Investigating the Impact of Lunar Rover Structure and Lunar Surface Characteristics on Antenna Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
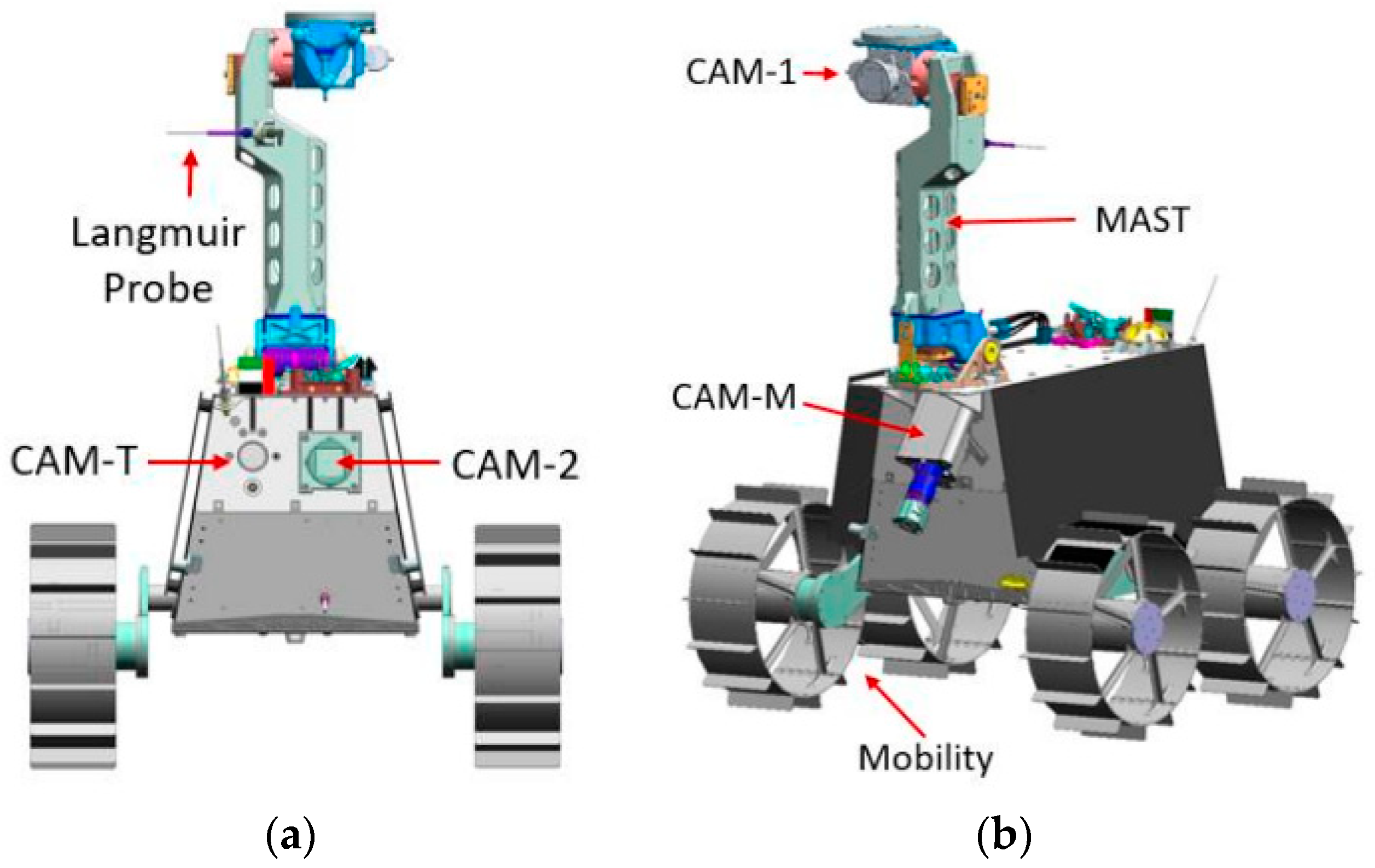
2. Rashid Rover
3. Lunar Regolith
4. Antenna Design
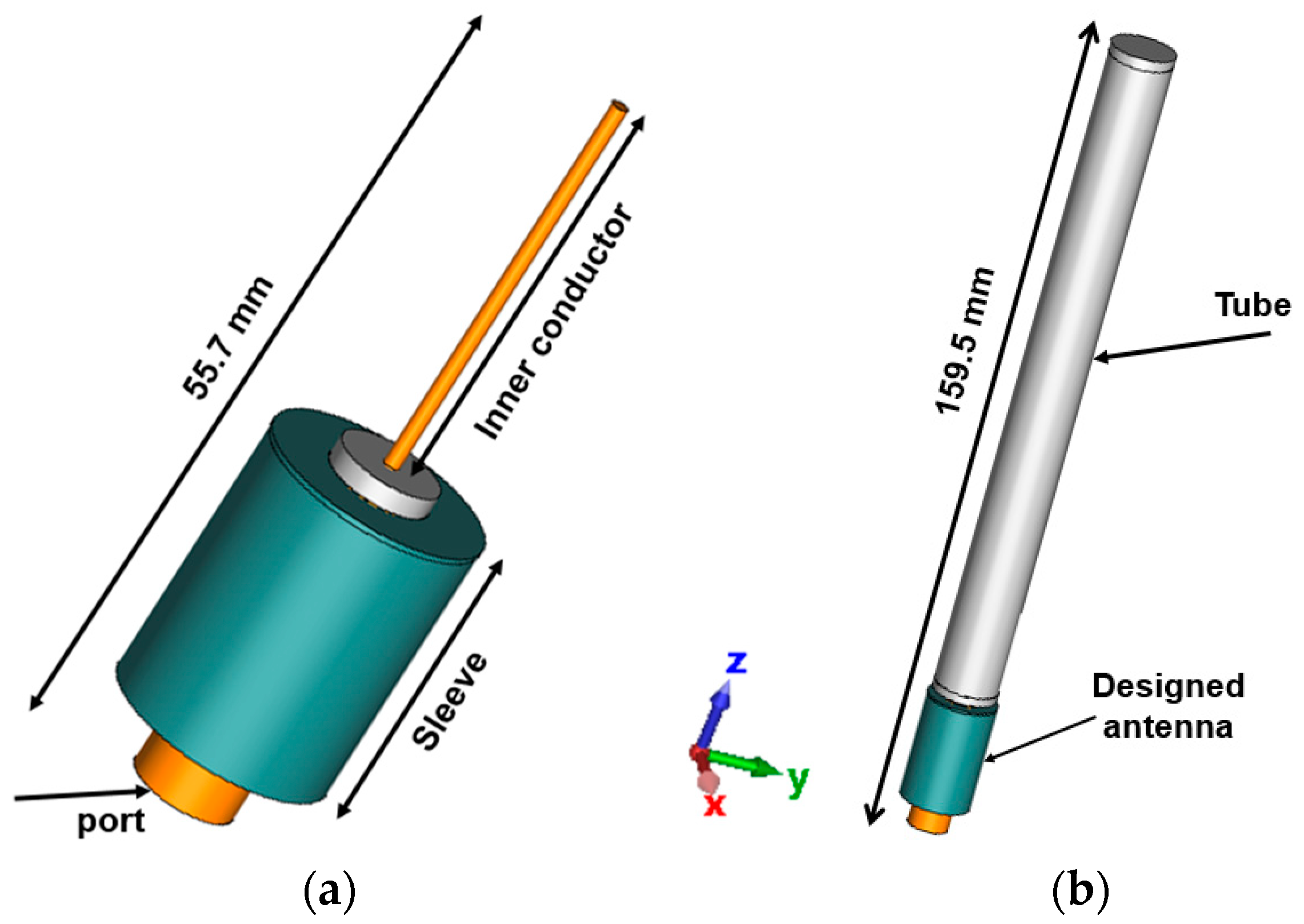
4.1. Sleeve Dipole Antenna Design
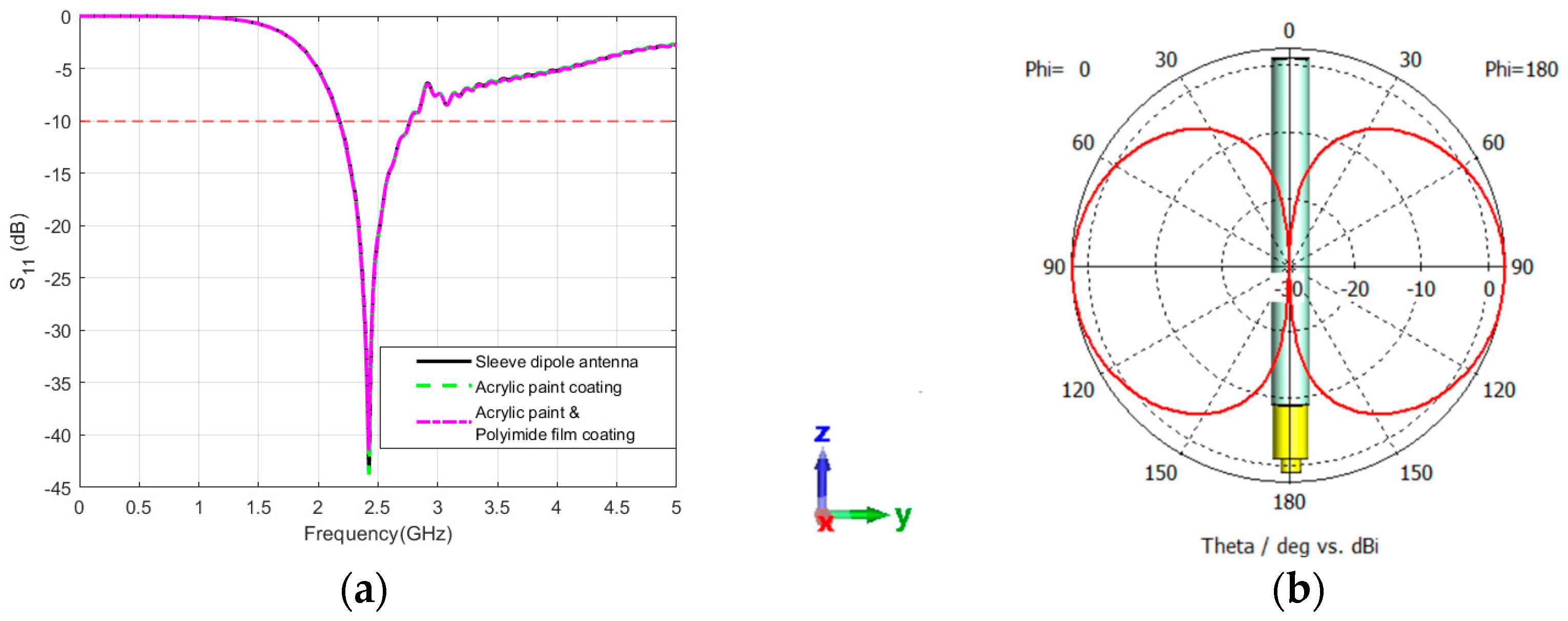
Sleeve Dipole Antenna with Coated Materials
4.2. All-Metal Patch Antenna Design
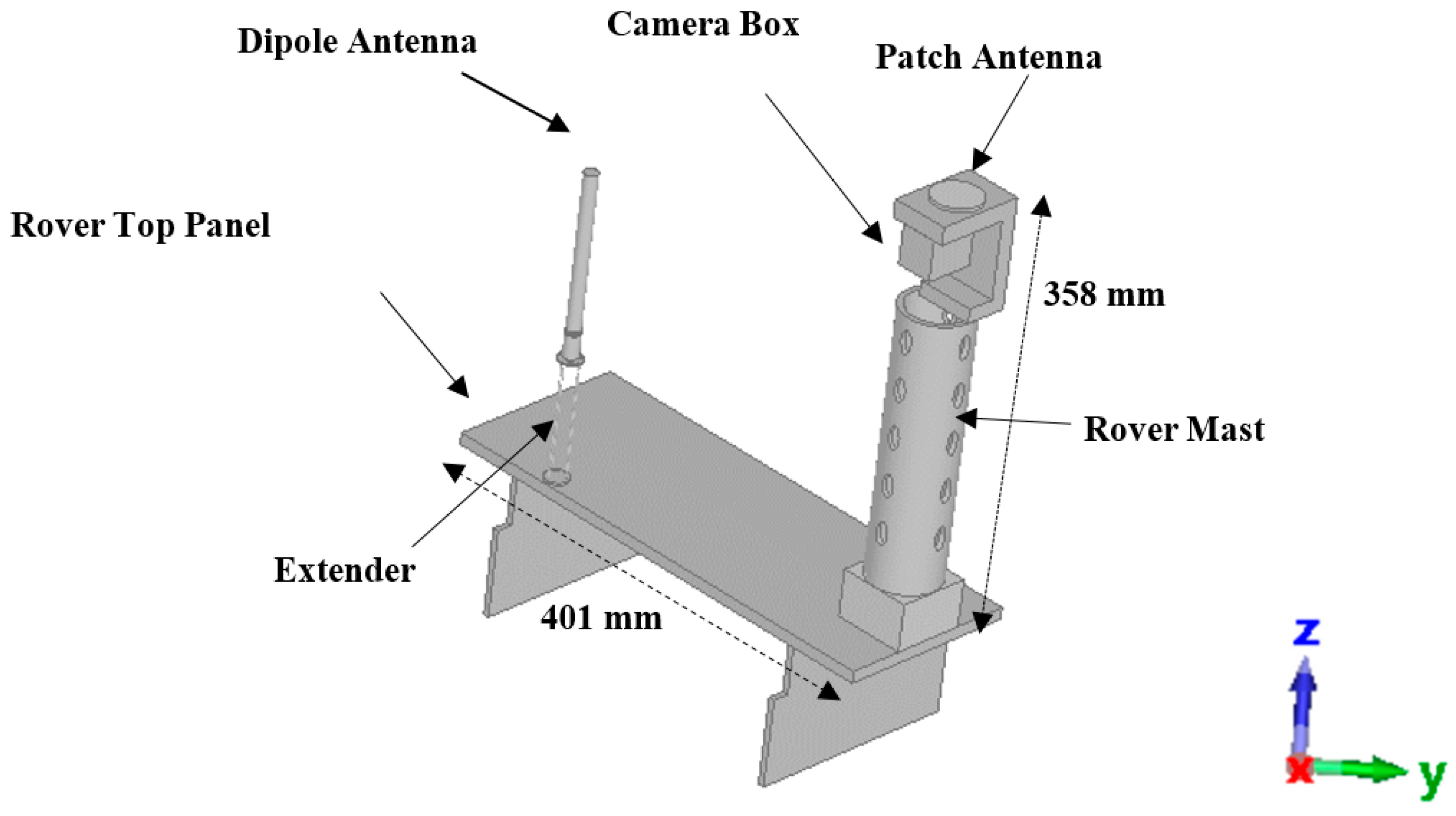
4.3. Antennas Integrated into Rover Structure
5. Results and Discussion
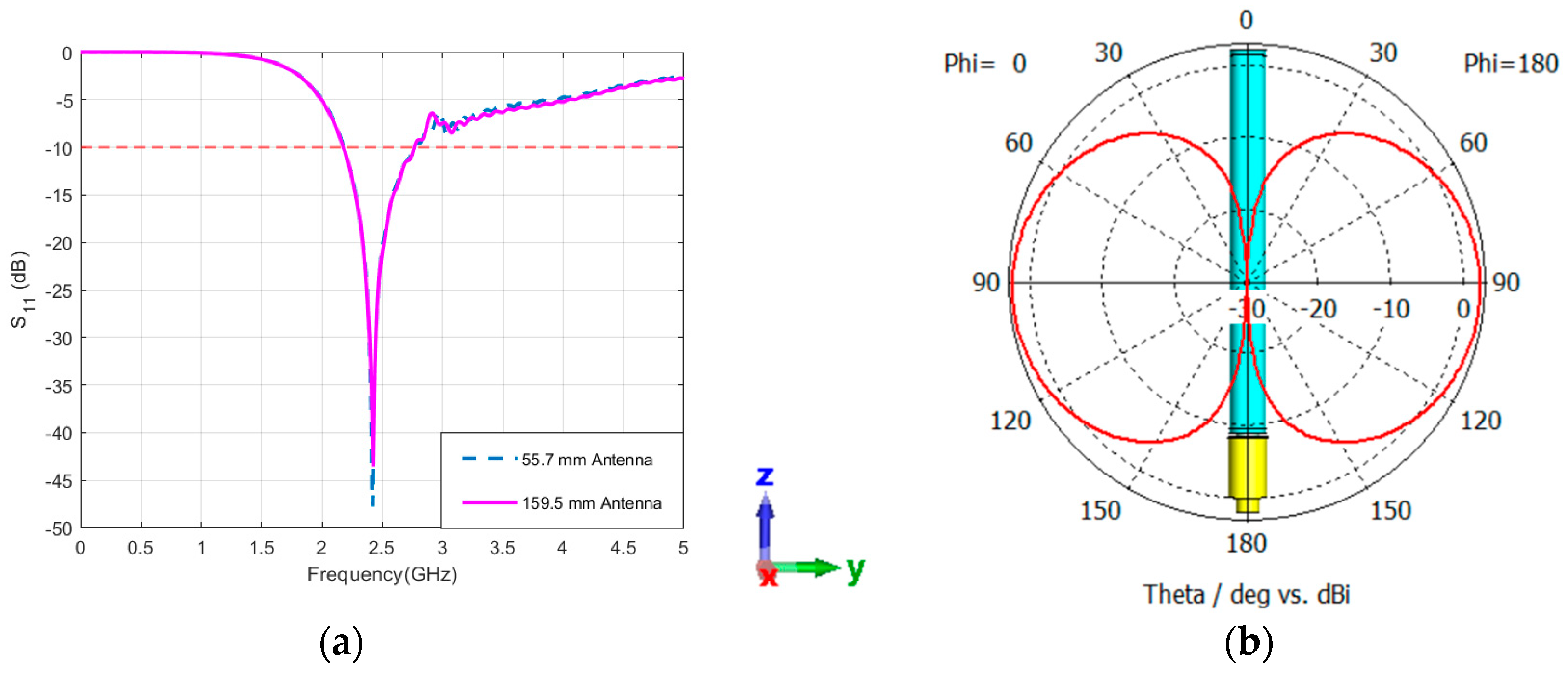
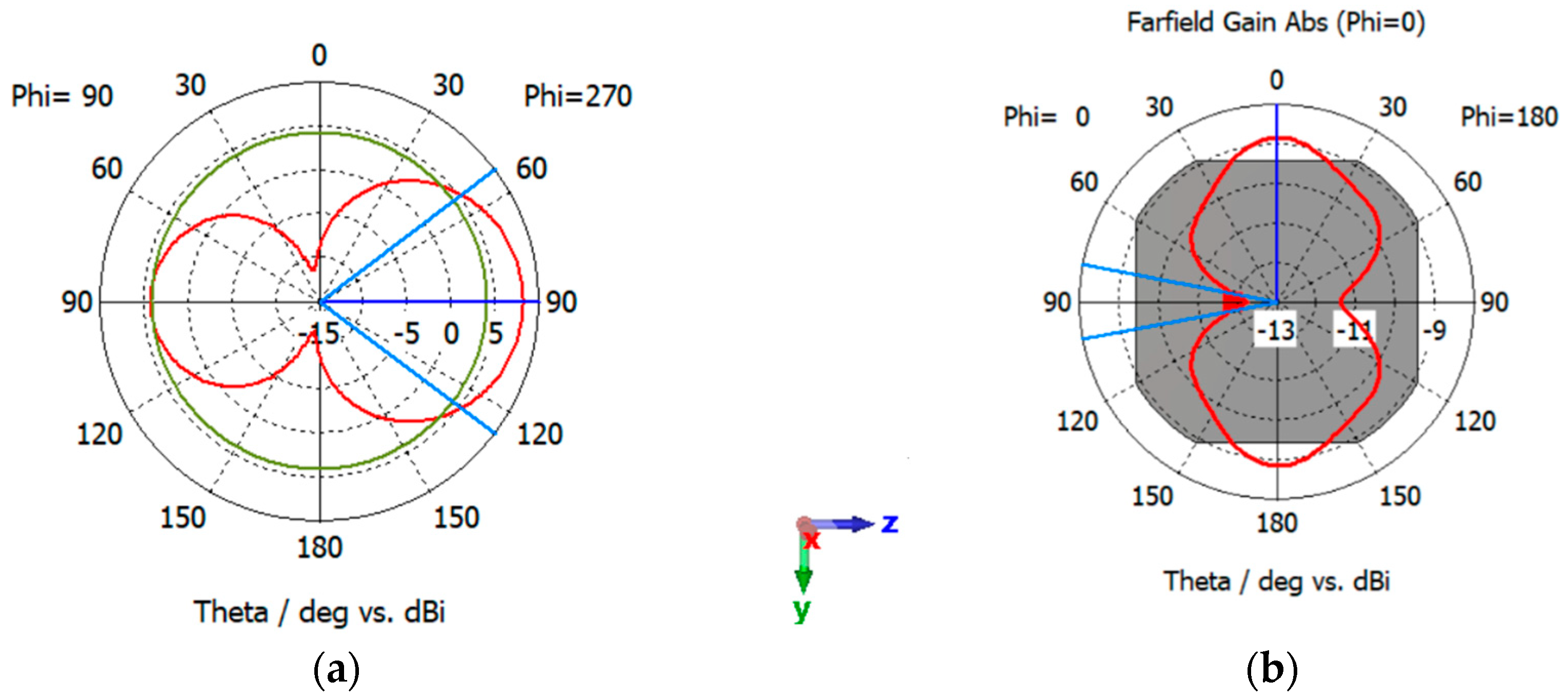
5.1. Performance of Standalone Antennas: Sleeve Antenna
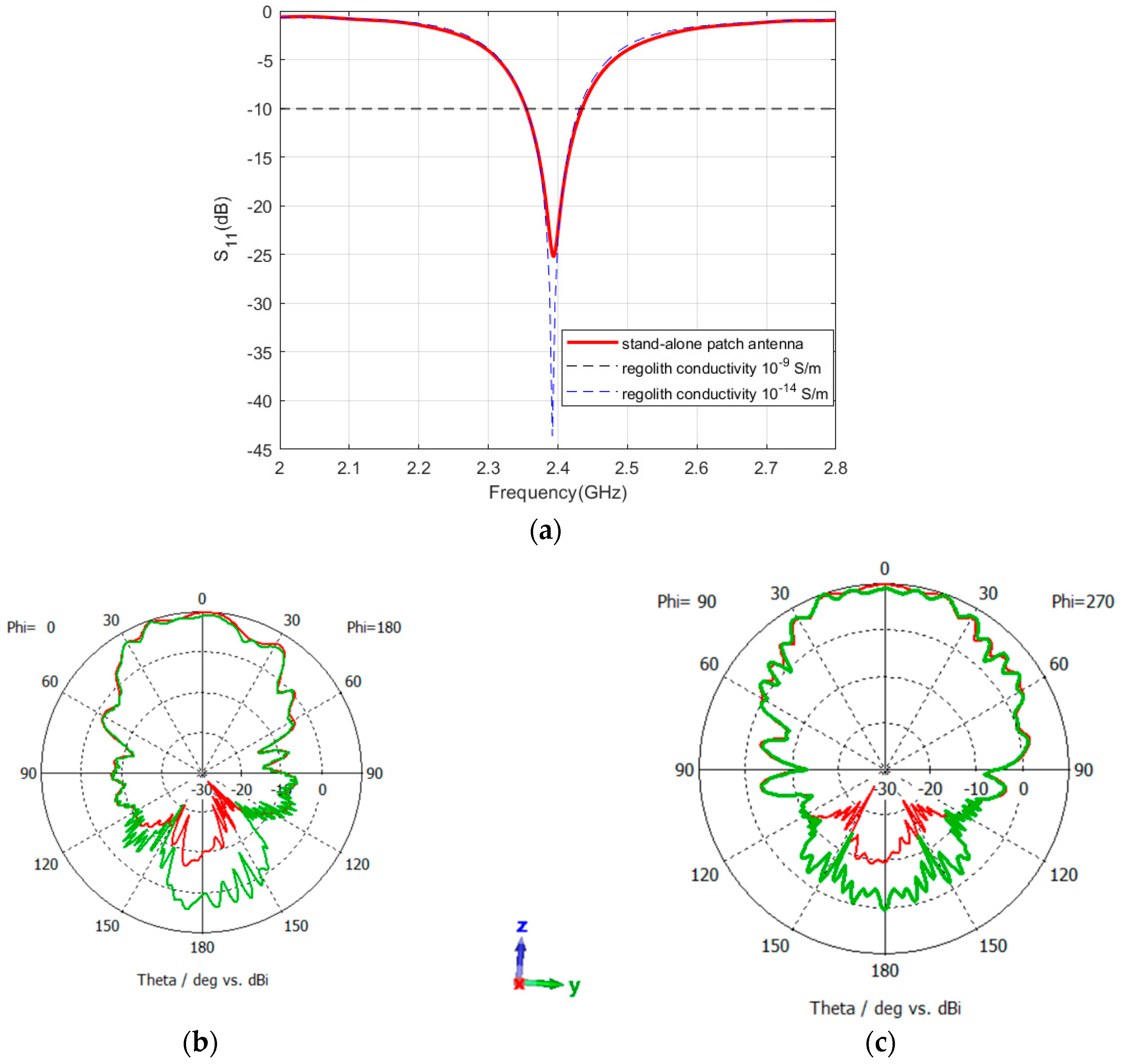
5.2. Performance of Standalone Antennas: Patch Antenna
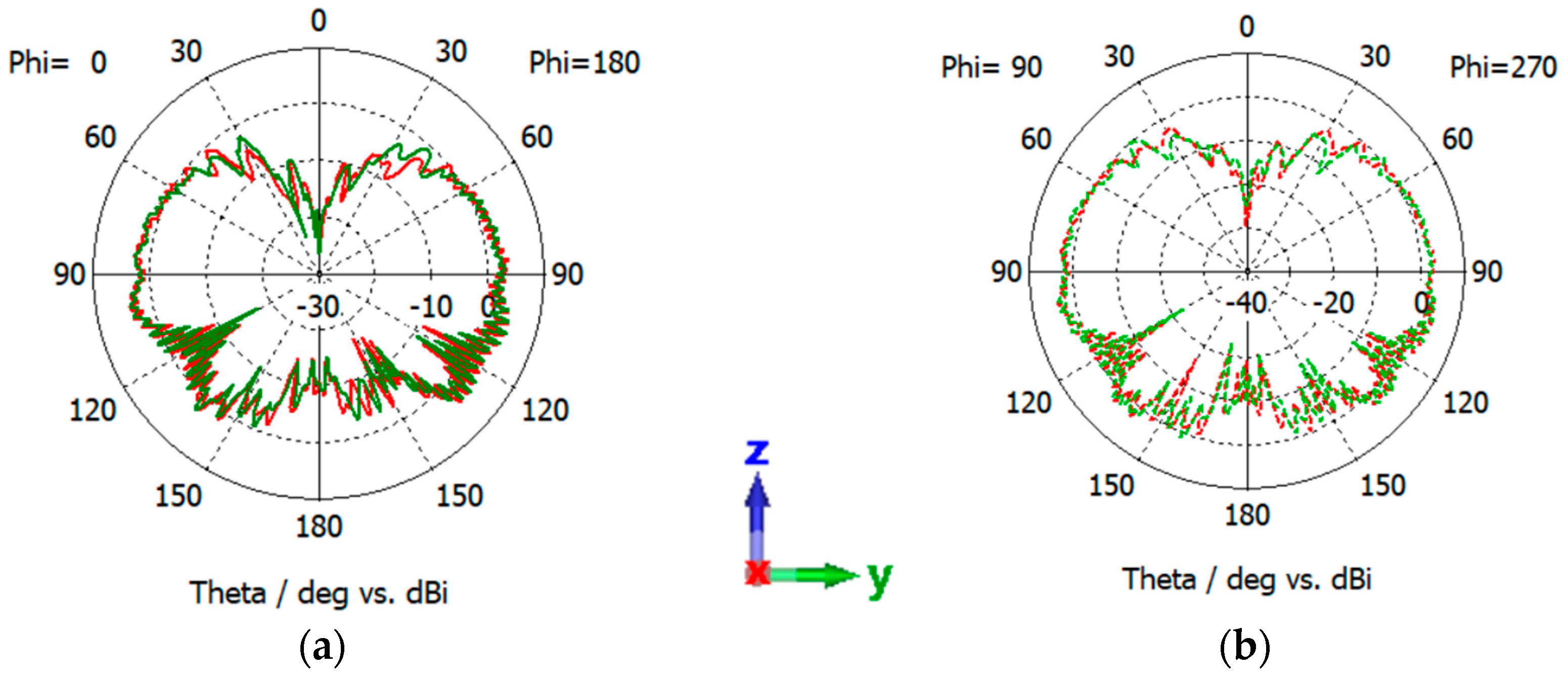
5.3. Antennas’ Performance on Atlas Regolith
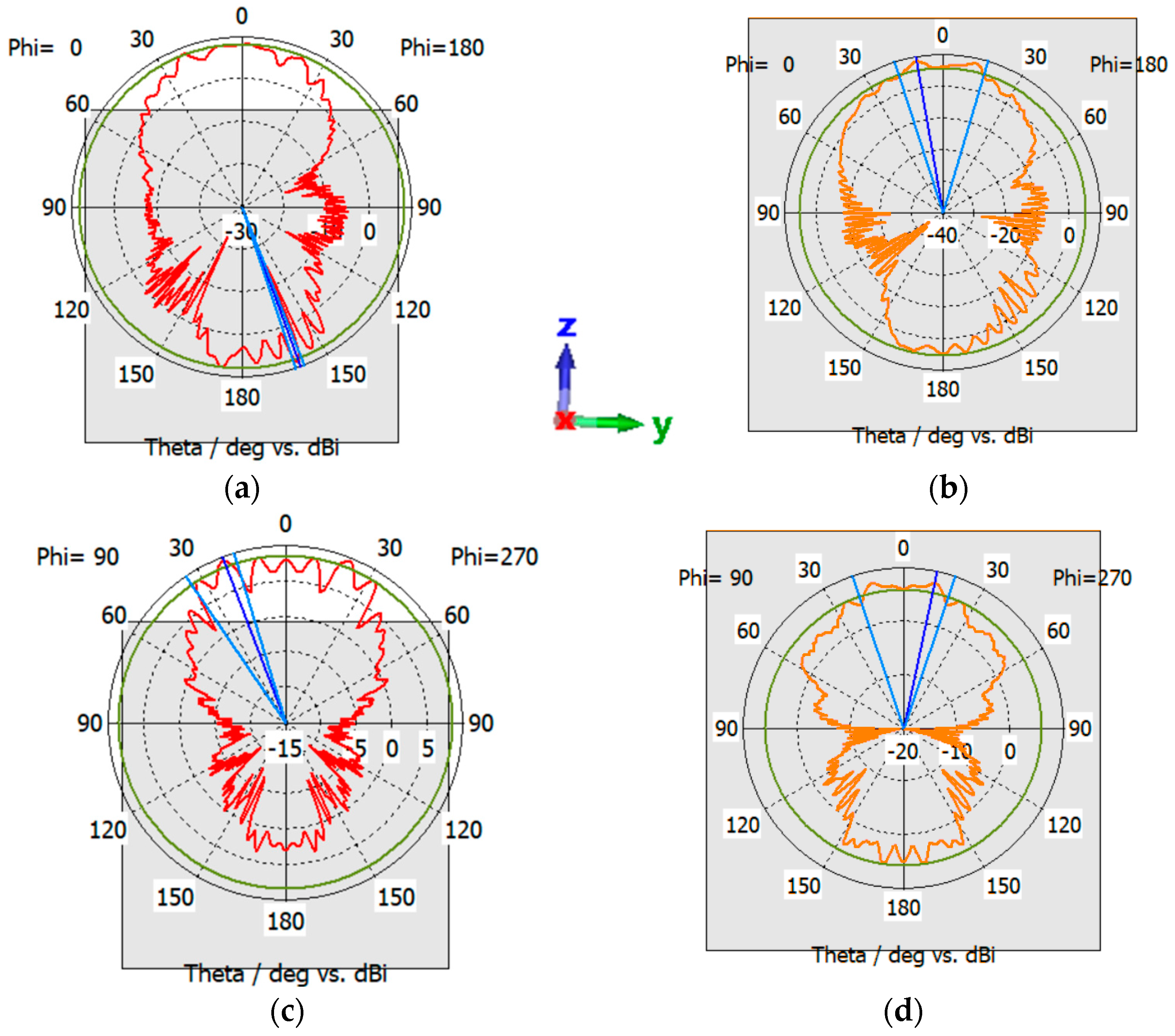
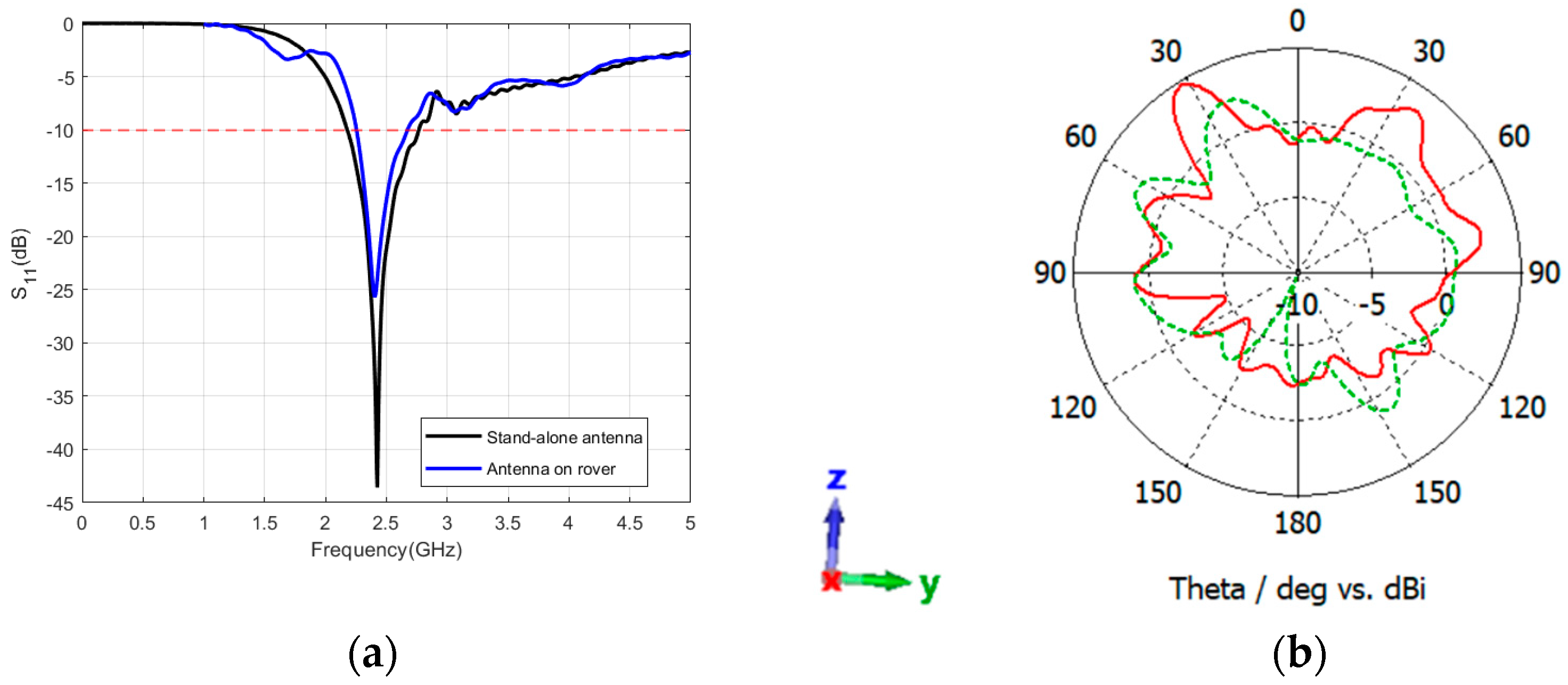
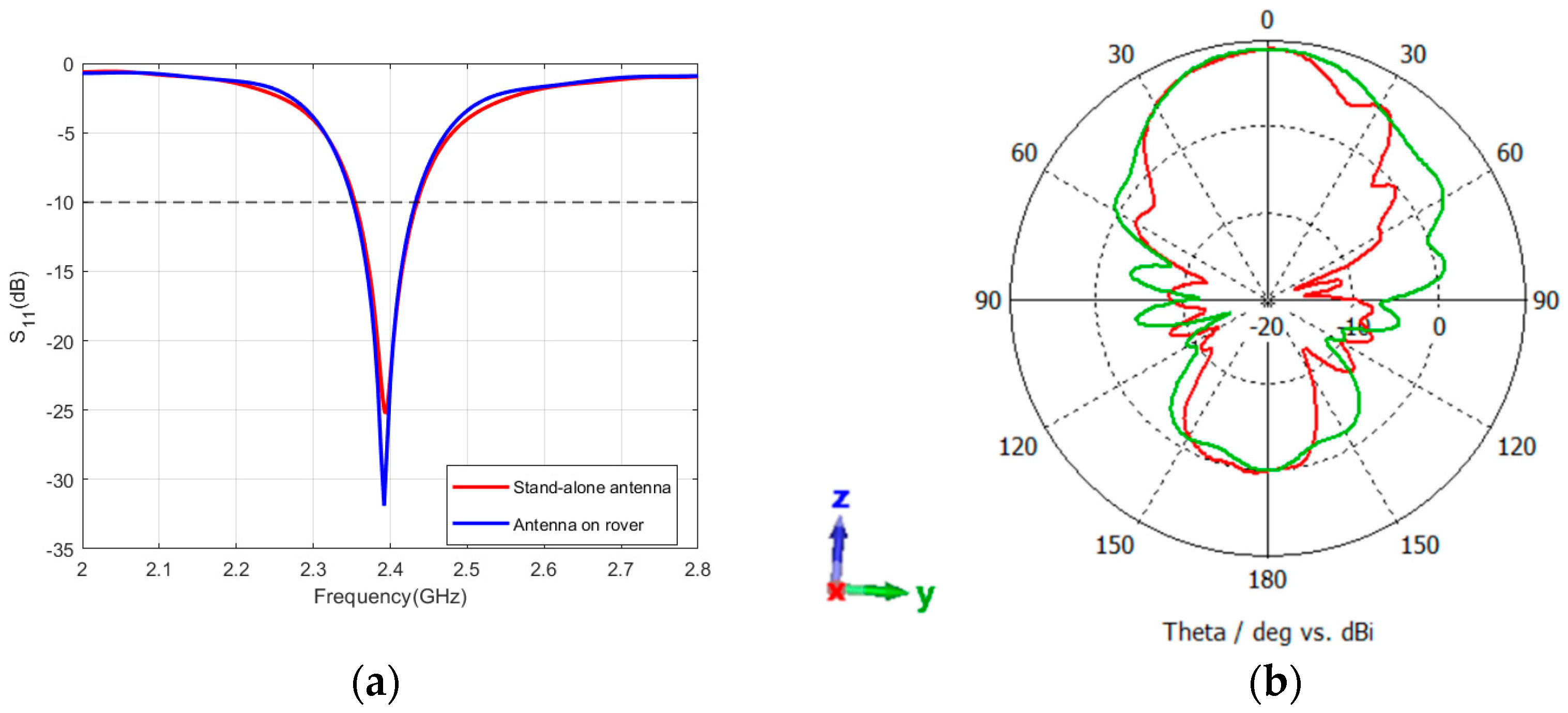
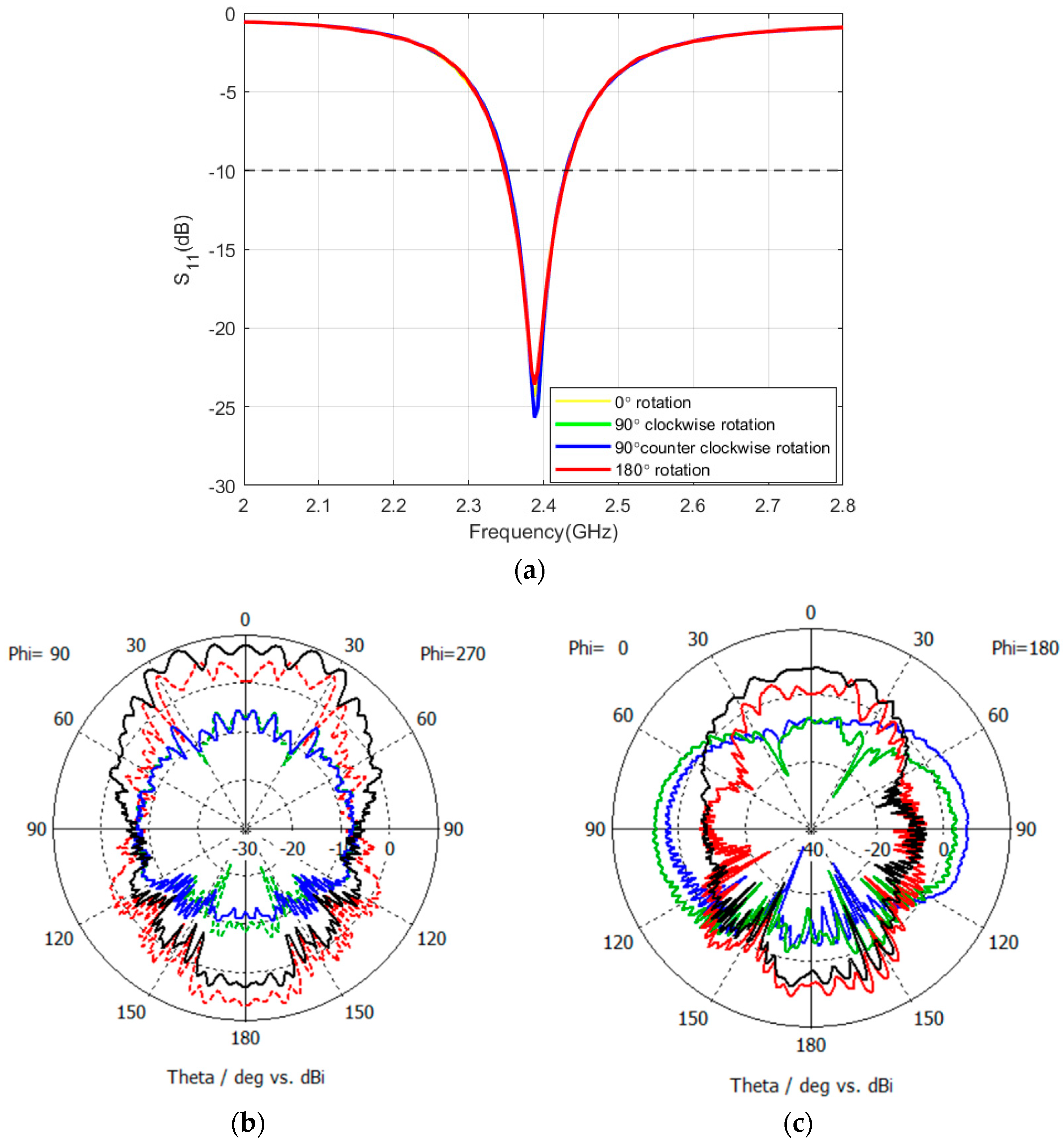
5.4. Antennas’ Performance on Rover Structure
Rotations of the Patch Antenna on Atlas Regolith
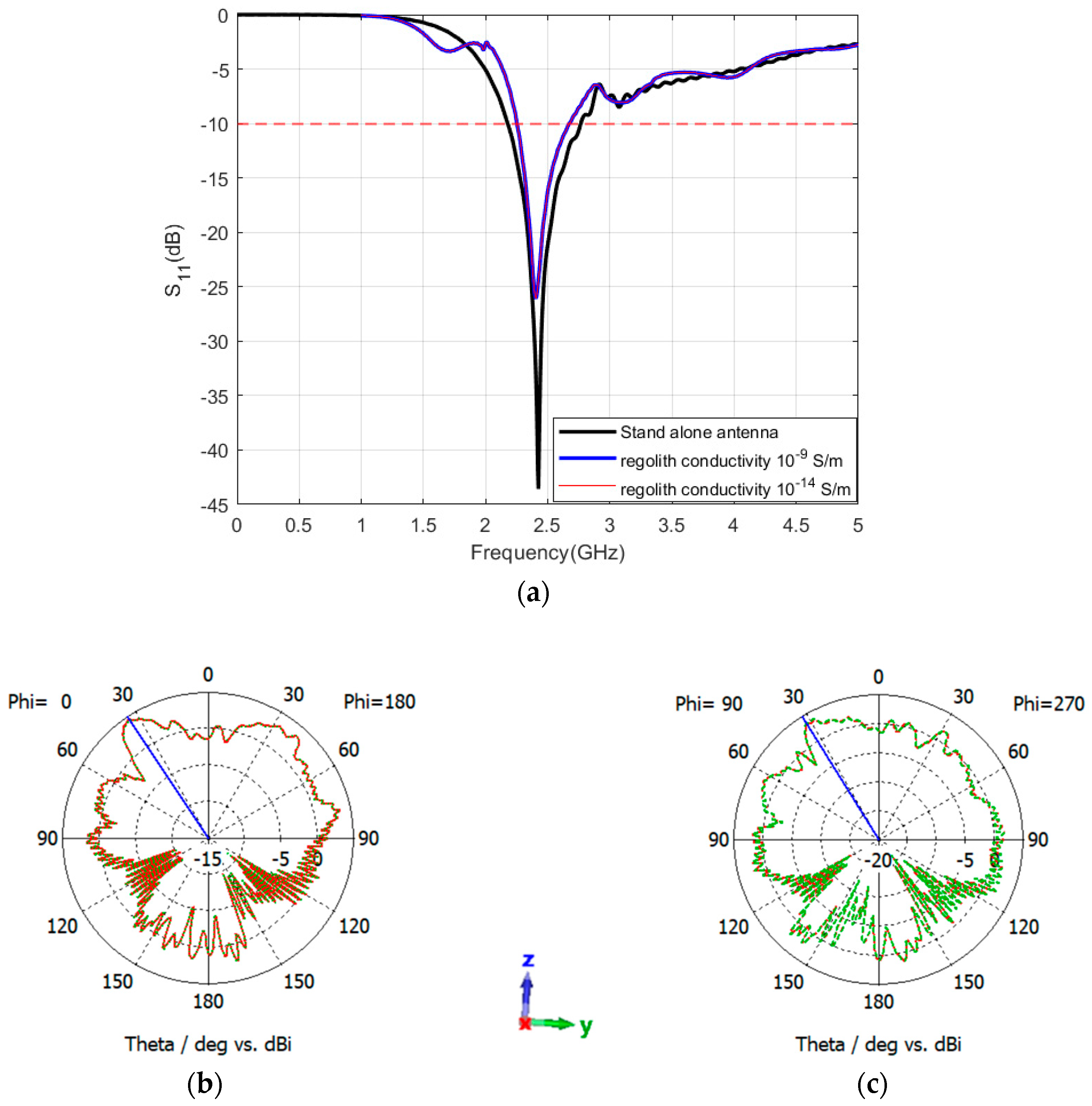
5.5. Antennas’ Performance on Rover Structure Placed on Top of Atlas Crater
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilhelms, D.E. To a Rocky Moon: A Geologist’s History of Lunar Exploration; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AR, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Pramono, S.; Sumantyo, J.T.S.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Takahashi, A.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Kashihara, H.; Santosa, C.E.; Gao, S.; Ito, K. Circularly Polarized Lunar Regolith Simulant Antenna for Future Communication and Remote Sensing in Lunar Environment. