Sooty Tern Optimization Algorithm-Based Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing NSCLC Tumours
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
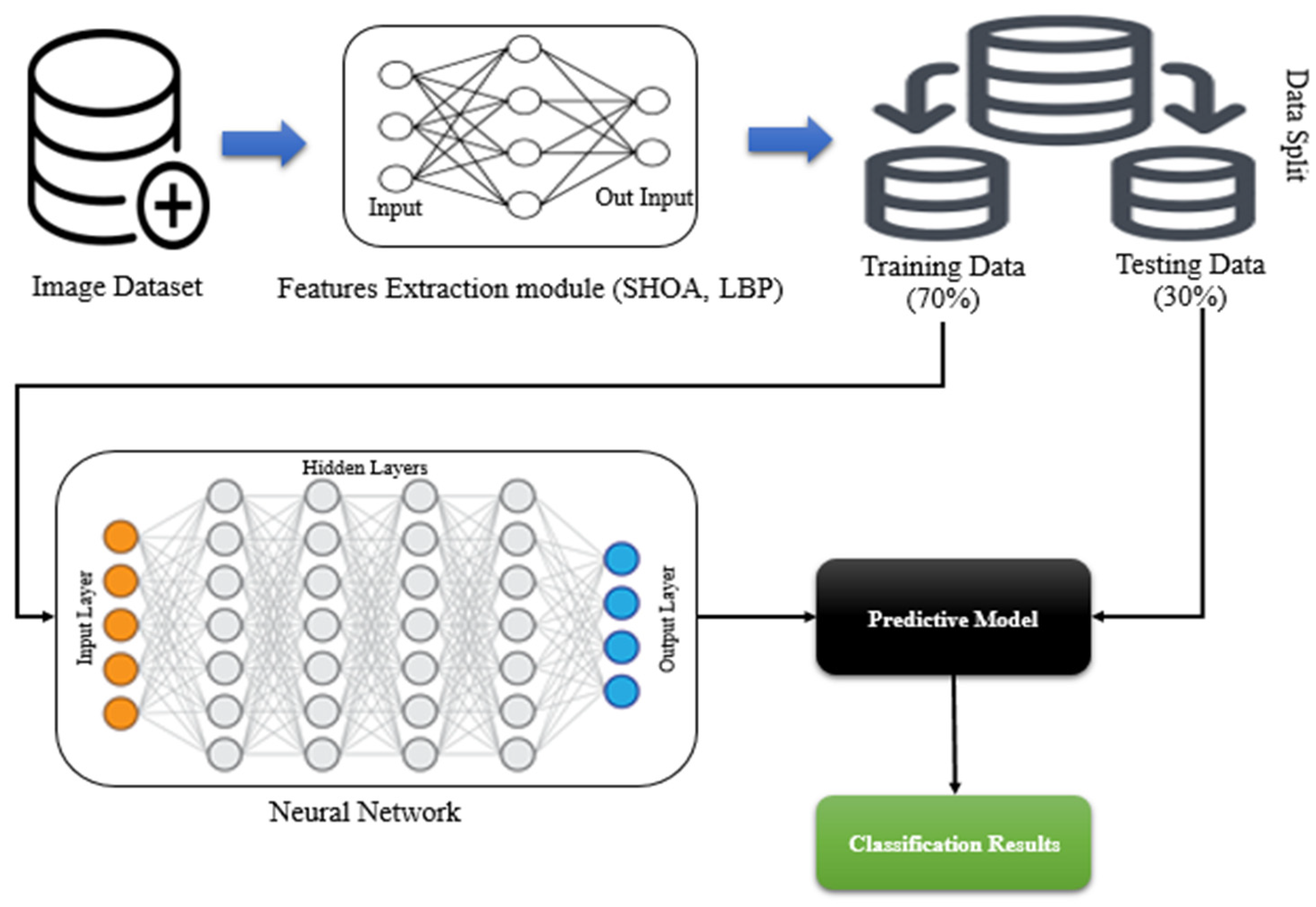
3. Proposed Methods
3.1. Automatic Lung Parenchyma Mining and Border Restoration (ALPM & BR)
3.1.1. Automatic Single-Seeded Region Growth (ASSRG) Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: ASSRG |
| Input: ‘IL’— Either right or left lung region Output: Lobe that is segmented
|
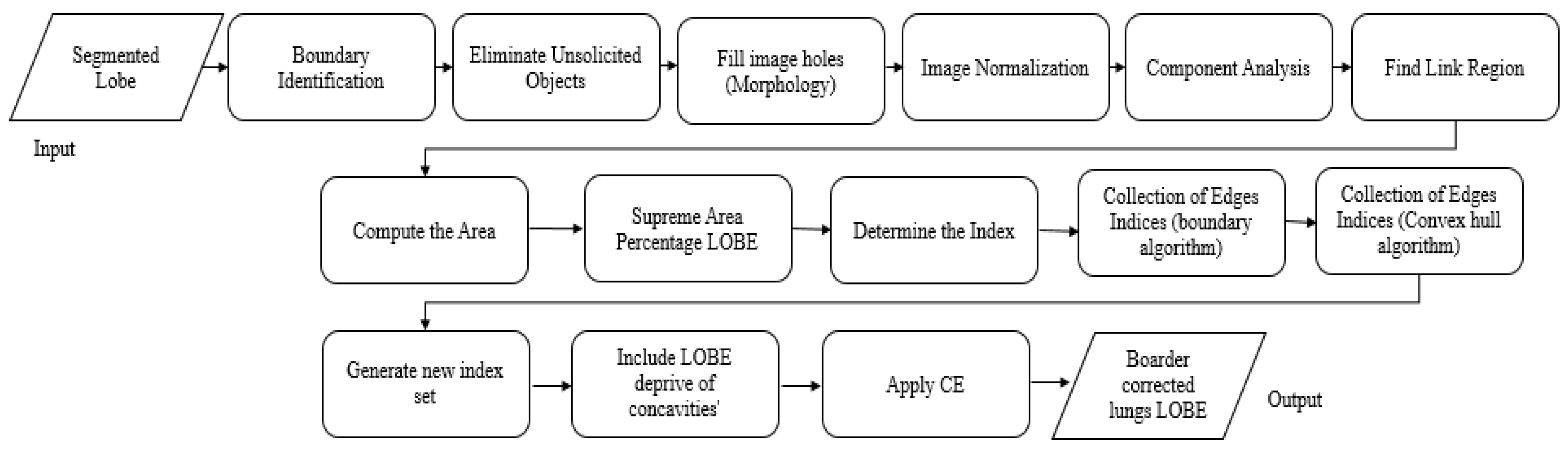
3.1.2. Novel Hybrid Border Concavity Closing (NHBCC) Algorithm
| Algorithm 2: NHBCC Algorithm |
| Input: ASSRG segmented lobe (right or left) (J), the width of the line (n) Output: Border-corrected lung lobe (Ibcl)
|
3.2. Optimization of Features Using the SHOA Algorithm
3.2.1. Migration (Exploration)
- Collision evasion: ‘’ gives the new position of a search agent (SA) that deals with avoiding collisions amid the adjacent SAs (STs).
