Sensor-Fused Nighttime System for Enhanced Pedestrian Detection in ADAS and Autonomous Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
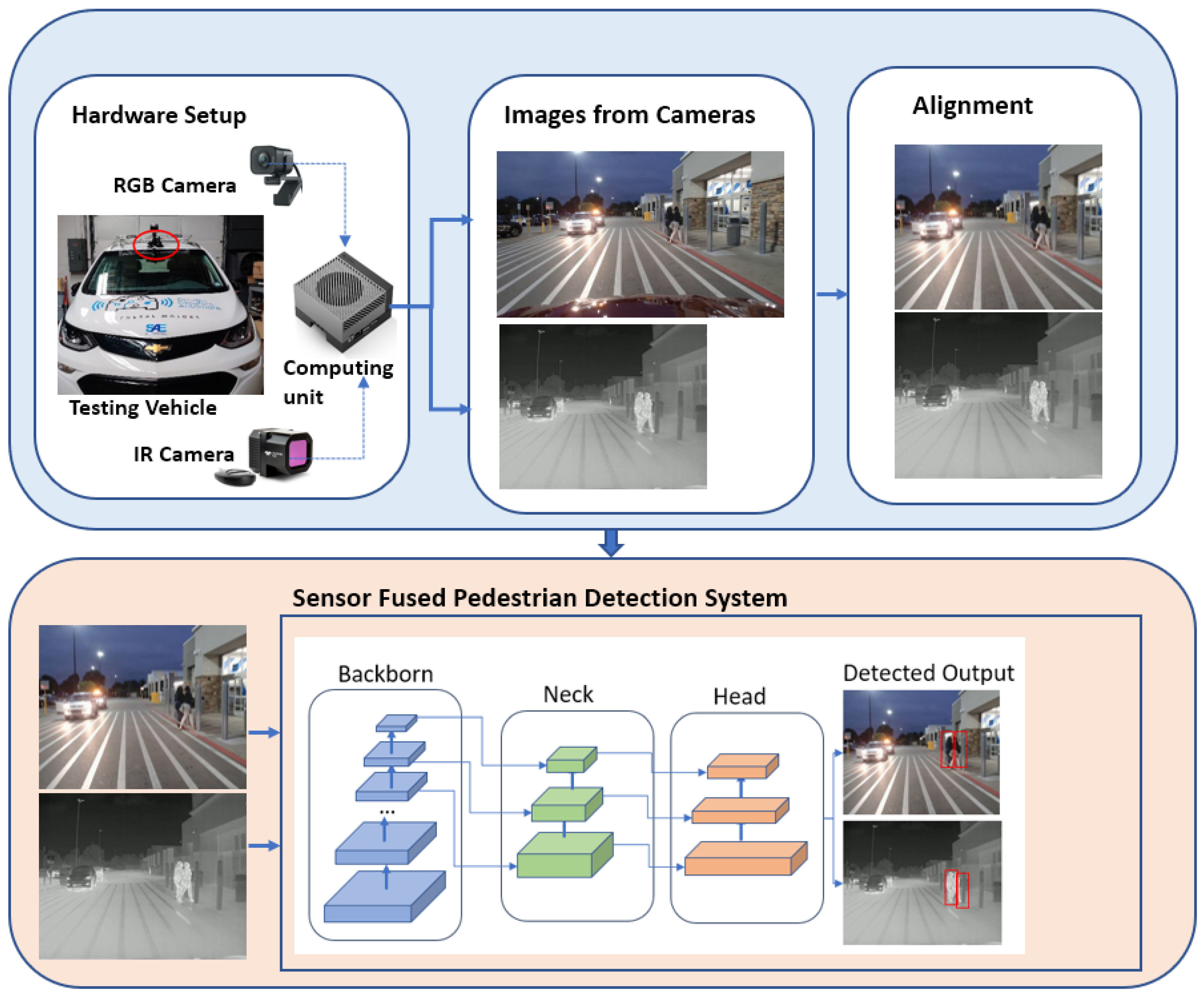
3. Development of a Sensor-Fused Nighttime Obstacle Detection System
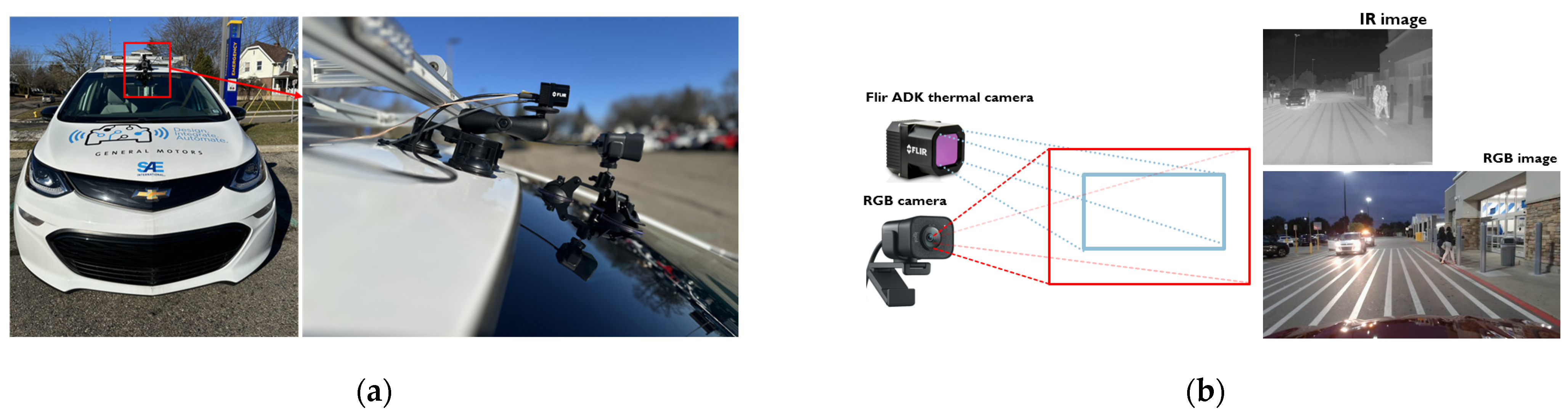
3.1. Hardware Setup for a Sensor-Fused Nighttime Obstacle Detection System
