Imbalanced Text Sentiment Classification Based on Multi-Channel BLTCN-BLSTM Self-Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
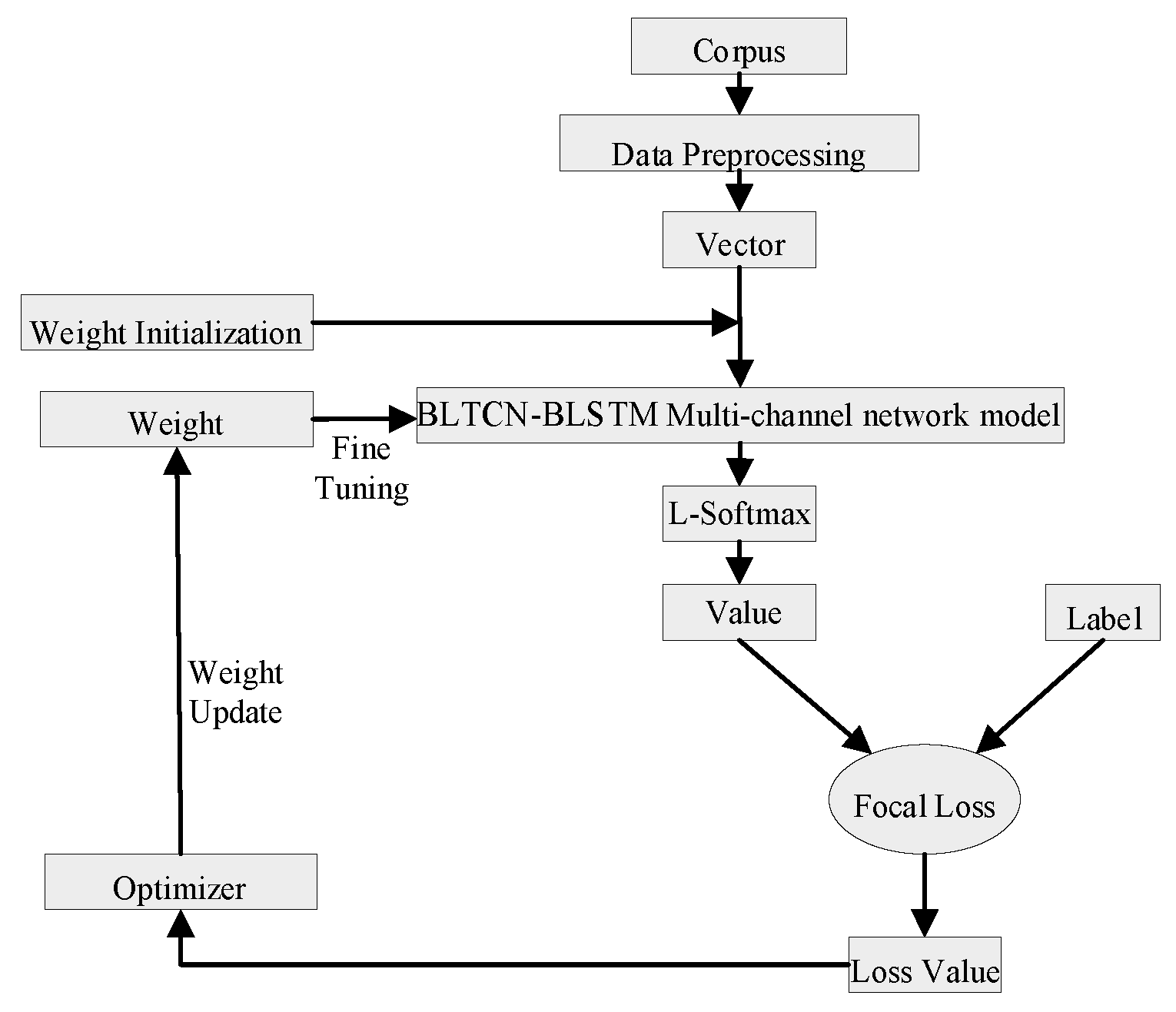
3. Construction of the Model
3.1. Sentiment Classification Modeling for Imbalanced Short Texts
3.2. Vector Embedding Layer
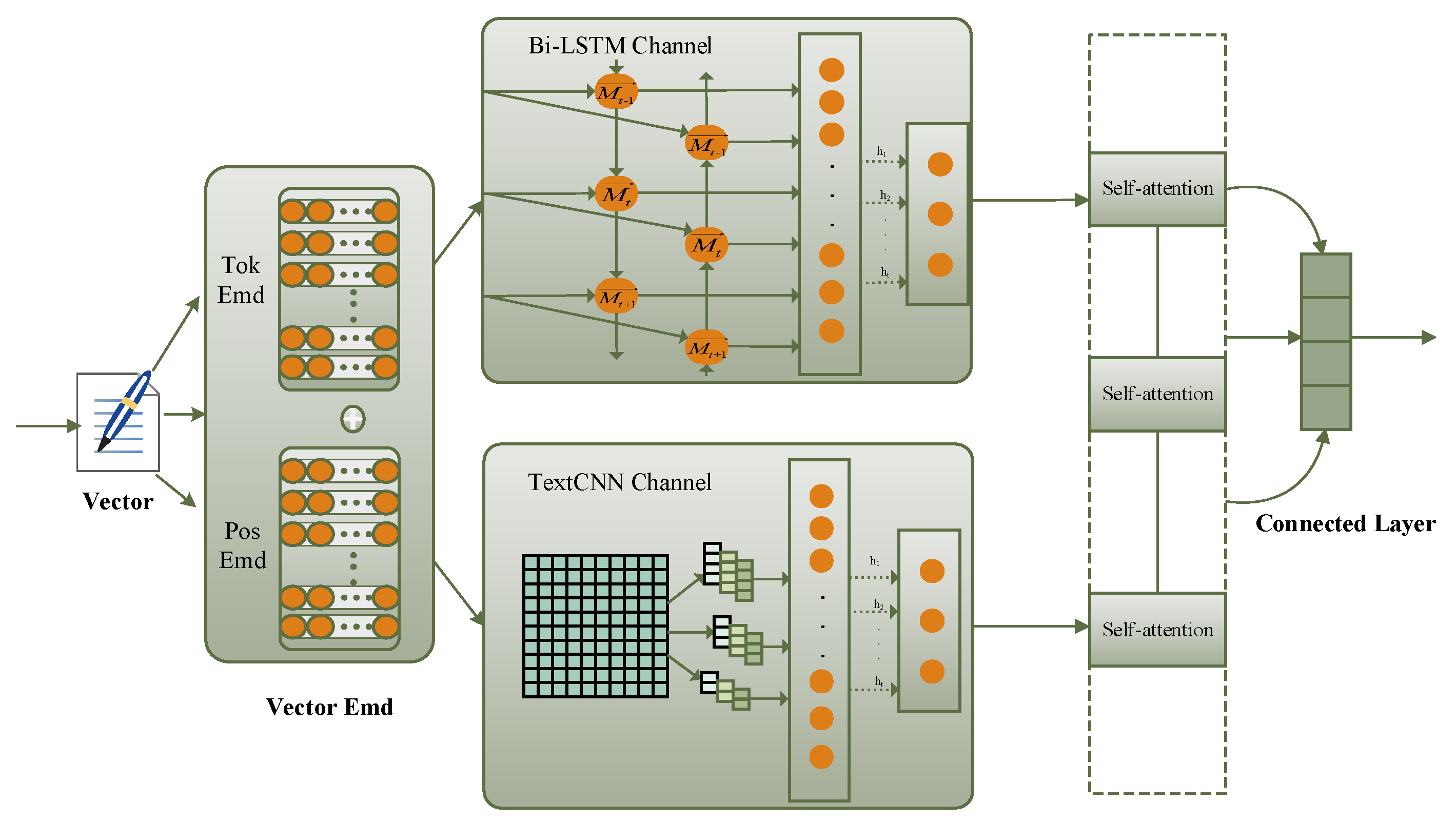
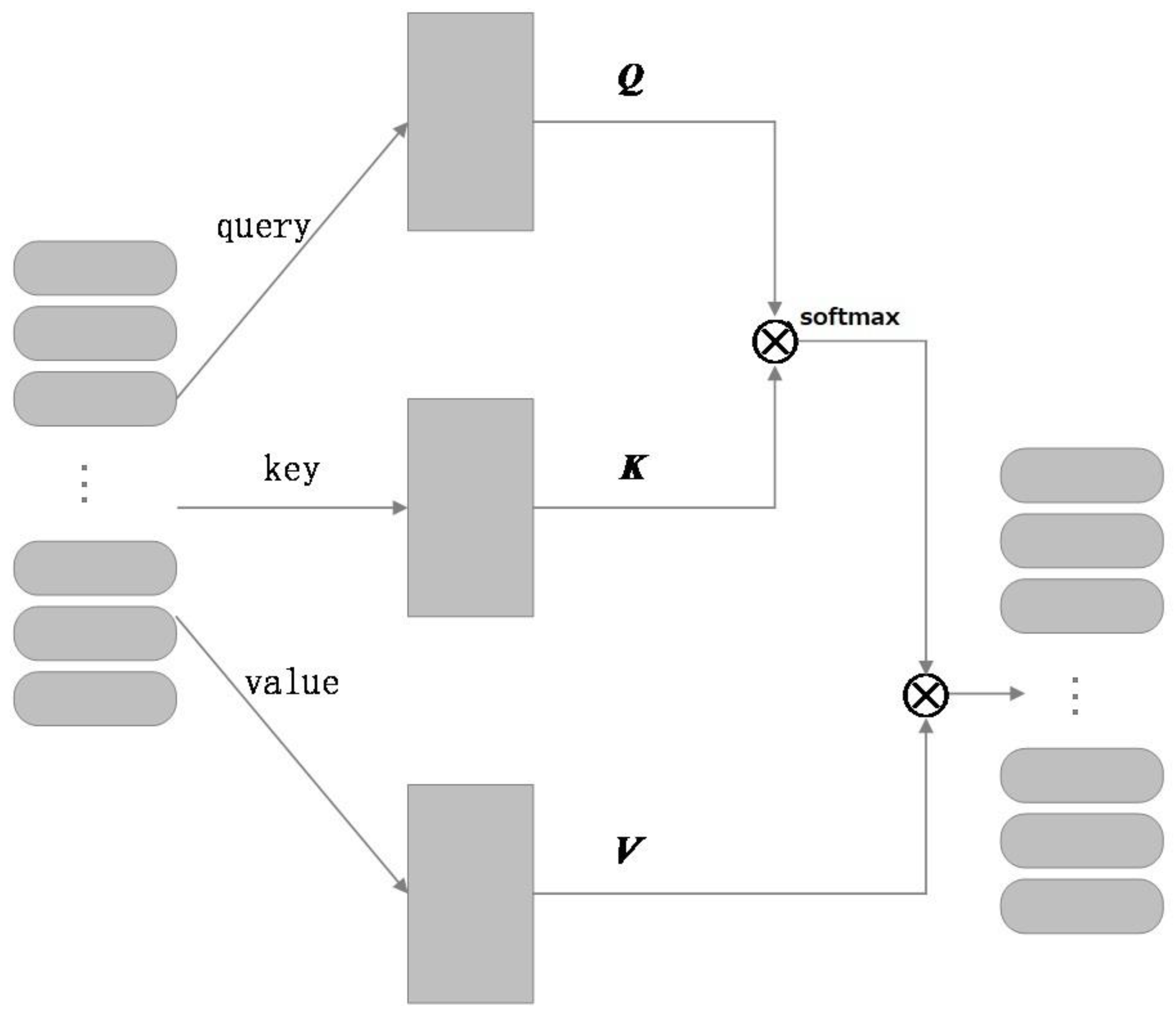
3.3. Multi-Channel BLTCN-BLSTM Self-Attention Network Model
3.4. L-Softmax Augmentation
3.5. Loss Rebalancing
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Environment
4.2. Experimental Data
4.3. Evaluation Index
4.4. Experimental Comparison
4.5. Ablation Experiment
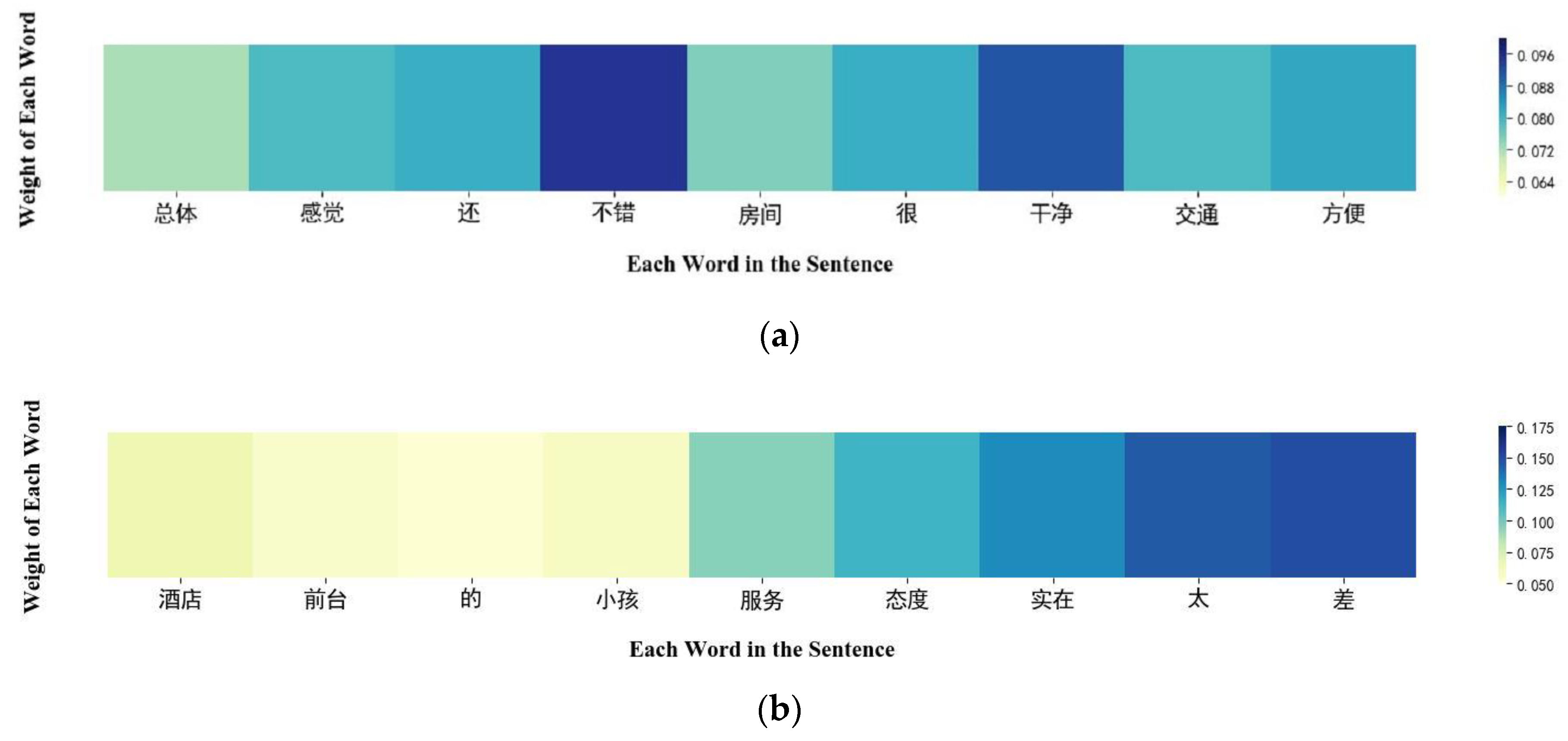
4.6. Predictive Text Self-Attention Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
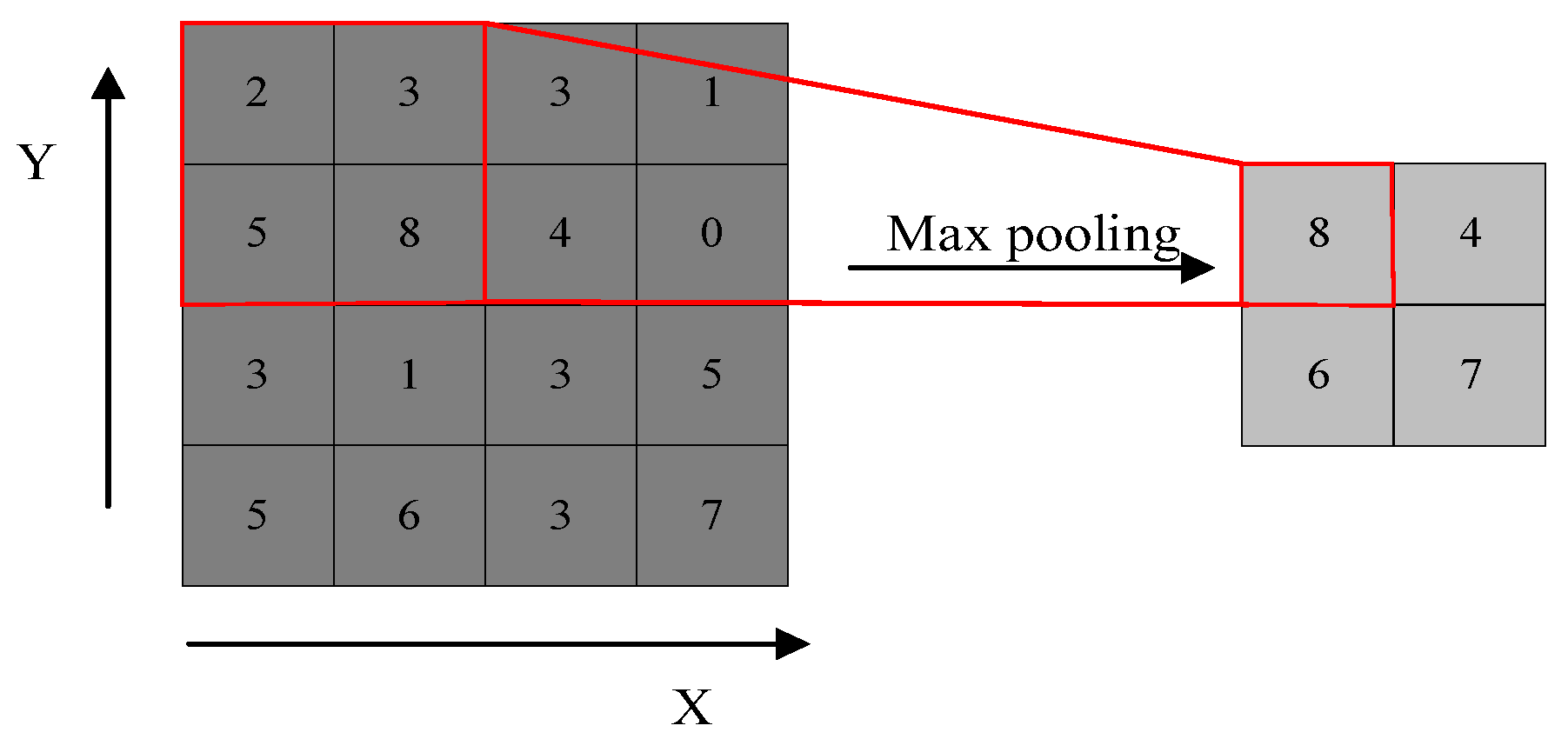
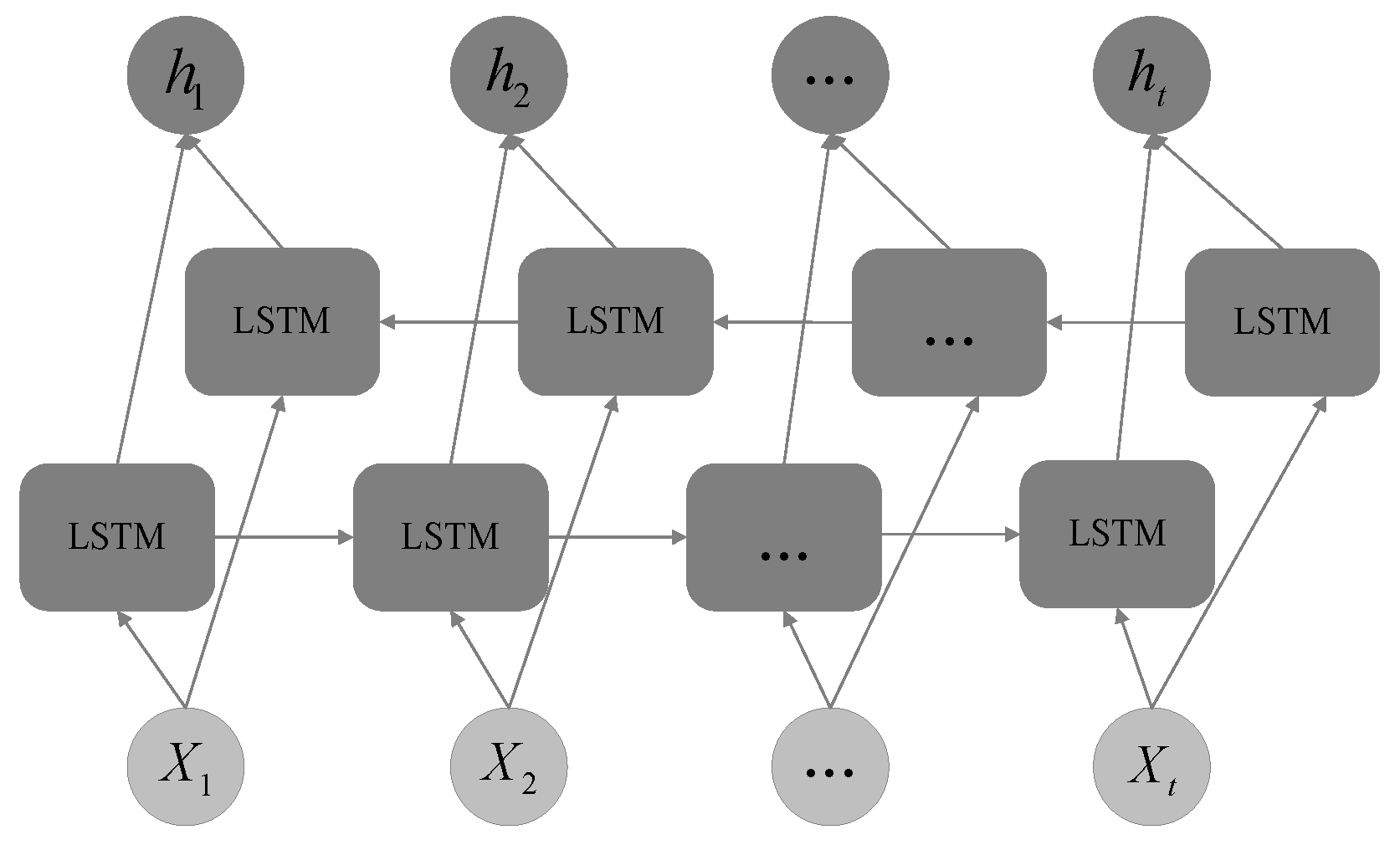
References
- Samuel, J.; Kashyap, R.; Samuel, Y.; Pelaez, A. Adaptive Cognitive Fit: Artificial Intelligence Augmented Management of Information Facets and Representations. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 65, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, N.; Sakti, S.; Yoshino, K.; Nakamura, S. Emotional Triggers and Responses in Spontaneous Affective Interaction: Recognition, Prediction, and Analysis. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Intell. 2018, 33, DSH-D_1-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, K.; van der Weijde, O.; Frasincar, F.; Dekker, R. Supervised and Unsupervised Aspect Category Detection for Sentiment Analysis with Co-Occurrence Data. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Ji, P.; Kwong, C.K. Review on Recent Advances in Information Mining From Big Consumer Opinion Data for Product Design. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2019, 19, 010801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J. Sentiment Analysis of Chinese Reviews Based on BiTCN-Attention Model. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 2022, 33, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.C.; Moreno-García, M.N.; De la Prieta, F. Sentiment Analysis Based on Deep Learning: A Comparative Study. Electronics 2020, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yan, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q. A Network-Based Feature Extraction Model for Imbalanced Text Data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 195, 116600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalchbrenner, N.; Grefenstette, E.; Blunsom, P. A Convolutional Neural Network for Modelling Sentences. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Baltimore, Maryland, 2014; pp. 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Predicting Polarities of Tweets by Composing Word Embeddings with Long Short-Term Memory. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 1343–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Joty, S.; Meng, H. Fine-Grained Opinion Mining with Recurrent Neural Networks and Word Embeddings. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; pp. 1433–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Irsoy, O.; Cardie, C. Opinion Mining with Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; Association for Computational Linguistics: Doha, Qatar, 2014; pp. 720–728. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification 2014. arXiv 2 September 2014. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.5882 (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Dobreva, J.; Mitrovikj, A.P.; Dimitrova, V. MalDeWe: New Malware Website Detector Model based on Natural Language Processing using Balanced Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence, CSCI, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–17 December 2021; pp. 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Chouhan, S.S.; Rathore, S.S. TextConvoNet: A Convolutional Neural Network Based Architecture for Text Classification. Appl. Intell. 2022, 50, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Qin, C.; Liu, P. Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Ensemble Model Applied to Classification of Unbalanced Data. Sci. Program. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Chen, Q.; Qi, X. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Imbalanced Classification. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 2488–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, S.; Gong, Z.; Zhou, G. Imbalanced Emotion Classification Based on Multi-channel LSTM. J. Chin. Inf. Technol. 2018, 32, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, H. An Emotion Analysis Method Using Multi-ChannelConvolution Neural Network in Social Networks. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 125, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, C.N.; Bukhari, S.S.; Dengel, A. Comparative Study between Traditional Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches for Text Classification. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Document Engineering 2018, New York, NY, USA, 28–31 August 2018; ACM: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kamps, J.; Marx, M. Words with attitude. In Proceedings of the BeIgian-NetherIands Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Leuven, Belgium, 22 October 2002; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 332–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Dong, Q. HowNet and the Computation of Meaning; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-981-256-491-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, B.; Lee, L. A Sentimental Education: Sentiment Analysis Using Subjectivity Summarization Based on Minimum Cuts. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics—ACL’04, Barcelona, Spain, 21–26 July 2004; Association for Computational Linguistics: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Iyyer, M.; Manjunatha, V.; Boyd-Graber, J.; Daumé III, H. Deep Unordered Composition Rivals Syntactic Methods for Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 1681–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Renganathan, H. Chinese Sentiment Analysis Using Maximum Entropy. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Sentiment Analysis where AI meets Psychology, SAAIP 2011, Chiang-Mai, Thailand, 13 November 2011; Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing: Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sitaula, C.; Basnet, A.; Mainali, A.; Shahi, T.B. Deep Learning-Based Methods for Sentiment Analysis on Nepali COVID-19-Related Tweets. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Bu, N. A CNN-Based Framework for Predicting Public Emotion and Multi-Level Behaviors Based on Network Public Opinion. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 909439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Zhou, J.; He, L. PG-RNN: Using Position-Gated Recurrent Neural Networks for Aspect-Based Sentiment Classification. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 4073–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, D.; Qiu, X.; Huang, X. Cached Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks for Document-Level Sentiment Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Austin, TX, USA, 2016; pp. 1660–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, L. Attention-Based LSTM for Aspect-Level Sentiment Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Austin, TX, USA, 2016; pp. 606–615. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, J.; Mathur, K. Sentiment Analysis Based on Aspect and Context Fusion Using Attention Encoder with LSTM. Int. J. Inf. Tecnol. 2022, 14, 3611–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.; Hasan, S.; Shamsuddin, S.M.; Idris, N.; Piran, J. A Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture for Opinion-Oriented Multi-Document Summarization Based on Multi-Feature Fusion. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 213, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Ding, F. Research and application of unbalanced data classification. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2018, 35, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, L.; Du, J.Y. Improving the Performance of Sentiment Classification on Imbalanced Datasets With Transfer Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28281–28290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wei, C.; Gaidon, A.; Ma, T. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss. Proceeding Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Wei, Z. Mixed Pooling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology; Miao, D., Pedrycz, W., Ślȩzak, D., Peters, G., Hu, Q., Wang, R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2014; Volume 8818, pp. 364–375. ISBN 978-3-319-11739-3. [Google Scholar]
- Palangi, H.; Deng, L.; Shen, Y.; Gao, J.; He, X.; Chen, J.; Song, X.; Ward, R. Deep Sentence Embedding Using Long Short-Term Memory Networks: Analysis and Application to Information Retrieval. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Che, W.; Liu, T.; Qin, B.; Yang, Z. Pre-Training with Whole Word Masking for Chinese BERT. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 3504–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhang, J. An Empirical Study of Sentiment Analysis for Chinese Documents. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 2622–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Tang, X.; Yuan, T. Fine-Tuning BERT for Multi-Label Sentiment Analysis in Unbalanced Code-Switching Text. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193248–193256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hyper Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Size of Word Vector | 128 |
| Filter_Size | (2,3,4) |
| Epochs | 10 |
| Learning Rate of Adam | 0.001 |
| Pooling | Max Pooling |
| Hyper Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Size of Word Vector | 128 |
| Epochs | 10 |
| Hidden_Size | 128 |
| Drop_out | 0.5 |
| Activation Function | RuLu |
| Comments | Label |
|---|---|
| 房间设施远达不到四星水平,勉强也就是三星。(“Room facilities are far from four stars, barely three.”) | Neg |
| 这个酒店,隔音太差,纯净饮用水坏了,也不配给免费矿泉水。(“In this hotel, the sound insulation is too poor, the pure drinking water is bad, and the free mineral water is not rationed.”) | Neg |
| 从价格来说,性价比很高168元,前台服务员态度很好。(“From the price, cost-effective 168 yuan, the front desk staff attitude is very good.”) | Pos |
| 很不错的酒店,尽管在火车站,但很安静,房间干净。(“It’s a nice hotel, even though it’s at the train station, it’s quiet and the rooms are clean.”) | Pos |
| Value Positive | Negative | |
|---|---|---|
| True | TP (True Positive) | TN (True Negative) |
| False | FP (False Positive) | FN (False Negative) |
| Model | ChnSentiCorp-Htl- 10,000 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Measure | |
| RNN | 0.852 | 0.850 | 0.856 | 0.853 |
| TextCNN | 0.841 | 0.838 | 0.842 | 0.840 |
| LSTM | 0.865 | 0.867 | 0.869 | 0.868 |
| BiLSTM | 0.874 | 0.871 | 0.873 | 0.872 |
