Fast Low-Sidelobe Pattern Synthesis Using the Symmetry of Array Geometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a fast low-sidelobe pattern synthesis method using the symmetry of array geometry, which reduces the dimension of the optimization variables and improves the computational efficiency significantly.
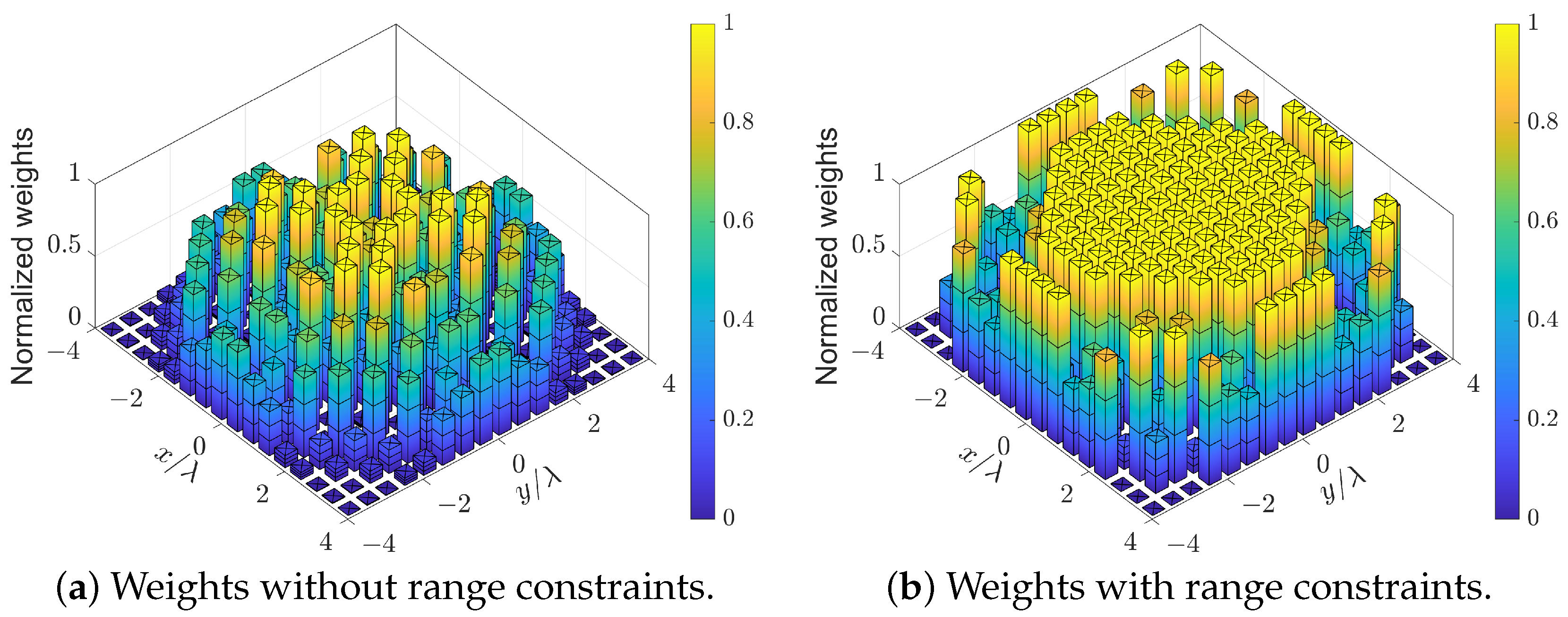
- The lower and upper bounds of the weighting coefficients can also be specified in the proposed method, which can control the dynamic range of the weighting coefficients.