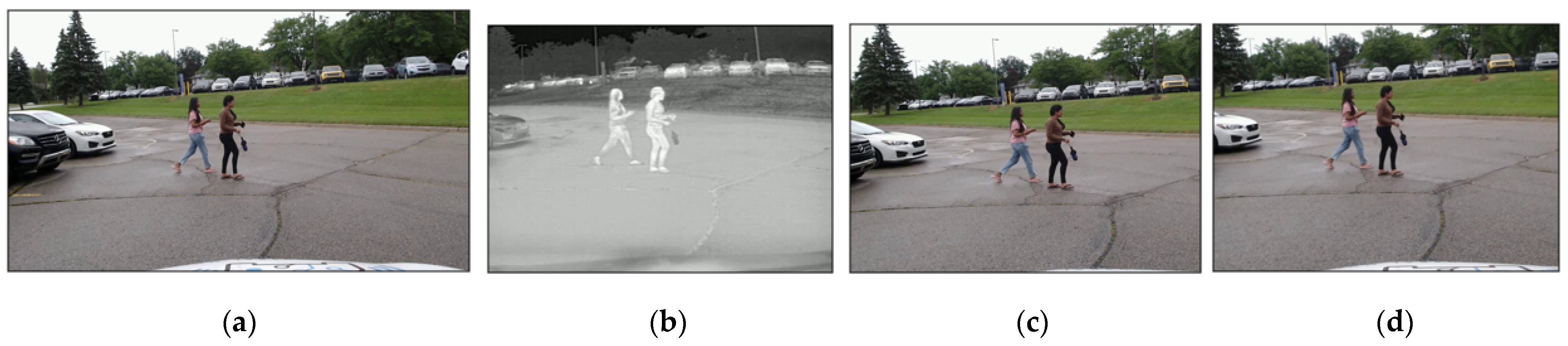
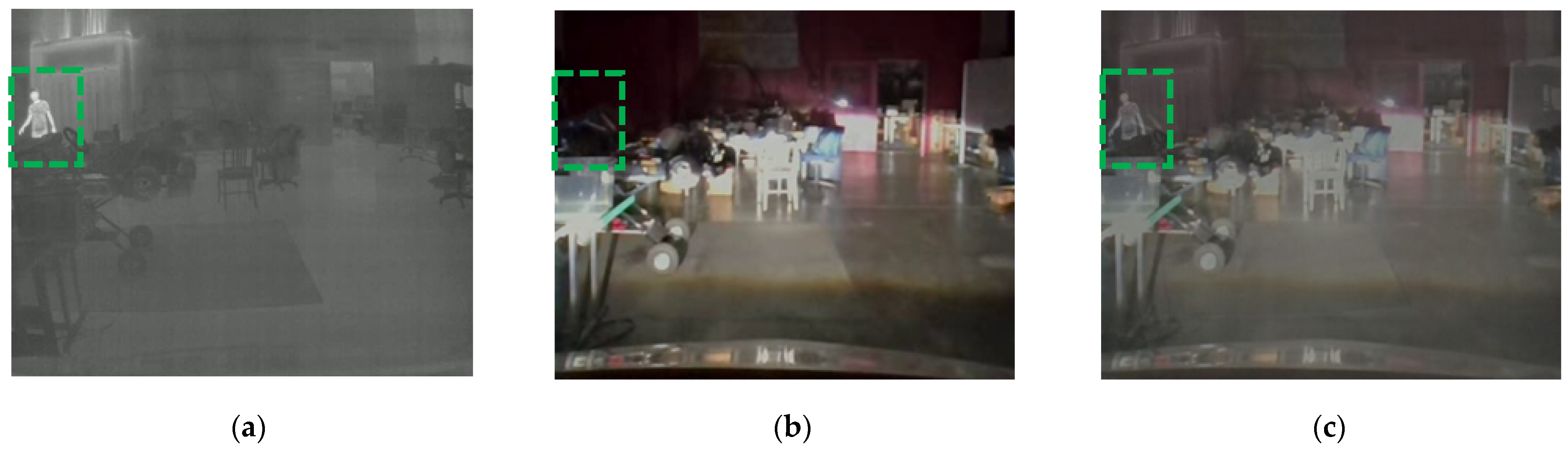
3.2. Alignment of Two Different Sensor Images
- Step (1)
- Capture paired images containing a single object (e.g., a pedestrian) using two cameras mounted on the test vehicle, as illustrated in Figure 3a. The authors utilized 20 paired images.
