The Effect of Ambient Illumination and Text Color on Visual Fatigue under Negative Polarity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
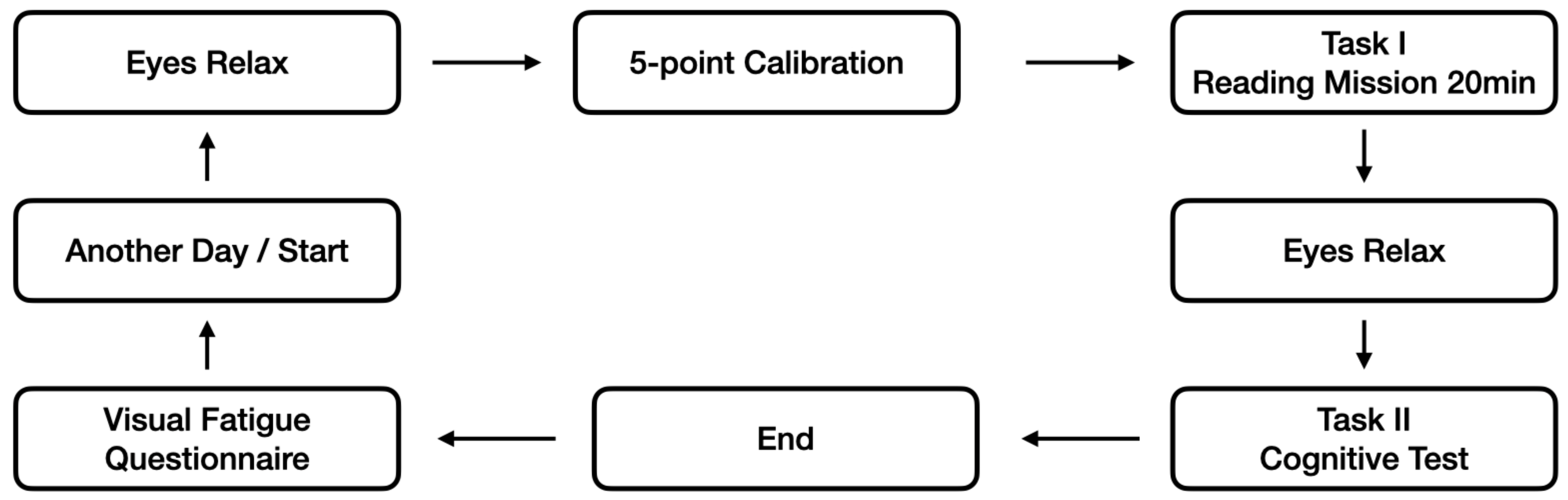
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Apparatus
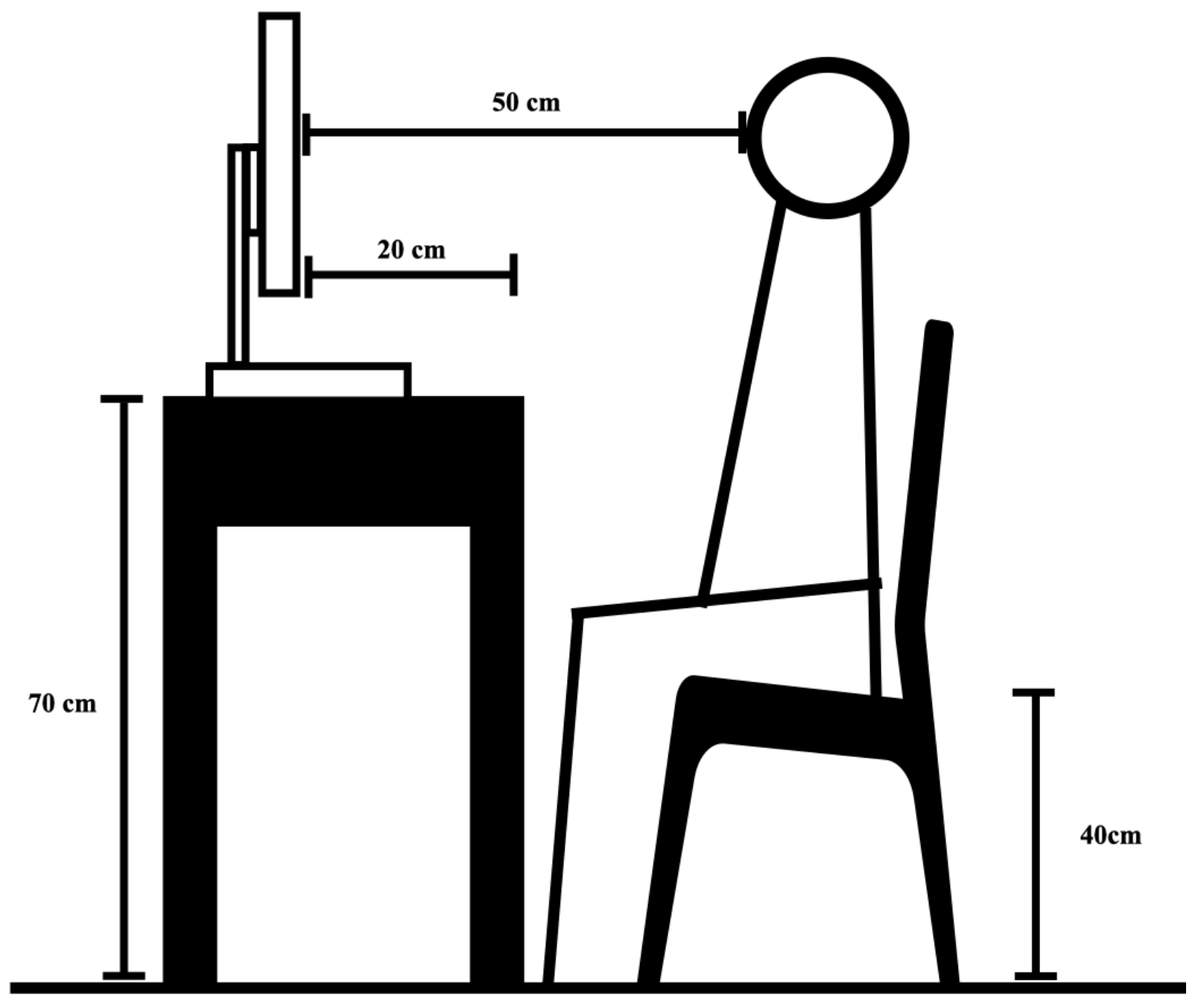
2.4. Conditions of the Workplace
2.5. Task and Procedure
2.6. Dependent Variables
2.6.1. Pupil Accommodation
2.6.2. Blink Rate
2.6.3. Cognitive Performance
2.6.4. Visual Fatigue Index
3. Results
3.1. Pupil Accommodation
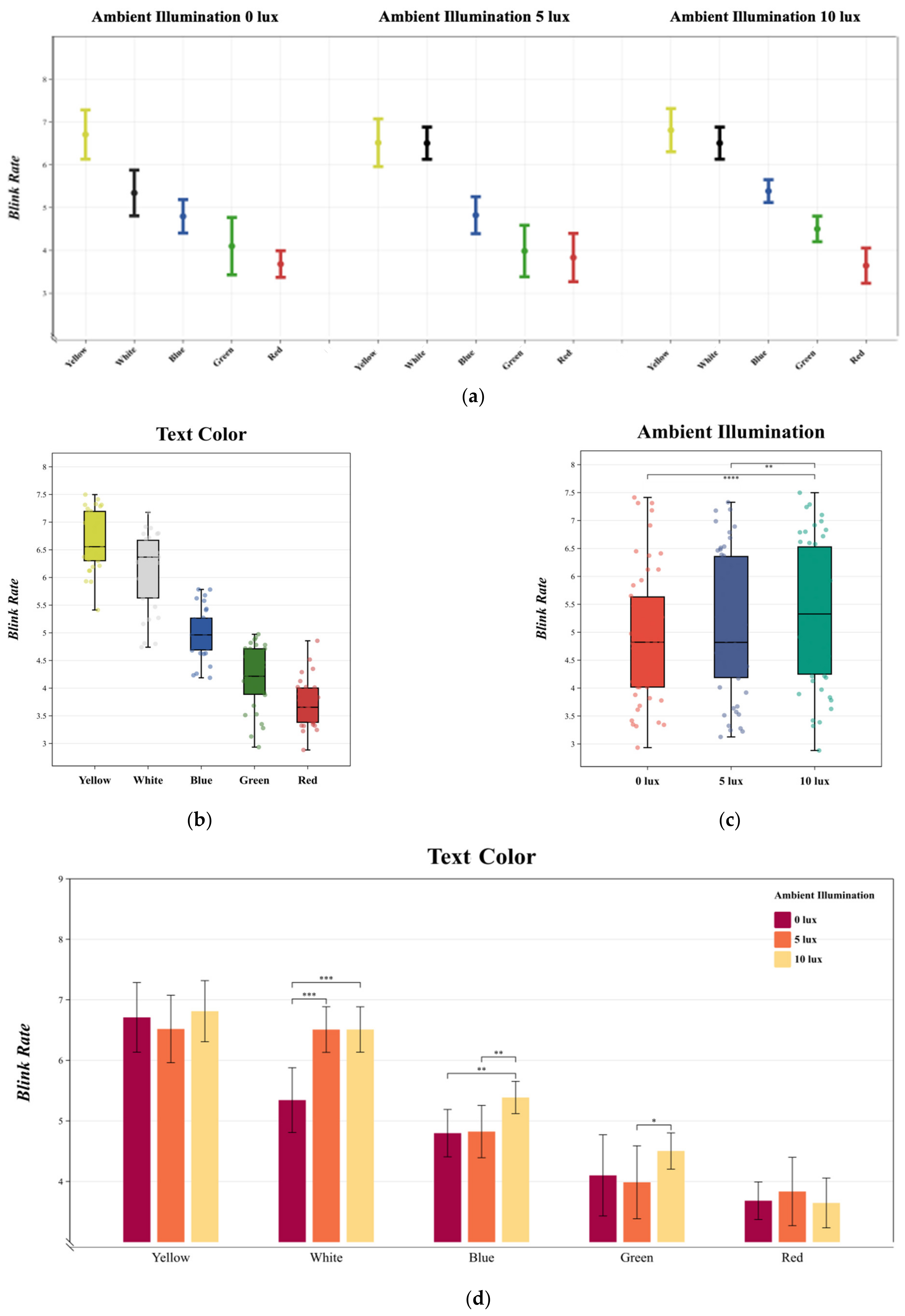
3.2. Blink Rate
3.3. Cognitive Performance
3.4. Visual Fatigue Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Ambient Illumination
4.2. Text Color
4.3. Interaction between Text Color and Ambient Illumination
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pramana, S.; Farhan, M.; Puspasari, M.A. Evaluation on the Effects of Visual Intervention on Emotion and Fatigue while Driving Using Brainwave Indicator. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Industrial and Business Engineering, Macau, China, 27–29 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Alamri, A.; Amer, K.A.; Aldosari, A.A.; Althubait, B.M.S.; Alqahtani, M.S.; AL Mudawi, A.A.M.; AL Mudawi, B.A.M.; Alqahtani, F.A.M.; Alhamoud, N.S.Y. Computer vision syndrome: Symptoms, risk factors, and practices. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 5110–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, A.; Kim, K.; Bruder, G.; Welch, G.F. Effects of dark mode graphics on visual acuity and fatigue with virtual reality head-mounted displays. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR), Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–26 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dillon, A. Reading from paper versus screens: A critical review of the empirical literature. Ergonomics 1992, 35, 1297–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Yeh, L.C. Impacts of TFT-LCD polarity, font size, and line space on visual performance with age-difference considerations. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering, Awaji, Japan, 25–28 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Piepenbrock, C.; Mayr, S.; Buchner, A. Smaller pupil size and better proofreading performance with positive than negative polarity displays. Ergonomics 2014, 57, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, T.; Ziat, M. Dark mode vogue: Do light-on-dark displays have measurable benefits to users? Ergonomics 2023, 66, 1814–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Song, Z.; Dong, J.; Bao, F.; Wang, X. Eye movement characteristics and visual fatigue assessment of virtual reality games with different interaction modes. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1173127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhamad, N.; Moktaeffendi, N.H.; Azni, N.S. Effect of Display Polarity on Amplitude of Accommodation and Visual Fatigue. Environ.-Behav. Proc. J. 2023, 8, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y. The impact of ambient illumination on visual fatigue while watching TV. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting (SSLCHINA), Shenzhen, China, 2–4 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W. Effect of illuminance and light strobe on attention and visual fatigue in indoor lighting. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting & 2019 International Forum on Wide Bandgap Semiconductors China (SSLChina: IFWS), Shenzhen, China, 25–27 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.J.; Feng, W.Y.; Chao, C.J.; Tseng, F.Y. Effects of VDT workstation lighting conditions on operator visual workload. Ind. Health 2008, 46, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. The effect of ambient illumination source and display type on visual fatigue. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting (SSLChina), Beijing, China, 15–17 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, R.; Zhu, R. Blue or red? Exploring the effect of color on cognitive task performances. Science 2009, 323, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilina, S. Delving into the Past, Pondering the Present, and Probing Cultural Nuances: The Multifaceted Exploration of Biometric Identity Verification; Paradigm Research Institute: Boise, ID, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, M.; Katsuura, T.; Harada, H.; Iwanaga, K. The effect of color temperature on visual fatigue. Appl. Hum. Sci. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 1997, 16, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Arefin, M.S.; Phillips, N.; Plopski, A.; Gabbard, J.L.; Swan, J.E. The effect of context switching, focal switching distance, binocular and monocular viewing, and transient focal blur on human performance in optical see-through augmented reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.-H.; Chien, C.-K.; Hsiao, C.