Data-Driven Robotic Manipulation of Cloth-like Deformable Objects: The Present, Challenges and Future Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models of Cloth-like Deformable Objects
2.1. Problem Modelling
2.2. Simulation Environments
3. Fundamentals of Robotics for CDO Manipulation
3.1. Data-Driven Control
3.2. Framework
- is a set of states;
- is a set of actions;
- is the transition probability function;
- is a primary reward function that produces a reward when transitioning from state to state by taking action ;
- is the initial state distribution.
3.3. Skills
3.4. Simulation to Reality
3.5. Safety
4. Imitation Learning for CDO Manipulation
4.1. Behaviour Cloning
4.2. State-Action BC
4.3. Trajectory BC
5. Reinforcement Learning for CDO Manipulation
5.1. Model-Free RL
5.1.1. Value-Based Methods
5.1.2. Policy-Gradient Methods
5.2. Representation Learning
5.2.1. Data Augmentation
5.2.2. Posterior Latent Distribution
5.3. Model-Based RL
5.3.1. Observational Dynamic Models
5.3.2. Latent Dynamic Models
5.4. Goal-Conditioned RL
5.5. Exploration
5.5.1. Maximum Entropy RL
5.5.2. Demonstration Learning
6. CDO-Manipulation Tasks and Systems
6.1. Cloth Shaping
6.1.1. Classical Control and Perception in Cloth Shaping
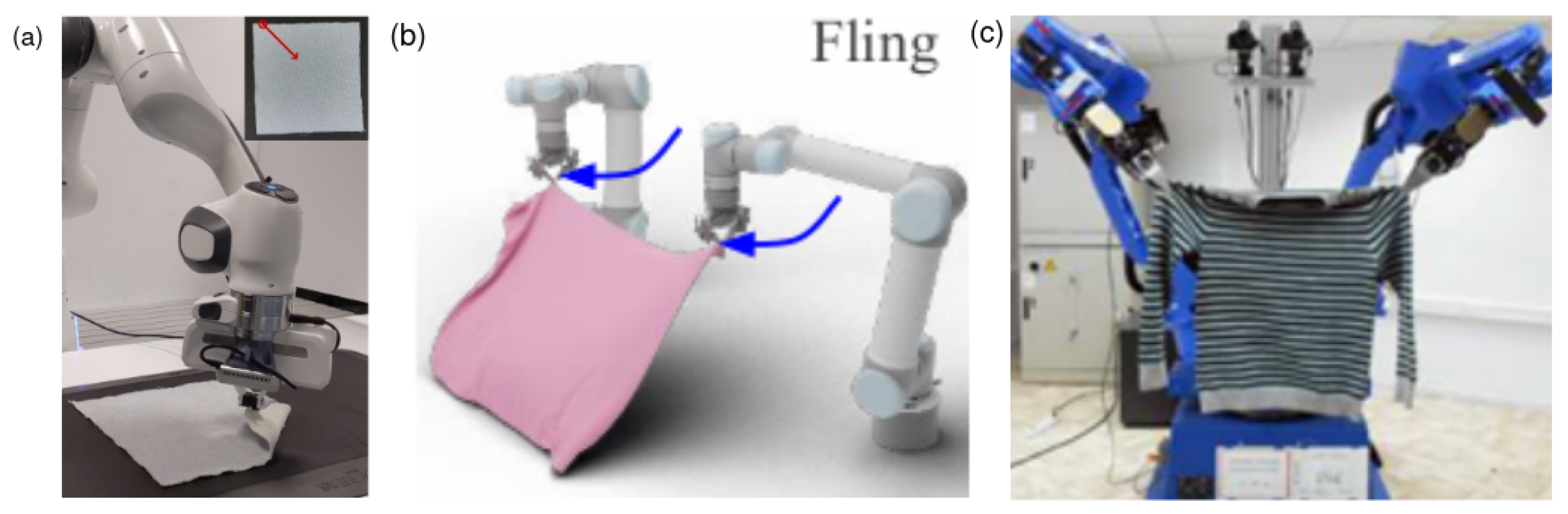
6.1.2. Data-Driven Control in Cloth Shaping
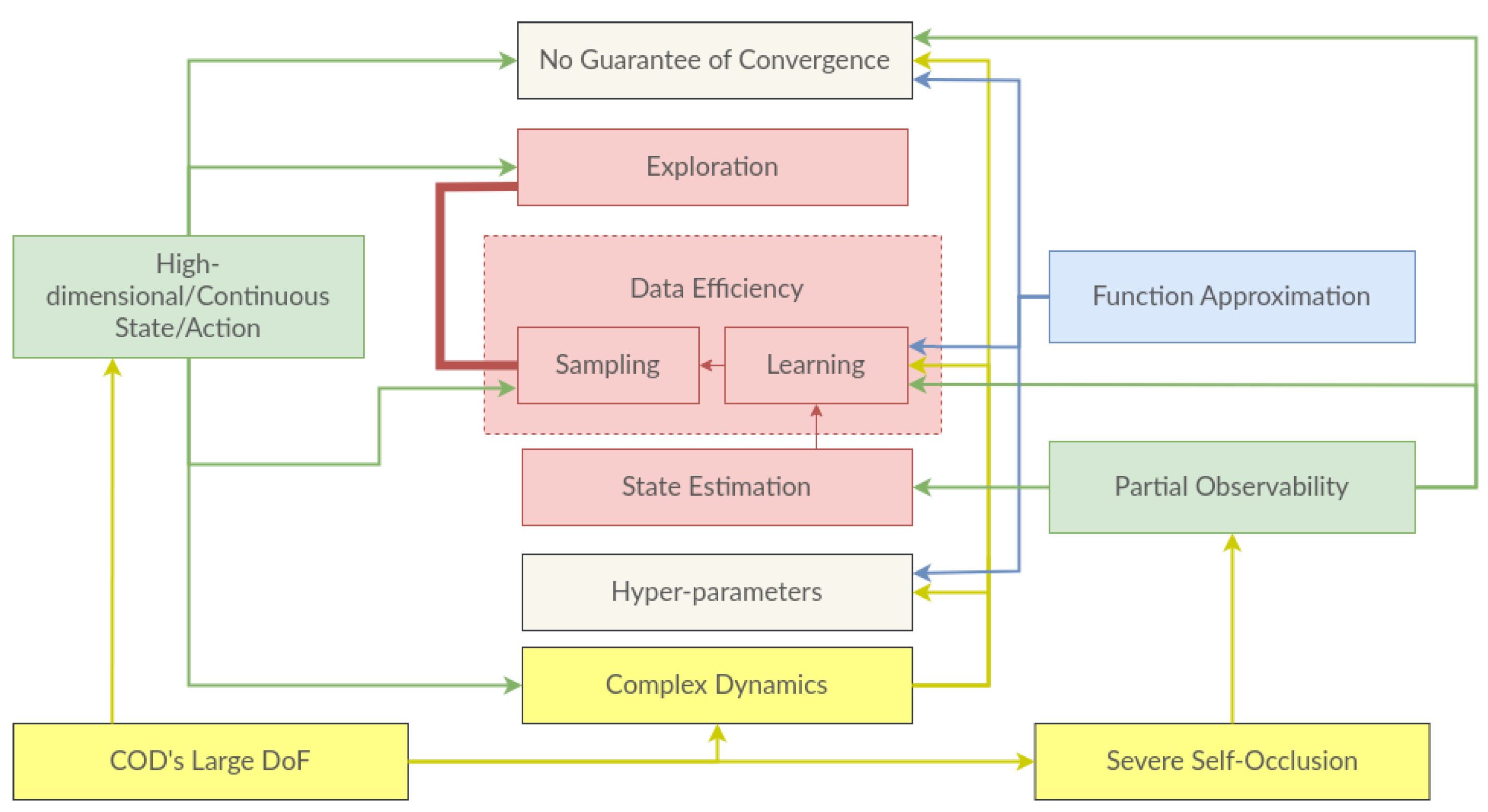
6.1.3. Challenges in Cloth Shaping
6.2. Knot Tying/Untying
6.2.1. Classical Manipulation in Knot Tying/Untying
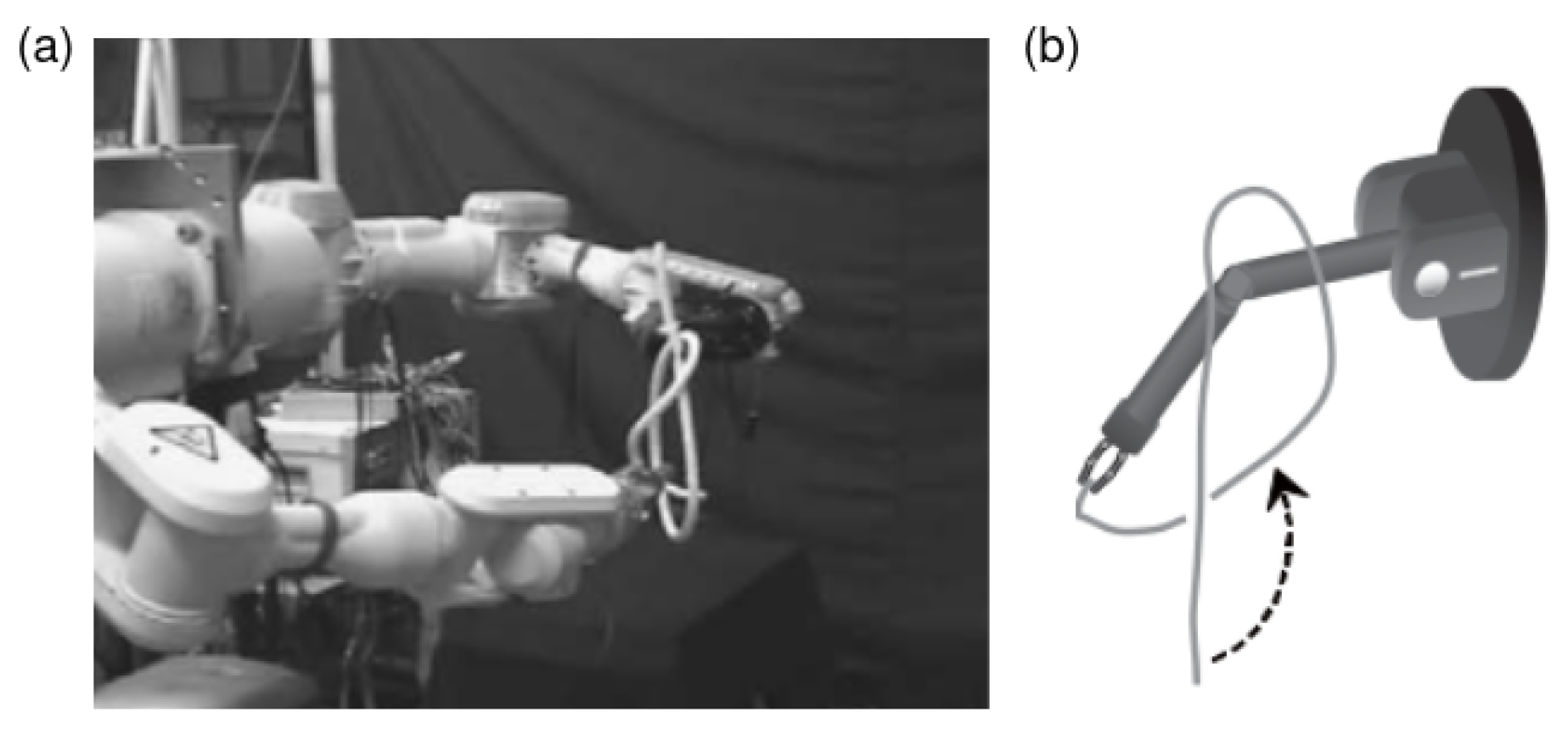
6.2.2. Data-Driven Manipulation in Knot Tying/Untying
6.2.3. Challenges in Knot Tying/Untying
6.3. Dressing
6.3.1. Classical Manipulation in Dressing
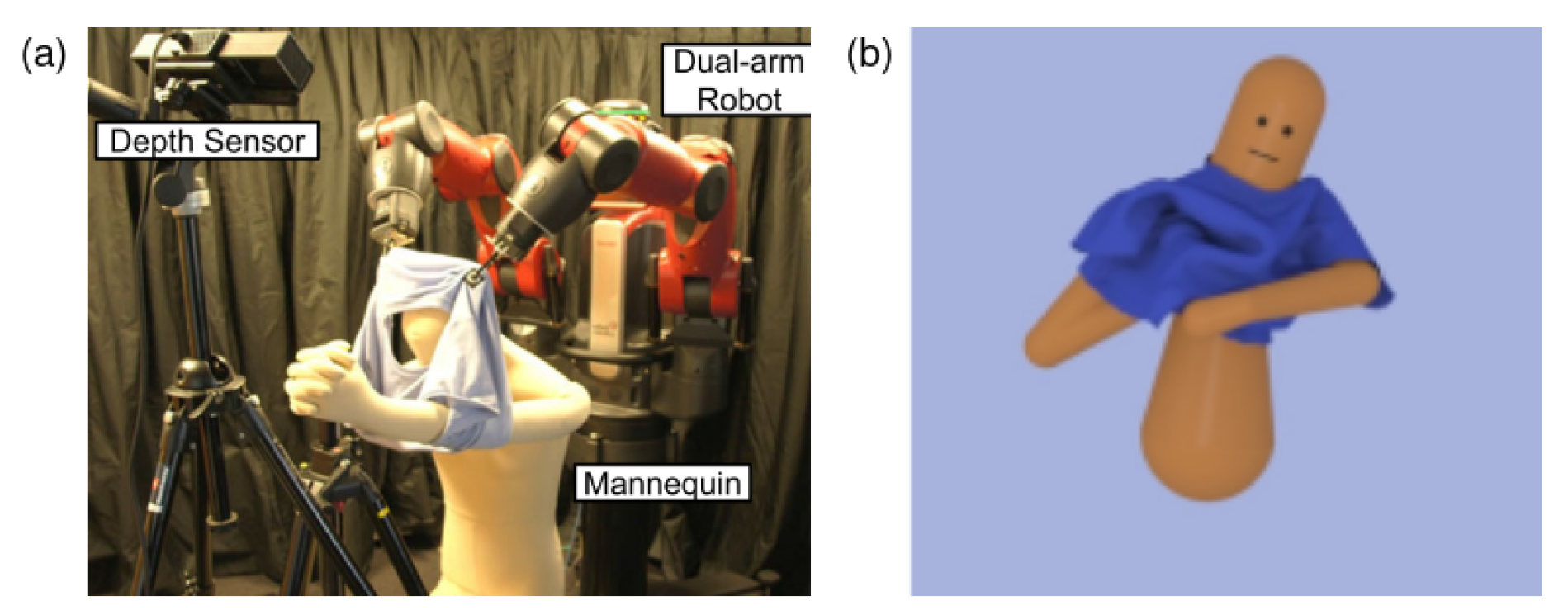
6.3.2. Data-Driven Manipulation in Dressing
6.3.3. Challenges in Dressing
6.4. Bag Manipulation
6.4.1. Classical and Data-Driven Manipulation in Bag Manipulation
6.4.2. Challenges in Bag Manipulation
7. Discussion and Future
Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamei, T.; Matsubara, T.; Rai, A.; Shibata, T. Reinforcement learning of clothing assistance with a dual-arm robot. In Proceedings of the 2011 11th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Bled, Slovenia, 26–28 October 2011; pp. 733–738. [Google Scholar]
- Varier, V.M.; Rajamani, D.K.; Goldfarb, N.; Tavakkolmoghaddam, F.; Munawar, A.; Fischer, G.S. Collaborative suturing: A reinforcement learning approach to automate hand-off task in suturing for surgical robots. In Proceedings of the 2020 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples, Italy, 31 August–4 September 2020; pp. 1380–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, X.; Peng, X.B.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S.; Berseth, G.; Sreenath, K. Reinforcement learning for robust parameterized locomotion control of bipedal robots. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 20 May–5 June 2021; pp. 2811–2817. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, B.R.; Sobh, I.; Talpaert, V.; Mannion, P.; Al Sallab, A.A.; Yogamani, S.; Pérez, P. Deep reinforcement learning for autonomous driving: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 4909–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswaran, A.; Kumar, V.; Gupta, A.; Vezzani, G.; Schulman, J.; Todorov, E.; Levine, S. Learning Complex Dexterous Manipulation with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Demonstrations. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 26–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarz, J.; Tan, J.; Finn, C.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Pastor, P.; Levine, S. How to train your robot with deep reinforcement learning: Lessons we have learned. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2021, 40, 698–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osa, T.; Pajarinen, J.; Neumann, G.; Bagnell, J.A.; Abbeel, P.; Peters, J. An algorithmic perspective on imitation learning. Found. Trends® Robot. 2018, 7, 1–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitin-Shepard, J.; Cusumano-Towner, M.; Lei, J.; Abbeel, P. Cloth grasp point detection based on multiple-view geometric cues with application to robotic towel folding. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2308–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Doumanoglou, A.; Kargakos, A.; Kim, T.K.; Malassiotis, S. Autonomous active recognition and unfolding of clothes using random decision forests and probabilistic planning. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–5 June 2014; pp. 987–993. [Google Scholar]
- Arriola-Rios, V.E.; Guler, P.; Ficuciello, F.; Kragic, D.; Siciliano, B.; Wyatt, J.L. Modeling of deformable objects for robotic manipulation: A tutorial and review. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.; Corrales, J.A.; Bouzgarrou, B.C.; Mezouar, Y. Robotic manipulation and sensing of deformable objects in domestic and industrial applications: A survey. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 688–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, D.; Wörn, H. Robot Manipulation of Deformable Objects; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Saadat, M.; Nan, P. Industrial applications of automatic manipulation of flexible materials. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2002, 29, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, P. Survey on model-based manipulation planning of deformable objects. Robot.-Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2012, 28, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, F.F.; Payeur, P. Dexterous Robotic Manipulation of Deformable Objects with Multi-Sensory Feedback—A Review; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Cherubini, A.; Dune, C.; Navarro-Alarcon, D.; Alambeigi, F.; Berenson, D.; Ficuciello, F.; Harada, K.; Kober, J.; Li, X.; et al. Challenges and outlook in robotic manipulation of deformable objects. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2022, 29, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borràs, J.; Alenyà, G.; Torras, C. A grasping-centered analysis for cloth manipulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Varava, A.; Kragic, D. Modeling, learning, perception, and control methods for deformable object manipulation. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabd8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matas, J.; James, S.; Davison, A.J. Sim-to-real reinforcement learning for deformable object manipulation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Zurich, Switzerland, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 734–743. [Google Scholar]
- Seita, D.; Jamali, N.; Laskey, M.; Tanwani, A.K.; Berenstein, R.; Baskaran, P.; Iba, S.; Canny, J.; Goldberg, K. Deep transfer learning of pick points on fabric for robot bed-making. In Proceedings of the The International Symposium of Robotics Research, Hanoi, Vietnam, 6–10 October 2019; pp. 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, D.; Yue, Y.; Grinspun, E.; Allen, P.K. Multi-sensor surface analysis for robotic ironing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 5670–5676. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Berenson, D.; Balkcom, D. An online method for tight-tolerance insertion tasks for string and rope. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2488–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.C.; Desai, V.; Castillo, J.P.; Çavuşoğlu, M.C. Needle-tissue interaction force state estimation for robotic surgical suturing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 3659–3664. [Google Scholar]
- Mott, N. The mechanical properties of metals. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1951, 64, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, M.; Müller, M.; Chentanez, N.; Kim, T.Y. Unified particle physics for real-time applications. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2014, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Tedrake, R.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Torralba, A. Learning Particle Dynamics for Manipulating Rigid Bodies, Deformable Objects, and Fluids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.; Heidelberger, B.; Teschner, M.; Gross, M. Meshless deformations based on shape matching. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2005, 24, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Olkin, J.; Held, D. Softgym: Benchmarking deep reinforcement learning for deformable object manipulation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), London, UK, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 432–448. [Google Scholar]