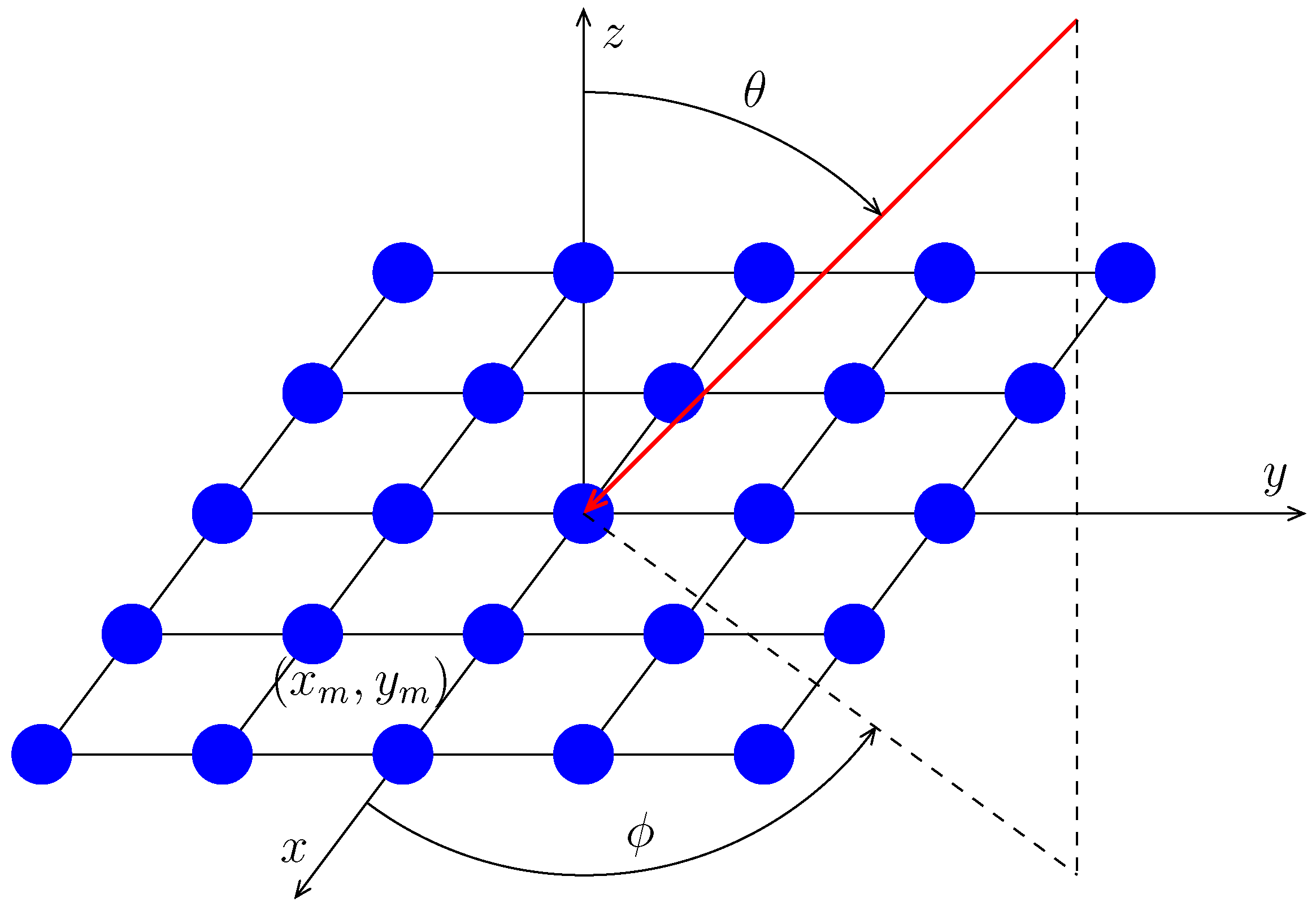
2. Problem Formulation
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Fast Amplitude Weighting for URA Using Mirror Symmetry
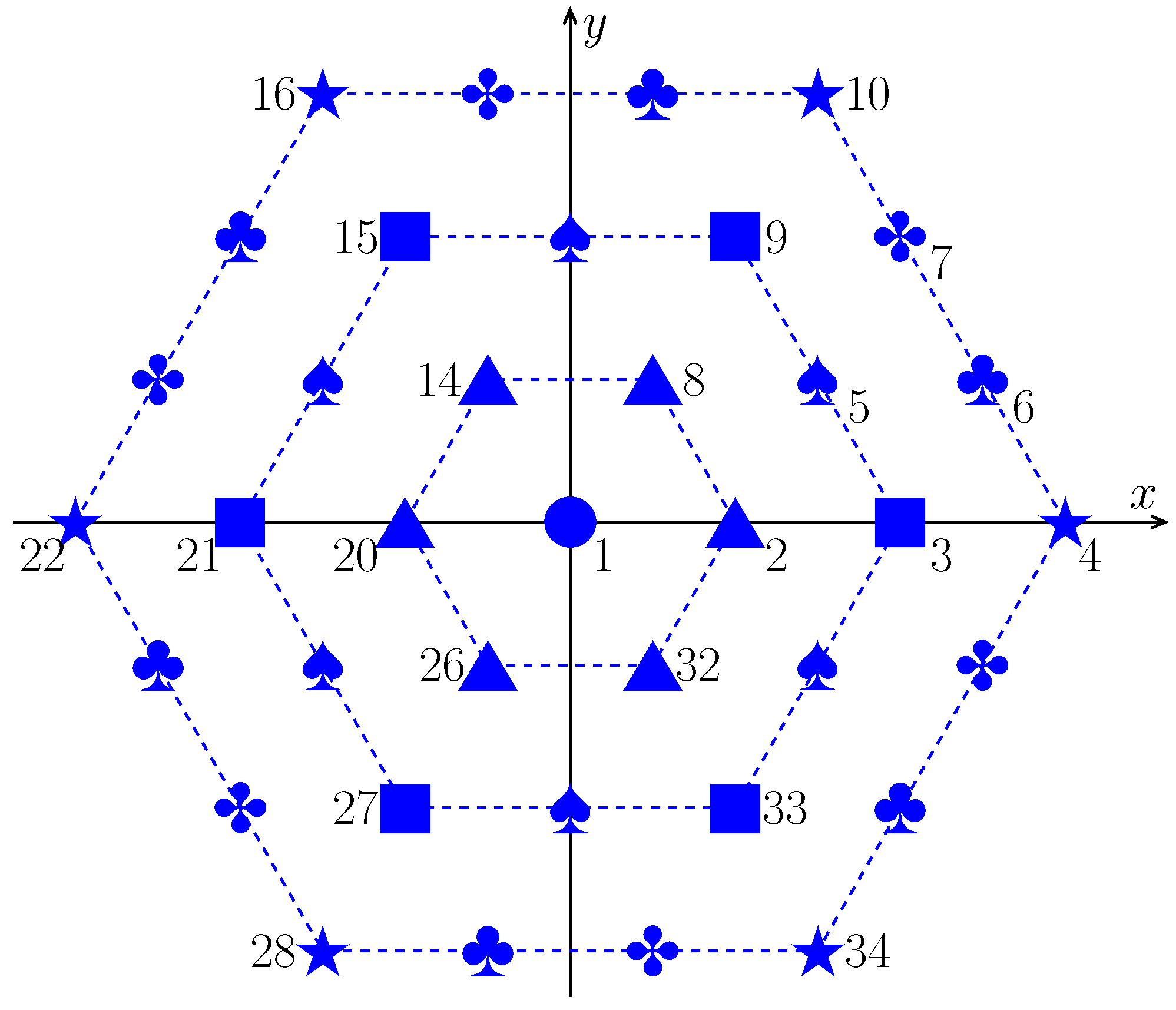
3.2. Fast Amplitude Weighting for UHA Using Rotational Symmetry
- The sensors in the region of are numbered in a consecutive way, starting with the origin () and proceeding in the x-direction and then in the y-direction ().
- If the position of a sensor is obtained by rotating the mth sensor () with an angle of (), then this sensor is numbered by .
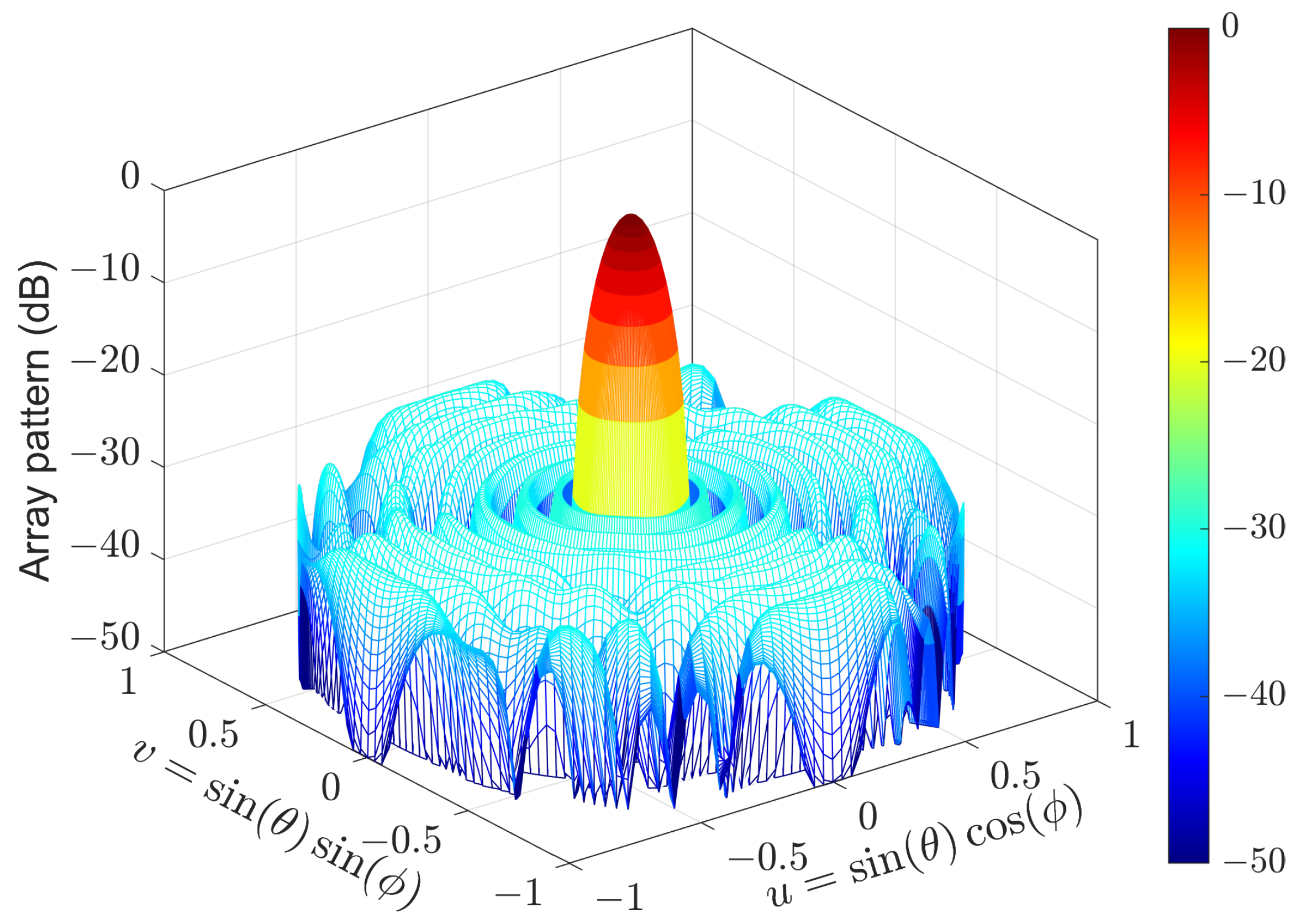
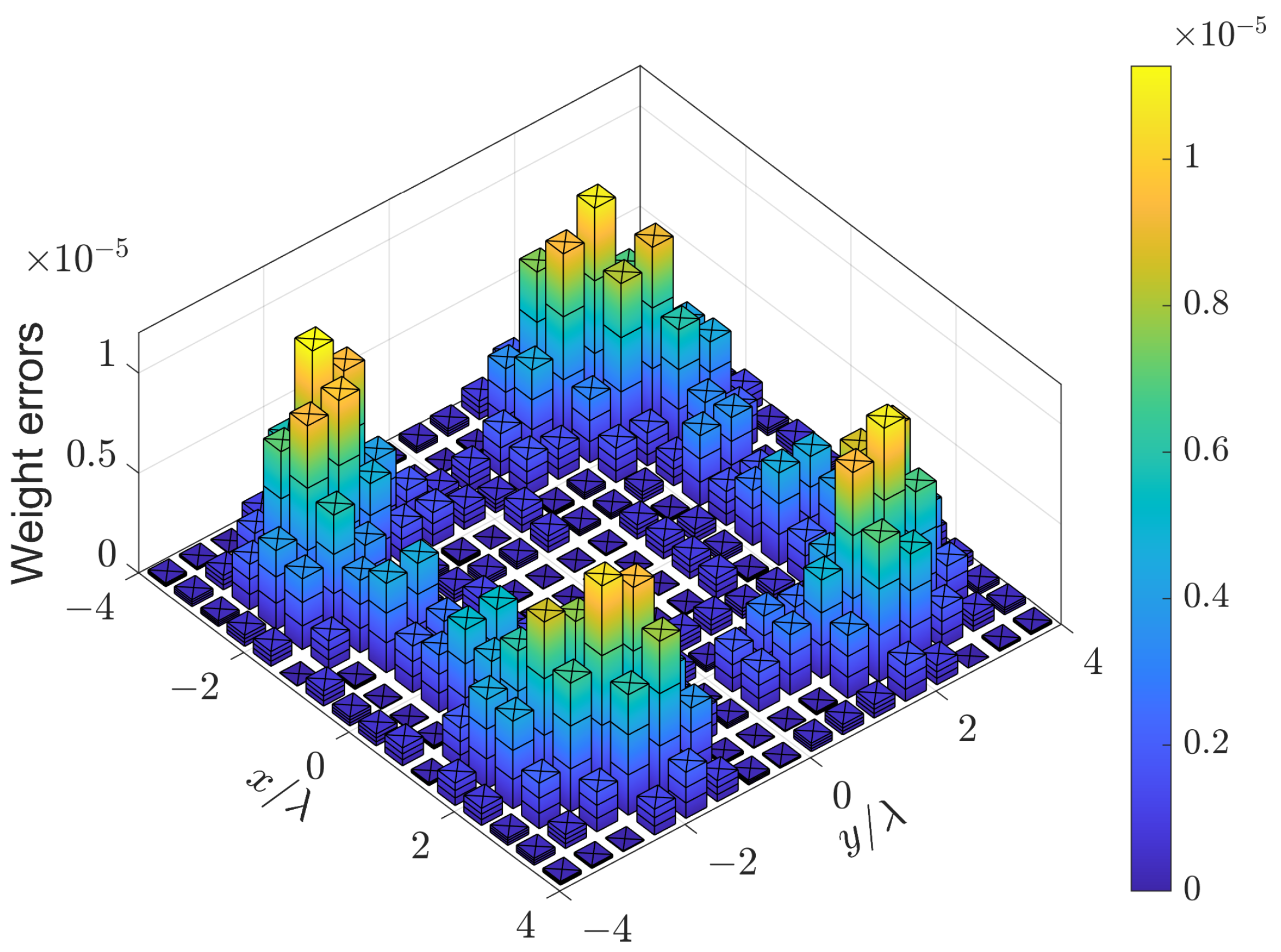
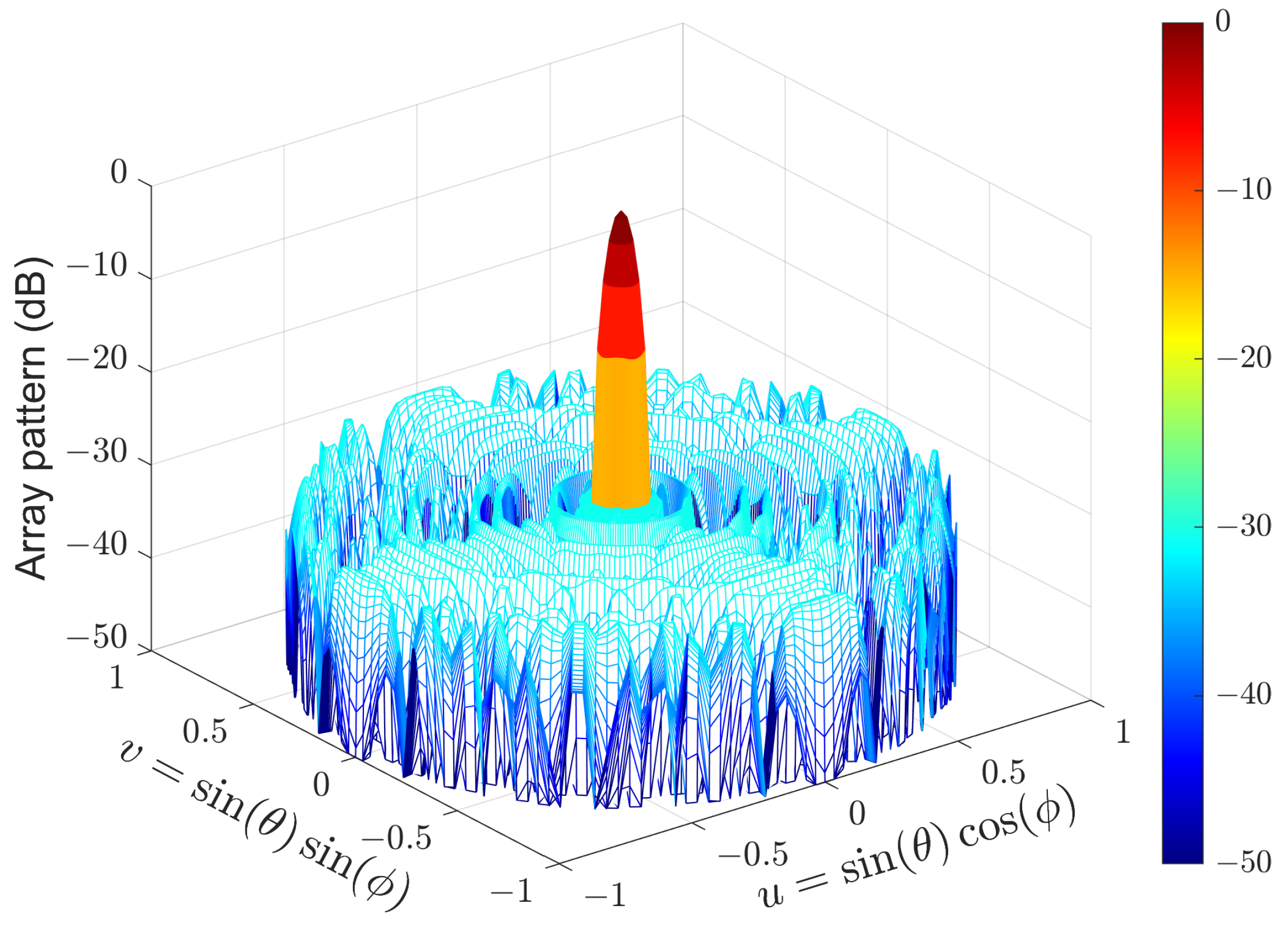
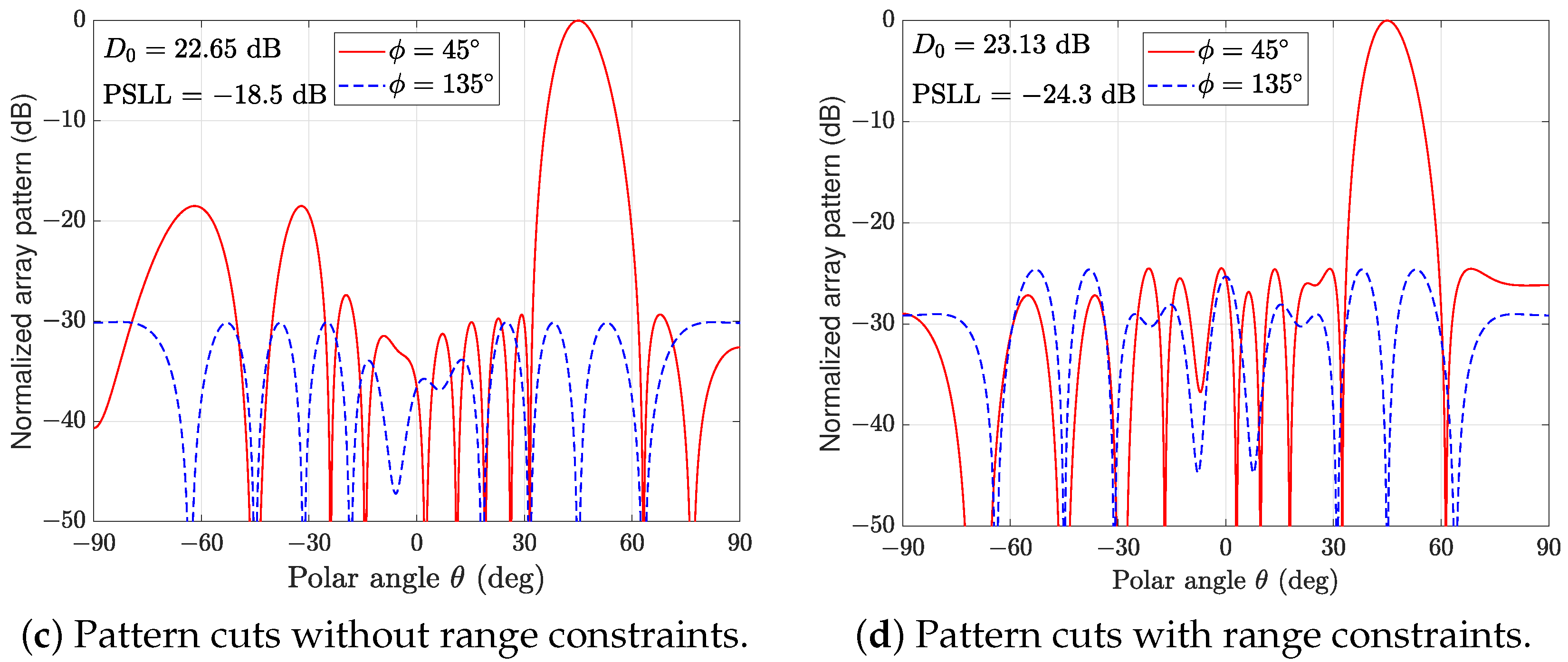
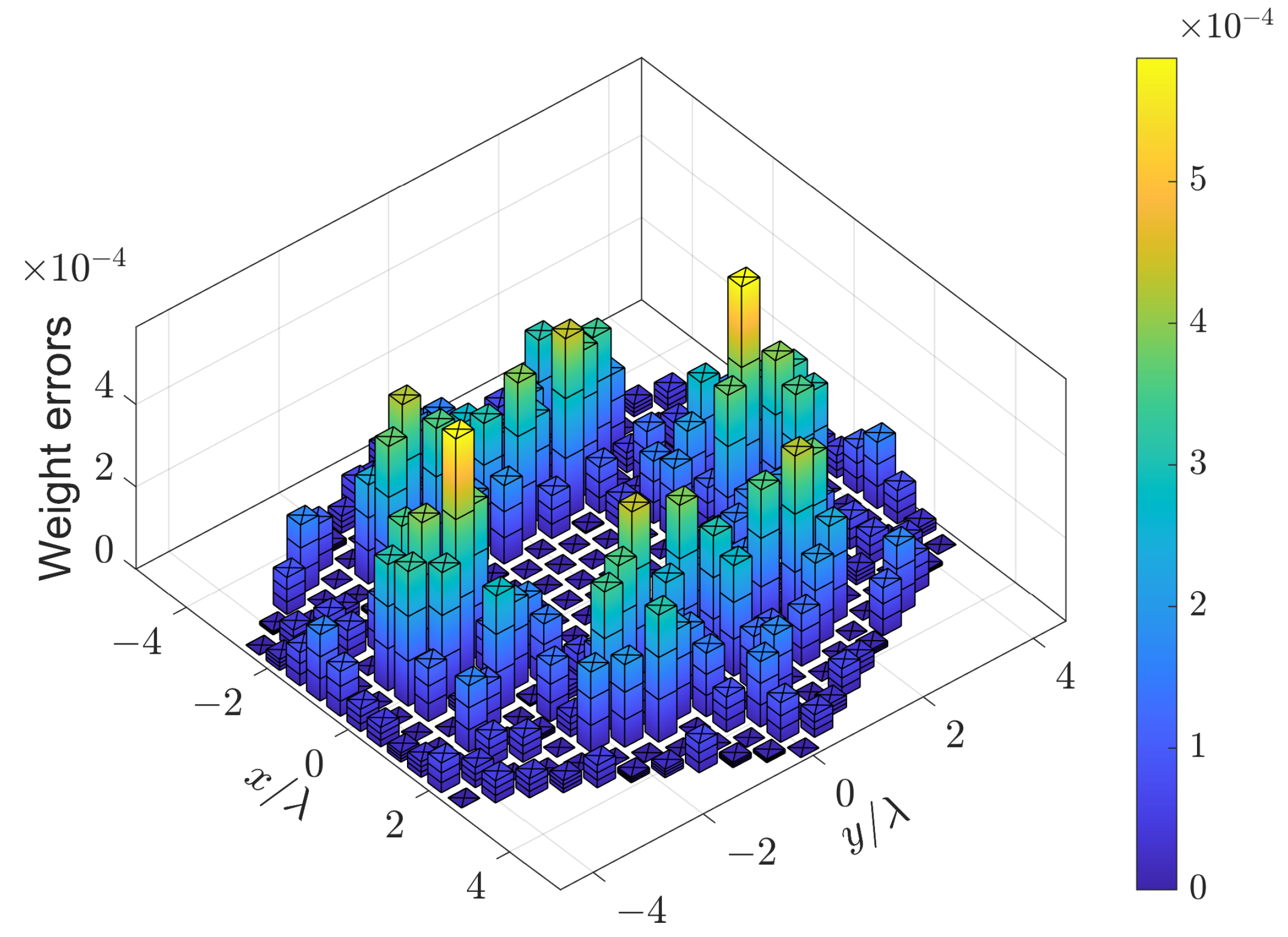
4. Numerical Results and Analyses
4.1. Experiment 1: URA with Mirror Symmetry
4.2. Experiment 2: UHA with Rotational Symmetry
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richards, M.A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, R.W.; Lozano, A. Foundations of MIMO Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, E.D.; Hegarty, C.J. Understanding GPS/GNSS: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Artech House: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Warnick, K.F.; Maaskant, R.; Ivashina, M.V.; Davidson, D.B.; Jeffs, B.D. Phased Arrays for Radio Astronomy, Remote Sensing, and Satellite