multi-Use Wax Valves for Controlled Sealing and Releasing of Fluids on Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines 2022, 13, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramoff, M.D.; Magalhães, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Pitts, K.L.; Abu-Mallouh, S.; Fenech, M. Contact Angle Study of Blood Dilutions on Common Microchip Materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 17, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peshin, S.; George, D.; Shiri, R.; Madou, M. Reusable Capillary Flow-Based Wax Switch Valve for Centrifugal Microfluidics. Meet. Abstr. 2021, MA2021-01, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitello, D.J.; Ripper, R.M.; Fettiplace, M.R.; Weinberg, G.L.; Vitello, J.M. Blood Density Is Nearly Equal to Water Density: A Validation Study of the Gravimetric Method of Measuring Intraoperative Blood Loss. J. Vet. Med. 2015, 2015, e152730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.S.; Sikarwar, B.S.; Ranjan, P.; Janardhanan, R.; Goyal, A. Surface Tension Measurement of Normal Human Blood Samples by Pendant Drop Method. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2020, 44, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, E.; Skinner, S.; Romana, M.; Fort, R.; Lemonne, N.; Guillot, N.; Gauthier, A.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; Renoux, C.; Hardy-Dessources, M.-D.; et al. Blood Rheology: Key Parameters, Impact on Blood Flow, Role in Sickle Cell Disease and Effects of Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulinsky, L.; Noroozi, Z.; Madou, M. Present Technology and Future Trends in Point-of-Care Microfluidic Diagnostics. In Microfluidic Diagnostics: Methods and Protocols; Jenkins, G., Mansfield, C.D., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 3–23. ISBN 978-1-62703-134-9. [Google Scholar]
- Perebikovsky, A.; Liu, Y.; Hwu, A.; Kido, H.; Shamloo, E.; Song, D.; Monti, G.; Shoval, O.; Gussin, D.; Madou, M. Rapid Sample Preparation for Detection of Antibiotic Resistance on a Microfluidic Disc Platform. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres Delgado, S.M.; Kinahan, D.J.; Nirupa Julius, L.A.; Mallette, A.; Ardila, D.S.; Mishra, R.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Korvink, J.G.; Ducrée, J.; Mager, D. Wirelessly Powered and Remotely Controlled Valve-Array for Highly Multiplexed Analytical Assay Automation on a Centrifugal Microfluidic Platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Property Type (Units) | Standard Reciprocation [1,2] | Integrated Reciprocation |
|---|---|---|
| Process time (minutes) | 25 | 7 |
| Sample Volume (mL) | 1 | 0.02 |
| Number of CDs required | two separate CDs | two processes on a single CD |
| Needs Trained Personnel | No | No |
| Property Type (Units) | Value |
|---|---|
| Contact angle of blood (with acrylic) [degrees] [14] θc | 70 |
| Density of blood [kg/m3] [16] ρ | 994 |
| Surface tension of blood [N/m] [17] γ | 0.053 |
| Viscosity of blood [N·s/m2] [18] µ | 0.0045 |
| CD Sample Number | RPM | Process Time/Lysis |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 10 min/Coagulation |
| 2 | 2500 | 8 min |
| 3 | 3800 | 6 min |
| 4 | 5500 | Lysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peshin, S.; Madou, M.; Kulinsky, L. Integrating Bio-Sensing Array with Blood Plasma Separation on a Centrifugal Platform. Sensors 2023, 23, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031710
Peshin S, Madou M, Kulinsky L. Integrating Bio-Sensing Array with Blood Plasma Separation on a Centrifugal Platform. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031710
Chicago/Turabian StylePeshin, Snehan, Marc Madou, and Lawrence Kulinsky. 2023. "Integrating Bio-Sensing Array with Blood Plasma Separation on a Centrifugal Platform" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031710
APA StylePeshin, S., Madou, M., & Kulinsky, L. (2023). Integrating Bio-Sensing Array with Blood Plasma Separation on a Centrifugal Platform. Sensors, 23(3), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031710