- NVIDIA PhysX 4.5 and 5.0 SDK. 2022. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/physx-sdk (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Clegg, A.; Erickson, Z.; Grady, P.; Turk, G.; Kemp, C.C.; Liu, C.K. Learning to collaborate from simulation for robot-assisted dressing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2746–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, A.; Yu, W.; Tan, J.; Liu, C.K.; Turk, G. Learning to dress: Synthesizing human dressing motion via deep reinforcement learning. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2018, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, E.; Bai, Y. PyBullet, a Python Module for Physics Simulation for Games, Robotics and Machine Learning. 2016–2021. Available online: http://pybullet.org (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Seita, D.; Florence, P.; Tompson, J.; Coumans, E.; Sindhwani, V.; Goldberg, K.; Zeng, A. Learning to rearrange deformable cables, fabrics, and bags with goal-conditioned transporter networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 4568–4575. [Google Scholar]
- Community, B.O. Blender—A 3D Modelling and Rendering Package; Blender Foundation, Stichting Blender Foundation: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan, P.; Grannen, J.; Thananjeyan, B.; Balakrishna, A.; Ichnowski, J.; Novoseller, E.R.; Hwang, M.; Laskey, M.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Goldberg, K. Untangling Dense Non-Planar Knots by Learning Manipulation Features and Recovery Policies. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08942. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, R.; Seita, D.; Balakrishna, A.; Ganapathi, A.; Tanwani, A.K.; Jamali, N.; Yamane, K.; Iba, S.; Goldberg, K. VisuoSpatial Foresight for Multi-Step, Multi-Task Fabric Manipulation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09044. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, R.; Seita, D.; Balakrishna, A.; Ganapathi, A.; Tanwani, A.K.; Jamali, N.; Yamane, K.; Iba, S.; Goldberg, K. Visuospatial foresight for physical sequential fabric manipulation. Auton. Robot. 2022, 46, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, E.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y. MuJoCo: A physics engine for model-based control. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vilamoura, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 5026–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Duriez, C.; Delingette, H.; Allard, J.; Gilles, B.; Marchesseau, S.; Talbot, H.; Courtecuisse, H.; Bousquet, G.; Peterlik, I.; et al. Sofa: A multi-model framework for interactive physical simulation. In Soft Tissue Biomechanical Modeling for Computer Assisted Surgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 283–321. [Google Scholar]
- Studio, V.M. Unified Particle Physics for Unity. Available online: http://obi.virtualmethodstudio.com/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Weng, Z.; Paus, F.; Varava, A.; Yin, H.; Asfour, T.; Kragic, D. Graph-based Task-specific Prediction Models for Interactions between Deformable and Rigid Objects. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 5741–5748. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Shao, W.; Hayashi, T.; Ohashi, T. Untying cable by combining 3D deep neural network with deep reinforcement learning. Adv. Robot. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narain, R.; Samii, A.; Pfaff, T.; O’Brien, J. ARCSim: Adaptive Refining and Coarsening Simulator; University of California: Berkley, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Lin, M.C. Learning-based cloth material recovery from video. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4383–4393. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, C.K. Coupling cloth and rigid bodies for dexterous manipulation. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Motion in Games, Guanajuato, Mexico, 3–5 November 2014; pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer, O.; Niekum, S.; Konidaris, G. A Review of Robot Learning for Manipulation: Challenges, Representations, and Algorithms. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 1395–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer, O.; Ugur, E.; Oztop, E.; Peters, J. A kernel-based approach to direct action perception. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE international Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2605–2610. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, M.; Inoue, H. Hand eye coordination in rope handling. J. Robot. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 3, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamajima, K.; Kakikura, M. Planning strategy for task of unfolding clothes. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2000, 32, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, F.; Seki, H.; Kamiya, Y. Clothes folding task by tool-using robot. J. Robot. Mechatronics 2006, 18, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, Y.; Namiki, A.; Ishikawa, M. Motion planning for dynamic knotting of a flexible rope with a high-speed robot arm. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Tassa, Y.; Mansard, N.; Todorov, E. Control-limited differential dynamic programming. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–5 June 2014; pp. 1168–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, J.; Stilman, M. Combining motion planning and optimization for flexible robot manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Nashville, TN, USA, 6–8 December 2010; pp. 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, Z.; Clegg, A.; Yu, W.; Turk, G.; Liu, C.K.; Kemp, C.C. What does the person feel? Learning to infer applied forces during robot-assisted dressing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 6058–6065. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Hendricks, L.A.; Kuchenbecker, K.J.; Darrell, T. Deep learning for tactile understanding from visual and haptic data. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Srinivasan, K.; Shah, P.; Savarese, S.; Fei-Fei, L.; Garg, A.; Bohg, J. Making sense of vision and touch: Self-supervised learning of multimodal representations for contact-rich tasks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 8943–8950. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.; Lenz, I.; Saxena, A. Deep multimodal embedding: Manipulating novel objects with point-clouds, language and trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 2794–2801. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Cheng, C.A.; Saigol, K.; Lee, K.; Yan, X.; Theodorou, E.A.; Boots, B. Agile Autonomous Driving using End-to-End Deep Imitation Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.07174. [Google Scholar]
- Codevilla, F.; Müller, M.; López, A.; Koltun, V.; Dosovitskiy, A. End-to-end driving via conditional imitation learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 4693–4700. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, T.; Takamatsu, J.; Ogawara, K.; Kimura, H.; Ikeuchi, K. Knot planning from observation. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; Volume 3, pp. 3887–3892. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Queralta, J.P.; Westerlund, T. Sim-to-real transfer in deep reinforcement learning for robotics: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Canberra, Australia, 1–4 December 2020; pp. 737–744. [Google Scholar]
- Vithayathil Varghese, N.; Mahmoud, Q.H. A survey of multi-task deep reinforcement learning. Electronics 2020, 9, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stooke, A.; Lee, K.; Abbeel, P.; Laskin, M. Decoupling representation learning from reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 9870–9879. [Google Scholar]
- Pong, V.H.; Nair, A.V.; Smith, L.M.; Huang, C.; Levine, S. Offline meta-reinforcement learning with online self-supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MA, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 17811–17829. [Google Scholar]
- Orsini, M.; Raichuk, A.; Hussenot, L.; Vincent, D.; Dadashi, R.; Girgin, S.; Geist, M.; Bachem, O.; Pietquin, O.; Andrychowicz, M. What matters for adversarial imitation learning? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 14656–14668. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Ermon, S. Generative adversarial imitation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 4565–4573. [Google Scholar]
