On Dispersion Compensation for GAW-Based Structural Health Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algorithmen
2.1.1. Total Focusing Method
2.1.2. Sign Coherence Factor
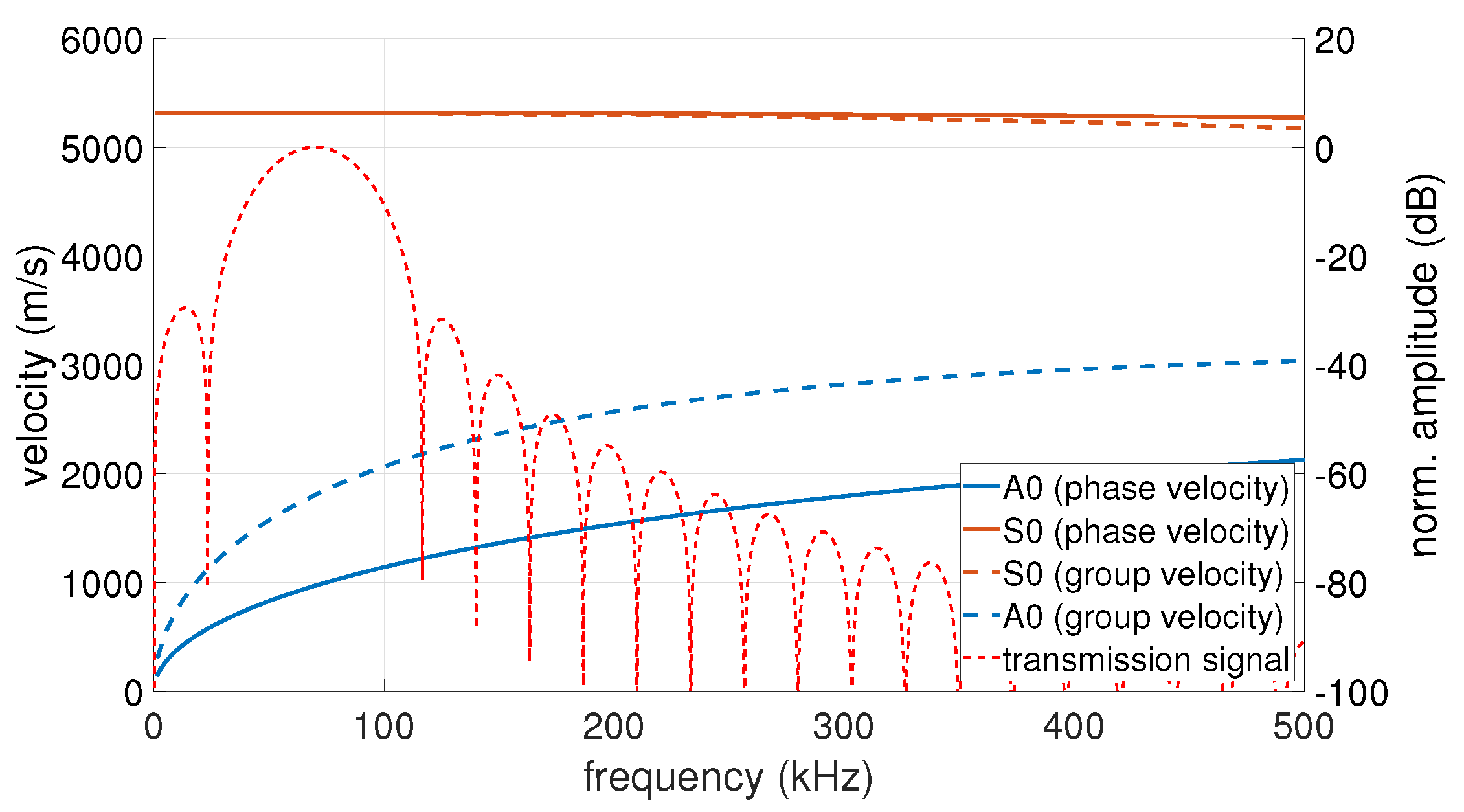
2.1.3. Dispersion Compensation
2.2. Generation of Test Data
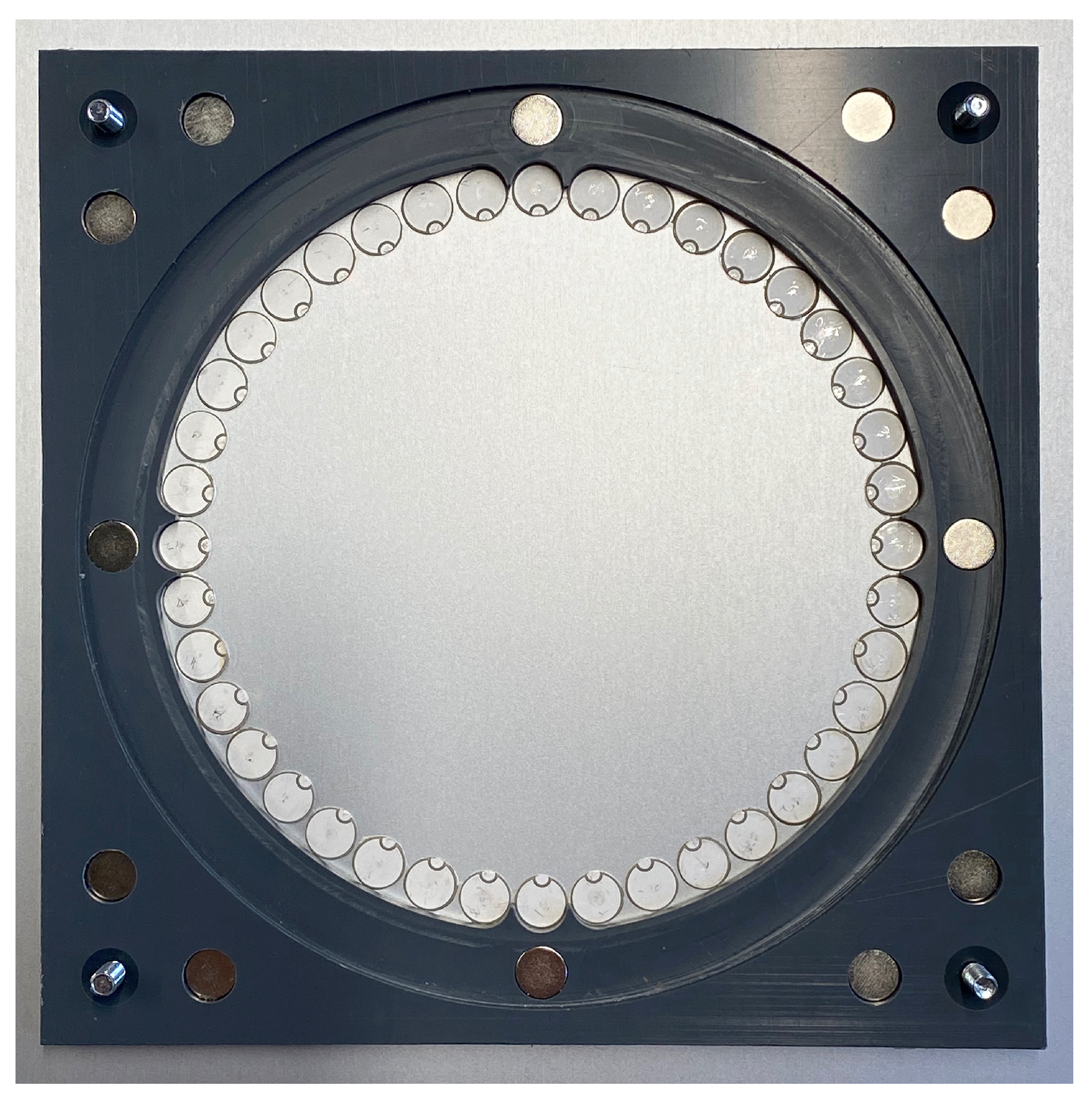
2.3. Measurement Setup
3. Results
3.1. Simulated Data
3.2. Experimental Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giurgiutiu, V. Structural Health Monitoring with Piezoelectric Wafer Active Sensors, 2nd ed.; AP Academic Press/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, M. A lamb wave-based icing sensor for aircraft ice detection. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Atmospheric Icing of Structures, Montreal QC, Canada, 19–23 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Ye, L. Identification of Damage Using LAMB Waves: From Fundamentals to Applications; Lecture notes in applied and computational mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 48. [Google Scholar]
- Philibert, M.; Yao, K.; Gresil, M.; Soutis, C. Lamb waves-based technologies for structural health monitoring of composite structures for aircraft applications. Eur. J. Mater. 2022, 2, 436–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Wilcox, P.D. Post-processing of the full matrix of ultrasonic transmit–receive array data for non-destructive evaluation. NDT E Int. 2005, 38, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Wilcox, P.D. Advanced post-processing for scanned ultrasonic arrays: Application to defect detection and classification in non-destructive evaluation. Ultrasonics 2008, 48, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumana; Ponseenivasan, S.; Kumar, A. Comparative Study on Using Ultrasonic Array-Based Techniques for Detection of Flaws in Thick and Attenuating Materials. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, H. Sound Field Modeling Method and Key Imaging Technology of an Ultrasonic Phased Array: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, P.; Wandowski, T.; Trendafilova, I.; Ostachowicz, W. A Phased Array-based Method for Damage Detection and Localization in Thin Plates. Struct. Health Monit. 2008, 8, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Q.; Chen, M.; Su, Z.; Lee, S.J. A high-resolution structural health monitoring system based on SH wave piezoelectric transducers phased array. Ultrasonics 2019, 97, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.E.; DeSimio, M.P.; Derriso, M.M. Beam Forming of Lamb Waves for Structural Health Monitoring. J. Vib. Acoust. 2007, 129, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgiutiu, V.; Bao, J. Embedded-Ultrasonics Structural Radar for Nondestructive Evaluation of Thin-Wall Structures. In Proceedings of the Adaptive Structures and Materials Systems ASMEDC, 2002, New Orleans, LA, USA, 17–22 November 2002; pp. 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Jiang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, L. Acoustic Signal Imaging Method Based on Synthetic Aperture Focusing and Full Matrix Capture. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 1, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Wilcox, P.D. The post-processing of ultrasonic array data using the total focusing method. Insight Non-Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2004, 46, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Robertson-Welsh, B.; Gaydecki, P.; Gresil, M.; Soutis, C. Structural Health Monitoring Using Lamb Wave Reflections and Total Focusing Method for Image Reconstruction. