Sensors 2023, 23(7), 3386; https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073386 - 23 Mar 2023
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1545
Abstract
Background: Children undergoing DDH correction surgery may experience gait abnormalities following soft tissue releases and bony procedures. The purpose of this study was to compare the residual gait changes, radiological outcomes, and functional outcomes in children who underwent DDH surgery with those in
[...] Read more.
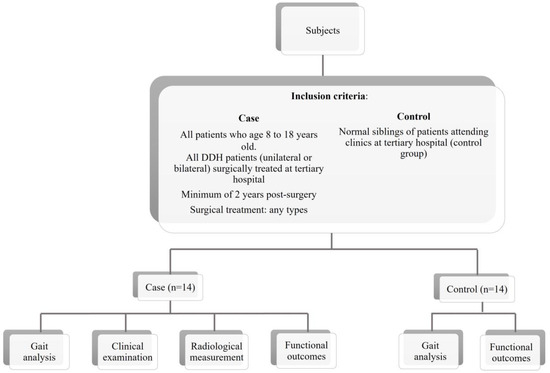
Background: Children undergoing DDH correction surgery may experience gait abnormalities following soft tissue releases and bony procedures. The purpose of this study was to compare the residual gait changes, radiological outcomes, and functional outcomes in children who underwent DDH surgery with those in healthy controls. Methods: Inertial motion sensors were used to record the gait of 14 children with DDH and 14 healthy children. Pelvic X-ray was performed to determine the Severin classification and the presence of femoral head osteonecrosis (Bucholz–Odgen classification). For functional evaluation, the Children’s Hospital Oakland Hip Evaluation Scale (CHOHES) was used. Results: There was no difference in spatial parameters between the two groups. In terms of temporal parameters, the DDH-affected limbs had a shorter stance phase (p < 0.001) and a longer swing phase (p < 0.001) than the control group. The kinematic study showed that the affected limb group had smaller hip adduction angle (p = 0.002) and increased internal rotation (p = 0.006) with reduced upward pelvic tilt (p = 0.020). Osteonecrosis was graded II, III, and IV in five, three, and one patients, respectively. Five patients had no AVN changes. The Severin classification was grade I, II, and III for six, three, and five patients, respectively. Most patients had good functional outcomes on the CHOHES, with a mean total score of 96.64 ± 5.719. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that weight, height, and femoral osteotomy were independent predictors for gait, radiological and functional outcome. Conclusion: Despite good functional scores overall, some children had poor radiological outcomes and gait abnormalities. Our results identified the risk factors for poor outcomes, and we recommend specified rehabilitative strategies for long-term management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wearable Devices and Sensors for Innovative Monitoring Systems in the 4.0 Era)
►
Show Figures