- Rafailov, R.; Yu, T.; Rajeswaran, A.; Finn, C. Visual adversarial imitation learning using variational models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 3016–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Bellman, R. A Markovian decision process. J. Math. Mech. 1957, 6, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.A. Dynamic Programming and Markov Processes; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.; Juang, B. An introduction to hidden Markov models. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1986, 3, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kapusta, A.; Yu, W.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Liu, C.K.; Turk, G.; Kemp, C.C. Data-driven haptic perception for robot-assisted dressing. In Proceedings of the 2016 25th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), New York, NY, USA, 26–31 August 2016; pp. 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Cusumano-Towner, M.; Singh, A.; Miller, S.; O’Brien, J.F.; Abbeel, P. Bringing clothing into desired configurations with limited perception. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 3893–3900. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelbling, L.P.; Littman, M.L.; Cassandra, A.R. Planning and acting in partially observable stochastic domains. Artif. Intell. 1998, 101, 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallak, A.; Castro, D.D.; Mannor, S. Contextual Markov Decision Processes. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.02259. [Google Scholar]
- Detry, R.; Ek, C.H.; Madry, M.; Kragic, D. Learning a dictionary of prototypical grasp-predicting parts from grasping experience. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 601–608. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Precup, D.; Singh, S. Between MDPs and semi-MDPs: A framework for temporal abstraction in reinforcement learning. Artif. Intell. 1999, 112, 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenbach, B.; Gupta, A.; Ibarz, J.; Levine, S. Diversity is All You Need: Learning Skills without a Reward Function. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, P.; Hoffmann, H.; Asfour, T.; Schaal, S. Learning and generalization of motor skills by learning from demonstration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, J.; Fong, R.; Ray, A.; Schneider, J.; Zaremba, W.; Abbeel, P. Domain randomization for transferring deep neural networks from simulation to the real world. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, R.; Kamar, E.; Dey, D.; Horvitz, E.; Shah, J. Blind spot detection for safe sim-to-real transfer. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2020, 67, 191–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, K.; Dumont, G. System identification and control using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1992, 22, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proc. IEEE 2020, 109, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, F.; Eilers, C.; Gienger, M.; Peters, J. Data-efficient domain randomization with bayesian optimization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanca, A.; Muradore, R.; Fiorini, P. A review of algorithms for compliant control of stiff and fixed-compliance robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2015, 21, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa, J.; Fernández, F. A comprehensive survey on safe reinforcement learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 16, 1437–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Schaal, S. Learning from demonstration. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1996, 9, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S. Learning agents for uncertain environments. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory, Madison, WI, USA, 24–26 July 1998; pp. 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kálmán, R.E. When Is a Linear Control System Optimal. J. Basic Eng. 1963, 86, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vinh, T.; Tomizawa, T.; Kudoh, S.; Suehiro, T. A new strategy for making a knot with a general-purpose arm. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2217–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Ebihara, Y.; Shintani, K. Dynamic analysis of casting and winding with hyper-flexible manipulator. In Proceedings of the ICAR’05, 12th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 July 2005; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.; Bechtle, S.; Davchev, T.; Jayaraman, D.; Rai, A.; Meier, F. Model-based inverse reinforcement learning from visual demonstrations. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), London, UK, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 1930–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, M.; Sammut, C. A Framework for Behavioural Cloning. In Machine Intelligence 15; Furukawa, K., Michie, D., Muggleton, S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 103–129. [Google Scholar]
- Baram, N.; Anschel, O.; Caspi, I.; Mannor, S. End-to-end differentiable adversarial imitation learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MA, USA, 17–23 July 2017; pp. 390–399. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; Chen, D.; Agrawal, P.; Isola, P.; Abbeel, P.; Malik, J.; Levine, S. Combining self-supervised learning and imitation for vision-based rope manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 2146–2153. [Google Scholar]
- Billard, A.; Calinon, S.; Dillmann, R.; Schaal, S. Robot programming by demonstration. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1371–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, A.; Dayan, S. Global overview of imitation learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.06503. [Google Scholar]
- Pomerleau, D.A. Alvinn: An autonomous land vehicle in a neural network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1988, 1, 205–313. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnell, J.A. An Invitation to Imitation; Technical Report; Carnegie-Mellon Univ Pittsburgh Pa Robotics Inst: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.; Gordon, G.; Bagnell, D. A reduction of imitation learning and structured prediction to no-regret online learning. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Eisner, J.; Daume, H. Imitation learning by coaching. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatraman, A.; Hebert, M.; Bagnell, J.A. Improving multi-step prediction of learned time series models. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Florence, P.; Tompson, J.; Welker, S.; Chien, J.; Attarian, M.; Armstrong, T.; Krasin, I.; Duong, D.; Sindhwani, V.; et al. Transporter networks: Rearranging the visual world for robotic manipulation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), London, UK, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 726–747. [Google Scholar]
- Kudoh, S.; Gomi, T.; Katano, R.; Tomizawa, T.; Suehiro, T. In-air knotting of rope by a dual-arm multi-finger robot. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 6202–6207. [Google Scholar]
- Calinon, S.; D’halluin, F.; Sauser, E.L.; Caldwell, D.G.; Billard, A.G. Learning and reproduction of gestures by imitation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2010, 17, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Z. Hidden semi-Markov models. Artif. Intell. 2010, 174, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozo, L.; Silverio, J.; Calinon, S.; Caldwell, D.G. Learning controllers for reactive and proactive behaviors in human—Robot collaboration. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemporad, A.; Morari, M.; Dua, V.; Pistikopoulos, E.N. The explicit linear quadratic regulator for constrained systems. Automatica 2002, 38, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijspeert, A.; Nakanishi, J.; Schaal, S. Learning attractor landscapes for learning motor primitives. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2002, 15, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Ijspeert, A.J.; Nakanishi, J.; Schaal, S. Movement imitation with nonlinear dynamical systems in humanoid robots. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 02CH37292), Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1398–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Ijspeert, A.J.; Nakanishi, J.; Hoffmann, H.; Pastor, P.; Schaal, S. Dynamical movement primitives: Learning attractor models for motor behaviors. Neural Comput. 2013, 25, 328–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaal, S.; Peters, J.; Nakanishi, J.; Ijspeert, A. Learning movement primitives. In Robotics Research. The Eleventh International Symposium: With 303 Figures; Dario, P., Chatila, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 561–572. [Google Scholar]
