Theories and Methods for Indoor Positioning Systems: A Comparative Analysis, Challenges, and Prospective Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We investigate the various measurement techniques and technological solutions used to address complicated indoor scenarios and present a comprehensive overview of the theories and methods of indoor positioning systems, focusing on the measurement techniques, technologies, and methods used for indoor positioning systems in general.
- We briefly discuss and explain how the impact of IoT as a pervasive paradigm could also open up a wide range of driving factors for IPSs, including the opportunities for and challenges of using IoT infrastructure for indoor location purposes.
- We aim to introduce the reader to some of the current location systems and evaluate these systems using multidimensional matrices, considering both efficiency and cost, as well as practicality, in line with the evaluation metrics described in the literature.
- We have also created a general framework for indoor location systems that allows us to provide a condensed overview of recent advances and developments in indoor positioning. This framework also serves researchers and practitioners to better understand the general milestones in the state of the art and identify challenges as future research directions.
- We briefly present the approaches and methods of transfer learning from the perspective of data and models to improve the performance of indoor positioning.
- We propose some feature engineering techniques that can be used as countermeasures to improve positioning performance by addressing irrelevant features that may affect the overall performance of the system model.
- We provide an overview of ensemble learning and explain how it can be effectively used to improve the overall estimation and positioning accuracy in IPSs.
- We explain in detail how data fusion techniques and multisensory technology can be used to minimize the real challenges in various applications of IPSs.
2. Fundamental Theories and Methods of IPSs
2.1. Indoor Positioning Overview
- Mobile Device-Based IPS (MDBIP)
- 2.
- Anchor-Based IPS (ANBIP)
- 3.
- Network-Based IPS (NWBIP)
2.2. Positioning Techniques
- Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
- 2.
- Channel State Information (CSI)
- 3.
- Time of Arrival (TOA)
- 4.
- Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA)
- 5.
- Angle of Arrival (AOA)
- 6.
- Hybrid signal features
2.3. Indoor Positioning Principle Algorithms
- 1.
- Pedestrian Dead Reckoning (PDR)
- 2.
- Fingerprinting and Pattern Matching Positioning
- 3.
- Spatial Geometric Relationship Positioning
2.4. Positioning Technologies
- 1.
- WLAN-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 2.
- Bluetooth-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 3.
- RFID-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 4.
- UWB-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 5.
- Inertial Navigation Systems (INSs)-based Indoor Positioning System
- 6.
- Cellular-Network-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 7.
- ZigBee-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 8.
- Visible Light Indoor Positioning System
- 9.
- Geomagnetic-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 10.
- Ultrasonic-Based Indoor Positioning System
- 11.
- Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
- 12.
- 5G/6G Network Positioning
3. Internet of Things and Indoor Positioning
Overview of Internet of Things
4. Data Fusion and Indoor Positioning
Overview of Data Fusion
5. Transfer Learning and Indoor Positioning
Overview of Transfer Learning
6. System Architecture, Challenges, and Prospective Measures
6.1. System Architecture
- Availability
- 2.
- Scalability
- (1)
- User Device Localization: This approach processes location data on the user’s device, minimizing the impact on other users or anchor nodes. It allows the simultaneous location of many users over a large area, enhancing scalability.
- (2)
- ANBP: In this model, localization occurs on a server linked to anchor nodes, which handles multiple user requests concurrently. This can create a processing burden and may limit scalability. In summary, the scalability of an IPS is influenced by various factors, including architecture, application needs, technology, cost, and ease of use. Optimizing these elements is essential for effective implementation.
- 3.
- Security and Privacy
- (a)
- Authentication
- (b)
- Authorization
- (c)
- Privacy
- (d)
- Confidentiality
- (e)
- Availability
- (f)
- Integrity
- (g)
- Encryption
- 4.
- Affordability
- 5.
- Energy efficiency
- 6.
- Coverage
- 7.
- Positioning Performance
- 8.
- Robustness
- 9.
- Latency
- 10.
- Reliability
6.2. Challenges
- Multipath Effects and Noise
- 2.
- Radio Environment
- 3.
- Heterogeneity of devices
- 4.
- Lack of Standardization
- 5.
- Side effect on the service of network technology
- 6.
- Requirement for Large Sample Size
6.3. Prospective Measures
- 1.
- Data Fusion
- 2.
- Transfer Learning
- 3.
- Feature Engineering techniques
- (a)
- Principal Component Analysis
- (b)
- Analysis of Multicollinearity Problem
- (c)
- Hybrid Feature Selection
- 4.
- Ensemble Learning
- 5.
- Crowdsourcing
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pecoraro, G.; Domenico, S.D.; Cianca, E.; Sanctis, M.D. CSI-based fingerprinting for indoor localization using lte signals. Eurasip J. Adv. Signal Process. 2018, 2018, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Sigg, S.; Chen, L.; Ji, Y. Accurate location tracking from csi-based passive device-free probabilistic fingerprinting. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5217–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Boateng, G.O.; Si, H.; Cao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lai, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, C. Automated Valet Parking and Charging: A Novel Collaborative AI-empowered Architecture. IEEE Commun. Mag. Early Access. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiekermann, S. General Aspects of Location-Based Services. In Location-Based Services; Schiller, J., Voisard, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mirama, V.F.; Diez, L.E.; Bahillo, A.; Quintero, V. A Survey of Machine Learning in Pedestrian Localization Systems: Applications, Open Issues and Challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 120138–120157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, M.; Wen, C.; Wang, C. Planar Primitive Group-Based Point Cloud Registration for Autonomous Vehicle Localization in Underground Parking Lots. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6500905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolcott, R.W.; Eustice, R.M. Visual localization within LIDAR maps for automated urban driving. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhousni, M.; Huang, X. A Survey on 3D LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19 October–13 November 2020; pp. 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.X.; La, H.M.; Feil-Seifer, D.; Deans, M.C. A Distributed Control Framework of Multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Dynamic Wildfire Tracking. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.J. Location-based services: The state of the art. E-Service 2003, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Elikplim, N.R.; Ansari, N.; Li, L.; Wang, L. Robust WiFi Localization by Fusing Derivative Fingerprints of RSS and Multiple Classifiers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ansari, N.; Li, L.; Duan, L. A Hybrid Positioning System for Location-Based Services: Design and Implementation. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, X.; Ansari, N. SmartLoc: Smart Wireless Indoor Localization Empowered by Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6883–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Enge, P. Global Positioning System: Signals, Measurements, and Performance, 2nd ed.; Ganga-Jamuna Press: Lincoln, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dardari, D.; Conti, A.; Ferner, U.; Giorgetti, A.; Win, M.Z. Ranging with ultrawide bandwidth signals in multipath environments. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 404–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekavat, S.A.; Buehrer, R.M. (Eds.) Handbook of Position Location: Theory, Practice, and Advances; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guvenc, I.; Chong, C.-C. A survey on TOA-based wireless localization and NLOS mitigation techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lymberopoulos, D.; Liu, J.; Priyantha, B. Indoor Localization Using FM Signals. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2013, 12, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoy, J.; Wendeberg, J.; Schindelhauer, C.; Reindl, L.M. Single transceiver device-free indoor localization using ultrasound body reflections and walls. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Banff, AB, Canada, 13–16 October 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shao, S.; Ansari, N.; Khreishah, A. Indoor Localization Using Visible Light Via Fusion of Multiple Classifiers. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 7803716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sengupta, R.; Fodero, J.; Li, X. DeepPositioning: Intelligent Fusion of Pervasive Magnetic Field and WiFi Fingerprinting for Smartphone Indoor Localization via Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh-Van, N.; Nashashibi, F.; Thanh-Huong, N.; Castelli, E. Indoor Intelligent Vehicle localization using WiFi received signal strength indicator. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Nagoya, Japan, 19–21 March 2017; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakre, M.P.; Borse, P.S.; Matale, N.P.; Sharma, P. Iot based smart vehicle parking system using rfid. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 27–29 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Ciravegna, F.; Bond, R.; Mulvenna, M. A Low Cost Indoor Positioning System Using Bluetooth Low Energy. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 136858–136871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y. Parking, intelligent parking system. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automat, Chengdu China, 20–22 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.S.; Chu, L.; Li, B.; Xu, B.; Wan, Q.; Shen, Y. A robust vector matching localization approach based on multiple channels SSD fingerprinting of Zigbee networks. Prog. Electromagn. Res 2014, 144, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Meng, M.Q.H. Pedestrian motion tracking by using inertial sensors on the smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Kudo, M.; Nonaka, H.; Toyama, J. Recording the Activities of Daily Living based on person localization using an infrared ceiling sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 8–10 November 2011; pp. 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chan, S.H.G. Wi-Fi Fingerprint-Based Indoor Positioning: Recent Advances and Comparisons. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 466–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, C.; El Khadimi, A. Survey on indoor localization system and recent advances of WIFI fingerprinting technique. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Multimedia Computing and Systems (ICMCS), Marrakech, Morocco, 29 September–1 October 2016; pp. 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoudias, C.; Moreira, A.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Wirola, L.; Fischione, C. A Survey of Enabling Technologies for Network Localization, Tracking, and Navigation. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 3607–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ansari, N.; Hu, F.; Shao, Y.; Elikplim, N.R.; Li, L. A Survey on Fusion-Based Indoor Positioning. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 566–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, Q.; Deng, Z.; Chen, H.; Fu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, S. Survey on CSI-based Indoor Positioning Systems and Recent Advances. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Pisa, Italy, 30 September–3 October 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.F.G.G.; Fernandes, D.M.A.; Catarino, A.P.; Monteiro, J.L. Localization and Positioning Systems for Emergency Responders: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2836–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Jung, S.; Lee, M.; Yoon, G. Building a practical Wi-Fi-based indoor navigation system. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2014, 13, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.; Moselhi, O. RFID indoor location identification for construction projects. Autom. Constr. 2014, 39, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinis, A.; Raspopoulos, M.; Kanaris, L.; Liotta, A.; Stavrou, S. Map-aided fingerprint-based indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pivato, P.; Palopoli, L.; Petri, D. Accuracy of RSS-based centroid localization algorithms in an indoor environment. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaris, L.; Kokkinis, A.; Fortino, G.; Liotta, A.; Stavrou, S. Sample Size Determination Algorithm for fingerprint-based indoor localization systems. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, Z.; Nordin, R.; Ismail, M. Recent advances in wireless indoor localization techniques and system. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2013, 2013, 185138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taponecco, L.; D’Amico, A.A.; Mengali, U. Joint TOA and AOA estimation for UWB localization applications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 10, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Chu, L. DOA estimation of mixed circular and non-circular signals using uniform circular array. In Proceedings of the 2014 7th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Dalian, China, 14–16 October 2014; pp. 1043–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Darabi, H.; Banerjee, P.; Liu, J. Survey of wireless indoor positioning techniques and systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. Part C—Appl. Rev. 2007, 37, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Xu, F.; Bai, S.; Wan, Q. A noise reduction fingerprint feature for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 18–20 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jondhale, S.R.; Deshpande, R.S.; Walke, S.M.; Jondhale, A.S. Issues and challenges in RSSI based target localization and tracking in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Techniques (ICACDOT), Pune, India, 9–10 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Wan, Q.; Yang, S.; Ho, K.C. A simple and accurate TDOA-AOA localization method using two stations. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, I.A.; Schoebel, J. Time of Arrival Prediction for WLAN Systems Using Prony Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2007 4th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Hannover, Germany, 22 March 2007; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargie, W.; Poellabauer, C. Fundamentals of Wireless Sensor Networks: Theory and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, S.; Hassan, M.; Seneviratne, A. Adaptive pedestrian activity classification for indoor dead reckoning systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Montbeliard, France, 28–31 October 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.K.M.M.; Jin, Y.; Soh, W.-S.; Van, H.N. SSD: A Robust RF Location Fingerprint Addressing Mobile Devices’ Heterogeneity. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2013, 12, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærgaard, M.B.; Munk, C.V. Hyperbolic Location Fingerprinting: A Calibration-Free Solution for Handling Differences in Signal Strength (concise contribution). In Proceedings of the 2008 Sixth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Hong Kong, China, 17–21 March 2008; pp. 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Tsuji, H.; Ohtsuki, T. Effects of spatial correlation between signal subspaces on indoor localization using subspace matching. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2007—2007 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Taipei, China, 30 October–2 November 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Kikuchi, S.; Kaveh, M. Indoor Localization using Subspace Matching: An Experimental Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE Workshop on Sensor Array and Multichannel Processing, Waltham, MA, USA, 12–14 July 2006; pp. 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öktem, T.; Slock, D. Power Delay Doppler Profile Fingerprinting for mobile localization in NLOS. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Istanbul, Turkey, 26–30 September 2010; pp. 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtadaiee, V.; Dempster, A.G.; Lim, S. Indoor localization using FM radio signals: A fingerprinting approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Guimaraes, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaemarungsi, K.; Krishnamurthy, P. Properties of indoor received signal strength for WLAN location fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the First Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking and Services, 2004. MOBIQUITOUS 2004, Guimaraes, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cuthbert, L. Bluetooth positioning using RSSI and triangulation methods. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 10th Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–14 January 2013; pp. 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Poslad, S.; Bigham, J.; Zhang, X.; Men, L. A BLE RSSI ranking based indoor positioning system for generic smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2017 Wireless Telecommunications Symposium (WTS), Chicago, IL, USA, 26–28 April 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, S.Y.; Rappaport, T.S. 914 MHz path loss prediction models for indoor wireless communications in multifloored buildings. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1992, 40, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Tel Aviv, Israel, 26–30 March 2000; pp. 775–784. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, C.; Boateng, G.O.; Si, H.; Qian, B.; Duan, L. TRAIL: A Three-step Robust Adversarial Indoor Localization Framework. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 10462–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ansari, N.; Li, L.; Li, H. Indoor localization by fusing a group of fingerprints based on random forests. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4686–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalajmehrabadi, A.; Gatsis, N.; Akopian, D. Modern WLAN Fingerprinting Indoor Positioning Methods and Deployment Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1974–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, H.T.; Guo, X.; Zhong, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. OHetTLAL: An Online Transfer Learning Method for Fingerprint-Based Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2022, 22, 9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaru, M.; Joshi, K.; Bharadia, D.; Katti, S. Spotfi: Decimeter level localization using wifi. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM Conference on Special Interest Group on Data Communication, London, UK, 17–21 August 2015; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Rohling, H. (Ed.) OFDM: Concepts for Future Communication Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gonultas, E.; Lei, E.; Langerman, J.; Huang, H.; Studer, C. CSI-based multi-antenna and multi-point indoor positioning using probability fusion. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 2162–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Mao, S.; Pandey, S. CSI-based fingerprinting for indoor localization: A deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wan, Y.; Li, Q.; Tian, X.; Wang, X. CSI fingerprinting localization with low human efforts. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2020, 29, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pasricha, S. A Framework for CSI-Based Indoor Localization with 1D Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.08068. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Xiao, J.; Yi, Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, X.; Ni, L.M. CSI-based indoor localization. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2013, 24, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, S.D.; Guevara, A.P.; Pollin, S. CSI-based positioning in massive MIMO systems using convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference, Antwerp, Belgium, 25–28 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Park, J.G. An enhanced indoor ranging method using CSI measurements with extended Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. From RSSI to CSI: Indoor localization via channel response. ACM Comput. Surv. 2013, 46, 25:1–25:32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Liang, C. Fine-grained indoor localization using single access point with multiple antennas. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Chapre, Y.; Ignjatovic, A.; Seneviratne, A.; Jha, S. CSI-MIMO: Indoor Wi-Fi fingerprinting system. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 8–11 September 2014; pp. 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kui, W.; Mao, S.; Hei, X.; Li, F. Towards Accurate Indoor Localization Using Channel State Information. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), Taichung, Taiwan, 19–21 May 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, S.; Deng, L.; Qu, M.; Zhang, C.; Cai, C. CSI-Based Indoor High-Precision Localization System. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Kyoto, Japan, 6–9 November 2018; pp. 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazrouei, E.; Al Sindi, N.; Al-Araji, S.R.; Ali, N.; Chaloupka, Z.; Aweya, J. Measurements and characterizations of spatial and temporal TOA based ranging for indoor WLAN channels. In Proceedings of the 2013, 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Gold Coast, Australia, 16–18 December 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, T. UWB Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on TDOA Technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Qingdao, China, 23–25 August 2019; pp. 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C. A non-line-of-sight error mitigation algorithm in location estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Wireless Communication Networking (WCNC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 September 1999; Volume 1, pp. 316–320. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, S.; Buehrer, R.M. A linear programming approach to NLOS error mitigation in sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Symp. Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), Nashville, Tennessee, 19–21 April 2006; pp. 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Dizdarevic, V.; Witrisal, K. On impact of topology and cost function on LSE position determination in wireless networks. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Positioning, Navigation, and Commun, (WPNC), Hannover, Germany, 16 March 2006; pp. 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Riba, J.; Urruela, A. A non-line-of-sight mitigation technique based on ML-detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Quebec, QC, Canada, 17–21 May 2004; Volume 2, pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Denis, B.; Pierrot, J.B.; Abou-Rjeily, C. Joint distributed synchronization and positioning in UWB ad hoc networks using TOA. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 2006, 54, 1896–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.; Giunta, G.; Guzzon, E. Enhanced TOA-based indoor-positioning algorithm for mobile LTE cellular systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Dresden, Germany, 7–8 April 2011; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.-T.; Ho, K.C. A simple and efficient estimator for hyperbolic location. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, I.; Chong, C.-C.; Watanabe, F. Analysis of a linear least squares localization technique in LOS and NLOS environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE 65th Vehicular Technology Conference Spring (VTC-Spring), Dublin, Ireland, 22–25 April 2007; pp. 1886–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, A.; Dardari, D.; Win, M.Z. Experimental results on cooperative UWB based positioning systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Ultra-Wideband (ICUWB), Hanover, Germany, 10–12 September 2008; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.-Y.; Hann, S.; Park, C.-S. TDOA-based optical wireless indoor localization using LED ceiling lamps. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2011, 57, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Höflinger, F.; Reindl, L. TDOA-based localization using interacting multiple model estimator and ultrasonic transmitter/receiver. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y. An Efficient Semidefinite Relaxation Algorithm for Moving Source Localization Using TDOA and FDOA Measurements. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yu, R.; Sun, G.; Yang, Z. Whistle: Synchronizationfree TDOA for localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE 31st International Conference Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 20–24 June 2011; pp. 760–769. [Google Scholar]
- Bocquet, M.; Loyez, C.; Benlarbi-Delai, A. Using enhanced-TDOA measurement for indoor positioning. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2005, 15, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Niu, K.; Dong, C.; Wang, Y. A novel angle of arrival (AOA) positioning algorithm aided by location reliability prior information. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 29 March–1 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pages-Zamora, A.; Vidal, J.; Brooks, D.H. Closed-form solution for positioning based on angle of arrival measurements. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Lisbon, Portugal, 18 September 2002; Volume 4, pp. 1522–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Krim, H.; Viberg, M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.X.; Goussetis, G. Wireless channel parameter estimation algorithms: Recent advances and future challenges. China Commun. 2018, 15, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, H. Lunar rover positioning based on TOA estimation for UWB signal using unitary-ESPRIT. In Proceedings of the 2009 9th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments, Beijing, China, 16–19 August 2009; pp. 2-646–2-650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobana, F.W. Survey of Inertial/Magnetic Sensors Based Pedestrian Dead Reckoning by Multi-Sensor Fusion Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 17–19 October 2018; pp. 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Reindl, L.M. Pedestrian motion based inertial sensor fusion by a modified complementary separate-bias Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, IEEE, San Antonio, TX, USA, 22–24 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Soh, Y.C. Smartphone inertial sensor-based indoor localization and tracking with ibeacon corrections. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, L.; Borenstein, J. Personal dead-reckoning system for GPS-denied environments. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Workshop on Safety, Security and Rescue Robotics, IEEE, Rome, Italy, 27–29 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.H. Bluetooth: A viable solution for IoT? [Industry Perspectives]. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaissa, B.; Hendrichovsky, F.; Yishida, K.; Koppen, M.; Sincak, P. Phone application for indoor localization based on BLE signal fingerprint. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th IFIP International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and Security (NTMS), Paris, France, 26–28 February 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski, S.; Spachos, P. Rssi-based indoor localization with the internet of things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 30149–30161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, S.; Kwon, G.R.; Shin, S.; Hwang, S.S.; Pyun, J.Y. Beacon based indoor positioning system using weighted centroid localization approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Vienna, Austria, 5–8 July 2016; pp. 1016–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Ren, F. Energy-efficient indoor localization of smart hand-held devices using Bluetooth. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, T.; Groba, C.; Springer, T. Trilateration, fingerprinting, and centroid: Taking indoor positioning with bluetooth LE to the wild. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 21st International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks” (WoWMoM), Cork, Ireland, 31 August–3 September 2020; 2020; pp. 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Faragher, R.; Harle, R. Location Fingerprinting with Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons. Sel. Areas Commun. IEEE J. 2015, 33, 2418–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.H.; Nguyen, Q.C.; Le, M.T.; Hoang, C.A. Indoor localization system based on passive RFID tags. In Proceedings of the 2014 5th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation, Langkawi, Malaysia, 27–29 January 2014; pp. 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Scherhaeufl, M.; Pichler, M.; Schimbaeck, E.; Mueller, D.J.; Ziroff, A.; Stelzer, A. Indoor localization of passive UHF RFID tags based on phase-of-arrival evaluation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 4724–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Zheng, L.J. An implementation of positioning system in indoor environment based on active RFID. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Conferences on Pervasive Computing (JCPC), Taipei, Taiwan, 3– 5 December 2009; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, M.C. Localization of Mobile Robot Based on Radio Frequency Identification Devices. In Proceedings of the SICE-ICASE, International Joint Conference, Busan, Korea, 18–21 October 2006; pp. 5934–5939. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Lau, Y.C.; Patil, A.P. LANDMARC: Indoor location Sensing Using Active RFID. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Pervasive Computing and Communications, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–26 March 2003; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, E.; Ma, R. The UWB based forklift trucks indoor positioning and safety management system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 25–26 March 2017; pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Alarifi, A.; Al-Salman, A.; Alsaleh, M.; Alnafessah, A.; Al-Hadhrami, S.; Al-Ammar, M.A.; Al-Khalifa, H.S. Ultra wideband indoor positioning technologies: Analysis and recent advances. Sensors 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, R.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, P. Review on UWB-based and multi-sensor fusion positioning algorithms in indoor environment. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 March 2021; Volume 5, pp. 1594–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Mazhar, F.; Khan, M.G.; Sällberg, B. Precise indoor positioning using UWB: A review of methods, algorithms and implementations. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 97, 4467–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, B. A UWB/Bluetooth fusion algorithm for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China, 27–30 July 2019; pp. 4142–4146. [Google Scholar]