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 553–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, Q. Sparse-TFM Imaging of Lamb Waves for the Near-Distance Defects in Plate-Like Structures. Metals 2019, 9, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yao, A.; Zhu, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. An Accelerated Post-processing Calculation Method of Curved Surface Profile Extraction Based on the Total Focusing Method of Ultrasonic Phased Array. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2242, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Arslan, T. Parallel Delay Multiply and Sum Algorithm for Microwave Medical Imaging Using Spark Big Data Framework. Algorithms 2021, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, M.; Fan, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, Q. Phase Coherence Imaging for Near-Surface Defects in Rails Using Cross-Correlation of Ultrasonic Diffuse Fields. Metals 2019, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Fan, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, R. The Auto-Correlation of Ultrasonic Lamb Wave Phased Array Data for Damage Detection. Metals 2019, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehami, L.; Moulin, E.; Rosny, J.; Prada, C.; Bou Matar, O.; Benmeddour, F.; Assaad, J. Detection and localization of a defect in a reverberant plate using acoustic field correlation. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, J.N.; Wilcox, P.D.; Croxford, A.J. Diffuse field full matrix capture for near surface ultrasonic imaging. Ultrasonics 2018, 82, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozinski, L.; Stepinski, T.; Uhl, T. Efficient tool for designing 2D phased arrays in lamb waves imaging of isotropic structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engholm, M.; Stepinski, T.; Olofsson, T. Imaging and suppression of Lamb modes using adaptive beamforming. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 085024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.C.; Lv, Z.J.; Ma, D.; Shi, L.H. A Method of Dispersion Compensation Based on Warped Frequency Transform. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 718–720, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shi, L.; Qing, X.P. A time–distance domain transform method for Lamb wave dispersion compensation considering signal waveform correction. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 119601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, J. Dispersion compensation in Lamb wave defect detection with step-pulse excitation and warped frequency transform. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 2075–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yuan, S.; Qing, X.P.; Chang, F.; Shi, L.; Qiu, L. Linearly dispersive signal construction of Lamb waves with measured relative wavenumber curves. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 221, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Tian, S.; Xie, Y. A guided wave dispersion compensation method based on compressed sensing. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 103, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Y. Dispersion Compensation Method for Lamb Waves Based on Measured Wavenumber. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yuan, F.G. Adaptive signal decomposition and dispersion removal based on the matching pursuit algorithm using dispersion-based dictionary for enhancing damage imaging. Ultrasonics 2020, 103, 106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, P.D. A signal processing technique to remove the effect of dispersion from guided wave signals. AIP Conf. Proc. 2000, 557, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, P.D. A rapid signal processing technique to remove the effect of dispersion from guided wave signals. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2003, 50, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yu, L.; Giurgiutiu, V. Lamb wave dispersion compensation in piezoelectric wafer active sensor phased-array applications. In Proceedings of the Health Monitoring of Structural and Biological Systems 2009, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 March 2009; Kundu, T., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2009; p. 729516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yuan, F.G. A Linear Mapping Technique for Dispersion Removal of Lamb Waves. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 9, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcreff, E.; Braconnier, D.; Dao, G. Fast total focusing method for ultrasonic imaging. hlAIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1706, 040001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, J.E. Enhanced Differential Methods for Guided Wave Phased Array Imaging Using Spatially Distributed Piezoelectric Transducers. AIP Conf. Proc. 2006, 820, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, J.E.; Michaels, T.E. An integrated strategy for detection and imaging of damage using a spatially distributed array of piezoelectric sensors. In Proceedings of the Health Monitoring of Structural and Biological Systems 2007, San Diego, CA, USA, 18 March 2007; Kundu, T., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2007; p. 653203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Yang, M.; Hong, D.