Communications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rafaely, B. Fundamentals of Spherical Array Processing, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aster, R.; Borchers, B.; Thurber, C. Parameter Estimation and Inverse Problems, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, Y.; Puskely, J.; Roederer, A.; Yarovoy, A. Phase-Only Control of Peak Sidelobe Level and Pattern Nulls Using Iterative Phase Perturbations. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Chu, R.; Ding, Z.; Zou, Y.; Li, H. Robust low-sidelobe transmit beamforming under peak-to-average-power ratio constraint. Sensors 2023, 23, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.J. Wide-angle beam scanning phased array antennas: A review. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2023, 4, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolph, C.L. A current distribution for broadside arrays which optimizes the relationship between beam width and side-lobe level. Proc. IRE 1946, 34, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riblet, H.J. Discussion on ‘a current distribution for broadside arrays which optimizes the relationship between beam width and side-lobe level’. Proc. IRE 1947, 35, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, T.T. Design of line-source antennas for narrow beamwidth and low sidelobes. IRE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1955, 3, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, A.T. Taylor patterns for discrete arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1984, 32, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucco, A. Weighting and thinning wide-band arrays by simulated annealing. Ultrasonics 2002, 40, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, R.L. Antenna Design with a Mixed Integer Genetic Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebret, H.; Boyd, S. Antenna array pattern synthesis via convex optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisco, G.; D’Urso, M. Maximally sparse arrays via sequential convex optimizations. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B. Application of convex relaxation to array synthesis problems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, J.; Xu, K.D.; Xu, Z.; Han, F.; Liu, Q.H.; Guo, Y.J. Linearly polarized shaped power pattern synthesis with sidelobe and cross-polarization control by using semidefinite relaxation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Adaptive interference suppression of phase-only thinned arrays via convex optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4583–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, F.; Lu, J.; Li, K. Synthesis of unequally spaced arrays with uniform excitation via iterative second-order cone programming. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 6013–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, R.; Liu, X. Optimization of sparse cross array synthesis via perturbed convex optimization. Sensors 2020, 20, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Cui, G.; Liu, R.; Yu, X. Beampattern synthesis via first-order iterative convex approximation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2021, 20, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Adaptive beamforming with continuous/discrete phase shifters via convex relaxation. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 3, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L.; Maki, A.; Gallstrom, A. Optimization method for wide beam sonar transmit beamforming. Sensors 2022, 22, 7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, A. An efficient broadband adaptive beamformer without presteering delays. Sensors 2021, 21, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Xiao, M.; Xiao, Z. Efficient beampattern synthesis for sparse frequency diverse array via matrix pencil method. Sensors 2022, 22, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipple, A.; Ruzindana, M.W.; Burnett, M.C.; Kunzler, J.W.; Lyman, K.; Jeffs, B.D.; Warnick, K.F. Wideband array signal processing with real-time adaptive interference mitigation. Sensors 2023, 23, 6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CVX: Matlab Software for Disciplined Convex Programming, Version 2.2. Available online: http://cvxr.com/cvx (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Sturm, J.F. Using SeDuMi 1.02, a Matlab toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones. Optim. Methods Software. 1999, 11–12, 625–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.D.; Roos, C.; Terlaky, T. On implementing a primal-dual interior-point method for conic quadratic optimization. Math. Program. Ser. B. 2003, 95, 249–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, F.; Haeberly, J.P.A.; Overton, M.L. Primal-dual interior-point methods for semidefinite programming: Convergence rates, stability and numerical results. SIAM J. Optm. 1998, 8, 746–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.J. Primal-Dual Interior-Point Methods; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Ma, W.; So, A.M.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, S. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2010, 27, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.D.; Namin, F.A.; Werner, D.H. Exploiting rotational symmetry for the design of ultra-wideband planar phased array layouts. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, R.J. Phased Array Antenna Handbook; Artech House: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van Trees, H.L. Optimum Array Processing; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nai, S.E.; Ser, W.; Yu, Z.L.; Chen, H. Beampattern synthesis for linear and planar arrays with antenna selection by convex optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wu, Q.