- Djosic, S.; Stojanovic, I.; Jovanovic, M.; Nikolic, T.; Djordjevic, G.L. Fingerprinting-assisted UWB-based localization technique for complex indoor environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, W.; Jia, Z.; Shen, L. A hybrid indoor positioning system based on UWB and inertial navigation. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Zhao, L. An indoor positioning algorithm based on Wi-Fi fingerprint and inertial navigation system. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 6067–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xie, L.; Spanos, C. Accurate indoor localization and tracking using mobile phone inertial sensors, WiFi and iBeacon. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (INERTIAL), Kauai, HI, USA, 27–30 March 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.; Meifeng, G.; Xinxi, Z.; Yongjian, Z.; Mingliang, S. An indoor pedestrian positioning system based on inertial measurement unit and wireless local area network. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015; pp. 5419–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wu, Y.-W.A.; Yao, L.; Liao, Z.Z. An integrated IMU and UWB sensor based indoor positioning system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sapporo, Japan, 18–21 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perttula, A.; Leppäkoski, H.; Kirkko-Jaakkola, M.; Davidson, P.; Collin, J.; Takala, J. Distributed indoor positioning system with inertial measurements and map matching. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 2682–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S. Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasijevic, A.; Nešković, A. A practical realisation of kNN indoor positioning model for GSM. In Proceedings of the 2012 20th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 20–22 November 2012; pp. 1788–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, F.; Gunnarsson, F. Mobile positioning using wireless networks: Possibilities and fundamental limitations based on available wireless network measurements. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, A.; Nasser, Y.; Awad, M.; Al-Dubai, A.; Liu, R.; Yuen, C.; Raulefs, R.; Aboutanios, E. Recent advances in indoor localization: A survey on theoretical approaches and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 19, 1327–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, G.; Baruffa, G.; Cacopardi, S. GNSS/cellular hybrid positioning system for mobile users in urban scenarios. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 14, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, D.; Kolev, G.; Bushminkin, K. A hybrid localization technique for patient tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE EMBC, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6728–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche, C.; Klein, A.; Wurtz, D. Hybrid GPS/GSM localization of mobile terminals using the extended Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2009 6th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Hannover, Germany, 19 March 2009; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- del Peral-Rosado, J.A.; Granados, G.S.; Raulefs, R.; Leitinger, E.; Grebien, S.; Wilding, T.; Dardari, D.; Lohan, E.S.; Wymeersch, H.; Floch, J.J.; et al. Whitepaper on New Localization Methods for 5G Wireless Systems and the Internet-of-Things. In White Paper of the COST Action CA15104 (IRACON); COST Action CA15104, IRACON; COST: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Geok, T.K.; Aung, K.Z.; Aung, M.S.; Soe, M.T.; Abdaziz, A.; Liew, C.P.; Hossain, F.; Tso, C.P.; Yong, W.H. Review of indoor positioning: Radio wave technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Das, S. Performance analysis of mobile patient network using AODV and DSR routing algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Green Computing Communication and Electrical Engineering (ICGCCEE), Coimbatore, India, 6–8 March 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, G. A Zigbee-based localization algorithm for indoor environments. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Harbin, China, 24–26 December 2011; Volume 3, pp. 1776–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Wang, B.; Shu, L.; Duong, T.Q.; Chen, Y. ZIL: An energy-efficient indoor localization system using ZigBee radio to detect WiFi fingerprints. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunatilaka, D.; Zafar, F.; Kalavally, V.; Parthiban, R. LED based indoor visible light communications: State of the art. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tuts. 2015, 17, 1649–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevincer, A.; Bhattarai, A.; Bilgi, M.; Yuksel, M.; Pala, N. LIGHTNETs: Smart lighting and mobile optical wireless networks—A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tuts. 2013, 15, 1620–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.H.; Feng, X.; Hu, P.; Mohapatra, P. Visible light communication, networking, and sensing: A survey, potential and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tuts. 2015, 17, 2047–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.U.; Naeem, A.; Pasha, M.A.; Jadoon, T.; Yuen, C. Indoor positioning using visible LED lights: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 48, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsters, R.; Holm, D.; Joly, J.; Demeester, E.; Stevens, N.; Slaets, P. Visible light positioning using Bayesian filters. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 5925–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fan, L.; Li, H. Indoor positioning systems based on visible light communication: State of the art. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2871–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, M.; Haruyama, S.; Nakagawa, M. High-accuracy positioning system using visible LED lights and image sensor. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 22–24 January 2008; pp. 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Yang, Z.; Long, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, F.; Jiang, Z.L.; Chen, Z. High-speed indoor navigation system based on visible light and mobile phone. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, P.; Peng, C.; Shen, G.; Zhao, F. Epsilon: A visible light based positioning system. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 14), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–4 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, N.; Lazik, P.; Rowe, A. Visual light landmarks for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IPSN 2014-Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (Part of CPS Week), Berlin, Germany, 15–17 April 2014; pp. 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Y.S.; Pannuto, P.; Hsiao, K.J.; Dutta, P. Luxapose: Indoor positioning with mobile phones and visible light. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 2014; pp. 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Wearables can afford: Light-weight indoor positioning with visible light. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, ACM, , Florence, Italy, 19–22 May 2015; pp. 317–330. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yuan, S.; Lin, P.; Wu, H.; Lei, W.; Fang, J.; Chen, Z. A fast and high-accuracy real-time visible light positioning system based on single LED lamp with a beacon. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, R. High accuracy indoor visible light positioning considering the shapes of illuminators. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), IEEE, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 5–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, N.; Alves, L.N.; Ghassemlooy, Z. Impact of transmitter positioning and orientation uncertainty on rss-based visible light positioning accuracy. Sensors 2021, 21, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Son, Y.-H.; Han, S.-K. Three-Dimensional Visible Light Indoor Localization Using AOA and RSS with Multiple Optical Receivers. J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Chi, X.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Deng, J. The research of indoor positioning based on visible light communication. China Commun. 2015, 12, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.-H.; Yoo, M. TDOA-based indoor positioning using visible light. Photon. Netw. Commun. 2014, 27, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Ho, S.-W.; Vellambi, B.N. Indoor positioning system using visible light and accelerometer. J. Light.Technol. 2014, 32, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Mao, S. DeepML: Deep LSTM for indoor localization with smartphone magnetic and light sensors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, G. Design of the Acquisition System of Indoor Positioning Reference Map Base on Magnetic Field Data. China Acad. J. Electron. Publ. House 2017, 25(2), 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Compagnon, P.; Lefebvre, G. Improved CNN-based Magnetic Indoor Positioning System using Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Lloret de Mar, Spain, 29 November–2 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Ahn, S.; Han, D. AMID: Accurate magnetic indoor localization using deep learning. Sensors 2018, 18, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Muhammad Zahid, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, D. Location fingerprint extraction for magnetic field magnitude based indoor positioning. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1945695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Bo, C.; Shen, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, F. Magicol: Indoor localization using pervasive magnetic field and opportunistic WiFi sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioua, S.; Messaadia, M.; Benatia, M.; Sahnoun, S.; Smart, A. Indoor geolocation based on earth magnetic field. In Proceedings of the 2018 Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage (MetroArchaeo), Cassino, Italy, 22–24 October 2018; pp. 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Poslad, S.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X. A fast path matching algorithm for indoor positioning systems using magnetic field measurements. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Han, D. Magnetic indoor positioning system using deep neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sapporo, Japan, 18–21 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Shao, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Luo, H. WiMag: Multimode fusion localization system based on Magnetic/WiFi/PDR. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Alcala de Henares, Spain, 4–7 October 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F.; Niu, J.; Duan, L. WAIPO: A fusion-based collaborative indoor localization system on smartphones. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2017, 25, 2267–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannay, K.; Ureña, J.; Hernández, Á.; Villadangos, J.M.; Machhout, M.; Aguili, T. Evaluation of Multi-Sensor Fusion Methods for Ultrasonic Indoor Positioning. Applied Sciences 2021, 11(15), 6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, F.; Motomura, Y.; Premachandra, C.; Kato, K. Absolute positioning control of indoor flying robot using ultrasonic waves and verification system. In Proceedings of the 2016 16th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, M.; Pang, W. Ultrasonic TDoA Indoor Localization Based on Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Virtual, 11–16 September 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, S.; Geiß, J.; Vossiek, M. An ultrasonic sensor network for high-quality range-bearing-based indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekleitis, I.M. A Particle Filter Tutorial for Mobile Robot Localization; Tech. Rep. TR-CIM-04-02; Centre for Intelligent Machines, McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S. Particle Filters in Robotics. In Proceedings of the Uncertainty in AI (UAI), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1–4 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, E.; Pérez, M.C.; Gualda, D.; Villadangos, J.M.; Ureña, J.; García, J.J. Ultrasonic indoor positioning for smart environments: A mobile application. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th Experiment@International Conference (exp.at’17), Faro, Portugal, 6–8 June 2017; pp. 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Huang, L.; Hussain, B.; Yue, C.P. Robust Robotic Localization Using Visible Light Positioning and Inertial Fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 4882–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S. Ultrasound positioning based on time-of-flight and signal strength. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweinzer, H.; Syafrudin, M. LOSNUS: An ultrasonic system enabling high accuracy and secure TDoA locating of numerous devices. In Proceedings of the Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), 2010 International Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, C.; Segura, J.C.; Holm, S. Feasibility of ultrasound positioning based on signal strength. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonenko, V.; Cullen, C.; Carswell, J. Investigating ultrasonic positioning on mobile phones. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleski, J.K.; Yamazato, T.; Katayama, M. TOA UWB position estimation with two receivers and a set of known reflectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–11 September 2009; pp. 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, S.; Yara, C.; Kaneta, K.; Ioroi, S.; Tanaka, H. Accurate Indoor Positioning System Using Near-Ultrasonic Sound from a Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2014 Eighth International Conference on Next Generation Mobile Apps, Services and Technologies, Oxford, UK, 10–12 September 2014; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Schwarzer, S.; Stelzer, A.; Vossiek, M. Multi-channel distance measurement with ieee 802.15.4 (zigbee) devices. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2009, 3, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherhäufl, M.; Pfeil, R.; Pichler, M.; Berger, A. A novel ultrasonic indoor localization system with simultaneous estimation of position and velocity. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Topical Conference on Wireless Sensors and Sensor Networks, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 15–18 January 2012; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, K. Beepbeep: A high accuracy acoustic ranging system using cots mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–9 November 2007; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Tewolde, G.; Kwon, J. Indoor localization and navigation for a mobile robot equipped with rotating ultrasonic sensors using a smartphone as the robot’s brain. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Electro/Information Technology (EIT), Dekalb, IL, USA, 21–23 May 2015; pp. 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, F.; Yang, H.K.; Ahmad, A.W.; Lee, C. Indoor positioning: A review of indoor ultrasonic positioning systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 15th International Conference on Advanced Communications Technology (ICACT), PyeongChang, Republic of Korea, 27–30 January 2013; pp. 1146–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Schweinzer, H.F.; Spitzer, G.F. Ultrasonic locating system optimized for low cost, high efficiency and secure application. In Proceedings of the 2009 35th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Porto, Portugal, 3–5 November 2009; pp. 2678–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, A.; Yayan, U.; Yücel, H. An ultrasonic based indoor positioning system. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications, Istanbul, Turkey, 15–18 June 2011; pp. 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S.; Nilsen, C.I.C. Robust ultrasonic indoor positioning using transmitter arrays. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, IEEE, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Durrant-Whyte, H.; Bailey, T. Simultaneous localization and mapping: Part I. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S. Robotic mapping: A survey. In Exploration and Robotics in the New Century; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Montemerlo, M.; Becker, J.; Bhat, S.; Dellaert, F. FastSLAM: A scalable method for the simultaneous localization and mapping problem. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2007, 2007, 364077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Self, M.; Cheeseman, P. Estimating uncertain spatial relationships in robotics. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1986, 2, 30–50. [Google Scholar]
- Baillard, C.; Faugeras, O. Robust estimation of the fundamental matrix. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2001, 83, 164–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, T.; Nieto, J.; Nebot, E. Consistency of the FastSLAM algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2006. Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zeybek, M. Indoor mapping and positioning applications of hand-held lidar simultaneous localization and mapping (slam) systems. Türkiye Lidar Dergisi 2021, 3, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Losada, D.; Matia, F.; Jimenez, A.; Galan, R. Local map fusion for real-time indoor simultaneous localization and mapping. J. Field Robot. 2006, 23, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, A.; Abbasi, M.; Piran, M.J.; Taherkordi, A. A comprehensive survey on 6G networks: Applications, core services, enabling technologies, and future challenges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.12475. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, S. 5G NR Positioning. In 5G and Beyond; Lin, X., Lee, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 429–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, C.; Kalla, A.; Pham, Q.V.; Kumar, P.; Dev, K.; Hwang, W.J.; Liyanage, M. Survey on 6G frontiers: Trends, applications, requirements, technologies and future research. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 836–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Zheng, K.; Shen, X.S. (Eds.) 5G Mobile Communications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alhammadi, A.; Shayea, I.; El-Saleh, A.A.; Azmi, M.H.; Ismail, Z.H.; Kouhalvandi, L.; Saad, S.A. Artificial Intelligence in 6G Wireless Networks: Opportunities, Applications, and Challenges. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2024, 8845070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Series, M. IMT Vision–Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond. Recomm. ITU 2015, 2083, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, J.R.; Alqahtani, S.A. 6G ecosystem: Current status and future perspective. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43134–43167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, R. From 5G-Advanced to 6G in 2030: New Services, 3GPP Advances, and Enabling Technologies. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43134–43167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson Mobility Report. More Than 1 Billion People Will Have Access to 5G Coverage by the End of 2020. 30 November 2020. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/press-releases/2020/11/more-than-1-billion-people-will-have-access-to-5g-coverage-by-the-end-of-2020 (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Chen, B.; Wan, J. Emerging Trends of ML-based Intelligent Services for Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). In Proceedings of the 2019 Computing, Communications and IoT Applications (ComComAp), Shenzhen, China, 26–28 October 2019; pp. 