- Step (2)
- For each pair of RGB and IR images:
- (i)
- Detect the object using the existing DNN model [33]: The DNN-based object detection algorithm is separately applied to both RGB and IR images, resulting in bounding box coordinates (depicted in Figure 4a and Figure 4b, respectively). In Figure 4a, the RGB image detection is represented by coordinates (X1RGB, Y1RGB) for the top-left and (X2RGB, Y2RGB) for the bottom-right. Similarly, the IR image detection in Figure 4b uses coordinates (X1IR, Y1IR) and (X2IR, Y2IR).
- (ii)
- Calculate the resizing factor: To quantify size differences between images from different sensors, resizing factors in the x and y directions are computed using Equations (1) and (2):RFactor_X = (X2IR − X1IR)/(X2RGB − X1RGB).RFactor_Y = (Y2IR − Y1IR)/(Y2RGB − Y1RGB).Here, RFactor_X represents the ratio of the IR image bounding box width to the RGB image bounding box width, and RFactor_Y calculates the ratio of the IR image bounding box height to the RGB image bounding box height.
- (iii)
- Calculate the translation factor: Positional differences between RGB and IR images arise from field of view (FOV) variations. Translation adjusts the RGB image coordinate system to align with the IR image coordinate system. Translation parameters in the x and y directions are determined using Equations (3) and (4):TranFactor_X = (X1IR − X1RGB) × RFactor_X.TranFactor_Y = (Y1IR − Y1RGB) × RFactor_Y.
- (iv)
- Record these four parameters: resizing factors and translation factors in the x and y directions.
- Step (3)
- For each parameter, calculate the average value using the data generated in Step 2.
3.3. Publicly Available Dataset and New Data Collection
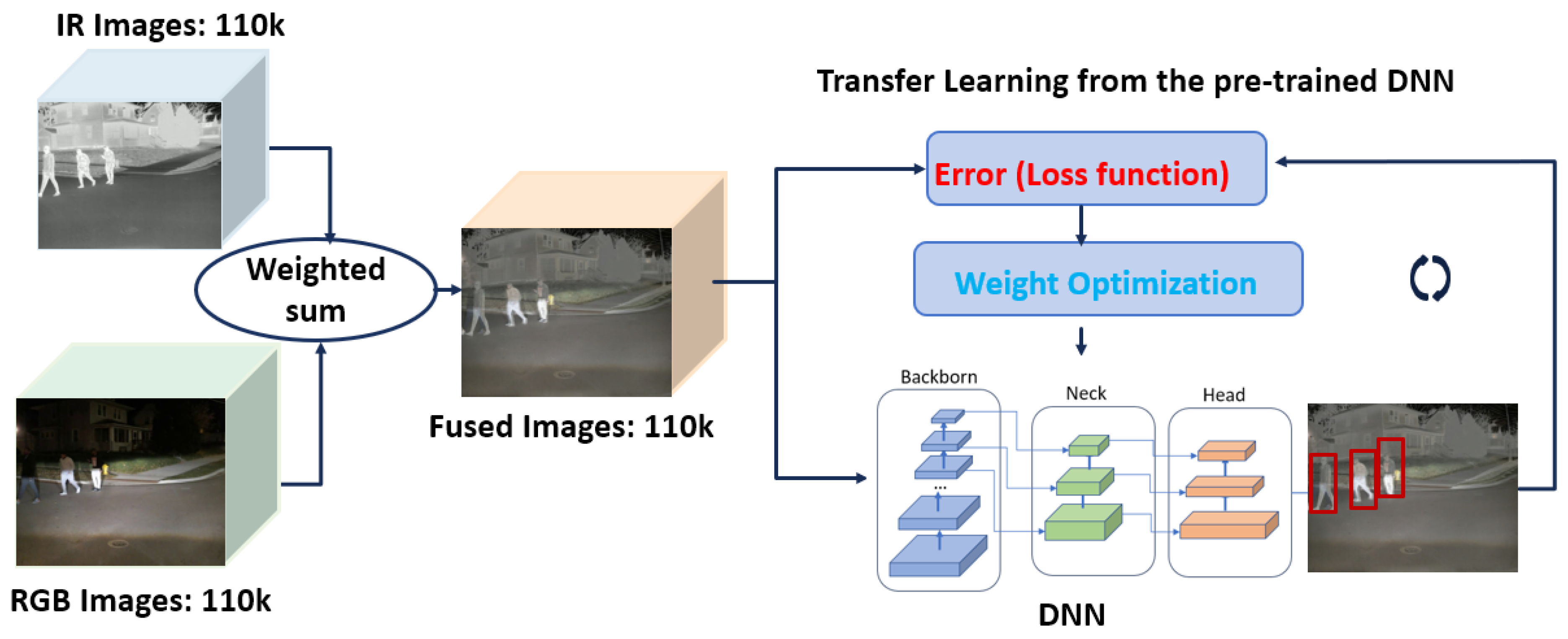
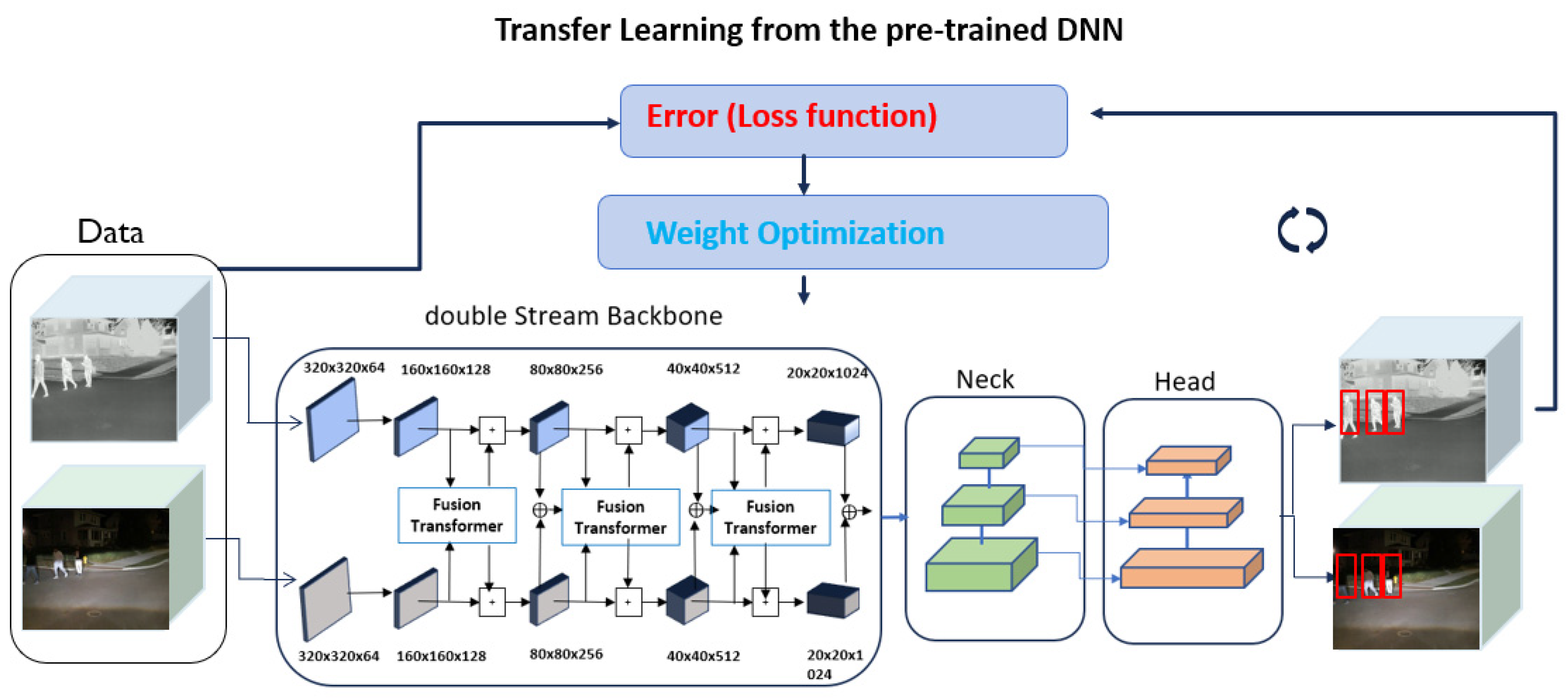
3.4. Development of the Sensor-Fusion DNN Models
- (i)
- Each RGB image is aligned using the proposed image alignment algorithm in Section 3.2. The aligned RGB has the same image width, imgW, and image height, imgH, as the corresponding IR thermal image.
- (ii)
- To generate the fused representation of the scene captured by two different sensors, the proposed weighted sum approach involves adding two weighted pixel values at each location (x, y) for each color channel.
