A Respiratory Sensor-Based Study of the Relationship between Voluntary Breathing Patterns and Aerobic and Anerobic Exercise Capacity—An Exploratory Applied Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
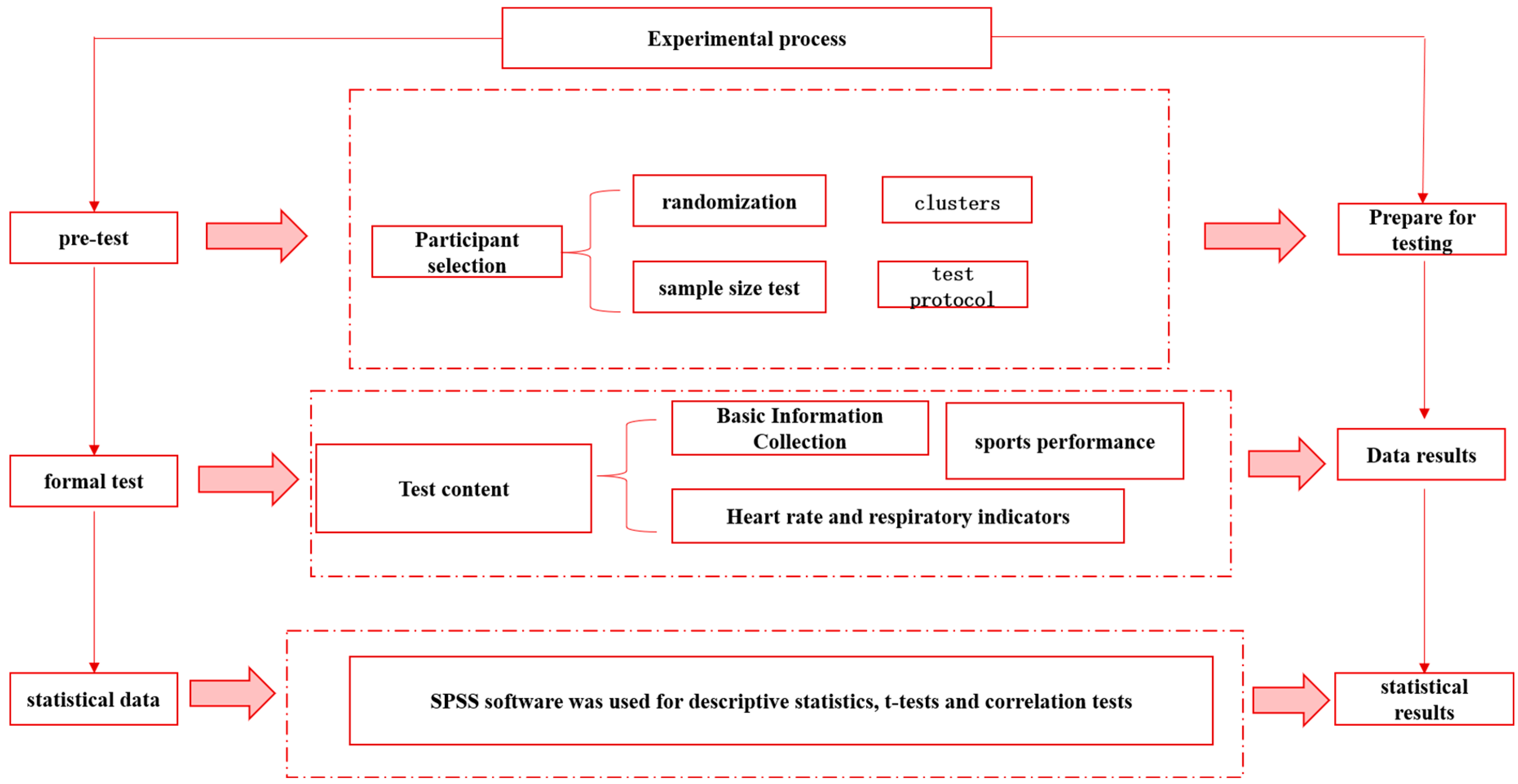
2. Participants and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sampling Method
- Randomization method
- Test protocols and blinding
- Test Protocol
- Blinded method
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion
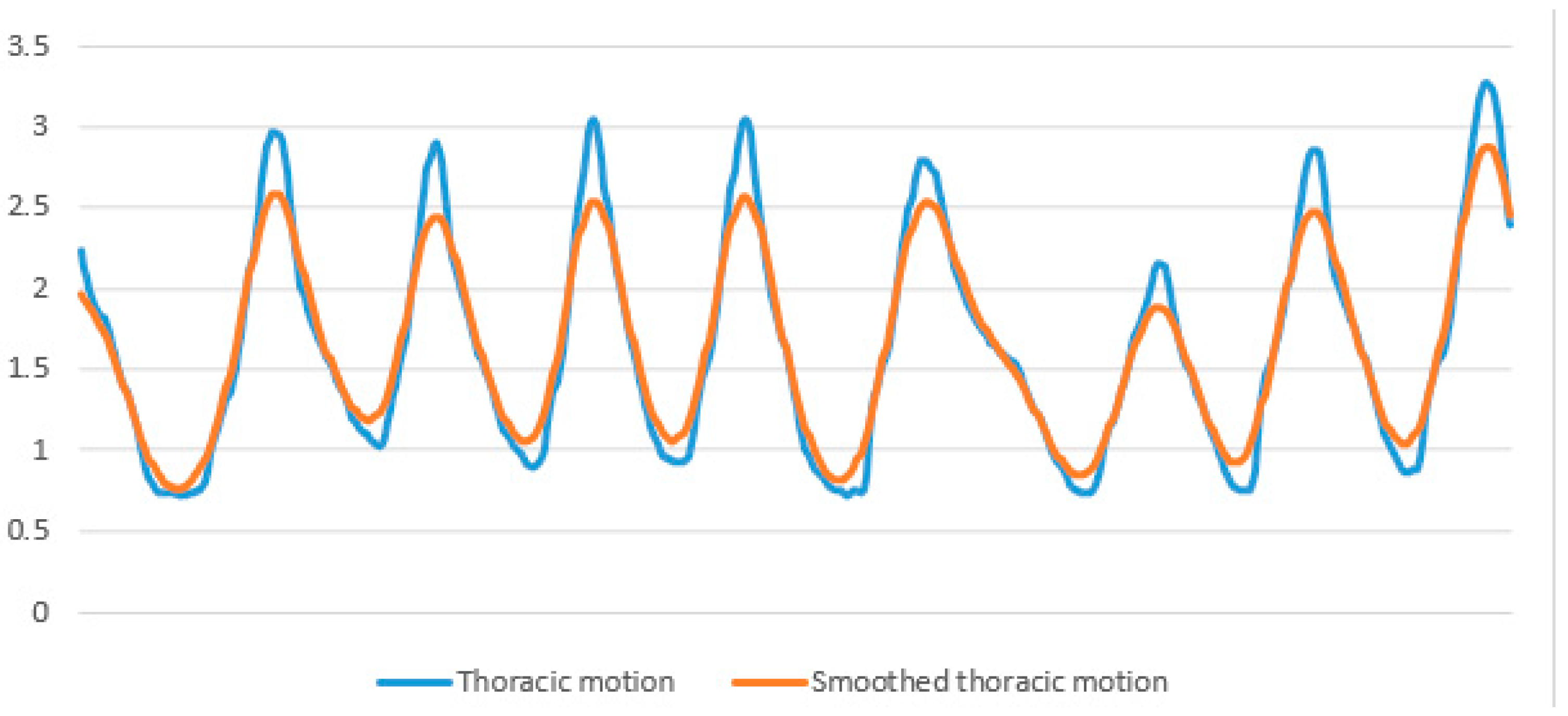
2.4. Respiratory Testing and Data Processing
2.5. Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability Testing
2.6. Tests for Aerobic and Anerobic Exercise Capacities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Data Description and Comparison between Men and Women
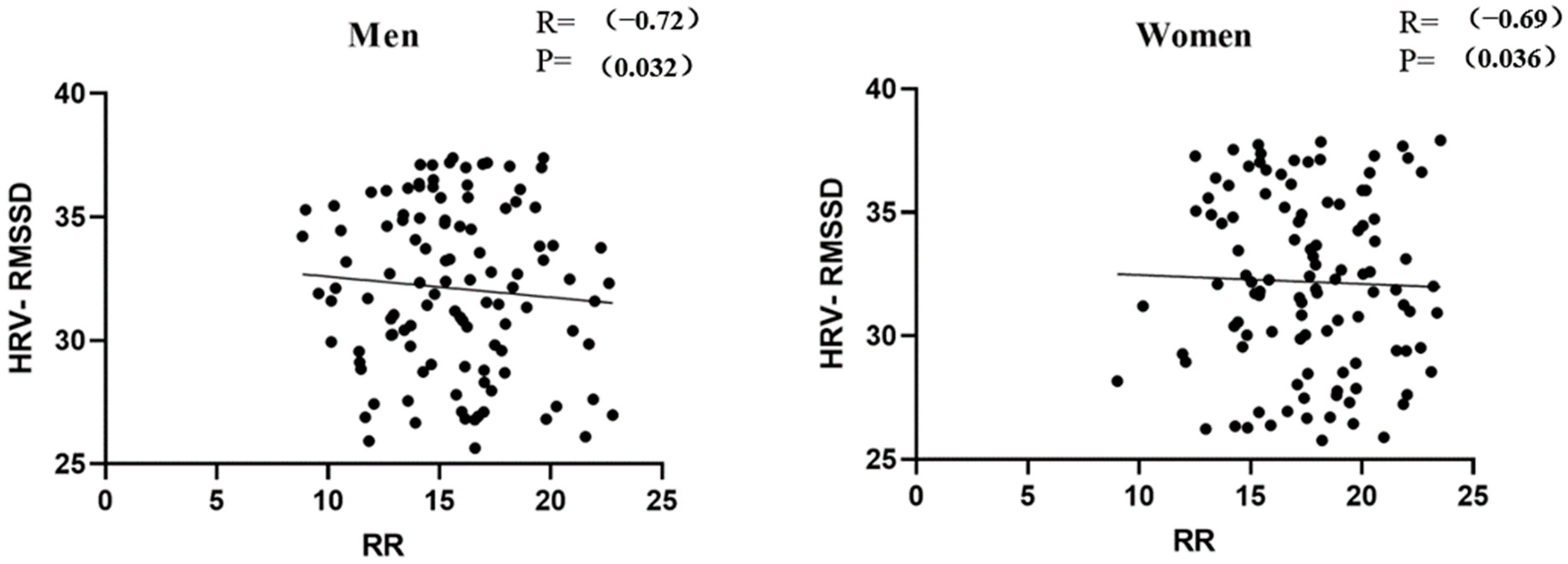
3.2. Correlation Test between RR and HRV-RMSSD
3.3. The Linearity Assumption for the Relationship between Respiratory Patterns and Running Performance Is an Important Consideration in Research Studies
3.4. The Correlation between Respiratory Patterns and Running Performance
3.5. Comparative Tests to Verify the Results of Correlation Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W.; et al. Forecasting Life Expectancy, Years of Life Lost, and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality for 250 Causes of Death: Reference and Alternative Scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 Countries and Territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.S.; Giles, W.H.; Dietz, W.H. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome among US Adults: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA 2002, 287, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolic Health and Cardiometabolic Risk Clusters: Implications for Prediction, Prevention, and Treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognmo, Ø.; Hetland, E.; Helgerud, J.; Hoff, J.; Slørdahl, S.A. High Intensity Aerobic Interval Exercise Is Superior to Moderate Intensity Exercise for Increasing Aerobic Capacity in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2004, 11, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Exercise Training Effects on the Cardiovascular System. Available online: https://read.qxmd.com/read/28289526/aerobic-vs-anaerobic-exercise-training-effects-on-the-cardiovascular-system (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Ferguson, B. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 9th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 58, p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.-M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P.; American College of Sports Medicine American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Nicol, C.W.; Bredin, S.S.D. Health Benefits of Physical Activity: The Evidence. CMAJ 2006, 174, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, W.L.; Lee, I.