DEHA-Net: A Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network with an Adaptive ROI Mechanism for Lung Nodule Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
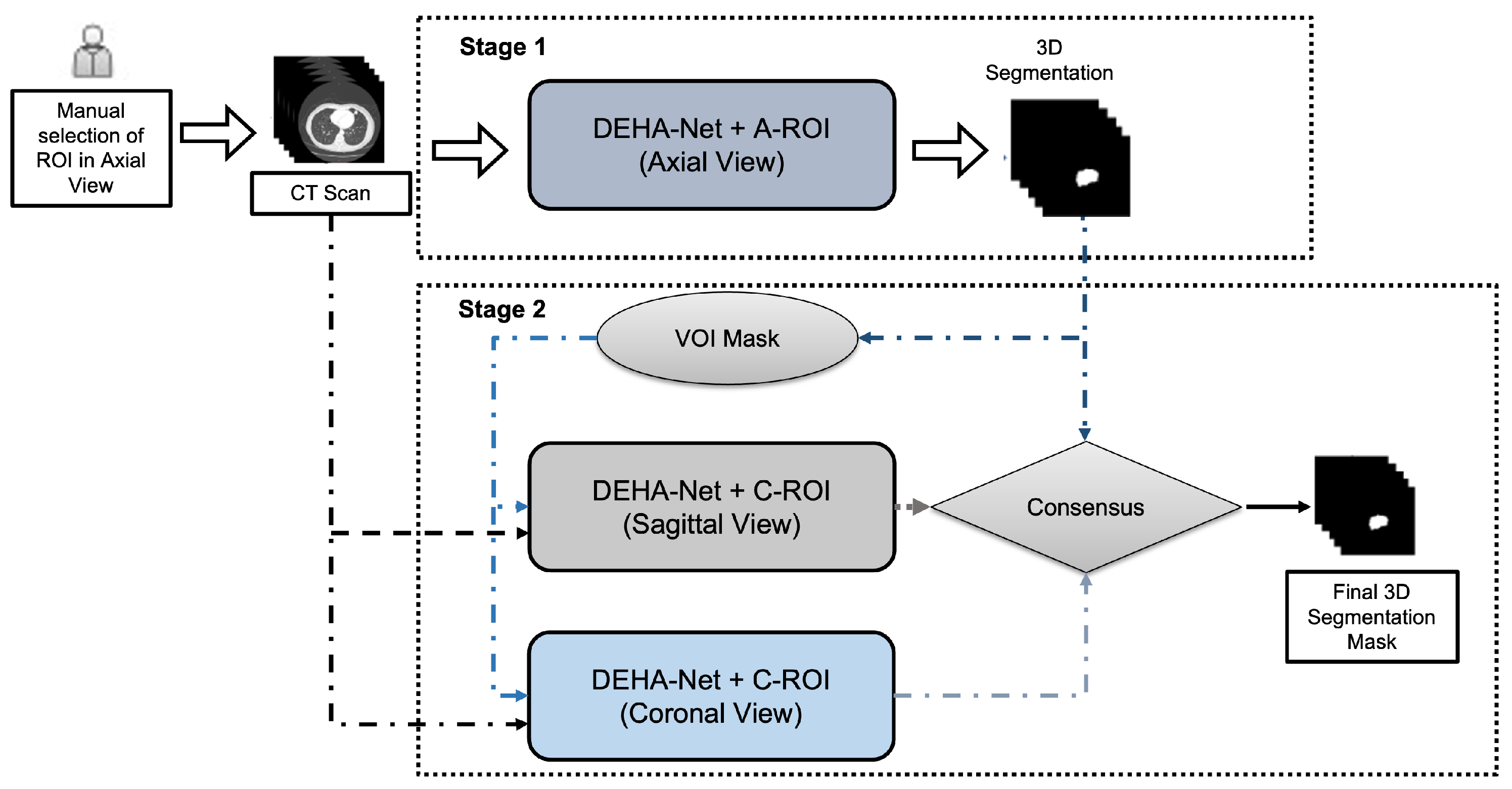
3.3. Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network with Adaptive ROI Mechanism
Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network
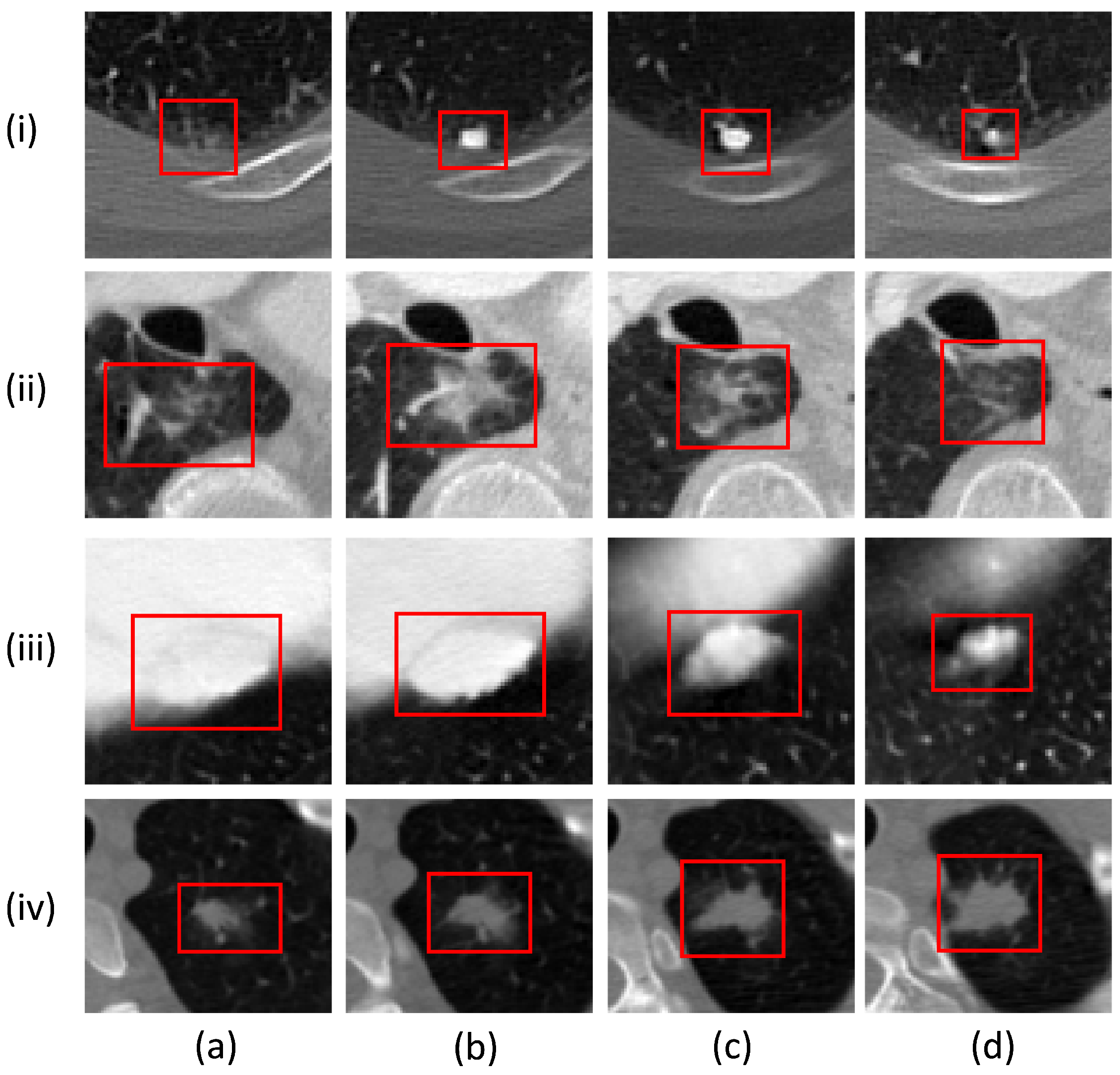
3.4. Adaptive ROI Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: The algorithmic steps followed in the proposed framework for nodule investigation along the axial view. |
|
3.5. Ensembling Mechanism
4. Experimental Setup and Implementation Details
4.1. Loss Function
4.2. Implementation Details and Training Strategy
4.3. Performance Measures
- Dice Similarity Coefficient: We used the dice similarity coefficient (DSC) [19,36], which measures the degree of overlap between the ground-truth mask and the predicted mask. The DSC values range from 0 to 1, where 1 and 0 indicate complete overlap and no overlap, respectively. It can be defined as follows:where and Y are the predicted segmentation mask and reference segment mask, respectively.