- Paraschos, A.; Daniel, C.; Peters, J.R.; Neumann, G. Probabilistic movement primitives. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 2616–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Khansari-Zadeh, S.M.; Billard, A. Learning stable nonlinear dynamical systems with gaussian mixture models. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Ho, J.; Lee, C.; Abbeel, P. Learning from demonstrations through the use of non-rigid registration. In Robotics Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 339–354. [Google Scholar]
- Chui, H.; Rangarajan, A. A new point matching algorithm for non-rigid registration. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2003, 89, 114–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.X.; Lu, H.; Gupta, A.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P. Learning force-based manipulation of deformable objects from multiple demonstrations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.X.; Goldstein, M.A.; Barratt, S.T.; Abbeel, P. A non-rigid point and normal registration algorithm with applications to learning from demonstrations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsekas, D. Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control: Volume I; Athena Scientific: Nashua, NH, USA, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsekas, D. Reinforcement Learning and Optimal Control; Athena Scientific: Nashua, NH, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, C.J.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillicrap, T.P.; Hunt, J.J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft actor–critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1861–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hasselt, H.; Guez, A.; Silver, D. Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, S.; Hoof, H.; Meger, D. Addressing function approximation error in actor–critic methods. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1587–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; McAllester, D.; Singh, S.; Mansour, Y. Policy gradient methods for reinforcement learning with function approximation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1999, 12, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; Schaal, S. Reinforcement learning of motor skills with policy gradients. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Schaal, S. Natural actor–critic. Neurocomputing 2008, 71, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.I. Natural gradient works efficiently in learning. Neural Comput. 1998, 10, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P.; Jordan, M.; Moritz, P. Trust region policy optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 1889–1897. [Google Scholar]
- Tassa, Y.; Doron, Y.; Muldal, A.; Erez, T.; Li, Y.; Casas, D.d.L.; Budden, D.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Merel, J.; Lefrancq, A.; et al. Deepmind control suite. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.00690. [Google Scholar]
- Laskin, M.; Srinivas, A.; Abbeel, P. Curl: Contrastive unsupervised representations for reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 5639–5650. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; McAllister, R.T.; Calandra, R.; Gal, Y.; Levine, S. Learning Invariant Representations for Reinforcement Learning without Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), online, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03748. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarats, D.; Kostrikov, I.; Fergus, R. Image Augmentation Is All You Need: Regularizing Deep Reinforcement Learning from Pixels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), online, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Laskin, M.; Lee, K.; Stooke, A.; Pinto, L.; Abbeel, P.; Srinivas, A. Reinforcement learning with augmented data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 19884–19895. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, N.; Wang, X. Generalization in reinforcement learning by soft data augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13611–13617. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm, R.D.; Fedorov, A.; Lavoie-Marchildon, S.; Grewal, K.; Bachman, P.; Trischler, A.; Bengio, Y. Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, D.; Lillicrap, T.; Ba, J.; Norouzi, M. Dream to Control: Learning Behaviors by Latent Imagination. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, D.; Lillicrap, T.P.; Norouzi, M.; Ba, J. Mastering Atari with Discrete World Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), online, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Vikram, S.; Smith, L.; Abbeel, P.; Johnson, M.; Levine, S. Solar: Deep structured representations for model-based reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 7444–7453. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.X.; Nagabandi, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Stochastic latent actor–critic: Deep reinforcement learning with a latent variable model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 741–752. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.; Lee, K.; James, S.L.; Abbeel, P. Reinforcement learning with action-free pre-training from videos. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Baltimore, MA, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 19561–19579. [Google Scholar]
- Yarats, D.; Zhang, A.; Kostrikov, I.; Amos, B.; Pineau, J.; Fergus, R. Improving Sample Efficiency in Model-Free Reinforcement Learning from Images. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, online, 2–9 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, A.; Racah, E.; Ozair, S.; Bengio, Y.; Côté, M.A.; Hjelm, R.D. Unsupervised state representation learning in atari. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8769–8782. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Fischer, I.; Liu, A.; Guo, Y.; Lee, H.; Canny, J.; Guadarrama, S. Predictive information accelerates learning in rl. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 11890–11901. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, P.S. Scalable methods for computing state similarity in deterministic markov decision processes. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 10069–10076. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, L.; Andrychowicz, M.; Welinder, P.; Zaremba, W.; Abbeel, P. Asymmetric actor critic for image-based robot learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.06542. [Google Scholar]
- Badia, A.P.; Sprechmann, P.; Vitvitskyi, A.; Guo, D.; Piot, B.; Kapturowski, S.; Tieleman, O.; Arjovsky, M.; Pritzel, A.; Bolt, A.; et al. Never give up: Learning directed exploration strategies. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.06038. [Google Scholar]
- Badia, A.P.; Piot, B.; Kapturowski, S.; Sprechmann, P.; Vitvitskyi, A.; Guo, Z.D.; Blundell, C. Agent57: Outperforming the atari human benchmark. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, D.; Lillicrap, T.; Fischer, I.; Villegas, R.; Ha, D.; Lee, H.; Davidson, J. Learning latent dynamics for planning from pixels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 2555–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.X.; Zhang, R.; Ebert, F.; Abbeel, P.; Finn, C.; Levine, S. Stochastic adversarial video prediction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.01523. [Google Scholar]
- Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Hubert, T.; Simonyan, K.; Sifre, L.; Schmitt, S.; Guez, A.; Lockhart, E.; Hassabis, D.; Graepel, T.; et al. Mastering atari, go, chess and shogi by planning with a learned model. Nature 2020, 588, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelhamer, E.; Mahmoudieh, P.; Argus, M.; Darrell, T. Loss is its own Reward: Self-Supervision for Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.07307. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, S.; Du, Y.; Neyshabur, B. Observational Overfitting in Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), online, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, C.; Gao, K.; Kos, J.; Krähenbühl, P.; Koltun, V.; Song, D. Assessing generalization in deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.12282. [Google Scholar]