- —Location of SA that does not affect that of other SAs;
- —Present location of SA;
- —Movement of SA in assumed search space.
- —Present iteration, ;
- —Controlling factor (set to 2), which modifies ‘’ linearly decreased to 0.
- Converge in the direction of the best neighbour: once a collision is overcome, SAs converge in the track of the best neighbour.
- —Diverse locations of SA towards the best, fittest SA ;
- —Random variable employed for improved exploration.
- —Random number that is in the range [0, 1].
- Updation conforming best SA: lastly, SA or ST modifies its location based on the best SA.
- —Gap amid the SA and fittest SA.
3.2.2. Attacking (Exploitation)
| Algorithm 3: STOA |
|
3.2.3. Improved LBP-Based Optimized Feature Extraction
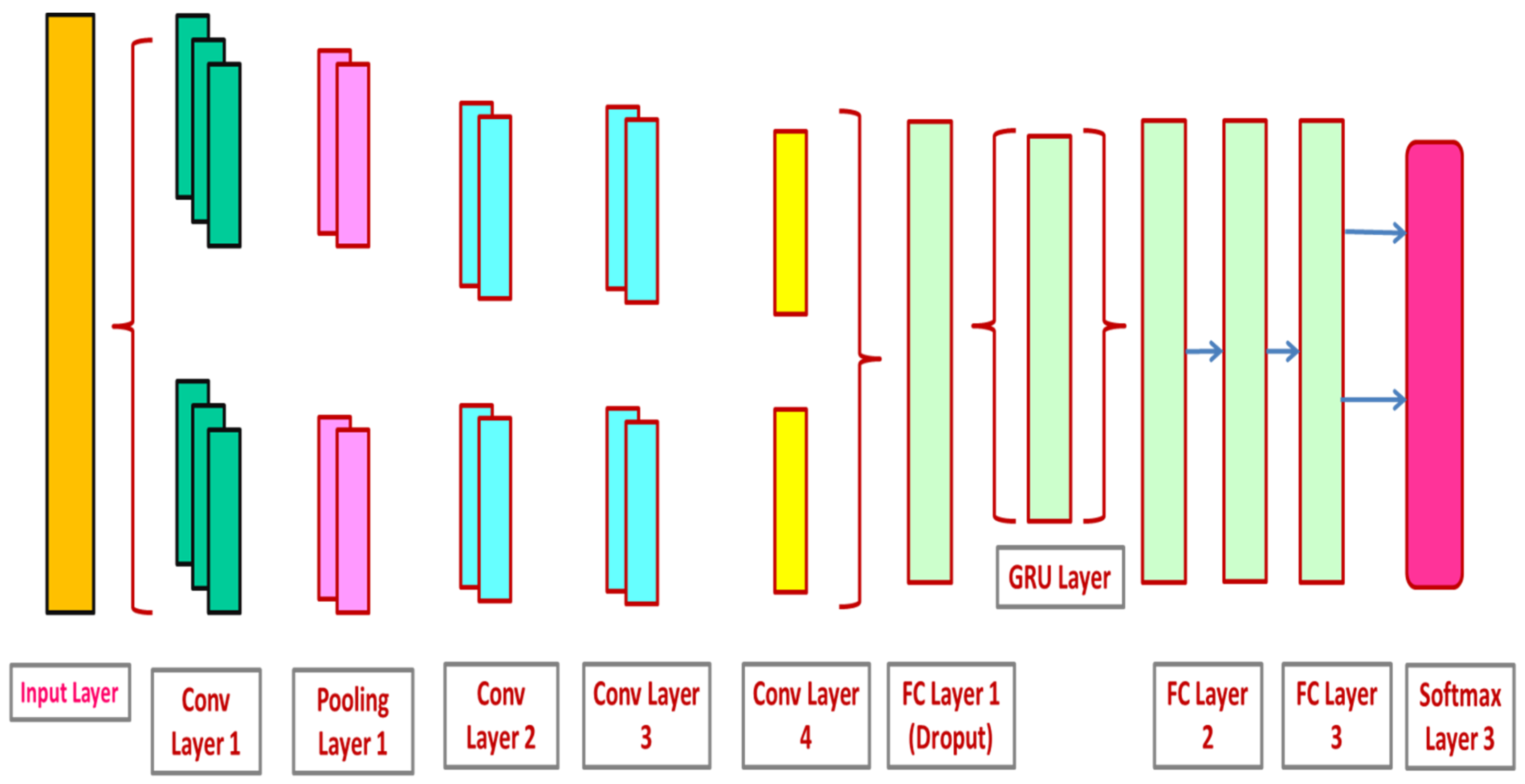
3.3. CNN and GRU-Based Lung Nodule Classification
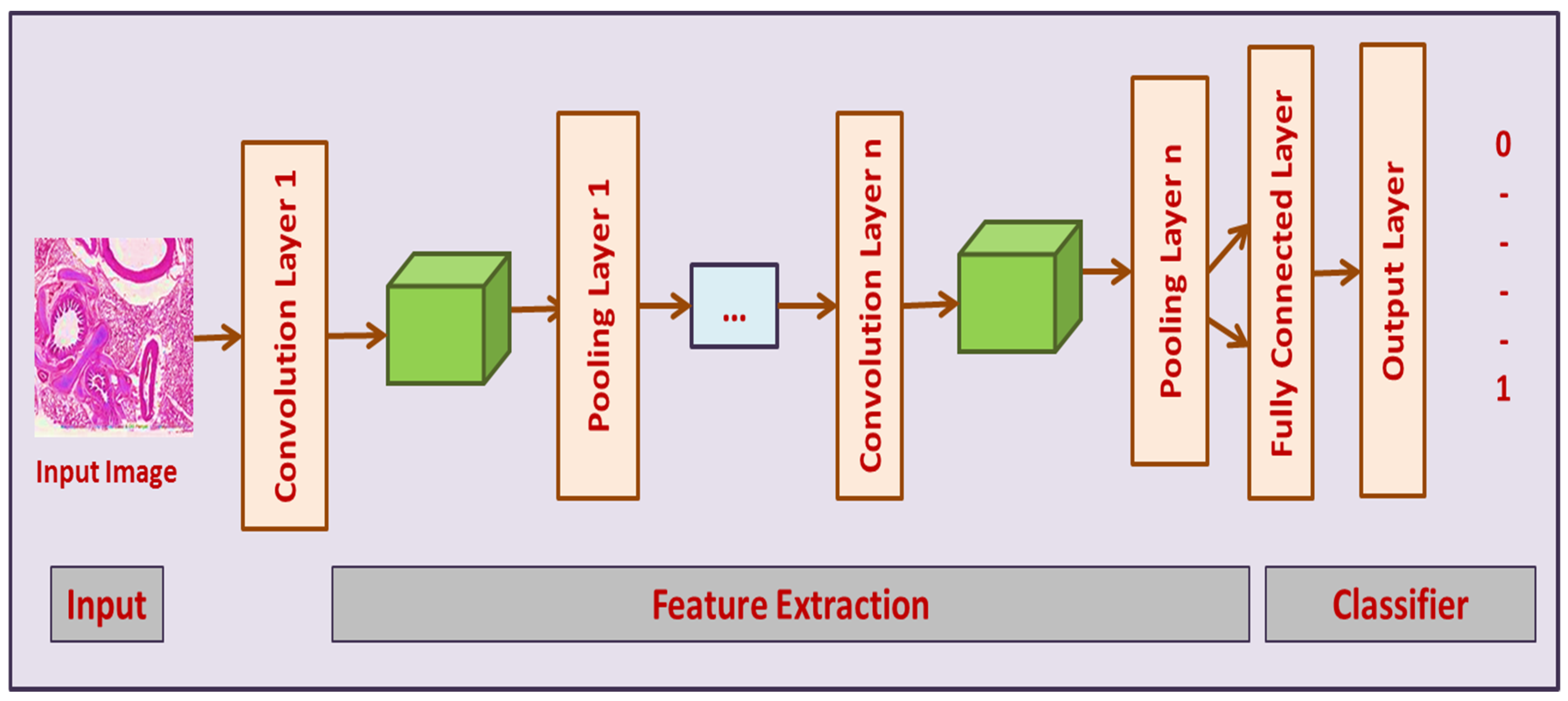
3.3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
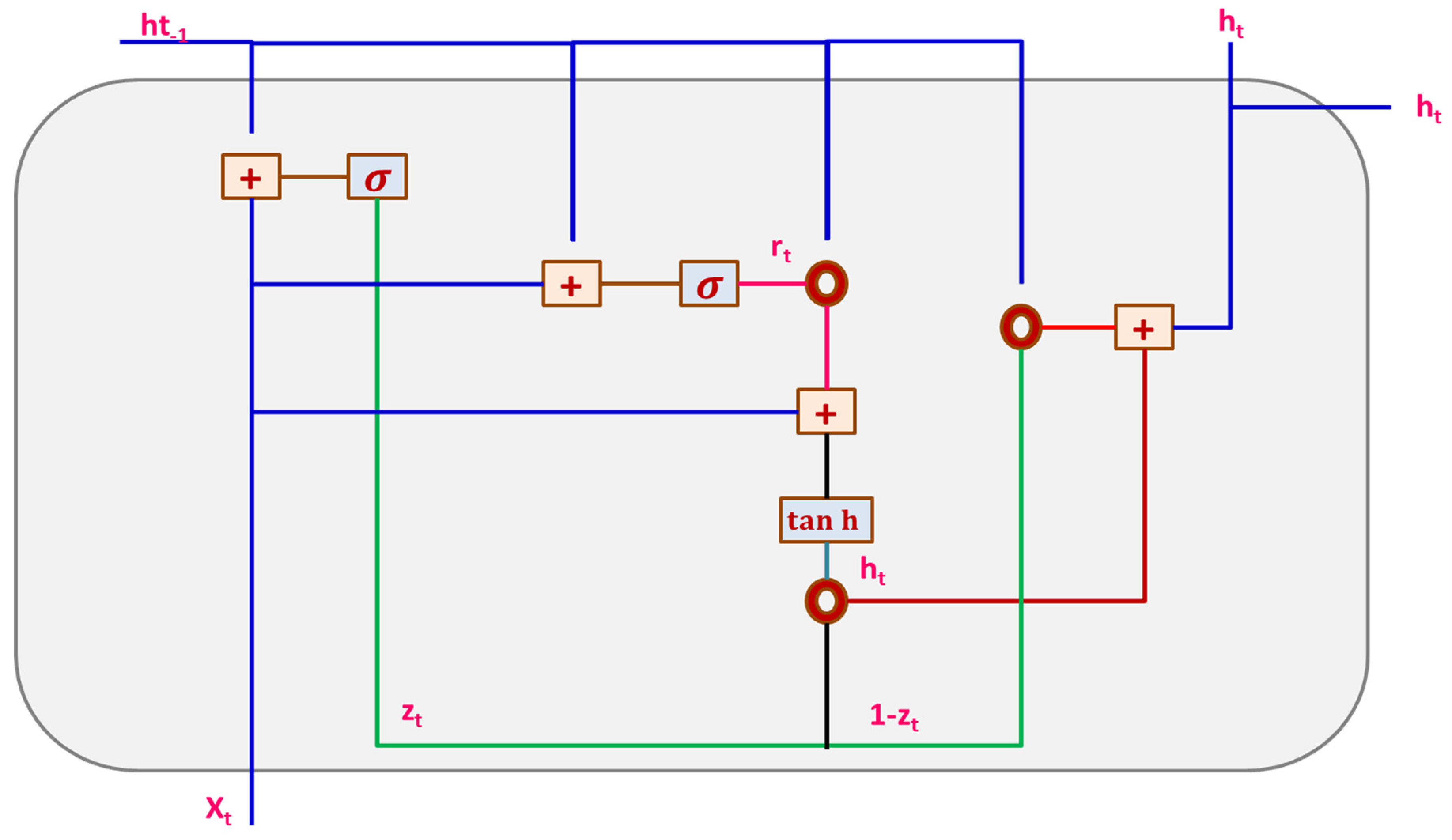
3.3.2. Gated Recurrent Unit Network (GRU)
3.3.3. CNN-GRU
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Performance Evaluation Using Training and Testing Data with Distinct Classes
4.2. Performance Assessment of Proposed SHOA-DNN Model and Compared Benchmarked Schemes
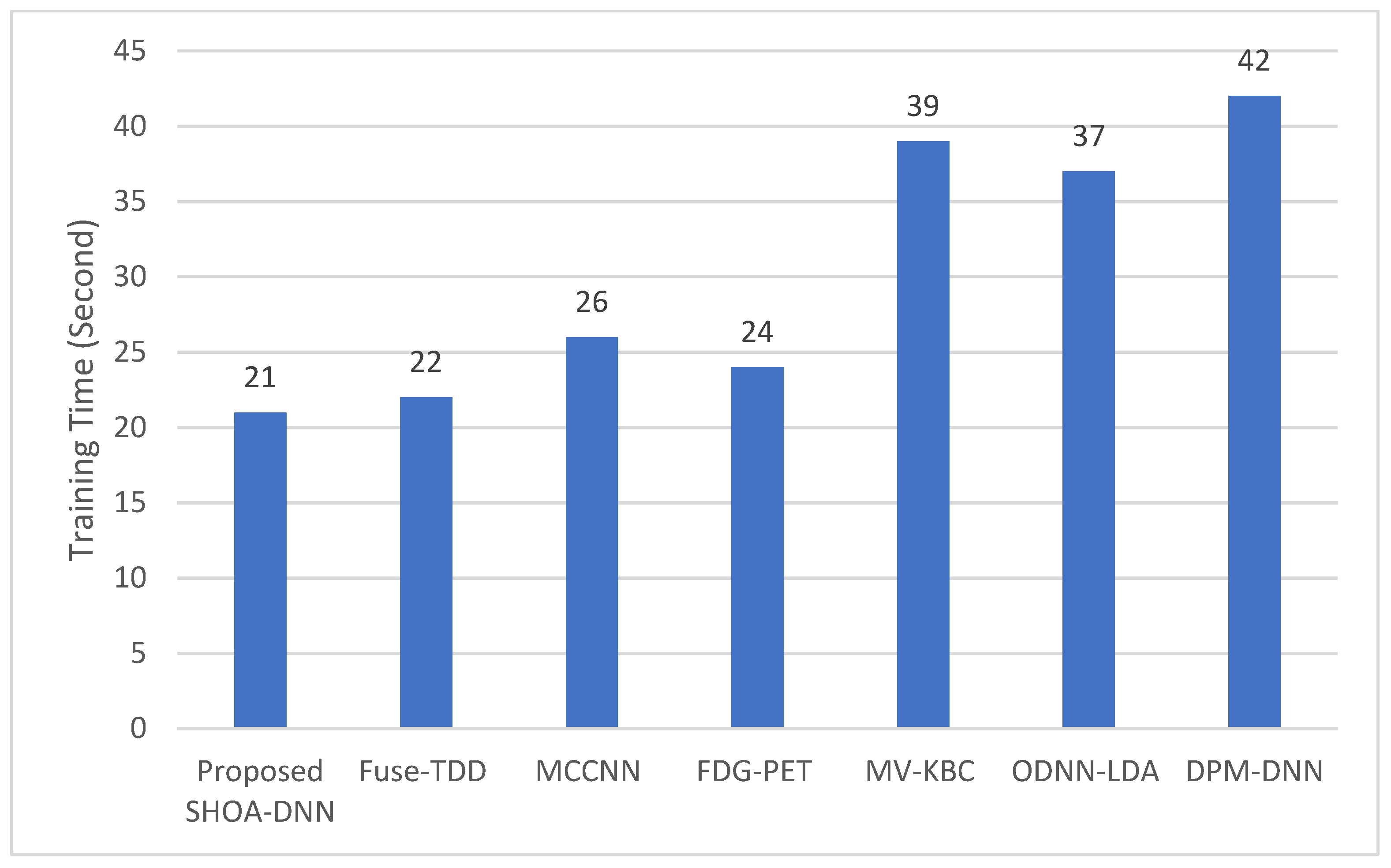
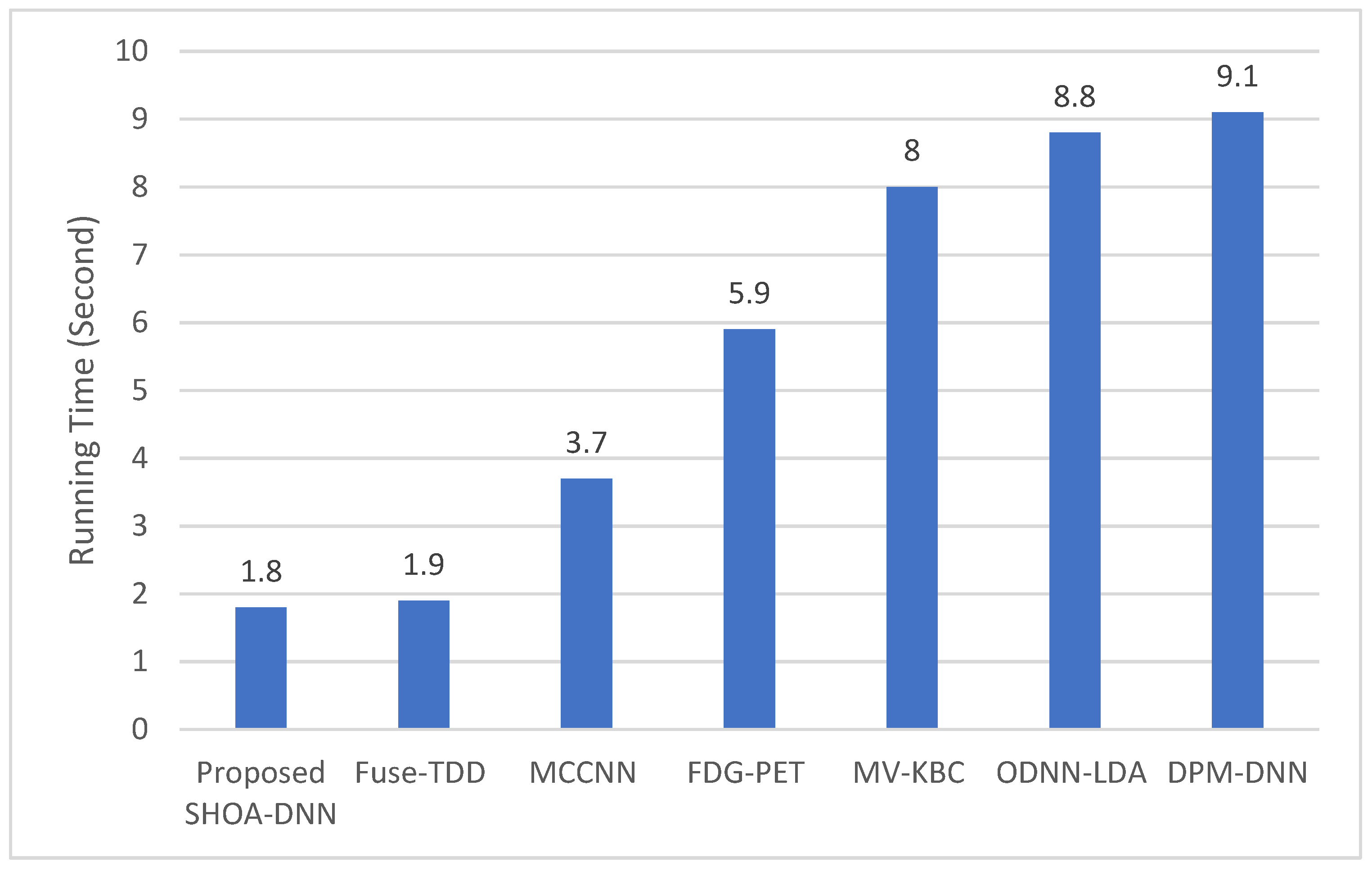
4.3. Performance Evaluation of the Proposed SHOA-DNN Using Training Time and Running Time
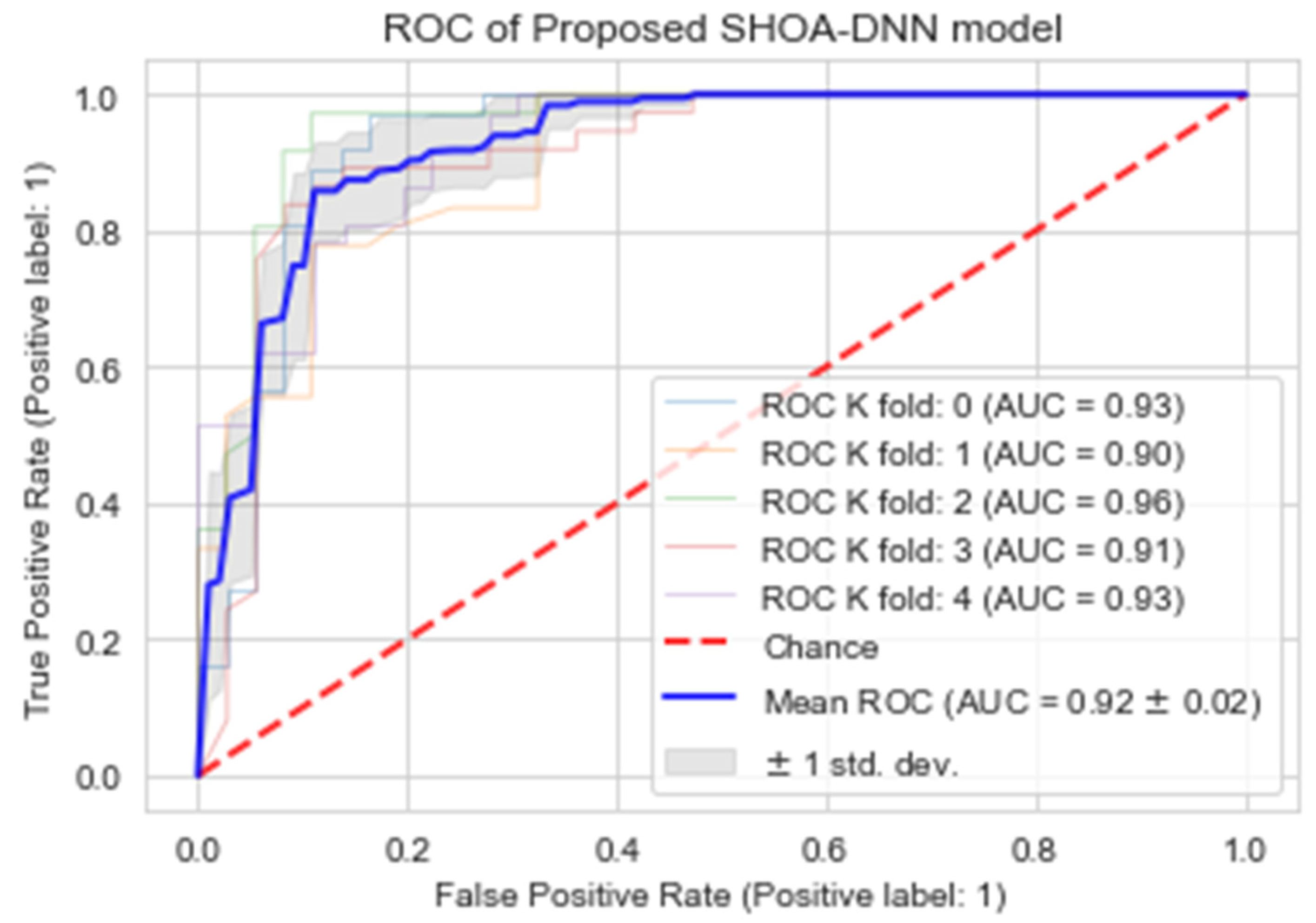