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 2988–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, S.J. NASA 50th Anniversary Proceedings: NASA’s First 50 Years: Historical Perspectives; US National Aeronautics & Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Volume 4704.
- Sarkissian, J. Dishing up the data: A decade of space missions. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1210.0980. [Google Scholar]
- Tamponnet, C. Life Support Systems for lunar missions. Adv. Space Res. 1996, 18, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R. The Apollo Program (1963–1972). Available online: https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/lunar/apollo.html (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Jolliff, B.L.; Robinson, M.S. The scientific legacy of the Apollo program. Phys. Today 2019, 72, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.; Mann, A. NASA’s Artemis Program: Everything You Need to Know. Available online: https://www.space.com/artemis-program.html (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Scardelletti, M.C.; Gasper, M.R.; Reinhart, R.C.; Zemba, M.J.; Rock, J.L.; Oleson, S.R.; Turnbull, E.R. Lunar surface network relay terminal: A lunar communications platform. In Proceedings of the 40th International Communications Satellite Systems Conference (ICSSC) and Its Colloquium, Bradford, UK, 24–26 October 2023; pp. 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, E. Missions to the Moon: Past, Present and Future. Available online: https://www.space.com/all-moon-missions (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Serria, E.; Gadhafi, R.; AlMaeeni, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Copiaco, A.; Abd-Alhameed, R.; Lemieux, F.; Mansoor, W. A Review of Lunar Communications and Antennas: Assessing Performance in the Context of Propagation and Radiation. Sensors 2023, 23, 9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaeeni, S.; Els, S.; Almarzooqi, H. To a dusty moon: Rashid’s mission to observe lunar surface processes close-up. In Proceedings of the 52nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Online, 15–19 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guardabasso, P.; Paternostro, S.; Bedialauneta, P.; Fonteyne, R. Lunar landing necessary building blocks and good practices for a sustainable development of human lunar activities. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 202, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Crater Atlas. European Space Agency. Available online: https://sci.esa.int/s/AGqPzrW (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Lawrence, P. A Guide to the Moon’s Atlas and Hercules Craters. Available online: www.skyatnightmagazine.com/astrophotography/moon/atlas-hercules-crater (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Nessel, J.; Barr, P.; Zaman, A.; Miranda, F. Miniature antennas for lunar and planetary surface communications. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 9–14 July 2006; pp. 631–634. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhou, B.; Fang, G. Ultra-Wideband MIMO Array for Penetrating Lunar Regolith Structures on the Chang’e-5 Lander. Electronics 2020, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhou, B.