-L. The Evaluation of Visual Fatigue for Users’ Magazines Reading. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Management Science and Application (ICIMSA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13–15 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M.R. Effect of Coloured Text and Background Combination on Visual Comfort for Reading on Display. In Proceedings of the 2023 20th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting & 2023 9th International Forum on Wide Bandgap Semiconductors (SSLCHINA: IFWS), Xiamen, China, 27–30 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Kale, S.; Chandel, S.; Pal, D.K. Likert Scale: Explored and Explained. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyaningsih, E.; Putranto, L.S.; Soelami, F.X.; Setiawan, M.I.; Abdullah, D. The Visual Perception of the Car Drivers Dealing with the Road Supporting Facilities, Road Median, Potholes, and Other Cars on Freeways with and without Lighting. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1114, 012125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, E.L.; He, Z.; Hung, Y.; Gou, F.; Lan, Y.F.; Wu, S.T. Optimal chip size for reducing the power consumption of micro-LED displays. Adv. Disp. Technol. XI 2021, 11708, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, B.; Cooper, M.; Reid, L.G.; Vanderheiden, G. Web content accessibility guidelines (WCAG) 2.0. WWW Consort. 2008, 290, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guilford, J.P.; Smith, P.C. A system of color-preferences. Am. J. Psychol. 1959, 72, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Song, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, D. Study on the effects of display color mode and luminance contrast on visual fatigue. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 35915–35923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.R. Applying new design principles to constructing an illiterate E chart. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1978, 55, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowrisankaran, S.; Nahar, N.K.; Hayes, J.R.; Sheedy, J.E. Asthenopia and blink rate under visual and cognitive loads. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, N.K.; Gowrisankaran, S.; Hayes, J.R.; Sheedy, J.E. Interactions of visual and cognitive stress. Optom.-J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 2011, 82, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobres, J.; Chahine, N.; Reimer, B. Effects of ambient illumination, contrast polarity, and letter size on text legibility under glance-like reading. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 60, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.-F.; Cai, D.; You, M. Applying image descriptors to the assessment of legibility in Chinese characters. Ergonomics 2003, 46, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Lee, E.C. Experimental verification of objective visual fatigue measurement based on accurate pupil detection of infrared eye image and multi-feature analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.A.; Garcia, D.M.; Pinto, C.T.; Cechetti, S.P. Spontaneous eyeblink activity. Ocul. Surf. 2011, 9, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentivoglio, A.R.; Bressman, S.B.; Cassetta, E.; Carretta, D.; Tonali, P.; Albanese, A. Analysis of blink rate patterns in normal subjects. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.K.; Labban, J.D.; Gapin, J.I.; Etnier, J.L. The effects of acute exercise on cognitive performance: A meta-analysis. Brain Res. 2012, 1453, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M. Effects of mental fatigue on brain activity and cognitive performance: A magnetoencephalography study. Anat. Physiol. 2015, 5, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, R.; Sato, H.; Hirayama, T.; Hirata, K.; Kokubu, M.; Ando, S. Effects of three-dimension movie visual fatigue on cognitive performance and brain activity. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 974406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer, H.; Hollendiek, G.; Kröger, H.; Römer, T. Rest position of the eyes and its effect on viewing distance and visual fatigue in computer display work. Z. Fur Exp. Und Angew. Psychol. 1989, 36, 538–566. [Google Scholar]
- Shieh, K.-K.; Lin, C.-C. Effects of screen type, ambient illumination, and color combination on VDT visual performance and subjective preference. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2000, 26, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L. Effects of contrast and ambient illumination on visual discomfort of autostereoscopic display. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2023, 31, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C. Visual fatigue and performances for the 40-min mixed visual work with a projected screen. Ergon. Open J. 2012, 5, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Xu, G.; Han, C.