- Sensitivity: To measure the pixel classification performance proposed framework, we used sensitivity (SEN), which can be defined as follows:
- Positive Predictive Value (PPV): To measure the correctness of the segmentation area produced by the proposed framework, we used the positive predictive value (PPV), which can be defined as follows:
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Overall Performance Analysis
5.2. Robustness Analysis
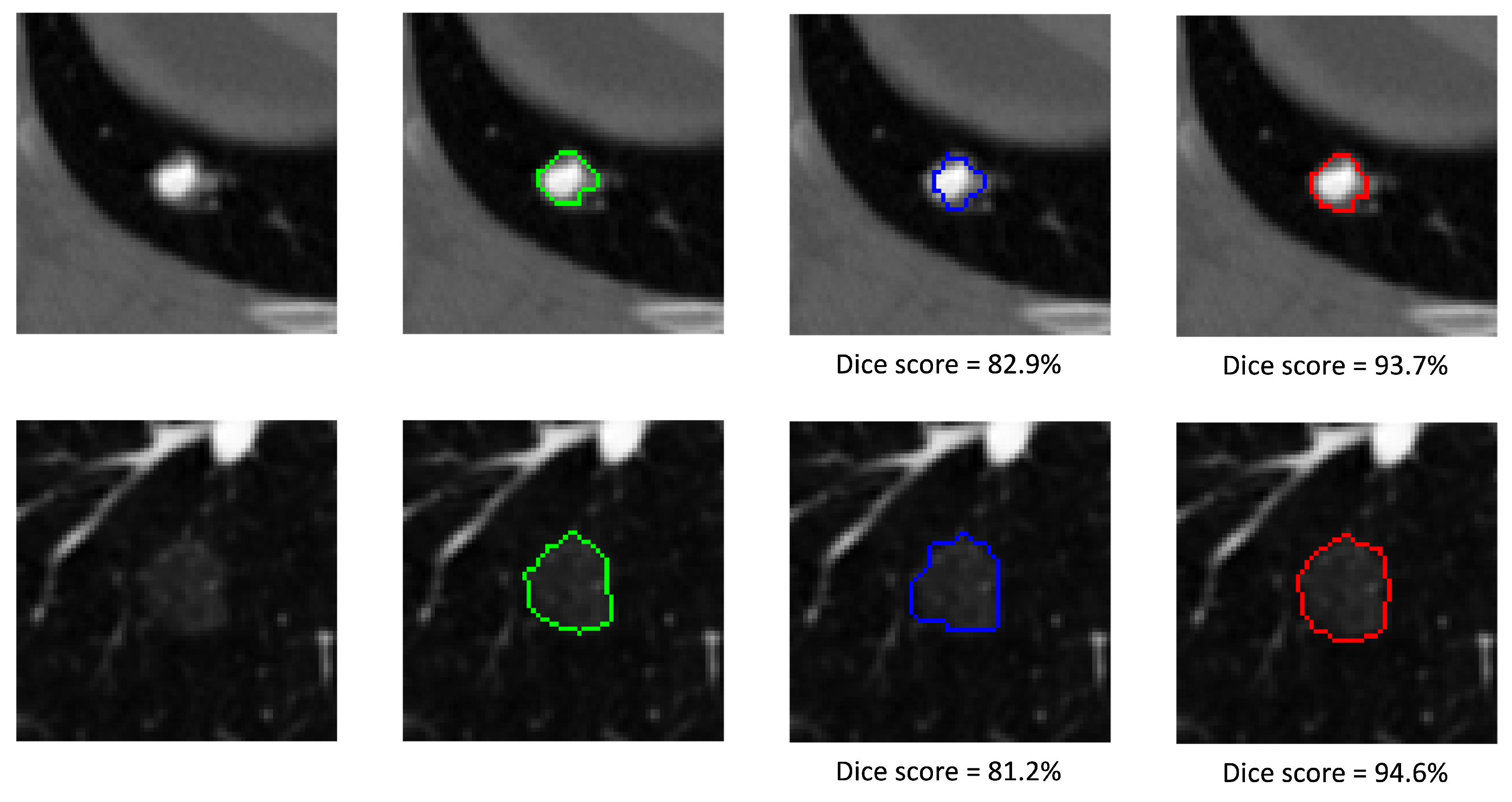
5.3. Qualitative Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozley, P.D.; Bendtsen, C.; Zhao, B.; Schwartz, L.H.; Thorn, M.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Perrone, A.; Korn, R.; Buckler, A.J. Measurement of tumor volumes improves RECIST-based response assessments in advanced lung cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, A.; van Ginneken, B.; Nair, A.; Baldwin, D. Use of volumetry for lung nodule management: Theory and practice. Radiology 2017, 284, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moltz, J.H.; Bornemann, L.; Kuhnigk, J.M.; Dicken, V.; Peitgen, E.; Meier, S.; Bolte, H.; Fabel, M.; Bauknecht, H.C.; Hittinger, M.; et al. Advanced segmentation techniques for lung nodules, liver metastases, and enlarged lymph nodes in CT scans. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2009, 3, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Rehman, A.; Shahid, A.; Latif, S.; Byon, S.S.; Lee, B.D.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, Y.G. MEDS-Net: Self-Distilled Multi-Encoders Network with Bi-Direction Maximum Intensity projections for Lung Nodule Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.00003. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, M.; Lee, B.D.; Byon, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, B.i.; Shin, Y.G. Volumetric lung nodule segmentation using adaptive roi with multi-view residual learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Qian, T. A survey of pulmonary nodule detection, segmentation and classification in computed tomography with deep learning techniques. J. Med. Artif. Intell. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato, S.G., III; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehmeshki, J.; Amin, H.; Valdivieso, M.; Ye, X. Segmentation of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT scans: A region growing approach. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diciotti, S.; Picozzi, G.; Falchini, M.; Mascalchi, M.; Villari, N.; Valli, G. 3-D segmentation algorithm of small lung nodules in spiral CT images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2008, 12, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diciotti, S.; Lombardo, S.; Falchini, M.; Picozzi, G.; Mascalchi, M. Automated segmentation refinement of small lung nodules in CT scans by local shape analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon-Gonzalez, E.; Ponomaryov, V. Automatic Lung nodule segmentation and classification in CT images based on SVM. In Proceedings of the 2016 9th International Kharkiv Symposium on Physics and Engineering of Microwaves, Millimeter and Submillimeter Waves (MSMW), Kharkiv, Ukraine, 20–24 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, Z.; Usman, M.; Gwak, J. MTSS-AAE: Multi-task semi-supervised adversarial autoencoding for COVID-19 detection based on chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 216, 119475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Georgiou, T.; Lew, M.S. A review of semantic segmentation using deep neural networks. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Cunha, A.; Mendonça, A.M. Comparison of Conventional and Deep Learning Based Methods for Pulmonary Nodule Segmentation in CT Images. In Proceedings of the EPIA Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vila Real, Portugal, 3–6 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, Z.; Usman, M.; Jeon, M.; Gwak, J. Cascade multiscale residual attention cnns with adaptive roi for automatic brain tumor segmentation. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 1541–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Talbar, S.N. CSE-GAN: A 3D conditional generative adversarial network with concurrent squeeze-and-excitation blocks for lung nodule segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Gu, D.; Zang, Y.; Dong, D.; Gevaert, O.; Tian, J. Central focused convolutional neural networks: Developing a data-driven model for lung nodule segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 40, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Gevaert, O.; Tang, Z.; Dong, D.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J. A multi-view deep convolutional neural networks for lung nodule segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1752–1755. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, H. Improved U-NET network for pulmonary nodules segmentation. Optik 2018, 174, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, M.C.; Magnan, J.F. Lung nodule segmentation via level set machine learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.03191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. End-to-End Multi-Task Learning for Lung Nodule Segmentation and Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 6710–6717. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Cao, H.; Song, E.; Ma, G.; Xu, X.; Jin, R.; Jin, Y.; Hung, C.C. A cascaded dual-pathway residual network for lung nodule segmentation in CT images. Phys. Medica 2019, 63, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xie, W.; Zhou, P.; Zheng, C.; Wu, D. Multi-Crop Convolutional Neural Networks for Fast Lung Nodule Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2021, 6, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Road extraction by deep residual u-net. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qi, S.; Wu, Y.; Pan, X.; Yao, Y.; Qian, W.; Guan, Y. Multi-Scale Segmentation Squeeze-and-Excitation UNet with Conditional Random Field for Segmenting Lung Tumor from CT Images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 222, 106946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Armato III, S.G.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; McLennan, G.; Pais, R.C.; Freymann, J.; Brown, M.S.; Engelmann, R.M.; Bland, P.H.; et al. The Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) data collection process for nodule detection and annotation. Acad. Radiol. 2007, 14, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yang, J.; Laine, A.F.; Angelini, E.D. Discriminative localization in CNNs for weakly-supervised segmentation of pulmonary nodules. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10–14 September 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Joint learning for pulmonary nodule segmentation, attributes and malignancy prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1109–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Jerebko, A.K.; Dewan, M.; Salganicoff, M.; Krishnan, A. Segmentation of pulmonary nodules of various densities with morphological approaches and convexity models. Med. Image Anal. 2011, 15, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Softneta. DICOM Library—Anonymize, Share, View DICOM Files ONLINE. Available online: https://www.dicomlibrary.com/dicom/dicom-tags/ (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Amorim, P.H.; de Moraes, T.F.; da Silva, J.V.; Pedrini, H. Lung Nodule Segmentation Based on Convolutional Neural Networks Using Multi-orientation and Patchwise Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing, Porto, Portugal, 16–18 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 286–295. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, K.H.; Warfield, S.K.; Bharatha, A.; Tempany, C.M.; Kaus, M.R.; Haker, S.J.; Wells III, W.M.; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R. Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index1: Scientific reports. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, François; Keras. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/fchollet/keras (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Jung, J.; Hong, H.; Goo, J.M. Ground-glass nodule segmentation in chest CT images using asymmetric multi-phase deformable model and pulmonary vessel removal. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 92, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Liu, H.; Song, E.; Hung, C.C.; Ma, G.; Xu, X.; Jin, R.; Lu, J. Dual-branch residual network for lung nodule segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, M.; Yasmin, S.; Mehmood, I.; Bukhari, M.; Kim, M. An efficient DA-net architecture for lung nodule segmentation. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gou, F.; Tan, Y.; Wu, J. A cascaded multi-stage framework for automatic detection and segmentation of pulmonary nodules in developing countries. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 5619–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Authors, Year | DSC (%) | SEN (%) | PPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al., 2017 [19] | 82.15 ± 10.76 | 92.75 ± 12.83 | 75.84 ± 13.14 |
| Tong et al., 2018 [21] | 73.6 ± – | – | – |
| Liu et al., 2019 [24] | 81.58 ± 11.05 | 87.30 ± 14.30 | 79.71 ± 13.59 |
| Chen et al., 2020 [23] | 86.43 ± – | – | – |
| Cao et al., 2020 [37] | 82.74 ± 10.20 | 89.35 ± 11.79 | 79.64 ± 13.34 |
| Usman et al., 2020 [5] | 87.55 ± 10.58 | 91.62 ± 8.47 | 88.24 ± 9.52 |
| Chen et al., 2021 [25] | 81.32 ± – | 92.33 ± – | 74.78 ± – |
| Maqsood et al., 2021 [38] | 81 ± – | – | – |
| Zhang et al., 2022 [27] | 85.1 ± 7.10 | 82.7 ± 10.8 | 90 ± 10.7 |
| Tyagi et al., 2022 [18] | 80.74 ± – | 85.46 ± – | 80.56 ± – |
| Chen et al., 2022 [25] | 81.32 ± – | 92.33 ± – | 74.78 ± – |
| Zhou et al., 2022 [39] | 86.75 ± 10.58 | 89.07 ± 8.31 | 83.26 ± 10.21 |
| Our Method 2023 | 87.91 ± 6.27 | 90.84 ± 8.22 | 89.56 ± 10.07 |
| Characteristics | Characteristic Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Calcification | - | - | 85.99 [18] | 91.25 [42] | 85.98 [27] | 87.77 [405] |
| Internal structure | 87.98 [487] | 78.04 [3] | - | 84.13 [2] | - | - |
| Lobulation | 91.07 [201] | 86.09 [164] | 84.79 [78] | 85.08 [31] | 87.54 [18] | - |
| Malignancy | 89.18 [39] | 87.76 [114] | 79.45 [163] | 89.14 [98] | 91.02 [78] | - |
| Margin | 92.08 [9] | 89.81 [37] | 79.25 [78] | 82.99 [232] | 92.97 [136] | - |
| Sphericity | 88.77 [38] | 83.22 [153] | 91.61 [218] | 90.24 [83] | - | |
| Speculation | 92.42 [257] | 82.69 [165] | 85.17 [32] | 80.39 [14] | 83.56 [24] | - |
| Subtlety | 80.3 [4] | 88.96 [22] | 82.88 [131] | 91.99 [238] | 86.03 [97] | - |
| Texture | 80.47 [11] | 85.73 [18] | 87.1 [26] | 82.27 [107] | 90.17 [330] | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usman, M.; Shin, Y.-G. DEHA-Net: A Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network with an Adaptive ROI Mechanism for Lung Nodule Segmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041989
Usman M, Shin Y-G. DEHA-Net: A Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network with an Adaptive ROI Mechanism for Lung Nodule Segmentation. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041989
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsman, Muhammad, and Yeong-Gil Shin. 2023. "DEHA-Net: A Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network with an Adaptive ROI Mechanism for Lung Nodule Segmentation" Sensors 23, no. 4: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041989
APA StyleUsman, M., & Shin, Y.-G. (2023). DEHA-Net: A Dual-Encoder-Based Hard Attention Network with an Adaptive ROI Mechanism for Lung Nodule Segmentation. Sensors, 23(4), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041989