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, S.; Li, Y.; Guan, H.; Tang, C.; Gao, Y.; Lu, W.; et al. Lunar Penetrating Radar onboard the Change-3 mission. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1607–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.; Kim, K. Inflatable impulse radiating antenna for lunar penetrating radar. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (IWAGPR), Edinburgh, UK, 28–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, R.N.; Zemba, M.J.; Piasecki, M.T.; Pember, T.C.; Dever, S.M.; Miranda, A.F.A. All-Metal Antennas for Lunar Exploration. In Proceedings of the United States National Committee of URSI National Radio Science Meeting (USNC-URSI NRSM), Boulder, CO, USA, 10–14 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.L.; Lazio, J.; Giersch, L.; Hartman, J.; Stewart, K.; Polisensky, E. Low frequency antenna options for the lunar surface. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2013; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lazio, T.J.W.; MacDowall, R.; Burns, J.O.; Jones, D.; Weiler, K.; Demaio, L. The Radio Observatory on the Lunar Surface for Solar studies. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 48, 1942–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwu, S.U.; Upanavage, M.; Sham, C.C. Lunar Surface Propagation Modeling and Effects on Communications. In Proceedings of the 26th International Communications Satellite Systems Conference (ICSSC), San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gadhafi, R.; Serria, E.; AlMaeeni, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Copiaco, A.; Abd-Alhameed, R.; Lemieux, F.; Mansoor, W. A Study on the Performance of Sleeve Dipole Antenna for Rashid Rover. