Image Quality Comparison of Three 3D Mobile X-Ray Imaging Guidance Devices Used in Spine Surgery: A Phantom Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition and Reconstruction Parameters
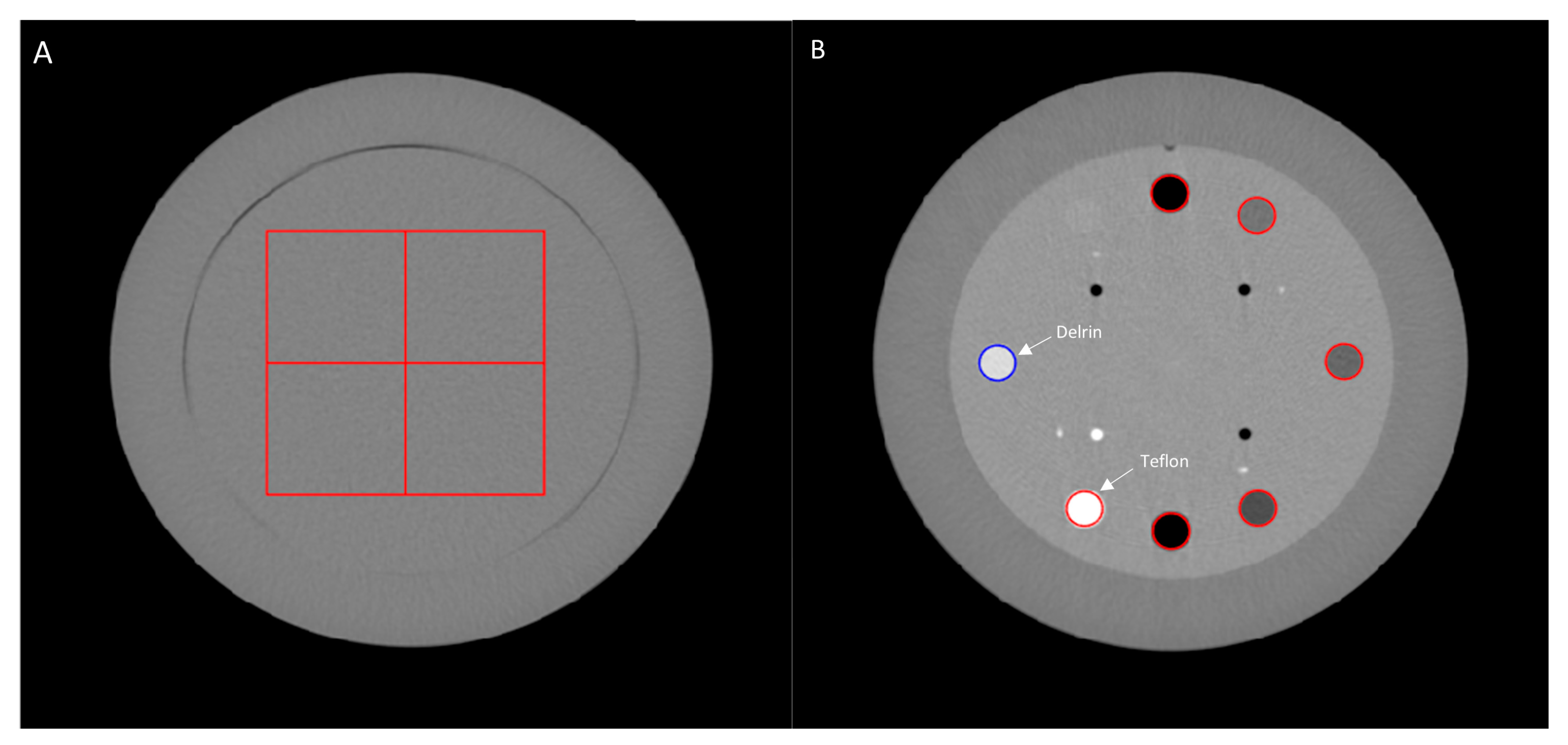
2.2. Task-Based Image Quality Assessment
2.2.1. Noise Power Spectrum
2.2.2. Task-Based Transfer Function
2.2.3. Detectability Index
3. Results
3.1. Noise Power Spectrum
3.2. Task-Based Transfer Function
3.3. Detectability Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonetti, J.; Boudissa, M.; Kerschbaumer, G.; Seurat, O. Role of 3D intraoperative imaging in orthopedic and trauma surgery. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 106, S19–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, H.; Trapp, O. Fluoroscopic imaging: New advances. Injury 2022, 53 (Suppl. S3), S8–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirnaz, S.; Gebhard, H.; Wong, T.; Nangunoori, R.; Schmidt, F.A.; Sato, K.; Härtl, R. Intraoperative image guidance for cervical spine surgery. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Ramirez, R.; Lang, G.; Lian, X.; Berlin, C.; Janssen, I.; Jada, A.; Alimi, M.; Härtl, R. Total Navigation in Spine Surgery; A Concise Guide to Eliminate Fluoroscopy Using a Portable Intraoperative Computed Tomography 3-Dimensional Navigation System. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Minnema, A.; Singh, V.; Grossbach, A. Retrospective analysis of pedicle screw accuracy for patients undergoing spinal surgery assisted by intraoperative computed tomography (CT) scanner AIRO® and BrainLab© navigation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 198, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, U.; Jendrewski, C.; Bartels, M. Navigation in surgery. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2013, 398, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Cosar, M.; Kirnaz, S.; Schmidt, F.A.; Wipplinger, C.; Wong, T.; Härtl, R. Evolving Navigation, Robotics, and Augmented Reality in Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10 (Suppl. S2), 22S–33S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Schmidt, F.A.; Kirnaz, S.; Wipplinger, C.; Schwartz, T.H.; Härtl, R. MIS approaches in the cervical spine. J. Spine Surg. 2019, 5, S74–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, L.; Eibach, S.; Seifert, V.; Setzer, M. Intraoperative 3D fluoroscopy in stereotactic surgery. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermaier, T.; Linsenmann, T.; Homola, G.A.; Loehr, M.; Stetter, C.; Willner, N.; Ernestus, R.I.; Solymosi, L.; Vince, G.H. 3D rotational fluoroscopy for intraoperative clip control in patients with intracranial aneurysms—Assessment of feasibility and image quality. BMC Med. Imaging 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerle, D.; Osterhoff, G.; Allemann, F.; Werner, C.M.L. Comparison of intraoperative 2D vs. 3D imaging in open reduction and fixation of distal radius fractures. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2020, 46, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, S.Y.; Euler, F.; von Recum, J.; Wendl, K.; Grützner, P.A.; Franke, J. Impact of Intraoperative Cone Beam Computed Tomography on Reduction Quality and Implant Position in Treatment of Tibial Plafond Fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2016, 37, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, H.; Beisemann, N.; Schnetzke, M.; Vetter, S.Y.; Grützner, P.A.; Franke, J. First experiences with the Airo mobile intraoperative CT scanner in acetabular surgery—An analysis of 10 cases. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2019, 15, e1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, A.; Pomme, J.; Moreau, E.; Camille, R.; Guillaume, R. Intraoperative Cone Beam Tomography and Navigation for Displaced Acetabular Fractures: A Comparative Study. J. Orthop. Trauma 2018, 32, 612–616. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/jorthotrauma/Abstract/2018/12000/Intraoperative_Cone_Beam_Tomography_and_Navigation.4.aspx (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Franke, J.; von Recum, J.; Suda, A.J.; Grützner, P.A.; Wendl, K. Intraoperative three-dimensional imaging in the treatment of acute unstable syndesmotic injuries. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichsel, O.; Oertel, M.F.; Stieglitz, L.H. Mobile intraoperative CT-assisted frameless stereotactic biopsies achieved single-millimeter trajectory accuracy for deep-seated brain lesions in a sample of 7 patients. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermakowicz, W.J.; Diaz, R.J.; Cass, S.H.; Ivan, M.E.; Komotar, R.J. Use of a Mobile Intraoperative Computed Tomography Scanner for Navigation Registration During Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy of Brain Tumors. World Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, N.; Kamphuis, M.; Czabanka, M.; Hamm, B.; König, S.; Woitzik, J.; Synowitz, M.; Vajkoczy, P. Accuracy and workflow of navigated spinal instrumentation with the mobile AIRO® CT scanner. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyn, M.; Pierzak, O.; Zapałowicz, K.; Radek, M. Use of O-arm with neuronavigation in percutaneous vertebroplasty reduces the surgeon’s exposure to intraoperative radiation. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, M.; Scarone, P.; Bellesi, L.; Piliero, M.A.; Pupillo, F.; Gaudino, D.; Fumagalli, G.; Del Grande, F.; Presilla, S. Effective dose and image quality for intraoperative imaging with a cone-beam CT and a mobile multi-slice CT in spinal surgery: A phantom study. Phys. Med. 2021, 81, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.; Shaffrey, C.; Buchholz, A.; Turner, R.; Yang, L.Z.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Goode, A. Image Quality and Dose Comparison of 3 Mobile Intraoperative Three-Dimensional Imaging Systems in Spine Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2022, 160, e142–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, H.; Luxenhofer, M.; Vetter, S.Y.; Beisemann, N.; Grützner, P.A.; Franke, J. Evaluation of image quality and assessability of a new flat-panel 3D C-arm compared to mobile and fixed computed tomography in posterior spinal fixation. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2021, 17, e2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachabe, R.; Strauss, K.; Schueler, B.; Bydon, M. Radiation dose and image quality comparison during spine surgery with two different, intraoperative 3D imaging navigation systems. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, J.; Karellas, A.; Street, J.; Eck, J.C.; Lapinsky, A.; Connolly, P.J.; DiPaola, C.P. Estimating the effective radiation dose imparted to patients by intraoperative cone-beam computed tomography in thoracolumbar spinal surgery. Spine 2013, 38, E306–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrêté du 23 mai 2019 Portant Homologation de la Décision n° 2019-DC-0667 de l’Autorité de Sûreté Nucléaire du 18 Avril 2019 Relative aux Modalités D’évaluation des Doses de Rayonnements Ionisants Délivrées aux Patients lors d’un acte de Radiologie, de Pratiques Interventionnelles Radioguidées ou de Médecine Nucléaire et à la Mise à Jour des Niveaux de Référence Diagnostiques Associés. Available online: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/loda/id/JORFTEXT000038529178 (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Greffier, J.; Barbotteau, Y.; Gardavaud, F. iQMetrix-CT: New software for task-based image quality assessment of phantom CT images. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 103, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, S.; Husarik, D.B.; Yadava, G.; Murphy, S.N.; Samei, E. Towards task-based assessment of CT performance: System and object MTF across different reconstruction algorithms. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samei, E.; Bakalyar, D.; Boedeker, K.L.; Brady, S.; Fan, J.; Leng, S.; Myers, K.J.; Popescu, L.M.; Ramirez Giraldo, J.C.; Ranallo, F.; et al. Performance evaluation of computed tomography systems: Summary of AAPM Task Group 233. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e735–e756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdun, F.R.; Racine, D.; Ott, J.G.; Tapiovaara, M.J.; Toroi, P.; Bochud, F.O.; Veldkamp, W.J.H.; Schegerer, A.; Bouwman, R.W.; Giron, I.H.; et al. Image quality in CT: From physical measurements to model observers. Phys. Medica 2015, 31, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorbau, R.; Hulthén, M.; Omar, A. Task-based image quality assessment of an intraoperative CBCT for spine surgery compared with conventional CT. Phys. Med. 2024, 124, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, M.P.; Bartroff, J.L.; Abbey, C.K.; Whiting, J.S.; Bochud, F.O. Automated computer evaluation and optimization of image compression of x-ray coronary angiograms for signal known exactly detection tasks. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffier, J.; Frandon, J.; Pereira, F.; Hamard, A.; Beregi, J.P.; Larbi, A.; Omoumi, P. Optimization of radiation dose for CT detection of lytic and sclerotic bone lesions: A phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, O.D.; Boldt, S.; Nadaes, M.; Devito, K.L. Evaluating the scattered radiation intensity in CBCT. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 144, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemink, M.J.; de Jong, P.A.; Leiner, T.; de Heer, L.M.; Nievelstein, R.A.; Budde, R.P.; Schilham, A.M. Iterative reconstruction techniques for computed tomography Part 1: Technical principles. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, L.L.; Schoepf, U.J.; Meinel, F.G.; Nance, J.W., Jr.; Bastarrika, G.; Leipsic, J.A.; Paul, N.S.; Rengo, M.; Laghi, A.; De Cecco, C.N. State of the Art: Iterative CT Reconstruction Techniques. Radiology 2015, 276, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greffier, J.; Boccalini, S.; Beregi, J.P.; Vlassenbroek, A.; Vuillod, A.; Dupuis-Girod, S.; Boussel, L.; Douek, P.; Si-Mohamed, S. CT dose optimization for the detection of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation (PAVM): A phantom study. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffier, J.; Frandon, J.; Larbi, A.; Beregi, J.P.; Pereira, F. CT iterative reconstruction algorithms: A task-based image quality assessment. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shaw, C.C.; Altunbas, M.C.; Lai, C.J.; Liu, X. Spatial resolution properties in cone beam CT: A simulation study. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolly, S.; Chen, H.C.; Anastasio, M.; Mutic, S.; Li, H. Practical considerations for noise power spectra estimation for clinical CT scanners. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.; Heil, U.; Gross, D.; Bruellmann, D.D.; Dranischnikow, E.; Schwanecke, U.; Schoemer, E. Artefacts in CBCT: A review. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2011, 40, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rossi, M.; Cerveri, P. Comparison of Supervised and Unsupervised Approaches for the Generation of Synthetic CT from Cone-Beam CT. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistelli, M.; Valeri, F.; D’Ercole, M.; Izzo, A.; Rapisarda, A.; Polli, F.M.; Montano, N. The use of intraoperative CT-neuronavigation in Wiltse approach. A technical note. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1433273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, L.; Ille, S.; Kirschke, J.S.; Meyer, B.; Krieg, S.M. Radiation doses and accuracy of navigated pedicle screw placement in cervical and thoracic spine surgery: A comparison of sliding gantry CT and mobile cone-beam CT in a homogeneous cohort. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2023, 39, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servello, D.; Saleh, C.; Zekaj, E. Intraoperative mobile computed tomography in deep brain stimulation: Comparison between Airo CT and O-arm CT. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2022, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Airo TruCT | Loop-X | O-Arm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free space (cm) | 107 | 102–121 | 96.5 |
| Detector type | Solid-State Array CdWO4 | CsI(Tl) | a-Si |
| Matrix size | 512 × 512 | 1024 × 1024 | 2048 × 1536 |
| FOV (cm) | 25.6–51.2 | 25–60 (2D) | 21.2–39.7 |
| 3–25–48 (3D) | |||
| Generator power (kW) | 30 | 14.4 | 32 |
| Nominal kV | 120 | 120 | 150 |
| kVp range | 80–120 | 40–120 | 40–140 * |
| mA range | 5–250 | 0.2–8 continuous | 10–100 * |
| 5–120 pulsed | |||
| Focus size (mm) | 1 × 1 | 0.3 (small) | 0.6 × 0.9 (small) |
| 0.6 (large) | 1.2 × 1.7 (large) | ||
| Total filtration (mmAl) | 6.8 (at 120 kVp) | 4.4 (at 75 kVp) | 4.7 (at 75 kVp) |
| Bow-Tie filter 0.3–3 mm Cu |
| Airo TruCT | Loop-X | O-Arm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition parameters | kVp | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Temps de rotation (s) | 1 | 50 | 7.5 | |
| Pitch factor | 1.415 | - | - | |
| Tube current (mAs) | 257 | 480 | 298 | |
| Acquisition field of view (SFOV) cm | 380 | 350 | 350 | |
| CTDIvol (mGy)/CTDIw | 27 | 26.7 | 26.2 | |
| Reconstruction parameters | Reconstruction algorithm | FBP | FBP | FBP |
| Displayed field of view (DFOV) cm | 256 | 250 | 250 | |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 1 | 1.2 | 0.833 | |
| Kernel | Soft | Std | Std |
| Noise Magnitude (HU) | fav (mm−1) | fpeak (mm−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airo TruCT | 7.6 | 0.22 | 0.26 |
| Loop-X | 12.31 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| O-Arm | 28.8 | 0.47 | 0.36 |
| TTF50 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Teflon | Delrin | |
| Airo TruCT | 0.32 | 0.34 |
| Loop-X | 0.39 | 0.37 |
| O-Arm | 0.49 | 0.48 |
| d’ | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lytic | Sclerotic | Bone | |
| Airo TruCT | 7.37 | 25.80 | 64.22 |
| Loop-X | 5.40 | 18.83 | 48.84 |
| O-Arm | 1.71 | 5.98 | 15.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabli, D.; Salvat, C.; Fitton, I.; Van Ngoc Ty, C.; Palanchon, P.; Beregi, J.-P.; Greffier, J.; Hadid-Beurrier, L. Image Quality Comparison of Three 3D Mobile X-Ray Imaging Guidance Devices Used in Spine Surgery: A Phantom Study. Sensors 2024, 24, 6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216883
Dabli D, Salvat C, Fitton I, Van Ngoc Ty C, Palanchon P, Beregi J-P, Greffier J, Hadid-Beurrier L. Image Quality Comparison of Three 3D Mobile X-Ray Imaging Guidance Devices Used in Spine Surgery: A Phantom Study. Sensors. 2024; 24(21):6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216883
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabli, Djamel, Cécile Salvat, Isabelle Fitton, Claire Van Ngoc Ty, Peggy Palanchon, Jean-Paul Beregi, Joël Greffier, and Lama Hadid-Beurrier. 2024. "Image Quality Comparison of Three 3D Mobile X-Ray Imaging Guidance Devices Used in Spine Surgery: A Phantom Study" Sensors 24, no. 21: 6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216883
APA StyleDabli, D., Salvat, C., Fitton, I., Van Ngoc Ty, C., Palanchon, P., Beregi, J.-P., Greffier, J., & Hadid-Beurrier, L. (2024). Image Quality Comparison of Three 3D Mobile X-Ray Imaging Guidance Devices Used in Spine Surgery: A Phantom Study. Sensors, 24(21), 6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216883