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Hong, W. Synthesis of a thinned prephased electronically steered phased array using excitation control of both the small amplitude dynamic range ratio and low-resolution phase. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; So, H.C.; Zhao, X. Shaped power pattern synthesis with minimization of dynamic range ratio. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; So, H.C. Linear arbitrary array pattern synthesis with shape constraints and excitation range control. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2021, 20, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, A. The robustness of pencil beam synthesis without considering sensor uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 8608–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, F.; Goldfarb, D. Second-order cone programming. Math. Program. Ser. B. 2003, 95, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isernia, T.; Iorio, P.D.; Soldovieri, F. An effective approach for the optimal focusing of array fields subject to arbitrary upper bounds. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2000, 48, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X. Fast and simple gradient projection algorithms for phase-only beamforming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10620–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; He, Z. Antenna Array Theory and Engineering Applications; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A. A simple tridiagonal loading method for robust adaptive beamforming. Signal Process. 2019, 157, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable/Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
| g | the maximum array gain in sidelobe region |
| steering vector of the scan angle | |
| weighting coefficients (optimization variables) | |
| steering vectors in sidelobe region | |
| lower bounds of the weighting coefficients | |
| upper bounds of the weighting coefficients |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A. Fast Low-Sidelobe Pattern Synthesis Using the Symmetry of Array Geometry. Sensors 2024, 24, 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134059
Zhang M, Liu Y, Zhou H, Zhang A. Fast Low-Sidelobe Pattern Synthesis Using the Symmetry of Array Geometry. Sensors. 2024; 24(13):4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134059
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ming, Yongxi Liu, Haidong Zhou, and Anxue Zhang. 2024. "Fast Low-Sidelobe Pattern Synthesis Using the Symmetry of Array Geometry" Sensors 24, no. 13: 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134059
APA StyleZhang, M., Liu, Y., Zhou, H., & Zhang, A. (2024). Fast Low-Sidelobe Pattern Synthesis Using the Symmetry of Array Geometry. Sensors, 24(13), 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134059