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21–24 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Serria, E.; Gadhafi, R.; AlMaeeni, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Copiaco, A.; AbdAlhameed, R.; Lemieux, F.; Mansoor, W. Lunar environment evaluation of sleeve antenna. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Antenna Measurements and Applications (CAMA), Genoa, Italy, 15–17 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Almaeeni, S.; Els, S.; Almarzooqi, H. The rashid rover: To guide the way for the next generation lunar missions and solar system exploration. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Online, 19–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Els, S.; Almaeeini, S.; Almarzooqi, H. The science instrumentation for the rashid rover of the emirates lunar mission. In Proceedings of the 52nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Online, 15–19 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Almehisni, R.; Gar, P.; Wali, M. Thermal Management System Design and Analysis of Rashid Rover—Emirates Lunar Mission. In Proceedings of the International Astronautical Congress, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 25–29 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, A.; Alhammadi, Z.Y.; Seneviratne, L. Advance simulation method for wheel-terrain interactions of space rovers: A case study on the UAE rashid rover. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12431. [Google Scholar]
- Joulaud, M.; Flahaut, J.; Allemand, P.; Füri, E.; Wöhler, C.; AlMaeeni, S.; Almarzooqi, H.; Els, S. Investigation of the Regolith Properties at The Four Emirates Lunar Mission Candidate Landing Sites. In Proceedings of the 11th European Lunar Symposium, SSERVI, Padua, Italy, 27–29 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Telewaveinc. Types of Antenna Coatings. 2017. Available online: https://www.telewave.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Types-of-Antenna-Coatings.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Kellomäki, T.; Virkki, J.; Merilampi, S.; Ukkonen, L. Towards Washable Wearable Antennas: A Comparison of Coating Materials for Screen-Printed Textile-Based UHF RFID Tags. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2012, 2012, 476570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAP. MAP Space Coatings. 2018. Available online: https://www.map-coatings.com (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Sheldahl. The RED Book. Available online: https://materialstandard.com/book/ (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- AlFiPa. Aluminum Foil for Industrial Applications. Available online: https://alfipa.com/applications/industrial-applications-aluminum-foil/ (accessed on 27 March 2014).
- HTS Coatings. Stainless Steel Material Information. Available online: https://htscoatings.com/pages/stainless-steel-coating (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- ATI. Technical Data Sheet. Zirconium Alloys. Available online: https://www.atimaterials.com/Products/Documents/datasheets/nickel-cobalt/nickel-based/ati_6230_tds.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, F.K.; Luk, K.M.; Lai, H.W. Microstrip Patch Antennas, 2nd ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-F.; Tong, K.-F. Microstrip Patch Antennas—Basic Characteristics and Some Recent Advances. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Meng, Z. Encyclopedia of Lunar Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stanislavsky, L.A.; Bubnov, I.N.; Konovalenko, A.A.; Tokarsky, P.L.; Yerin, S.N. The first detection of the solar U+III association with an antenna prototype for the future lunar observatory. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ref. | Antenna Name | Objective | Design Type | Key Lunar Constraints Considered in This Study | Simulation Tool | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | Microstrip monopole antenna | Research purpose | Stand-alone antenna | Miniature antenna size | Zeland’s IE3D electromagnetic simulator | Lunar surface communications |
| [16] | Fractal antenna | Research purpose | Stand-alone antenna | Miniature antenna size | Zeland’s IE3D electromagnetic simulator | Lunar surface communications |
| [17] | Vivaldi antenna | Real mission | Antennas on lander | Coating, lander | n/a | Lunar regolith penetrating radar |
| [18] | Channel 1 antenna | Real mission | Antenna on rover | Rover, coating | FEKO | Lunar penetrating radar |
| [18] | Channel 2 antenna | Real mission | Antenna on rover | Rover, coating | FEKO | Lunar penetrating radar |
| [19] | Inflatable impulse radiating antenna | Research purpose | Stand-alone antenna | Suitable thin-film materials | FEKO | Radar |
| [20] | Backfire antenna | Research purpose | Stand-alone antenna | All-metal antenna | Ansys HFSS | Communication and navigation |
| [22] | Dipole antenna | Real mission | Antenna arrays on radio observatory | Coating, terrestrial ground, extreme temperature, radio observatory system | CST | Near-side low radio frequency imaging |