-M.; Pate, R.R.; Powell, K.E.; Blair, S.N.; Franklin, B.A.; Macera, C.A.; Heath, G.W.; Thompson, P.D.; Bauman, A. Physical Activity and Public Health: Updated Recommendation for Adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnethon, M.R.; Gidding, S.S.; Nehgme, R.; Sidney, S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Liu, K. Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Young Adulthood and the Development of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. JAMA 2003, 290, 3092–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito-Ruiz, P.; Camacho-Zambrano, M.M.; Carrillo-Arcentales, J.N.; Mestanza-Peralta, M.A.; Vallejo-Flores, C.A.; Vargas-López, S.V.; Villacís-Tamayo, R.A.; Zurita-Gavilanes, L.A. A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Efficacy and Safety of a Food Ingredient, Collagen Hydrolysate, for Improving Joint Comfort. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60 (Suppl. S2), 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laukkanen, J.A.; Rauramaa, R.; Salonen, J.T.; Kurl, S. The Predictive Value of Cardiorespiratory Fitness Combined with Coronary Risk Evaluation and the Risk of Cardiovascular and All-Cause Death. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak Aerobic Capacity Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18657659/ (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Prevalence, Phenotype and Cardiometabolic Risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome under Different Diagnostic Criteria—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22777527/ (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- The Blood Lactate Response to Exercise|Semantic Scholar. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-blood-lactate-response-to-exercise-Weltman/ce6415e100a2971ef02dc53b3c3303e8f5f042cd (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Schoenfeld, B.J. The Mechanisms of Muscle Hypertrophy and Their Application to Resistance Training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2857–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fundamentals of Resistance Training: Progression and Exercise Prescription—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15064596/ (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Parkes, R. Rate of Respiration: The Forgotten Vital Sign. Available online: https://journals.rcni.com/emergency-nurse/rate-of-respiration-the-forgotten-vital-sign-en2011.05.19.2.12.c8504 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Paz, J.C.; West, M.P. Acute Care Handbook for Physical Therapists, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Available online: https://shop.elsevier.com/books/acute-care-handbook-for-physical-therapists/paz/978-0-323-63919-4 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- (PDF) Pre-Exercise Hyperventilation Can Significantly Increase Performance in the 50-Meter Front Crawl. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275671458_Pre-exercise_hyperventilation_can_significantly_increase_performance_in_the_50-meter_front_crawl (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Hyperventilation as a Strategy for Improved Repeated Sprint: The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/Fulltext/2014/04000/Hyperventilation_as_a_Strategy_for_Improved.33.aspx (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Wallin, B.G.; Hart, E.C.; Wehrwein, E.A.; Charkoudian, N.; Joyner, M.J. Relationship between Breathing and Cardiovascular Function at Rest: Sex-Related Differences. Acta Physiol. 2010, 200, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.A.; Santarelli, D.M.; O’Rourke, D. The Physiological Effects of Slow Breathing in the Healthy Human. Breathe 2017, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliaccio, G.M.; Russo, L.; Maric, M.; Padulo, J. Sports Performance and Breathing Rate: What Is the Connection? A Narrative Review on Breathing Strategies. Sports 2023, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragnarsdóttir, M.; Kristinsdóttir, E.K. Breathing Movements and Breathing Patterns among Healthy Men and Women 20–69 Years of Age. Reference Values. Respiration 2006, 73, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, D.; Matthews, J.J.L.; Chen, J.J.; Mah, L. Increased Exhalation to Inhalation Ratio during Breathing Enhances High-Frequency Heart Rate Variability in Healthy Adults. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Diest, I.; Verstappen, K.; Aubert, A.E.; Widjaja, D.; Vansteenwegen, D.; Vlemincx, E. Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio Modulates the Effect of Slow Breathing on Heart Rate Variability and Relaxation. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2014, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenk Gürkan, A.; Söyler, M.; Subak, E. Efectos de diez semanas de entrenamiento funcional en niños de 8-10 años sobre parámetros respiratorios y motores. Apunt. Univ. 2022, 12, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, E.G.; Jelinek, C.; O’Connell, S.; Butler, J.; McBurney, C.; Gozali, C.; Reda, D.; Laghi, F. Contrasting breathing retraining and helium–oxygen during pulmonary rehabilitation in COPD: A randomized clinical trial. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Lin, P.; Jia, T.; Ji, L.; Li, C. Motor-Respiratory Coupling Improves Endurance Performance during Rhythmic Isometric Handgrip Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2023, 56, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csepregi, É.; Szekanecz, Z.; Szántó, S. The effects of breathing exercises in comparison with other exercise programs on cardiorespiratory fitness among healthy female college students. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2020, 60, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbour, E.; Lasshofer, M.; Genitrini, M.; Schwameder, H. Enhanced Breathing Pattern Detection during Running Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Gu, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Lu, W. Airflow-Induced Flexoelectric Bending Sensors for Human Breath Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 5950–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.S.; Ahmed, H.E.U.; Motaghedi, F.; Lester, N.J.; Khalil, A.; Janaideh, M.A.; Anees, S.; Carmichael, T.B.; Bain, A.R. A Wearable Multisensor Patch for Breathing Pattern Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 10924–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Formenti, F.; Obeid, A.; Hahn, C.E.W.; Farmery, A.D. A fibre-optic oxygen sensor for monitoring human breathing. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, N71–N81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaphragmatic Breathing vs. Chest Breathing. Available online: https://www.lifelongwellness.org/wellness-academy/health/diaphragmatic-breathing-vs-chest-breathing/ (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Figueroba, A. Types of Breathing: Diaphragmatic, Thoracic, Clavicular. Available online: https://healthywaymag.com/psychology/types-of-breathing (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- (PDF) Relationship of Breathing Exercises with Improvement of Postural Stability in Healthy Adults. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320196403_RELATIONSHIP_OF_BREATHING_EXERCISES_WITH_IMPROVEMENT_OF_POSTURAL_STABILITY_IN_HEALTHY_ADULTS (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Kocjan, J.; Gzik-Zroska, B.; Nowakowska, K.; Burkacki, M.; Suchoń, S.; Michnik, R.; Czyżewski, D.; Adamek, M. Impact of Diaphragm Function Parameters on Balance Maintenance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.; Martins, F.; Silva, A.; Coelho, A.; Intelangelo, L.; Vieira, E. Activity of Lower Limb Muscles During Squat with and Without Abdominal Drawing-In and Pilates Breathing. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.-M.; Bai, Z.-M.; Aihemaiti, M.; Yuan, L.; Hong, Z.-M.; Xiao, J.; Ren, F.-F.; Rukšėnas, O. Women’s Respiratory Movements during Spontaneous Breathing and Physical Fitness: A Cross-Sectional, Correlational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardouri, W.; Selmi, M.A.; Sassi, R.H.; Gharbi, Z.; Rebhi, A.; Yahmed, M.H.; Moalla, W. Relationship Between Repeated Sprint Performance and Both Aerobic and Anaerobic Fitness. J. Hum. Kinet. 2014, 40, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnett, A.M.; Berg, K.; Latin, R.W.; Noble, J.M. The Relationship between Field Tests of Anaerobic Power and 10-Km Run Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2001, 15, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duffield, R.; Dawson, B.; Goodman, C. Energy System Contribution to 400-Metre and 800-Metre Track Running. J. Sports Sci. 2005, 23, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutcheon, M.C.; Sticha, S.A.; Giese, M.D.; Nagle, F.J. A Further Analysis of the 12-Minute Run Prediction of Maximal Aerobic Power. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1990, 61, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmageed, R.I.; Elhenawy, Y.I.; Zaafar, D.K.; Abdelaziz, A.W. Coping Strategies among Children and Adolescents: Validity and Reliability of the Arabic Version of the Kidcope Scale. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascret, N.; Nicolleau, M.; Ragot-Court, I. Development and Validation of a Scale Assessing Achievement Goals in Driving. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheus, G.B.; Dragosavac, D.; Trevisan, P.; Costa, C.E.d.; Lopes, M.M.; Ribeiro, G.C.d.A. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Tidal Volume and Vital Capacity after CABG Surgery. Rev. Bras. Cir. Cardiovasc. 2012, 27, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Duffty, P.; Spriet, L.; Bryan, M.H.; Bryan, A.C. Respiratory Induction Plethysmography (Respitrace): An Evaluation of Its Use in the Infant. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1981, 123, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hallett, S.; Toro, F.; Ashurst, J.V. Physiology, Tidal Volume; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, R. Spirometry: An Essential Clinical Measurement. Aust. Fam. Physician 2005, 34, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Research on the Correlation between Body Mass Index and Physical Health Index of Medical College Students. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354558683_Research_on_the_Correlation_between_Body_Mass_Index_and_Physical_Health_Index_of_Medical_College_Students (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Chen, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, W. The Association between BMI and Health-Related Physical Fitness among Chinese College Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, L.J.; Boileau, R.A. Influence of Metabolic, Mechanical and Physique Variables on Middle Distance Running. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 1992, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lacour, J.R.; Padilla-Magunacelaya, S.; Barthélémy, J.C.; Dormois, D. The Energetics of Middle-Distance Running. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 60, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashino, M.; Miyata, K.; Kudo, K. Coordination Dynamics of Thoracic and Abdominal Movements during Voluntary Breathing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Troyer, A.; Boriek, A.M. Mechanics of the Respiratory Muscles. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 1273–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, K.A.; Dhamoon, A.S. Physiology, Pulmonary Ventilation and Perfusion; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Vitacca, M.; Clini, E.; Bianchi, L.; Ambrosino, N. Acute Effects of Deep Diaphragmatic Breathing in COPD Patients with Chronic Respiratory Insufficiency. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, N.; Paggiaro, P.L.; Macchi, M.; Filieri, M.; Toma, G.; Lombardi, F.A.; Del Cesta, F.; Parlanti, A.; Loi, A.M.; Baschieri, L. A Study of Short-Term Effect of Rehabilitative Therapy in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respiration 1981, 41, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunk, R.C.; Mascia, A.V.; Lipkowitz, M.A.; Wolf, S.I. Rehabilitation of a Patient with Asthma in the Outpatient Setting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 87, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxel Bliven, K.C.; Anderson, B.E. Core Stability Training for Injury Prevention. Sports Health 2013, 5, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byars, A.; Gandy-Moodie, N.; Greenwood, L.; Stanford, M.S.; Greenwood, M. An Evaluation of the Relationships between Core Stability, Core Strength, and Running Economy in Trained Runners. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On the Capacity of the Lungs, and on the Respiratory Functions, with a View of Establishing a Precise and Easy Method of Detecting Disease by the Spirometer—Abstract—Europe PMC. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/MED/20895846 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Verschakelen, J.A.; Demedts, M.G. Normal Thoracoabdominal Motions. Influence of Sex, Age, Posture, and Breath Size. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.; Auchincloss, J.H.; Peppi, D. Relationship of Rib Cage and Abdomen Motion to Diaphragm Function during Quiet Breathing. Chest 1981, 80, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binazzi, B.; Lanini, B.; Bianchi, R.; Romagnoli, I.; Nerini, M.; Gigliotti, F.; Duranti, R.; Milic-Emili, J.; Scano, G. Breathing Pattern and Kinematics in Normal Subjects during Speech, Singing and Loud Whispering. Acta Physiol. 2006, 186, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemare, F.; Jeanneret, A.; Couture, J. Sex Differences in Thoracic Dimensions and Configuration. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoMauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Respiratory Physiology of Pregnancy. Breathe 2015, 11, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoMauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Sex Differences in Respiratory Function. Breathe 2018, 14, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesdottir, F.; Allaire, B.; Anderson, D.E.; Samelson, E.J.; Kiel, D.P.; Bouxsein, M.L. Population-Based Study of Age- and Sex-Related Differences in Muscle Density and Size in Thoracic and Lumbar Spine: The Framingham Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Men | Women | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Parameters | n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | F | p | η2 |
| Age (year) | 109 | 19.8 ± 0.82 | 110 | 19.9 ± 0.78 | 0.19 | 0.665 | 0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 109 | 174 ± 6.28 | 110 | 162 ± 5.24 | 224 | <0.001 | 0.508 |
| Weight (kg) | 109 | 65.1 ± 8.88 | 110 | 55.1 ± 6.78 | 88.1 | <0.001 | 0.289 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 109 | 21.5 ± 2.41 | 110 | 20.9 ± 2.28 | 3.11 | 0.079 | 0.014 |
| HR (rep/min) | 109 | 84.7 ± 10.3 | 110 | 89.8 ± 10.4 | 12.9 | <0.001 | 0.056 |
| HRV-RMSSD (ms) | 109 | 31.31 ± 6.18 | 110 | 31.50 ± 6.42 | 9.13 | 0.456 | 0.013 |
