A Remote Two-Point Magnetic Localization Method Based on SQUID Magnetometers and Magnetic Gradient Tensor Invariants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
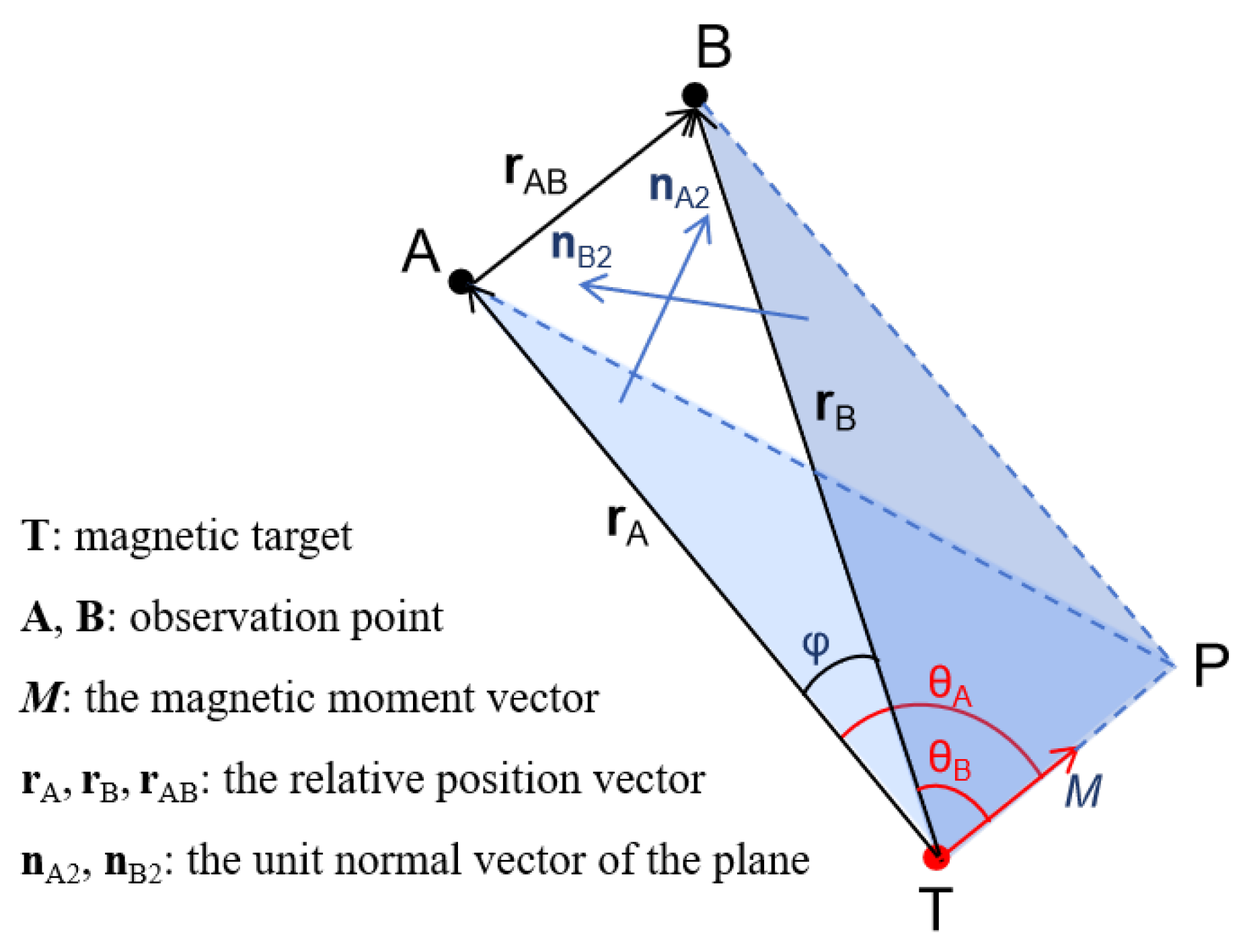
2.1. Magnetic Gradient Tensor and Tensor Invariants
2.2. Superconducting MGT Measurement System
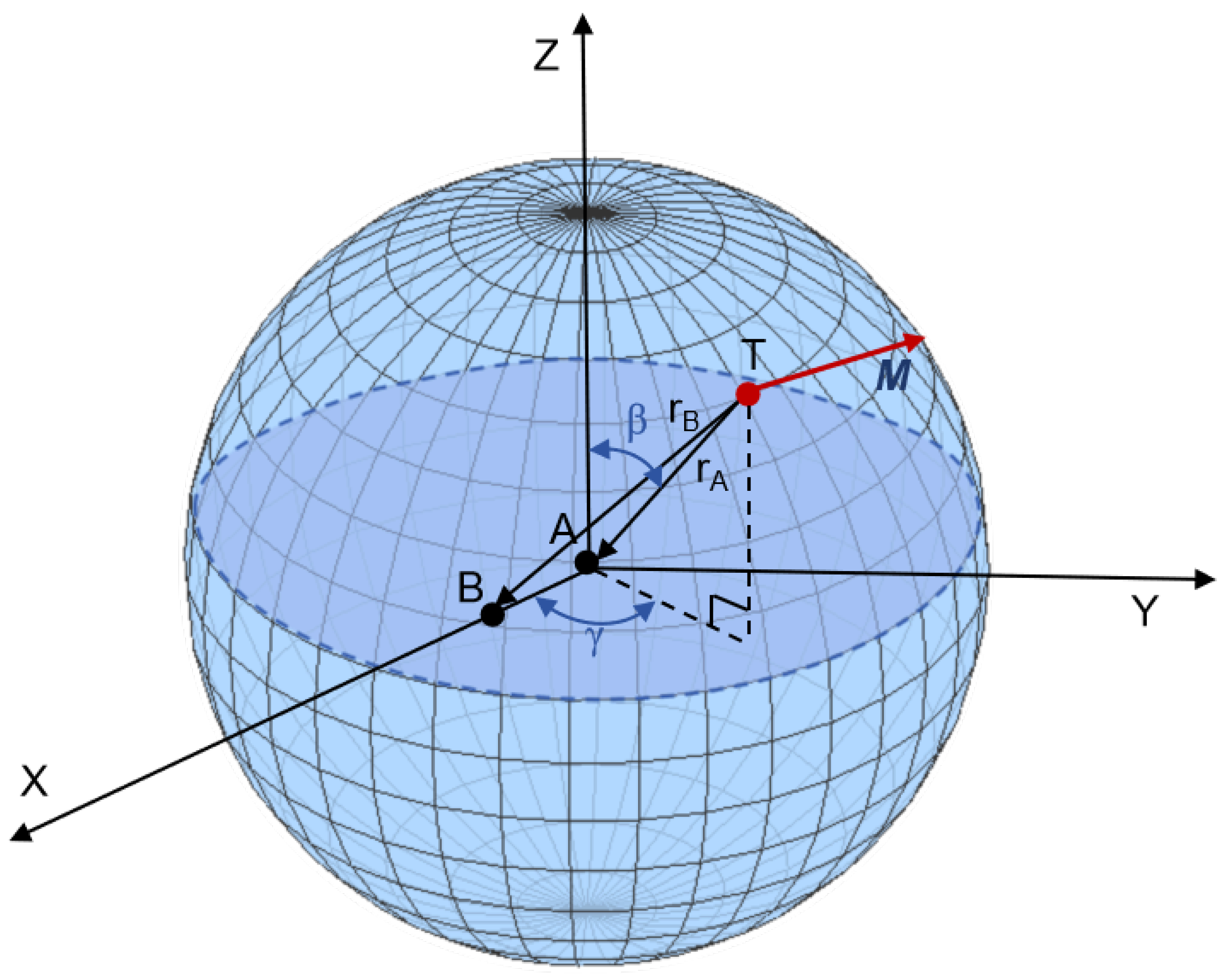
2.3. Inversion Algorithm Based on MGT Invariants
3. Simulations
3.1. Without the Influence of Noise
3.2. With the Influence of Noise
3.3. Positioning Blind-Area Analysis
3.4. With and without the Optimization Algorithm
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
4.1. Equivalent Experimental Setup
4.2. Analysis of Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, X.; Yan, S.; Li, B. A Novel Method of Localization for Moving Objects with an Alternating Magnetic Field. Sensors 2017, 17, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Gu, H.; Chang, M.; Fang, L.; Lin, P.; Lin, C. Magnetic Target Linear Location Method Using Two-Point Gradient Full Tensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 6007808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Ge, J.; Dong, H.; Liu, Z. Magnetic Dipole Two-Point Tensor Positioning Based on Magnetic Moment Constraints. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 9700410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, R.; Zakosarenko, V.; Schulz, M.; Chwala, A.; Fritzsch, L.; Meyer, H.G.; Kostlin, E. Magnetic full-tensor SQUID gradiometer system for geophysical applications. Lead. Edge 2006, 25, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Osten-Woldenburg, H.; Chaume, B.; Reinhard, W. New archaeological discoveries through magnetic gradiometry: The early Celtic settlement on Mont Lassois, France. Lead. Edge 2006, 25, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, S.D. Superconducting Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer System for Detection of Underwater Military Munitions. Ph.D. Thesis, Black Tusk Geophysics Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chwala, A.; Schmelz, M.; Zakosarenko, V.; Schiffler, M.; Schneider, M.; Thürk, M.; Bräuer, S.; Bauer, F.; Schulz, M.; Krüger, A.; et al. Underwater operation of a full tensor SQUID gradiometer system. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 32, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Structural Design and Parameter Optimization of Magnetic Gradient Tensor Measurement System. Sensors 2024, 24, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Keenan, S.; Clark, D.; Sullivan, P.; Billings, S. Development of a high temperature superconducting magnetic tensor gradiometer for underwater UXO detection. In Proceedings of the OCEANS’10 IEEE SYDNEY, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 24–27 May 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, R.; Schmelz, M.; Zakosarenko, V.; Foley, C.; Tanabe, K.; Xie, X.; Fagaly, R.L. Superconducting sensors and methods in geophysical applications. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 34, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, H.; Yin, G. Integrated Compensation and Rotation Alignment for Three-Axis Magnetic Sensors Array. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 4001011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, R.; Schmelz, M.; Anders, S.; Kunert, J.; Franke, D.; Zakosarenko, V. Long baseline LTS SQUID gradiometers with sub-μm sized Josephson junctions. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2020, 33, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, R.; Schiffler, M.; Becken, M.; Thiede, A.; Schneider, M.; Chubak, G.; Marsden, P.; Bergshjorth, A.B.; Schaefer, M.; Terblanche, O. SQUIDs for magnetic and electromagnetic methods in mineral exploration. Miner. Econ. 2022, 35, 467–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, W. Dipole Tracking with a Gradiometer; Technical Report 3493; Informal Report NSRDL/PC; Naval Ship Research and Development Laboratory: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Wynn, W.; Frahm, C.; Carroll, P.; Clark, R.; Wellhoner, J.; Wynn, M. Advanced superconducting gradiometer/Magnetometer arrays and a novel signal processing technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1975, 11, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, C.P. Inversion of the Magnetic Field Gradient Equation for a Magnetic Dipole Field; Technical report; Informal Report; NCSL: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, H. Analysis of the Magnetic Gradient Tensor. In Technical Memorandum, Defence Research Establishment Pacific; Defence Research Establishment Pacific: Research and Development Branch, Department of National Defence Canada: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, D. New methods for interpretation of magnetic vector and gradient tensor data I: Eigenvector analysis and the normalised source strength. Explor. Geophys. 2012, 43, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Wei, Z.; Xie, Y. A closed-form formula for magnetic dipole localization by measurement of its magnetic field vector and magnetic gradient tensor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 499, 166274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, T.; Suzuki, S.; Ando, S. A Closed-Form Formula for Magnetic Dipole Localization by Measurement of Its Magnetic Field and Spatial Gradients. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3291–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, T.; Ito, W. Moore–Penrose generalized inverse of the gradient tensor in Euler’s equation for locating a magnetic dipole. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17E504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Nara, T.; Ando, S. A Truncated Singular Value Decomposition Approach for Locating a Magnetic Dipole with Euler’s Equation. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 52, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Huang, G.; Li, G.; Yang, G. Eigenvector Constraint-Based Method for Eliminating Dead Zone in Magnetic Target Localization. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Leslie, K.; Clark, D. Multiple-Order Magnetic Gradient Tensors for Localization of a Magnetic Dipole. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2017, 8, 6506605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ren, G.; Li, Z.; Li, Q. A third-order magnetic gradient tensor optimization algorithm based on the second-order improved central difference method. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 065302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.; Lee, K.; Oeschger, J. Improved magnetic STAR methods for real-time, point-by-point localization of unexploded ordnance and buried mines. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2008, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.F. Magnetic STAR technology for real-time localization and classification of unexploded ordnance and buried mines. In Proceedings of the Defense + Commercial Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 1 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yan, S.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y. Novel Magnetic Localization Methods for Minimizing the Ellipse Error Based on Tensor Invariants. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2022, 13, 8105205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Pan, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Improvement and Omnidirectional Analysis of Magnetic Gradient Tensor Invariants Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2021, 68, 7603–7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Qu, X.; Pan, X.; Fang, G.; Chen, L. A Modified Magnetic Gradient Contraction Based Method for Ferromagnetic Target Localization. Sensors 2016, 16, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, X. Online magnetic target location method based on the magnetic gradient tensor of two points. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 3995–4004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, W. A New Magnetic Target Localization Method Based on Two-Point Magnetic Gradient Tensor. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiki, M.; Clark, D.; Austin, J.; Foss, C. Estimating source location using normalized magnetic source strength calculated from magnetic gradient tensor data. Geophysics 2012, 77, J23–J37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spantideas, S.T.; Kapsalis, N.C.; Kakarakis, S.D.J.; Capsalis, C.N. A Method of Predicting Composite Magnetic Sources Employing Particle Swarm Optimization. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2014, 39, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, C.; Engelke, S.; Bubeck, K.; Lange, J.; Tenacci, Z.; Junge, A. Reliable Distance Scaling of AC Magnetic Fields for Space Mission Verification Campaigns. In Proceedings of the 2019 ESA Workshop on Aerospace EMC (Aerospace EMC), Budapest, Hungary, 20–22 May 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spantideas, S.T.; Giannopoulos, A.E.; Kapsalis, N.C.; Capsalis, C.N. A Deep Learning Method for Modeling the Magnetic Signature of Spacecraft Equipment Using Multiple Magnetic Dipoles. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2021, 12, 2100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name | Coil Specification | Coil Turns | Effective Diameter | Total Coil Inductance | Total Coil Resistance (25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-dimensional coil | 1.5 mm | 150 | 200 mm | 6.823 mH | 0.93 |
| Sets | Current (A) | Relative Localization Error (%) | Magnetic Moment (A·m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.828 | 338.5185 | 9.2624 × 1012 |
| 2 | 0.966 | 104.9234 | 3.8083 × 1011 |
| 3 | 1.104 | 42.2661 | 1.1361 × 1011 |
| 4 | 1.242 | 10.1966 | 2.4411 × 1010 |
| 5 | 1.380 | 4.5229 | 3.3940 × 1010 |
| 6 | 2.760 | 5.0574 | 2.8727 × 1010 |
| 7 | 4.140 | 6.0444 | 3.2539 × 1010 |
| 8 | 5.520 | 10.3482 | 3.0586 × 1010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. A Remote Two-Point Magnetic Localization Method Based on SQUID Magnetometers and Magnetic Gradient Tensor Invariants. Sensors 2024, 24, 5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185917
Zhang Y, Liu G, Wang C, Qiu L, Wang H, Liu W. A Remote Two-Point Magnetic Localization Method Based on SQUID Magnetometers and Magnetic Gradient Tensor Invariants. Sensors. 2024; 24(18):5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185917
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yingzi, Gaigai Liu, Chen Wang, Longqing Qiu, Hongliang Wang, and Wenyi Liu. 2024. "A Remote Two-Point Magnetic Localization Method Based on SQUID Magnetometers and Magnetic Gradient Tensor Invariants" Sensors 24, no. 18: 5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185917
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, G., Wang, C., Qiu, L., Wang, H., & Liu, W. (2024). A Remote Two-Point Magnetic Localization Method Based on SQUID Magnetometers and Magnetic Gradient Tensor Invariants. Sensors, 24(18), 5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185917