- Henaff, O. Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 4182–4192. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Le-Khac, P.H.; Healy, G.; Smeaton, A.F. Contrastive representation learning: A framework and review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193907–193934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Moerland, T.M.; Broekens, J.; Jonker, C.M. Model-based reinforcement learning: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.16712. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, E.F.; Alba, C.B. Model Predictive Control; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, C.B.; Powley, E.; Whitehouse, D.; Lucas, S.M.; Cowling, P.I.; Rohlfshagen, P.; Tavener, S.; Perez, D.; Samothrakis, S.; Colton, S. A survey of monte carlo tree search methods. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2012, 4, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerland, T.M.; Broekens, J.; Jonker, C.M. A framework for reinforcement learning and planning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.15009. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, C.; Levine, S. Deep visual foresight for planning robot motion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 2786–2793. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Caluwaerts, K.; Iscen, A.; Zhang, T.; Tan, J.; Sindhwani, V. Data efficient reinforcement learning for legged robots. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Cambridge, MA, USA, 14–16 November 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Rumelhart, D.E. Forward models: Supervised learning with a distal teacher. Cogn. Sci. 1992, 16, 307–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Schmidhuber, J. World models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.10122. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, F.; Finn, C.; Dasari, S.; Xie, A.; Lee, A.X.; Levine, S. Visual Foresight: Model-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning for Vision-Based Robotic Control. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.00568. [Google Scholar]
- Babaeizadeh, M.; Finn, C.; Erhan, D.; Campbell, R.H.; Levine, S. Stochastic Variational Video Prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, E.; Fergus, R. Stochastic video generation with a learned prior. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1174–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gülçehre, Ç.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Held, D. Learning visible connectivity dynamics for cloth smoothing. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 December 2022; pp. 256–266. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandriello, D.; Lazaric, A.; Restelli, M. Sparse multi-task reinforcement learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrychowicz, M.; Wolski, F.; Ray, A.; Schneider, J.; Fong, R.; Welinder, P.; McGrew, B.; Tobin, J.; Pieter Abbeel, O.; Zaremba, W. Hindsight experience replay. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5048–5058. [Google Scholar]
- Chane-Sane, E.; Schmid, C.; Laptev, I. Goal-conditioned reinforcement learning with imagined subgoals. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 1430–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Florensa, C.; Abbeel, P.; Phielipp, M. Goal-conditioned imitation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 15324–15335. [Google Scholar]
- Kaelbling, L.P. Learning to achieve goals. IJCAI 1993, 2, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Baweja, H.S.; Held, D. Reinforcement learning without ground-truth state. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.07866. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Lin, D. Policy continuation with hindsight inverse dynamics. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 10265–10275. [Google Scholar]
- Eysenbach, B.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Levine, S. C-Learning: Learning to Achieve Goals via Recursive Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), online, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schaul, T.; Horgan, D.; Gregor, K.; Silver, D. Universal value function approximators. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 1312–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Osband, I.; Blundell, C.; Pritzel, A.; Van Roy, B. Deep exploration via bootstrapped DQN. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 4026–4034. [Google Scholar]
- Mankowitz, D.J.; Zídek, A.; Barreto, A.; Horgan, D.; Hessel, M.; Quan, J.; Oh, J.; van Hasselt, H.; Silver, D.; Schaul, T. Unicorn: Continual Learning with a Universal, Off-policy Agent. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.08294. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Sastry, S. Surprise-based intrinsic motivation for deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.01732. [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane, R. A Survey of Exploration Strategies in Reinforcement Learning; McGill University: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, S.; Gomrokchi, M.; Satija, H.; van Hoof, H.; Precup, D. A survey of exploration methods in reinforcement learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.00157. [Google Scholar]
- Ladosz, P.; Weng, L.; Kim, M.; Oh, H. Exploration in deep reinforcement learning: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2022, 85, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimore, T.; Szepesvári, C. Bandit Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Auer, P. Using confidence bounds for exploitation-exploration trade-offs. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2002, 3, 397–422. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, W.R. On the likelihood that one unknown probability exceeds another in view of the evidence of two samples. Biometrika 1933, 25, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubret, A.; Matignon, L.; Hassas, S. A survey on intrinsic motivation in reinforcement learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.06976. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. A possibility for implementing curiosity and boredom in model-building neural controllers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior: From Animals to Animats, Paris, France, 14 February 1991; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Osband, I.; Van Roy, B. Why is posterior sampling better than optimism for reinforcement learning? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2701–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Azizzadenesheli, K.; Brunskill, E.; Anandkumar, A. Efficient exploration through bayesian deep q-networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–16 February 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Plappert, M.; Houthooft, R.; Dhariwal, P.; Sidor, S.; Chen, R.Y.; Chen, X.; Asfour, T.; Abbeel, P.; Andrychowicz, M. Parameter Space Noise for Exploration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhbaatar, S.; Lin, Z.; Kostrikov, I.; Synnaeve, G.; Szlam, A.; Fergus, R. Intrinsic Motivation and Automatic Curricula via Asymmetric Self-Play. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.; Eysenbach, B.; Parisotto, E.; Xing, E.; Levine, S.; Salakhutdinov, R. Efficient exploration via state marginal matching. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05274. [Google Scholar]
- Hazan, E.; Kakade, S.; Singh, K.; Van Soest, A. Provably efficient maximum entropy exploration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 2681–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Tang, H.; Bai, C.; Liu, J.; Hao, J.; Meng, Z.; Liu, P. Exploration in deep reinforcement learning: A comprehensive survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.06668. [Google Scholar]
- Ecoffet, A.; Huizinga, J.; Lehman, J.; Stanley, K.O.; Clune, J. Go-Explore: A New Approach for Hard-Exploration Problems. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.10995. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Agarwal, A.; Langford, J.; Schapire, R.E. Contextual decision processes with low bellman rank are pac-learnable. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1704–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, M.C.; Bellemare, M.G.; Bowling, M. Count-based exploration with the successor representation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 5125–5133. [Google Scholar]
- Burda, Y.; Edwards, H.; Storkey, A.; Klimov, O. Exploration by random network distillation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.12894. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.V.; Pong, V.; Dalal, M.; Bahl, S.; Lin, S.; Levine, S. Visual reinforcement learning with imagined goals. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 9191–9200. [Google Scholar]
- Pong, V.H.; Dalal, M.; Lin, S.; Nair, A.; Bahl, S.; Levine, S. Skew-fit: State-covering self-supervised reinforcement learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.03698. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, M.; Lang, T.; Toussaint, M.; Oudeyer, P.Y. Exploration in Model-based Reinforcement Learning by Empirically Estimating Learning Progress. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Conference (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012; pp. 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ziebart, B.D.; Maas, A.L.; Bagnell, J.A.; Dey, A.K. Maximum entropy inverse reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Chicago, IL, USA, 13–17 July 2008; Volume 8, pp. 1433–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S. Reinforcement learning and control as probabilistic inference: Tutorial and review. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00909. [Google Scholar]