4.4. Performance Evaluation of the Proposed SHOA-DNN Using Cross-Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, R.; Rezaei, T. Lung cancer diagnosis based on an ANN optimized by an improved TEO algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 6078524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijh, S.; Gaurav, P.; Pandey, H.M. Hybrid bio-inspired algorithm and convolutional neural network for automatic lung tumor detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 3, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, P.M.; Burhanuddin, M.A.; Desa, M.I. Automatic lung cancer detection from CT image using improved deep neural network and ensemble classifier. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 34, 9579–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Babyn, P.; Zhong, H. Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) of a pulmonary nodule of thoracic CT image using transfer learning. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Lei, Q.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q. Deep transfer convolutional neural network and extreme learning machine for lung nodule diagnosis on CT images. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 204, 106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chi, W.; Li, Z.; Duan, W.; Liu, H.; Liang, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, P.; He, J.; et al. Deep learning aided decision support for pulmonary nodules diagnosing: A review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S867–S875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; Huang, X.; Chang, J.; Hou, D.; Lu, H. Research on key algorithms of the lung CAD system based on deep feature fusion and MKL-SVM-IPSO recognition. Wireless Personal 2022, 3, 21203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, M.P.; Mano Paul, P.D.; Maram, B.; Ananth, J.P. Deep maxout network for lung cancer detection using optimization algorithm in intelligent Internet of things. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famitha, S.; Moorthi, M. Intelligent and novel multi-type cancer prediction model using optimized ensemble learning. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 3, 1879–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanglia, P.; Kumar, S.; Mahajan, A.N.; Singh, P.; Rathee, D. A hybrid algorithm for lung cancer classification using SVM and neural networks. ICT Express 2021, 7, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, B.R.; Alsadoon, A.; Prasad, P.W.; Al Aloussi, S.; Rashid, T.A.; Alsadoon, O.H.; Jerew, O.D. Deep learning neural network for lung cancer classification: Enhanced optimization function. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 8, 6605–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, K.; Chawla, P.; Rawat, S. A deep learning-based approach for detection of lung cancer using self-adaptive sea lion optimization algorithm (SA-slno). J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 3, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargavi, V.R.; Rajesh, V. Computer-aided bright lesion classification in fundus image based on feature extraction. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32, 1850034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, C.; Ramana, K.; Lakkisetty, S.Y.; Band, S.S.; Agarwal, S.; Mosavi, A. A neural network and optimization-based lung cancer detection system in CT images. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, T.; Liyakathunisa Alaskar, H.; Parvathi, R.; Pattabiraman, V.; Hussain, A. Cat swarm optimization-based computer-aided diagnosis model for lung cancer classification in computed tomography images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.; Muhammad, G.; Hossain, M.S.; Alhumyani, H.; Alshamrani, S.S.; Cheikhrouhou, O.; Ibrahim, S. Light deep model for pulmonary nodule detection from CT scan images for mobile devices. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 8893494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ma, H.; Qian, W.; Gao, M.; Li, Y. An automatic detection system of lung nodule based on multigroup patch-based deep learning network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 22, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Fulham, M.; Zhang, Y. Fusing texture, shape and deep model-learned information at the decision level for automated classification of lung nodules on chest CT. Inf. Fusion 2018, 42, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madero Orozco, H.; Vergara Villegas, O.O.; Cruz Sánchez, V.G.; Ochoa Domínguez, H.D.J.; Nandayapa Alfaro, M.D.J. Automated system for lung nodules classification based on wavelet feature descriptor and support vector machine. Biomed. Eng. Online 2015, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, F.; Yu, D.; Dong, D.; Yang, C.; Zang, Y.; Tian, J. Multi-crop convolutional neural networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrullah, N.; Sang, J.; Alam, M.S.; Mateen, M.; Cai, B.; Hu, H. Automated lung nodule detection and classification using deep learning combined with multiple strategies. Sensors 2019, 19, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirienko, M.; Sollini, M.; Silvestri, G.; Mognetti, S.; Voulaz, E.; Antunovic, L.; Chiti, A. Convolutional neural networks are promising in lung cancer T-parameter assessment on baseline FDG-PET/CT. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 1382309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Feng, D.; Fulham, M.; Cai, W. Knowledge-based collaborative deep learning for benign-malignant lung nodule classification on chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanaprabu, S.K.; Mohanty, S.N.; Shankar, K.; Arunkumar, N.; Ramirez, G. The optimal deep learning model for classification of lung cancer on CT images. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Causey, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Jiang, B.; Qualls, J.A.; Politte, D.G.; Prior, F.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X. Highly accurate model for prediction of lung nodule malignancy with CT scans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astaraki, M.; Zakko, Y.; Dasu, I.T.; Smedby, Ö.; Wang, C. Benign-malignant pulmonary nodule classification in low-dose CT with convolutional features. Phys. Med. 2021, 83, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuriwal, N.; Mishra, N. Breast cancer detection from histopathological images using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference and Workshops on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Jaipur, India, 22–25 November 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J.B. The Behavior of Noddy and Sooty Terns. Pap. Tortugas Lab. Carnegie Inst. Wash. 1908, 102, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Yasuda, K. The spiral optimization algorithm: Convergence conditions and settings. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 50, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, A.; Ali, L.; Mohammed Seid, A.; Ali, A.; Khan, D.; Imrana, Y. A Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) for Unbiased Prediction of Caesarean Section Based on Features Extraction and Optimized Classification. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1901735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, A.; Dallora, A.L.; Berglund, J.S.; Ali, A.; Ali, L.; Anderberg, P. Machine Learning for Dementia Prediction: A Systematic Review and Future Research Directions. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, A.; Dallora, A.L.; Berglund, J.S.; Anderberg, P. An Intelligent Learning System for Unbiased Prediction of Dementia Based on Autoencoder and Adaboost Ensemble Learning. Life 2022, 12, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Training/Testing-70:30 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCC | Specificity | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F-Score | |
| Normal | 92.34 | 100.00 | 90.28 | 96.18 | 98.16 | 85.45 |
| Malignant | 96.15 | 97.88 | 93.56 | 88.29 | 90.58 | 89.42 |
| Benign | 98.78 | 98.15 | 91.19 | 100.00 | 74.94 | 86.71 |
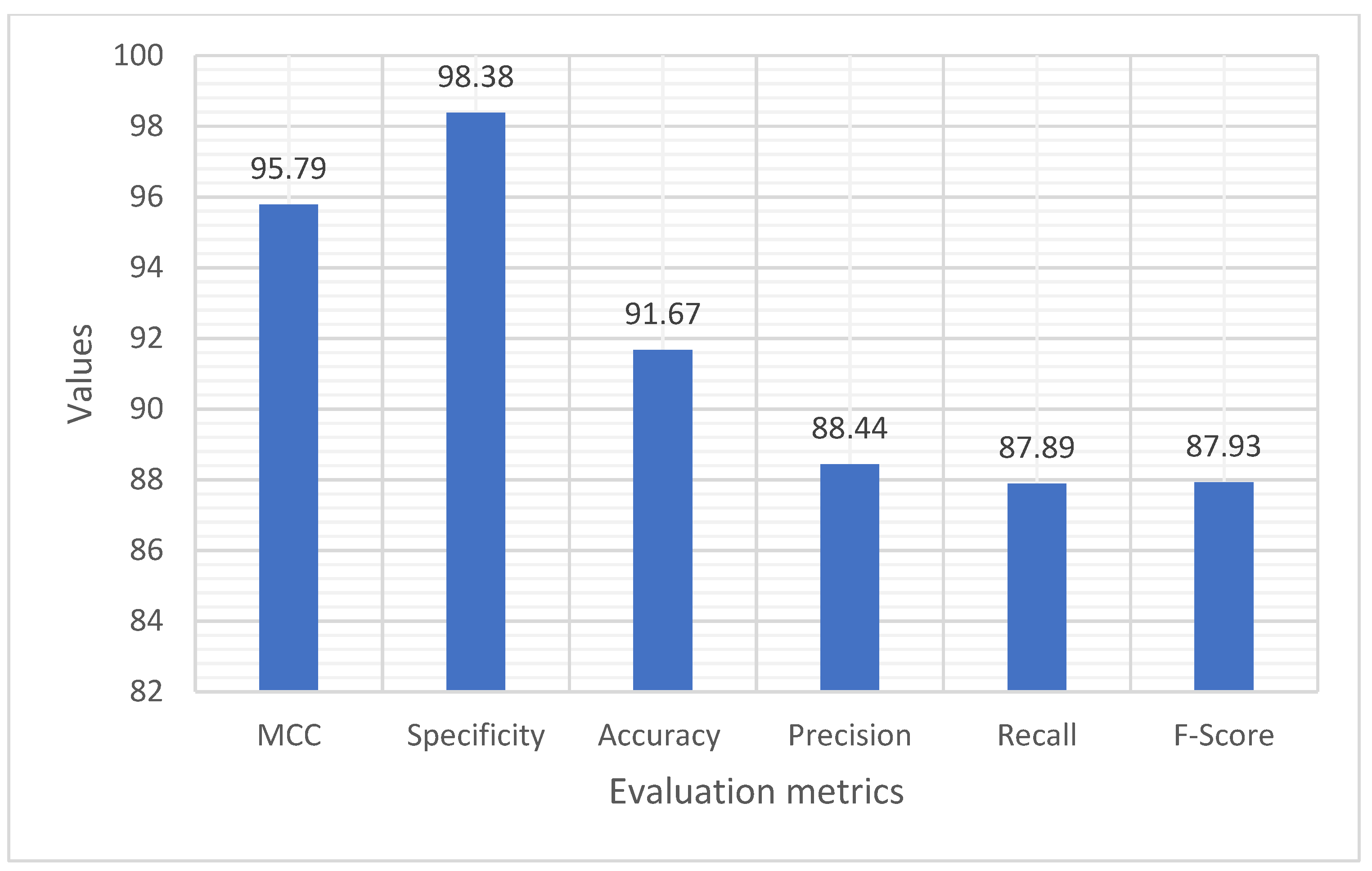
| Average | 95.79 | 98.38 | 91.67 | 88.44 | 87.89 | 87.93 |
| Compared Schemes | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Specificity | F-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
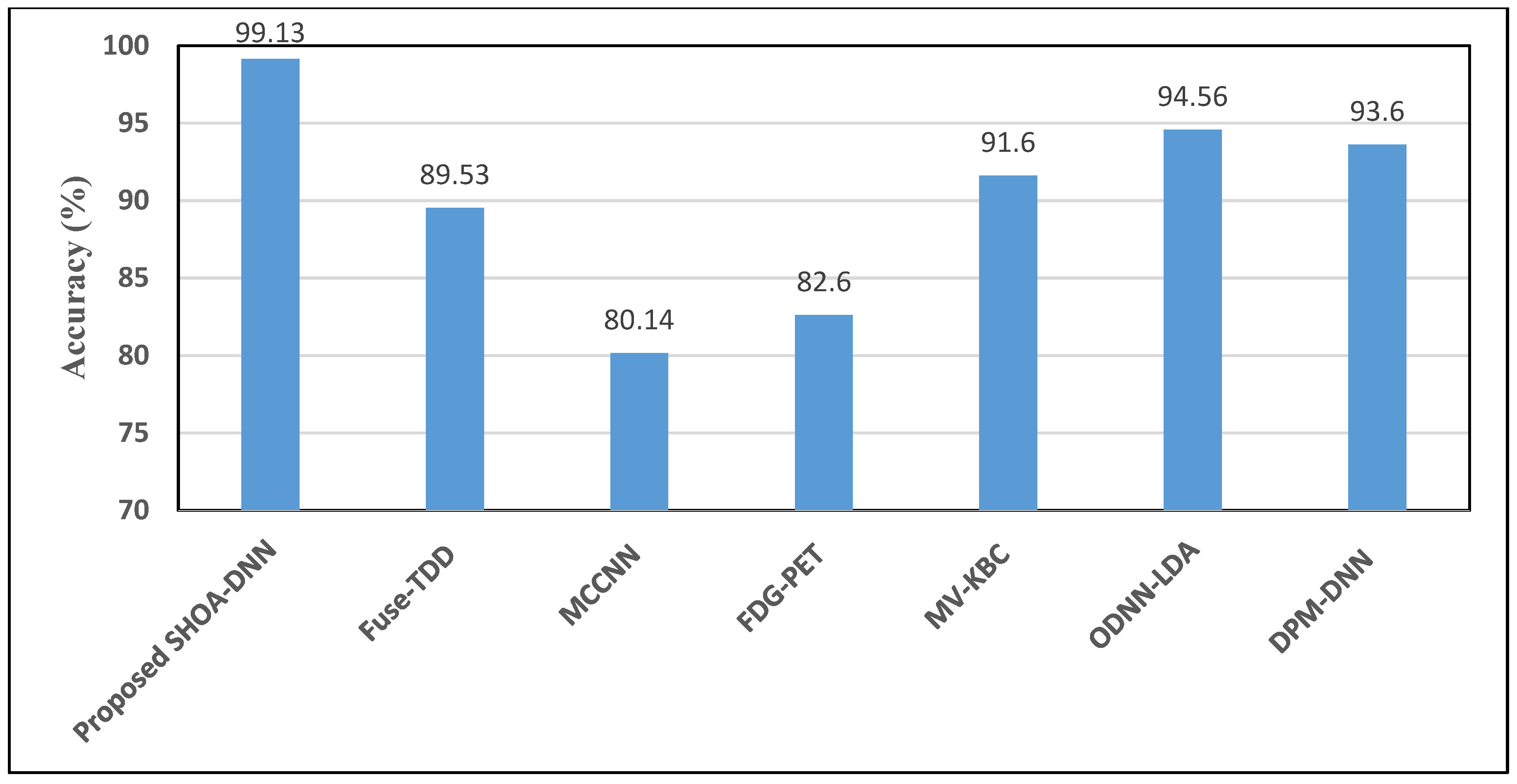
| Proposed SHOA-DNN Model | 99.13 | 98.84 | 98.64 | 99.32 | 98.72 |
| Fuse-TDD [18] | 89.53 | - | 84.19 | 92.02 | 89.00 |
| MCCNN [20] | 80.14 | - | 77.00 | 93.00 | 87.00 |
| FDG-PET [22] | 82.60 | - | 92.10 | 53.40 | 82.00 |
| MV-KBC [23] | 91.60 | 87.75 | 86.52 | 94.00 | 87.13 |