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Qawy, A.S.; Pramod, P.J.; Magesh, E.; Srinivasulu, T. The internet of things (iot): An overview. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2015, 5, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Tan, C. Application of indoor positioning technology in smart home management system. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE), Nanchang, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markets and Markets. Indoor Location Market by Component (Hardware, Solutions, and Services), Deployment Mode, Organization Size, Technology, Application, Vertical (Retail, Transportation and Logistics, Entertainment), and Region-Global Forecast to 2025; Global, Rep. TC 2878, May 2020. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/indoorlocation-market-989.html (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Chen, L.; Thombre, S.; Jarvinen, K.; Lohan, E.S.; Alen-Savikko, A.; Leppakoski, H.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.H.; Bu-Pasha, S.; Ferrara, G.N.; Honkala, S.; et al. Robustness, Security and Privacy in Location-Based Services for Future IoT: A Survey. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8956–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, F.; Gkelias, A.; Leung, K. A Survey of Indoor Localization Systems and Technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2568–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Kumar, D. IoT ecosystem: A survey on devices, gateways, operating systems, middleware and communication. Int. J. Wirel. Inf. Netw. 2020, 27, 340–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantakokko, J.; Rydell, J.; Strömbäck, P.; Händel, P.; Callmer, J.; Törnqvist, D.; Gustafsson, F.; Jobs, M.; Grudén, M. Accurate and reliable soldier and first responder indoor positioning: Multisensor systems and cooperative localization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2011, 18, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xia, X.; Wozniak, M.; Fan, X.; Damaševičius, R.; Li, Y. Multisink distributed power control algorithm for cyber-physical-systems in coal mine tunnels. Comput. Netw. 2019. to be published. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wo, M.; Damaševičius, R.; Fan, X.; Li, Y. Algorithm research of known-plaintext attack on double random phase mask based on WSNs. J. Internet Technol. 2019, 20, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chan, F.T.S.; Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, F.; Shi, B.; Shi, Y.; Lin, F. A life cycle framework of green IoT-based agriculture and its finance, operation, and management issues. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porambage, P.; Okwuibe, J.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M.; Taleb, T. Survey on multi-access edge computing for Internet of Things realization. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2961–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahsari, P.S.; Farahzadi, A.; Rezazadeh, J.; Bagheri, A. A survey on indoor positioning systems for IoT-based applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 7680–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, S.; Pérez, J.; Bernardos, A.M.; Casar, J.R. A fusion method based on Bluetooth and WLAN technologies for indoor location. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 20–22 August 2008; pp. 487–491. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wong, W.-C. Fusion of multiple positioning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing (ICICS), Singapore, 13–16 December 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Ansari, N. Localization by fusing a group of fingerprints via multiple antennas in indoor environment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 9904–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Huang, P.; Xue, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, L. Kalman filter-based data fusion of Wi-Fi RTT and PDR for indoor localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8479–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Hancke, G.P. Industrial wireless sensor networks: Challenges, design principles, and technical approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4258–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Nevatia, R. Multiple target tracking by learning-based hierarchical association of detection responses. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. IEEE Trans. 2013, 35, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreibich, O.; Neuzil, J.; Smid, R. Quality-based Multiple Sensor Fusion in an Industrial Wireless Sensor Network for MCM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 4903–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Xing, G.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Jia, X. Exploiting data fusion to improve the coverage of wireless sensor networks. Netw. IEEE/ACM Trans. 2012, 20, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhpour, K.S.; Atia, M.M. Calibration-free visual-inertial fusion with deep convolutional recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GNSS+ 2019, Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 2198–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Panyov, A.A.; Golovan, A.A.; Smirnov, A.S. Indoor positioning using Wi-Fi fingerprinting pedestrian dead reckoning and aided INS. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISISS), Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 25–26 February 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, E.H.; Jin, M.; Chen, G. Intelligent Fusion of Wi-Fi and Inertial Sensor-Based Positioning Systems for Indoor Pedestrian Navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 4034–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jia, X.; Zhao, J. A Novel Hybrid Fusion Algorithm for Low-Cost GPS/INS Integrated Navigation System During GPS Outages. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53984–53996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaraiedh, M.; Avrillon, S.; Uguen, B. Hybrid Data Fusion techniques for localization in UWB networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 6th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Hannover, Germany, 19 March 2009; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemzadeh, P.; Fontanelli, D.; Macii, D. An indoor position tracking technique based on data fusion for ambient assisted living. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIVEMSA), Milan, Italy, 15–17 July 2013; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-S.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, J.-J. Localization and map-building of mobile robot based on RFID sensor fusion system. In Proceedings of the 2008 6th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 13–16 July 2008; pp. 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Park, K. A Hierarchical Algorithm for Indoor Mobile Robot Localization Using RFID Sensor Fusion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Li, F.; Liao, L.; Huang, M. Data Fusion of UWB and IMU Based on Unscented Kalman Filter for Indoor Localization of Quadrotor UAV. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 64971–64981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.E.; Buede, D.M. Data fusion lexicon: Data fusion subpanel of the joint directors of laboratories technical panel for C3. IEEE Trans. 1991. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA529661.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Dai, Q.; Qian, B.; Boateng, G.O.; Guo, X.; Ansari, N. GRIDLoc: A Gradient Blending and Deep Learning based Localization Approach Combining RSS and CSI. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. Early Access. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, H.T.; Guo, X.; Zhong, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Data fusion methods for indoor positioning systems based on channel state information fingerprinting. Sensors 2022, 22, 8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, L.; Ansari, N.; Liao, B. Accurate WiFi localization by fusing a group of fingerprints via a global fusion profile. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 7314–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, L.; Ansari, N.; Liao, B. Knowledge aided adaptive localization via global fusion profile. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, G.O.; Si, H.; Xia, H.; Guo, X.; Chen, C.; Agyemang, I.O.; Ansari, N. Automated Valet Parking and Charging: A Dynamic Pricing and Reservation-based Framework Leveraging Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024. Early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Ding, W.; Ouyang, J. An Experimental Study on WeChat-Based Large-Scale Indoor Localization System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 24th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Singapore, 11–13 December 2018; pp. 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ansari, N. EdgeIoT: Mobile edge computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, Y.; Jain, R.; Kawahara, T. Robust Indoor Location Estimation of Stationary and Mobile Users. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2004, Hong Kong, China, 7–11 March 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, E.; Cheung, B.K.S. An Improved Neural Network Training Algorithm for Wi-Fi Fingerprinting Positioning. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2013, 2, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Song, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Gao, X. A wireless LAN-based indoor positioning technology. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2004, 48, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, D.; Viswanath, P. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Fattouche, M.; Ghannouchi, F.M. Bounds of mmWave-Based Ranging and Positioning in Multipath Channels. In Proceedings of the Globecom Workshops IEEE, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 9–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.; Qi, J.; Liu, J. Adaptive localization through transfer learning in indoor Wi-Fi environment. In Proceedings of the 2008 Seventh International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–13 December 2008; IEEE; pp. 