- Haarnoja, T.; Tang, H.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Reinforcement learning with deep energy-based policies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1352–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Hester, T.; Vecerik, M.; Pietquin, O.; Lanctot, M.; Schaul, T.; Piot, B.; Horgan, D.; Quan, J.; Sendonaris, A.; Osband, I.; et al. Deep q-learning from demonstrations. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Vecerík, M.; Hester, T.; Scholz, J.; Wang, F.; Pietquin, O.; Piot, B.; Heess, N.; Rothörl, T.; Lampe, T.; Riedmiller, M.A. Leveraging Demonstrations for Deep Reinforcement Learning on Robotics Problems with Sparse Rewards. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.08817. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; McGrew, B.; Andrychowicz, M.; Zaremba, W.; Abbeel, P. Overcoming exploration in reinforcement learning with demonstrations. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 6292–6299. [Google Scholar]
- Chebotar, Y.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Yahya, A.; Li, A.; Schaal, S.; Levine, S. Path integral guided policy search. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 3381–3388. [Google Scholar]
- Hessel, M.; Modayil, J.; Van Hasselt, H.; Schaul, T.; Ostrovski, G.; Dabney, W.; Horgan, D.; Piot, B.; Azar, M.; Silver, D. Rainbow: Combining improvements in deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Piot, B.; Geist, M.; Pietquin, O. Boosted bellman residual minimization handling expert demonstrations. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Nancy, France, 15–19 September 2014; pp. 549–564. [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa, M.; Yao, Z.; Onda, H.; Kudoh, S.; Suehiro, T. Learning from observation of tabletop knotting using a simple task model. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Paris, France, 14–16 January 2019; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, W.; Kurutach, T.; Pinto, L.; Abbeel, P. Learning to manipulate deformable objects without demonstrations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13439. [Google Scholar]
- Jangir, R.; Alenyà, G.; Torras, C. Dynamic cloth manipulation with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–5 August 2020; pp. 4630–4636. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, H.; Song, S. Flingbot: The unreasonable effectiveness of dynamic manipulation for cloth unfolding. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 December 2022; pp. 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hietala, J.; Blanco-Mulero, D.; Alcan, G.; Kyrki, V. Closing the Sim2Real Gap in Dynamic Cloth Manipulation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.04771. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.; Ward, D.; Dasagi, V.; Cosgun, A.; Leitner, J.; Corke, P. Learning arbitrary-goal fabric folding with one hour of real robot experience. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), London, UK, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 2317–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Clegg, A.; Yu, W.; Erickson, Z.; Tan, J.; Liu, C.K.; Turk, G. Learning to navigate cloth using haptics. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 2799–2805. [Google Scholar]
- Gonnochenko, A.; Semochkin, A.; Egorov, D.; Statovoy, D.; Zabihifar, S.; Postnikov, A.; Seliverstova, E.; Zaidi, A.; Stemmler, J.; Limkrailassiri, K. Coinbot: Intelligent Robotic Coin Bag Manipulation Using Artificial Brain. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), Prague, Czech Republic, 4–6 February 2021; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chi, C.; Burchfiel, B.; Cousineau, E.; Feng, S.; Song, S. DextAIRity: Deformable Manipulation Can be a Breeze. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), New York, NY, USA, 27 June–1 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Vangipuram, A.; Abbeel, P.; Pinto, L. Learning predictive representations for deformable objects using contrastive estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), London, UK, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 564–574. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Hsu, D.; Lee, W.S. Learning Latent Graph Dynamics for Deformable Object Manipulation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.12149. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, S.; Tanaka, D.; Yamazaki, K. Cloth Manipulation Planning on Basis of Mesh Representations with Incomplete Domain Knowledge and Voxel-to-Mesh Estimation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.08137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seita, D.; Ganapathi, A.; Hoque, R.; Hwang, M.; Cen, E.; Tanwani, A.K.; Balakrishna, A.; Thananjeyan, B.; Ichnowski, J.; Jamali, N.; et al. Deep imitation learning of sequential fabric smoothing from an algorithmic supervisor. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 9651–9658. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, T.; Bajracharya, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, K.; Held, D. Fabricflownet: Bimanual cloth manipulation with a flow-based policy. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 December 2022; pp. 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Kamiya, T.; Nakatoh, Y.; Serikawa, S.; Gao, P. Multidimensional Deformable Object Manipulation Based on DN-Transporter Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kanamura, M.; Suga, Y.; Mori, H.; Ogata, T. In-air knotting of rope using dual-arm robot based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 6724–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Grannen, J.; Sundaresan, P.; Thananjeyan, B.; Ichnowski, J.; Balakrishna, A.; Hwang, M.; Viswanath, V.; Laskey, M.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Goldberg, K. Untangling dense knots by learning task-relevant keypoints. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04999. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanath, V.; Grannen, J.; Sundaresan, P.; Thananjeyan, B.; Balakrishna, A.; Novoseller, E.; Ichnowski, J.; Laskey, M.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Goldberg, K. Disentangling Dense Multi-Cable Knots. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 3731–3738. [Google Scholar]
- Seita, D.; Kerr, J.; Canny, J.; Goldberg, K. Initial Results on Grasping and Lifting Physical Deformable Bags with a Bimanual Robot. In Proceedings of the IROS Workshop on Robotic Manipulation of Deformable Objects in Real-World Applications, Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; Volume 2, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.X.; Huang, S.H.; Hadfield-Menell, D.; Tzeng, E.; Abbeel, P. Unifying scene registration and trajectory optimization for learning from demonstrations with application to manipulation of deformable objects. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 4402–4407. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.H.; Pan, J.; Mulcaire, G.; Abbeel, P. Leveraging appearance priors in non-rigid registration, with application to manipulation of deformable objects. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 878–885. [Google Scholar]
- Tallec, C.; Blier, L.; Ollivier, Y. Making deep q-learning methods robust to time discretization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 6096–6104. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, T.; Shinohara, D.; Kidode, M. Reinforcement learning of a motor skill for wearing a T-shirt using topology coordinates. Adv. Robot. 2013, 27, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomé, A.; Planells, A.; Torras, C. A friction-model-based framework for reinforcement learning of robotic tasks in non-rigid environments. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 5649–5654. [Google Scholar]
- Pignat, E.; Calinon, S. Learning adaptive dressing assistance from human demonstration. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 93, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.P.; Koganti, N.; Shibata, T. A framework for robotic clothing assistance by imitation learning. Adv. Robot. 2019, 33, 1156–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, P.; Grannen, J.; Thananjeyan, B.; Balakrishna, A.; Laskey, M.; Stone, K.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Goldberg, K. Learning rope manipulation policies using dense object descriptors trained on synthetic depth data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–5 August 2020; pp. 9411–9418. [Google Scholar]