| [23] | Dipole antenna | Research purpose | Stand-alone antenna | Regolith, crater terrain | Geometrical Theory of Diffraction | Lunar wireless communication and sensor systems |
| [42] | Small-sized active dipoles | Research purpose | Stand-alone antenna (active antenna) | Solar U + III bursts | n/a | Lunar radio telescopes |
| [This work] | Sleeve dipole and all-metal patch antennas | Real mission | Antennas on rover placed over regolith | Rover, coating, and regolith | CST | Lunar surface communication |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gadhafi, R.; Serria, E.; AlMaeeni, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Abd-Alhameed, R.; Mansoor, W. Investigating the Impact of Lunar Rover Structure and Lunar Surface Characteristics on Antenna Performance. Sensors 2024, 24, 5361. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165361
Gadhafi R, Serria E, AlMaeeni S, Mukhtar H, Abd-Alhameed R, Mansoor W. Investigating the Impact of Lunar Rover Structure and Lunar Surface Characteristics on Antenna Performance. Sensors. 2024; 24(16):5361. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165361
Chicago/Turabian StyleGadhafi, Rida, Elham Serria, Sara AlMaeeni, Husameldin Mukhtar, Raed Abd-Alhameed, and Wathiq Mansoor. 2024. "Investigating the Impact of Lunar Rover Structure and Lunar Surface Characteristics on Antenna Performance" Sensors 24, no. 16: 5361. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165361
APA StyleGadhafi, R., Serria, E., AlMaeeni, S., Mukhtar, H., Abd-Alhameed, R., & Mansoor, W. (2024). Investigating the Impact of Lunar Rover Structure and Lunar Surface Characteristics on Antenna Performance. Sensors, 24(16), 5361. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165361