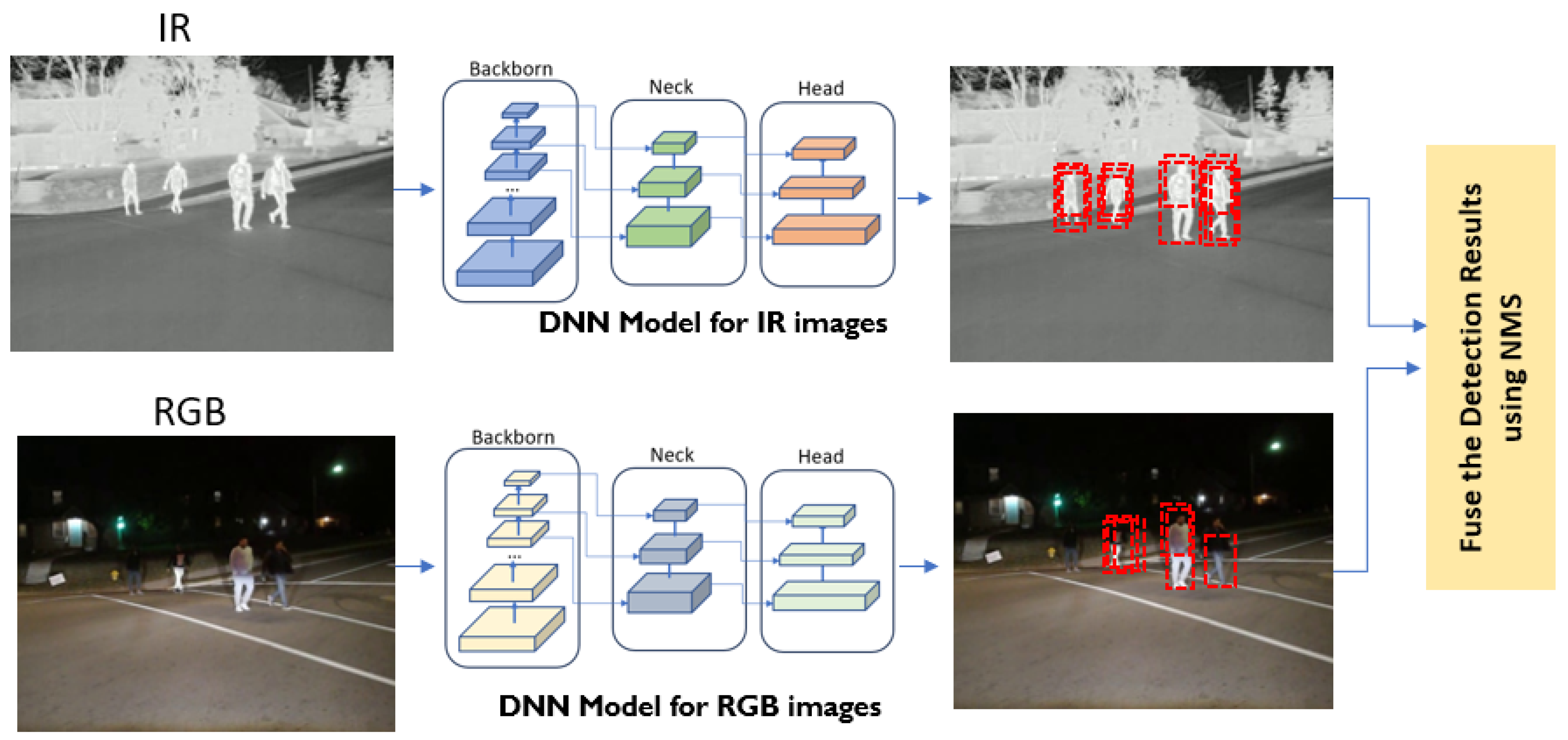
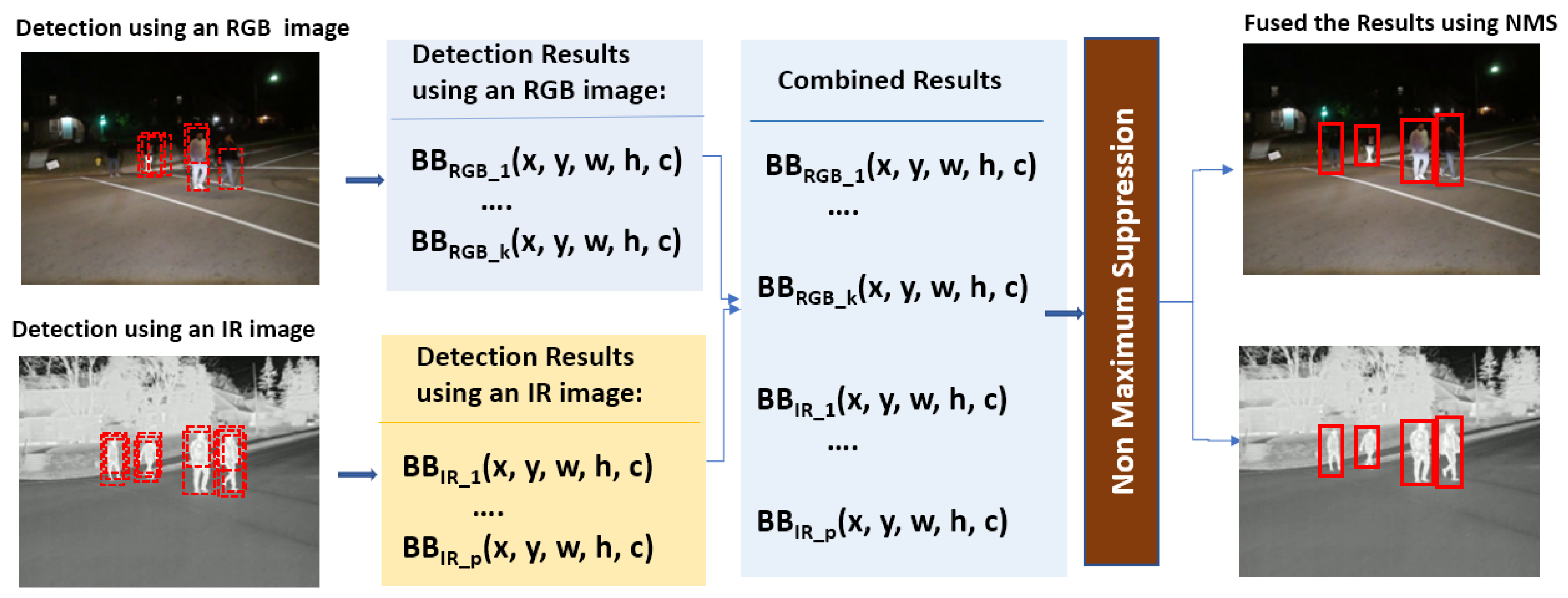
- Step 1
- Merge detection results in the form of a set of bounding boxes along with their associated confidence scores from two different object detection DNN models.