- Hamajima, K. Planning strategy for task untangling laundry-isolating clothes from a washed mass. Robotics Mechatron. 1998, 10, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Van Den Berg, J.; Fritz, M.; Darrell, T.; Goldberg, K.; Abbeel, P. A geometric approach to robotic laundry folding. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumanoglou, A.; Stria, J.; Peleka, G.; Mariolis, I.; Petrik, V.; Kargakos, A.; Wagner, L.; Hlaváč, V.; Kim, T.K.; Malassiotis, S. Folding clothes autonomously: A complete pipeline. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Kakikura, M. Planning strategy for putting away laundry-isolating and unfolding task. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Symposium on Assembly and Task Planning (ISATP2001). Assembly and Disassembly in the Twenty-First Century (Cat. No. 01TH8560), Fukuoka, Japan, 28–29 May 2001; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Willimon, B.; Birchfield, S.; Walker, I. Classification of clothing using interactive perception. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 1862–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Aragon-Camarasa, G.; Cockshott, P.; Rogers, S.; Siebert, J.P. A heuristic-based approach for flattening wrinkled clothes. In Proceedings of the Conference Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems (TAROS), Oxford, UK, 28–30 August 2013; pp. 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bersch, C.; Pitzer, B.; Kammel, S. Bimanual robotic cloth manipulation for laundry folding. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 1413–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, K.; Inaba, M. A Cloth Detection Method Based on Image Wrinkle Feature for Daily Assistive Robots. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Yokohama, Japan, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ramisa, A.; Alenya, G.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Torras, C. Using depth and appearance features for informed robot grasping of highly wrinkled clothes. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 1703–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Aragon-Camarasa, G.; Rogers, S.; Siebert, J.P. Accurate garment surface analysis using an active stereo robot head with application to dual-arm flattening. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Willimon, B.; Birchfield, S.; Walker, I. Model for unfolding laundry using interactive perception. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 4871–4876. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, M. Flexible Object Manipulation; Dartmouth College: Hanover, NH, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.v.d.; Miller, S.; Goldberg, K.; Abbeel, P. Gravity-based robotic cloth folding. In Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics IX; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 409–424. [Google Scholar]
- Farin, G. Curves and Surfaces for Computer-Aided Geometric Design: A Practical Guide; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.; Fritz, M.; Darrell, T.; Abbeel, P. Parametrized shape models for clothing. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 4861–4868. [Google Scholar]
- Stria, J.; Průša, D.; Hlaváč, V.; Wagner, L.; Petrík, V.; Krsek, P.; Smutný, V. Garment perception and its folding using a dual-arm robot. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lin, X.; Held, D. Mesh-based Dynamics with Occlusion Reasoning for Cloth Manipulation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02881. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Hazirbas, C.; Golkov, V.; Van Der Smagt, P.; Cremers, D.; Brox, T. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff, T.; Fortunato, M.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Battaglia, P. Learning Mesh-Based Simulation with Graph Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), online, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Godwin, J.; Pfaff, T.; Ying, R.; Leskovec, J.; Battaglia, P. Learning to simulate complex physics with graph networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 8459–8468. [Google Scholar]
- Salhotra, G.; Liu, I.C.A.; Dominguez-Kuhne, M.; Sukhatme, G.S. Learning Deformable Object Manipulation from Expert Demonstrations. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 8775–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, R.; Shivakumar, K.; Aeron, S.; Deza, G.; Ganapathi, A.; Wong, A.; Lee, J.; Zeng, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Goldberg, K. Learning to Fold Real Garments with One Arm: A Case Study in Cloud-Based Robotics Research. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, A.; Zeng, A.; Bose, A.; Wahid, A.; Kalashnikov, D.; Krasin, I.; Varley, J.; Lee, J.; Tompson, J.; Attarian, M.; et al. PyReach—Python Client SDK for Robot Remote Control. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/google-research/pyreach (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Crowell, R.H.; Fox, R.H. Introduction to Knot Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu, H.; Tsumaya, A.; Arai, E.; Hirai, S. Planning of one-handed knotting/raveling manipulation of linear objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1719–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, J.K. Energy functions for polygonal knots. J. Knot Theory Its Ramifications 1994, 3, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharein, R.G. Interactive Topological Drawing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ligocki, T.J.; Sethian, J.A. Recognizing knots using simulated annealing. J. Knot Theory Its Ramif. 1994, 3, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Grzeszczuk, R.P.; Kauffman, L.H. Untangling knots by stochastic energy optimization. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual IEEE Visualization’96, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 October–1 November 1996; pp. 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd, A.M.; Kavraki, L.E. Using motion planning for knot untangling. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2004, 23, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, H.; Tsumaya, A.; Arai, E.; Hirai, S. Manipulation planning for unraveling linear objects. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 2485–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu, H.; Arai, E.; Hirai, S. Knotting/unknotting manipulation of deformable linear objects. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidemeister, K. Knot Theory; BCS Associates: Moscow, ID, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa, Y.; Namiki, A.; Ishikawa, M.; Shimojo, M. Knotting manipulation of a flexible rope by a multifingered hand system based on skill synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 2691–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno, T.; Tamaki, D.; Arai, F.; Fukuda, T. Manipulation of deformable linear objects using knot invariants to classify the object condition based on image sensor information. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2006, 11, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopcroft, J.E.; Kearney, J.K.; Krafft, D.B. A case study of flexible object manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1991, 10, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, P.; Goldberg, K.; Gonzalez, J. Robotic Untangling and Disentangling of Cables via Learned Manipulation and Recovery Strategies. Master’s Thesis, University of Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Balkcom, D. Tying knot precisely. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3639–3646. [Google Scholar]