| ODNN-LDA [24] | 94.56 | - | 96.2 | 94.2 | 95.12 |
| DPM-DNN [26] | 93.60 | - | - | - | - |
| CV1 | Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | Specificity (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | 0.93 | 95.82 | 90.10 | 0.91 |
| K = 2 | 0.90 | 98.35 | 88.56 | 0.87 |
| K = 3 | 0.96 | 97.01 | 92.14 | 0.94 |
| K = 4 | 0.91 | 89.25 | 100.00 | 0.88 |
| K = 5 | 0.93 | 91.55 | 96.33 | 0.92 |
| Mean | 0.92 | 94.39 | 93.42 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleem, M.A.; Thien Le, N.; Asdornwised, W.; Chaitusaney, S.; Javeed, A.; Benjapolakul, W. Sooty Tern Optimization Algorithm-Based Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing NSCLC Tumours. Sensors 2023, 23, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042147
Saleem MA, Thien Le N, Asdornwised W, Chaitusaney S, Javeed A, Benjapolakul W. Sooty Tern Optimization Algorithm-Based Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing NSCLC Tumours. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042147
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleem, Muhammad Asim, Ngoc Thien Le, Widhyakorn Asdornwised, Surachai Chaitusaney, Ashir Javeed, and Watit Benjapolakul. 2023. "Sooty Tern Optimization Algorithm-Based Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing NSCLC Tumours" Sensors 23, no. 4: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042147
APA StyleSaleem, M. A., Thien Le, N., Asdornwised, W., Chaitusaney, S., Javeed, A., & Benjapolakul, W. (2023). Sooty Tern Optimization Algorithm-Based Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing NSCLC Tumours. Sensors, 23(4), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042147