- Step 2
- Sort the bounding boxes based on their confidence scores in descending order. This ensures that the box with the highest confidence score is considered first.
- Step 3
- Start with the bounding box that has the highest confidence score, high_bb, in the sorted list. This box is considered a potential detection.
- Step 4
- Iterate over remaining boxes in the sorted list.
- i.
- Calculate the intersection over union (IoU) with the current bounding box, bb_i, and the highest confidence score bounding box, high_bb.IoU = | high_bb ∩ bb_i |/| high_bb ∪ bb_i |
- ii.
- If the IoU is above a certain threshold (0.5 is used), discard the bounding box, bb_i, as it significantly overlaps with the currently selected box, high_bb, and is likely to represent the same object; otherwise, keep the bounding box.
4. Experimental Results and Deployment for Real-Time Inferencing
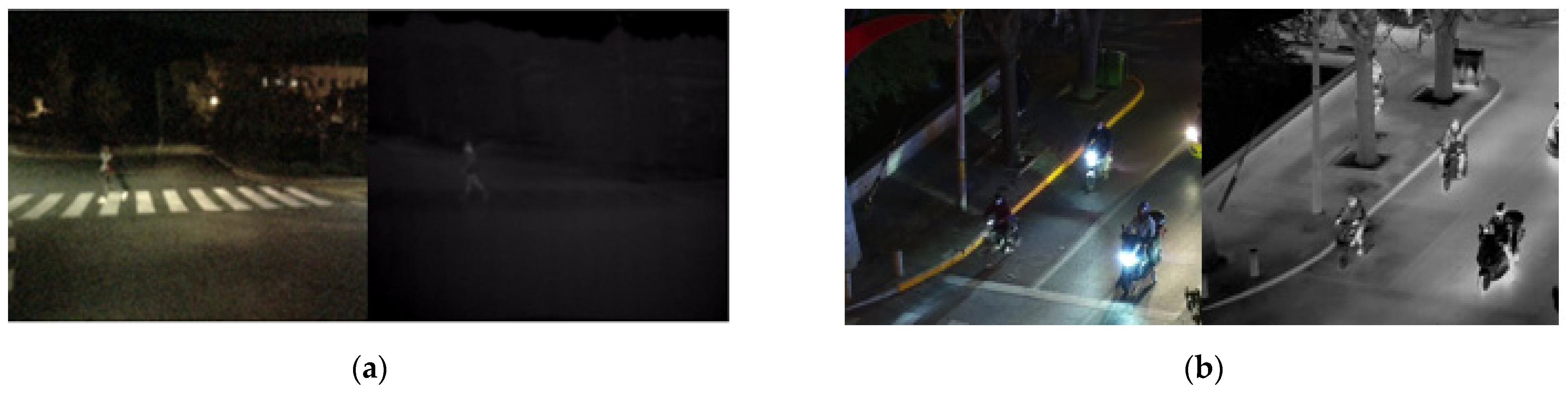
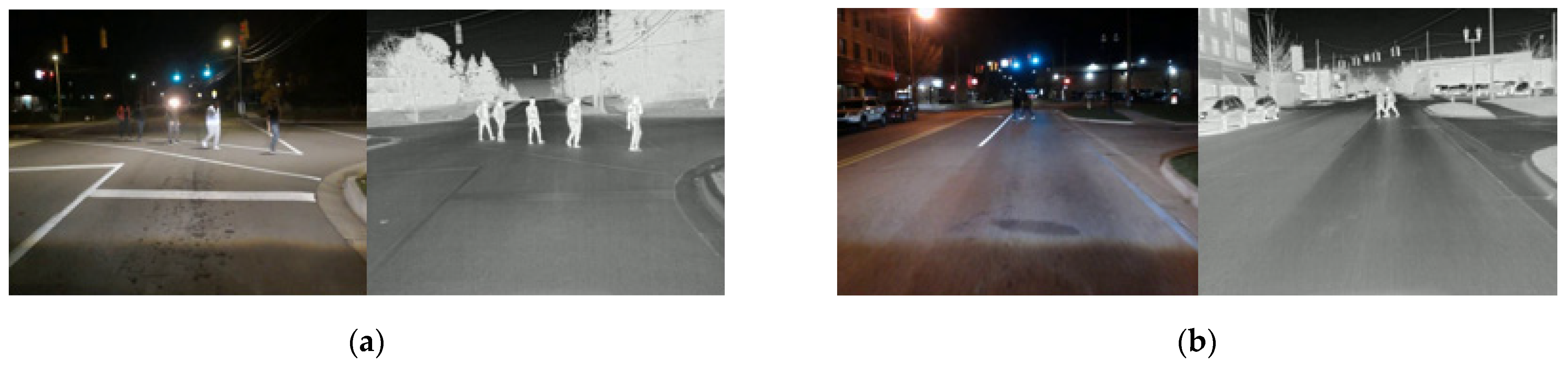
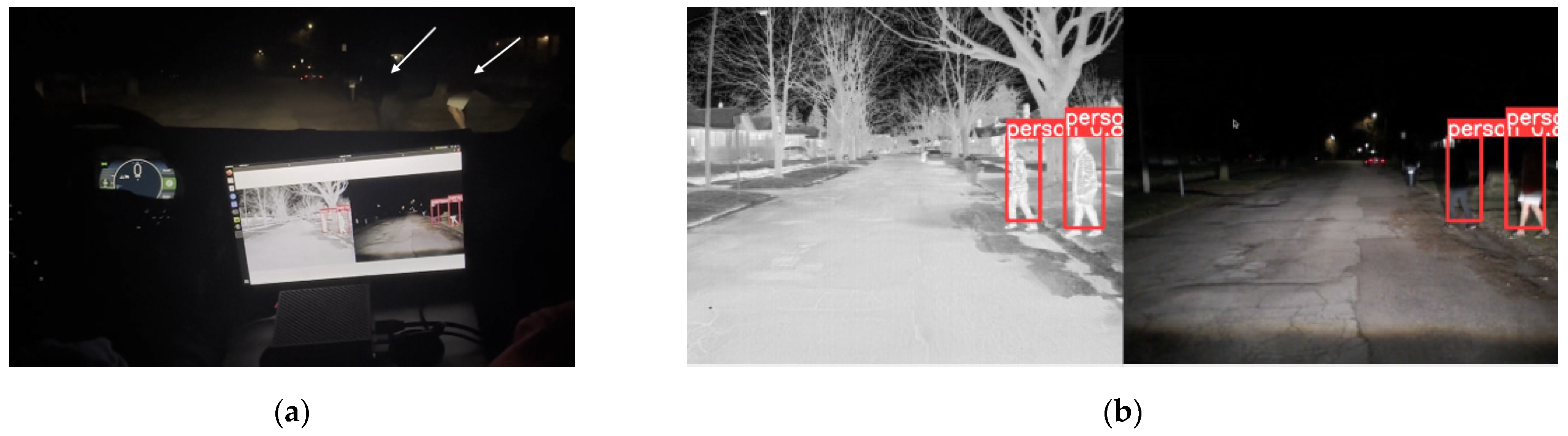
4.1. Experimental Results of the Pedestrian Detection System under Low Lighting Conditions
4.2. Deployment of the DNN Model for Real-Time Inferencing
- Detailed optimization procedures can be found in [41].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC). 2012–2017. Available online: https://www.image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/ (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi, S.; Ansari, M.; Aslam, A.; Kanwal, N.; Asghar, M. A Survey of Modern Deep Learning Based Object Detection Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ahmar, W.; Massoud, Y.; Kolhatkar, D.; AlGhamdi, H.; Alja’afreh, M.; Hammoud, R.; Laganiere, R. Enhanced Thermal-RGB Fusion for Robust Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18 June 2023; pp. 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, M.; Ren, X.; Wang, X. Visible Thermal Image Object Detection via the Combination of Illumination Conditions and Temperature Information. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin Developer Kit User Guide. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/learn/jetson-agx-orin-devkit-user-guide/index.html (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Ippalapally, R.; Mudumba, S.; Adkay, M.; Vardhan, N. Object Detection Using Thermal Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th India Council International Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 10–13 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tumas, P.; Nowosielski, A.; Serackis, A. Pedestrian Detection in Severe Weather Conditions. IEEE Access 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszyk, K.; Nowicki, M.R.; Skrzypczynski, P. Adopting the YOLOv4 Architecture for Low-Latency Multispectral Pedestrian Detection in Autonomous Driving. Sensors 2022, 22, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Metaxas, D.N. Multispectral Deep Neural Networks for Pedestrian Detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.02644. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, J.E.; Oughton, E.J. Assessing Thermal Imagery Integration into Object Detection Methods on Air-Based Collection Platforms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Illumination-Aware Faster R-CNN for Robust Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 83, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, J.; Bai, C.; Feng, H.; Dong, F.; Lo, T.L. Explicit Attention-Enhanced Fusion for RGB-Thermal Perception Tasks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.15710. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Ye, Z.; Mertz, C.; Ramanan, D.; Kong, S. Multimodal Object Detection via Probabilistic Ensembling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.02904. [Google Scholar]