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Seok, H.-S.; Hwang, K.-B.; Zhang, B.-T. Feature Relevance Network-Based Transfer Learning for Indoor Location Estimation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2011, 41, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C. An indoor positioning system using Channel State Information based on TrAdaBoost Tranfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Advanced Electronic Materials, Computers and Software Engineering (AEMCSE), Changsha, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Philip, S.Y. Domain invariant transfer kernel learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2014, 27, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, B.; Xie, L.; Spanos, C. Adaptive Localization in Dynamic Indoor Environments by Transfer Kernel Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Abbasi, A.; Liu, H. WiFi-based Environment Adaptive Positioning with Transferable Fingerprint Features. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 11th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Virtual Conference, 27–30 January 2021; pp. 0123–0128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, H.T.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Heterogeneous Transfer Learning for Wi-Fi Indoor Positioning Based Hybrid Feature Selection. Sensors 2022, 22, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Guo, X.; Ansari, N. Multi-Agent Interactive Localization: A Positive Transfer Learning Perspective. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2024, 10, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, V.W.; Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q.; Pan, J.J. Transferring MultiDevice Localization Models Using Latent Multi-Task Learning. In Proceedings of the 23rd Assoc. for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) Conference Artificial Intelligence, Chicago, IL, USA, 13–17 July 2008; pp. 1427–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, V.W.; Yang, Q.; Xiang, W.; Shen, D. Transferring Localization Models over Time. In Proceedings of the 23rd Assoc. for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) Conference Artificial Intelligence, Chicago, IL, USA, 13–17 July 2008; pp. 1421–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Shen, D.; Yang, Q.; Kwok, J.T. Transferring Localization Models across Space. In Proceedings of the 23rd Assoc. for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) Conference Artificial Intelligence, Chicago, IL, USA, 13–17 July 2008; pp. 1383–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Gökçe, B.; Akın, H.L. Implementation of Reinforcement Learning by transfering sub-goal policies in robot navigation. In Proceedings of the 2013 21st Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Haspolat, Turkey, 24–26 April 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaiti, M.; Liu, Y.; Luan, H.; Sun, M. Enriching the transfer learning with pre-trained lexicon embedding for low-resource neural machine translation. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutong, Z. Multi-lingual Transfer Learning for Intent Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICNLP), Beijing, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Zeng, Q.; Lee, R. Language Chatbot–The Design and Implementation of English Language Transfer Learning Agent Apps. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Automation, Electronics and Electrical Engineering (AUTEEE), Shenyang, China, 20–23 November 2020; pp. 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, E.S.; Dadi, A.K.; Singh, K.K.; Nayak, S.R.; Bhoi, A.K.; Singh, A. A distributed identity-based authentication scheme for internet of things devices using permissioned blockchain system. Expert Systems 2022, 39, e12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Internet of Things Identity Authentication System Based on Blockchain; Xidian University: Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xingzhong, J.; Qingshui, X.; Haifeng, M.; Jiageng, C.; Haozhi, Z. The research on identity authentication scheme of internet of things equipment in 5G network environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Xi’an, China, 16–19 October 2019; pp. 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Riyami, S.S.; Paterson, K.G. Certificateless public key cryptography. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques: Eurocrypt 2003, Warsaw, Poland, 4–8 May 2003; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 452–473. [Google Scholar]
- Migiro, L.; Shahriar, H.; Sneha, S. Analyzing Security and Privacy Concerns of Contact Tracing Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Digital Health (ICDH), Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 September 2021; pp. 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Tripp, O.; Pistoia, M.; Centonze, P. Application-and user-sensitive privacy enforcement in mobile systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd ACM International Conference on Mobile Software Engineering and Systems, Florence, Italy, 16–17 May 2015; pp. 162–163. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, E.; Mohiuddin, I.; Manzoor, A. Internet of Things (IoT): Security and privacy threats. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1–3 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Negi, M.C.; Pandey, N. Proposing an encryption/decryption scheme for IoT communications using binary-bit sequence and multistage encryption. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 29–31 August 2018; pp. 709–713. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.C.; Singh, R.S.; Jaiswal, S. Secure and privacy enhanced authentication framework for cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 February 2015; pp. 1631–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Cattani, M.; Boano, C.A.; Römer, K. An experimental evaluation of the reliability of lora long-range low-power wireless communication. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, L.; Xu, F.; Ansari, N. Expectation maximization indoor localization utilizing supporting set for Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traini, S.; Sciullo, L.; Trotta, A.; Di Felice, M. Practical Indoor Localization via Smartphone Sensor Data Fusion Techniques: A Performance Study. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–14 January 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, B.; Bao, S.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q. A data-driven inertial navigation/Bluetooth fusion algorithm for indoor localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 5288–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csik, D.; Odry, Á.; Sarcevic, P. Fingerprinting-based indoor positioning using data fusion of different radiocommunication-based technologies. Machines 2023, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagusuku, R.; Yamashita, A.; Asama, H. Data information fusion from multiple access points for wifi-based self-localization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 4, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Alexandropoulos, G.C. Self-calibrating indoor localization with crowdsourcing fingerprints and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications, IEEE, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- AlHajri, M.I.; Shubair, R.M.; Chafii, M. Indoor localization under limited measurements: A cross-environment joint semi-supervised and transfer learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), IEEE, Lucca, Italy, 27–30 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maghdid, H.S.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; Al-Talabani, A.; Sadiq, A.S.; Singh, P.K.; Rawat, D.B. Enabling accurate indoor localization for different platforms for smart cities using a transfer learning algorithm. Internet Technol. Lett. 2022, 5, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klus, R.; Klus, L.; Talvitie, J.; Pihlajasalo, J.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Valkama, M. Transfer learning for convolutional indoor positioning systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), IEEE, Lloret de Mar, Spain, 29 November–2 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Zheng, V.W.; Yang, Q.; Hu, D.H. Transfer learning for wifi-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) Workshop, Chicago, IL, USA, 13–14 July 2008; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hailu, T.G.; Guo, X.; Si, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Ada-LT IP: Functional Discriminant Analysis of Feature Extraction for Adaptive Long-Term Wi-Fi Indoor Localization in Evolving Environments. Sensors 2024, 24, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanam, T.F.; Godrich, H. An improved CSI based device free indoor localization using machine learning based classification approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), IEEE, Roma, Italy, 3–7 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, S. Indoor Positioning System Using Wifi Fingerprint; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, T.; Gong, Y.; Yang, W. Fingerprint database reconstruction based on robust PCA for indoor localization. Sensors 2019, 19, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstweiler, G.; Vonach, E.; Kaufmann, H. HyMoTrack: A mobile AR navigation system for complex indoor environments. Sensors 2015, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bregar, K.; Mohorčič, M. Improving indoor localization using convolutional neural networks on computationally restricted devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17429–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Gellersen, H. Location and navigation support for emergency responders: A survey. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2010, 9, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazıcı, A.; Keser, S.B.; Gunal, S. Integration of classification algorithms for indoor positioning system. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), Antalya, Turkey, 5–8 October 2017; pp. 