- Baranska, J.; Przybyl, S.; Pieranski, P. Curvature and torsion of the tight closed trefoil knot. Eur. Phys. J. B 2008, 66, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdon, E.J. Approximating the thickness of a knot. In Ideal Knots; World Scientific: Singapore, 1998; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, T.; Cantarella, J.; Piatek, M.; Rawdon, E.J. Knot tightening by constrained gradient descent. Exp. Math. 2011, 20, 57–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlen, M.; Laurie, B.; Maddocks, J.H.; Smutny, J. Biarcs, global radius of curvature, and the computation of ideal knot shapes. In Physical and Numerical Models in Knot Theory: Including Applications to the Life Sciences; World Scientific: Sinapore, 2005; pp. 75–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, T.; Mao, Y. The 85 Ways to Tie a Tie: The Science and Aesthetics of Tie Knots; Broadway: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dowker, C.H.; Thistlethwaite, M.B. Classification of knot projections. Topol. Its Appl. 1983, 16, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Gupta, A.; Venkatesan, S.; Tayson-Frederick, M.; Abbeel, P. A case study of trajectory transfer through non-rigid registration for a simplified suturing scenario. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4111–4117. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, W.H.; Saxena, A. Tangled: Learning to untangle ropes with rgb-d perception. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- I-Dress: Assistive Interactive Robotic System for Support in Dressing. Available online: https://i-dress-project.iri.upc.edu/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Yamazaki, K.; Oya, R.; Nagahama, K.; Okada, K.; Inaba, M. Bottom dressing by a life-sized humanoid robot provided failure detection and recovery functions. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Tokyo, Japan, 13–15 December 2014; pp. 564–570. [Google Scholar]
- Klee, S.D.; Ferreira, B.Q.; Silva, R.; Costeira, J.P.; Melo, F.S.; Veloso, M. Personalized assistance for dressing users. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Social Robotics (ICSR), Paris, France, 26–30 October 2015; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Koganti, N.; Tamei, T.; Ikeda, K.; Shibata, T. Bayesian nonparametric learning of cloth models for real-time state estimation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, G.; Camilleri, A.; Winstone, B.; Caleb-Solly, P.; Dogramadzi, S. An assistive robot to support dressing-strategies for planning and error handling. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 6–29 June 2016; pp. 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Figueroa, N.; Shah, A.J.; Shah, J.A. Provably Safe and Efficient Motion Planning with Uncertain Human Dynamics. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), online, 12–16 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Cully, A.; Demiris, Y. Personalized robot-assisted dressing using user modeling in latent spaces. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 3603–3610. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Cully, A.; Demiris, Y. Probabilistic real-time user posture tracking for personalized robot-assisted dressing. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulić, D.; Croft, E.A. Safe planning for human-robot interaction. J. Robot. Syst. 2005, 22, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chang, H.J.; Demiris, Y. Iterative path optimisation for personalised dressing assistance using vision and force information. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4398–4403. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, Z.; Collier, M.; Kapusta, A.; Kemp, C.C. Tracking human pose during robot-assisted dressing using single-axis capacitive proximity sensing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, R.; Bicchi, A.; Flacco, F. Integration of active and passive compliance control for safe human-robot coexistence. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, K.; Oya, R.; Nagahama, K.; Okada, K.; Inaba, M. Bottom dressing by a dual-arm robot using a clothing state estimation based on dynamic shape changes. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganti, N.; Tamei, T.; Matsubara, T.; Shibata, T. Estimation of human cloth topological relationship using depth sensor for robotic clothing assistance. In Proceedings of the Conference on Advances in Robotics, Pune, India, 4–6 July 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Koganti, N.; Tamei, T.; Matsubara, T.; Shibata, T. Real-time estimation of human-cloth topological relationship using depth sensor for robotic clothing assistance. In Proceedings of the The 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Edinburgh, UK, 25–29 August 2014; pp. 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Koganti, N.; Ngeo, J.G.; Tomoya, T.; Ikeda, K.; Shibata, T. Cloth dynamics modeling in latent spaces and its application to robotic clothing assistance. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 3464–3469. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Chang, H.J.; Demiris, Y. User modelling for personalised dressing assistance by humanoid robots. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 1840–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, Z.; Clever, H.M.; Turk, G.; Liu, C.K.; Kemp, C.C. Deep haptic model predictive control for robot-assisted dressing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 4437–4444. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, K.; Oya, R.; Nagahama, K.; Inaba, M. A method of state recognition of dressing clothes based on dynamic state matching. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Kobe, Japan, 15–17 December 2013; pp. 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Chance, G.; Jevtić, A.; Caleb-Solly, P.; Dogramadzi, S. A quantitative analysis of dressing dynamics for robotic dressing assistance. Front. Robot. AI 2017, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Kapusta, A.; Tan, J.; Kemp, C.C.; Turk, G.; Liu, C.K. Haptic simulation for robot-assisted dressing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 6044–6051. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, D.; Matsubara, T.; Kidode, M. Learning motor skills with non-rigid materials by reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Karon Beach, Thailand, 7–11 December 2011; pp. 2676–2681. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, H.; Schaal, S.; Gandolfo, F.; Gomi, H.; Koike, Y.; Osu, R.; Nakano, E.; Wada, Y.; Kawato, M. A kendama learning robot based on bi-directional theory. Neural Netw. 1996, 9, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, E.; Buchli, J.; Schaal, S. A generalized path integral control approach to reinforcement learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3137–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Eickeler, S.; Kosmala, A.; Rigoll, G. Hidden markov model based continuous online gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Pattern Recognition (Cat. No. 98EX170), Brisbane, Australia, 20 August 1998; Volume 2, pp. 1206–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, W. A survey on curriculum learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4555–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardon, L.; Ritter, H. Active boundary component models for robotic dressing assistance. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 2811–2818. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheim, A.; Burwinkel, M.; Echelmeyer, W. Automatic unloading of heavy sacks from containers. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Qingdao, China, 3 September 2008; pp. 946–951. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Chen, D.; Li, T.; Wu, F.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K. Multi-Scale Dense Networks for Resource Efficient Image Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Barto, A.G.; Mahadevan, S. Recent advances in hierarchical reinforcement learning. Discret. Event Dyn. Syst. 2003, 13, 41–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cloth Shaping | Knot Tying/Untying | Dressing | Bag Manipulation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFRL | [20,29,225,226,227,228,229] | [43] | [31,32,230] | [231,232] |
| MBRL | [29,38,179,233,234,235] | - | - | - |
| State-action BC | [34,236,237,238] | [36,239,240,241] | - | [34,238,242] |
| Trajectory BC | - | [91,105,243,244,245] | [1,246,247,248,249] | - |
| LfO | - | [61,250] | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadi, H.A.; Terzić, K. Data-Driven Robotic Manipulation of Cloth-like Deformable Objects: The Present, Challenges and Future Prospects. Sensors 2023, 23, 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052389
Kadi HA, Terzić K. Data-Driven Robotic Manipulation of Cloth-like Deformable Objects: The Present, Challenges and Future Prospects. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052389
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadi, Halid Abdulrahim, and Kasim Terzić. 2023. "Data-Driven Robotic Manipulation of Cloth-like Deformable Objects: The Present, Challenges and Future Prospects" Sensors 23, no. 5: 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052389
APA StyleKadi, H. A., & Terzić, K. (2023). Data-Driven Robotic Manipulation of Cloth-like Deformable Objects: The Present, Challenges and Future Prospects. Sensors, 23(5), 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052389