- John, V.; Mita, S. Deep Feature-Level Sensor Fusion Using Skip Connections for Real-Time Object Detection in Autonomous Driving. Electronics 2021, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; He, D.; Wang, Z. Cross-Modality Fusion Transformer for Multispectral Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Liu, M. RTFNet: RGB-Thermal Fusion Network for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnakian, F.; Poikonen, J.; Laurinen, M.; Heikkonen, J. Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Fusion of RGB and IR Images in Marine Environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, E.; Mota, K.O.S.; Gomes, I.P.; Garrote, L.; Wolf, D.F.; Premebida, C. Late-Fusion Multimodal Human Detection Based on RGB and Thermal Images for Robotic Perception. In Proceedings of the 2023 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), Coimbra, Portugal, 4–7 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humblot-Renaux, G.; Li, V.; Pinto, D.; Marchegiani, L. Thermal Imaging on Smart Vehicles for Person and Road Detection: Can a Lazy Approach Work? In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rhodes, Greece, 20–23 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Ma, R.; Zakhor, A. Drone Object Detection Using RGB/IR Fusion. In Proceedings of the IS&T International Symposium on Electronic Imaging: Computational Imaging, Online, 17–26 January 2022; pp. 179-1–179-6. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, M.; Reyes, N.H.; Susnjak, T.; Barczak, A.L.C. RGB-D and Thermal Sensor Fusion: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 82410–82442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuijee, Y.; Park, D. Deep Learning Based Human Detection Using Thermal-RGB Data Fusion for Safe Automotive Guided-Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2024 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, Biarritz, France, 11–15 March 2024; pp. 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; Kweon, I. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection: Benchmark Dataset and Baselines. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W. LLVIP: A Visible-Infrared Paired Dataset for Low-Light Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- FLIR ADK. Available online: https://www.flir.com/products/adk/?vertical=automotive&segment=oem (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Logitech StreamCam. Available online: https://www.logitech.com/en-us/products/webcams/streamcam.960-001286.html (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Jocher, G. Comprehensive Guide to Ultralytics YOLOv5 (Version 7.0). Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- MATLAB. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/vision/ug/get-started-with-the-image-labeler.html (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Liu, H.; Fang, S.; Jiang, J. An Improved Weighted Fusion Algorithm of Multi-Sensor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1453, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yu, W.; Aryal, P.; Ciroski, V. Comparative Study on Transfer Learning for Object Detection and Classification Systems In AI-Enabled Technologies for Autonomous and Connected Vehicles; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Girshick, R.B.; McAllester, D.; Ramanan, D. Object Detection with Discriminatively Trained Part-Based Models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1627–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y. An Interpretable Deep Learning Method for Identifying Extreme Events under Faulty Data Interference. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TensorRT. Available online: https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/developer-guide/index.html (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- ONNX. Available online: https://onnx.ai/get-started.html (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Park, J.; Aryal, P.; Mandumula, S.; Asolkar, R. An Optimized DNN Model for Real-Time Inferencing on an Embedded Device. Sensors 2023, 23, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| RAM | 32 GB |
| GPU/CPU | 56 Tensor Cores |
| GPU max frequency | 930 MHz |
| CPU max frequency | 2.2 GHz |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Resizing factor in the x direction | 1.04 |
| Resizing factor in the y direction | 1.08 |
| Translation factor in the x direction | 16.50 |
| Translation factor in the y direction | 12.95 |
| KAIST | LLVIP | Kettering | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 80,000 | 10,000 | 20,000 | 110,000 |
| Validation | 5000 | 2200 | 6000 | 13,200 |
| Testing | 5000 | 2200 | 6000 | 13,200 |
| DNN Models | Precision/Recall | F1-Score | mAP50 | fps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB only | 55.8/52.8 | 54.26 | 54.3 | 66.67 |
| Thermal only | 65.7/57.6 | 61.4 | 62.3 | 67.11 |
| Early Fusion | 70.3/63.0 | 66.5 | 64.1 | 60.25 |
| Mid Fusion | 75.1/68.3 | 71.5 | 69.4 | 45.25 |
| Late Fusion | 75.5/63.6 | 69.0 | 65.9 | 55.65 |
| Model in [21] | 66.5/58.7 | 62.4 | 63.5 | 42.12 |
| DNN Models | Precision/Recall | F1-Score | mAP50 | fps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB only | 88.5/70.2 | 78.3 | 75.4 | 66.67 |
| Thermal only | 97.0/89.3 | 93.0 | 96.1 | 67.11 |
| Early Fusion | 97.3/90.8 | 93.9 | 96.9 | 60.25 |
| Mid Fusion | 97.7/91.8 | 94.7 | 97.5 | 45.25 |
| Late Fusion | 97.5/91.3 | 94.3 | 97.3 | 55.65 |
| Model in [21] | 97.3/91.2 | 94.2 | 97.2 | 42.12 |
| DNN Models | Precision/Recall | F1-Score | mAP50 | fps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB only | 87.3/63.4 | 73.45 | 72.8 | 66.67 |
| Thermal only | 93.2/88.7 | 90.9 | 91.2 | 67.11 |
| Early Fusion | 94.7/90.4 | 92.5 | 92.6 | 60.25 |
| Mid Fusion | 96.8/91.6 | 94.1 | 95.6 | 45.25 |
| Late Fusion | 97.1/90.8 | 93.8 | 95.5 | 55.65 |
| Model in [21] | 96.6/80.2 | 94.1 | 87.6 | 42.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Thota, B.K.; Somashekar, K. Sensor-Fused Nighttime System for Enhanced Pedestrian Detection in ADAS and Autonomous Vehicles. Sensors 2024, 24, 4755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144755
Park J, Thota BK, Somashekar K. Sensor-Fused Nighttime System for Enhanced Pedestrian Detection in ADAS and Autonomous Vehicles. Sensors. 2024; 24(14):4755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144755
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jungme, Bharath Kumar Thota, and Karthik Somashekar. 2024. "Sensor-Fused Nighttime System for Enhanced Pedestrian Detection in ADAS and Autonomous Vehicles" Sensors 24, no. 14: 4755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144755
APA StylePark, J., Thota, B. K., & Somashekar, K. (2024). Sensor-Fused Nighttime System for Enhanced Pedestrian Detection in ADAS and Autonomous Vehicles. Sensors, 24(14), 4755. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144755