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Qing, X. The Design and Verification of an Active SAMSR Ultrasonic Guided Wave Monitoring System with Ultra-Low Crosstalk. Sensors 2020, 20, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Graullera, O.; Romero-Laorden, D.; Martín-Arguedas, C.J.; Ibañez, A.; Ullate, L.G. A new beamforming process based on the phase dispersion analysis. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1433, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, J.; Parrilla, M.; Fritsch, C. Phase coherence imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 56, 958–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, J.; Fritsch, C.; Fernandez-Cruza, J.; Parrilla, M. Phase Coherence Imaging: Principles, applications and current developments. In Proceedings of the 178th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America ASA, San Diego, CA, USA, 2–6 December 2019; p. 055012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, P.D.; Lowe, M.J.S.; Cawley, P. Mode and Transducer Selection for Long Range Lamb Wave Inspection. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2001, 12, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, V.T.; Higuti, R.T.; Kitano, C.; Martinez-Graullera, O.; Adamowski, J.C. Lamb mode diversity imaging for non-destructive testing of plate-like structures. NDT E Int. 2013, 59, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.L. Ultrasonic Guided Waves in Solid Media; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.V.; Doroshenko, O.V.; Arsenov, M.A.; Bareiko, I.A.; Eremin, A.A. Identification of Material Properties of Elastic Plate Using Guided Waves Based on the Matrix Pencil Method and Laser Doppler Vibrometry. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Crespo, B.; Courtney, C.; Engineer, B. Calculation of Guided Wave Dispersion Characteristics Using a Three-Transducer Measurement System. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairuschin, V.; Brand, F.; Backer, A.; Drese, K.S. Elastic Properties Measurement Using Guided Acoustic Waves. Sensors 2021, 21, 6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

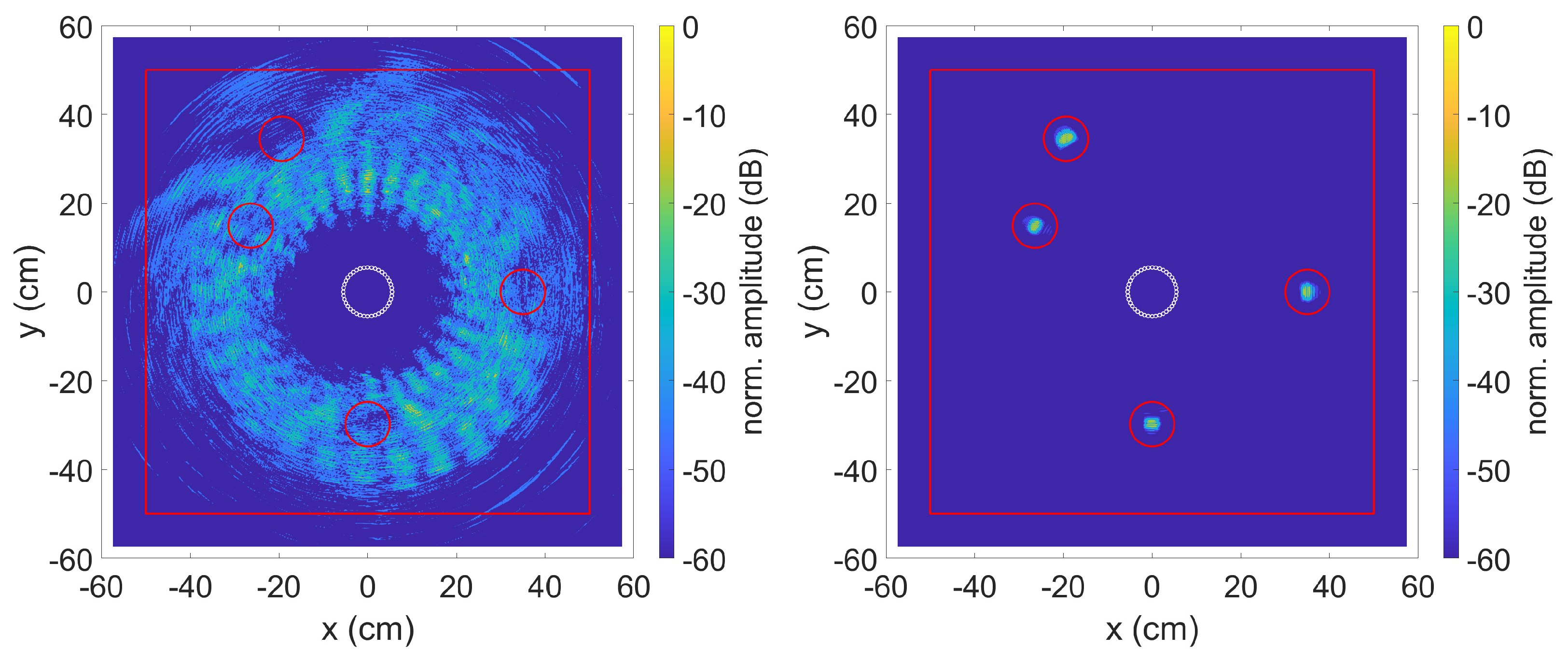
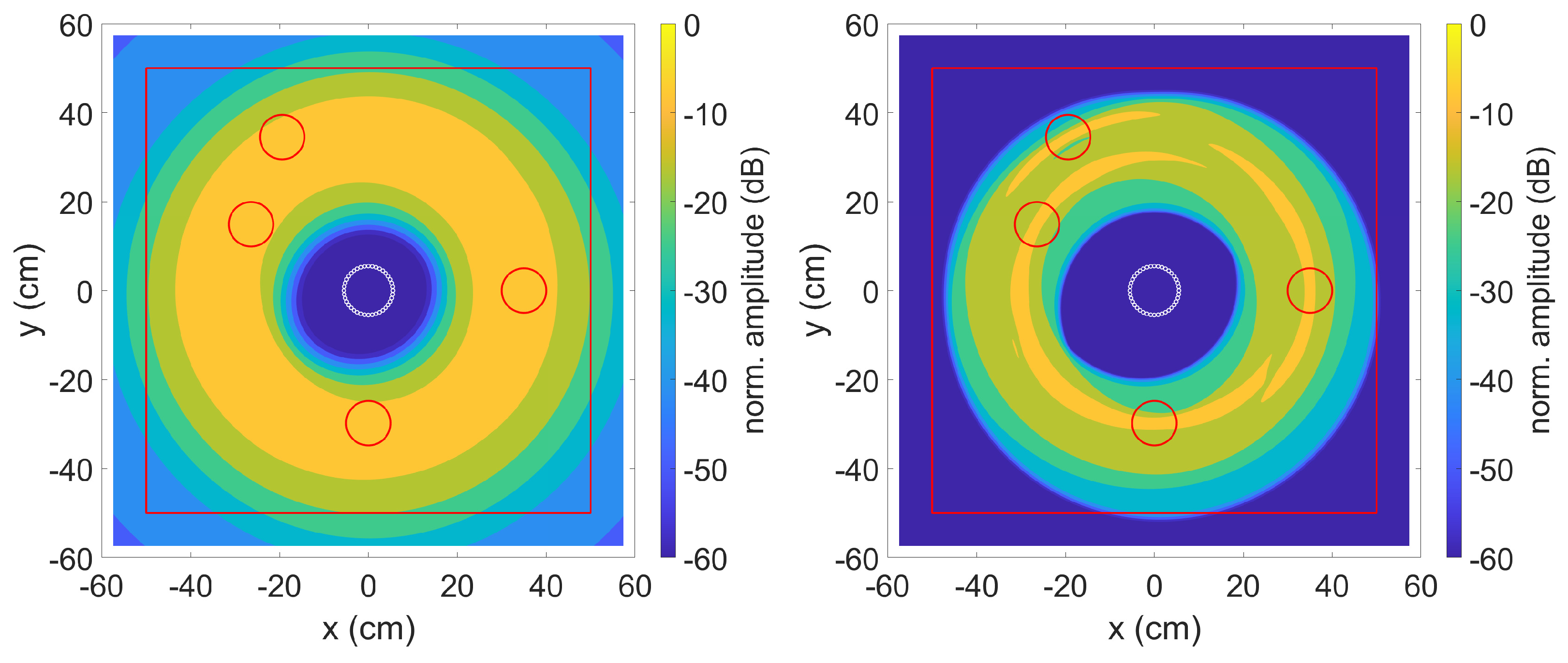
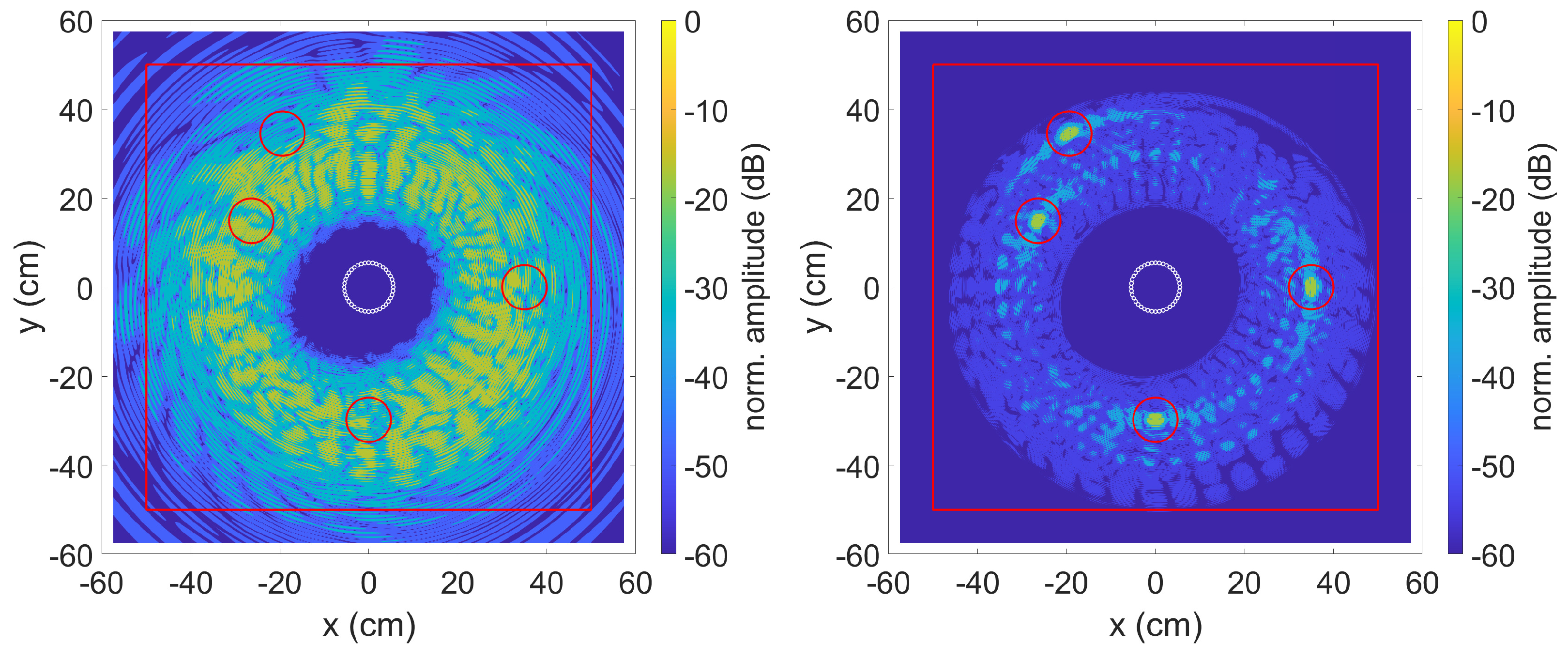


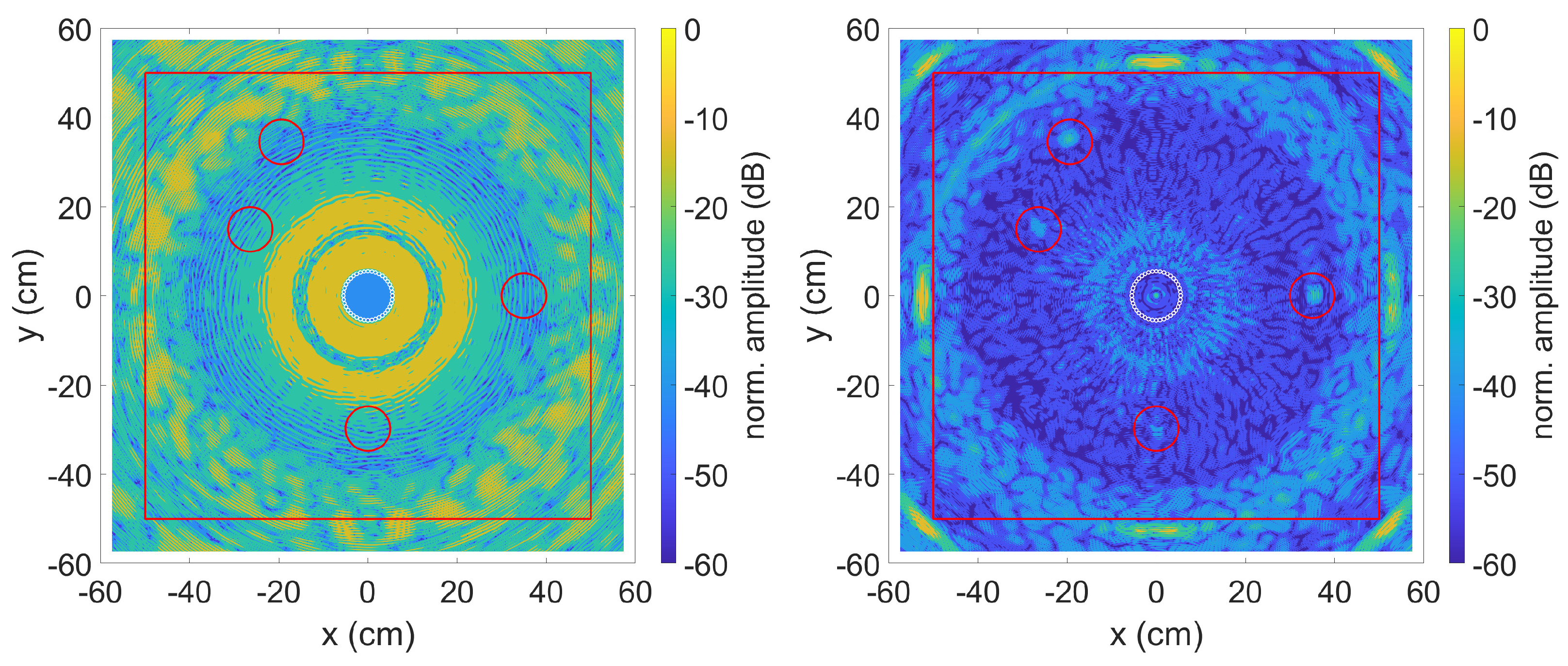
| Defect | Material | x (mm) | y (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Epoxy | 350 | 0 |
| 2 | Epoxy | −194 | 345 |
| 3 | PU | −264 | 149 |
| 4 | PU | 0 | −298 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Backer, A.; Fairuschin, V.; Drese, K.S. On Dispersion Compensation for GAW-Based Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094282
Backer A, Fairuschin V, Drese KS. On Dispersion Compensation for GAW-Based Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors. 2023; 23(9):4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094282
Chicago/Turabian StyleBacker, Alexander, Viktor Fairuschin, and Klaus Stefan Drese. 2023. "On Dispersion Compensation for GAW-Based Structural Health Monitoring" Sensors 23, no. 9: 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094282
APA StyleBacker, A., Fairuschin, V., & Drese, K. S. (2023). On Dispersion Compensation for GAW-Based Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors, 23(9), 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094282