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Du, C.; Wei, F.; Zhang, S. Effects of paradigm color and screen brightness on visual fatigue in a light environment of the night based on eye tracker and EEG acquisition equipment. Sensors 2022, 22, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaka, N. The effect of VDU color on visual fatigue in the fovea and periphery of the visual field. Displays 1985, 6, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.G.; Pelech, M.T.; Foster, S.F. Color preference and stimulation seeking. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1984, 59, 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yin, E.; Jiang, J.; Hu, D. A novel single-character visual BCI paradigm with multiple active cognitive tasks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Color appearance phenomena under high ambient illumination. Optik 2017, 145, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés Sans, M. Estudi del Parpelleig en Usuaris/es de Pantalles Digitals: Anàlisi D‘estratègies pel Condicionament del Parpelleig i la Distància de Manera no Intrusiva. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, J.L. Vicarious trauma as applied to the professional sign language interpreter. Montview J. Res. Scholarsh. 2015, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, H.; Chen, Q.-W.; Ru, T.; Zhou, G. Investigation of the optimum display luminance of an LCD screen under different ambient illuminances in the evening. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, E.C. EEG-based comparative measurement of visual fatigue caused by 2D and 3D displays. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2011—Posters’ Extended Abstracts: International Conference, HCI International 2011, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–14 July 2011; Proceedings, Part II. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
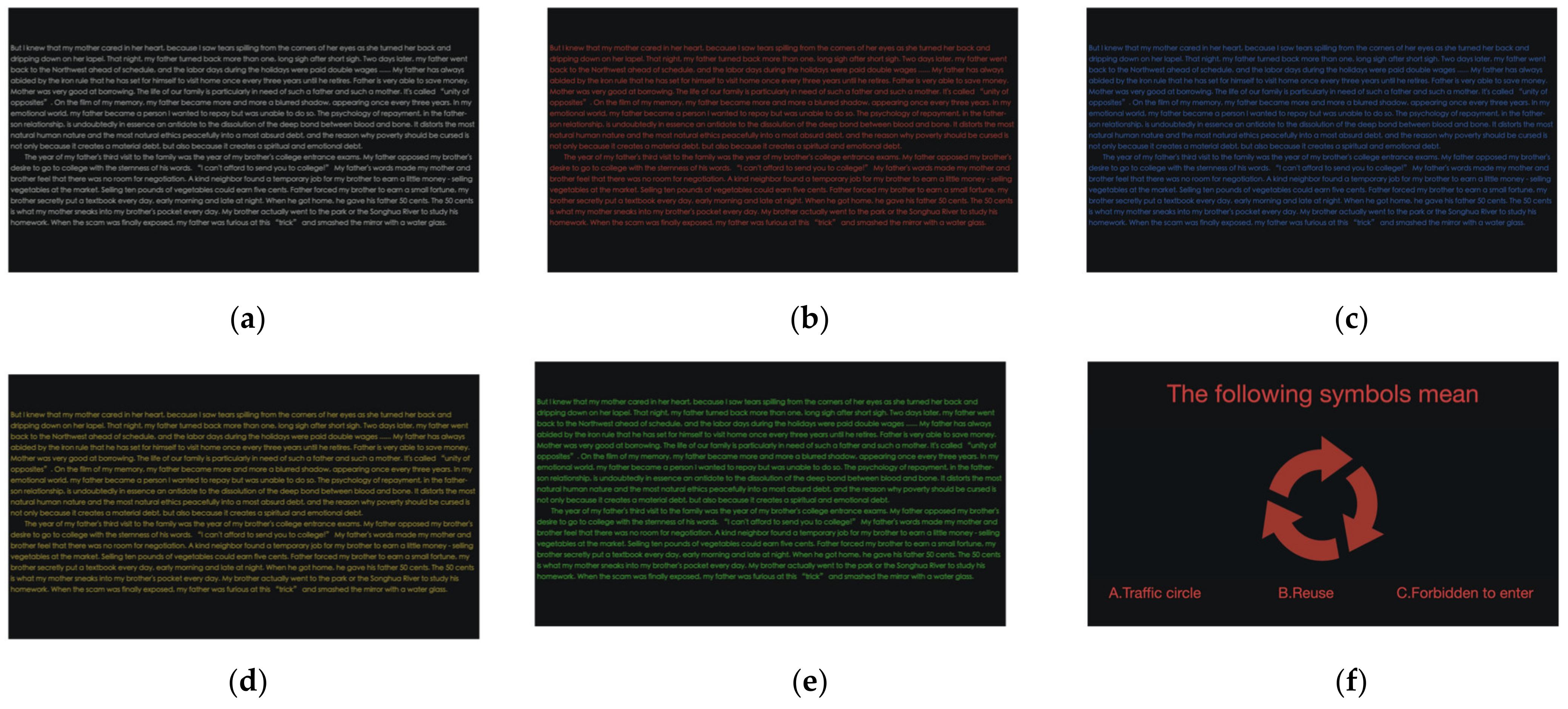




| Text Color | HSB | RGB | Luminance Contrasted with Background |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | (0°, 0%, 95%) | (242, 242, 242) | 19.60 |
| Yellow | (49°, 70%, 62%) | (158, 138, 47) | 6.13 |
| Blue | (218°, 70%, 62%) | (47, 88, 158) | 3.01 |
| Green | (113°, 70%, 62%) | (60, 158, 47) | 6.12 |
| Red | (3°, 70%, 62%) | (158, 53, 47) | 3.00 |
| Background | (0°, 0%, 0%) | (0, 0, 0) | - |
| Dependent Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | Pupil Accommodation | Blink Rate | Cognitive Performance | Visual Fatigue Index |