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Alvarez, F.J.; Quezada-Gaibor, D.; Silva, I.; Pendao, C.; Moreira, A. Ensembling Multiple Radio Maps with Dynamic Noise in Fingerprint-based Indoor Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Spring), Virtual Event, 25–28 April 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, C. A WiFi Indoor Location Tracking Algorithm Based on Improved Weighted K Nearest Neighbors and Kalman Filter. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 32907–32918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhao, C.; Meng, W.; Li, C. Cosine similarity based fingerprinting algorithm in WLAN indoor positioning against device diversity. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 2710–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Han, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hedgpeth, T. IndoorWaze: A Crowdsourcing-Based Context-Aware Indoor Navigation System. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 5461–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; Agrawala, A. The Horus WLAN location determination system. In Proceedings of the International Conference Mobile Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–8 June 2005; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Mirowski, P.; Milioris, D.; Whiting, P.; Ho, T.K. Probabilistic radiofrequency fingerprinting and localization on the run. Bell Labs Tech. J. 2014, 18, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milioris, D.; Kriara, L.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Tzagkarakis, G.; Tsakalides, P.; Papadopouli, M. Empirical evaluation of signal-strength fingerprint positioning in wireless LANs. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM International Conference Modeling, Anal., Simulation Wireless Mobile Systems, Bodrum, Turkey, 17–21 October 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, L.; Zhang, M.; Zou, D.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y. A survey of crowd sensing opportunistic signals for indoor localization. Mobile Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 4041291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Yang, L.T.; Chao, H.-C. Indoor smartphone localization via fingerprint crowdsourcing: Challenges and approaches. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, B. Finccm: Fingerprint crowdsourcing, clustering and matching for indoor subarea localization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2015, 4, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M. Static power of mobile devices: Self-updating radio maps for wireless indoor localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference Computer Communications (INFOCOM), Hong Kong, China, 26 April–1 May 2015; pp. 2497–2505. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, H. Automatic construction of radio maps by crowdsourcing PDR traces for indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Communications (ICC), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Si, H.; Guo, X.; Ansari, N.; Chen, C.; Duan, L.; Huang, J. Environment-Aware Positioning by Leveraging Unlabeled Crowdsourcing Data. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 16436–16449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

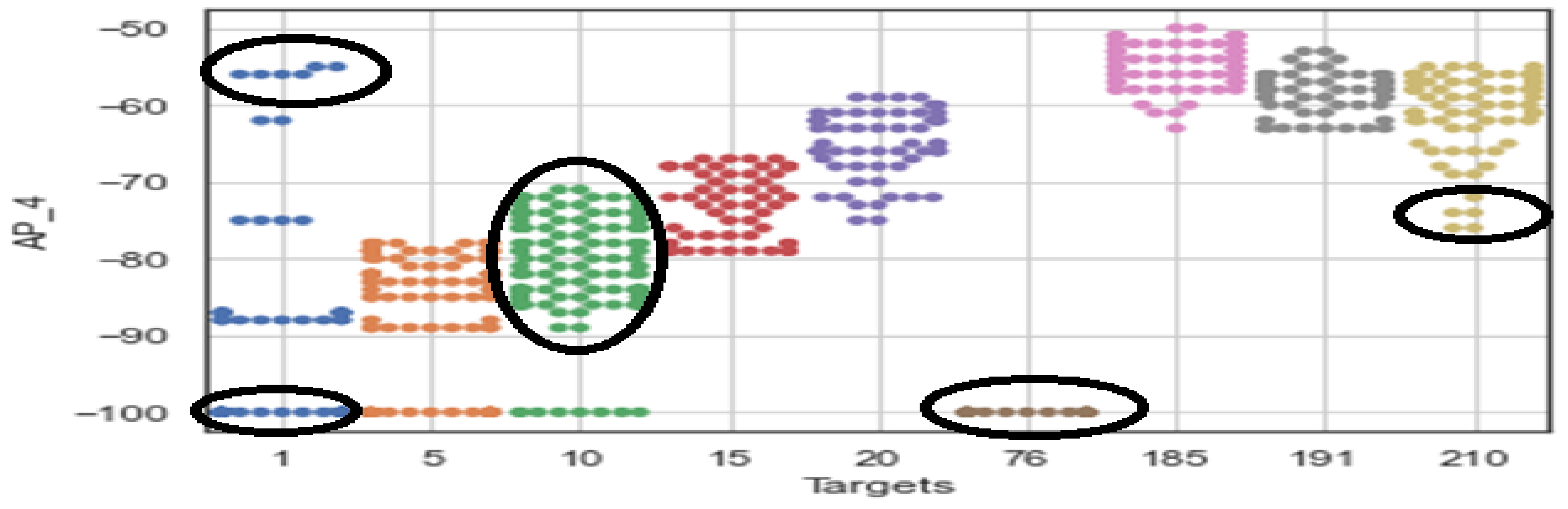


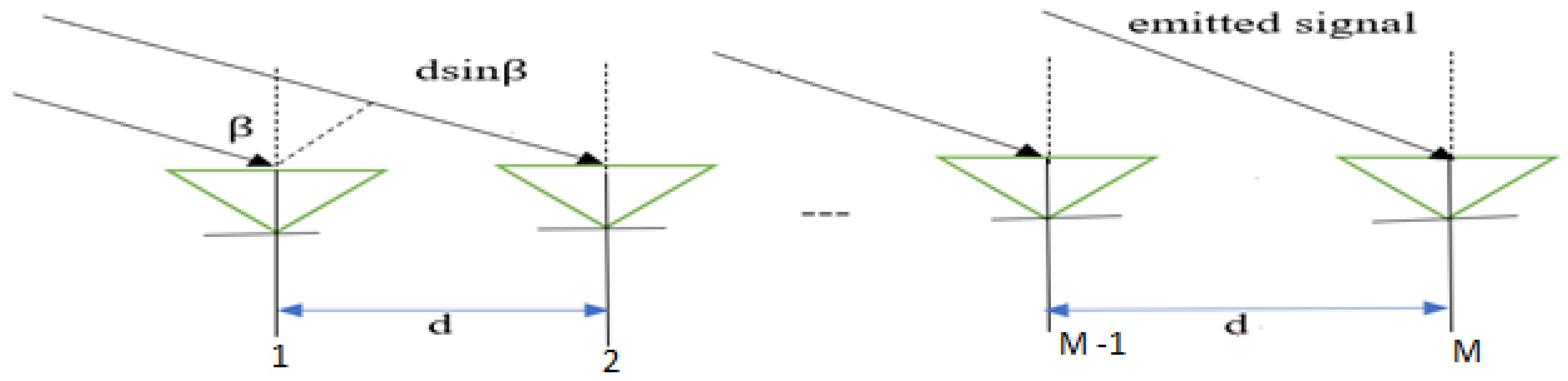
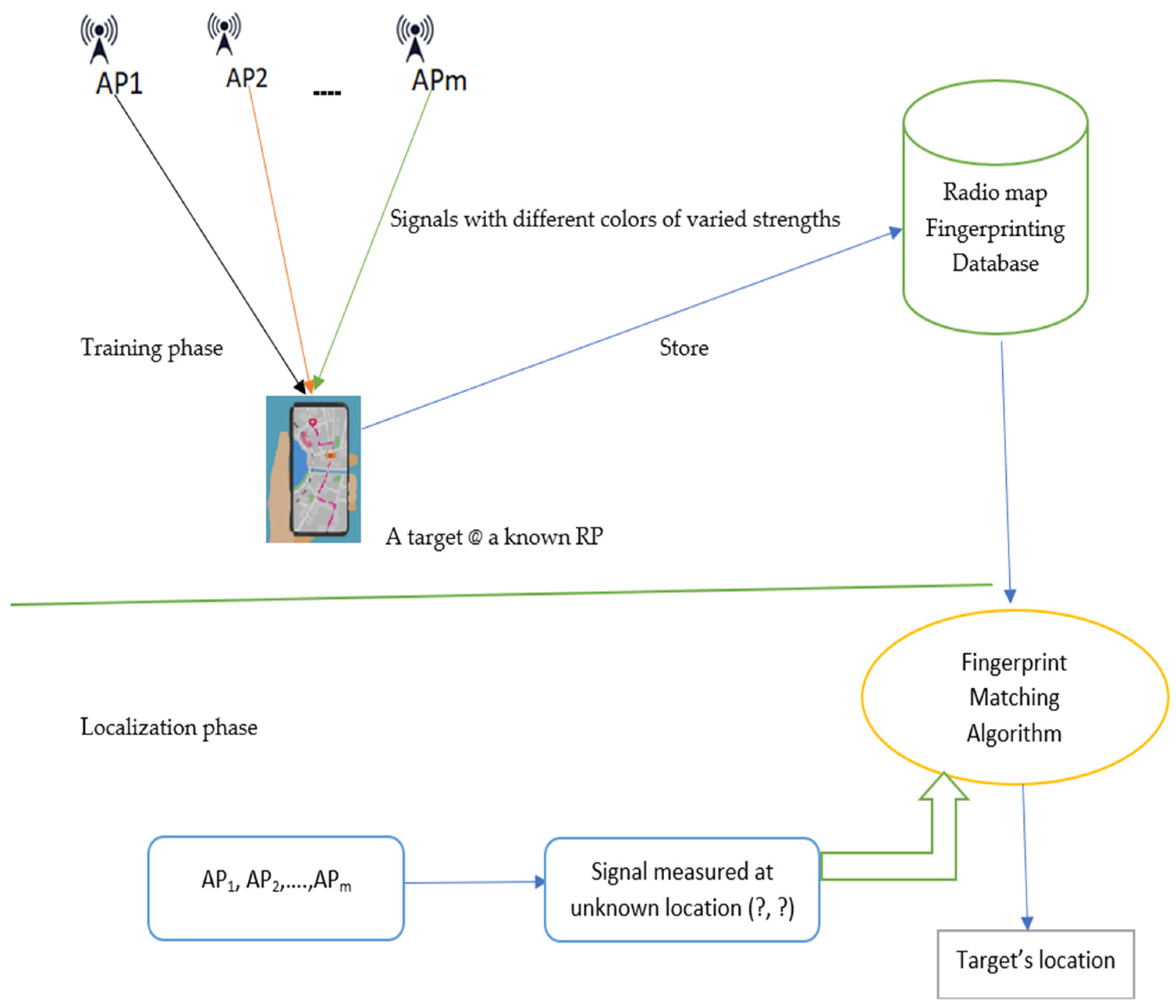

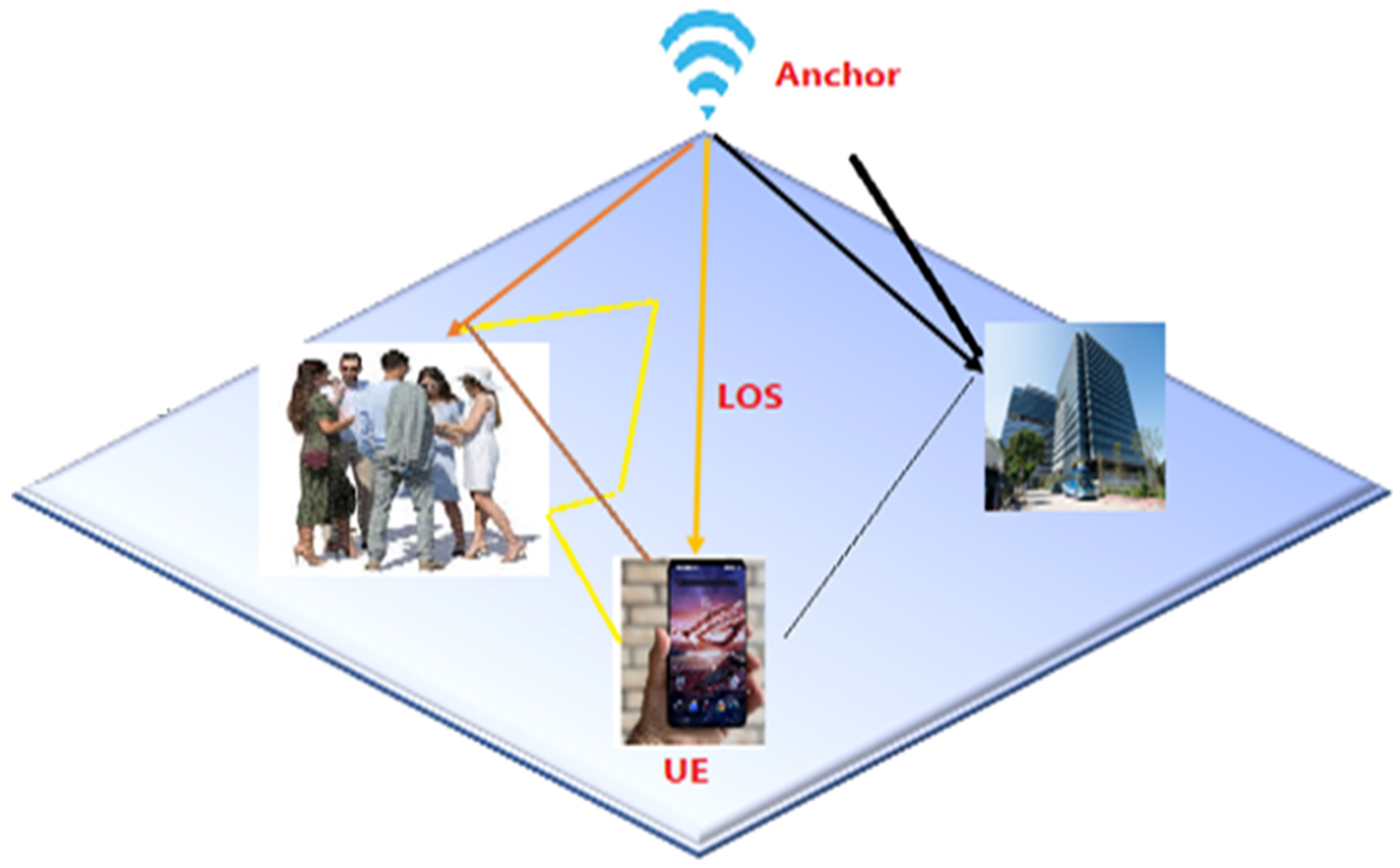

| Strengths | Weakness | Opportunity | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Strengths | Weakness | Opportunity | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Strengths | Weakness | Opportunity | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Strengths | Weakness | Opportunity | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Strengths | Weakness | Opportunity | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Strengths | Weakness | Opportunity | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Approaches | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Model-Based | Fingerprinting |
| Method | Uses mathematical models to estimate position. | Matches real-time RSS to pre-recorded signal data. |
| Accuracy | Affected by environmental factors, leading to lower accuracy. | Matches real-time RSS to pre-recorded signal data. |
| Setup Effort | Minimal, as no pre-survey is required. | High, due to the need for offline data collection. |
| Adaptability | Sensitive to changes in the environment. | Requires updates when the environment changes. |
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| WLAN-Based IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| ||
| BLE IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| RFID-Based IPS |
|
|
| ||
| UWB IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| INS |
|
|
|
| |
| Cellular-Network-Based IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| ZigBee IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| VL-Based IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| Geomagnetic IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| Ultrasonic IPS |
|
|
|
| |
| 5G N/W Positioning |
|
|
| 6G N/W Positioning |
|
|
| Fusion Technique | Technologies Integrated | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-Step Fusion | Inertial sensors, short-range and long-range radio | Improved accuracy through pattern matching and PDR | Complexity in implementation and processing | [280] |
| Data-Driven Inertial Navigation with BLE | Inertial sensors, BLE | Up to 45.37% reduction in positional error using deep learning | Requires significant data for model training | [281] |
| Fingerprint Fusion | Wi-Fi, UWB, 433 MHz | In total, 11% accuracy improvement in complex environments | Dependency on the quality of fingerprint database | [282] |
| Information-Theory-Based Fusion | Multiple Wi-Fi access points | Enhances localization performance in crowded environments | Requires sophisticated algorithms and processing power | [283] |
| Data fusion Knowledge Transfer for CSI | Multiple Wi-Fi access points based CSI | Improves accuracy in dynamic settings, like parking lots | Involves complex data handling; requires calibration | [243] |
| September 2020 | Labels (#RPs = 225) | 0 | 1 | 127 | 159 | 187 | 224 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 28 | 29 | 30 | ||
| Number of CSI values per Label | Dataset 1 (#Labels = 31) | 793 | 811 | 742 | 836 | 806 | 1183 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | ||
| Dataset 2 (#Labels = 6) | 899 | 673 | 820 | 831 | 842 | 1017 | |
| 37 | 38 | 39 | 59 | 60 | 61 | ||
| Dataset 3 (#Labels = 25) | 931 | 805 | 803 | 810 | 1060 | 1254 | |
| 62 | 63 | 64 | 96 | 97 | 98 | ||
| Dataset 4 (#Labels = 37) | 798 | 841 | 863 | 930 | 795 | 806 | |
| 99 | 100 | 101 | 132 | 133 | 134 | ||
| Dataset 5 (#Labels = 36) | 822 | 785 | 797 | 791 | 804 | 841 | |
| 135 | 136 | 137 | 159 | 160 | 161 | ||
| Dataset 6 (#Labels = 27) | 870 | 861 | 994 | 822 | 799 | 833 | |
| 162 | 163 | 164 | 190 | 191 | 192 | ||
| Dataset 7 (#Labels = 31) | 1009 | 804 | 801 | 857 | 792 | 832 | |
| 193 | 194 | 195 | 222 | 223 | 224 | ||
| Dataset 8 (#Labels = 32) | 814 | 804 | 819 | 799 | 857 | 832 | |
| October 2020 | Labels (#RPs = 110) | 0 | 1 | 127 | 99 | 107 | 109 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 19 | 20 | 21 | ||
| Number of CSI values per Label | Dataset 1 (#Labels = 22) | 928 | 805 | 875 | 847 | 1128 | 903 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 41 | 42 | 43 | ||
| Dataset 2 (#Labels = 22) | 824 | 823 | 816 | 803 | 819 | 865 | |
| 44 | 45 | 46 | 63 | 64 | 65 | ||
| Dataset 3 (#Labels = 22) | 815 | 798 | 808 | 848 | 829 | 814 | |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 85 | 86 | 87 | ||
| Dataset 4 (#Labels = 22) | 834 | 828 | 809 | 828 | 821 | 912 | |
| 88 | 89 | 90 | 107 | 108 | 109 | ||
| Dataset 5 (#Labels = 22) | 1025 | 891 | 843 | 810 | 941 | 1008 |
| PCAs Account for 95% Model’s Variations | Explained Variance Ratio (EVR) of Each Principal Component | |
|---|---|---|
| List of Principal Components | Training Data | Testing Data |
| PC1 | 42.71% | 35.75% |
| PC2 | 13.89% | 19.60% |
| PC3 | 12.49% | 10.64% |
| PC4 | 8.863% | 7.443% |
| PC5 | 7.669% | 7.077% |
| PC6 | 4.756% | 5.881% |
| PC7 | 4.671% | 5.456% |
| PC8 | - | 4.384% |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X2 | 0.4370 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X3 | 0.0701 | −0.0439 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X4 | −0.3447 | −0.4317 | 0.0748 | 1.000 | |||||
| X5 | 0.4292 | 0.2644 | 0.2307 | −0.0714 | 1.000 | ||||
| X6 | 0.4376 | 0.3687 | 0.0986 | −0.0794 | 0.3869 | 1.000 | |||
| X7 | −0.1143 | −0.1789 | 0.1685 | 0.4785 | 0.0297 | 0.0457 | 1.000 | ||
| X8 | 0.5413 | 0.5607 | 0.1154 | −0.5414 | 0.3588 | 0.3585 | −0.2629 | 1.000 | |
| X9 | −0.2844 | −0.3194 | 0.2860 | 0.4452 | −0.0601 | −0.0791 | 0.3008 | −0.3028 | 1.000 |
| Mean Absolute Error (MAE in Meter) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Classifiers | Before TL | After TL |
| Decision Tree | 2.29 | 1.07 |
| K-Neighbor (KNN) | 1.81 | 1.26 |
| Support Vector Machine (SVC) | 1.75 | 0.98 |
| Logistic Regression (LR) | 2.51 | 2.04 |
| Random Forest | 2.48 | 1.21 |
| Neural Network (MLP) | 1.93 | 1.36 |
| Proposed algorithm (Hybrid-based) | 1.76 | 1.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hailu, T.G.; Guo, X.; Si, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Theories and Methods for Indoor Positioning Systems: A Comparative Analysis, Challenges, and Prospective Measures. Sensors 2024, 24, 6876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216876
Hailu TG, Guo X, Si H, Li L, Zhang Y. Theories and Methods for Indoor Positioning Systems: A Comparative Analysis, Challenges, and Prospective Measures. Sensors. 2024; 24(21):6876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216876
Chicago/Turabian StyleHailu, Tesfay Gidey, Xiansheng Guo, Haonan Si, Lin Li, and Yukun Zhang. 2024. "Theories and Methods for Indoor Positioning Systems: A Comparative Analysis, Challenges, and Prospective Measures" Sensors 24, no. 21: 6876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216876
APA StyleHailu, T. G., Guo, X., Si, H., Li, L., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Theories and Methods for Indoor Positioning Systems: A Comparative Analysis, Challenges, and Prospective Measures. Sensors, 24(21), 6876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216876