| RR (rep/min) | 109 | 15.7 ± 3.22 | 110 | 17.5 ± 3.17 | 18.5 | <0.001 | 0.079 |
| AM+TM (N) | 109 | 3.69 ± 1.49 | 110 | 2.08 ± 0.56 | 112 | <0.001 | 0.341 |
| AM/(AM+TM) (N) | 109 | 0.41 ± 0.14 | 110 | 0.35 ± 0.11 | 11.6 | 0.001 | 0.051 |
| IE ratio | 109 | 0.84 ± 0.11 | 110 | 0.78 ± 0.11 | 15.9 | <0.001 | 0.068 |
| 50 m sprint time (s) | 109 | 7.86 ± 0.55 | 110 | 9.62 ± 0.76 | 385 | <0.001 | 0.640 |
| 800 m run time (min) | 110 | 3.66 ± 0.40 | |||||
| 1000 m run time (min) | 109 | 4.13 ± 0.41 | |||||
| 12 min run distance (m) | 109 | 2548 ± 228 | 109 | 2092 ± 197 | 250 | <0.001 | 0.537 |
| Dependent Variables | Independent Variables | B | 95% CI | β | pβ | R2 | F | pF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 50 m sprint time (s) | BMI | 0.107 | 0.047–0.168 | 0.321 | <0.001 | 0.189 | 6.098 | <0.001 |
| AM+TM | −1.351 | −2.700–−0.003 | −0.993 | 0.050 | |||||
| 800 m run time (s) | BMI | 0.041 | 0.009–0.074 | 0.234 | 0.013 | 0.083 | 4.869 | 0.009 | |
| AM/(AM+TM) | −0.722 | −1.410–−0.035 | −0.194 | 0.040 | |||||
| 12 min run Distance (m) | AM+TM | 96.659 | 32.383–161.817 | 0.276 | 0.004 | 0.076 | 8.847 | 0.004 |
| Sex | Respiratory Patterns and Running Performance | Group 1 | Group 2 | F | p | η2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | |||||
| Men | I/E ratio | 41 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 68 | 0.90 ± 0.06 | 185 | <0.001 | 0.63 |
| 12 min run distance residuals | 56.4 ± 210 | −34.0 ± 223 | 4.41 | 0.038 | 0.04 | |||
| Women | AM+TM | 58 | 1.66 ± 0.33 | 51 | 2.56 ± 0.34 | 194 | <0.001 | 0.64 |
| 12 min run distance residuals | −39.1 ± 192 | 44.4 ± 181 | 5.42 | 0.022 | 0.05 | |||
| AM/(AM+TM) | 54 | 0.44 ± 0.06 | 56 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 206 | <0.001 | 0.66 | |
| 800 m run time residuals | −0.08 ± 0.38 | 0.08 ± 0.40 | 4.589 | 0.034 | 0.04 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Jiang, K.; Li, H. A Respiratory Sensor-Based Study of the Relationship between Voluntary Breathing Patterns and Aerobic and Anerobic Exercise Capacity—An Exploratory Applied Study. Sensors 2024, 24, 6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196310
Du Y, Jiang K, Li H. A Respiratory Sensor-Based Study of the Relationship between Voluntary Breathing Patterns and Aerobic and Anerobic Exercise Capacity—An Exploratory Applied Study. Sensors. 2024; 24(19):6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196310
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yinling, Kai Jiang, and Haojie Li. 2024. "A Respiratory Sensor-Based Study of the Relationship between Voluntary Breathing Patterns and Aerobic and Anerobic Exercise Capacity—An Exploratory Applied Study" Sensors 24, no. 19: 6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196310
APA StyleDu, Y., Jiang, K., & Li, H. (2024). A Respiratory Sensor-Based Study of the Relationship between Voluntary Breathing Patterns and Aerobic and Anerobic Exercise Capacity—An Exploratory Applied Study. Sensors, 24(19), 6310. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196310