| TextCNN-BiLSTM | 0.882 | 0.886 | 0.880 | 0.883 |
| RNN-FL-LS | 0.856 | 0.855 | 0.859 | 0.857 |
| TextCNN-FL-LS | 0.846 | 0.843 | 0.847 | 0.845 |
| LSTM-FL-LS | 0.869 | 0.871 | 0.873 | 0.872 |
| BiLSTM-FL-LS | 0.879 | 0.876 | 0.878 | 0.877 |
| TextCNN-BiLSTM-FL-LS | 0.887 | 0.892 | 0.886 | 0.889 |
| BLTCN-BLSTM | 0.891 | 0.894 | 0.892 | 0.893 |
| Model | ChnSentiCorp-Htl- 10,000 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Measure | |
| TCN-BLSTM | 0.882 | 0.886 | 0.880 | 0.883 |
| Att-TCN-BLSTM | 0.884 | 0.888 | 0.882 | 0.885 |
| Att-TCN-BLSTM-FL | 0.886 | 0.889 | 0.885 | 0.887 |
| Att-TCN-BLSTM-LS | 0.885 | 0.882 | 0.886 | 0.884 |
| BLTCN-BLSTM | 0.891 | 0.894 | 0.892 | 0.893 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, T.; Zhang, X. Imbalanced Text Sentiment Classification Based on Multi-Channel BLTCN-BLSTM Self-Attention. Sensors 2023, 23, 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042257
Cai T, Zhang X. Imbalanced Text Sentiment Classification Based on Multi-Channel BLTCN-BLSTM Self-Attention. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042257
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Tiantian, and Xinsheng Zhang. 2023. "Imbalanced Text Sentiment Classification Based on Multi-Channel BLTCN-BLSTM Self-Attention" Sensors 23, no. 4: 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042257
APA StyleCai, T., & Zhang, X. (2023). Imbalanced Text Sentiment Classification Based on Multi-Channel BLTCN-BLSTM Self-Attention. Sensors, 23(4), 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042257