| White.0 lux | 0.0259 (0.0063) | 5.343 (0.535) | 46.7 (2.16) | 5.75 (0.75) |
| White.5 lux | 0.0310 (0.0074) | 6.507 (0.535) | 47.0 (2.26) | 5.40 (1.07) |
| White.10 lux | 0.0310 (0.0075) | 6.508 (0.375) | 46.2 (2.86) | 5.30 (1.13) |
| Yellow.0 lux | 0.0396 (0.0050) | 6.709 (0.576) | 46.4 (4.74) | 5.90 (0.74) |
| Yellow.5 lux | 0.0408 (0.0025) | 6.517 (0.558) | 47.1 (1.60) | 5.75 (0.78) |
| Yellow.10 lux | 0.0489 (0.0052) | 6.811 (0.505) | 46.4 (4.74) | 5.78 (0.74) |
| Blue.0 lux | 0.0144 (0.0045) | 4.797 (0.391) | 45.2 (2.49) | 2.50 (1.11) |
| Blue.5 lux | 0.0190 (0.0075) | 4.823 (0.431) | 47.1 (1.60) | 2.73 (1.22) |
| Blue.10 lux | 0.0200 (0.0066) | 5.386 (0.266) | 47.0 (2.26) | 2.87 (1.16) |
| Green.0 lux | 0.0053 (0.0022) | 4.101 (0.670) | 45.2 (2.49) | 2.52 (0.84) |
| Green.5 lux | 0.0056 (0.0020) | 3.987 (0.602) | 43.8 (5.83) | 2.62 (1.30) |
| Green.10 lux | 0.0097 (0.0033) | 4.503 (0.299) | 41.6 (4.79) | 2.39 (0.87) |
| Red.0 lux | 0.0021 (0.0003) | 3.683 (0.310) | 42.0 (5.08) | 1.58 (0.54) |
| Red.5 lux | 0.0025 (0.0005) | 3.834 (0.564) | 40.4 (6.04) | 1.78 (0.60) |
| Red.10 lux | 0.0030 (0.0006) | 3.646 (0.411) | 41.6 (4.01) | 2.11 (0.64) |
| Pupil Accommodation | Blink Rate | Cognitive Performance | Visual Fatigue Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupil Accommodation | 1 | |||
| Blink Rate | 0.814 ** | 1 | ||
| Cognitive Performance | 0.398 ** | 0.403 ** | 1 | |
| Visual Fatigue Index | 0.747 ** | 0.752 * | 0.359 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.; Xie, J.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y. The Effect of Ambient Illumination and Text Color on Visual Fatigue under Negative Polarity. Sensors 2024, 24, 3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113516
Fan Q, Xie J, Dong Z, Wang Y. The Effect of Ambient Illumination and Text Color on Visual Fatigue under Negative Polarity. Sensors. 2024; 24(11):3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113516
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qiangqiang, Jinhan Xie, Zhaoyang Dong, and Yang Wang. 2024. "The Effect of Ambient Illumination and Text Color on Visual Fatigue under Negative Polarity" Sensors 24, no. 11: 3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113516
APA StyleFan, Q., Xie, J., Dong, Z., & Wang, Y. (2024). The Effect of Ambient Illumination and Text Color on Visual Fatigue under Negative Polarity. Sensors, 24(11), 3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113516




